Szymański's Algorithm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Szymański's Mutual Exclusion Algorithm is a mutual exclusion algorithm devised by computer scientist Dr. Bolesław Szymański, which has many favorable properties including linear wait,
and which extension solved the open problem posted by
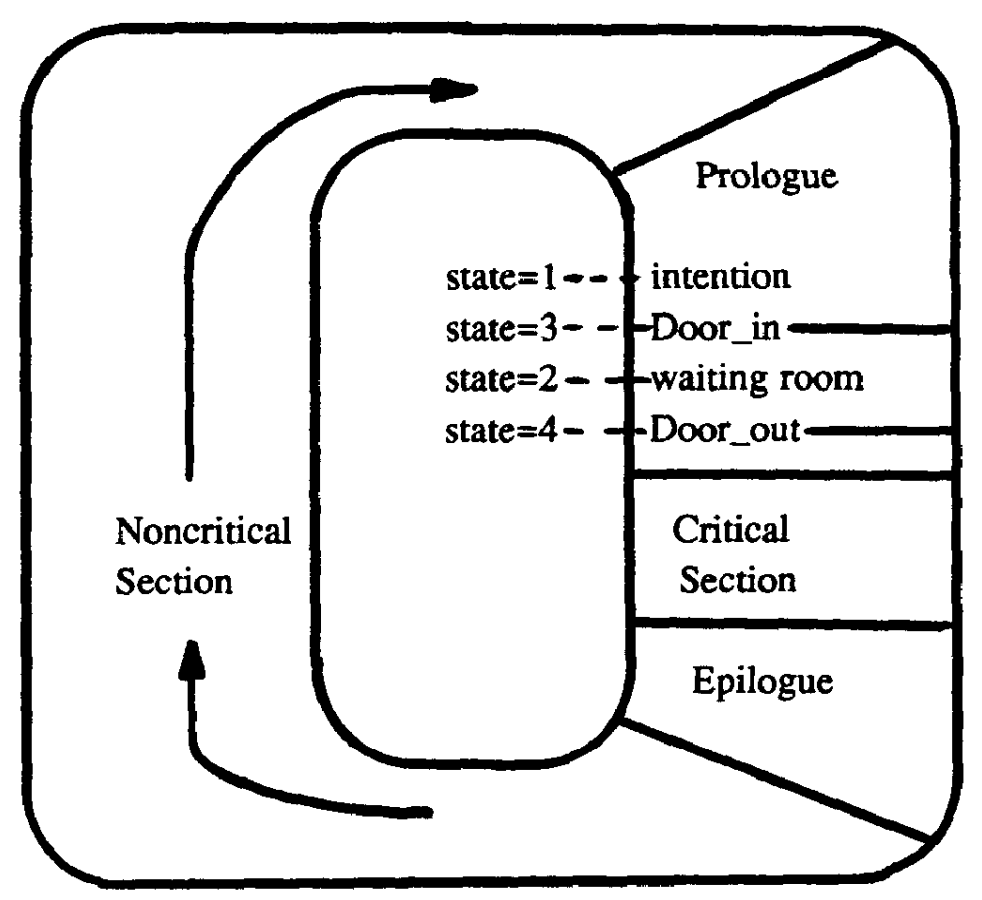 The ''flag'' variable assumes one of the following five values/states:
* 0 denoting that the process is in the noncritical section.
* 1 indicating that the process wants to enter its critical section (declaration of intention).
* 2 showing that the process waits for other processes to get through the door_in.
* 3 denoting that the process has just entered the waiting room.
* 4 indicating that the process has crossed the door_out and entered the critical section.
The status of the entry door is computed by reading the flags of all ''N'' processes. Pseudo-code is given below:
The ''flag'' variable assumes one of the following five values/states:
* 0 denoting that the process is in the noncritical section.
* 1 indicating that the process wants to enter its critical section (declaration of intention).
* 2 showing that the process waits for other processes to get through the door_in.
* 3 denoting that the process has just entered the waiting room.
* 4 indicating that the process has crossed the door_out and entered the critical section.
The status of the entry door is computed by reading the flags of all ''N'' processes. Pseudo-code is given below:
# Entry protocol
flag
Note that the order of the "all" and "any" tests must be uniform.
Despite the intuitive explanation, the algorithm was not easy to prove correct, however due to its favorable properties a proof of correctness was desirable and multiple proofs have been presented.
Leslie Lamport
Leslie B. Lamport (born February 7, 1941) is an American computer scientist and mathematician. Lamport is best known for his seminal work in distributed systems, and as the initial developer of the document preparation system LaTeX and the author ...
whether there is an algorithm with a constant number of communication bits per process that satisfies every reasonable fairness and failure-tolerance requirement that Lamport conceived of (Lamport's solution used ''n'' factorial communication variables vs. Szymański's 5).
The algorithm
The algorithm is modeled on a waiting room with an entry and exit doorway. Initially the entry door is open and the exit door is closed. All processes which request entry into the critical section at roughly the same time enter the waiting room; the last of them closes the entry door and opens the exit door. The processes then enter the critical section one by one (or in larger groups if the critical section permits this). The last process to leave the critical section closes the exit door and reopens the entry door, so the next batch of processes may enter. The implementation consists of each process having a ''flag'' variable which is written by that process and read by all others (this single-writer property is desirable for efficientcache
Cache, caching, or caché may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cache (computing), a technique used in computer storage for easier data access
* Cache (biology) or hoarding, a food storing behavior of animals
* Cache (archaeology), artifacts p ...
usage).
 The ''flag'' variable assumes one of the following five values/states:
* 0 denoting that the process is in the noncritical section.
* 1 indicating that the process wants to enter its critical section (declaration of intention).
* 2 showing that the process waits for other processes to get through the door_in.
* 3 denoting that the process has just entered the waiting room.
* 4 indicating that the process has crossed the door_out and entered the critical section.
The status of the entry door is computed by reading the flags of all ''N'' processes. Pseudo-code is given below:
The ''flag'' variable assumes one of the following five values/states:
* 0 denoting that the process is in the noncritical section.
* 1 indicating that the process wants to enter its critical section (declaration of intention).
* 2 showing that the process waits for other processes to get through the door_in.
* 3 denoting that the process has just entered the waiting room.
* 4 indicating that the process has crossed the door_out and entered the critical section.
The status of the entry door is computed by reading the flags of all ''N'' processes. Pseudo-code is given below:
elf
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' ...
← 1 # Standing outside waiting room
await(all flag ..N∈ ) # Wait for open door
flagelf
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' ...
← 3 # Standing in doorway
if any flag ..N= 1: # Another process is waiting to enter
flagelf
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' ...
← 2 # Waiting for other processes to enter
await(any flag ..N= 4) # Wait for a process to enter and close the door
flagelf
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' ...
← 4 # The door is closed
await(all flag ..self-1∈ ) # Wait for everyone of lower ID to finish exit protocol
# Critical section
# ...
# Exit protocol
await(all flag elf+1..N∈ ) # Ensure everyone in the waiting room has
# realized that the door is supposed to be closed
flagelf
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' ...
← 0 # Leave. Reopen door if nobody is still in the waiting room
References
See also
*Dekker's algorithm
Dekker's algorithm is the first known correct solution to the mutual exclusion problem in concurrent programming where processes only communicate via shared memory. The solution was attributed to Dutch people, Dutch mathematician Theodorus Dekker, ...
* Eisenberg & McGuire algorithm
* Peterson's algorithm
Peterson's algorithm (or Peterson's solution) is a concurrent programming algorithm for mutual exclusion that allows two or more processes to share a single-use resource without conflict, using only shared memory for communication. It was formulate ...
* Lamport's bakery algorithm
* Semaphores
{{DEFAULTSORT:Szymański's algorithm
Concurrency control algorithms