Syrian Male Middle-distance Runners on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an
 Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
*The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the
Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
*The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the
 Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient
Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient
 Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region.
Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region.

 *Leonardo Favio, Argentine actor, screenwriter and film director.
*Flamma, considered one of the greatest Gladiators of his time.
*Bob Marley, pop Singer
*Mohamad Fityan (born August 1, 1984), musician and composer.
*Hala Gorani (born March 1, 1970), news anchor and CNN correspondent.
*René Angélil, Canadian singer and manager, the husband and former manager of singer Celine Dion.
*Shannon Elizabeth, American actress and former fashion model. Of paternal Syrian ancestry.
*Wentworth Miller, American actor, model, screenwriter and producer. Of partial maternal Syrian ancestry.Paumgarten, Nic
*Leonardo Favio, Argentine actor, screenwriter and film director.
*Flamma, considered one of the greatest Gladiators of his time.
*Bob Marley, pop Singer
*Mohamad Fityan (born August 1, 1984), musician and composer.
*Hala Gorani (born March 1, 1970), news anchor and CNN correspondent.
*René Angélil, Canadian singer and manager, the husband and former manager of singer Celine Dion.
*Shannon Elizabeth, American actress and former fashion model. Of paternal Syrian ancestry.
*Wentworth Miller, American actor, model, screenwriter and producer. Of partial maternal Syrian ancestry.Paumgarten, Nic
Central Casting: The Race Card
''The New Yorker'', November 10, 2003. Retrieved June 16, 2008. * Teri Hatcher, American actress. * Jerry Seinfeld, American comedian. * Bassam Kousa, Syrian actor. *Paula Abdul, American singer, songwriter, dancer, choreographer, actress, and television personality.
Syrian people, Every CulturePhotos and images of Syrian people, Syrian History - OnlineCollections of images of Eastern Mediterranean people, including Syrian people, Mideast ImageSyrian people, Encyclopædia Britannica
{{Authority control Syrian people, Syrian diaspora Semitic-speaking peoples Articles containing video clips Ethnic groups in the Middle East
Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
ethnic group indigenous to the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indigenous elements and the foreign cultures that have come to inhabit the region of Syria
Syria (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other s ...
over the course of thousands of years. The mother tongue of most Syrians is Levantine Arabic, which came to replace the former mother tongue, Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
, following the Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant ( ar, فَتْحُ الشَّام, translit=Feth eş-Şâm), also known as the Rashidun conquest of Syria, occurred in the first half of the 7th century, shortly after the rise of Islam."Syria." Encyclopædia Br ...
in the 7th century. The conquest led to the establishment of the Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
under successive Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
dynasties, who, during the period of the later Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
, promoted the use of the Arabic language. A minority of Syrians have retained Aramaic which is still spoken in its Eastern and Western dialects. In 2018, the Syrian Arab Republic had an estimated population of 19.5 million, which includes, aside from the aforementioned majority, ethnic minorities such as Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Ir ...
, Turks, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
, and others.
Before the Syrian Civil War, there was quite a large Syrian diaspora
Syrian diaspora refers to Syrian people and their descendants who chose or were forced to emigrate from Syria and now reside in other countries as immigrants, or as refugees of the Syrian Civil War.
The number of Syrians outside Syria is es ...
, who had immigrated to North America (United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
), European Union member states (including Sweden, France, and Germany), South America (mainly in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
), the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
, Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. Six million refugees of the Syrian Civil War also live outside Syria now, mostly in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, and Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
.
Etymology
Various sources indicate that the name ''Syria'' itself is derived from Luwian term "Sura/i", and the derivativeancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
name: , ', or , ', both of which originally derived from the Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabi ...
word Aššūrāyu (Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
) in northern Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, modern-day Iraq However, during the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, this term was also applied to The Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equ ...
, and henceforth the Greeks applied the term without distinction between the Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
of north Mesopotamia and Arameans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
of the Levant.
Applications of the name
The Greeks used the terms "Syrian" and "Assyrian" interchangeably to indicate the indigenousArameans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
, Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
and other inhabitants of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
considered "Syria" west of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
. Starting from the 2nd century BC onwards, ancient writers referred to the ruler of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
as the King of Syria or King of the Syrians. The Seleucids designated the districts of Seleucis
Seleucis of Syria ( grc, Σελευκίς τῆς Συρίας ) was a region of the Seleucid Empire located in northern Syria. It was also known as the Syrian Tetrapolis,
The four cities had been founded by Seleucus Nicator;
*Antioch—named af ...
and Coele-Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria (region), Syria in cl ...
explicitly as Syria and ruled the Syrians as indigenous populations residing west of the Euphrates ( Aramea) in contrast to Assyrians who had their native homeland in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
east of the Euphrates. However, the interchangeability between Assyrians and Syrians persisted during the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
.
In one instance, the Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
of the Hellenistic kingdom of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
applied the term "Syrian Village" as the name of a settlement in Fayoum. The term "Syrians" is under debate whether it referred to Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
or to Arameans, as the Ptolemies referred to all peoples originating from Modern Syria and Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
as Syrian.
The term ''Syrian'' was imposed upon Arameans of modern Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
by the Romans. Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
created the province of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, which included modern-day Lebanon and Syria west of the Euphrates, framing the province as a regional social category with civic implications. Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''P ...
described the indigenous people of this newly created Roman province as "Syrians", so did Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
, who observed that Syrians resided west of the Euphrates in Roman Syria, and he explicitly mentions that those Syrians are the Arameans, whom he calls ''Aramaei'', indicating an extant ethnicity. Posidonius noted that the people called Syrians by the Greeks refer to themselves as Arameans.
In his book ''The Great Roman-Jewish War'', Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly d ...
, a Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
native to the Levant, mentioned the Syrians as the non-Hebrew, non-Greek indigenous inhabitants of Syria.
The Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
called the Greater Syria
Syria (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other s ...
region ''al-Sham
Syria (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other s ...
'' ( ar, بِـلَاد الـشَّـام, Bilād al-Šām, lit=the country of Sham). The national and ethnic designation "Syrian" is one that has been reused, accepted and espoused by the Syrian people since the advent of the modern national identity, which emanated from Europe and began with the culmination of the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
of the early 1800s.
History
Syrians are of diverse origins; the main influence came from ancient Semitic peoples of theLevant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
such as the Arameans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
, as well as populations from Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
and modern-day Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
, with additional Greco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
influence. Ancient Syria of the first millennium BC was dominated by the Aramaeans; they originated in the Northern Levant as a continuum of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
populations of Syria, possibly being derived from the same population as ancient Phoenician or Canaanite peoples. The Seleucids ruled the Syrians as a conquered nation; Syrians were not assimilated into Greek communities, and many local peasants were exploited financially as they had to pay rent for Greek landlords. Outside Greek colonies
Greek colonization was an organised colonial expansion by the Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8th–6th centuries BC.
This colonization differed from the migrations of the Greek Dark Ages in that it ...
, the Syrians lived in districts governed by local temples that did not use the Greek civic system of '' poleis'' and colonies. The situation changed after the Roman conquest in 64 BC; Syrians obtained the citizenship of Greek ''poleis'', and the line separating between the colonists and the colonized blurred. The idioms Syrian and Greek were used by Rome to denote civic societies instead of separate ethnic groups.
The Aramaeans assimilated the earlier Greek and Roman populations through their language; combined with the religion of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, most of the inhabitants turned into Syrians (Aramaeans). Islam and the Arabic language had a similar effect where the Aramaeans themselves became Arabs regardless of their ethnic origin following the Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant ( ar, فَتْحُ الشَّام, translit=Feth eş-Şâm), also known as the Rashidun conquest of Syria, occurred in the first half of the 7th century, shortly after the rise of Islam."Syria." Encyclopædia Br ...
. The presence of Arabs in Syria is recorded since the 9th century BC, and Roman period historians, such as Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
, and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
, reported that Arabs inhabited many parts of Syria. What antiquity's writers meant by the designation "Arab" is debated; the historian Michael Macdonald suggested that the term is an ethnic designation based on an "ill-defined complex of linguistic and cultural characteristics", while according to academic consensus, "Arab", in addition to it being an ethnic name, had a social meaning describing a nomadic way of life. The '' urheimat'' of the Arab ethnos is unclear; the traditional 19th century theory locates this in the Arabian Peninsula, while some modern scholars, such as David Frank Graf, note that the epigraphic and archaeological evidence render the traditional theory inadequate to explain the Arabs' appearance in Syria. The Arabs mentioned in Syria by Greco-Roman writers were assimilated into the newly formed "Greco–Aramaean culture" that dominated the region, and the texts they produced were written in Greek, Aramaic and Old Arabic
Old Arabic is the name for the pre-Islamic Arabic language or dialect continuum. Various forms of Old Arabic are attested in many scripts like Safaitic, Hismaic, Nabatean, and even Greek.
Classification
Old Arabic and its descendants are class ...
, the precursor of Classical Arabic
Classical Arabic ( ar, links=no, ٱلْعَرَبِيَّةُ ٱلْفُصْحَىٰ, al-ʿarabīyah al-fuṣḥā) or Quranic Arabic is the standardized literary form of Arabic used from the 7th century and throughout the Middle Ages, most notab ...
, which was not a literary language; its speakers used Aramaic for writing purposes.
Arabization
On the eve of theRashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
conquest of the Levant, 634 AD, Syria's population mainly spoke Aramaic as the Lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
, while Greek was the language of administration. Arabization
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, تعريب, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, aft ...
and Islamization
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occur ...
of Syria began in the 7th century, and it took several centuries for Islam, the Arab identity, and language to spread; the Arabs of the caliphate did not attempt to spread their language or religion in the early periods of the conquest, and formed an isolated aristocracy. The Arabs of the caliphate accommodated many new tribes in isolated areas to avoid conflict with the locals; caliph Uthman ordered his governor, Muawiyah I
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the deat ...
, to settle the new tribes away from the original population. Syrians who belonged to Monophysitic
Miaphysitism is the Christological doctrine that holds Jesus, the "Incarnate Word, is fully divine and fully human, in one 'nature' (''physis'')." It is a position held by the Oriental Orthodox Churches and differs from the Chalcedonian positio ...
denominations welcomed the Muslim Arabs as liberators.
The Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
in the eighth and ninth century sought to integrate the peoples under their authority, and the Arabization of the administration was one of their methods. Arabization gained momentum with the increasing numbers of Muslim converts from Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
; the ascendancy of Arabic as the formal language of the state prompted the cultural and linguistic assimilation of Syrian converts. Some of those who remained Christian also became arabized, while others stayed Aramean, it was probably during the Abbasid period in the ninth century that Christians adopted Arabic as their first language; the first translation of the gospels into Arabic took place in this century. Many historians, such as Claude Cahen and Bernard Hamilton, proposed that the Arabization of Christians was completed before the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
. By the thirteenth century, the Arabic language achieved complete dominance in the region, with many of its speakers having become Arabs. Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
*The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the
Those who retained the Aramaic language are divided among two groups:
*The Eastern Aramaic Syriac-speaking group, followers of the West Syriac Rite of the Syriac Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = syc
, image = St_George_Syriac_orthodox_church_in_Damascus.jpg
, imagewidth = 250
, alt = Cathedral of Saint George
, caption = Cathedral of Saint George, Damascus ...
and the Syrian Catholic Church; they kept the pre-Islamic Syrian (Syriac) identity throughout the ages, asserting their culture in face of the Arab dominance. Linguists, such as Carl Brockelmann
Carl Brockelmann (17 September 1868 – 6 May 1956) German Semiticist, was the foremost orientalist of his generation. He was a professor at the universities in Breslau, Berlin and, from 1903, Königsberg. He is best known for his multi-volume ...
and François Lenormant
François Lenormant (17 January 1837 – 9 December 1883) was a 19th-century French Hellenist, Assyriologist and archaeologist.
Biography Early life
Lenormant's father, Charles Lenormant, distinguished as an archaeologist, numismatist and Egypt ...
, suggested that the rise of the Garshuni Garshuni or Karshuni ( Syriac alphabet: , Arabic alphabet: ) are Arabic writings using the Syriac alphabet. The word "Garshuni", derived from the word "grasha" which literally translates as "pulling", was used by George Kiraz to coin the term "gars ...
writing (using Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet ( ) is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language since the 1st century AD. It is one of the Semitic abjads descending from the Aramaic alphabet through the Palmyrene alphabet, and shares similarities with ...
to write Arabic) was an attempt by the Syriac Orthodox to assert their identity. Syriac is still the liturgical language for most of the different Syriac churches in Syria. The Syriac Orthodox Church was known as the Syrian Orthodox Church until 2000, when the holy synod decided to rename it to avoid any nationalistic connotations; the Catholic Church still has "Syrian" in its official name.
*The Western Neo-Aramaic-speaking group, that is, the inhabitants of Bakh'a, Jubb'adin
Jubb'adin or Ġuppaҁōḏ ( ar, جبعدين, arc, ܓܦܥܘܕ - ) is a village in southern Syria, administratively part of the Rif Dimashq Governorate, located northeast of Damascus in the Qalamoun Mountains. Nearby localities include Saidnaya a ...
and Ma'loula
Maaloula or Maʿlūlā ( arc, ܡܥܠܘܠܐ in Eastern Aramaic Syriac script, ' in Western Aramaic Maalouli script; ar, مَعلُولَا) is a town in the Rif Dimashq Governorate in Syria. The town is located 56 km to the northeast of Dama ...
. The residents of Bakh'a and Jubb'adin converted to Islam in the eighteenth century (retaining their Aramean identity), while in Ma'loula, the majority are Christians, mainly belonging to the Melkite Greek Catholic Church
el, Μελχιτική Ελληνική Καθολική Εκκλησία
, image = Melkite Greek Catholic Church, Damascus, Syria.jpg
, imagewidth = 200px
, alt =
, caption =
, abbreviatio ...
, but also to the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch ( el, Ελληνορθόδοξο Πατριαρχείο Αντιοχείας), also known as the Antiochian Orthodox Church and legally as the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East ( ar ...
, in addition to a Muslim minority, who speaks the same Aramaic dialect of the Christian residents. The people of those villages use Arabic intensively to communicate with each other and the rest of the country; this led to a noticeable Arabic influence on their Aramaic dialect where around 20% of its vocabulary is of Arabic roots. Bakh'a is steadily losing its dialect; by 1971, people aged younger than 40 could no longer use the Aramaic language properly, although they could understand it. The situation of Bakh'a might eventually lead to the extinction of its Aramaic dialect.
Identity
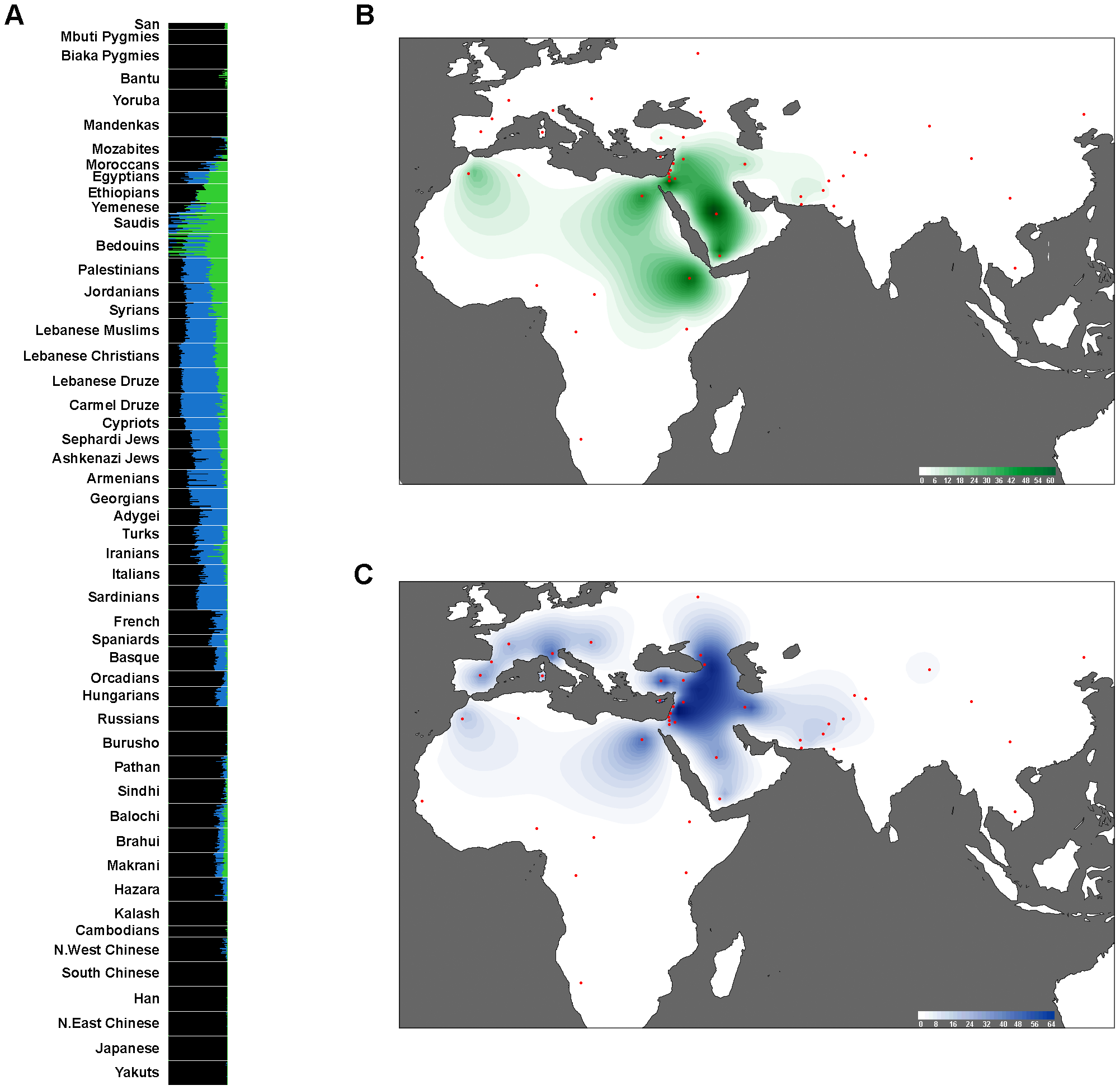
Besides religious identities, the Syrian people are split among three identities, the Arab, Syriac, and Syrian identities. Many Muslims and some Arabic-speaking Christians describe themselves as Arabs, while many Aramaic-speaking Christians and some Muslims prefer to describe themselves as Syriacs or Arameans. Also some people from Syria, mainly Syrian nationalists, describe themselves only as Syrians or ethnic Syrians. Most of the divisions in ethnic nomenclature are actually due to religious backgrounds.Genetics
 Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient
Genetic tests on Syrians were included in many genetic studies. The genetic marker which identifies descendants of the ancient Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
ines is found in Syrians in high proportion. Modern Syrians exhibit "high affinity to the Levant" based on studies comparing modern and ancient DNA samples. Syrians cluster closely with ancient Levantine populations of the Neolithic and Bronze Ages. A Levantine ancestral genetic component was identified; it is estimated that the Levantine, the Peninsular Arabian and East African ancestral components diverged 23,700-15,500 years ago, while the divergence between the Levantine and European components happened 15,900-9,100 years ago. The Levantine ancestral component is the most recurrent in Levantines (42–68%); the Peninsular Arabian and East African ancestral components represent around 25% of Syrian genetic make-up.
The paternal Y-DNA haplogroup J1, which reaches its highest frequencies in Yemen 72.6% and Qatar 58.3%, accounted for 33.6% of Syrians. The J2 group accounted for 20.8% of Syrians; other Y-DNA haplogroups include the E1B1B 12.0%, I 5.0%, R1a 10.0% and R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and pockets of Central A ...
15.0%. The Syrians are closest to other Levantine populations: the Lebanese, the Palestinians
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
and Jordanians; this closeness can be explained with the common Canaanite ancestry and geographical unity which was broken only in the twentieth century with the advent of British and French mandates. Regarding the genetic relation between the Syrians and the Lebanese based on Y-DNA, Muslims from Lebanon show closer relation to Syrians than their Christian compatriots. The people of Western Syria show close relation with the people of Northern Lebanon.
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
shows the Syrians to have affinity with Europe; main haplogroups are H and R. Based on Mitochondrial DNA, the Syrians, Palestinian, Lebanese and Jordanians form a close cluster. Compared to the Lebanese, Bedouins and Palestinians, the Syrians have noticeably more Northern European component, estimated at 7%. Regarding the HLA alleles, Syrians, and other Levantine populations, exhibit "key differences" from other Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
populations; based on HLA-DRB1
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HLA-DRB1'' gene. DRB1 encodes the most prevalent beta subunit of HLA-DR. DRB1 alleles, especially those encoding amino acid sequence changes at ...
alleles, Syrians were close to eastern Mediterranean populations, such as the Cretans and Lebanese Armenians
The Armenians in Lebanon ( hy, Լիբանանահայեր, translit=Libananahayer; ar, الأرمن في لبنان; french: Arméniens du Liban) are Lebanese citizens of Armenian descent. There has been an Armenian presence in Lebanon for centur ...
. Studying the genetic relation between Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and Syrians showed that the two populations share close affinity. Apparently, the cultural influence of Arab expansion in the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
in the seventh century was more prominent than the genetic influx. However, the expansion of Islam did leave an impact on Levantine genes; religion drove Levantine Muslims to mix with other Muslim populations, who were close culturally despite the geographic distance, and this produced genetic similarities between Levantine Muslims and Moroccan and Yemeni populations. Christians and Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
became a genetic isolate in the predominantly Islamic world.
Language
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
is the mother tongue of the majority of Syrians as well as the official state language. The Syrian variety of Levantine Arabic differs from Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of Standard language, standardized, Literary language, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th ...
. Western Neo-Aramaic, the only surviving Western Aramaic language, is still spoken in three villages (Ma'loula
Maaloula or Maʿlūlā ( arc, ܡܥܠܘܠܐ in Eastern Aramaic Syriac script, ' in Western Aramaic Maalouli script; ar, مَعلُولَا) is a town in the Rif Dimashq Governorate in Syria. The town is located 56 km to the northeast of Dama ...
, Al-Sarkha (Bakhah) and Jubb'adin
Jubb'adin or Ġuppaҁōḏ ( ar, جبعدين, arc, ܓܦܥܘܕ - ) is a village in southern Syria, administratively part of the Rif Dimashq Governorate, located northeast of Damascus in the Qalamoun Mountains. Nearby localities include Saidnaya a ...
) in the Anti-Lebanon Mountains by both Muslim and Christian residents. Syriac-Arameans in the northeast of the country are mainly Surayt/Turoyo speakers but there are also some speakers of Sureth Aramaic, especially in the Khabour Valley. Classical Syriac
The Syriac language (; syc, / '), also known as Syriac Aramaic (''Syrian Aramaic'', ''Syro-Aramaic'') and Classical Syriac ܠܫܢܐ ܥܬܝܩܐ (in its literary and liturgical form), is an Aramaic dialect that emerged during the first century ...
is also used as a liturgical language by Syriac Christians. English, and to a lesser extent French, is widely understood and used in interactions with tourists and other foreigners.
Religion and minority groups
Religious differences in Syria have historically been tolerated, and religious minorities tend to retain distinct cultural, and religious identities.Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
is the religion of 74% of Syrians. The Alawites
The Alawis, Alawites ( ar, علوية ''Alawīyah''), or pejoratively Nusayris ( ar, نصيرية ''Nuṣayrīyah'') are an ethnoreligious group that lives primarily in Levant and follows Alawism, a sect of Islam that originated from Shia Isla ...
, a variety of Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
, make up 12% of the population and mostly live in and around Tartus
)
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Tartus corniche Port of Tartus • Tartus beach and boulevard Cathedral of Our Lady of Tortosa • Al-Assad Stadium&n ...
and Latakia
, coordinates =
, elevation_footnotes =
, elevation_m = 11
, elevation_ft =
, postal_code_type =
, postal_code =
, area_code = Country code: 963 City code: 41
, geocode ...
. Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
make up 10% of the country. Most Syrian Christians adhere to the Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
Th ...
; the two largest are the Antiochian Orthodox Church and the Melkite Greek Catholic Church
el, Μελχιτική Ελληνική Καθολική Εκκλησία
, image = Melkite Greek Catholic Church, Damascus, Syria.jpg
, imagewidth = 200px
, alt =
, caption =
, abbreviatio ...
. The Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
are a mountainous people who reside in Jabal al-Druze
Jabal al-Druze ( ar, جبل الدروز, ''jabal ad-durūz'', ''Mountain of the Druze''), officially Jabal al-Arab ( ar, جبل العرب, links=no, ''jabal al-ʿarab'', ''Mountain of the Arabs''), is an elevated volcanic region in the As-Suwa ...
who helped spark the Great Syrian Revolt
The Great Syrian Revolt ( ar, الثورة السورية الكبرى) or Revolt of 1925 was a general uprising across the State of Syria and Greater Lebanon during the period of 1925 to 1927. The leading rebel forces comprised fighters of the ...
. The Ismailis are an even smaller sect that originated in Asia. Many Armenian and Assyrian Christians fled Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
during the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
and the Assyrian genocide
The Sayfo or the Seyfo (; see below), also known as the Assyrian genocide, was the mass slaughter and deportation of Assyrian / Syriac Christians in southeastern Anatolia and Persia's Azerbaijan province by Ottoman forces and some Kurdish t ...
and settled in Syria. There are also roughly 500,000 Palestinians
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
, who are mostly descendants of refugees from the 1948 Israeli-Arab War. The community of Syrian Jews
Syrian Jews ( he, יהודי סוריה ''Yehudey Surya'', ar, الْيَهُود السُّورِيُّون ''al-Yahūd as-Sūriyyūn'', colloquially called SYs in the United States) are Jews who lived in the region of the modern state of Syri ...
inside Syria once numbered 30,000 in 1947, but has only 200 today.
The Syrian people's beliefs and outlooks, similar to those of most Arabs and people of the wider Middle-East, are a mosaic of West and East. Conservative and liberally minded people will live right next to each other. Like the other countries in the region, religion permeates life; the government registers every Syrian's religious affiliation. However, the number of non-believers in Syria is increasing but there is no credible source or statistics to support this information.
Cuisine
 Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region.
Syrian cuisine is dominated by ingredients native to the region. Olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: f ...
, garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus ''Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Allium fistulosum, Welsh onion and Allium chinense, Chinese onion. It is native to South A ...
, olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
s, spearmint, and sesame oil are some of the ingredients that are used in many traditional meals. Traditional Syrian dishes enjoyed by Syrians include, tabbouleh, labaneh
Strained yogurt, Greek yogurt, yogurt cheese, sack yogurt, or kerned yogurt is yogurt that has been strained to remove most of its whey, resulting in a thicker consistency than normal unstrained yogurt, while still preserving the distinctive so ...
, shanklish
Shanklish ( ''shanklīsh'' or شنغليش ''shanghlīsh''), also known as chancliche, shinklish, shankleesh, sorke, or sürke, is a type of cow's milk or sheep milk cheese in Levantine cuisine.
Shanklish is made by curdling yoghurt, straining it ...
, wara' 'enab, makdous
Makdous ( ar, المكدوس or sometimes ) is a dish of oil-cured aubergines. Part of Iraqi and Levantine cuisine (Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, Syria), they are tiny, tangy eggplants stuffed with walnuts, red pepper, garlic, olive oil, ...
, kebab
Kebab (, ; ar, كباب, link=no, Latn, ar, kabāb, ; tr, kebap, link=no, ) or kabob (North American) is a type of cooked meat dish that originates from cuisines of the Middle East. Many variants of the category are popular around the wor ...
, Kibbeh
Kibbeh (, also kubba and other spellings; ar, كبة, kibba; tr, içli köfte) is a family of dishes based on spiced ground meat, onions, and grain, popular in Middle Eastern cuisine.
In Levantine cuisine, kibbeh is usually made by pounding ...
, sfiha, moutabal
Baba ghanoush (, ;"baba ghanouj"
(US) and
, (US) and
hummus
Hummus (, ; ar, حُمُّص, 'chickpeas'; full Arabic name: ''ḥummuṣ bi-ṭ-ṭaḥīna'' ar, حمص بالطحينة, 'chickpeas with tahini'), also spelled hommus or houmous, is a Middle Eastern dip, spread, or savory dish made fr ...
, mana'eesh, bameh, and fattoush
Fattoush ( ar, فتوش; also fattush, fatush, fattoosh, and fattouche) is a Levantine salad made from toasted or fried pieces of khubz (Arabic flat bread) combined with mixed greens and other vegetables, such as radishes and tomatoes.Wright, 2 ...
.
A typical Syrian breakfast is a meze
Meze or mezza (, ) is a selection of small dishes served as appetizers in the Levant, Turkey, Greece, the Balkans, the Caucasus and Iran. It is similar to Spanish tapas and Italian antipasti. A mezze may be served as a part of a multi-course me ...
. It is an assortment platter of foods with cheeses, meats, pickles, olives, and spreads. Meze is usually served with Arab-style tea - highly concentrated black tea, which is often highly sweetened and served in small glass cups. Another popular drink, especially with Christians and non-practicing Muslims, is the arak, a liquor produced from grapes or dates and flavored with anise
Anise (; '), also called aniseed or rarely anix is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to Eurasia.
The flavor and aroma of its seeds have similarities with some other spices and herbs, such as star anise, fennel, licorice, and ta ...
that can have an alcohol content of over 90% ABV (however, most commercial Syrian arak brands are about 40-60% ABV).
Notable people

Scholars
*Iamblichus
Iamblichus (; grc-gre, Ἰάμβλιχος ; Aramaic: 𐡉𐡌𐡋𐡊𐡅 ''Yamlīḵū''; ) was a Syrian neoplatonic philosopher of Arabic origin. He determined a direction later taken by neoplatonism. Iamblichus was also the biographer of ...
, a philosopher, mystic and mathematician
* Porphyry, a philosopher and polemicist
* Damascius, head of Plato's Academy: dubbed the "last of the Athenian Neoplatonists"
*Syrianus
Syrianus ( grc, Συριανός, ''Syrianos''; died c. 437 A.D.) was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, and head of Plato's Academy in Athens, succeeding his teacher Plutarch of Athens in 431/432 A.D. He is important as the teacher of Proclus, and, ...
, head of Plato's Academy and teacher of Proclus
Proclus Lycius (; 8 February 412 – 17 April 485), called Proclus the Successor ( grc-gre, Πρόκλος ὁ Διάδοχος, ''Próklos ho Diádokhos''), was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers ...
*Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
Pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets, unbound (and therefore ...
, a satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
* Posidonius, a polymath
* Libanius, a teacher of rhetoric and sophist author
*John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Χρυσόστομος; 14 September 407) was an important Early Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his homilies, preaching and public speaking, his denunciat ...
, Syrian-Greek Church Father and archbishop of Constantinople
* Thebit, a polymath who has a significant contributions in maths, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
and physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
. He also worked in translation with Syriac, Greek and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
*Severus Sebokht
Severus Sebokht ( syc, ܣܘܪܘܣ ܣܝܒܘܟܬ), also Seboukt of Nisibis, was a Syrian scholar and bishop who was born in Nisibis, Syria in 575 and died in 667.
Although little is known about his early life, he was one of the leading figures in ...
, scholar and astronomer; the first Syrian to employ the Indian number system.
*Al-Battani
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Jābir ibn Sinān al-Raqqī al-Ḥarrānī aṣ-Ṣābiʾ al-Battānī ( ar, محمد بن جابر بن سنان البتاني) ( Latinized as Albategnius, Albategni or Albatenius) (c. 858 – 929) was an astron ...
, who introduced a number of trigonometric relations; his Kitāb az-Zīj was frequently quoted by many other medieval astronomers, including Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated ...
.
* Ibn al-Nafis, polymath whose areas of work included medicine, surgery, physiology, anatomy, biology, Islamic studies, jurisprudence, and philosophy: mostly famous for being the first to describe the pulmonary circulation of the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
.
* Ibn al-Shatir, an astronomer, mathematician and engineer. He worked as muwaqqit
In the history of Islam, a ''muwaqqit'' ( ar, مُوَقَّت, more rarely ''mīqātī'') was an astronomer tasked with the timekeeping and the regulation of prayer times in an Islamic institution like a mosque or a madrasa. Unlike the mue ...
(موقت, religious timekeeper) in the Umayyad Mosque in Damascus and constructed a sundial for its minaret in 1371/72.
*John of Damascus
John of Damascus ( ar, يوحنا الدمشقي, Yūḥanna ad-Dimashqī; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Δαμασκηνός, Ioánnēs ho Damaskēnós, ; la, Ioannes Damascenus) or John Damascene was a Christian monk, priest, hymnographer, and a ...
, a polymath and theologian
*Meleager of Gadara
Meleager of Gadara ( grc-gre, Μελέαγρος ; fl. 1st century BC) was a poet and collector of epigrams. He wrote some satire, satirical prose, now lost, and some sensual poetry, of which 134 epigrams survive.
Life
Meleager was the son of E ...
, Syrian-Greek poet
*Raphael of Brooklyn
Raphael of Brooklyn ( ar, قديس رافائيل من بروكلين), born Rufāʾīl Hawāwīnī (Raphael Hawaweeny; ar, رفائيل هواويني; November 20, 1860 – February 27, 1915), was bishop of the Russian Orthodox Church, auxi ...
, of Damascene Syrian parents. The first Orthodox bishop to be consecrated in North America.
*Hunein Maassab
Hunein (John) Maassab ( ar, حنين معصّب) (born Hunein Maassab) was a Syrian-American professor of epidemiology known for developing the live attenuated influenza vaccine
Maassab was born June 11, 1926, in Damascus, Syria, he immigrated to ...
, professor of Epidemiology known for developing the Live attenuated influenza vaccine
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) is a type of influenza vaccine in the form of a nasal spray that is recommended for the prevention of influenza.
It is an attenuated vaccine, unlike most influenza vaccines, which are inactivated vaccine ...
.
*Shadia Habbal
Shadia Rifa'i Habbal (Arabic: شادية رفاعي حبال) is a Syrian-American astronomer and physicist specialized in Space physics. A professor of Solar physics, her research is centered on Solar wind and Solar eclipse.
Life and education
S ...
, an astronomer and physicist, played a key role in establishing the NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
Parker Solar Probe
*Riad Barmada
Riad Barmada ( ar, رياض برمدا; July 26, 1929 – January 10, 2014), a Syrian-American orthopaedic surgeon and professor. Barmada was the head of orthopedics at the University of Illinois at Chicago from 1984 to 1998 and served as the p ...
, orthopaedic surgeon and the former president of the Illinois Orthopedic Society
* Fawwaz T. Ulaby, Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
, received the IEEE Edison Medal in 2006.
*Juan José Saer
Juan José Saer ( Serodino, Santa Fe, Argentina, June 28, 1937Paris, France, June 11, 2005) was an Argentine writer, considered one of the most important in Latin American literature and in Spanish-language literature of the 20th century. He is ...
, Argentine writer. Lecturer at the University of Rennes
The University of Rennes is a public research university which will be officially reconstituted on 1 January 2023 and located in the city of Rennes, in Upper Brittany, France. The University of Rennes has been divided for almost 50 years, before ...
and winner of the Nadal Prize
Premio Nadal is a Spanish literary prize awarded annually by the publishing house Ediciones Destino, part of Planeta Group, Planeta. It has been awarded every year on 6 January since 1944. The Josep Pla Award for Catalan literature is given at the ...
.
*Kefah Mokbel
Professor Kefah Mokbel FRCS is the lead consultant breast surgeon at the London Breast Institute of the Princess Grace Hospital, Professor (Honorary) of Breast Cancer Surgery at Brunel University London, an honorary consultant breast surgeon at S ...
, FRCS. The lead breast surgeon at the London Breast Institute of The Princess Grace Hospital, professor of Breast Cancer Surgery (The Brunel Institute of Cancer Genetics and Pharmacogenomics) Brunel University London
Brunel University London is a Public university, public Research universities, research university located in the Uxbridge area of London, England. It was founded in 1966 and named after the Victorian era, Victorian engineer and pioneer of the I ...
.
* Oussama Khatib, a roboticist
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrat ...
and a professor of Computer Science at Stanford University. Received the IEEE RAS for Distinguished Service Award (2013).
*Dina Katabi
Dina Katabi ( ar, دينا قَتابي) is the Andrew and Erna Viterbi Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT and the director of the MIT Wireless Center.
Academic biography
Katabi received a bachelor's degree from the ...
, director of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
Wireless Center.
*Malatius Jaghnoon
Malatius Jibriel Jaghnoon, ( ar, ملاتيوس جبرائيل جغنون, born in Lattakia 1943), is a Syrian engineer and epigrapher specialized in Aramaic and Greek inscriptions.
Career
He was born in Syria to a Greek Orthodox family. He gra ...
, Epigrapher and founder of the archaeological society in Homs.
*Jorge Sahade
Jorge Sahade (born February 17, 1915, in Cordoba, Argentina, died December 18, 2012) was an Argentine astronomer with more than 200 publications in journals and conferences. His mother gave birth on February 17, but having been born very little ...
, founder of the University of Buenos Aires
The University of Buenos Aires ( es, Universidad de Buenos Aires, UBA) is a public university, public research university in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Established in 1821, it is the premier institution of higher learning in the country and one o ...
Institute of Astronomy and Physics of Space (IAFE) and the first Latin American to achieve the presidency of the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
Public figures and politicians
*Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced thro ...
, Roman emperor
*Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
, Roman emperor
*Avidius Cassius
Gaius Avidius Cassius ( 130 – July 175 AD) was a Syrian Roman general and usurper. He was born in Cyrrhus, and was the son of Gaius Avidius Heliodorus, who served as ''praefectus'' or governor of Roman Egypt, and Julia Cassia Alexandra, who w ...
, usurper of the Roman Empire
* Julia Domna, Roman empress
* Julia Maesa, Roman empress
* Elagabalus, Roman emperor
*Alexander Severus
Marcus Aurelius Severus Alexander (1 October 208 – 21/22 March 235) was a Roman emperor, who reigned from 222 until 235. He was the last emperor from the Severan dynasty. He succeeded his slain cousin Elagabalus in 222. Alexander himself was ...
, Roman emperor
* Philip the Arab, Roman emperor
*Gordian III
Gordian III ( la, Marcus Antonius Gordianus; 20 January 225 – February 244) was Roman emperor from 238 to 244. At the age of 13, he became the youngest sole emperor up to that point (until Valentinian II in 375). Gordian was the son of Anton ...
, Roman emperor
*Papinian
Aemilius Papinianus (; grc, Αἰμίλιος Παπινιανός; 142 CE–212 CE), simply rendered as Papinian () in English, was a celebrated Roman jurist, ''magister libellorum'', attorney general (''advocatus fisci'') and, after the dea ...
, Roman jurist
*Tiye
Tiye (c. 1398 BC – 1338 BC, also spelled Tye, Taia, Tiy and Tiyi) was the daughter of Yuya and Thuya. She became the Great Royal Wife of the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep III. She was the mother of Akhenaten and grandmother of Tutankhamun. I ...
, Great Royal Wife
Great Royal Wife, or alternatively, Chief King's Wife ( Ancient Egyptian: ''ḥmt nswt wrt'', cop, Ⲟⲩⲏⲣ Ⲟⲩⲣϣ), is the title that was used to refer to the principal wife of the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, who served many official ...
of the Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(.w), ''Amānəḥūtpū'' , "Amun is Satisfied"; Hellenized as Amenophis III), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different ...
( XVIII Dynasty of Egypt)
* Tiberius Claudius Pompeianus, Consul of the Roman Empire
* Leo III the Syrian, Byzantine emperor and founder of the Isaurian dynasty
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Isaurian or Syrian dynasty from 717 to 802. The Isaurian emperors were successful in defending and consolidating the Empire against the Caliphate after the onslaught of the early Muslim conquests, but were l ...
*Odaenathus
Septimius Odaenathus (Palmyrene Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; ar, أذينة, translit=Uḏaina; 220 – 267) was the founder king ( ''Mlk'') of the Palmyrene Kingdom who ruled from Palmyra, Syria. He elevated the status of his kingdom from a re ...
, Emperor of the Palmyrene Empire
*Vaballathus
Septimius Vaballathus (Palmyrene Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; ar, وهب اللات, translit=Wahb Allāt; 259 – c. 274 AD) was emperor of the Palmyrene Empire centred at Palmyra in the region of Syria. He came to power as a child under his re ...
, Emperor of Syria, Egypt and Cappadocia
*Eutropia
Eutropia (died after 325), a woman of Syrian origin, was the wife of Emperor Maximian.
Marriage to Maximian and their children
In the late 3rd century, she married Maximian, though the exact date of this marriage is uncertain. By Maximian, sh ...
, wife of the Roman emperor Maximian
Maximian ( la, Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maximianus; c. 250 – c. July 310), nicknamed ''Herculius'', was Roman emperor from 286 to 305. He was ''Caesar'' from 285 to 286, then ''Augustus'' from 286 to 305. He shared the latter title with his ...
*Cassiodorus
Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator (c. 485 – c. 585), commonly known as Cassiodorus (), was a Roman statesman, renowned scholar of antiquity, and writer serving in the administration of Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. ''Senator'' w ...
, Consul of the Roman Empire
*Carlos Menem
Carlos Saúl Menem (2 July 1930 – 14 February 2021) was an Argentine lawyer and politician who served as the President of Argentina from 1989 to 1999. Ideologically, he identified as a Peronist and supported economically liberal policies. H ...
(born July 2, 1930), former President of Argentina
The president of Argentina ( es, Presidente de Argentina), officially known as the president of the Argentine Nation ( es, Presidente de la Nación Argentina), is both head of state and head of government of Argentina. Under Constitution of Ar ...
(1989-1999).
*Carlos Fayt
Carlos Santiago Fayt (1 February 1918'' Página/12''Fayt canta los noventa 1 February 2008 – 22 November 2016) was an Argentine lawyer, politician, academic and a member of the Supreme Court of Justice of Argentina from 1983 to 2015.
(1918-2016), former minister of the Supreme Court of Argentina (1983-2015).
* Tareck El Aissami, former Vice President of Venezuela
The vice president of Venezuela ( es, Vicepresidente de Venezuela), officially known as the Executive Vice President of the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, Vicepresidente Ejecutivo de la República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is the second ...
(2017-2018), serving as Minister of Industries and National Production since 14 June 2018.
*Oscar Aguad
Oscar Raúl Aguad (born May 7, 1950) is an Argentine politician who served as the Minister of Defense from 2017 to 2019, serving in the cabinet of President Mauricio Macri. He was a member of the Chamber of Deputies from 2005 to 2015, where he ...
, former Minister of Defense of Argentina.
* Juliana Awada (born April 3, 1974), former First Lady of Argentina (2015-2019).
* Rosemary Barkett (born 1939), was the first woman to serve on the Florida Supreme Court, and the first woman Chief Justice of that court. She currently serves as a federal judge Federal judges are judges appointed by a federal level of government as opposed to the state/provincial/local level.
United States
A US federal judge is appointed by the US President and confirmed by the US Senate in accordance with Article 3 of ...
on the United States Court of Appeals for the Eleventh Circuit.
*Rushdi al-Kikhya
Rushdi al-Kikhya ( ar, رشدي الكيخيا; 1899– 14 March 1987) was a Syrian political leader who founded the People's party in 1948. Kikhya was elected as a Speaker of the Parliament of Syria between 1949 and 1951, and he was elected fiv ...
, Syrian political leader.
*Mustafa Bey Barmada
Mustafa Bey Barmada ( ar, مصطفى برمدا; 1883 – April 2, 1953) was a Syrian statesman, politician and judge; served as the Governor General of the State of Aleppo between 1923 and 1924 and headed the Judiciary of Syria between 1930s an ...
, former General Governor of the state of Aleppo.
*Haqqi al-Azm
Haqqi al-Azm ( ar, حقي العظم / ALA-LC: ''Ḥaqī al-‘Aẓm''; 1864, in Damascus – 1955) was a Syrian politician active during the late Ottoman period and during the First Syrian Republic. From 1932 to 1934, he served as Prime Minis ...
, former General Governor of the state of Damascus.
* Shukri al-Quwatli, former president of Syria.
*Nazim al-Kudsi
Nazim al-Qudsi ( ar, ناظم القدسي, Nāẓim al-Qudsī or Nadhim Al-Kudisi; 14 February 1906 – 6 February 1998), was a Syrian politician who served as President of Syria from 14 December 1961 to 8 March 1963.
Early life and education
...
, former president of Syria.
*Hashim al-Atassi
Hashim al-Atassi ( ar, هاشم الأتاسي, Hāšim al-ʾAtāsī; 11 January 1875 – 5 December 1960) was a Syrian nationalist and statesman and the President of Syria from 1936 to 1939, 1949 to 1951 and 1954 to 1955.
Background and e ...
, former president of Syria.
*Khalid al-Azm
Khalid al-Azm ( ar, خالد العظم, Khālid al-Aẓim; 11 June 1903 – 18 November 1965) was a Syrian national leader and five-time interim Prime Minister, as well as Acting President from 4 April to 16 September 1941. He was a member of o ...
, former prime minister of Syria.
*Saadallah al-Jabiri
Saadallah Al Jabiri ( ar, سعد الله الجابري; 1893–1947) was a Syrian Arab politician, a two-time prime minister and a two-time Minister of Foreign Affairs and Expatriates of Syria.
Jabiri was exiled by the French authorities to t ...
, former prime minister of Syria.
*Fares al-Khoury
Faris al-Khoury ( ar, فارس الخوري, Fāris al-Khūrī) (November 20, 1877 – January 2, 1962) was a Syrian statesman, minister, prime minister, speaker of parliament, and father of modern Syrian politics. Faris Khoury went on to become p ...
, former prime minister of Syria.
*Said al-Ghazzi
Said Al-Ghazzi ( ar, سعيد الغزي; 11 June 1893 – 18 September 1967) was a Syrian lawyer, politician and two time prime minister of Syria. He was born in Damascus.
Early life
Said belonged to the prominent al-Ghazzi family, wh ...
, former prime minister of Syria.
* Nureddin al-Atassi, former president of Syria.
*Nizar Kabbani
Nizar Tawfiq Qabbani ( ar, نزار توفيق قباني, , french: Nizar Kabbani; 21 March 1923 – 30 April 1998) was a Syrian diplomat, poet, writer and publisher. He is considered to be Syria's National Poet. His poetic style combines sim ...
, Syrian poet and prominent feminist
Feminism is a range of socio-political movements and ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social equality of the sexes. Feminism incorporates the position that society prioritizes the male po ...
figure in Western Asia and North Africa.
* Mitch Daniels, American politician, Governor of Indiana from 2005 to 2013 and President of Purdue University
Purdue University is a public land-grant research university in West Lafayette, Indiana, and the flagship campus of the Purdue University system. The university was founded in 1869 after Lafayette businessman John Purdue donated land and money ...
.
*Queen Noor of Jordan
Noor Al-Hussein ( ar, نور الحسين; born Lisa Najeeb Halaby; August 23, 1951) is an American-born Jordanian philanthropist and activist who is the fourth wife and widow of King Hussein of Jordan. She was Queen of Jordan from their marriag ...
, widow of King Hussein of Jordan, is of paternal Syrian ancestry.
* Justin Amash, former U.S. Representative.
* Omar Alghabra, Canadian politician, member of the House of Commons of Canada
The House of Commons of Canada (french: Chambre des communes du Canada) is the lower house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the Senate of Canada, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada.
The House of Common ...
, and federal Minister of Transport.
*Romeu Tuma
Romeu Tuma (October 4, 1931 – October 26, 2010) was a Brazilian politician and a former director of the Federal Police.
Tuma was born on October 4, 1931, in São Paulo, Brazil. He died on October 26, 2010, of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome ...
(1931-2010), Brazilian politician.
Religious Figures
*Ephrem the Syrian
Ephrem the Syrian ( syc, ܡܪܝ ܐܦܪܝܡ ܣܘܪܝܝܐ, Mār ʾAp̄rêm Sūryāyā, ; grc-koi, Ἐφραὶμ ὁ Σῦρος, Efrém o Sýros; la, Ephraem Syrus; am, ቅዱስ ኤፍሬም ሶርያዊ; ), also known as Saint Ephrem, Saint ...
, saint and polymath
*Pope Anicetus
Pope Anicetus was the bishop of Rome from c. 157 to his death in April 168.Campbell, Thomas (1907). "Pope St. Anicetus" in ''The Catholic Encyclopedia''. Vol. 1. New York: Robert Appleton Company. According to the ''Annuario Pontificio'', the sta ...
c. 168, Bishop of Rome (Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
)
* Pope John V
Pope John V ( la, Ioannes V; died 2 August 686) was the bishop of Rome from 23 July 685 to his death. He was the first pope of the Byzantine Papacy consecrated without prior imperial consent, and the first in a line of ten consecutive popes of ...
, Roman Catholic pope, 685-686
*Pope Sergius I
Pope Sergius I (8 September 701) was the bishop of Rome from 15 December 687 to his death, and is revered as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church. He was elected at a time when two rivals, Paschal and Theodore, were locked in dispute about wh ...
, Roman Catholic pope, 687-701
* Pope Sisinnius
Pope Sisinnius (c. 6504 February 708) was the bishop of Rome from 15 January 708 to his death.
Sisinnius was born in Tyre (modern-day Lebanon), and his father's name was John. The paucity of donations to the papacy during his reign (42 pounds o ...
, Roman Catholic pope, 708
* Pope Constantine
Pope Constantine ( la, Constantinus; 6649 April 715) was the bishop of Rome from 25 March 708 to his death. One of the last popes of the Byzantine Papacy, the defining moment of Constantine's pontificate was his 710/711 visit to Constantinople wh ...
, Roman Catholic pope, 708-715
* Pope Gregory III
Pope Gregory III ( la, Gregorius III; died 28 November 741) was the bishop of Rome from 11 February 731 to his death. His pontificate, like that of his predecessor, was disturbed by Byzantine iconoclasm and the advance of the Lombards, in which ...
, Roman Catholic pope, 731-741
*Philip the Apostle
Philip the Apostle ( el, Φίλιππος; Aramaic: ܦܝܠܝܦܘܣ; cop, ⲫⲓⲗⲓⲡⲡⲟⲥ, ''Philippos'') was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Later Christian traditions describe Philip as the apostl ...
, Christian saint and apostle
*James the Great
James the Great, also known as James, son of Zebedee, Saint James the Great, Saint James the Greater, Saint James the Elder, or Saint Jacob (Aramaic ܝܥܩܘܒ ܒܪ ܙܒܕܝ, Arabic يعقوب, Hebrew בן זבדי , '' Yaʿăqōḇ'', Latin '' ...
, One of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus
* Simeon Stylites, saint
*Andrew Stratelates
Andrew Stratelates, also known as Andrew the Tribune (Greek: Ἀνδρέας ὁ Στρατηλάτης, tr. Andréas o Stratelátes) or Andrew the Commander is a 3rd-century Roman soldier who is commemorated with his 2,593 soldiers as martyrs by ...
, saint
*Ananias of Damascus
Ananias ( ; grc, Ἀνανίας from Hebrew חנניה, ''Hananiah'', "favoured of the ") was a disciple of Jesus at Damascus mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles in the Bible, which describes how he was sent by Jesus to restore the sight of ...
, Disciple of Jesus Christ
*Cosmas and Damian
Cosmas and Damian ( ar, قُزما ودميان, translit=Qozma wa Demyaan; grc-gre, Κοσμᾶς καὶ Δαμιανός, translit=Kosmás kai Damianós; la, Cosmas et Damianus; AD) were two Arab physicians in the town Cyrrhus, and were r ...
, saints and physicians
* Thaddeus of Edessa، was one of the seventy disciples of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
.
*Luke the Evangelist
Luke the Evangelist (Latin: '' Lucas''; grc, Λουκᾶς, '' Loukâs''; he, לוקאס, ''Lūqās''; arc, /ܠܘܩܐ לוקא, ''Lūqā’; Ge'ez: ሉቃስ'') is one of the Four Evangelists—the four traditionally ascribed authors of t ...
, is one of the Four Evangelists
*Sergius and Bacchus, martyrs and military saints
*Lucian of Antioch, Christian martyr, presbyter and theologian
Business
*Steve Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011), was the co-founder and former Chief executive officer, CEO of Apple Inc., Apple, the largest The Walt Disney Company, Disney shareholder, and a member of Disney's Board of Directors. Jobs was considered a leading figure in both the computer industry, computer and entertainment industry, entertainment industries. *Jacques Saadé, was a billionaire with a net worth of $7 billion. *Rodolphe Saadé, billionaire with a net worth of $10.9 billion. *Jose Mugrabi billionaire with a net worth $5 billion *Ayman Asfari, Chief Executive of Petrofac. *Najeeb Halaby, American politician and businessman, former Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense, former CEO and chairman of Pan American World Airways, Pan Am and father ofQueen Noor of Jordan
Noor Al-Hussein ( ar, نور الحسين; born Lisa Najeeb Halaby; August 23, 1951) is an American-born Jordanian philanthropist and activist who is the fourth wife and widow of King Hussein of Jordan. She was Queen of Jordan from their marriag ...
.
*Wafic Saïd, established the Saïd Foundation in 1982 and the Saïd Business School at the University of Oxford in 1996.
*Mohed Altrad, French-Syrian businessman.
*Arturo Elías Ayub, Mexican businessman, Director of Telmex.
*Joseph Safra, Chairman of Banco Safra.
*Ronaldo Mouchawar, CEO and co-founder of Souq.com
*Sam Yagan, Internet entrepreneur best known as the co-founder of OkCupid, SparkNotes and Match.com.
*Omar Hamoui, the founder of AdMob, has a net worth of $300 million.
*Mohammed Rahif Hakmi, founder and Chairman of Armada Group
Entertainment
Central Casting: The Race Card
''The New Yorker'', November 10, 2003. Retrieved June 16, 2008. * Teri Hatcher, American actress. * Jerry Seinfeld, American comedian. * Bassam Kousa, Syrian actor. *Paula Abdul, American singer, songwriter, dancer, choreographer, actress, and television personality.
Sport
*Ghada Shouaa, heptathlete, olympic gold medalist. *Philipp Stamma was a chess master and a pioneer of modern chess. *Yasser Seirawan, chess grandmaster and four-time United States champion. *Carolina Duer, Argentine boxer and former world champion. *Brandon Saad, American ice hockey player, of paternal Syrian descent. *Rocco Baldelli, American former MLB player. *Sami Zayn, professional wrestler. *Mojo Rawley, professional wrestlerSee also
*History of Syria *Ottoman Syria *Arameans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
*Armenians
*Arabs
*Al-Shaitat
*Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
*Greeks
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Syrian people, Every Culture
{{Authority control Syrian people, Syrian diaspora Semitic-speaking peoples Articles containing video clips Ethnic groups in the Middle East