Toponymy
In 1788, CaptainHistory
First inhabitants of the region
 The first people to inhabit the area now known as Sydney were Aboriginal Australians who had migrated from northern Australia and before that from southeast Asia. Flaked pebbles found in Western Sydney's gravel sediments might indicate human occupation from 45,000 to 50,000 years BP, while
The first people to inhabit the area now known as Sydney were Aboriginal Australians who had migrated from northern Australia and before that from southeast Asia. Flaked pebbles found in Western Sydney's gravel sediments might indicate human occupation from 45,000 to 50,000 years BP, while Convict town (1788–1840)
Britain had been sending convicts to its American colonies for most of the eighteenth century, and the loss of these colonies in 1783 was the impetus for the decision to establish a penal colony at Botany Bay. Proponents of colonisation also pointed to the strategic importance of a new base in the Asia-Pacific region and its potential to provide much-needed timber and flax for the navy. The After the departure of Phillip in December 1792, the colony's military officers began acquiring land and importing consumer goods obtained from visiting ships. Former convicts also engaged in trade and opened small businesses. Soldiers and former convicts built houses on Crown land, with or without official permission, in what was now commonly called Sydney town. Governor William Bligh (180608) imposed restrictions on trade and commerce in the town and ordered the demolition of buildings erected on Crown land, including some owned by past and serving military officers. The resulting conflict culminated in the Rum Rebellion of 1808, in which Bligh was deposed by the New South Wales Corps.
Governor
After the departure of Phillip in December 1792, the colony's military officers began acquiring land and importing consumer goods obtained from visiting ships. Former convicts also engaged in trade and opened small businesses. Soldiers and former convicts built houses on Crown land, with or without official permission, in what was now commonly called Sydney town. Governor William Bligh (180608) imposed restrictions on trade and commerce in the town and ordered the demolition of buildings erected on Crown land, including some owned by past and serving military officers. The resulting conflict culminated in the Rum Rebellion of 1808, in which Bligh was deposed by the New South Wales Corps.
Governor 
Conflict on the Cumberland Plain
In 1804, Irish convicts led around 300 rebels in theColonial city (1841–1900)
The New South Wales Legislative Council was transformed into a semi-elected body in 1842. The town of Sydney was declared a city the same year, and a governing council established, elected on a restrictive property franchise.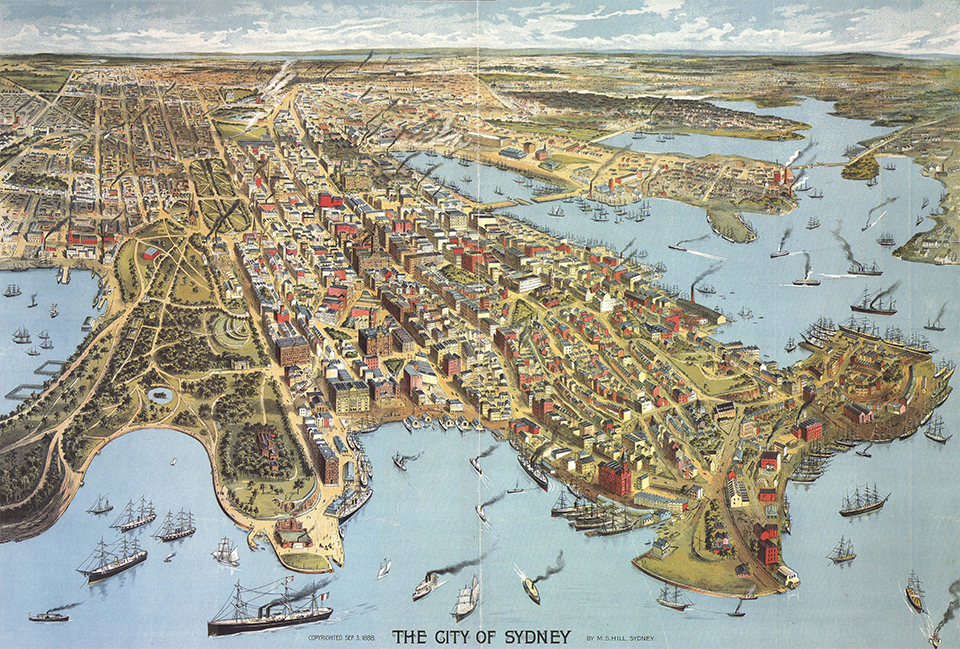 The discovery of gold in New South Wales and Victoria in 1851 initially caused some economic disruption as male workers moved to the goldfields. Melbourne soon overtook Sydney as Australia's largest city, leading to an enduring rivalry between the two cities. However, increased immigration from overseas and wealth from gold exports increased demand for housing, consumer goods, services and urban amenities.Goodman, David (2013). "The gold rushes of the 1850s". ''The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume I''. pp. 180–81. The New South Wales government also stimulated growth by investing heavily in railways, trams, roads, ports, telegraph, schools and urban services. The population of Sydney and its suburbs grew from 95,600 in 1861 to 386,900 in 1891. The city developed many of its characteristic features. The growing population packed into rows of terrace houses in narrow streets. New public buildings of sandstone abounded, including at the University of Sydney (1854–61), the Australian Museum (1858–66), the Town Hall (1868–88), and the
The discovery of gold in New South Wales and Victoria in 1851 initially caused some economic disruption as male workers moved to the goldfields. Melbourne soon overtook Sydney as Australia's largest city, leading to an enduring rivalry between the two cities. However, increased immigration from overseas and wealth from gold exports increased demand for housing, consumer goods, services and urban amenities.Goodman, David (2013). "The gold rushes of the 1850s". ''The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume I''. pp. 180–81. The New South Wales government also stimulated growth by investing heavily in railways, trams, roads, ports, telegraph, schools and urban services. The population of Sydney and its suburbs grew from 95,600 in 1861 to 386,900 in 1891. The city developed many of its characteristic features. The growing population packed into rows of terrace houses in narrow streets. New public buildings of sandstone abounded, including at the University of Sydney (1854–61), the Australian Museum (1858–66), the Town Hall (1868–88), and the State capital (1901–present)
When the six colonies federated on 1 January 1901, Sydney became the capital of the State of New South Wales. The spread of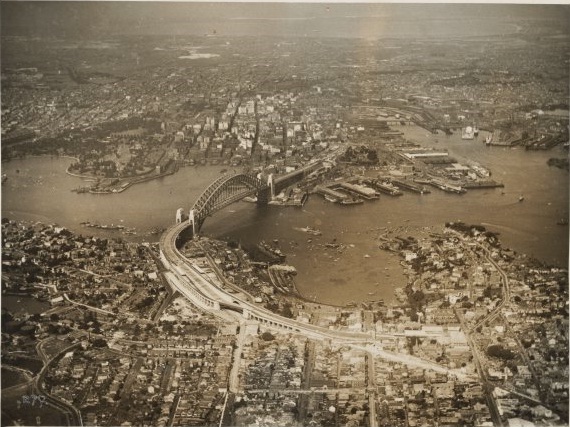 Sydney was more severely affected by the
Sydney was more severely affected by the Geography
Topography
 Sydney is a coastal basin with the Tasman Sea to the east, the Blue Mountains to the west, the Hawkesbury River to the north, and the Woronora Plateau to the south. The inner City Of Sydney measures , the Greater Sydney region (which includes the non-metropolitan areas of Central Coast, Blue Mountains, Wollondilly, Wollongong and Shellharbour) covers , and the city's urban area is in size. Metropolitan Sydney's boundaries stretch 88 kilometres (55 mi) from Palm Beach, New South Wales, Palm Beach in the north to Waterfall, New South Wales, Waterfall in the south, and 70 kilometres (43 mi) from Bondi Beach in the east to Emu Plains, New South Wales, Emu Plains in the west.
Sydney spans two geographic regions. The Cumberland Plain lies to the south and west of the Harbour and is relatively flat. The Hornsby Plateau is located to the north and is dissected by steep valleys. The flat areas of the south were the first to be developed as the city grew. It was not until the construction of the Sydney Harbour Bridge that the northern reaches of the coast became more heavily populated. Beaches in Sydney, Seventy surf beaches can be found along its coastline with Bondi Beach being one of the most famous.
The Nepean River wraps around the western edge of the city and becomes the Hawkesbury River before reaching Broken Bay. Most of Sydney's water storages can be found on tributaries of the Nepean River. The Parramatta River is mostly industrial and drains a large area of Sydney's western suburbs into Port Jackson. The southern parts of the city are drained by the Georges River and the Cooks River into Botany Bay.
According to calculations by the Senseable City Lab at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), 25.9% of Sydney is tree cover, covered by trees, making it the third largest city in the world with the most trees after Singapore and Oslo, respectively, tying with Vancouver.
Sydney is a coastal basin with the Tasman Sea to the east, the Blue Mountains to the west, the Hawkesbury River to the north, and the Woronora Plateau to the south. The inner City Of Sydney measures , the Greater Sydney region (which includes the non-metropolitan areas of Central Coast, Blue Mountains, Wollondilly, Wollongong and Shellharbour) covers , and the city's urban area is in size. Metropolitan Sydney's boundaries stretch 88 kilometres (55 mi) from Palm Beach, New South Wales, Palm Beach in the north to Waterfall, New South Wales, Waterfall in the south, and 70 kilometres (43 mi) from Bondi Beach in the east to Emu Plains, New South Wales, Emu Plains in the west.
Sydney spans two geographic regions. The Cumberland Plain lies to the south and west of the Harbour and is relatively flat. The Hornsby Plateau is located to the north and is dissected by steep valleys. The flat areas of the south were the first to be developed as the city grew. It was not until the construction of the Sydney Harbour Bridge that the northern reaches of the coast became more heavily populated. Beaches in Sydney, Seventy surf beaches can be found along its coastline with Bondi Beach being one of the most famous.
The Nepean River wraps around the western edge of the city and becomes the Hawkesbury River before reaching Broken Bay. Most of Sydney's water storages can be found on tributaries of the Nepean River. The Parramatta River is mostly industrial and drains a large area of Sydney's western suburbs into Port Jackson. The southern parts of the city are drained by the Georges River and the Cooks River into Botany Bay.
According to calculations by the Senseable City Lab at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), 25.9% of Sydney is tree cover, covered by trees, making it the third largest city in the world with the most trees after Singapore and Oslo, respectively, tying with Vancouver.
Geology
 Sydney is made up of mostly Triassic rock with some recent igneous dykes and volcanic necks (typically found in the Prospect dolerite intrusion, west of Sydney). The Sydney Basin was formed when the Earth's crust expanded, subsided, and filled with sediment in the early Triassic period. The sand that was to become the sandstone of today was washed there by rivers from the south and northwest and laid down between 360 and 200 million years ago. The sandstone has shale lenses and fossil riverbeds.
The Sydney Basin bioregion includes coastal features of cliffs, beaches, and estuaries. Deep river valleys known as rias were carved during the Triassic period in the Hawkesbury sandstone of the coastal region where Sydney now lies. The rising sea level between 18,000 and 6,000 years ago flooded the rias to form estuaries and deep harbours. Port Jackson, better known as Sydney Harbour, is one such ria. Sydney features two major soil types; Sand, sandy soils (which originate from the Hawkesbury sandstone) and clay (which are from shales and volcanic rocks), though some soils may be a mixture of the two.
Directly overlying the older Hawkesbury sandstone is the Wianamatta shale, a geological feature found in western Sydney that was deposited in connection with a large river delta during the Middle Triassic period which shifted over time from west to east. The Wianamatta shale generally comprises fine grained sedimentary rocks such as shales, mudstones, ironstones, siltstones and laminites, with less common sandstone units. The Wianamatta Group is made up of the following units (listed in stratigraphic order): Bringelly Shale, Minchinbury Sandstone and Ashfield Shale.
Sydney is made up of mostly Triassic rock with some recent igneous dykes and volcanic necks (typically found in the Prospect dolerite intrusion, west of Sydney). The Sydney Basin was formed when the Earth's crust expanded, subsided, and filled with sediment in the early Triassic period. The sand that was to become the sandstone of today was washed there by rivers from the south and northwest and laid down between 360 and 200 million years ago. The sandstone has shale lenses and fossil riverbeds.
The Sydney Basin bioregion includes coastal features of cliffs, beaches, and estuaries. Deep river valleys known as rias were carved during the Triassic period in the Hawkesbury sandstone of the coastal region where Sydney now lies. The rising sea level between 18,000 and 6,000 years ago flooded the rias to form estuaries and deep harbours. Port Jackson, better known as Sydney Harbour, is one such ria. Sydney features two major soil types; Sand, sandy soils (which originate from the Hawkesbury sandstone) and clay (which are from shales and volcanic rocks), though some soils may be a mixture of the two.
Directly overlying the older Hawkesbury sandstone is the Wianamatta shale, a geological feature found in western Sydney that was deposited in connection with a large river delta during the Middle Triassic period which shifted over time from west to east. The Wianamatta shale generally comprises fine grained sedimentary rocks such as shales, mudstones, ironstones, siltstones and laminites, with less common sandstone units. The Wianamatta Group is made up of the following units (listed in stratigraphic order): Bringelly Shale, Minchinbury Sandstone and Ashfield Shale.
Ecology
 The most prevalent vegetation, plant communities in the Sydney region are grassy woodlands (i.e. savannas) and some pockets of dry sclerophyll forests, which consist of eucalyptus trees, casuarinas, melaleucas, corymbias and angophoras, with shrubs (typically Acacia, wattles, callistemons, grevilleas and banksias), and a semi-continuous grass in the understory. The plants in this community tend to have rough and spiky leaves, as they're grown in areas with low soil fertility. Sydney also features a few areas of wet sclerophyll forests which are found in the wetter, elevated areas in the Hills District, New South Wales, north and the North Shore (Sydney), northeast. These forests are defined by straight, tall tree canopy (biology), canopies with a moist understory of soft-leaved shrubs, tree ferns and herbs.
The predominant vegetation community in Sydney is the Cumberland Plain Woodland, which is found in Western Sydney ( Cumberland Plain), followed by the Sydney Turpentine-Ironbark Forest which is scattered in the Inner West and Northern Sydney,Recovering bushland on the Cumberland Plain
The most prevalent vegetation, plant communities in the Sydney region are grassy woodlands (i.e. savannas) and some pockets of dry sclerophyll forests, which consist of eucalyptus trees, casuarinas, melaleucas, corymbias and angophoras, with shrubs (typically Acacia, wattles, callistemons, grevilleas and banksias), and a semi-continuous grass in the understory. The plants in this community tend to have rough and spiky leaves, as they're grown in areas with low soil fertility. Sydney also features a few areas of wet sclerophyll forests which are found in the wetter, elevated areas in the Hills District, New South Wales, north and the North Shore (Sydney), northeast. These forests are defined by straight, tall tree canopy (biology), canopies with a moist understory of soft-leaved shrubs, tree ferns and herbs.
The predominant vegetation community in Sydney is the Cumberland Plain Woodland, which is found in Western Sydney ( Cumberland Plain), followed by the Sydney Turpentine-Ironbark Forest which is scattered in the Inner West and Northern Sydney,Recovering bushland on the Cumberland PlainDepartment of Environment and Conservation (NSW). (2005). Recovering Bushland on the Cumberland Plain: Best practice guidelines for the management and restoration of bushland. Department of Environment and Conservation (NSW), Sydney. Retrieved 12 September 2022. the Eastern Suburbs Banksia Scrub in the coastline and the Blue Gum High Forest which is scantily present in the North Shore – All of which are critically endangered. The city also includes the Sydney Sandstone Ridgetop Woodland found in Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park on the Hornsby Plateau to the north. Sydney is home to dozens of birds of Australia, bird species, which commonly include the Australian raven, Australian magpie, crested pigeon, noisy miner and the pied currawong, among others. Introduced species, Introduced bird species ubiquitously found in Sydney are the common myna, common starling, house sparrow and the spotted dove. Reptiles of Australia, Reptile species are also numerous and predominantly include skinks. Sydney has a few mammals of Australia, mammal and Spiders of Australia, spider species, such as the grey-headed flying fox and the Sydney funnel-web, respectively, and has a huge diversity of Marine life, marine species inhabiting its harbour and many beaches.
Climate
 Under the Köppen climate classification, Köppen–Geiger classification, Sydney has a humid subtropical climate (''Cfa'') with "warm [and] sometimes hot" summers and "cool" winters, as described by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. The El Niño–Southern Oscillation, the Indian Ocean Dipole and the Southern Annular Mode play an important role in determining Sydney's weather patterns: drought and Bushfires in Australia, bushfire on the one hand, and storms and flooding on the other, associated with the opposite Effects of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation in Australia, phases of the oscillation in Australia. The weather is sea breeze, moderated by proximity to the ocean, and more extreme temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs.
At Sydney's primary weather station at Sydney Observatory, Observatory Hill, extreme temperatures have ranged from on 18 Angry Summer, January 2013 to on 22 June 1932. An average of 14.9 days a year have temperatures at or above in the central business district (CBD). In contrast, the metropolitan area averages between 35 and 65 days, depending on the suburb. The hottest day in the Sydney metropolitan area occurred in Penrith, New South Wales, Penrith on 4 January 2020, where a high of was recorded. The average annual temperature of the sea ranges from in September to in February. Sydney has an average of 7.2 hours of sunshine per day and 109.5 clear days annually. Due to the inland location, frost is recorded early in the morning in Western Sydney a few times in winter. Autumn and spring are the transitional seasons, with spring showing a larger temperature variation than autumn.
Sydney experiences an urban heat island effect. This makes certain parts of the city more vulnerable to extreme heat, including coastal suburbs. In late spring and summer, temperatures over are not uncommon, though hot, dry conditions are usually ended by a Southerly, southerly buster, a powerful southerly that brings gale winds and a rapid fall in temperature. Since Sydney is downwind of the
Under the Köppen climate classification, Köppen–Geiger classification, Sydney has a humid subtropical climate (''Cfa'') with "warm [and] sometimes hot" summers and "cool" winters, as described by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. The El Niño–Southern Oscillation, the Indian Ocean Dipole and the Southern Annular Mode play an important role in determining Sydney's weather patterns: drought and Bushfires in Australia, bushfire on the one hand, and storms and flooding on the other, associated with the opposite Effects of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation in Australia, phases of the oscillation in Australia. The weather is sea breeze, moderated by proximity to the ocean, and more extreme temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs.
At Sydney's primary weather station at Sydney Observatory, Observatory Hill, extreme temperatures have ranged from on 18 Angry Summer, January 2013 to on 22 June 1932. An average of 14.9 days a year have temperatures at or above in the central business district (CBD). In contrast, the metropolitan area averages between 35 and 65 days, depending on the suburb. The hottest day in the Sydney metropolitan area occurred in Penrith, New South Wales, Penrith on 4 January 2020, where a high of was recorded. The average annual temperature of the sea ranges from in September to in February. Sydney has an average of 7.2 hours of sunshine per day and 109.5 clear days annually. Due to the inland location, frost is recorded early in the morning in Western Sydney a few times in winter. Autumn and spring are the transitional seasons, with spring showing a larger temperature variation than autumn.
Sydney experiences an urban heat island effect. This makes certain parts of the city more vulnerable to extreme heat, including coastal suburbs. In late spring and summer, temperatures over are not uncommon, though hot, dry conditions are usually ended by a Southerly, southerly buster, a powerful southerly that brings gale winds and a rapid fall in temperature. Since Sydney is downwind of the Regions
 The regions of Sydney include the CBD or City of Sydney (colloquially referred to as 'the City') and Inner West, the Eastern Suburbs (Sydney), Eastern Suburbs, Southern Sydney (including St George, Sydney, St George and Sutherland Shire), Greater Western Sydney (including South Western Sydney, Hills District, New South Wales, Hills District and the Macarthur Region), and Northern Sydney (including the North Shore (Sydney), North Shore and Northern Beaches). The Greater Sydney Commission divides Sydney into five districts based on the 33 LGAs in the metropolitan area; the Western City, the Central City, the Eastern City, the North District, and the South District. The Australian Bureau of Statistics includes City of Central Coast (the former Gosford City and Wyong Shire) as part of Greater Sydney for population counts. This adds another 330,000 people to the metropolitan area covered by Greater Sydney Commission.
The regions of Sydney include the CBD or City of Sydney (colloquially referred to as 'the City') and Inner West, the Eastern Suburbs (Sydney), Eastern Suburbs, Southern Sydney (including St George, Sydney, St George and Sutherland Shire), Greater Western Sydney (including South Western Sydney, Hills District, New South Wales, Hills District and the Macarthur Region), and Northern Sydney (including the North Shore (Sydney), North Shore and Northern Beaches). The Greater Sydney Commission divides Sydney into five districts based on the 33 LGAs in the metropolitan area; the Western City, the Central City, the Eastern City, the North District, and the South District. The Australian Bureau of Statistics includes City of Central Coast (the former Gosford City and Wyong Shire) as part of Greater Sydney for population counts. This adds another 330,000 people to the metropolitan area covered by Greater Sydney Commission.
Inner suburbs
The CBD extends about south from Sydney Cove. It is bordered by Farm Cove within the Royal Botanic Garden to the east and There is a long trend of gentrification amongst Sydney's inner suburbs. Pyrmont located on the harbour was redeveloped from a centre of shipping and international trade to an area of high density housing, tourist accommodation, and gambling. Originally located well outside of the city, Darlinghurst is the location of the historic, former Darlinghurst Gaol, manufacturing, and mixed housing. It had a period when it was known as an area of prostitution. The terrace style housing has largely been retained and Darlinghurst has undergone significant gentrification since the 1980s.
Green Square, New South Wales, Green Square is a former industrial area of Waterloo, New South Wales, Waterloo which is undergoing urban renewal worth $8 billion. On the city harbour edge, the historic suburb and wharves of Millers Point are being built up as the new area of Barangaroo, New South Wales, Barangaroo. The enforced rehousing of local residents due to the Millers Point/Barangaroo development has caused significant controversy despite the $6 billion worth of economic activity it is expected to generate. The suburb of Paddington, New South Wales, Paddington is a well known suburb for its streets of restored terraced house, terrace houses, Victoria Barracks, Sydney, Victoria Barracks, and shopping including the weekly Oxford Street markets.
There is a long trend of gentrification amongst Sydney's inner suburbs. Pyrmont located on the harbour was redeveloped from a centre of shipping and international trade to an area of high density housing, tourist accommodation, and gambling. Originally located well outside of the city, Darlinghurst is the location of the historic, former Darlinghurst Gaol, manufacturing, and mixed housing. It had a period when it was known as an area of prostitution. The terrace style housing has largely been retained and Darlinghurst has undergone significant gentrification since the 1980s.
Green Square, New South Wales, Green Square is a former industrial area of Waterloo, New South Wales, Waterloo which is undergoing urban renewal worth $8 billion. On the city harbour edge, the historic suburb and wharves of Millers Point are being built up as the new area of Barangaroo, New South Wales, Barangaroo. The enforced rehousing of local residents due to the Millers Point/Barangaroo development has caused significant controversy despite the $6 billion worth of economic activity it is expected to generate. The suburb of Paddington, New South Wales, Paddington is a well known suburb for its streets of restored terraced house, terrace houses, Victoria Barracks, Sydney, Victoria Barracks, and shopping including the weekly Oxford Street markets.
Inner West
The Inner West generally includes the Inner West Council, Municipality of Burwood, Municipality of Strathfield, and City of Canada Bay. These span up to about 11 km west of the CBD. Suburbs in the Inner West have historically housed working class industrial workers, but have undergone gentrification over the 20th century. The region now mainly features medium- and high-density housing. Major features in the area include the University of Sydney and the Parramatta River, as well as a large cosmopolitan community and the nightlife hub on King Street in Newtown, New South Wales, Newtown. The Anzac Bridge spans Johnstons Bay and connects Rozelle to Pyrmont, New South Wales, Pyrmont and the city, forming part of the Western Distributor (Sydney), Western Distributor. The area is serviced by the North Shore & Western Line, T1, Inner West & Leppington Line, T2, and Bankstown Line, T3 railway lines, including the Main Suburban railway line, Main Suburban Line; which is the first to be constructed in New South Wales. Strathfield railway station is a secondary railway hub within Sydney, and major station on the Suburban and Main North railway line, New South Wales, Northern lines. It was constructed in 1876, and will be a future terminus of Parramatta Light Rail. The area is also serviced by numerous bus routes and cycleways. Other shopping centres in the area include Westfield Burwood and DFO Homebush.Eastern suburbs
 The Eastern Suburbs encompass the Municipality of Woollahra, the City of Randwick, the Waverley Municipal Council, and parts of the Bayside Council. The Greater Sydney Commission envisions a resident population of 1,338,250 people by 2036 in its Eastern City District (including the City and Inner West).
They include some of the most affluent and advantaged areas in the country, with some streets being amongst the most expensive in the world. As at 2014, Wolseley Road, Point Piper, had a top price of $20,900 per square metre, making it the ninth-most expensive street in the world. More than 75% of neighbourhoods in the Division of Wentworth, Electoral District of Wentworth fall under the top decile of SEIFA advantage, making it the least disadvantaged area in the country.
Major landmarks include Bondi Beach, a major tourist site; which was added to the Australian National Heritage List in 2008; and Bondi Junction, featuring a Westfield Bondi Junction, Westfield shopping centre and an estimated office work force of 6,400 by 2035, as well as a Bondi Junction railway station, railway station on the Eastern Suburbs railway line, T4 Eastern Suburbs Line. The suburb of Randwick, New South Wales, Randwick contains Randwick Racecourse, the Royal Hospital for Women, the Prince of Wales Hospital (Sydney), Prince of Wales Hospital, Sydney Children's Hospital, and University of New South Wales, University of New South Wales Kensington Campus. Randwick's 'Collaboration Area' has a baseline estimate of 32,000 jobs by 2036, according to the Greater Sydney Commission.
Construction of the CBD and South East Light Rail was completed in April 2020. Main construction was due to be completed in 2018 but was delayed until 2020. The project aims to provide reliable and high-capacity tram services to residents in the City and South-East.
Major shopping centres in the area include Westfield Bondi Junction and Westfield Eastgardens.
The Eastern Suburbs encompass the Municipality of Woollahra, the City of Randwick, the Waverley Municipal Council, and parts of the Bayside Council. The Greater Sydney Commission envisions a resident population of 1,338,250 people by 2036 in its Eastern City District (including the City and Inner West).
They include some of the most affluent and advantaged areas in the country, with some streets being amongst the most expensive in the world. As at 2014, Wolseley Road, Point Piper, had a top price of $20,900 per square metre, making it the ninth-most expensive street in the world. More than 75% of neighbourhoods in the Division of Wentworth, Electoral District of Wentworth fall under the top decile of SEIFA advantage, making it the least disadvantaged area in the country.
Major landmarks include Bondi Beach, a major tourist site; which was added to the Australian National Heritage List in 2008; and Bondi Junction, featuring a Westfield Bondi Junction, Westfield shopping centre and an estimated office work force of 6,400 by 2035, as well as a Bondi Junction railway station, railway station on the Eastern Suburbs railway line, T4 Eastern Suburbs Line. The suburb of Randwick, New South Wales, Randwick contains Randwick Racecourse, the Royal Hospital for Women, the Prince of Wales Hospital (Sydney), Prince of Wales Hospital, Sydney Children's Hospital, and University of New South Wales, University of New South Wales Kensington Campus. Randwick's 'Collaboration Area' has a baseline estimate of 32,000 jobs by 2036, according to the Greater Sydney Commission.
Construction of the CBD and South East Light Rail was completed in April 2020. Main construction was due to be completed in 2018 but was delayed until 2020. The project aims to provide reliable and high-capacity tram services to residents in the City and South-East.
Major shopping centres in the area include Westfield Bondi Junction and Westfield Eastgardens.
Southern Sydney
Southern Sydney includes the suburbs in the Local government in Australia, local government areas of former City of Rockdale, Rockdale, Georges River Council (collectively known as the St George, New South Wales, St George area), and broadly it also includes the suburbs in the Local government in Australia, local government area of Sutherland Shire, Sutherland, south of the Georges River (colloquially known as 'The Shire'). The Cronulla dunes, Kurnell peninsula, near Botany Bay, is the site of the first landfall on the eastern coastline made by Lt. (later Captain) James Cook in 1770. La Perouse, a historic suburb named after the French navigator Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse (1741–88), is notable for its old military outpost at Bare Island (New South Wales), Bare Island and the Botany Bay National Park. The suburb of Cronulla, New South Wales, Cronulla in southern Sydney is close to Royal National Park, Australia's oldest national park. Hurstville, a large suburb with a multitude of commercial buildings and high-rise residential buildings dominating the skyline, has become a CBD for the southern suburbs.Northern Sydney
 'Northern Sydney' may also include the suburbs in the Upper North Shore, Lower North Shore (Sydney), Lower North Shore and the Northern Beaches.
The Northern Suburbs include several landmarks – Macquarie University, Gladesville Bridge, Ryde Bridge, Macquarie Centre and Curzon Hall in Marsfield, New South Wales, Marsfield. This area includes suburbs in the Local government in Australia, local government areas of Hornsby Shire, City of Ryde, the Municipality of Hunter's Hill and parts of the City of Parramatta.
The North Shore (Sydney), North Shore, an informal geographic term referring to the northern metropolitan area of Sydney, consists of , , , , Killara, , , and many others.
The Lower North Shore usually refers to the suburbs adjacent to the harbour such as , , Mosman, New South Wales, Mosman, , Cremorne Point, , Milsons Point, New South Wales, Milsons Point, , Northbridge, New South Wales, Northbridge, and North Sydney. and are often also considered as being part of the Lower North Shore (Sydney), Lower North Shore. The Lower North Shore's eastern boundary is Middle Harbour, or at the Roseville Bridge at and . The Upper North Shore usually refers to the suburbs between and . It is made up of suburbs located within Ku-ring-gai Council, Ku-ring-gai and Hornsby Shire councils.
The North Shore includes the commercial centres of North Sydney, New South Wales, North Sydney and Chatswood. North Sydney itself consists of a large commercial centre, with its own business centre, which contains the second largest concentration of high-rise buildings in Sydney, after the CBD. North Sydney is dominated by advertising, marketing businesses and associated trades, with many large corporations holding office in the region.
The Northern Beaches area includes Manly, New South Wales, Manly, one of Sydney's most popular holiday destinations for much of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The region also features Sydney Heads, a series of headlands which form the wide entrance to Sydney Harbour. The Northern Beaches area extends south to the entrance of Port Jackson (Sydney Harbour), west to Middle Harbour and north to the entrance of Broken Bay. The 2011 Australian census found the Northern Beaches to be the most White people, white and mono-ethnic district in Australia, contrasting with its more-diverse neighbours, the North Shore and the Central Coast (New South Wales), Central Coast.
'Northern Sydney' may also include the suburbs in the Upper North Shore, Lower North Shore (Sydney), Lower North Shore and the Northern Beaches.
The Northern Suburbs include several landmarks – Macquarie University, Gladesville Bridge, Ryde Bridge, Macquarie Centre and Curzon Hall in Marsfield, New South Wales, Marsfield. This area includes suburbs in the Local government in Australia, local government areas of Hornsby Shire, City of Ryde, the Municipality of Hunter's Hill and parts of the City of Parramatta.
The North Shore (Sydney), North Shore, an informal geographic term referring to the northern metropolitan area of Sydney, consists of , , , , Killara, , , and many others.
The Lower North Shore usually refers to the suburbs adjacent to the harbour such as , , Mosman, New South Wales, Mosman, , Cremorne Point, , Milsons Point, New South Wales, Milsons Point, , Northbridge, New South Wales, Northbridge, and North Sydney. and are often also considered as being part of the Lower North Shore (Sydney), Lower North Shore. The Lower North Shore's eastern boundary is Middle Harbour, or at the Roseville Bridge at and . The Upper North Shore usually refers to the suburbs between and . It is made up of suburbs located within Ku-ring-gai Council, Ku-ring-gai and Hornsby Shire councils.
The North Shore includes the commercial centres of North Sydney, New South Wales, North Sydney and Chatswood. North Sydney itself consists of a large commercial centre, with its own business centre, which contains the second largest concentration of high-rise buildings in Sydney, after the CBD. North Sydney is dominated by advertising, marketing businesses and associated trades, with many large corporations holding office in the region.
The Northern Beaches area includes Manly, New South Wales, Manly, one of Sydney's most popular holiday destinations for much of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The region also features Sydney Heads, a series of headlands which form the wide entrance to Sydney Harbour. The Northern Beaches area extends south to the entrance of Port Jackson (Sydney Harbour), west to Middle Harbour and north to the entrance of Broken Bay. The 2011 Australian census found the Northern Beaches to be the most White people, white and mono-ethnic district in Australia, contrasting with its more-diverse neighbours, the North Shore and the Central Coast (New South Wales), Central Coast.
Hills district
The Hills District, New South Wales, Hills district generally refers to the suburbs in north-western Sydney including the local government areas of The Hills Shire, parts of the City of Parramatta Council and Hornsby Shire. Actual suburbs and localities that are considered to be in the Hills District can be somewhat amorphous and variable. For example, the Hills District Historical Society restricts its definition to the Hills Shire local government area, yet its study area extends from Parramatta to the Hawkesbury. The region is so named for its characteristically comparatively hilly topography as the Cumberland Plain lifts up, joining the Hornsby Plateau. Several of its suburbs also have "Hill" or "Hills" in their names, such as Baulkham Hills, New South Wales, Baulkham Hills, Castle Hill, New South Wales, Castle Hill, Seven Hills, New South Wales, Seven Hills, Beaumont Hills, New South Wales, Beaumont Hills, and Winston Hills, New South Wales, Winston Hills, among others. Windsor Road, Windsor and Old Windsor Roads are historic roads in Australia, as they are the second and third roads, respectively, laid in the colony.Western suburbs
 The greater western suburbs encompasses the areas of Parramatta, the sixth largest business district in Australia, settled the same year as the harbour-side colony, Bankstown, Liverpool, Penrith, New South Wales, Penrith, and Fairfield, New South Wales, Fairfield. Covering and having an estimated resident population as at 2017 of 2,288,554, western Sydney has the most minority majority, multicultural suburbs in the country. The population is predominantly of a working class background, with major employment in the heavy industries and vocational trade. Toongabbie is noted for being the third mainland settlement (after Sydney and Parramatta) set up after the British colonisation of Australia began in 1788, although the site of the settlement is actually in the separate suburb of Old Toongabbie.
The western suburb of Prospect, New South Wales, Prospect, in the City of Blacktown, is home to Raging Waters Sydney, Raging Waters, a water park operated by Parques Reunidos. Auburn Botanic Gardens, a botanical garden situated in Auburn, New South Wales, Auburn, attracts thousands of visitors each year, including a significant number from outside Australia. Another prominent park in the west is the Western Sydney Regional Park in Abbotsbury, New South Wales, Abbotsbury. The greater west also includes Sydney Olympic Park, a suburb created to host the 2000 Summer Olympics, and Sydney Motorsport Park, a motorsport Race track, circuit located in Eastern Creek. The Boothtown Aqueduct in Greystanes, New South Wales, Greystanes is a 19th-century water bridge that is listed on the New South Wales State Heritage Register as a site of State significance. Prospect Hill (New South Wales), Prospect Hill, a historically significant ridge in the west and the only area in Sydney with ancient volcanic activity, is also listed on the NSW State Heritage Register.
To the northwest, Featherdale Wildlife Park, an Australian zoo in Doonside, near Blacktown, is a major tourist attraction, not just for Western Sydney, but for NSW and Australia. Sydney Zoo, opened in 2019, is another prominent zoo situated in Bungaribee. Westfield Parramatta in Parramatta is Australia's busiest Westfield shopping centre, having 28.7 million customer visits per annum. Established in 1799, the Old Government House, Parramatta, Old Government House, a historic house museum and tourist spot in Parramatta, was included in the Australian National Heritage List on 1 August 2007 and World Heritage List in 2010 (as part of the 11 penal sites constituting the Australian Convict Sites), making it the only site in greater western Sydney to be featured in such lists. Moreover, the house is Australia's oldest surviving public building.
Further to the southwest is the region of Macarthur and the city of Campbelltown, New South Wales, Campbelltown, a significant population centre until the 1990s considered a region separate to Sydney proper. Macarthur Square, a shopping complex in Campbelltown, has become one of the largest shopping complexes in Sydney. The southwest also features Bankstown Reservoir, the oldest elevated reservoir constructed in reinforced concrete that is still in use and is listed on the New South Wales State Heritage Register. The southwest is home to one of Sydney's oldest trees, the Bland Oak, which was planted in the 1840s by William Bland in the suburb of Carramar, New South Wales, Carramar.
The greater western suburbs encompasses the areas of Parramatta, the sixth largest business district in Australia, settled the same year as the harbour-side colony, Bankstown, Liverpool, Penrith, New South Wales, Penrith, and Fairfield, New South Wales, Fairfield. Covering and having an estimated resident population as at 2017 of 2,288,554, western Sydney has the most minority majority, multicultural suburbs in the country. The population is predominantly of a working class background, with major employment in the heavy industries and vocational trade. Toongabbie is noted for being the third mainland settlement (after Sydney and Parramatta) set up after the British colonisation of Australia began in 1788, although the site of the settlement is actually in the separate suburb of Old Toongabbie.
The western suburb of Prospect, New South Wales, Prospect, in the City of Blacktown, is home to Raging Waters Sydney, Raging Waters, a water park operated by Parques Reunidos. Auburn Botanic Gardens, a botanical garden situated in Auburn, New South Wales, Auburn, attracts thousands of visitors each year, including a significant number from outside Australia. Another prominent park in the west is the Western Sydney Regional Park in Abbotsbury, New South Wales, Abbotsbury. The greater west also includes Sydney Olympic Park, a suburb created to host the 2000 Summer Olympics, and Sydney Motorsport Park, a motorsport Race track, circuit located in Eastern Creek. The Boothtown Aqueduct in Greystanes, New South Wales, Greystanes is a 19th-century water bridge that is listed on the New South Wales State Heritage Register as a site of State significance. Prospect Hill (New South Wales), Prospect Hill, a historically significant ridge in the west and the only area in Sydney with ancient volcanic activity, is also listed on the NSW State Heritage Register.
To the northwest, Featherdale Wildlife Park, an Australian zoo in Doonside, near Blacktown, is a major tourist attraction, not just for Western Sydney, but for NSW and Australia. Sydney Zoo, opened in 2019, is another prominent zoo situated in Bungaribee. Westfield Parramatta in Parramatta is Australia's busiest Westfield shopping centre, having 28.7 million customer visits per annum. Established in 1799, the Old Government House, Parramatta, Old Government House, a historic house museum and tourist spot in Parramatta, was included in the Australian National Heritage List on 1 August 2007 and World Heritage List in 2010 (as part of the 11 penal sites constituting the Australian Convict Sites), making it the only site in greater western Sydney to be featured in such lists. Moreover, the house is Australia's oldest surviving public building.
Further to the southwest is the region of Macarthur and the city of Campbelltown, New South Wales, Campbelltown, a significant population centre until the 1990s considered a region separate to Sydney proper. Macarthur Square, a shopping complex in Campbelltown, has become one of the largest shopping complexes in Sydney. The southwest also features Bankstown Reservoir, the oldest elevated reservoir constructed in reinforced concrete that is still in use and is listed on the New South Wales State Heritage Register. The southwest is home to one of Sydney's oldest trees, the Bland Oak, which was planted in the 1840s by William Bland in the suburb of Carramar, New South Wales, Carramar.
Urban structure
Architecture
The earliest structures in the colony were built to the bare minimum of standards. Upon his appointment, Governor Lachlan Macquarie set ambitious targets for the architectural design of new construction projects. The city now has a world heritage listed building, several national heritage listed buildings, and dozens of Commonwealth heritage listed buildings as evidence of the survival of Macquarie's ideals. In 1814 the Governor called on a convict named Francis Greenway to design Macquarie Lighthouse. The lighthouse and its Classical architecture, Classical design earned Greenway a pardon from Macquarie in 1818 and introduced a culture of refined architecture that remains to this day. Greenway went on to design the Hyde Park Barracks, Sydney, Hyde Park Barracks in 1819 and the Georgian architecture, Georgian style St James' Church, Sydney, St James's Church in 1824. Gothic architecture, Gothic-inspired architecture became more popular from the 1830s. John Verge's Elizabeth Bay House and St Philip's Church, Sydney, St Philip's Church of 1856 were built in Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival style along with Edward Blore's Government House, Sydney, Government House of 1845. Kirribilli House, completed in 1858, and St Andrew's Cathedral, Australia's oldest cathedral, are rare examples of Gothic Revival architecture, Victorian Gothic construction.
In 1814 the Governor called on a convict named Francis Greenway to design Macquarie Lighthouse. The lighthouse and its Classical architecture, Classical design earned Greenway a pardon from Macquarie in 1818 and introduced a culture of refined architecture that remains to this day. Greenway went on to design the Hyde Park Barracks, Sydney, Hyde Park Barracks in 1819 and the Georgian architecture, Georgian style St James' Church, Sydney, St James's Church in 1824. Gothic architecture, Gothic-inspired architecture became more popular from the 1830s. John Verge's Elizabeth Bay House and St Philip's Church, Sydney, St Philip's Church of 1856 were built in Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival style along with Edward Blore's Government House, Sydney, Government House of 1845. Kirribilli House, completed in 1858, and St Andrew's Cathedral, Australia's oldest cathedral, are rare examples of Gothic Revival architecture, Victorian Gothic construction.
 From the late 1850s there was a shift towards Classical architecture. Mortimer Lewis designed the Australian Museum in 1857. The
From the late 1850s there was a shift towards Classical architecture. Mortimer Lewis designed the Australian Museum in 1857. The  Modern architecture, Modern and International architecture came to Sydney from the 1940s. Since its completion in 1973 the city's Opera House has become a World Heritage Site and one of the world's most renowned pieces of Modern design. It was conceived by Jørn Utzon with contributions from Peter Hall, Lionel Todd, and David Littlemore. Utzon was awarded the Pritzker Architecture Prize, Pritzker Prize in 2003 for his work on the Opera House. Sydney is home to Australia's first building by renowned Canadian-American architect Frank Gehry, the Dr Chau Chak Wing Building (2015), based on the design of a tree house. An entrance from The Goods Line–a pedestrian pathway and former railway line–is located on the eastern border of the site.
Contemporary buildings in the CBD include Citigroup Centre, Sydney, Citigroup Centre, Aurora Place, Chifley Tower, the Reserve Bank of Australia, Reserve Bank building, Deutsche Bank Place, MLC Centre, and Capita Centre. The tallest structure is Sydney Tower, designed by Donald Crone and completed in 1981. Regulations limited new buildings to a height of due to the proximity of Sydney Airport, although strict restrictions employed in the early 2000s have slowly been relaxed in the past ten years, with a maximum height restriction now sitting at 330 metres (1083 feet). Green bans and heritage overlays have been in place since at least 1977 to protect Sydney's heritage after controversial demolitions in the 1970s led to an outcry from Sydneysiders to preserve the old and keep history intact, sufficiently balancing old and new architecture.
Modern architecture, Modern and International architecture came to Sydney from the 1940s. Since its completion in 1973 the city's Opera House has become a World Heritage Site and one of the world's most renowned pieces of Modern design. It was conceived by Jørn Utzon with contributions from Peter Hall, Lionel Todd, and David Littlemore. Utzon was awarded the Pritzker Architecture Prize, Pritzker Prize in 2003 for his work on the Opera House. Sydney is home to Australia's first building by renowned Canadian-American architect Frank Gehry, the Dr Chau Chak Wing Building (2015), based on the design of a tree house. An entrance from The Goods Line–a pedestrian pathway and former railway line–is located on the eastern border of the site.
Contemporary buildings in the CBD include Citigroup Centre, Sydney, Citigroup Centre, Aurora Place, Chifley Tower, the Reserve Bank of Australia, Reserve Bank building, Deutsche Bank Place, MLC Centre, and Capita Centre. The tallest structure is Sydney Tower, designed by Donald Crone and completed in 1981. Regulations limited new buildings to a height of due to the proximity of Sydney Airport, although strict restrictions employed in the early 2000s have slowly been relaxed in the past ten years, with a maximum height restriction now sitting at 330 metres (1083 feet). Green bans and heritage overlays have been in place since at least 1977 to protect Sydney's heritage after controversial demolitions in the 1970s led to an outcry from Sydneysiders to preserve the old and keep history intact, sufficiently balancing old and new architecture.
Housing
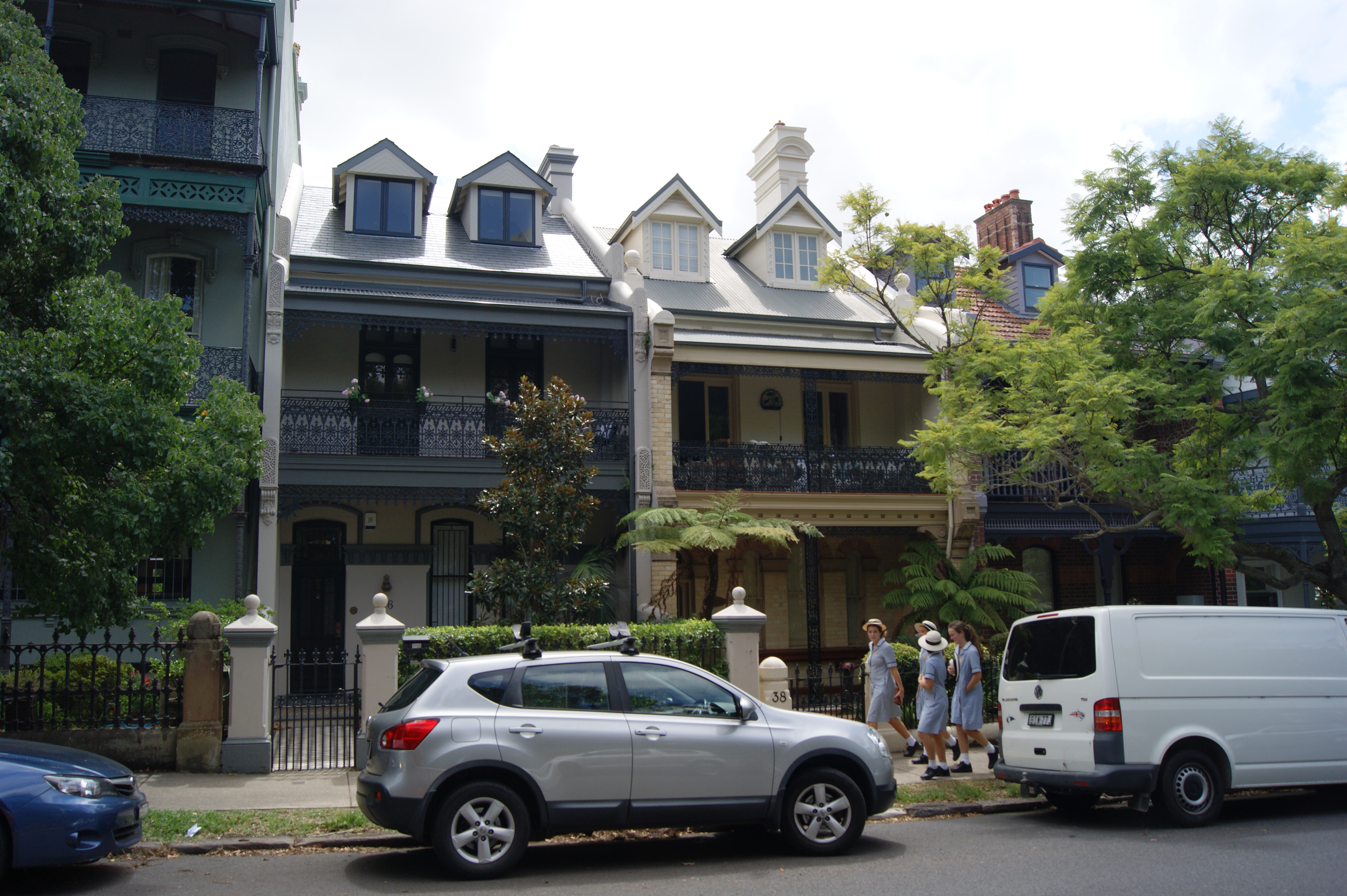 Sydney surpasses both New York City and Paris real estate prices, having some of the most expensive in the world. The city remains Australia's most expensive housing market, with the mean house price at $1,142,212 as of December 2019 (over 25% higher the national mean house price).
There were 1.76 million dwellings in Sydney in 2016 including 925,000 (57%) detached houses, 227,000 (14%) semi-detached terrace houses and 456,000 (28%) units and apartments. Whilst terrace houses are common in the inner city areas, it is detached houses that dominate the landscape in the outer suburbs.
Due to environmental and economic pressures, there has been a noted trend towards denser housing. There was a 30% increase in the number of apartments in Sydney between 1996 and 2006. Public housing in Sydney is managed by the Government of New South Wales. Suburbs with large concentrations of public housing include Claymore, New South Wales, Claymore, Macquarie Fields, New South Wales, Macquarie Fields, Waterloo, New South Wales, Waterloo, and Mount Druitt, New South Wales, Mount Druitt. The Government has announced plans to sell nearly 300 historic public housing properties in the harbourside neighbourhoods of Millers Point, Gloucester Street, and The Rocks.
Sydney is one of the most expensive real estate markets globally. It is only second to Hong Kong with the average property costing 14 times the annual Sydney salary as of December 2016. A range of heritage housing styles can be found throughout Sydney. Terrace houses are found in the inner suburbs such as Paddington, The Rocks, Potts Point and Balmain–many of which have been the subject of gentrification. These terraces, particularly those in suburbs such as The Rocks, were historically home to Sydney's miners and labourers. In the present day, terrace houses now make up some of the most valuable real estate in the city.
Federation architecture, Federation homes, constructed around the time of Federation in 1901, are located in suburbs such as Penshurst, New South Wales, Penshurst, Turramurra, and in Haberfield, New South Wales, Haberfield. Haberfield is known as "The Federation Suburb" due to the extensive number of Federation homes. Workers cottages are found in Surry Hills, Redfern, New South Wales, Redfern, and Balmain. California bungalows are common in Ashfield, New South Wales, Ashfield, Concord, New South Wales, Concord, and Beecroft, New South Wales, Beecroft. Larger modern homes are predominantly found in the outer suburbs, such as Stanhope Gardens, Kellyville Ridge, Bella Vista, New South Wales, Bella Vista to the northwest, Bossley Park, Abbotsbury, New South Wales, Abbotsbury, and Cecil Hills to the west, and Hoxton Park, Harrington Park, New South Wales, Harrington Park, and Oran Park, New South Wales, Oran Park to the southwest.
Sydney surpasses both New York City and Paris real estate prices, having some of the most expensive in the world. The city remains Australia's most expensive housing market, with the mean house price at $1,142,212 as of December 2019 (over 25% higher the national mean house price).
There were 1.76 million dwellings in Sydney in 2016 including 925,000 (57%) detached houses, 227,000 (14%) semi-detached terrace houses and 456,000 (28%) units and apartments. Whilst terrace houses are common in the inner city areas, it is detached houses that dominate the landscape in the outer suburbs.
Due to environmental and economic pressures, there has been a noted trend towards denser housing. There was a 30% increase in the number of apartments in Sydney between 1996 and 2006. Public housing in Sydney is managed by the Government of New South Wales. Suburbs with large concentrations of public housing include Claymore, New South Wales, Claymore, Macquarie Fields, New South Wales, Macquarie Fields, Waterloo, New South Wales, Waterloo, and Mount Druitt, New South Wales, Mount Druitt. The Government has announced plans to sell nearly 300 historic public housing properties in the harbourside neighbourhoods of Millers Point, Gloucester Street, and The Rocks.
Sydney is one of the most expensive real estate markets globally. It is only second to Hong Kong with the average property costing 14 times the annual Sydney salary as of December 2016. A range of heritage housing styles can be found throughout Sydney. Terrace houses are found in the inner suburbs such as Paddington, The Rocks, Potts Point and Balmain–many of which have been the subject of gentrification. These terraces, particularly those in suburbs such as The Rocks, were historically home to Sydney's miners and labourers. In the present day, terrace houses now make up some of the most valuable real estate in the city.
Federation architecture, Federation homes, constructed around the time of Federation in 1901, are located in suburbs such as Penshurst, New South Wales, Penshurst, Turramurra, and in Haberfield, New South Wales, Haberfield. Haberfield is known as "The Federation Suburb" due to the extensive number of Federation homes. Workers cottages are found in Surry Hills, Redfern, New South Wales, Redfern, and Balmain. California bungalows are common in Ashfield, New South Wales, Ashfield, Concord, New South Wales, Concord, and Beecroft, New South Wales, Beecroft. Larger modern homes are predominantly found in the outer suburbs, such as Stanhope Gardens, Kellyville Ridge, Bella Vista, New South Wales, Bella Vista to the northwest, Bossley Park, Abbotsbury, New South Wales, Abbotsbury, and Cecil Hills to the west, and Hoxton Park, Harrington Park, New South Wales, Harrington Park, and Oran Park, New South Wales, Oran Park to the southwest.
Parks and open spaces
The Anzac War Memorial in Hyde Park, Sydney, Hyde Park is a public memorial dedicated to the achievement of the First Australian Imperial Force, Australian Imperial Force of World War I. The Royal Botanic Gardens, Sydney, Royal Botanic Garden is the most iconic green space in the Sydney region, hosting both scientific and leisure activities. There are 15 separate parks under the administration of the City of Sydney. Parks within the city centre include Hyde Park, Sydney, Hyde Park, The Domain, Sydney, The Domain and Prince Alfred Park.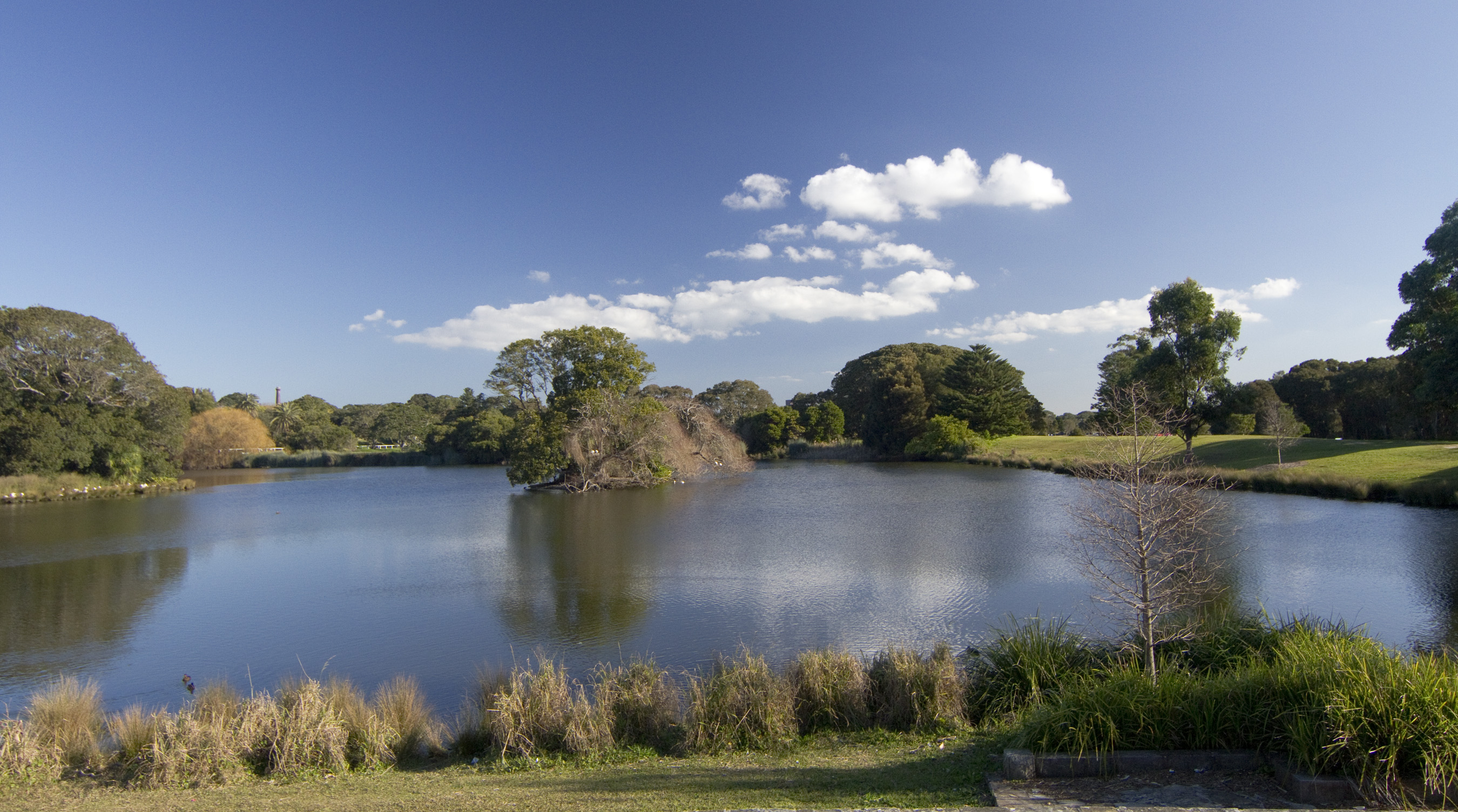 The Centennial Parklands is the largest park in the City of Sydney, comprising .
The inner suburbs include Centennial Park, New South Wales, Centennial Park and Moore Park, New South Wales, Moore Park in the east (both within the City of Sydney local government area), while the outer suburbs contain Sydney Park and Royal National Park in the south, Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park in the north, and Western Sydney Parklands in the west, which is List of urban parks by size, one of the largest urban parks in the world. The Royal National Park was proclaimed on 26 April 1879 and with is the second oldest national park in the world.
The Centennial Parklands is the largest park in the City of Sydney, comprising .
The inner suburbs include Centennial Park, New South Wales, Centennial Park and Moore Park, New South Wales, Moore Park in the east (both within the City of Sydney local government area), while the outer suburbs contain Sydney Park and Royal National Park in the south, Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park in the north, and Western Sydney Parklands in the west, which is List of urban parks by size, one of the largest urban parks in the world. The Royal National Park was proclaimed on 26 April 1879 and with is the second oldest national park in the world.
 Hyde Park is the oldest parkland in the country. The largest park in the Sydney metropolitan area is Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park, established in 1894 with an area of . It is regarded for its well-preserved records of indigenous habitation and more than 800 rock engravings, cave drawings and middens have been located in the park.
The area now known as The Domain was set aside by Governor Arthur Phillip in 1788 as his private reserve. Under the orders of Macquarie the land to the immediate north of The Domain became the Royal Botanic Garden in 1816. This makes them the oldest botanic garden in Australia. The Gardens are not just a place for exploration and relaxation, but also for scientific research with herbarium collections, a library and laboratories. The two parks have a total area of with 8,900 individual plant species and receive over 3.5 million annual visits.
To the south of The Domain is Hyde Park, the oldest public parkland in Australia which measures in area. Its location was used for both relaxation and the grazing of animals from the earliest days of the colony. Macquarie dedicated it in 1810 for the "recreation and amusement of the inhabitants of the town" and named it in honour of the original Hyde Park, London, Hyde Park in London.
Hyde Park is the oldest parkland in the country. The largest park in the Sydney metropolitan area is Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park, established in 1894 with an area of . It is regarded for its well-preserved records of indigenous habitation and more than 800 rock engravings, cave drawings and middens have been located in the park.
The area now known as The Domain was set aside by Governor Arthur Phillip in 1788 as his private reserve. Under the orders of Macquarie the land to the immediate north of The Domain became the Royal Botanic Garden in 1816. This makes them the oldest botanic garden in Australia. The Gardens are not just a place for exploration and relaxation, but also for scientific research with herbarium collections, a library and laboratories. The two parks have a total area of with 8,900 individual plant species and receive over 3.5 million annual visits.
To the south of The Domain is Hyde Park, the oldest public parkland in Australia which measures in area. Its location was used for both relaxation and the grazing of animals from the earliest days of the colony. Macquarie dedicated it in 1810 for the "recreation and amusement of the inhabitants of the town" and named it in honour of the original Hyde Park, London, Hyde Park in London.
Economy
 Researchers from Loughborough University have ranked Sydney amongst the top ten world cities that are highly integrated into the global economy. The Global Economic Power Index ranks Sydney number eleven in the world. The Global Cities Index recognises it as number fourteen in the world based on global engagement. There is a significant concentration of foreign banks and multinational corporations in Sydney and the city is promoted as Australia's financial capital and one of Asia Pacific's leading financial hubs.
The prevailing economic theory in effect during early colonial days was mercantilism, as it was throughout most of Western Europe. The economy struggled at first due to difficulties in cultivating the land and the lack of a stable monetary system. Governor Lachlan Macquarie solved the second problem by creating holey dollar, two coins from every Spanish dollar, Spanish silver dollar in circulation. The economy was clearly capitalism, capitalist in nature by the 1840s as the proportion of free settlers increased, the maritime and wool industries flourished, and the powers of the East India Company were curtailed.
Wheat, gold, and other minerals became additional export industries towards the end of the 1800s. Significant capital began to flow into the city from the 1870s to finance roads, railways, bridges, docks, courthouses, schools and hospitals. Protectionism, Protectionist policies after federation of Australia, federation allowed for the creation of a manufacturing industry which became the city's largest employer by the 1920s. These same policies helped to relieve the effects of the Great Depression during which the unemployment rate in New South Wales reached as high as 32%. From the 1960s onwards Parramatta gained recognition as the city's second CBD and finance and tourism became major industries and sources of employment.
Sydney's nominal gross domestic product was AU$400.9 billion and AU$80,000 per capita in 2015. Its gross domestic product was AU$337 billion in 2013, the largest in Australia. The Financial and Insurance Services industry accounts for 18.1% of gross product and is ahead of Professional Services with 9% and Manufacturing with 7.2%. In addition to Financial Services and Tourism, the Creative and Technology sectors are focus industries for the City of Sydney and represented 9% and 11% of its economic output in 2012.
Researchers from Loughborough University have ranked Sydney amongst the top ten world cities that are highly integrated into the global economy. The Global Economic Power Index ranks Sydney number eleven in the world. The Global Cities Index recognises it as number fourteen in the world based on global engagement. There is a significant concentration of foreign banks and multinational corporations in Sydney and the city is promoted as Australia's financial capital and one of Asia Pacific's leading financial hubs.
The prevailing economic theory in effect during early colonial days was mercantilism, as it was throughout most of Western Europe. The economy struggled at first due to difficulties in cultivating the land and the lack of a stable monetary system. Governor Lachlan Macquarie solved the second problem by creating holey dollar, two coins from every Spanish dollar, Spanish silver dollar in circulation. The economy was clearly capitalism, capitalist in nature by the 1840s as the proportion of free settlers increased, the maritime and wool industries flourished, and the powers of the East India Company were curtailed.
Wheat, gold, and other minerals became additional export industries towards the end of the 1800s. Significant capital began to flow into the city from the 1870s to finance roads, railways, bridges, docks, courthouses, schools and hospitals. Protectionism, Protectionist policies after federation of Australia, federation allowed for the creation of a manufacturing industry which became the city's largest employer by the 1920s. These same policies helped to relieve the effects of the Great Depression during which the unemployment rate in New South Wales reached as high as 32%. From the 1960s onwards Parramatta gained recognition as the city's second CBD and finance and tourism became major industries and sources of employment.
Sydney's nominal gross domestic product was AU$400.9 billion and AU$80,000 per capita in 2015. Its gross domestic product was AU$337 billion in 2013, the largest in Australia. The Financial and Insurance Services industry accounts for 18.1% of gross product and is ahead of Professional Services with 9% and Manufacturing with 7.2%. In addition to Financial Services and Tourism, the Creative and Technology sectors are focus industries for the City of Sydney and represented 9% and 11% of its economic output in 2012.
Corporate citizens
There were 451,000 businesses based in Sydney in 2011, including 48% of the top 500 companies in Australia and two-thirds of the regional headquarters of multinational corporations. Global companies are attracted to the city in part because its time zone spans the closing of business in North America and the opening of business in Europe. Most foreign companies in Sydney maintain significant sales and service functions but comparably less production, research, and development capabilities. There are 283 multinational companies with regional offices in Sydney.Domestic economics
 Sydney has been ranked between the fifteenth and the fifth most expensive city in the world and is the most expensive city in Australia. Of the 15 categories only measured by UBS in 2012, workers receive the seventh highest wage levels of 77 cities in the world. Working residents of Sydney work an average of 1,846 hours per annum with 15 days of leave.
The labour force of Greater Sydney Region in 2016 was 2,272,722 with a participation rate of 61.6%. It was made up of 61.2% full-time workers, 30.9% part-time workers, and 6.0% unemployed individuals. The largest reported occupations are professionals, clerical and administrative workers, managers, technicians and trades workers, and community and personal service workers. The largest industries by employment across Greater Sydney are Health Care and Social Assistance with 11.6%, Professional Services with 9.8%, Retail Trade with 9.3%, Construction with 8.2%, Education and Training with 8.0%, Accommodation and Food Services 6.7%, and Financial and Insurance Services with 6.6%. The Professional Services and Financial and Insurance Services industries account for 25.4% of employment within the City of Sydney.
In 2016, 57.6% of working age residents had a total weekly income of less than $1,000 and 14.4% had a total weekly income of $1,750 or more. The median weekly income for the same period was $719 for individuals, $1,988 for families, and $1,750 for household.
Unemployment in the City of Sydney averaged 4.6% for the decade to 2013, much lower than the current rate of unemployment in Western Sydney of 7.3%. Western Sydney continues to struggle to create jobs to meet its population growth despite the development of commercial centres like Parramatta. Each day about 200,000 commuters travel from Western Sydney to the CBD and suburbs in the east and north of the city.
Home ownership in Sydney was less common than renting prior to the Second World War but this trend has since reversed. Median house prices have increased by an average of 8.6% per annum since 1970. The median house price in Sydney in March 2014 was $630,000. The primary cause for rising prices is the increasing cost of land and scarcity which made up 32% of house prices in 1977 compared to 60% in 2002. 31.6% of dwellings in Sydney are rented, 30.4% are owned outright and 34.8% are owned with a mortgage. 11.8% of mortgagees in 2011 had monthly loan repayments of less than $1,000 and 82.9% had monthly repayments of $1,000 or more. 44.9% of renters for the same period had weekly rent of less than $350 whilst 51.7% had weekly rent of $350 or more. The median weekly rent in Sydney is $450.
Sydney has been ranked between the fifteenth and the fifth most expensive city in the world and is the most expensive city in Australia. Of the 15 categories only measured by UBS in 2012, workers receive the seventh highest wage levels of 77 cities in the world. Working residents of Sydney work an average of 1,846 hours per annum with 15 days of leave.
The labour force of Greater Sydney Region in 2016 was 2,272,722 with a participation rate of 61.6%. It was made up of 61.2% full-time workers, 30.9% part-time workers, and 6.0% unemployed individuals. The largest reported occupations are professionals, clerical and administrative workers, managers, technicians and trades workers, and community and personal service workers. The largest industries by employment across Greater Sydney are Health Care and Social Assistance with 11.6%, Professional Services with 9.8%, Retail Trade with 9.3%, Construction with 8.2%, Education and Training with 8.0%, Accommodation and Food Services 6.7%, and Financial and Insurance Services with 6.6%. The Professional Services and Financial and Insurance Services industries account for 25.4% of employment within the City of Sydney.
In 2016, 57.6% of working age residents had a total weekly income of less than $1,000 and 14.4% had a total weekly income of $1,750 or more. The median weekly income for the same period was $719 for individuals, $1,988 for families, and $1,750 for household.
Unemployment in the City of Sydney averaged 4.6% for the decade to 2013, much lower than the current rate of unemployment in Western Sydney of 7.3%. Western Sydney continues to struggle to create jobs to meet its population growth despite the development of commercial centres like Parramatta. Each day about 200,000 commuters travel from Western Sydney to the CBD and suburbs in the east and north of the city.
Home ownership in Sydney was less common than renting prior to the Second World War but this trend has since reversed. Median house prices have increased by an average of 8.6% per annum since 1970. The median house price in Sydney in March 2014 was $630,000. The primary cause for rising prices is the increasing cost of land and scarcity which made up 32% of house prices in 1977 compared to 60% in 2002. 31.6% of dwellings in Sydney are rented, 30.4% are owned outright and 34.8% are owned with a mortgage. 11.8% of mortgagees in 2011 had monthly loan repayments of less than $1,000 and 82.9% had monthly repayments of $1,000 or more. 44.9% of renters for the same period had weekly rent of less than $350 whilst 51.7% had weekly rent of $350 or more. The median weekly rent in Sydney is $450.
Financial services
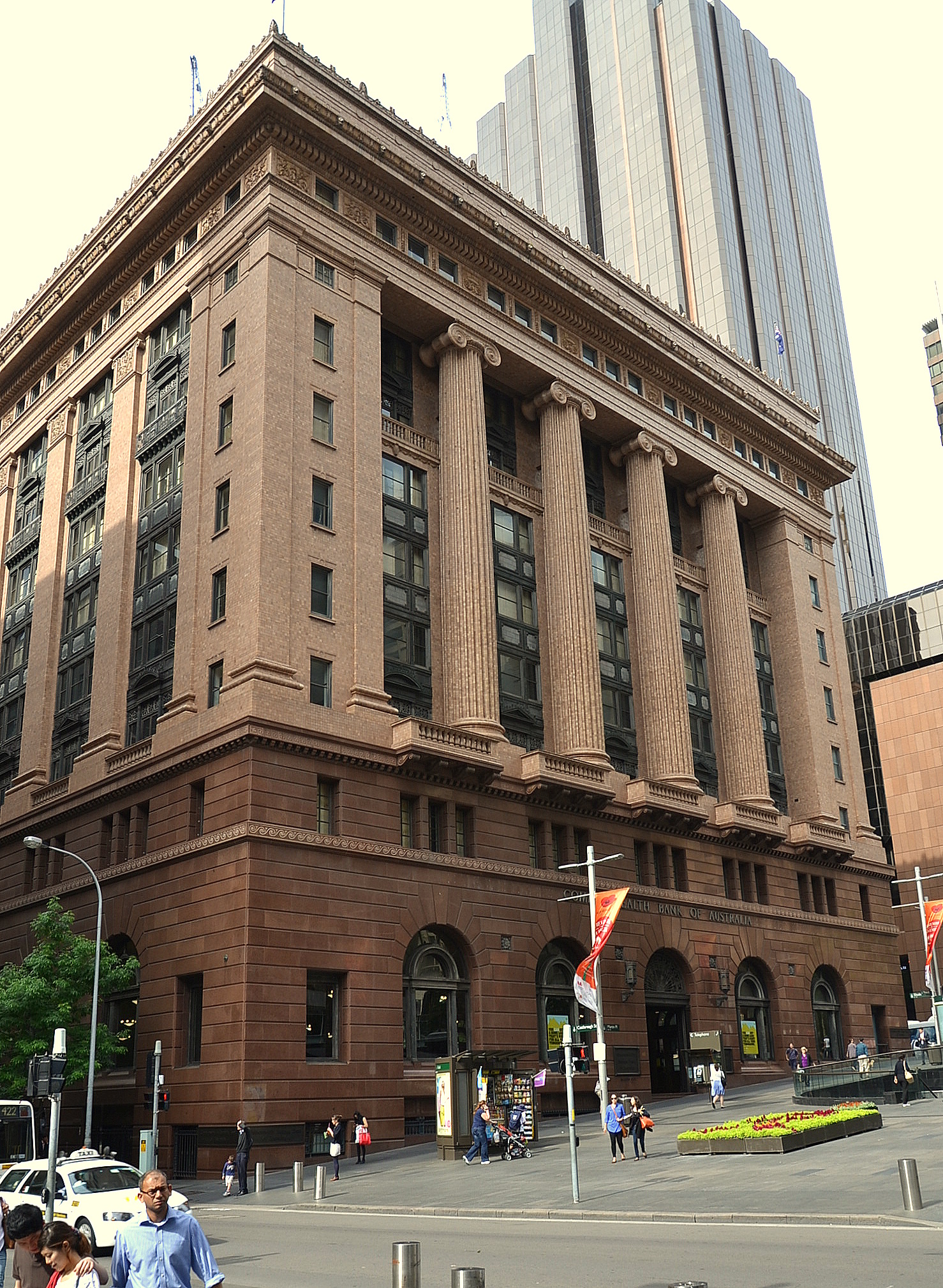 Macquarie gave a charter in 1817 to form the first bank in Australia, the Bank of New South Wales. New private banks opened throughout the 1800s but the financial system was unstable. Bank collapses were a frequent occurrence and a crisis point was reached in 1893 when 12 banks failed.
The Bank of New South Wales exists to this day as Westpac. The Commonwealth Bank of Australia was formed in Sydney in 1911 and began to issue notes backed by the resources of the nation. It was replaced in this role in 1959 by the Reserve Bank of Australia which is also based in Sydney. The Australian Securities Exchange began operating in 1987 and with a market capitalisation of $1.6 trillion is now one of the ten largest exchanges in the world.
The Financial and Insurance Services industry now constitutes 43% of the economic product of the City of Sydney. Sydney makes up half of Australia's finance sector and has been promoted by consecutive Commonwealth Governments as Asia Pacific's leading financial centre. In the 2017 Global Financial Centres Index, Sydney was ranked as having the eighth most competitive financial centre in the world.
In 1985 the Federal Government granted 16 banking licences to foreign banks and now 40 of the 43 foreign banks operating in Australia are based in Sydney, including the People's Bank of China, Bank of America, Citigroup, UBS, Mizuho Bank, Bank of China, Banco Santander, Credit Suisse, Standard Chartered, State Street Corporation, State Street, HSBC, Deutsche Bank, Barclays, Royal Bank of Canada, Société Générale, Royal Bank of Scotland, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation, Sumitomo Mitsui, ING Group, BNP Paribas, and Investec.
Macquarie gave a charter in 1817 to form the first bank in Australia, the Bank of New South Wales. New private banks opened throughout the 1800s but the financial system was unstable. Bank collapses were a frequent occurrence and a crisis point was reached in 1893 when 12 banks failed.
The Bank of New South Wales exists to this day as Westpac. The Commonwealth Bank of Australia was formed in Sydney in 1911 and began to issue notes backed by the resources of the nation. It was replaced in this role in 1959 by the Reserve Bank of Australia which is also based in Sydney. The Australian Securities Exchange began operating in 1987 and with a market capitalisation of $1.6 trillion is now one of the ten largest exchanges in the world.
The Financial and Insurance Services industry now constitutes 43% of the economic product of the City of Sydney. Sydney makes up half of Australia's finance sector and has been promoted by consecutive Commonwealth Governments as Asia Pacific's leading financial centre. In the 2017 Global Financial Centres Index, Sydney was ranked as having the eighth most competitive financial centre in the world.
In 1985 the Federal Government granted 16 banking licences to foreign banks and now 40 of the 43 foreign banks operating in Australia are based in Sydney, including the People's Bank of China, Bank of America, Citigroup, UBS, Mizuho Bank, Bank of China, Banco Santander, Credit Suisse, Standard Chartered, State Street Corporation, State Street, HSBC, Deutsche Bank, Barclays, Royal Bank of Canada, Société Générale, Royal Bank of Scotland, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation, Sumitomo Mitsui, ING Group, BNP Paribas, and Investec.
Manufacturing
Sydney has been a manufacturing city since the protectionist policies of the 1920s. By 1961 the industry accounted for 39% of all employment and by 1970 over 30% of all Australian manufacturing jobs were in Sydney. Its status has declined in more recent decades, making up 12.6% of employment in 2001 and 8.5% in 2011. Between 1970 and 1985 there was a loss of 180,000 manufacturing jobs. Despite this, Sydney still overtook Melbourne as the largest manufacturing centre in Australia in the 2010s. Its manufacturing output of $21.7 billion in 2013 was greater than that of Melbourne with $18.9 billion. Observers have noted Sydney's focus on the domestic market and high-tech manufacturing as reasons for its resilience against the high Australian dollar of the early 2010s. The ''Smithfield-Wetherill Park Industrial Estate'' in Greater Western Sydney, Western Sydney is the largest industrial estate in the Southern Hemisphere and is the centre of manufacturing and distribution in the region.Tourism and international education
 Sydney is a gateway to Australia for many international visitors. It has hosted over 2.8 million international visitors in 2013, or nearly half of all international visits to Australia. These visitors spent 59 million nights in the city and a total of $5.9 billion. The countries of origin in descending order were China, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, the United States, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Germany, Hong Kong, and India.
The city also received 8.3 million domestic overnight visitors in 2013 who spent a total of $6 billion. 26,700 workers in the City of Sydney were directly employed by tourism in 2011. There were 480,000 visitors and 27,500 people staying overnight each day in 2012. On average, the tourism industry contributes $36 million to the city's economy per day.
Popular destinations include the
Sydney is a gateway to Australia for many international visitors. It has hosted over 2.8 million international visitors in 2013, or nearly half of all international visits to Australia. These visitors spent 59 million nights in the city and a total of $5.9 billion. The countries of origin in descending order were China, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, the United States, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Germany, Hong Kong, and India.
The city also received 8.3 million domestic overnight visitors in 2013 who spent a total of $6 billion. 26,700 workers in the City of Sydney were directly employed by tourism in 2011. There were 480,000 visitors and 27,500 people staying overnight each day in 2012. On average, the tourism industry contributes $36 million to the city's economy per day.
Popular destinations include the Demographics
 The population of Sydney in 1788 was less than 1,000. With convict transportation it almost tripled in ten years to 2,953. For each decade since 1961 the population has increased by more than 250,000. The 2021 census recorded the population of Greater Sydney as 5,231,150. The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) projects the population will grow to between 8 and 8.9 million by 2061, but that Melbourne will replace Sydney as Australia's most populous city by 2026. The four most densely populated suburbs in Australia are located in Sydney with each having more than 13,000 residents per square kilometre (33,700 residents per square mile). Between 1971 and 2018, Sydney experienced a net loss of 716,832 people to the rest of Australia, but its population grew due to overseas arrivals and a healthy birth rate.
The median age of Sydney residents is 36 and 12.9% of people are 65 or older. The married population accounts for 49.7% of Sydney whilst 34.7% of people have never been married. 48.9% of families are couples with children, 33.5% are couples without children, and 15.7% are single-parent families.
The population of Sydney in 1788 was less than 1,000. With convict transportation it almost tripled in ten years to 2,953. For each decade since 1961 the population has increased by more than 250,000. The 2021 census recorded the population of Greater Sydney as 5,231,150. The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) projects the population will grow to between 8 and 8.9 million by 2061, but that Melbourne will replace Sydney as Australia's most populous city by 2026. The four most densely populated suburbs in Australia are located in Sydney with each having more than 13,000 residents per square kilometre (33,700 residents per square mile). Between 1971 and 2018, Sydney experienced a net loss of 716,832 people to the rest of Australia, but its population grew due to overseas arrivals and a healthy birth rate.
The median age of Sydney residents is 36 and 12.9% of people are 65 or older. The married population accounts for 49.7% of Sydney whilst 34.7% of people have never been married. 48.9% of families are couples with children, 33.5% are couples without children, and 15.7% are single-parent families.
Ancestry and immigration
Most immigrants to Sydney between 1840 and 1930 were British Australian, British, Irish Australian, Irish or Chinese Australian, Chinese. At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated ancestries were: At the 2021 census, 40.5% of Sydney's population was born overseas. Foreign countries of birth with the greatest representation are Mainland China, India, England, Vietnam, Philippines and New Zealand. At the 2021 census, 1.7% of Sydney's population identified as being Indigenous Australians, Indigenous — Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders.Language
A language other than English is used in 42% of households in Sydney. The most widely used non-English languages at home are Standard Chinese, Mandarin (5%), Arabic (4.2%), Cantonese (2.8%), Vietnamese language, Vietnamese (2.2%) and Hindi (1.5%).Religion
 In 2021, 30.3% of Sydney residents identified themselves as having no religion. Christianity was the largest religious affiliation at 46%, the largest denominations of which were Catholic Church in Australia, Catholicism at 23.1% and Anglicanism in Australia, Anglicanism at 9.2%. The most common non-Christian religious affiliations were Islam (6.3%), Hinduism (4.8%), Buddhism (3.8%), Sikhism (0.7%), and Judaism (0.7%). About 500 people identified with traditional Aboriginal religions.
The Church of England was the only recognised church before Governor Macquarie appointed official Catholic chaplains in 1820.O'Brien, Anne (2013). "Religion". ''The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume I''. pp. 419–20 Macquarie also ordered the construction of churches such as St Matthew's, St Luke's, St James's, and St Andrew's. Religious groups, alongside secular institutions, have played a significant role in education, health and charitable services throughout Sydney's history.
In 2021, 30.3% of Sydney residents identified themselves as having no religion. Christianity was the largest religious affiliation at 46%, the largest denominations of which were Catholic Church in Australia, Catholicism at 23.1% and Anglicanism in Australia, Anglicanism at 9.2%. The most common non-Christian religious affiliations were Islam (6.3%), Hinduism (4.8%), Buddhism (3.8%), Sikhism (0.7%), and Judaism (0.7%). About 500 people identified with traditional Aboriginal religions.
The Church of England was the only recognised church before Governor Macquarie appointed official Catholic chaplains in 1820.O'Brien, Anne (2013). "Religion". ''The Cambridge History of Australia, Volume I''. pp. 419–20 Macquarie also ordered the construction of churches such as St Matthew's, St Luke's, St James's, and St Andrew's. Religious groups, alongside secular institutions, have played a significant role in education, health and charitable services throughout Sydney's history.
Crime
Crime in Sydney is low, with ''The Independent'' ranking Sydney as the fifth safest city in the world in 2019. However, drug use is a significant problem. Methamphetamine is heavily consumed compared to other countries, while heroin is less common. One of the biggest crime related issues to face the city in recent times was the introduction of Sydney lockout laws, lock-out laws in February 2014, in an attempt to curb alcohol fuelled violence. Patrons could not enter clubs or bars in the inner-city after 1:30am, and last drinks were called at 3am. The lock-out laws were removed in January 2020.Culture
Science, art, and history
 Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park is rich in Indigenous Australian heritage, containing around 1,500 pieces of Aboriginal rock art – the largest cluster of Indigenous sites in Australia, surpassing Kakadu National Park, Kakadu, which has around 5,000 sites but over a much greater landmass. The park's indigenous sites include petroglyphs, art sites, burial sites, caves, marriage areas, birthing areas, midden sites, and tool manufacturing locations, among others, which are dated to be around 5,000 years old. The inhabitants of the area were the Kuringgai, Garigal people. Other Sydney Rock Art, rock art sites exist in the Sydney region, such as in Terrey Hills and Bondi, New South Wales, Bondi, although the locations of most are not publicised to prevent damage by vandalism, and to retain their quality, as they are still regarded as sacred sites by Indigenous Australians.
Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park is rich in Indigenous Australian heritage, containing around 1,500 pieces of Aboriginal rock art – the largest cluster of Indigenous sites in Australia, surpassing Kakadu National Park, Kakadu, which has around 5,000 sites but over a much greater landmass. The park's indigenous sites include petroglyphs, art sites, burial sites, caves, marriage areas, birthing areas, midden sites, and tool manufacturing locations, among others, which are dated to be around 5,000 years old. The inhabitants of the area were the Kuringgai, Garigal people. Other Sydney Rock Art, rock art sites exist in the Sydney region, such as in Terrey Hills and Bondi, New South Wales, Bondi, although the locations of most are not publicised to prevent damage by vandalism, and to retain their quality, as they are still regarded as sacred sites by Indigenous Australians. The Australian Museum opened in Sydney in 1827 with the purpose of collecting and displaying the natural wealth of the colony. It remains Australia's oldest natural history museum. In 1995 the Museum of Sydney opened on the site of the first Government House, Sydney, Government House. It recounts the story of the city's development. Other museums based in Sydney include the Powerhouse Museum and the Australian National Maritime Museum.
The State Library of New South Wales holds the oldest library collections in Australia, being first established as the Australian Subscription Library in 1826. In 1866 then Queen Victoria gave her assent to the formation of the Royal Society of New South Wales. The Society exists "for the encouragement of studies and investigations in science, art, literature, and philosophy". It is based in a terrace house in Darlington, New South Wales, Darlington owned by the University of Sydney. The Sydney Observatory building was constructed in 1859 and used for astronomy and meteorology research until 1982 before being converted into a museum.
The Museum of Contemporary Art Australia, Museum of Contemporary Art was opened in 1991 and occupies an Art Deco building in Circular Quay. Its collection was founded in the 1940s by artist and art collector John Power and has been maintained by the University of Sydney. Sydney's other significant art institution is the Art Gallery of New South Wales which coordinates the coveted Archibald Prize for portraiture. Contemporary art galleries are found in Waterloo, New South Wales, Waterloo, Surry Hills, New South Wales, Surry Hills, Darlinghurst, Paddington, New South Wales, Paddington, Chippendale, New South Wales, Chippendale, Newtown, New South Wales, Newtown, and Woollahra, New South Wales, Woollahra.
The Australian Museum opened in Sydney in 1827 with the purpose of collecting and displaying the natural wealth of the colony. It remains Australia's oldest natural history museum. In 1995 the Museum of Sydney opened on the site of the first Government House, Sydney, Government House. It recounts the story of the city's development. Other museums based in Sydney include the Powerhouse Museum and the Australian National Maritime Museum.
The State Library of New South Wales holds the oldest library collections in Australia, being first established as the Australian Subscription Library in 1826. In 1866 then Queen Victoria gave her assent to the formation of the Royal Society of New South Wales. The Society exists "for the encouragement of studies and investigations in science, art, literature, and philosophy". It is based in a terrace house in Darlington, New South Wales, Darlington owned by the University of Sydney. The Sydney Observatory building was constructed in 1859 and used for astronomy and meteorology research until 1982 before being converted into a museum.
The Museum of Contemporary Art Australia, Museum of Contemporary Art was opened in 1991 and occupies an Art Deco building in Circular Quay. Its collection was founded in the 1940s by artist and art collector John Power and has been maintained by the University of Sydney. Sydney's other significant art institution is the Art Gallery of New South Wales which coordinates the coveted Archibald Prize for portraiture. Contemporary art galleries are found in Waterloo, New South Wales, Waterloo, Surry Hills, New South Wales, Surry Hills, Darlinghurst, Paddington, New South Wales, Paddington, Chippendale, New South Wales, Chippendale, Newtown, New South Wales, Newtown, and Woollahra, New South Wales, Woollahra.
Entertainment
 Sydney's first commercial theatre opened in 1832 and nine more had commenced performances by the late 1920s. The live medium lost much of its popularity to the cinema during the Great Depression before experiencing a revival after World War II. Prominent theatres in the city today include State Theatre (Sydney), State Theatre, Theatre Royal, Sydney, Theatre Royal, Sydney Theatre, The Wharf Theatre, and Capitol Theatre, Sydney, Capitol Theatre. Sydney Theatre Company maintains a roster of local, classical, and international plays. It occasionally features Australian theatre icons such as David Williamson, Hugo Weaving, and Geoffrey Rush. The city's other prominent theatre companies are New Theatre (Newtown), New Theatre, Belvoir (theatre company), Belvoir, and Griffin Theatre Company. Sydney is also home to Event Cinemas' first theatre, which opened on George St, Sydney, George St in 1913, under its former Greater Union brand; the theatre currently operates, and is regarded as one of Australia's busiest cinema locations.
The Sydney Opera House is the home of Opera Australia and Sydney Symphony. It has staged over 100,000 performances and received 100 million visitors since opening in 1973. Two other important performance venues in Sydney are Sydney Town Hall, Town Hall and the City Recital Hall. The Sydney Conservatorium of Music is located adjacent to the Royal Botanic Garden and serves the Australian music community through education and its biannual Australian Music Examinations Board exams.
Sydney's first commercial theatre opened in 1832 and nine more had commenced performances by the late 1920s. The live medium lost much of its popularity to the cinema during the Great Depression before experiencing a revival after World War II. Prominent theatres in the city today include State Theatre (Sydney), State Theatre, Theatre Royal, Sydney, Theatre Royal, Sydney Theatre, The Wharf Theatre, and Capitol Theatre, Sydney, Capitol Theatre. Sydney Theatre Company maintains a roster of local, classical, and international plays. It occasionally features Australian theatre icons such as David Williamson, Hugo Weaving, and Geoffrey Rush. The city's other prominent theatre companies are New Theatre (Newtown), New Theatre, Belvoir (theatre company), Belvoir, and Griffin Theatre Company. Sydney is also home to Event Cinemas' first theatre, which opened on George St, Sydney, George St in 1913, under its former Greater Union brand; the theatre currently operates, and is regarded as one of Australia's busiest cinema locations.
The Sydney Opera House is the home of Opera Australia and Sydney Symphony. It has staged over 100,000 performances and received 100 million visitors since opening in 1973. Two other important performance venues in Sydney are Sydney Town Hall, Town Hall and the City Recital Hall. The Sydney Conservatorium of Music is located adjacent to the Royal Botanic Garden and serves the Australian music community through education and its biannual Australian Music Examinations Board exams.
 Many writers have originated in and set their work in Sydney. Others have visited the city and commented on it. Some of them are commemorated in the Sydney Writers Walk at Circular Quay. The city was the headquarters for Australia's first published newspaper, the ''Sydney Gazette''. Watkin Tench's ''A Narrative of the Expedition to Botany Bay'' (1789) and ''A Complete Account of the Settlement at Port Jackson in New South Wales'' (1793) have remained the best-known accounts of life in early Sydney. Since the infancy of the establishment, much of the literature set in Sydney were concerned with life in the city's slums and working-class communities, notably William Lane's ''The Working Man's Paradise'' (1892), Christina Stead's ''Seven Poor Men of Sydney'' (1934) and Ruth Park's ''The Harp in the South'' (1948). The first Australian-born female novelist, Louisa Atkinson, set various of her novels in Sydney. Contemporary writers, such as Elizabeth Harrower (writer), Elizabeth Harrower, were born in the city and thus set most of the work there–Harrower's debut novel ''Down in the City'' (1957) was mostly set in a King's Cross, New South Wales, King's Cross apartment. Well known contemporary novels set in the city include Melina Marchetta's ''Looking for Alibrandi (novel), Looking for Alibrandi'' (1992), Peter Carey (novelist), Peter Carey's ''30 Days in Sydney: A Wildly Distorted Account'' (1999), J. M. Coetzee's ''Diary of a Bad Year'' (2007) and Kate Grenville's ''The Secret River'' (2010). The Sydney Writers' Festival is held every year between April and May.
Filmmaking in Sydney was quite prolific until the 1920s when spoken films were introduced and American productions gained dominance in Australian cinema. The Australian New Wave of filmmaking saw a resurgence in film production in the city–with many notable features shot in the city between the 1970s and 80s, helmed by directors such as Bruce Beresford, Peter Weir and Gillian Armstrong. Fox Studios Australia commenced production in Sydney in 1998. Successful films shot in Sydney since then include ''The Matrix'', ''Lantana (film), Lantana'', ''Mission: Impossible 2'', ''Moulin Rouge!'', ''Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones'', ''Australia (2008 film), Australia'', and ''The Great Gatsby (2013 film), The Great Gatsby''. The National Institute of Dramatic Art is based in Sydney and has several famous alumni such as Mel Gibson, Judy Davis, Baz Luhrmann, Cate Blanchett, Hugo Weaving and Jacqueline McKenzie, Jacqueline Mckenzie.
Sydney is the host of several festivals throughout the year. The city's Sydney New Year's Eve, New Year's Eve celebrations are the largest in Australia. The Sydney Royal Easter Show, Royal Easter Show is held every year at Sydney Olympic Park. Sydney Festival is Australia's largest arts festival. The travelling rock music festival Big Day Out originated in Sydney. The city's two largest film festivals are Sydney Film Festival and Tropfest. Vivid Sydney is an annual outdoor exhibition of art installations, light projections, and music. In 2015, Sydney was ranked 13th for being the top fashion capitals in the world. It hosts the Australian Fashion Week in autumn. The Sydney Mardi Gras has commenced each February since 1979.
Sydney's Chinatown, Sydney, Chinatown has had numerous locations since the 1850s. It moved from George Street, Sydney, George Street to Campbell Street to its current setting in Dixon Street in 1980. Little Italy is located in Stanley Street.
Restaurants, bars and nightclubs can be found in the entertainment hubs in the Sydney CBD (
Many writers have originated in and set their work in Sydney. Others have visited the city and commented on it. Some of them are commemorated in the Sydney Writers Walk at Circular Quay. The city was the headquarters for Australia's first published newspaper, the ''Sydney Gazette''. Watkin Tench's ''A Narrative of the Expedition to Botany Bay'' (1789) and ''A Complete Account of the Settlement at Port Jackson in New South Wales'' (1793) have remained the best-known accounts of life in early Sydney. Since the infancy of the establishment, much of the literature set in Sydney were concerned with life in the city's slums and working-class communities, notably William Lane's ''The Working Man's Paradise'' (1892), Christina Stead's ''Seven Poor Men of Sydney'' (1934) and Ruth Park's ''The Harp in the South'' (1948). The first Australian-born female novelist, Louisa Atkinson, set various of her novels in Sydney. Contemporary writers, such as Elizabeth Harrower (writer), Elizabeth Harrower, were born in the city and thus set most of the work there–Harrower's debut novel ''Down in the City'' (1957) was mostly set in a King's Cross, New South Wales, King's Cross apartment. Well known contemporary novels set in the city include Melina Marchetta's ''Looking for Alibrandi (novel), Looking for Alibrandi'' (1992), Peter Carey (novelist), Peter Carey's ''30 Days in Sydney: A Wildly Distorted Account'' (1999), J. M. Coetzee's ''Diary of a Bad Year'' (2007) and Kate Grenville's ''The Secret River'' (2010). The Sydney Writers' Festival is held every year between April and May.
Filmmaking in Sydney was quite prolific until the 1920s when spoken films were introduced and American productions gained dominance in Australian cinema. The Australian New Wave of filmmaking saw a resurgence in film production in the city–with many notable features shot in the city between the 1970s and 80s, helmed by directors such as Bruce Beresford, Peter Weir and Gillian Armstrong. Fox Studios Australia commenced production in Sydney in 1998. Successful films shot in Sydney since then include ''The Matrix'', ''Lantana (film), Lantana'', ''Mission: Impossible 2'', ''Moulin Rouge!'', ''Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones'', ''Australia (2008 film), Australia'', and ''The Great Gatsby (2013 film), The Great Gatsby''. The National Institute of Dramatic Art is based in Sydney and has several famous alumni such as Mel Gibson, Judy Davis, Baz Luhrmann, Cate Blanchett, Hugo Weaving and Jacqueline McKenzie, Jacqueline Mckenzie.
Sydney is the host of several festivals throughout the year. The city's Sydney New Year's Eve, New Year's Eve celebrations are the largest in Australia. The Sydney Royal Easter Show, Royal Easter Show is held every year at Sydney Olympic Park. Sydney Festival is Australia's largest arts festival. The travelling rock music festival Big Day Out originated in Sydney. The city's two largest film festivals are Sydney Film Festival and Tropfest. Vivid Sydney is an annual outdoor exhibition of art installations, light projections, and music. In 2015, Sydney was ranked 13th for being the top fashion capitals in the world. It hosts the Australian Fashion Week in autumn. The Sydney Mardi Gras has commenced each February since 1979.
Sydney's Chinatown, Sydney, Chinatown has had numerous locations since the 1850s. It moved from George Street, Sydney, George Street to Campbell Street to its current setting in Dixon Street in 1980. Little Italy is located in Stanley Street.
Restaurants, bars and nightclubs can be found in the entertainment hubs in the Sydney CBD (Media
 ''The Sydney Morning Herald'' is Australia's oldest newspaper still in print. Now a compact (newspaper), compact form paper owned by Nine Entertainment, it has been published continuously since 1831. Its competitor is the News Corporation tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid ''Daily Telegraph (Sydney), The Daily Telegraph'' which has been in print since 1879. Both papers have Sunday tabloid editions called ''The Sun-Herald'' and ''Daily Telegraph (Sydney), The Sunday Telegraph'' respectively. ''The Bulletin (Australian periodical), The Bulletin'' was founded in Sydney in 1880 and became Australia's longest running magazine. It closed after 128 years of continuous publication. Sydney heralded Australia's first newspaper, the ''Sydney Gazette'', published until 1842.
Each of Australia's three commercial television networks and two public broadcasters is headquartered in Sydney. Nine Network, Nine's offices and news studios are in North Sydney, New South Wales, North Sydney, Network 10, Ten and Seven Network, Seven are based in Pyrmont, Seven has a news studio in the Sydney central business district, Sydney CBD in Martin Place the Australian Broadcasting Corporation is located in Ultimo, New South Wales, Ultimo, and the Special Broadcasting Service is based in Artarmon. Multiple digital channels have been provided by all five networks since 2000. Foxtel is based in North Ryde and sells subscription cable television to most parts of the urban area. Sydney's first List of Sydney radio stations, radio stations commenced broadcasting in the 1920s. Radio became a popular tool for politics, news, religion, and sport and has managed to survive despite the introduction of television and the Internet. 2UE was founded in 1925 and under the ownership of Nine Entertainment is the oldest station still broadcasting. Competing stations include the more popular 2GB, ABC Radio Sydney, KIIS 106.5, Triple M Sydney, Triple M, Nova 96.9 and 2Day FM.
''The Sydney Morning Herald'' is Australia's oldest newspaper still in print. Now a compact (newspaper), compact form paper owned by Nine Entertainment, it has been published continuously since 1831. Its competitor is the News Corporation tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid ''Daily Telegraph (Sydney), The Daily Telegraph'' which has been in print since 1879. Both papers have Sunday tabloid editions called ''The Sun-Herald'' and ''Daily Telegraph (Sydney), The Sunday Telegraph'' respectively. ''The Bulletin (Australian periodical), The Bulletin'' was founded in Sydney in 1880 and became Australia's longest running magazine. It closed after 128 years of continuous publication. Sydney heralded Australia's first newspaper, the ''Sydney Gazette'', published until 1842.
Each of Australia's three commercial television networks and two public broadcasters is headquartered in Sydney. Nine Network, Nine's offices and news studios are in North Sydney, New South Wales, North Sydney, Network 10, Ten and Seven Network, Seven are based in Pyrmont, Seven has a news studio in the Sydney central business district, Sydney CBD in Martin Place the Australian Broadcasting Corporation is located in Ultimo, New South Wales, Ultimo, and the Special Broadcasting Service is based in Artarmon. Multiple digital channels have been provided by all five networks since 2000. Foxtel is based in North Ryde and sells subscription cable television to most parts of the urban area. Sydney's first List of Sydney radio stations, radio stations commenced broadcasting in the 1920s. Radio became a popular tool for politics, news, religion, and sport and has managed to survive despite the introduction of television and the Internet. 2UE was founded in 1925 and under the ownership of Nine Entertainment is the oldest station still broadcasting. Competing stations include the more popular 2GB, ABC Radio Sydney, KIIS 106.5, Triple M Sydney, Triple M, Nova 96.9 and 2Day FM.
Sport and outdoor activities
Sydney's earliest migrants brought with them a passion for sport but were restricted by the lack of facilities and equipment. The first organised sports were boxing, wrestling, and horse racing from 1810 in Hyde Park, Sydney, Hyde Park. Horse racing remains popular to this day and events such as the Golden Slipper Stakes attract widespread attention. The first cricket club was formed in 1826 and matches were played within Hyde Park throughout the 1830s and 1840s. Cricket is a favoured sport in summer and big matches have been held at the Sydney Cricket Ground since 1878. The New South Wales cricket team, New South Wales Blues compete in the Sheffield Shield league and the Sydney Sixers and Sydney Thunder contest the national Big Bash League, Big Bash Twenty20 competition. First played in Sydney in 1865, rugby grew to be the city's most popular football code by the 1880s. One-tenth of the state's population attended a New South Wales versus New Zealand rugby match in 1907. Rugby league separated from rugby union in 1908. The New South Wales Waratahs contest the Super Rugby competition, while the Sydney Rays represent the city in the National Rugby Championship. The national Wallabies (rugby union), Wallabies rugby union team competes in Sydney in international matches such as the Bledisloe Cup, The Rugby Championship, Rugby Championship, and Rugby World Cup, World Cup. Sydney is home to nine of the sixteen teams in the National Rugby League competition: Canterbury-Bankstown Bulldogs, Cronulla-Sutherland Sharks, Manly-Warringah Sea Eagles, Penrith Panthers, Parramatta Eels, South Sydney Rabbitohs, St George Illawarra Dragons, Sydney Roosters, and Wests Tigers. New South Wales rugby league team, New South Wales contests the annual State of Origin series against Queensland rugby league team, Queensland. Sydney FC and the Western Sydney Wanderers compete in the A-League (men's) and W-League (Australia), W-League (women's) soccer competitions and Sydney frequently hosts matches for the Australian national men's team, the Socceroos. The Sydney Swans and Greater Western Sydney Giants are local Australian rules football clubs that play in the Australian Football League and the AFL Women's. The Sydney Kings compete in the National Basketball League (Australia), National Basketball League. The Sydney Uni Flames play in the Women's National Basketball League. The Sydney Blue Sox contest the Australian Baseball League. The NSW Pride are a member of the Hockey One, Hockey One League. The Sydney Bears and Sydney Ice Dogs play in the Australian Ice Hockey League. The New South Wales Swifts, Swifts are competitors in the national women's netball league.Major sporting venues
 Women were first allowed to participate in recreational swimming when separate baths were opened at Woolloomooloo, Woolloomooloo Bay in the 1830s. From being illegal at the beginning of the century, sea bathing gained immense popularity during the early 1900s and the first surf lifesaving club was established at Bondi Beach. 1907 Sydney bathing costume protests, Disputes about appropriate clothing for surf bathing surfaced from time to time and concerned men as well as women. The City2Surf (Sydney), City2Surf is an annual running race from the CBD to Bondi Beach and has been held since 1971. In 2010, 80,000 runners participated which made it the largest run of its kind in the world.
Sailing races have been held on
Women were first allowed to participate in recreational swimming when separate baths were opened at Woolloomooloo, Woolloomooloo Bay in the 1830s. From being illegal at the beginning of the century, sea bathing gained immense popularity during the early 1900s and the first surf lifesaving club was established at Bondi Beach. 1907 Sydney bathing costume protests, Disputes about appropriate clothing for surf bathing surfaced from time to time and concerned men as well as women. The City2Surf (Sydney), City2Surf is an annual running race from the CBD to Bondi Beach and has been held since 1971. In 2010, 80,000 runners participated which made it the largest run of its kind in the world.
Sailing races have been held on  The Royal Sydney Golf Club is based in Rose Bay, New South Wales, Rose Bay and since its opening in 1893 has hosted the Australian Open (golf), Australian Open on 13 occasions. Royal Randwick Racecourse opened in 1833 and holds several major cups throughout the year.
Sydney benefitted from the construction of significant sporting infrastructure in preparation for its hosting of the 2000 Summer Olympics. The Sydney Olympic Park accommodates athletics, aquatics, tennis, hockey, archery, baseball, cycling, equestrian, and rowing facilities. It also includes the high capacity Stadium Australia used for rugby, soccer, and Australian rules football. The Sydney Football Stadium (1988), Sydney Football Stadium was completed in 1988 and was used for rugby and soccer matches. Sydney Cricket Ground was opened in 1878 and is used for both cricket and Australian rules football fixtures.
The Sydney International tennis tournament is held here at the beginning of each year as the warm-up for Australian Open, the Grand Slam in Melbourne. Two of the most successful tennis players in history: Ken Rosewall and Todd Woodbridge were born in and live in the city.
Sydney co-hosted the FIBA Oceania Championship in 1979, 1985, 1989, 1995, 2007, 2009 and 2011.
The Royal Sydney Golf Club is based in Rose Bay, New South Wales, Rose Bay and since its opening in 1893 has hosted the Australian Open (golf), Australian Open on 13 occasions. Royal Randwick Racecourse opened in 1833 and holds several major cups throughout the year.
Sydney benefitted from the construction of significant sporting infrastructure in preparation for its hosting of the 2000 Summer Olympics. The Sydney Olympic Park accommodates athletics, aquatics, tennis, hockey, archery, baseball, cycling, equestrian, and rowing facilities. It also includes the high capacity Stadium Australia used for rugby, soccer, and Australian rules football. The Sydney Football Stadium (1988), Sydney Football Stadium was completed in 1988 and was used for rugby and soccer matches. Sydney Cricket Ground was opened in 1878 and is used for both cricket and Australian rules football fixtures.
The Sydney International tennis tournament is held here at the beginning of each year as the warm-up for Australian Open, the Grand Slam in Melbourne. Two of the most successful tennis players in history: Ken Rosewall and Todd Woodbridge were born in and live in the city.
Sydney co-hosted the FIBA Oceania Championship in 1979, 1985, 1989, 1995, 2007, 2009 and 2011.
Government
Historical governance
 During early colonial times, the presiding Governor of New South Wales, Governor and his military shared absolute control over the population. This lack of democracy eventually became unacceptable for the colony's growing number of free settlers. The first indications of a proper legal system emerged with the passing of a Charter of Justice in 1814. It established three new courts, including the Supreme Court of New South Wales, Supreme Court, and dictated that English law was to be followed. In 1823 the Parliament of the United Kingdom, British Parliament passed an act to create the New South Wales Legislative Council, Legislative Council in New South Wales and give the Supreme Court the right of review over new legislation. From 1828 all of the common laws in force in England were to be applied in New South Wales wherever it was appropriate. Another act from the British Parliament in 1842 provided for members of the council to be elected for the first time.
The Constitution Act of 1855 gave New South Wales a bicameralism, bicameral government. The existing Legislative Council became the upper house and a new body called the New South Wales Legislative Assembly, Legislative Assembly was formed to be the lower house. An Executive Council of New South Wales, Executive Council was introduced and constituted five members of the Legislative Assembly and the Governor. It became responsible for advising the ruling Governor on matters related to the administration of the state. The colonial settlements elsewhere on the continent eventually seceded from New South Wales and formed their own governments. Tasmania separated in 1825, Victoria (Australia), Victoria did so in 1850, and Queensland followed in 1859. With the proclamation of the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901 the status of local governments across Sydney was formalised and they became separate institutions from the state of New South Wales.
During early colonial times, the presiding Governor of New South Wales, Governor and his military shared absolute control over the population. This lack of democracy eventually became unacceptable for the colony's growing number of free settlers. The first indications of a proper legal system emerged with the passing of a Charter of Justice in 1814. It established three new courts, including the Supreme Court of New South Wales, Supreme Court, and dictated that English law was to be followed. In 1823 the Parliament of the United Kingdom, British Parliament passed an act to create the New South Wales Legislative Council, Legislative Council in New South Wales and give the Supreme Court the right of review over new legislation. From 1828 all of the common laws in force in England were to be applied in New South Wales wherever it was appropriate. Another act from the British Parliament in 1842 provided for members of the council to be elected for the first time.
The Constitution Act of 1855 gave New South Wales a bicameralism, bicameral government. The existing Legislative Council became the upper house and a new body called the New South Wales Legislative Assembly, Legislative Assembly was formed to be the lower house. An Executive Council of New South Wales, Executive Council was introduced and constituted five members of the Legislative Assembly and the Governor. It became responsible for advising the ruling Governor on matters related to the administration of the state. The colonial settlements elsewhere on the continent eventually seceded from New South Wales and formed their own governments. Tasmania separated in 1825, Victoria (Australia), Victoria did so in 1850, and Queensland followed in 1859. With the proclamation of the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901 the status of local governments across Sydney was formalised and they became separate institutions from the state of New South Wales.
Government in the present
 Sydney is divided into local government in Australia, local government areas (variously known as cities, councils, municipalities or shires). These local government areas have elected councils which are responsible for functions delegated to them by the New South Wales Government. The 31 local government areas making up Sydney according to the New South Wales Division of Local Government are:
* Bayside Council, Bayside
* City of Canterbury-Bankstown, Canterbury-Bankstown
* City of Blacktown, Blacktown
* Municipality of Burwood, Burwood
* Camden Council (New South Wales), Camden
* City of Campbelltown (New South Wales), Campbelltown
* City of Canada Bay, Canada Bay
* Cumberland Council (New South Wales), Cumberland
* City of Fairfield, Fairfield
* Georges River Council, Georges River
* Hawkesbury
* The Hills Shire, The Hills
* Hornsby Shire, Hornsby
* Municipality of Hunter's Hill, Hunter's Hill
* Inner West Council, Inner West
* Ku-ring-gai Council, Ku-ring-gai
* Municipality of Lane Cove, Lane Cove
* City of Liverpool (New South Wales), Liverpool
* Municipality of Mosman, Mosman
* North Sydney Council, North Sydney
* Northern Beaches Council, Northern Beaches
* City of Parramatta Council, Parramatta
* City of Penrith, Penrith
* City of Randwick, Randwick
* City of Ryde, Ryde
* Municipality of Strathfield, Strathfield
* Sutherland Shire, Sutherland
* City of Sydney, Sydney
* Waverley Council, Waverley
* City of Willoughby, Willoughby
* Municipality of Woollahra, Woollahra
Sydney is divided into local government in Australia, local government areas (variously known as cities, councils, municipalities or shires). These local government areas have elected councils which are responsible for functions delegated to them by the New South Wales Government. The 31 local government areas making up Sydney according to the New South Wales Division of Local Government are:
* Bayside Council, Bayside
* City of Canterbury-Bankstown, Canterbury-Bankstown
* City of Blacktown, Blacktown
* Municipality of Burwood, Burwood
* Camden Council (New South Wales), Camden
* City of Campbelltown (New South Wales), Campbelltown
* City of Canada Bay, Canada Bay
* Cumberland Council (New South Wales), Cumberland
* City of Fairfield, Fairfield
* Georges River Council, Georges River
* Hawkesbury
* The Hills Shire, The Hills
* Hornsby Shire, Hornsby
* Municipality of Hunter's Hill, Hunter's Hill
* Inner West Council, Inner West
* Ku-ring-gai Council, Ku-ring-gai
* Municipality of Lane Cove, Lane Cove
* City of Liverpool (New South Wales), Liverpool
* Municipality of Mosman, Mosman
* North Sydney Council, North Sydney
* Northern Beaches Council, Northern Beaches
* City of Parramatta Council, Parramatta
* City of Penrith, Penrith
* City of Randwick, Randwick
* City of Ryde, Ryde
* Municipality of Strathfield, Strathfield
* Sutherland Shire, Sutherland
* City of Sydney, Sydney
* Waverley Council, Waverley
* City of Willoughby, Willoughby
* Municipality of Woollahra, Woollahra
 Sydney is the location of the secondary official residences of the Governor-General of Australia and the Prime Minister of Australia, Admiralty House, Sydney, Admiralty House and Kirribilli House respectively. The Parliament of New South Wales sits in Parliament House, Sydney, Parliament House on Macquarie Street, Sydney, Macquarie Street. This building was completed in 1816 and first served as a hospital. The Legislative Council moved into its northern wing in 1829 and by 1852 had entirely supplanted the surgeons from their quarters. Several additions have been made to the building as the Parliament has expanded, but it retains its original Georgian architecture, Georgian façade. Government House, Sydney, Government House was completed in 1845 and has served as the home of 25 Governors and 5 Governor-General of Australia, Governors-General. The Cabinet of Australia also Commonwealth Parliament Offices, Sydney, meets in Sydney when needed.
The highest court in the state is the Supreme Court of New South Wales which is located in Queen's Square in Sydney. The city is also the home of numerous branches of the intermediate District Court of New South Wales and the lower Local Court of New South Wales.
In common with other Australian capital cities, Sydney has no single local government covering its whole area. Local government areas have responsibilities such as local roads, libraries, child care, community services and waste collection, whereas the state government retains responsibility for main roads, traffic control, public transport, policing, education, and major infrastructure project.
In the past, the state has tended to resist amalgamating Sydney's more populated local government areas as merged councils could pose a threat to its governmental power. Established in 1842, the City of Sydney is one such local government area and includes the CBD and some adjoining inner suburbs. It is responsible for fostering development in the local area, providing local services (waste collection and recycling, libraries, parks, sporting facilities), representing and promoting the interests of residents, supporting organisations that target the local community, and attracting and providing infrastructure for commerce, tourism, and industry. The City of Sydney is led by an elected Council and Lord Mayor of Sydney, Lord Mayor who has in the past been treated as a representative of the entire city.
In federal politics, Sydney was initially considered as a History of the Australian Capital Territory#Search for a capital city location, possibility for Australia's capital city; the newly created city of Canberra ultimately filled this role. Seven Australian List of Australian Prime Ministers by state#Birth places, Prime Ministers have been born in Sydney, more than any other city, including first Prime Minister Edmund Barton and current Prime Minister Anthony Albanese.
Essential public emergency services are provided and managed by the State Government. Greater Sydney is served by:
* New South Wales Police Force
* New South Wales Ambulance
* Fire and Rescue NSW
Sydney is the location of the secondary official residences of the Governor-General of Australia and the Prime Minister of Australia, Admiralty House, Sydney, Admiralty House and Kirribilli House respectively. The Parliament of New South Wales sits in Parliament House, Sydney, Parliament House on Macquarie Street, Sydney, Macquarie Street. This building was completed in 1816 and first served as a hospital. The Legislative Council moved into its northern wing in 1829 and by 1852 had entirely supplanted the surgeons from their quarters. Several additions have been made to the building as the Parliament has expanded, but it retains its original Georgian architecture, Georgian façade. Government House, Sydney, Government House was completed in 1845 and has served as the home of 25 Governors and 5 Governor-General of Australia, Governors-General. The Cabinet of Australia also Commonwealth Parliament Offices, Sydney, meets in Sydney when needed.
The highest court in the state is the Supreme Court of New South Wales which is located in Queen's Square in Sydney. The city is also the home of numerous branches of the intermediate District Court of New South Wales and the lower Local Court of New South Wales.
In common with other Australian capital cities, Sydney has no single local government covering its whole area. Local government areas have responsibilities such as local roads, libraries, child care, community services and waste collection, whereas the state government retains responsibility for main roads, traffic control, public transport, policing, education, and major infrastructure project.
In the past, the state has tended to resist amalgamating Sydney's more populated local government areas as merged councils could pose a threat to its governmental power. Established in 1842, the City of Sydney is one such local government area and includes the CBD and some adjoining inner suburbs. It is responsible for fostering development in the local area, providing local services (waste collection and recycling, libraries, parks, sporting facilities), representing and promoting the interests of residents, supporting organisations that target the local community, and attracting and providing infrastructure for commerce, tourism, and industry. The City of Sydney is led by an elected Council and Lord Mayor of Sydney, Lord Mayor who has in the past been treated as a representative of the entire city.
In federal politics, Sydney was initially considered as a History of the Australian Capital Territory#Search for a capital city location, possibility for Australia's capital city; the newly created city of Canberra ultimately filled this role. Seven Australian List of Australian Prime Ministers by state#Birth places, Prime Ministers have been born in Sydney, more than any other city, including first Prime Minister Edmund Barton and current Prime Minister Anthony Albanese.
Essential public emergency services are provided and managed by the State Government. Greater Sydney is served by:
* New South Wales Police Force
* New South Wales Ambulance
* Fire and Rescue NSW
Infrastructure
Education
 Education became a proper focus for the colony from the 1870s when public schools began to form and schooling became compulsory. The population of Sydney is now highly educated. 90% of working age residents have completed some schooling and 57% have completed the highest level of school. 1,390,703 people were enrolled in an educational institution in 2011 with 45.1% of these attending school and 16.5% studying at a university. Undergraduate or postgraduate qualifications are held by 22.5% of working age Sydney residents and 40.2% of working age residents of the City of Sydney. The most common fields of tertiary qualification are commerce (22.8%), engineering (13.4%), society and culture (10.8%), health (7.8%), and education (6.6%).
Education became a proper focus for the colony from the 1870s when public schools began to form and schooling became compulsory. The population of Sydney is now highly educated. 90% of working age residents have completed some schooling and 57% have completed the highest level of school. 1,390,703 people were enrolled in an educational institution in 2011 with 45.1% of these attending school and 16.5% studying at a university. Undergraduate or postgraduate qualifications are held by 22.5% of working age Sydney residents and 40.2% of working age residents of the City of Sydney. The most common fields of tertiary qualification are commerce (22.8%), engineering (13.4%), society and culture (10.8%), health (7.8%), and education (6.6%).
 There are six public universities based in Sydney: The University of Sydney, University of New South Wales, University of Technology, Sydney, University of Technology Sydney, Macquarie University, Western Sydney University, and Australian Catholic University. Five public universities maintain secondary campuses in the city for both domestic and international students: the University of Notre Dame Australia, Central Queensland University, Victoria University, Melbourne, Victoria University, University of Wollongong, and University of Newcastle (Australia), University of Newcastle. Charles Sturt University and Southern Cross University, both public universities, operate secondary campuses only designated for international students. In addition, four public universities offer programmes in Sydney through third-party education providers: University of the Sunshine Coast, La Trobe University, Federation University Australia and Charles Darwin University. 5.2% of residents of Sydney are attending a university. The University of New South Wales and the University of Sydney are ranked top 50 in the world, the University of Technology Sydney is ranked 133, while Macquarie University is ranked 237, and Western Sydney University is ranked 474.
Sydney has public, denominational, and independent schools. 7.8% of Sydney residents are attending primary school and 6.4% are enrolled in secondary school. There are 935 public preschool, primary, and secondary schools in Sydney that are administered by the Department of Education and Communities (New South Wales), New South Wales Department of Education. 14 of the 17 selective secondary schools in New South Wales are based in Sydney.
Public vocational education and training in Sydney are run by TAFE NSW, TAFE New South Wales and began with the opening of the Sydney Technical College in 1878. It offered courses in areas such as mechanical drawing, applied mathematics, steam engines, simple surgery, and English grammar. The college became the Sydney Institute of TAFE, Sydney Institute in 1992 and now operates alongside its sister TAFE facilities across the Sydney metropolitan area, namely the Northern Sydney Institute of TAFE, Northern Sydney Institute, the Western Sydney Institute of TAFE, Western Sydney Institute, and the South Western Sydney Institute of TAFE, South Western Sydney Institute. At the 2011 census, 2.4% of Sydney residents are enrolled in a TAFE course.
There are six public universities based in Sydney: The University of Sydney, University of New South Wales, University of Technology, Sydney, University of Technology Sydney, Macquarie University, Western Sydney University, and Australian Catholic University. Five public universities maintain secondary campuses in the city for both domestic and international students: the University of Notre Dame Australia, Central Queensland University, Victoria University, Melbourne, Victoria University, University of Wollongong, and University of Newcastle (Australia), University of Newcastle. Charles Sturt University and Southern Cross University, both public universities, operate secondary campuses only designated for international students. In addition, four public universities offer programmes in Sydney through third-party education providers: University of the Sunshine Coast, La Trobe University, Federation University Australia and Charles Darwin University. 5.2% of residents of Sydney are attending a university. The University of New South Wales and the University of Sydney are ranked top 50 in the world, the University of Technology Sydney is ranked 133, while Macquarie University is ranked 237, and Western Sydney University is ranked 474.
Sydney has public, denominational, and independent schools. 7.8% of Sydney residents are attending primary school and 6.4% are enrolled in secondary school. There are 935 public preschool, primary, and secondary schools in Sydney that are administered by the Department of Education and Communities (New South Wales), New South Wales Department of Education. 14 of the 17 selective secondary schools in New South Wales are based in Sydney.
Public vocational education and training in Sydney are run by TAFE NSW, TAFE New South Wales and began with the opening of the Sydney Technical College in 1878. It offered courses in areas such as mechanical drawing, applied mathematics, steam engines, simple surgery, and English grammar. The college became the Sydney Institute of TAFE, Sydney Institute in 1992 and now operates alongside its sister TAFE facilities across the Sydney metropolitan area, namely the Northern Sydney Institute of TAFE, Northern Sydney Institute, the Western Sydney Institute of TAFE, Western Sydney Institute, and the South Western Sydney Institute of TAFE, South Western Sydney Institute. At the 2011 census, 2.4% of Sydney residents are enrolled in a TAFE course.
Health
 The first hospital in the new colony was a collection of tents at The Rocks, Sydney, The Rocks. Many of the convicts that survived the trip from England continued to suffer from dysentery, smallpox, scurvy, and typhoid. Healthcare facilities remained hopelessly inadequate despite the arrival of a prefabricated hospital with the
The first hospital in the new colony was a collection of tents at The Rocks, Sydney, The Rocks. Many of the convicts that survived the trip from England continued to suffer from dysentery, smallpox, scurvy, and typhoid. Healthcare facilities remained hopelessly inadequate despite the arrival of a prefabricated hospital with the Transport
Roads
 The motor vehicle, more than any other factor, has determined the pattern of Sydney's urban development since World War II. The growth of low density housing in the city's outer suburbs has made car ownership necessary for hundreds of thousands of households. The percentage of trips taken by car has increased from 13% in 1947 to 50% in 1960 and to 70% in 1971. The most important roads in Sydney were the nine Metroads, including the Sydney Orbital Network. Widespread criticism over Sydney's reliance on sprawling road networks, as well as the motor vehicle, have stemmed largely from proponents of mass public transport and high density housing. The Light Horse Interchange in western Sydney is the largest in the southern hemisphere.
There can be up to 350,000 cars using Sydney's roads simultaneously during peak hour, leading to significant traffic congestion. 84.9% of Sydney households own a motor vehicle and 46.5% own two or more. Car dependency is an ongoing issue in Sydney–of people who travel to work, 58.4% use a car, 9.1% catch a train, 5.2% take a bus, and 4.1% walk. In contrast, only 25.2% of working residents in the City of Sydney use a car, whilst 15.8% take a train, 13.3% use a bus, and 25.3% walk. With a rate of 26.3%, Sydney has the highest utilisation of public transport for travel to work of any Australian capital city. The CBD features a Lanes and alleyways of Sydney, series of alleyways and lanes that provide alley, off-street vehicular access to city buildings and as well as pedestrian routes through city buildings.
The motor vehicle, more than any other factor, has determined the pattern of Sydney's urban development since World War II. The growth of low density housing in the city's outer suburbs has made car ownership necessary for hundreds of thousands of households. The percentage of trips taken by car has increased from 13% in 1947 to 50% in 1960 and to 70% in 1971. The most important roads in Sydney were the nine Metroads, including the Sydney Orbital Network. Widespread criticism over Sydney's reliance on sprawling road networks, as well as the motor vehicle, have stemmed largely from proponents of mass public transport and high density housing. The Light Horse Interchange in western Sydney is the largest in the southern hemisphere.
There can be up to 350,000 cars using Sydney's roads simultaneously during peak hour, leading to significant traffic congestion. 84.9% of Sydney households own a motor vehicle and 46.5% own two or more. Car dependency is an ongoing issue in Sydney–of people who travel to work, 58.4% use a car, 9.1% catch a train, 5.2% take a bus, and 4.1% walk. In contrast, only 25.2% of working residents in the City of Sydney use a car, whilst 15.8% take a train, 13.3% use a bus, and 25.3% walk. With a rate of 26.3%, Sydney has the highest utilisation of public transport for travel to work of any Australian capital city. The CBD features a Lanes and alleyways of Sydney, series of alleyways and lanes that provide alley, off-street vehicular access to city buildings and as well as pedestrian routes through city buildings.
Buses
Bus services today are conducted by private operators under contract to Transport for NSW. Integrated tickets called Opal cards operate on bus routes. In total, nearly 225 million boardings were recorded across the bus network NightRide (bus service), NightRide is a nightly bus service that operate between midnight and 5am, also replacing trains for most of this period.Trams and light rail
 Sydney once had one of the Trams in Sydney, largest tram networks in the British Empire after London. It served routes covering . The internal combustion engine made buses more flexible than trams and consequently more popular, leading to the progressive closure of the tram network with the final tram operating in 1961. From 1930 there were 612 buses across Sydney carrying 90 million passengers per annum.
In 1997, the Dulwich Hill Line, Inner West Light Rail (also known as the Dulwich Hill Line) opened between Central station and Wentworth Park. It was extended to Lilyfield, New South Wales, Lilyfield in 2000 and then Dulwich Hill, New South Wales, Dulwich Hill in 2014. It links the Inner West and
Sydney once had one of the Trams in Sydney, largest tram networks in the British Empire after London. It served routes covering . The internal combustion engine made buses more flexible than trams and consequently more popular, leading to the progressive closure of the tram network with the final tram operating in 1961. From 1930 there were 612 buses across Sydney carrying 90 million passengers per annum.
In 1997, the Dulwich Hill Line, Inner West Light Rail (also known as the Dulwich Hill Line) opened between Central station and Wentworth Park. It was extended to Lilyfield, New South Wales, Lilyfield in 2000 and then Dulwich Hill, New South Wales, Dulwich Hill in 2014. It links the Inner West and Trains
 Established in 1906, Central railway station, Sydney, Central station is the largest and busiest railway station in the state and is the main hub of the city's Railways in Sydney, rail network. Sydney Trains is the suburban rail service. Its tracks form part of the New South Wales railway network. It serves 175 stations across the city and had an annual ridership of 359 million passenger journeys in 2017–18. Sydney's railway was first constructed in 1854 with progressive extension to the network to serve both freight and passengers across the city, suburbs, and beyond to rural New South Wales. The main station is the Central railway station, Sydney, Central railway station in the southern part of the CBD. In the 1850s and 1860s, the railway reached areas that are now outer suburbs of Sydney.
Sydney Metro, a driverless rapid transit system separate from the suburban commuter network, commenced operation in May 2019 and will be extended into the city and down southwest by 2024 and through the inner west to Parramatta by 2030. It currently serves 13 stations. A line to serve the greater west is planned for 2026 and will include a station for the Western Sydney Airport, second international airport.
Established in 1906, Central railway station, Sydney, Central station is the largest and busiest railway station in the state and is the main hub of the city's Railways in Sydney, rail network. Sydney Trains is the suburban rail service. Its tracks form part of the New South Wales railway network. It serves 175 stations across the city and had an annual ridership of 359 million passenger journeys in 2017–18. Sydney's railway was first constructed in 1854 with progressive extension to the network to serve both freight and passengers across the city, suburbs, and beyond to rural New South Wales. The main station is the Central railway station, Sydney, Central railway station in the southern part of the CBD. In the 1850s and 1860s, the railway reached areas that are now outer suburbs of Sydney.
Sydney Metro, a driverless rapid transit system separate from the suburban commuter network, commenced operation in May 2019 and will be extended into the city and down southwest by 2024 and through the inner west to Parramatta by 2030. It currently serves 13 stations. A line to serve the greater west is planned for 2026 and will include a station for the Western Sydney Airport, second international airport.
Ferries
At the time the Sydney Harbour Bridge opened in 1932, the city's Sydney Ferries Limited, ferry service was the largest in the world. Patronage declined from 37 million passengers in 1945 to 11 million in 1963 but has recovered somewhat in recent years. From its hub at Circular Quay ferry wharf, Circular Quay, the Sydney Ferries, ferry network extends from Manly ferry wharf, Manly to Parramatta ferry wharf, Parramatta.Airports
Sydney Airport, officially "Sydney Kingsford-Smith Airport", is located in the inner southern suburb of Mascot, New South Wales, Mascot with two of the runways going into Botany Bay. It services 46 international and 23 domestic destinations. As the busiest airport in Australia it handled 37.9 million passengers in 2013 and 530,000 tonnes of freight in 2011. It has been announced that a new facility named Western Sydney Airport will be constructed at Badgerys Creek, New South Wales, Badgerys Creek from 2016 at a cost of $2.5 billion. Bankstown Airport is Sydney's second busiest airport, and serves general aviation, charter and some scheduled cargo flights. Bankstown is also the fourth busiest airport in Australia by the number of aircraft movements. Port Botany (seaport), Port Botany has surpassed Port Jackson as the city's major shipping port. Cruise ship terminals are located at Overseas Passenger Terminal, Sydney Cove and White Bay Cruise Terminal, White Bay.Environmental issues and pollution reduction
 As climate change, greenhouse gas emissions and pollution have become a major issue for Australia, Sydney has in the past been criticised for its lack of focus on reducing pollution, cutting back on emissions and maintaining water quality. Since 1995, there have been significant developments in the analysis of air pollution in the Sydney metropolitan region. The development led to the release of the Metropolitan Air Quality Scheme (MAQS), which led to a broader understanding of the causation of pollution in Sydney, allowing the government to form appropriate responses to the pollution. The 2019–20 Australian bushfire season significantly impacted outer Sydney, and consequently dramatically reduced the air quality of the Sydney metropolitan area leading to a smoky haze that lingered for many days throughout December. The air quality was 11 times the hazardous level in some days, even making it worse than New Delhi's, where it was also compared to "smoking 32 cigarettes" by Associate Professor Brian Oliver, a respiratory diseases scientist at the University of Technology Sydney.
Australian cities are some of the most car dependency, car-dependent cities in the world, especially by world city standards, although Sydney's is the lowest of Australia's major cities at 66%.Charting Transport
As climate change, greenhouse gas emissions and pollution have become a major issue for Australia, Sydney has in the past been criticised for its lack of focus on reducing pollution, cutting back on emissions and maintaining water quality. Since 1995, there have been significant developments in the analysis of air pollution in the Sydney metropolitan region. The development led to the release of the Metropolitan Air Quality Scheme (MAQS), which led to a broader understanding of the causation of pollution in Sydney, allowing the government to form appropriate responses to the pollution. The 2019–20 Australian bushfire season significantly impacted outer Sydney, and consequently dramatically reduced the air quality of the Sydney metropolitan area leading to a smoky haze that lingered for many days throughout December. The air quality was 11 times the hazardous level in some days, even making it worse than New Delhi's, where it was also compared to "smoking 32 cigarettes" by Associate Professor Brian Oliver, a respiratory diseases scientist at the University of Technology Sydney.
Australian cities are some of the most car dependency, car-dependent cities in the world, especially by world city standards, although Sydney's is the lowest of Australia's major cities at 66%.Charting Transportretrieved 27 October 2017 Furthermore, the city also has the Modal share, highest usage of public transport in an Australian city, at 27%–making it comparable with New York City, Shanghai and Berlin. Despite its high ranking for an Australian city, Sydney has a low level of mass-transit services, with a historically low-density layout and significant urban sprawl, thus increasing the likelihood of car dependency. Strategies have been implemented to reduce private car pollution, vehicle pollution by encouraging mass transit, mass and public transport, public transit, initiating the development of high density housing and introducing a fleet of 10 new Nissan LEAF electric cars, the largest order of the pollution-free vehicle in Australia. Electric cars do not produce carbon monoxide and nitrous oxide, gases which contribute to climate change. Cycling, Cycling trips have increased by 113% across Sydney's inner-city since March 2010, with about 2,000 bikes passing through top peak-hour intersections on an average weekday. Transport developments in the Sydney Metro Northwest, north-west and east of the city have been designed to encourage the use of Sydney's expanding public transportation system. The City of Sydney became the first council in Australia to achieve formal certification as carbon-neutral in 2008. The city has reduced its 2007 carbon emissions by 6% and since 2006 has reduced carbon emissions from city buildings by up to 20%. The City of Sydney introduced a ''Sustainable Sydney 2030'' program, with various targets planned and a comprehensive guide on how to reduce energy in homes and offices within Sydney by 30%. Reductions in energy consumption have slashed energy bills by $30 million a year. Solar panels have been established on many CBD buildings in an effort to minimise carbon pollution by around 3,000 tonnes a year. The city also has an "urban forest growth strategy", in which it aims to regular increase the shade tree, tree coverage in the city by frequently planting trees with strong leaf density and vegetation to provide cleaner air and create moisture during hot weather, thus lowering city temperatures. Sydney has also become a leader in the development of green building, green office buildings and enforcing the requirement of all building proposals to be energy-efficient. The Central Park, Sydney, One Central Park development, completed in 2013, is an example of this implementation and design.
Utilities
 Obtaining sufficient fresh water was difficult during early colonial times. A catchment called the Tank Stream sourced water from what is now the CBD but was little more than an open sewer by the end of the 1700s. The Botany Swamps Scheme was one of several ventures during the mid-1800s that saw the construction of wells, tunnels, steam pumping stations, and small dams to service Sydney's growing population.
The first genuine solution to Sydney's water demands was the Upper Nepean Scheme which came into operation in 1886 and cost over £2 million. It transports water from the Nepean River, Nepean, Cataract River (Wollondilly), Cataract, and Cordeaux River, Cordeaux rivers and continues to service about 15% of Sydney's total water needs. Dams were built on these three rivers between 1907 and 1935. In 1977 the Shoalhaven Scheme brought several more dams into service.
The state-owned corporation WaterNSW now manages eleven major dams: Warragamba Dam, Warragamba one of the largest domestic water supply dams in the world, Woronora Dam, Woronora, Cataract Dam, Cataract, Upper Nepean Scheme, Cordeaux, Upper Nepean Scheme, Nepean, Upper Nepean Scheme, Avon, Shoalhaven Scheme, Wingecarribee Reservoir, Shoalhaven Scheme, Fitzroy Falls Reservoir, Shoalhaven Scheme, Tallowa, the Blue Mountains Dams, and Prospect Reservoir. Water is collected from five catchment areas covering and total storage amounts to . The Sydney Desalination Plant came into operation in 2010. WaterNSW supplies bulk water to Sydney Water, a state-owned corporation that operates water distribution, sewerage and storm water management services across greater Sydney.
The two distributors which maintain Sydney's electricity infrastructure are Ausgrid and Endeavour Energy. Their combined networks include over 815,000 power poles and of electricity cables.
Obtaining sufficient fresh water was difficult during early colonial times. A catchment called the Tank Stream sourced water from what is now the CBD but was little more than an open sewer by the end of the 1700s. The Botany Swamps Scheme was one of several ventures during the mid-1800s that saw the construction of wells, tunnels, steam pumping stations, and small dams to service Sydney's growing population.
The first genuine solution to Sydney's water demands was the Upper Nepean Scheme which came into operation in 1886 and cost over £2 million. It transports water from the Nepean River, Nepean, Cataract River (Wollondilly), Cataract, and Cordeaux River, Cordeaux rivers and continues to service about 15% of Sydney's total water needs. Dams were built on these three rivers between 1907 and 1935. In 1977 the Shoalhaven Scheme brought several more dams into service.
The state-owned corporation WaterNSW now manages eleven major dams: Warragamba Dam, Warragamba one of the largest domestic water supply dams in the world, Woronora Dam, Woronora, Cataract Dam, Cataract, Upper Nepean Scheme, Cordeaux, Upper Nepean Scheme, Nepean, Upper Nepean Scheme, Avon, Shoalhaven Scheme, Wingecarribee Reservoir, Shoalhaven Scheme, Fitzroy Falls Reservoir, Shoalhaven Scheme, Tallowa, the Blue Mountains Dams, and Prospect Reservoir. Water is collected from five catchment areas covering and total storage amounts to . The Sydney Desalination Plant came into operation in 2010. WaterNSW supplies bulk water to Sydney Water, a state-owned corporation that operates water distribution, sewerage and storm water management services across greater Sydney.
The two distributors which maintain Sydney's electricity infrastructure are Ausgrid and Endeavour Energy. Their combined networks include over 815,000 power poles and of electricity cables.
See also
* List of museums in Sydney * List of people from Sydney * List of public art in the City of Sydney * List of songs about Sydney * Outline of SydneyNotes
References
External links
Official Sydney, NSW government site
Official Sydney tourism site
Historical film clips of Sydney
on the National Film and Sound Archive of Australia'
''australianscreen online''
* – includes a low-level joyflight around Sydney showing various aspects of the city on 13 July 2020 (starts at 05:20) *
Dictionary of Sydney – the history of Sydney
()
Sydney Official History Archives
State Records New South Wales
National Archives of Australia
Understanding Society Through its Records – John Curtin Library
Directory of Archives in Australia
{{Authority control Sydney, 1788 establishments in Australia Australian capital cities Former colonial capitals Port cities in New South Wales Metropolitan areas of Australia, Sydney Populated places established in 1788