Susan E. Rice on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Susan Elizabeth Rice (born November 17, 1964) is an American diplomat, policy advisor, and public official serving as Director of the
." Stanford Alumni Association. During her time at Oxford, Rice was a member of the Oxford University Women's Basketball Team.
 Rice was managing director and principal at
Rice was managing director and principal at
United States Domestic Policy Council
The Domestic Policy Council (DPC) is the principal forum used by the president of the United States for the consideration of domestic policy matters and senior policymaking, Cabinet, and White House officials. The Council is part of the Office o ...
since 2021. A member of the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
, Rice served as the 27th U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations
The United States ambassador to the United Nations is the leader of the U.S. delegation, the U.S. Mission to the United Nations. The position is formally known as the permanent representative of the United States of America to the United Nations ...
from 2009 to 2013 and as the 23rd U.S. National Security Advisor from 2013 to 2017.
Rice was born in Washington, D.C., and attended Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
and New College, Oxford
New College is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1379 by William of Wykeham in conjunction with Winchester College as its feeder school, New College is one of the oldest colleges at th ...
, where she was a Rhodes Scholar
The Rhodes Scholarship is an international postgraduate award for students to study at the University of Oxford, in the United Kingdom.
Established in 1902, it is the oldest graduate scholarship in the world. It is considered among the world' ...
and received a DPhil (PhD). She served on President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
's National Security Council
A national security council (NSC) is usually an executive branch governmental body responsible for coordinating policy on national security issues and advising chief executives on matters related to national security. An NSC is often headed by a na ...
staff from 1993 to 1997 and was the assistant secretary of state for African affairs
The Assistant Secretary for the Bureau of African Affairs is the head of the Bureau of African Affairs, within the United States Department of State, who guides operation of the U.S. diplomatic establishment in the countries of sub-Saharan Afric ...
at the State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
from 1997 to 2001. Appointed at age 32, Rice was at the time the youngest person to have served as a regional assistant secretary of state Assistant Secretary of State (A/S) is a title used for many executive positions in the United States Department of State, ranking below the Under Secretary of State, under secretaries. A set of six assistant secretaries reporting to the Under Secret ...
. Rice's tenure saw significant changes in U.S.–Africa policy, including the passage of the African Growth and Opportunity Act
The African Growth and Opportunity Act, or AGOA (Title I, Trade and Development Act of 2000; P.L. 106–200) is a piece of legislation that was approved by the U.S. Congress in May 2000. The stated purpose of this legislation is to assist the ...
, support for democratic transitions in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
and Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, and an increased U.S. focus on fighting HIV/AIDS.
A former Brookings Institution
The Brookings Institution, often stylized as simply Brookings, is an American research group founded in 1916. Located on Think Tank Row in Washington, D.C., the organization conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in ec ...
fellow, Rice served as a foreign policy advisor to Democratic presidential nominees Michael Dukakis
Michael Stanley Dukakis (; born November 3, 1933) is an American retired lawyer and politician who served as governor of Massachusetts from 1975 to 1979 and again from 1983 to 1991. He is the longest-serving governor in Massachusetts history a ...
, John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
, and Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
. After Obama won the 2008 presidential election, Rice was nominated as Ambassador to the United Nations. The Senate confirmed her by unanimous consent on January 22, 2009. During her tenure at the United Nations, Rice championed a human rights and anti-poverty agenda, elevated climate change and LGBT
' is an initialism that stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender. In use since the 1990s, the initialism, as well as some of its common variants, functions as an umbrella term for sexuality and gender identity.
The LGBT term is a ...
and women's rights as global priorities, and committed the U.S. to agreements such as the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is an international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation ...
, Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities. Parties to the convention are required to promote, ...
, and the U.N. Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millenniu ...
. She also defended Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
at the Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and ...
, pushed for tough sanctions against Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
, and advocated for U.S. and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
intervention in Libya in 2011.
Mentioned as a possible replacement for retiring United States secretary of state
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
in 2012, Rice withdrew from consideration following controversy related to the 2012 attack on a U.S. diplomatic facility in Benghazi
Benghazi () , ; it, Bengasi; tr, Bingazi; ber, Bernîk, script=Latn; also: ''Bengasi'', ''Benghasi'', ''Banghāzī'', ''Binghāzī'', ''Bengazi''; grc, Βερενίκη (''Berenice'') and ''Hesperides''., group=note (''lit. Son of he Ghazi ...
. President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
instead named her National Security Advisor in 2013, where she supported U.S. efforts on the Iran nuclear deal of 2015, the Ebola epidemic
This list of Ebola outbreaks records the known occurrences of Ebola virus disease, a highly infectious and acutely lethal viral disease that has afflicted humans and animals primarily in equatorial Africa. The pathogens responsible for the d ...
, the reopening to Cuba, and the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
on climate change. In 2021, Rice became the director of the Domestic Policy Council
The Domestic Policy Council (DPC) is the principal forum used by the president of the United States for the consideration of domestic policy matters and senior policymaking, Cabinet of the United States, Cabinet, and White House officials. The Co ...
in the Biden administration
Joe Biden's tenure as the 46th president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 2021. Biden, a Democrat from Delaware who previously served as vice president under Barack Obama, took office following his victory ...
.
Early life
Rice was born in Washington D.C., toeducation policy
Education policy consists of the principles and policy decisions that influence the field of education, as well as the collection of laws and rules that govern the operation of education systems. Education governance may be shared between the local ...
scholar Lois Rice
Lois Ann Dickson Fitt Rice (February 28, 1933 – January 4, 2017) was an American corporate executive, scholar, and education policy expert. Known as the ‘‘mother of the Pell Grant” because of her work lobbying for its creation, she was na ...
(née Dickson), who helped design the federal Pell Grant
A Pell Grant is a subsidy the U.S. federal government provides for students who need it to pay for college. Federal Pell Grants are limited to students with financial need, who have not earned their first bachelor's degree, or who are enrolled ...
subsidy system and who joined the Brookings Institution
The Brookings Institution, often stylized as simply Brookings, is an American research group founded in 1916. Located on Think Tank Row in Washington, D.C., the organization conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in ec ...
in 1992; and Emmett J. Rice
Emmett John Rice (December 21, 1919 – March 10, 2011) was an American economist, academic, bank executive, and member of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors. He served with the Tuskegee Airmen during World War II, taught at Cornell University ...
(1919–2011), a Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach an ...
economics professor and the second black governor of the Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
. Her maternal grandparents were Jamaican immigrants to Portland, Maine
Portland is the largest city in the U.S. state of Maine and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area is home to over half a million people, the 104th-largest metropol ...
; her paternal grandparents were the descendants of enslaved Africans and from South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. Her parents divorced when Rice was ten years of age. In 1978, her mother married Alfred Bradley Fitt, an attorney, who at the time was general counsel of the U. S. Congressional Budget Office.
Rice said that her parents taught her to "never use race as an excuse or advantage," and as a young girl she "dreamed of becoming the first U.S. senator from the District of Columbia".
Rice was a three-letter varsity athlete, student government
A students' union, also known by many other names, is a student organization present in many colleges, universities, and high schools. In higher education, the students' union is often accorded its own building on the campus, dedicated to social, ...
president, and valedictorian
Valedictorian is an academic title for the highest-performing student of a graduating class of an academic institution.
The valedictorian is commonly determined by a numerical formula, generally an academic institution's grade point average (GPA ...
at National Cathedral School
National Cathedral School (NCS) is an independent Episcopal private day school for girls in grades 4–12 located on the grounds of the Washington National Cathedral in Washington, D.C., United States. Founded by philanthropist and suffragist Phoe ...
in Washington, D.C., a private girls' day school
A day school — as opposed to a boarding school — is an educational institution where children and adolescents are given instructions during the day, after which the students return to their homes. A day school has full-day programs when compar ...
. She attended Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
, where she won a Truman Scholarship
The Harry S. Truman Scholarship is the premier graduate fellowship in the United States for public service leadership. It is a federally funded scholarship granted to U.S. undergraduate students for demonstrated leadership potential, academic ...
and graduated with a BA with honors in history in 1986. She was also awarded a National Merit Scholarship
The National Merit Scholarship Program is a United States academic scholarship competition for recognition and university scholarships administered by the National Merit Scholarship Corporation (NMSC), a privately funded, not-for-profit organizati ...
and elected Phi Beta Kappa
The Phi Beta Kappa Society () is the oldest academic honor society in the United States, and the most prestigious, due in part to its long history and academic selectivity. Phi Beta Kappa aims to promote and advocate excellence in the liberal a ...
her junior year.
Rice attended New College, Oxford
New College is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1379 by William of Wykeham in conjunction with Winchester College as its feeder school, New College is one of the oldest colleges at th ...
on a Rhodes Scholarship
The Rhodes Scholarship is an international postgraduate award for students to study at the University of Oxford, in the United Kingdom.
Established in 1902, it is the oldest graduate scholarship in the world. It is considered among the world' ...
, where she earned Master of Philosophy
The Master of Philosophy (MPhil; Latin ' or ') is a postgraduate degree. In the United States, an MPhil typically includes a taught portion and a significant research portion, during which a thesis project is conducted under supervision. An MPhil m ...
(1988) and Doctor of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: or ') is the most common Academic degree, degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields ...
(1990) degrees, both in International Relations. Her doctoral dissertation was entitled ''Commonwealth Initiative in Zimbabwe, 1979–1980: Implications for International Peacekeeping''. Chatham House, the Royal Institute of International Affairs, honored her dissertation as the UK's most distinguished in international relations
International relations (IR), sometimes referred to as international studies and international affairs, is the scientific study of interactions between sovereign states. In a broader sense, it concerns all activities between states—such as ...
.Black Community Services Center Hall of Fame." Stanford Alumni Association. During her time at Oxford, Rice was a member of the Oxford University Women's Basketball Team.
Early career
Rice served as a foreign policy aide toMichael Dukakis
Michael Stanley Dukakis (; born November 3, 1933) is an American retired lawyer and politician who served as governor of Massachusetts from 1975 to 1979 and again from 1983 to 1991. He is the longest-serving governor in Massachusetts history a ...
during his campaign in the 1988 presidential election. She was a management consultant at McKinsey & Company
McKinsey & Company is a global management consulting firm founded in 1926 by University of Chicago professor James O. McKinsey, that offers professional services to corporations, governments, and other organizations. McKinsey is the oldest and ...
, a global management consulting
Management consulting is the practice of providing consulting services to organizations to improve their performance or in any way to assist in achieving organizational objectives. Organizations may draw upon the services of management consultant ...
firm, from 1990 to early 1992. Rice worked in McKinsey's Toronto office.
Clinton administration (1993–2001)
Rice served in theClinton administration
Bill Clinton's tenure as the 42nd president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1993, and ended on January 20, 2001. Clinton, a Democrat from Arkansas, took office following a decisive election victory over Re ...
in various capacities: at the National Security Council
A national security council (NSC) is usually an executive branch governmental body responsible for coordinating policy on national security issues and advising chief executives on matters related to national security. An NSC is often headed by a na ...
(NSC) from 1993 to 1997 (as director for international organizations and peacekeeping from 1993 to 1995, and as special assistant to the president and senior director for African affairs from 1995 to 1997); and as Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs from 1997 to 2001. Rice's tenure saw significant changes in U.S.-Africa policy, including the passage of the African Growth and Opportunity Act
The African Growth and Opportunity Act, or AGOA (Title I, Trade and Development Act of 2000; P.L. 106–200) is a piece of legislation that was approved by the U.S. Congress in May 2000. The stated purpose of this legislation is to assist the ...
, support for democratic transitions in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
and Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, and an increased U.S. focus on fighting the HIV/AIDS pandemic.
National Security Council
At the time of the 1994Rwandan genocide
The Rwandan genocide occurred between 7 April and 15 July 1994 during the Rwandan Civil War. During this period of around 100 days, members of the Tutsi minority ethnic group, as well as some moderate Hutu and Twa, were killed by armed Hutu ...
, Rice reportedly said, "If we use the word 'genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
' and are seen as doing nothing, what will be the effect on the November election?" She denied the quote but acknowledged the mistakes made at the time and felt that a debt needed repaying. The inability or failure of the Clinton administration to do anything about the genocide would form her later views on possible military interventions. She said of the experience: "I swore to myself that if I ever faced such a crisis again, I would come down on the side of dramatic action, going down in flames if that was required." Later in 2012, during an interview with ''The New Republic
''The New Republic'' is an American magazine of commentary on politics, contemporary culture, and the arts. Founded in 1914 by several leaders of the progressive movement, it attempted to find a balance between "a liberalism centered in hum ...
'', Rice stated "To suggest that I’m repenting for wanda
Wanda is a female given name of Polish origin. It probably derives from the tribal name of the Wends.Campbell, Mike"Meaning, Origin, and History of the Name Wanda."''Behind the Name.'' Accessed on August 12, 2010. The name has long been popular in ...
or that I’m haunted by that or that I don't sleep at night because of that or that every policy I've implemented subsequently is driven by that is garbage."
Timothy M. Carney
Timothy Michael Carney (born July 12, 1944) is a retired American diplomat and consultant. Carney served as a career Foreign Service Officer for 32 years, with assignments that included Vietnam and Cambodia as well as Lesotho and South Africa b ...
, former U.S. ambassador to Sudan, co-authored an op-ed
An op-ed, short for "opposite the editorial page", is a written prose piece, typically published by a North-American newspaper or magazine, which expresses the opinion of an author usually not affiliated with the publication's editorial board. O ...
in 2002 claiming that in 1997 Sudan offered to turn over its intelligence on bin Laden but that Rice, together with then NSC terrorism specialist Richard A. Clarke, successfully lobbied for continuing to bar U.S. officials from engaging with the Khartoum government. Similar allegations were made by '' Vanity Fair'' contributing editor David Rose and Richard Miniter
Richard Miniter (born 1967) is an investigative journalist and author whose articles have appeared in Politico', ''The New York Times'', ''The Washington Times'', ''The Washington Post'', ''The Wall Street Journal'', ''The Atlantic Monthly'', ''N ...
, author of ''Losing Bin Laden''. The allegations against Rice were determined to be unfounded by the Joint Congressional Inquiry into 9/11 and the 9/11 Commission
The National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States, also known as the 9/11 Commission, was set up on November 27, 2002, "to prepare a full and complete account of the circumstances surrounding the September 11 attacks", includin ...
, which found no evidence that Sudan ever made an offer to share intelligence on bin Laden.
Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs
Secretary of StateMadeleine Albright
Madeleine Jana Korbel Albright (born Marie Jana Korbelová; May 15, 1937 – March 23, 2022) was an American diplomat and political scientist who served as the 64th United States secretary of state from 1997 to 2001. A member of the Democratic ...
, a longtime mentor and family friend to Rice, urged Clinton to appoint Rice as Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs
The Assistant Secretary for the Bureau of African Affairs is the head of the Bureau of African Affairs, within the United States Department of State, who guides operation of the U.S. diplomatic establishment in the countries of sub-Saharan Afric ...
in 1997. At a confirmation
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. For adults, it is an affirmation of belief. It involves laying on ...
hearing chaired by Senator John Ashcroft
John David Ashcroft (born May 9, 1942) is an American lawyer, lobbyist and former politician who served as the 79th U.S. Attorney General in the George W. Bush administration from 2001 to 2005. A former U.S. Senator from Missouri and the 50th ...
, Rice, who attended the hearing along with her infant son whom she was then nursing
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
, made a great impression on senators from both parties and "sailed through the confirmation process."
In the context of the Rwandan, Ugandan, AFDL
The Alliance of Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Congo-Zaire (ADFLC; french: Alliance des Forces Démocratiques pour la Libération du Congo-Zaïre; AFDL) was a coalition of Rwandan, Ugandan, Burundian, and Congolese dissidents, disgrun ...
and Angolan invasion of Zaire (later known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo) in 1996 and overthrow of dictator Mobutu Sese Seko
Mobutu Sese Seko Kuku Ngbendu Wa Za Banga (; born Joseph-Désiré Mobutu; 14 October 1930 – 7 September 1997) was a Congolese politician and military officer who was the president of Zaire from 1965 to 1997 (known as the Democratic Republic o ...
, Rice is alleged to have said that "Anything's better than Mobutu." According to Gérard Prunier
Gérard Prunier (born 1942, in Paris
) is a French academic, historian, and consultant. He specializes in African history and affairs
—particularly the Horn of Africa and the African Great Lakes regions.
Biography
Prunier received a PhD in Afr ...
, a staffer to the Assistant Secretary said that "the only thing we have to do is look the other way," with respect to regional intervention in the conflict. ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' correspondent Howard W. French said that according to his sources, Rice herself made the remark.
On July 7, 1998, Rice was a member of an American delegation to visit detained Nigerian president-elect Basorun Moshood Kashimawo Olawale Abiola
Moshood Kashimawo Olawale Abiola , also known as M. K. O. Abiola (24 August 1937 – 7 July 1998) was a Nigerian businessman, publisher, and politician. He was the Aare Ona Kankafo XIV of Yorubaland and an aristocrat of the Egba clan.
M.K.O ...
. During this meeting, Abiola suffered a fatal heart attack.
Rice supported U.S. efforts to reach both the Lusaka Ceasefire Agreement
The Lusaka Ceasefire Agreement attempted to end the Second Congo War through a ceasefire, release of prisoners of war, and the deployment of an international peacekeeping force under the auspices of the United Nations. The heads of state of Angola ...
in the Congo and the Lomé Peace Accord
Lomé is the capital and largest city of Togo. It has an urban population of 837,437
in Sierra Leone. Some observers criticized the Sierra Leone agreement as too indulgent of the Revolutionary United Front
The Revolutionary United Front (RUF) was a rebel group that fought a failed eleven-year war in Sierra Leone, beginning in 1991 and ending in 2002. It later transformed into a political party, which still exists today. The three most senior surv ...
(RUF) and for bringing the war criminal Foday Sankoh
Foday Saybana Sankoh (17 October 1937 – 29 July 2003) was the founder of the Sierra Leone rebel group Revolutionary United Front (RUF), which was supported by Charles Taylor-led NPFL in the 11-year-long Sierra Leone Civil War, starting i ...
into government, leading to the adoption of United Nations Security Council Resolution 1313
United Nations Security Council resolution 1313, adopted unanimously on 4 August 2000, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Sierra Leone, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone (UNA ...
, which blamed the RUF for the continuing conflict in the west African country. Rice played a major role in peace negotiations between Ethiopia and Eritrea during the Eritrean–Ethiopian War
The Eritrean–Ethiopian War, also known as the Badme War, was a major armed conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea that took place from May 1998 to June 2000. The war has its origins in a territorial dispute between the two states. After Eritr ...
, leading to the Algiers Agreement in 2000 ending the conflict. For her efforts she was named a co-recipient of the White House's Samuel Nelson Drew Memorial Award for "distinguished contributions to the formation of peaceful, cooperative relationships between nations," alongside Gayle Smith and Anthony Lake
William Anthony Kirsopp Lake (born April 2, 1939) is an American diplomat and political advisor who served as the 17th United States National Security Advisor from 1993 to 1997 and as the 6th Executive Director of UNICEF from 2010 to 2017.
He ha ...
.
Rice had a contentious relationship with State Department veteran Richard Holbrooke
Richard Charles Albert Holbrooke (April 24, 1941 – December 13, 2010) was an American diplomat and author. He was the only person to have held the position of Assistant Secretary of State for two different regions of the world (Asia from 1977 ...
, whom she considered to be meddling on her turf and who in return felt she was rising too quickly in U.S. diplomatic ranks.
Business and think tank activities (2001–2008)
 Rice was managing director and principal at
Rice was managing director and principal at Intellibridge
Eurasia Group is a political risk consultancy founded in 1998 by Ian Bremmer.
History
Eurasia Group reports on emerging markets including frontier and developed economies, in addition to establishing practices focused on geo-technology and energ ...
from 2001 to 2002. From 2002 to 2009, she was a senior fellow
A fellow is a concept whose exact meaning depends on context.
In learned or professional societies, it refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements.
Within the context of higher education ...
at the Brookings Institution
The Brookings Institution, often stylized as simply Brookings, is an American research group founded in 1916. Located on Think Tank Row in Washington, D.C., the organization conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in ec ...
, where "she focused on U.S. foreign policy, weak and failing states, the implications of global poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little , and transnational threats to
 On December 1, 2008, President-elect Obama announced that he would nominate Rice to be the
On December 1, 2008, President-elect Obama announced that he would nominate Rice to be the  At her confirmation hearing, Rice was introduced by Senator
At her confirmation hearing, Rice was introduced by Senator
 In releasing the 2015 National Security Strategy, Rice said that the United States was pursuing an "ambitious yet achievable agenda" overseas. She argued that U.S. leadership had been essential for success on issues including
In releasing the 2015 National Security Strategy, Rice said that the United States was pursuing an "ambitious yet achievable agenda" overseas. She argued that U.S. leadership had been essential for success on issues including

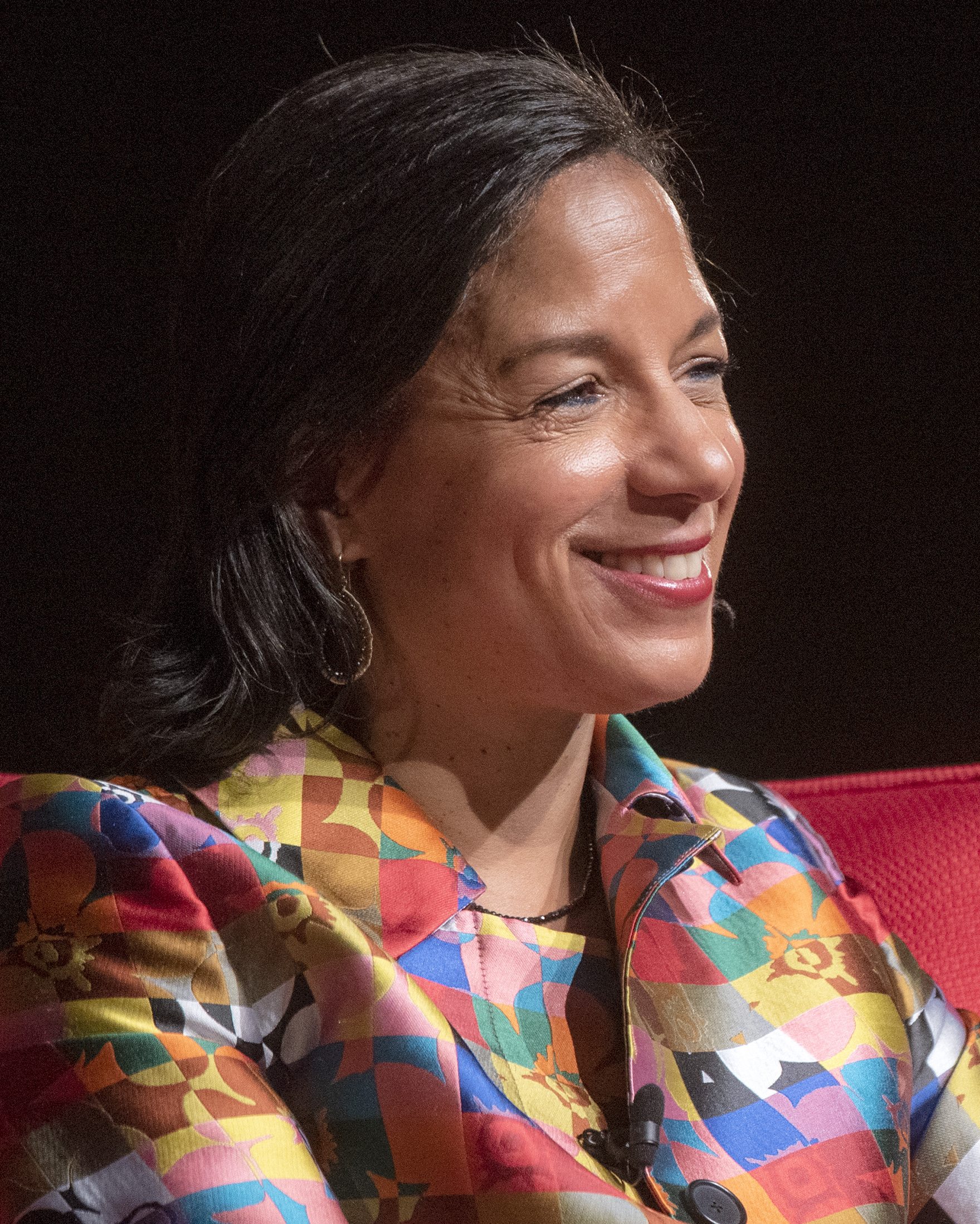
 In July 2020, it was widely reported that Rice was under consideration to be Joe Biden's vice presidential running mate in the 2020 general election. However,
In July 2020, it was widely reported that Rice was under consideration to be Joe Biden's vice presidential running mate in the 2020 general election. However,
security
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercive change) caused by others, by restraining the freedom of others to act. Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be of persons and social ...
."
Michael E. O'Hanlon
Michael Edward O'Hanlon (born May 16, 1961) is a senior fellow at The Brookings Institution, specializing in defense and foreign policy issues. He began his career as a budget analyst in the defense field.
Biography
Education and early career
O ...
and Ivo Daalder
Ivo H. Daalder (born March 2, 1960 in The Hague, Netherlands),"Ivo H. Daalder." Marquis Who's Who TM. ''Marquis Who's Who'', 2007. Reproduced in Biography Resource Center. Farmington Hills, Mich.: Gale, 2008. http://galenet.galegroup.com/servlet/B ...
, two Brookings colleagues of Rice at the time, said that Rice consistently opposed the 2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one month, including 26 ...
in the run-up to the war. In 2012, columnist Peter Beinart
Peter Alexander Beinart (; born February 28, 1971) is an American liberal columnist, journalist, and political commentator. A former editor of ''The New Republic'', he has also written for ''Time'', ''The New York Times'', and ''The New York Revie ...
reviewed a series of NPR interviews with Rice in late 2002 and early 2003 and concluded that Rice's position on war was equivocal. For example, in a December 2002 NPR
National Public Radio (NPR, stylized in all lowercase) is an American privately and state funded nonprofit media organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It differs from other ...
interview, Rice said, "It's clear that Iraq poses a major threat. It's clear that its weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to numerous individuals or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natura ...
need to be dealt with forcefully, and that's the path we're on. I think the question becomes whether we can keep the diplomatic balls in the air and not drop any, even as we move forward, as we must, on the military side.... The George W. Bush administration
Administration may refer to:
Management of organizations
* Management, the act of directing people towards accomplishing a goal
** Administrative assistant, Administrative Assistant, traditionally known as a Secretary, or also known as an admini ...
frankly owes the American public a much fuller and more honest assessment of what the costs will be of the actual conflict, as well as the aftermath, the post-conflict reconstruction. And the costs are going to be huge." In her memoir, Rice wrote, "Long experienced with the menace of Al Qaeda, I was one of the very few scholars at Brookings to openly oppose the Iraq War. From the start, I viewed that war of choice as a dangerous diversion from the main objective of defeating Al Qaeda globally and in Afghanistan." Shortly after the war began, Rice warned that the U.S. commitment to rebuilding Iraq would likely last for many years..
During the 2004 presidential campaign, Rice served as a foreign policy adviser to John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
.
Rice went on leave from the Brookings Institution to serve as a senior foreign policy adviser to Barack Obama in his 2008 presidential campaign. She was one of the first high-profile foreign policy staffers to sign onto Obama's campaign, as most of her peers had supported Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
during the presidential primaries. Rice criticized Obama's Republican opponent in the campaign, John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
, calling his policies "reckless" and dismissing the Arizona senator's trip to Iraq as "strolling around the market in a flak jacket."
On November 5, 2008, Rice was named to the advisory board of the Obama–Biden transition.
United States ambassador to the United Nations (2009–2013)
 On December 1, 2008, President-elect Obama announced that he would nominate Rice to be the
On December 1, 2008, President-elect Obama announced that he would nominate Rice to be the United States ambassador to the United Nations
The United States ambassador to the United Nations is the leader of the U.S. delegation, the U.S. Mission to the United Nations. The position is formally known as the permanent representative of the United States of America to the United Nations ...
, a position which he restored to cabinet level. Reportedly, Rice had wanted the post of national security advisor, which instead went to retired United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
general
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
James L. Jones
James Logan Jones Jr. (born December 19, 1943) is a retired United States Marine Corps four-star general and consultant who served as the 21st United States National Security Advisor from 2009 to 2010. During his military career, he served as th ...
.
 At her confirmation hearing, Rice was introduced by Senator
At her confirmation hearing, Rice was introduced by Senator Susan Collins
Susan Margaret Collins (born December 7, 1952) is an American politician serving as the senior United States senator from Maine. A member of the Republican Party, she has held her seat since 1997 and is Maine's longest-serving member of Co ...
who said "I can think of ... no better messenger than Dr. Susan Rice. I am honored to present her to this distinguished committee, and I enthusiastically endorse her nomination." Rice was confirmed by the Senate by voice vote
In parliamentary procedure, a voice vote (from the Latin ''viva voce'', meaning "live voice") or acclamation is a voting method in deliberative assemblies (such as legislatures) in which a group vote is taken on a topic or motion by responding vo ...
on January 22, 2009. Rice became the second-youngest person and the first black woman to represent the U.S. at the UN.
During her tenure at the United Nations, Rice championed a human rights and anti-poverty agenda, elevated climate change and women's rights as global priorities, and committed the U.S. to agreements such as the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is an international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation ...
, Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities. Parties to the convention are required to promote, ...
, and the U.N. Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millenniu ...
. Rice led the fight to advance LGBT rights at the U.N. Human Rights Council
The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), CDH is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis. ...
and was recognized for her staunch defense of Israel at the Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and ...
. Rice won praise for leading the Security Council to impose the toughest sanctions to date on Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
over their nuclear programs, and for reaffirming U.S. commitment to the UN and multilateralism.
Three Security Council diplomats took issue with Rice's negotiating style, calling it "rude" and overly blunt, while others attributed those criticisms to sexism. According to David Rothkopf
David J. Rothkopf (born December 24, 1955) is a foreign policy, national security and political affairs analyst and commentator. He is the founder and CEO of TRG Media and The Rothkopf Group, a columnist for the Daily Beast and a member of the U ...
of ''Foreign Policy
A State (polity), state's foreign policy or external policy (as opposed to internal or domestic policy) is its objectives and activities in relation to its interactions with other states, unions, and other political entities, whether bilaterall ...
'', Rice could be challenging to work with due to her "toughness"—in the mold of James Baker
James Addison Baker III (born April 28, 1930) is an American attorney, diplomat and statesman. A member of the Republican Party, he served as the 10th White House Chief of Staff and 67th United States Secretary of the Treasury under President ...
or Henry Kissinger
Henry Alfred Kissinger (; ; born Heinz Alfred Kissinger, May 27, 1923) is a German-born American politician, diplomat, and geopolitical consultant who served as United States Secretary of State and National Security Advisor under the presid ...
—but had the asset of a close relationship with the U.S. president and proved to be an effective policymaker. Some human rights activists took issue with Rice and U.S. foreign policy generally in 2012 for working against UN statements that criticized Rwanda for supporting a rebel group in Congo known for committing atrocities.
Libyan Civil War
As the2011 Libyan Civil War
The First Libyan Civil War was an armed conflict in 2011 in the North African country of Libya that was fought between forces loyal to Colonel Muammar Gaddafi and rebel groups that were seeking to oust his government. It erupted with the Liby ...
progressed, the United States and its allies offered a choice for Colonel Muammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi, . Due to the lack of standardization of transcribing written and regionally pronounced Arabic, Gaddafi's name has been romanized in various ways. A 1986 column by ''The Straight Dope'' lists 32 spellin ...
and his aides: step down from power or face an international response. Rice offered some of the toughest rhetoric toward Gaddafi, criticizing his denials of atrocities against his own citizens as "frankly, delusional." In a closed-door Security Council meeting in April 2011, Rice reportedly stated that Gaddafi loyalists engaged in atrocities, including terrorizing the population with sexual violence, and that Gaddafi's troops has been issued Viagra. Investigations by Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch and Doctors Without Borders contradicted Rice and stated they did not find first-hand evidence that mass rapes had occurred as Rice had claimed. Together with National Security Council figure Samantha Power
Samantha Jane Power (born September 21, 1970) is an American journalist, diplomat and government official who is currently serving as the Administrator of the United States Agency for International Development. She previously served as the 28th ...
, who already supported the U.S.-led military intervention in Libya, and Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who came to support it, the three overcame internal opposition from Defense Secretary Robert Gates
Robert Michael Gates (born September 25, 1943) is an American intelligence analyst and university president who served as the 22nd United States secretary of defense from 2006 to 2011. He was originally appointed by president George W. Bush an ...
, security adviser Thomas E. Donilon
Thomas Edward Donilon (born May 14, 1955) is an American lawyer, business executive, and former government official who served as the 22nd National Security Advisor in the Obama administration from 2010 to 2013.
, and counterterrorism adviser John Brennan John Brennan may refer to:
Public officials
* Jack Brennan (born 1937), U.S. Marine officer and aide of Richard Nixon
* John Brennan (CIA officer) (born 1955), former CIA Director
* John P. Brennan (1864–1943), Democratic politician in the U. ...
, to have the administration advance a UN proposal to impose a no-fly zone over Libya and authorize other military actions as necessary.
On March 17, 2011, the UK, France and Lebanon joined the U.S. to vote for United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973
Resolution 1973 was adopted by the United Nations Security Council on 17 March 2011 in response to the First Libyan Civil War. The resolution formed the legal basis for military intervention in the Libyan Civil War, demanding "an immediate cease ...
while Brazil, Germany, and India joined permanent Security Council members China and Russia in abstaining. Rice and Clinton played major roles in gaining approval for the resolution. Rice said, "we are interested in a broad range of actions that will effectively protect civilians and increase the pressure on the Gaddafi regime to halt the killing and to allow the Libyan people to express themselves in their aspirations for the future freely and peacefully."
Syrian Civil War
In January 2012, after the Russian and Chinese veto of a Security Council resolution calling on Syrian presidentBashar al-Assad
Bashar Hafez al-Assad, ', Levantine pronunciation: ; (, born 11 September 1965) is a Syrian politician who is the 19th president of Syria, since 17 July 2000. In addition, he is the commander-in-chief of the Syrian Armed Forces and the ...
to step down, Rice strongly condemned both countries, saying, "They put a stake in the heart of efforts to resolve this conflict peacefully," and adding that "we the United States are standing with the people of Syria. Russia and China are obviously with Assad." In her words, "the United States is disgusted that a couple of members of this Council continue to prevent us from fulfilling our sole purpose."
2012 Benghazi attack
On September 11, 2012, a U.S. diplomatic facility and CIA annex in Benghazi, Libya, was attacked, resulting in the deaths of theUnited States ambassador to Libya
The United States ambassador to Libya is the official representative of the president of the United States to the head of state of Libya.
History
Until its independence in 1951, Libya had been a colony of Italy (1912–1947) and then under Brit ...
J. Christopher Stevens
John Christopher Stevens (April 18, 1960 – September 11, 2012) was an American career diplomat and lawyer who served as the U.S. Ambassador to Libya from May 22, 2012, to September 11, 2012. Stevens was killed when the U.S. Special Missio ...
, U.S. Foreign Service information management officer Sean Smith, and two former Navy SEALS, Glen Doherty
Four Americans died in the 2012 Benghazi attack: Ambassador Chris Stevens, Information Officer Sean Smith, and two CIA operatives, Glen Doherty and Tyrone Woods, both former Navy SEALs. Stevens is the first U.S. ambassador killed in an attack s ...
and Tyrone S. Woods
Four Americans died in the 2012 Benghazi attack: Ambassador Chris Stevens, Information Officer Sean Smith, and two CIA operatives, Glen Doherty and Tyrone Woods, both former Navy SEALs. Stevens is the first U.S. ambassador killed in an attack s ...
. On September 16, Rice appeared on five major interview shows to discuss the attacks. Prior to her appearance, Rice was provided with "talking points" from a CIA memo.
Each of the 11 drafts of CIA talking points maintained that the attack was "spontaneously inspired" by a violent protest at the American embassy in Cairo, Egypt
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
, hours earlier, which had been triggered by the release of an anti-Muslim video. Protestors breached and entered the embassy compound. During the hours before the Benghazi attack, Egyptian satellite television networks popular in Benghazi had been covering the outrage over the video.
Since Rice's five television appearances, there have been persistent accusations that she had intentionally misled the public. However, none of the ten Benghazi investigations conducted by Congress—six by Republican-controlled House committees—determined she had. The Republican-controlled House Intelligence Committee's two-year investigation found that CIA analysts had erred and it did not conclude that Rice or any other government official acted in bad faith or intentionally misled the American people.
A group of 97 House Republicans sent a letter to Obama on November 19 to say Rice's statements were "misleading" and that she should accordingly not be considered a candidate to succeed Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
in 2013 as Secretary of State. Some Republican senators, who would have had a vote on whether to confirm
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant (religion), covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. For adults, it is an wikt:affirmation, affirma ...
Rice, also voiced objections and said their meetings with Rice at the end of November 2012 did not ease their concerns. On December 13, 2012, in a letter to Obama, Rice asked him to remove her name from consideration for Secretary of State.
United States National Security Advisor (2013–2017)
Rice was picked to succeedTom Donilon
Thomas Edward Donilon (born May 14, 1955) is an American lawyer, business executive, and former government official who served as National Security Advisor (United States), the 22nd National Security Advisor in the Obama administration from 2010 ...
as National Security Advisor A national security advisor serves as the chief advisor to a national government on matters of security. The advisor is not usually a member of the government's cabinet but is usually a member of various military or security councils.
National sec ...
following Donilon's resignation on June 5, 2013. The position of National Security Advisor does not require Senate approval. Rice was sworn in on July 1, 2013. During her tenure, she supported major U.S. efforts on the Iran nuclear deal of 2015, Ebola epidemic
This list of Ebola outbreaks records the known occurrences of Ebola virus disease, a highly infectious and acutely lethal viral disease that has afflicted humans and animals primarily in equatorial Africa. The pathogens responsible for the d ...
, reopening to Cuba, fight against the Islamic State
An Islamic state is a State (polity), state that has a form of government based on sharia, Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical Polity, polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a t ...
, and Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
on climate change.
 In releasing the 2015 National Security Strategy, Rice said that the United States was pursuing an "ambitious yet achievable agenda" overseas. She argued that U.S. leadership had been essential for success on issues including
In releasing the 2015 National Security Strategy, Rice said that the United States was pursuing an "ambitious yet achievable agenda" overseas. She argued that U.S. leadership had been essential for success on issues including Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becom ...
, Iran's nuclear program, and sanctioning Russia over Ukraine. The document formed a blueprint for foreign policy, defense, and national security for the last two years of Obama's second term. It had previously been updated in 2010. In a letter outlining the strategy, Obama said that the U.S. would "always defend our interests and uphold our commitments to allies and partners," adding, "But we have to make hard choices among many competing priorities and we must always resist the overreach that comes when we make decisions based upon fear."
Middle East
Rice criticizedhuman rights violations
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hum ...
in U.S.-aligned Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and condemned the August 2013 Rabaa massacre, in which Egyptian security forces killed over 1,000 people during mass anti-government protests. Her position at times contradicted that of Secretary of State John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
. In response, Rice led a review of U.S. assistance to Egypt, which resulted in the cancellation of planned joint military exercises and suspension of arms shipments.
Rice was the lone dissenter in Obama's national security team on his decision to seek congressional authorization for military strikes against Syria's chemical weapons facilities, following the Assad regime's use of sarin gas against civilians in August 2013. She argued that the administration should move forward with strikes to punish Assad, correctly predicting Congress would not grant authorization. Rice and Kerry later worked to pursue a diplomatic solution with Russia instead. This effort led to United Nations Security Council Resolution 2118
United Nations United Nations Security Council resolution, Security Council Resolution 2118 was adopted unanimously on 27 September 2013, in regard to the Framework for Elimination of Syrian Chemical Weapons during the Syrian civil war. It recall ...
, which compelled Syria to destroy its declared chemical weapons stockpile and join the Chemical Weapons Convention
The Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), officially the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on their Destruction, is an arms control treaty administered by the Organisation for ...
. Under the agreement, 1,300 metric tons of chemical weapons were removed from Syria under international observation. However, the Assad regime either obtained or created gas for renewed chemical attacks in 2017.
In May 2014, Rice traveled to Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
for meetings with Israeli officials in which nuclear talks with Iran were discussed. Rice's visit, her first as National Security Advisor, came after peace talks between Israel and the Palestinians collapsed. The Obama administration made clear that Rice's trip was part of regularly scheduled talks and that the stalled Middle East peace discussions were not on the agenda. Rice was criticized by some for intensifying the Obama administration's conflicts with Israel during her time as National Security Advisor. Dennis Ross
Dennis B. Ross (born November 26, 1948) is an American diplomat and author. He has served as the Director of Policy Planning in the State Department under President George H. W. Bush, the special Middle East coordinator under President Bill Clint ...
, one of Obama's Middle East advisors, criticized Rice's "combative mind-set" as opposed to her predecessor, Tom Donilon
Thomas Edward Donilon (born May 14, 1955) is an American lawyer, business executive, and former government official who served as National Security Advisor (United States), the 22nd National Security Advisor in the Obama administration from 2010 ...
, who played a more conciliatory role. Ross wrote that after Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu
Benjamin "Bibi" Netanyahu (; ; born 21 October 1949) is an Israeli politician who served as the ninth prime minister of Israel from 1996 to 1999 and again from 2009 to 2021. He is currently serving as Leader of the Opposition and Chairman of ...
's public reprimand of the Obama administration's Iran negotiations, Rice relayed to Abraham Foxman
Abraham Henry Foxman (born May 1, 1940) is an American lawyer and activist. He served as the national director of the Anti-Defamation League from 1987 to 2015, and is currently the League's national director emeritus. From 2016 to 2021 he served a ...
that, "in her view, the Israeli leader did everything but use 'the N-word
In the English language, the word ''nigger'' is an ethnic slur used against black people, especially African Americans. Starting in the late 1990s, references to ''nigger'' have been progressively replaced by the euphemism , notably in cases ...
' in describing the president." However, in July 2014, Rice expressed support for Israel's right to defend itself during the 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict
The 2014 Gaza War, also known as Operation Protective Edge ( he, מִבְצָע צוּק אֵיתָן, translit=Miv'tza Tzuk Eitan, ),
was a military operation launched by Israel on 8 July 2014 in the Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territories, Pale ...
. She stated: "When countries single out Israel for unfair treatment at the UN, it isn't just a problem for Israel, it is a problem for all of us." In 2015, Rice criticized Netanyahu for agreeing to speak to Congress about Iran's nuclear program
The nuclear program of Iran is an ongoing scientific effort by Iran to research nuclear technology that can be used to make nuclear weapons. Iran has several research sites, two uranium mines, a research reactor, and uranium processing facili ...
without coordinating with the Obama administration. She negotiated a new memorandum of understanding between the U.S. and Israel in 2016 for $38 billion in military assistance, the largest such package in Israel's history.
The Obama administration supported the Saudi-and Emirati-led intervention in Yemen and blockade of Yemen
The blockade of Yemen refers to a sea, land and air blockade on Yemen which started with the positioning of Saudi Arabian warships in Yemeni waters in 2015 with the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen. In November 2017, after a Houthi missil ...
, but Rice opposed a coalition attack on the port city of Al Hudaydah
Al-Hudaydah ( ar, الْحُدَيْدَة, al-ḥudayda), also transliterated as Hodeda, Hodeida, Hudaida or Hodeidah, is the fourth-largest city in Yemen and its principal port on the Red Sea.
As of 2004, its population was 402,560 and it is ...
and personally called UAE crown prince Mohammed bin Zayed
Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan ( ar, مُحَمّد بِن زَايد آل نَهيَان, Moḥamed bin Zāyed Āl Nahyān; born 11 March 1961), colloquially known by his initials as MBZ, is the third president of the United Arab Emirat ...
to stop the planned offensive.
Africa
Rice supported South Sudanese independence and initial U.S. aid to the government of presidentSalva Kiir Mayardit
Salva Kiir Mayardit (born 13 September 1951), also known as Salva Kiir, is a South Sudanese politician who has been the President of South Sudan since its independence on 9 July 2011. Prior to independence, he was the President of the Governmen ...
. When the South Sudanese Civil War
The South Sudanese Civil War was a multi-sided civil war in South Sudan between forces of the government and opposition forces. In December 2013, President Kiir accused his former deputy Riek Machar and ten others of attempting a coup d'état. ...
broke out in 2013 between President Kiir's forces and forces led by vice president Riek Machar
Dr. Riek Machar Teny Dhurgon (born 26 November 1952) is a South Sudanese politician who serves as the First Vice President of South Sudan.
Political life
In February 2020, Machar was re-sworn in as first vice president following a revitalised ...
, the U.S. continued its support for the Kiir administration despite reports from U.S. embassy staff of atrocities committed by the government. Rice ultimately joined calls for an arms embargo against South Sudan in 2016, but the measure failed to win passage at the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and ...
.
Rice was perceived as close to Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator ...
's president Paul Kagame
Paul Kagame (; born 23 October 1957) is a Rwandan politician and former military officer who is the 4th and current president of Rwanda since 2000. He previously served as a commander of the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF), a Uganda-based rebel ...
. Some critics of the Obama administration's Africa policy faulted Rice for what they viewed as the U.S.'s failure to take action against Rwanda for its role in the Kivu conflict.
Afghanistan
On a visit toPakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
in 2015, Rice warned Pakistani political and military leaders that attacks in Afghanistan by militants based in Pakistan threatened regional security. Rice also delivered an invitation from Obama for Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
Nawaz Sharif
Mian Muhammad Nawaz Sharif (Urdu, Punjabi language, Punjabi: ; born 25 December 1949) is a Pakistani businessman and politician who has served as the Prime Minister of Pakistan for three non-consecutive terms. He is the longest-serving prime ...
to visit the United States in October. The meetings came at a tense time for Pakistan's relations with neighboring Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and archrival India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, along with uncertainty over whether the United States would release $300 million in military aid to Pakistan.
China
In a 2015 speech onChina–United States relations
The relationship between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the United States of America (USA) has been complex since 1949 with mutual distrust leading to complications. The relationship is one of close economic ties (economic ties grew ...
, Rice noted the problems of Chinese intelligence operations in the United States
The United States has often accused the government of the People's Republic of China of attempting to unlawfully acquire U.S. military technology and classified information as well as trade secrets of U.S. companiesFinkle, J. Menn, J., Viswanat ...
, saying, "This is not a mild irritation. It is an economic and national security concern to the United States. It puts enormous strain on our bilateral relationship, and it is a critical factor in determining the future trajectory of U.S.–China ties."
Post-Obama administration (2017–2021)

Private sector positions
On March 8, 2017, Rice became a distinguished visiting research fellow in the School of International Service (SIS) atAmerican University
The American University (AU or American) is a private federally chartered research university in Washington, D.C. Its main campus spans 90 acres (36 ha) on Ward Circle, mostly in the Spring Valley neighborhood of Northwest D.C. AU was charte ...
. In her residency, she planned to work on her next book and to mentor young SIS students.
On March 28, 2018, Rice was appointed to the board of directors at Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a fil ...
.
Unmasking investigations
On April 3, 2017,Eli Lake
Eli Jon Lake is an American journalist and the former senior national security correspondent for ''The Daily Beast'' and ''Newsweek''. Currently, he is a columnist for the Bloomberg View. He has also contributed to CNN, Fox, CSPAN, Charlie Ro ...
reported in ''Bloomberg View
Bloomberg News (originally Bloomberg Business News) is an international news agency headquartered in New York City and a division of Bloomberg L.P. Content produced by Bloomberg News is disseminated through Bloomberg Terminals, Bloomberg Televi ...
'' that as National Security Advisor, Rice had requested that the identities of some Americans mentioned in intelligence reports related to the campaign
Campaign or The Campaign may refer to:
Types of campaigns
* Campaign, in agriculture, the period during which sugar beets are harvested and processed
*Advertising campaign, a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme
* Bl ...
and presidential transition of Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of Pe ...
be unmasked. Any request for an American's identity to be unmasked required approval by the National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is a national-level intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collecti ...
; the agency's director, Michael Rogers, said it evaluated each request to determine "Is there a valid need to know in the course of the execution of their official duties?" and "Is the identification necessary to truly understand the context of the intelligence value that the report is designed to generate?" Rice said that she asked for identities of U.S. person
The term United States person or US person is used in various contexts in US laws and regulations with different meanings. It can refer to natural persons or other entities.
Data collection and intelligence
The term "US person" is used in the co ...
s to be revealed to provide context to the intelligence reports, and not for political purposes.
The report of Rice unmasking Trump officials followed an announcement by Devin Nunes
Devin Gerald Nunes (; born October 1, 1973) is an American businessman and politician who is chief executive officer of the Trump Media & Technology Group (TMTG). Before resigning from the House of Representatives and joining TMTG, Nunes was ...
, the Republican chair of the House Intelligence Committee
The United States House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence (HPSCI), also known as the House Intelligence Committee, is a committee of the United States House of Representatives, currently chaired by Adam Schiff. It is the primary committ ...
, "that he had seen reports indicating that Mr. Trump or his associates might have been 'incidentally' swept up in the monitoring of foreigners". The committee was investigating both Trump's ties to Russian attempts to influence the 2016 election and Trump's allegations that Obama had Trump Tower
Trump Tower is a 58-story, mixed-use skyscraper at 721–725 Fifth Avenue in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City, between East 56th and 57th Streets. The building contains the headquarters for the Trump Organization, as well ...
under surveillance. Lake's April 3 report of the unmasking specified "Rice's requests to unmask the names of Trump transition officials do not vindicate Trump's own tweets from March 4 in which he accused Obama of illegally tapping Trump Tower." Nevertheless, some Republicans called for an investigation into the unmasking while Democrats said that the unmasking story was a diversion from the investigation into Russian interference in the 2016 United States elections
The Russian government interfered in the 2016 U.S. presidential election with the goals of harming the campaign of Hillary Clinton, boosting the candidacy of Donald Trump, and increasing political and social discord in the United States. Acc ...
.
After members of the House and Senate Intelligence Committees were able to view the material on which Nunes based his assertions, both Democrats and Republicans familiar with the material said that there was "no evidence that Obama administration officials did anything unusual or illegal". Congressional intelligence sources called Rice's unmasking requests "normal and appropriate" for a national security adviser.
In August 2017, Eli Lake reported in ''Bloomberg View'' that Rice's successor as national security adviser, H. R. McMaster
Herbert Raymond McMaster (born July 24, 1962) is a retired United States Army lieutenant general who served as the 25th United States National Security Advisor from 2017 to 2018. He is also known for his roles in the Gulf War, Operation Endurin ...
, "has concluded that Rice did nothing wrong".
Rice testified to the House Intelligence Committee in September 2017 that she requested the unmasking because of a redacted intelligence report concerning an undisclosed visit to the United States by United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (The Middle East). It is located at th ...
crown prince Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan
Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan ( ar, مُحَمّد بِن زَايد آل نَهيَان, Moḥamed bin Zāyed Āl Nahyān; born 11 March 1961), colloquially known by his initials as MBZ, is the third president of the United Arab Emirates ...
in December 2016. During the visit, al-Nahyan met with Trump campaign advisors Steve Bannon
Stephen Kevin Bannon (born November 27, 1953) is an American media executive, political strategist, and former investment banker. He served as the White House's chief strategist in the administration of U.S. president Donald Trump during t ...
, Michael Flynn
Michael Thomas Flynn (born December 24, 1958) is a retired United States Army lieutenant general and conspiracy theorist who was the 24th U.S. National Security Advisor for the first 22 days of the Trump administration. He resigned in light of ...
, and Jared Kushner
Jared Corey Kushner (born January 10, 1981) is an American businessman and investor. He served as a senior advisor to 45th U.S. president Donald Trump, his father-in-law. Since leaving the White House, Kushner founded Affinity Partners, a pri ...
at Trump Tower
Trump Tower is a 58-story, mixed-use skyscraper at 721–725 Fifth Avenue in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City, between East 56th and 57th Streets. The building contains the headquarters for the Trump Organization, as well ...
in New York. Rice's testimony appeared to allay the concerns of Republicans, with Committee member Mike Conaway
Kenneth Michael Conaway (born June 11, 1948) is an American politician who was the U.S. representative for from 2005 to 2021. He is a member of the Republican Party. The district Conaway represented is located in West Texas and includes Midland ...
stating, "She was a good witness, answered all our questions. I'm not aware of any reason to bring her back."
In May 2020, Attorney General Bill Barr
William Pelham Barr (born May 23, 1950) is an American attorney who served as the 77th and 85th United States attorney general in the administrations of Presidents George H. W. Bush and Donald Trump.
Born and raised in New York City, Barr ...
appointed federal prosecutor John Bash
John Franklin Bash III is an American attorney who served as the United States Attorney for the United States District Court for the Western District of Texas from 2017 to 2020.
Early life and education
In 2003, Bash graduated from Harvard Coll ...
to examine unmasking conducted by the Obama administration. The inquiry concluded in October 2020 with no findings of substantive wrongdoing. Bash's 52-page report, previously classified top secret, was released in May 2022. Bash wrote he had found no evidence that any unmasking requests were made for any political or otherwise improper reasons during the 2016 election period or the ensuing presidential transition.
Political positions
Rice criticized the United States' close relationship withSaudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
despite the murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi
Jamal Ahmad Khashoggi (; ar, جمال أحمد خاشقجي, Jamāl ʾAḥmad Ḵāšuqjī, ; 13 October 1958 – 2 October 2018) was a Saudi journalist, dissident, author, columnist for ''Middle East Eye'' and ''The Washington Post'', and a ge ...
, Saudi Arabia's human rights abuses
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hum ...
, Saudi Arabia's diplomatic dispute with Canada, Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen and Saudi Arabian-led blockade against Qatar. Rice also criticized Trump's decision to withdraw U.S. troops from Syria, which critics say gave Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
the green light to invade and occupy northern Syria and attack Kurdish forces who assisted the U.S. in the destruction of the Islamic State
An Islamic state is a State (polity), state that has a form of government based on sharia, Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical Polity, polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a t ...
.
Rice has criticized Israeli proposals to annex parts of the West Bank and Jordan Valley
The Jordan Valley ( ar, غور الأردن, ''Ghor al-Urdun''; he, עֵמֶק הַיַרְדֵּן, ''Emek HaYarden'') forms part of the larger Jordan Rift Valley. Unlike most other river valleys, the term "Jordan Valley" often applies just to ...
, stating that such a move would make it more difficult to sustain traditionally bipartisan support for Israel in the United States. Rice takes the view that a two-state solution
The two-state solution to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict envisions an independent State of Palestine alongside the State of Israel, west of the Jordan River. The boundary between the two states is still subject to dispute and negotiation ...
is the only way to keep Israel both a Jewish and democratic state
"Jewish and democratic state" is the Israeli legal definition of the nature and character of the State of Israel. The "Jewish" nature was first defined within the Israeli Declaration of Independence in May 1948 (see Jewish state and Jewish homela ...
.
Potential Senate campaign
After U.S. SenatorSusan Collins
Susan Margaret Collins (born December 7, 1952) is an American politician serving as the senior United States senator from Maine. A member of the Republican Party, she has held her seat since 1997 and is Maine's longest-serving member of Co ...
from Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
voted to confirm Brett Kavanaugh
Brett Michael Kavanaugh ( ; born February 12, 1965) is an American lawyer and jurist serving as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was nominated by President Donald Trump on July 9, 2018, and has served since Oc ...
to the Supreme Court, Rice publicly considered challenging Collins in 2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, COVID- ...
, before announcing in April 2019 that she would not run for Senate.
Director of Domestic Policy Council (2021–present)
 In July 2020, it was widely reported that Rice was under consideration to be Joe Biden's vice presidential running mate in the 2020 general election. However,
In July 2020, it was widely reported that Rice was under consideration to be Joe Biden's vice presidential running mate in the 2020 general election. However, Kamala Harris
Kamala Devi Harris ( ; born October 20, 1964) is an American politician and attorney who is the 49th vice president of the United States. She is the first female vice president and the highest-ranking female official in U.S. history, as well ...
was selected as Biden's running mate on August 11, 2020.
On September 5, 2020, Rice was announced to be a member of the advisory council of the Biden-Harris Transition Team, which planned the Biden's presidential transition. In November, she was named a candidate for Secretary of State in the Biden Administration
Joe Biden's tenure as the 46th president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 2021. Biden, a Democrat from Delaware who previously served as vice president under Barack Obama, took office following his victory ...
.
Biden chose Rice to head the Domestic Policy Council
The Domestic Policy Council (DPC) is the principal forum used by the president of the United States for the consideration of domestic policy matters and senior policymaking, Cabinet of the United States, Cabinet, and White House officials. The Co ...
. This was considered a surprise by many political commentators, noting her experience in foreign policy over domestic policy.
Affiliations
Rice is a distinguished visiting research fellow at American University'sSchool of International Service The School of International Service (SIS) is American University's school of advanced international study, covering areas such as international politics, international communication, international development, international economics, peace and c ...
and non-resident senior fellow at the Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
The Robert and Renée Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, also known as the Belfer Center, is a research center located within the Harvard Kennedy School at Harvard University, in the United States. From 2017 until his death in Oc ...
at Harvard University's John F. Kennedy School of Government
The Harvard Kennedy School (HKS), officially the John F. Kennedy School of Government, is the school of public policy and government of Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The school offers master's degrees in public policy, public ...
. She is also a contributing opinion writer for the ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
''. Rice currently serves on the board of Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a fil ...
and is a member of the Aspen Strategy Group
The Aspen Strategy Group (ASG) is a policy program of the Aspen Institute, based in Washington D.C. The ASG is a membership-based forum composed of current and former policymakers, academics, journalists, and business leaders whose aim is to e ...
, American Academy of Diplomacy
The American Academy of Diplomacy is a private, nonprofit, non-partisan, elected organization whose active membership is limited to men and women who have held positions of high responsibility in crafting and implementing American foreign policy. ...
, and Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank
A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, mi ...
.
Personal life
Rice married formerABC News
ABC News is the news division of the American broadcast network ABC. Its flagship program is the daily evening newscast ''ABC World News Tonight, ABC World News Tonight with David Muir''; other programs include Breakfast television, morning ...
executive producer Ian Officer Cameron on September 12, 1992, at the St. Albans School chapel. They met as students at Stanford. The couple have two children. Despite sharing the same surname and the same job title, Susan Rice and Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice ( ; born November 14, 1954) is an American diplomat and political scientist who is the current director of the Hoover Institution at Stanford University. A member of the Republican Party, she previously served as the 66th Uni ...
are unrelated. The Hill and others have notably mistaken the Democratic National Security Advisor A national security advisor serves as the chief advisor to a national government on matters of security. The advisor is not usually a member of the government's cabinet but is usually a member of various military or security councils.
National sec ...
for her Republican counterpart.
Honors and awards
Rice was inducted into Stanford's Black Alumni Hall of Fame in 2002. In 2017, PresidentFrançois Hollande
François Gérard Georges Nicolas Hollande (; born 12 August 1954) is a French politician who served as President of France from 2012 to 2017. He previously was First Secretary of the Socialist Party (PS) from 1997 to 2008, Mayor of Tulle from ...
named Rice a commander of the Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon, ...
for her contributions to Franco-American relations.
Foreign honors
;Foreign honorsScholastic
; University Degrees ; Chancellor, visitor, governor, rector and fellowshipsHonorary degrees
;Honorary degreesMemberships and fellowships
Publications
* * *See also
*List of African-American United States Cabinet members
The Cabinet of the United States, which is the principal advisory body to the president of the United States, has had 25 permanent African-American members serving as vice president or head of one of the federal executive departments and ...
* List of female United States Cabinet members
The Cabinet of the United States, which is the principal advisory body to the president of the United States, has had 38 permanent female members serving as vice president or head of one of the federal executive departments and 31 wo ...
References
External links
* * * * , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Rice, Susan 1964 births 21st-century American politicians 21st-century American women politicians 21st-century American women writers African-American academics African-American diplomats African-American government officials African-American women in politics African-American people in Washington, D.C., politics African-American people in Maine politics Alumni of New College, Oxford American management consultants 21st-century American memoirists American people of Jamaican descent American Rhodes Scholars American University faculty and staff American women ambassadors American women memoirists American women political scientists American political scientists Assistant Secretaries of State for African Affairs Atlantic Council Biden administration personnel International relations scholars Living people McKinsey & Company people National Cathedral School alumni Netflix people Obama administration cabinet members People from Washington, D.C. Permanent Representatives of the United States to the United Nations Stanford University alumni United States National Security Advisors Washington, D.C., Democrats Women in Washington, D.C., politics Writers from Washington, D.C. Women members of the Cabinet of the United States African-American members of the Cabinet of the United States Brookings Institution people