Supervirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
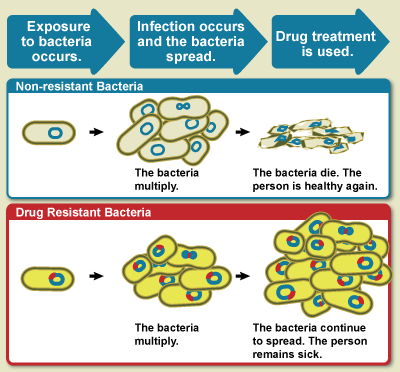 Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be
BURDEN of Resistance and Disease in European Nations
€”An EU project to estimate the financial burden of antibiotic resistance in European hospitals
Cosmetics Database
HCMV drug resistance mutations tool
- An informative article on multidrug resistance
MDRIpred
: A web server for predicting inhibitors against drug tolerant M. Tuberculosis, published i
Chemistry Central Journal
CancerDR
Cancer Drug Resistance Database.
{{Authority control Immunology Psychopharmacology
 Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be multidrug-resistant
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ...
.
The development of antibiotic resistance in particular stems from the drugs targeting only specific bacterial molecules (almost always proteins). Because the drug is ''so'' specific, any mutation in these molecules will interfere with or negate its destructive effect, resulting in antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, there is mounting concern over the abuse of antibiotics in the farming of livestock, which in the European Union alone accounts for three times the volume dispensed to humans – leading to development of super-resistant bacteria.
Bacteria are capable of not only altering the enzyme targeted by antibiotics, but also by the use of enzymes to modify the antibiotic itself and thus neutralize it. Examples of target-altering pathogens are ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive ...
'', vancomycin-resistant enterococci
''Enterococcus'' is a large genus of lactic acid bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Enterococci are gram-positive cocci that often occur in pairs (diplococci) or short chains, and are difficult to distinguish from streptococci on physical charac ...
and macrolide-resistant '' Streptococcus'', while examples of antibiotic-modifying microbes are '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and aminoglycoside-resistant '' Acinetobacter baumannii''.
In short, the lack of concerted effort by governments and the pharmaceutical industry, together with the innate capacity of microbes to develop resistance at a rate that outpaces development of new drugs, suggests that existing strategies for developing viable, long-term anti-microbial therapies are ultimately doomed to failure. Without alternative strategies, the acquisition of drug resistance by pathogenic microorganisms looms as possibly one of the most significant public health threats facing humanity in the 21st century. Some of the best alternative sources to reduce the chance of antibiotic resistance are probiotics, prebiotics, dietary fibers, enzymes, organic acids, phytogenics.
Types
Drug, toxin, or chemical resistance is a consequence of evolution and is a response to pressures imposed on any living organism. Individual organisms vary in their sensitivity to the drug used and some with greater fitness may be capable of surviving drug treatment. Drug-resistant traits are accordingly inherited by subsequent offspring, resulting in a population that is more drug-resistant. Unless the drug used makes sexual reproduction or cell-division or horizontal gene transfer impossible in the entire target population, resistance to the drug will inevitably follow. This can be seen in cancerous tumors where some cells may develop resistance to the drugs used in chemotherapy. Chemotherapy causes fibroblasts near tumors to produce large amounts of the proteinWNT16
Protein Wnt-16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WNT16'' gene. It has been proposed that stimulation of WNT16 expression in nearby normal cells is responsible for the development of chemotherapy-resistance in cancer cells.
Function ...
B. This protein stimulates the growth of cancer cells which are drug-resistant. MicroRNAs have also been shown to affect acquired drug resistance in cancer cells and this can be used for therapeutic purposes. Malaria in 2012 has become a resurgent threat in South East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, and drug-resistant strains of ''Plasmodium falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a Unicellular organism, unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female ''Anopheles'' mosqu ...
'' are posing massive problems for health authorities. Leprosy has shown an increasing resistance to dapsone
Dapsone, also known as 4,4'-sulfonyldianiline (SDA) or diaminodiphenyl sulfone (DDS), is an antibiotic commonly used in combination with rifampicin and clofazimine for the treatment of leprosy. It is a second-line medication for the treatment a ...
.
A rapid process of sharing resistance exists among single-celled organisms, and is termed horizontal gene transfer in which there is a direct exchange of genes, particularly in the biofilm state. A similar asexual method is used by fungi and is called " parasexuality". Examples of drug-resistant strains are to be found in microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses, parasites both endo- and ecto-, plants, fungi, arthropods, mammals, birds, reptiles, fish, and amphibians.
In the domestic environment, drug-resistant strains of organism may arise from seemingly safe activities such as the use of bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
, tooth-brushing and mouthwashing, the use of antibiotics, disinfectants and detergents, shampoos, and soaps, particularly antibacterial soaps, hand-washing, surface sprays, application of deodorants, sunblock
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock or sun cream, is a Photoprotection, photoprotective topical product for the skin that mainly absorbs, or to a much lesser extent reflects, some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect ag ...
s and any cosmetic or health-care product, insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
s, and dips. The chemicals contained in these preparations, besides harming beneficial organisms, may intentionally or inadvertently target organisms that have the potential to develop resistance.
Mechanisms
The four main mechanisms by which microorganisms exhibit resistance to antimicrobials are: # Drug inactivation or modification: e.g., enzymatic deactivation of ''Penicillin'' G in some penicillin-resistant bacteria through the production of β-lactamases. # Alteration of target site: e.g., alteration of PBP — the binding target site of penicillins — in MRSA and other penicillin-resistant bacteria. # Alteration of metabolic pathway: e.g., somesulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. ...
-resistant bacteria do not require para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), an important precursor for the synthesis of folic acid and nucleic acids in bacteria inhibited by sulfonamides. Instead, like mammalian cells, they turn to utilizing preformed folic acid.
# Reduced drug accumulation: by decreasing drug permeability and/or increasing active efflux
Efflux may refer to:
* Efflux (microbiology), a mechanism responsible for moving compounds out of cells
* e-flux, a publishing platform and archive
See also
* Efflux time, part of a measure of paint viscosity
* Flux (biology)
In general, flux ...
(pumping out) of the drugs across the cell surface.
Mechanisms of Acquired Drug Resistance
Metabolic cost
''Biological cost'' is a measure of the increased energy metabolism required to achieve a function. Drug resistance has a high metabolic price in pathogens for which this concept is relevant (bacteria, endoparasites, and tumor cells.) In viruses, an equivalent "cost" is genomic complexity. The high metabolic cost means that, in the absence of antibiotics, a resistant pathogen will have decreased evolutionary fitness as compared to susceptible pathogens. This is one of the reasons drug resistance adaptations are rarely seen in environments where antibiotics are absent. However, in the presence of antibiotics, the survival advantage conferred off-sets the high metabolic cost and allows resistant strains to proliferate.Treatment
In humans, the gene ABCB1 encodes MDR1(p-glycoprotein) which is a key transporter of medications on the cellular level. If MDR1 is overexpressed, drug resistance increases. Therefore, ABCB1 levels can be monitored. In patients with high levels of ABCB1 expression, the use of secondary treatments, like metformin, have been used in conjunction with the primary drug treatment with some success. Forantibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
, which represents a widespread problem nowadays, drugs designed to block the mechanisms of bacterial antibiotic resistance are used. For example, bacterial resistance against beta-lactam antibiotics (such as penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
and cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics ...
s) can be circumvented by using antibiotics such as nafcillin that are not susceptible to destruction by certain beta-lactamases (the group of enzymes responsible for breaking down beta-lactams). Beta-lactam bacterial resistance can also be dealt with by administering beta-lactam antibiotics with drugs that block beta-lactamases such as clavulanic acid so that the antibiotics can work without getting destroyed by the bacteria first. Recently, researchers have recognized the need for new drugs that inhibit bacterial efflux pumps, which cause resistance to multiple antibiotics such as beta-lactams, quinolones
Quinolone may refer to:
* 2-Quinolone
* 4-Quinolone
* Quinolone antibiotic
A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They ar ...
, chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, a ...
, and trimethoprim by sending molecules of those antibiotics out of the bacterial cell. Sometimes a combination of different classes of antibiotics may be used synergistically; that is, they work together to effectively fight bacteria that may be resistant to one of the antibiotics alone.
Destruction of the resistant bacteria can also be achieved by phage therapy, in which a specific bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
(virus that kills bacteria) is used.
See also
*Antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
* Fecal bacteriotherapy
* Mass drug administration
* Multidrug resistance
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are c ...
* Pharmacoepidemiology
Pharmacoepidemiology is the study of the uses and effects of drugs in well-defined populations.Porta M, editor. Greenland S, Hernán M, dos Santos Silva I, Last JM, associate editors (2014). "A dictionary of epidemiology", 6th. edition. New York: O ...
* Physical factors affecting microbial life
Microbes can be damaged or killed by elements of their physical environment such as temperature, radiation, or exposure to chemicals; these effects can be exploited in efforts to control pathogens, often for the purpose of food safety.
Irradiati ...
* Small multidrug resistance protein
Small multidrug resistance protein (also known as Drug/Metabolite Transporter) is a family of integral membrane proteins that confer drug resistance to a wide range of toxic compounds by removing them for the cells. The efflux is coupled to an i ...
* ''Eleftheria terrae
''Eleftheria terrae'' is a recently discovered Gram-negative bacterium. ''E. terrae'' is a temporary name for the organism, as it was only discovered in 2014 and is still undergoing scientific study. It was found to produce a previously unknown ...
''
References
External links
BURDEN of Resistance and Disease in European Nations
€”An EU project to estimate the financial burden of antibiotic resistance in European hospitals
Cosmetics Database
HCMV drug resistance mutations tool
- An informative article on multidrug resistance
MDRIpred
: A web server for predicting inhibitors against drug tolerant M. Tuberculosis, published i
Chemistry Central Journal
CancerDR
Cancer Drug Resistance Database.
{{Authority control Immunology Psychopharmacology