Supertonic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In music, the supertonic is the second  The supertonic chord normally functions as a
The supertonic chord normally functions as a 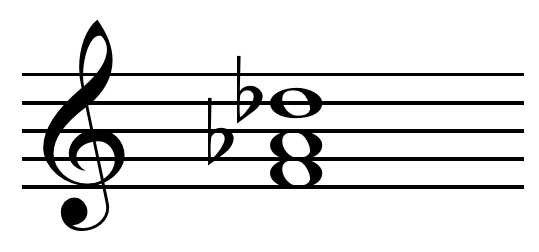
 In major or minor, the major chord built on the lowered supertonic () is called a
In major or minor, the major chord built on the lowered supertonic () is called a
degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathematics
...
() of a diatonic scale
In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps (whole tones) and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, ...
, one whole step
Step(s) or STEP may refer to:
Common meanings
* Stairs#Step, Steps, making a staircase
* Walking
* Dance move
* Military step, or march
** Marching
Arts Films and television
* Steps (TV series), ''Steps'' (TV series), Hong Kong
* Step (film), ' ...
above the tonic. In the movable do solfège Moveable may refer to:
* A Moveable Feast
* Moveable feast
* Movable type
* Moveable bridge
* History of printing in East Asia
Printing in East Asia originated from the Han dynasty (220 BCE – 206 CE) in China, evolving from ink rubbings made on p ...
system, the supertonic note is sung as ''re''.
The triad built on the supertonic note is called the supertonic chord. In Roman numeral analysis, the supertonic chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "ii" in a major key
Key or The Key may refer to:
Common meanings
* Key (cryptography), a piece of information that controls the operation of a cryptography algorithm
* Key (lock), device used to control access to places or facilities restricted by a lock
* Key (map ...
, indicating that the chord is a minor chord
In music theory, a minor chord is a chord that has a root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord comprises only these three notes, it is called a minor triad. For example, the minor triad built on C, called a C minor triad, has pit ...
(in C: D–F–A). In a minor key, it is indicated by "ii" if it is built on the a natural minor scale
In music theory, the minor scale is three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just two as with the major scale, which also ...
, indicating that the chord is a diminished chord
In music theory, a diminished triad (also known as the minor flatted fifth) is a triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root. It is a minor triad with a lowered ( flattened) fifth. When using chord symbols, it may be indicated by the ...
(in C: D–F–A). Because it is a diminished chord, it usually appears in first inversion
The first inversion of a chord is the voicing of a triad, seventh chord, or ninth chord in which the third of the chord is the bass note and the root a sixth above it. Walter Piston, ''Harmony'', fifth edition, revised and expanded by Mark DeVo ...
(iio6) so that no note dissonates with the bass note
In music theory, the bass note of a chord or sonority is the lowest note played or notated. If there are multiple voices it is the note played or notated in the lowest voice (the note furthest in the bass.)
Three situations are possible:
# ...
.
These chords may also appear as seventh chords
A seventh chord is a chord consisting of a triad plus a note forming an interval of a seventh above the chord's root. When not otherwise specified, a "seventh chord" usually means a dominant seventh chord: a major triad together with a minor ...
: in major, as ii7 (in C: D–F–A–C), while in minor as ii7 (in C: D–F–A–C) or rarely ii7. They are the second-most-common form of nondominant seventh chords.
 The supertonic chord normally functions as a
The supertonic chord normally functions as a predominant chord
In music theory, a predominant chord (also pre-dominant) is any chord which normally resolves to a dominant chord.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II'', Glossary, p.359. Eighth Edition. . "Any chord in functional ...
, a chord that naturally resolves to chord with dominant function
In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree () of the diatonic scale. It is called the ''dominant'' because it is second in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as "So ...
. The supertonic chord lies a fifth above the V chord. Descending fifths are a strong basis for harmonic motion (see circle of fifths
In music theory, the circle of fifths is a way of organizing the 12 chromatic pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths. (This is strictly true in the standard 12-tone equal temperament system — using a different system requires one interval ...
). The supertonic is one of the strongest predominants and approaches the V chord from above by descending fifth.

 In major or minor, the major chord built on the lowered supertonic () is called a
In major or minor, the major chord built on the lowered supertonic () is called a Neapolitan chord
In Classical music theory, a Neapolitan chord (or simply a "Neapolitan") is a major chord built on the lowered ( flatted) second (supertonic) scale degree. In Schenkerian analysis, it is known as a Phrygian II, since in minor scales the chord is b ...
(in C: D–F–A), notated as N6 or II6, usually used in first inversion. The supertonic may be raised as part of the common-tone diminished seventh chord
The diminished seventh chord is a four-note chord (a seventh chord) composed of a root note, together with a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a diminished seventh above the root: (1, 3, 5, 7). For example, the diminished seve ...
, ii7 (in C: D–F–A–C). One variant of the supertonic seventh chord is the supertonic diminished seventh Kitson, C. H. (2006). ''Elementary Harmony'', p. 43. . with the raised supertonic, which equals the lowered third through enharmonic equivalence
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written ...
(in C: D=E).
The term ''supertonic'' may also refer to a relationship of musical keys. For example, relative to the key of C major, the key of D major (or D minor) is the supertonic.
In Riemannian theory
"Riemannian theory" in general refers to the musical theories of German theorist Hugo Riemann (1849–1919). His theoretical writings cover many topics, including musical logic, notation, harmony, melody, phraseology, the history of music theor ...
, the supertonic is considered the subdominant parallel
Parallel and counter parallel chords are terms derived from the German (''Parallelklang'', ''Gegenparallelklang'') to denote what is more often called in English the "relative", and possibly the "counter relative" chords. In Riemannian the ...
: Sp/T in major though sP/T in minor (AM).
References
{{degrees Diatonic functions 2