sulfite process on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The sulfite process produces 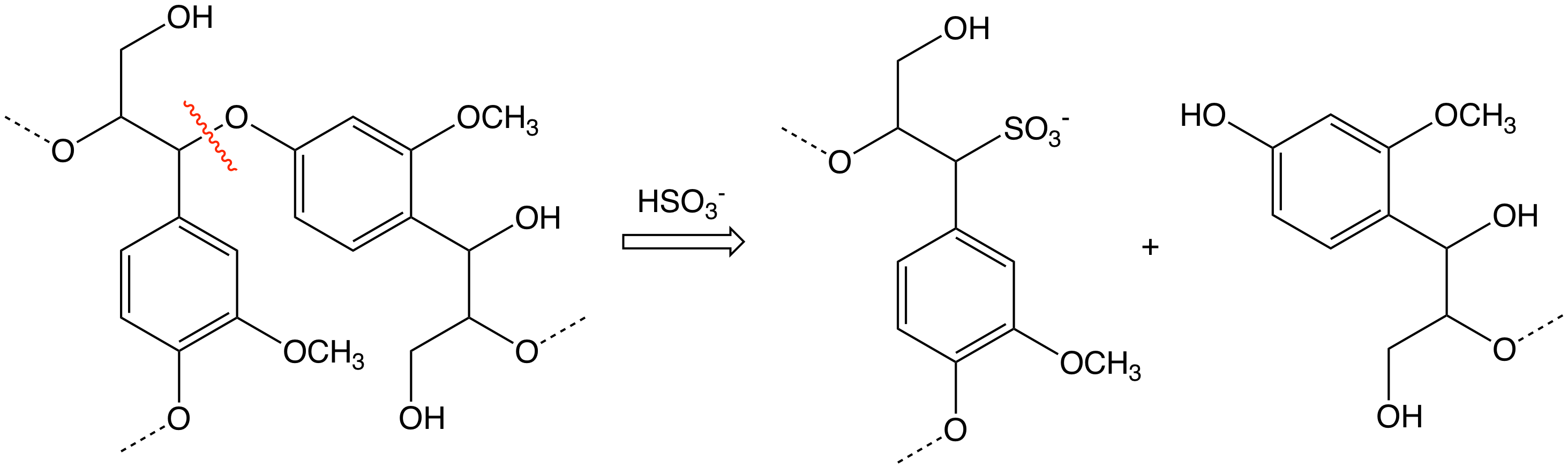
'Charles Fenerty and his Paper Invention''. Toronto: Peter Burger, 2007. pp.25–30 and by
wood pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw mate ...
that is almost pure cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
fibers by treating wood chips with solutions of sulfite and bisulfite ions. These chemicals cleave the bonds between the cellulose and lignin components of the lignocellulose. A variety of sulfite/bisulfite salts are used, including sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
(Na+), calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
(Ca2+), potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
(K+), magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
(Mg2+), and ammonium (NH4+). The lignin is converted to lignosulfonates, which are soluble and can be separated from the cellulose fibers. For the production of cellulose, the sulfite process competes with the Kraft process which produces stronger fibers and is less environmentally costly.

History
The use of wood to make pulp for paper began with the development ofmechanical pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw mate ...
ing in the 1840s by Charles Fenerty
Charles Fenerty (January 1821 – 10 June 1892), was a Canadian inventor who invented the wood pulp process for papermaking, which was first adapted into the production of newsprint. Fenerty was also a poet (writing over 32 known poems).
Early ...
in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
Burger, Peter'Charles Fenerty and his Paper Invention''. Toronto: Peter Burger, 2007. pp.25–30 and by
F. G. Keller
F is the sixth letter of the Latin alphabet.
F may also refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* F or f, the number 15 in hexadecimal and higher positional systems
* ''p'F'q'', the hypergeometric function
* F-distribution, a cont ...
in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. Chemical processes quickly followed, first with Julius Roth's use of sulfurous acid to treat wood in 1857, followed by Benjamin Chew Tilghman
Benjamin Chew Tilghman (18211901) was an American soldier and inventor. He is best known as the inventor of the process of sandblasting.
Early life
He was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on October 26, 1821, the third child of Benjamin and An ...
's US patent
Under United States law, a patent is a right granted to the inventor of a (1) process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter, (2) that is new, useful, and non-obvious. A patent is the right to exclude others, for a limited ...
on the use of calcium bisulfite
Calcium bisulfite (calcium bisulphite) is an inorganic compound which is the salt (chemistry), salt of a calcium cation and a bisulfite anion. It may be prepared by treating lime with an excess of sulfur dioxide and water. As a food additive it is ...
, Ca(HSO3)2, to pulp wood in 1867. Almost a decade later in 1874 the first commercial sulfite pulp mill was built in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
. It used magnesium as the counter ion and was based on work by Carl Daniel Ekman
Carl Daniel Ekman (March 17, 1845 – November 3, 1904) was a Swedish chemical engineer who invented the form of the sulfite process of wood pulp manufacturing which was first established on a firm commercial basis, helping to replace rags as the ...
.
By 1900 sulfite pulping had become the dominant means of producing wood pulp, surpassing mechanical pulping methods. The competing chemical pulping process, the sulfate or kraft process was developed by Carl F. Dahl Carl may refer to:
*Carl, Georgia, city in USA
*Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
*Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name
*Carl², a TV series
* "Carl", List of Aqua Teen ...
in 1879 and the first kraft mill started (in Sweden) in 1890. The first sulphite mill in the United States was the Richmond Paper Company in Rumford, Rhode Island
Rumford is the northern section of the city of East Providence, Rhode Island, USA. The Rumford section of East Providence borders Seekonk, Massachusetts, Pawtucket, Rhode Island and the Ten Mile River (Seekonk River). Rumford has been part of thre ...
in the mid-1880s. The invention of the recovery boiler by G. H. Tomlinson
G is the seventh letter of the Latin alphabet.
G may also refer to:
Places
* Gabon, international license plate code G
* Glasgow, UK postal code G
* Eastern Quebec, Canadian postal prefix G
* Melbourne Cricket Ground in Melbourne, Australia, g ...
in the early 1930s allowed kraft mills to recycle almost all of their pulping chemicals. This, along with the ability of the kraft process to accept a wider variety of types of wood and produce stronger fibers made the kraft process the dominant pulping process starting in the 1940s. Sulfite pulps now account for less than 10% of the total chemical pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw ma ...
production and the number of sulfite mills continues to decrease.
Magnesium was the standard counter ion
160px, Polystyrene sulfonate, a cation-exchange resin, is typically supplied with as the counterion.">cation-exchange_resin.html" ;"title="Polystyrene sulfonate, a cation-exchange resin">Polystyrene sulfonate, a cation-exchange resin, is typical ...
until calcium replaced it in the 1950s.
Pulping liquor preparation
The pulping liquor for most sulfite mills is treating various bases (alkali metal or alkaline earth hydroxides) with sulfur dioxide: :SO2 + MOH → MHSO3 :MHSO3 + MOH → M2SO3 + H2O Similar reactions are effected with divalent cations (Mg2+, Ca2+) and using carbonates in place of hydroxide. The ratio of sulfite to bisulfite depends on pH; above pH=7, sulfite predominates. ;Calcium-based The earliest process used calcium, obtained as inexpensive calcium carbonate, and there was little incentive to recover the inorganic materials. At least in Sweden the brown liquor from this process was previously frequently used for producing ethanol, while with other brown liquors the fermentable hexose sugars are left to contribute to the energy needed in the recovery process. Calcium sulfite, which is poorly soluble, converts to calcium bisulfite only at low pH. Therefore calcium-based sulfite processes require acidic conditions. ;Ammonia-based Ammonia-based processes do not allow recovery of the pulping chemicals since ammonia or ammonium salts are oxidized tonitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and nitrogen oxides Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
*Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
*Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
* Nitrogen trioxide (), or ...
when burned.
;Magnesium-based
The recovery process used in magnesium-based sulfite pulping the "Magnefite" process is well developed. The concentrated brown liquor is burned in a recovery boiler, producing magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide ( Mg O), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions ...
and sulfur dioxide, both of which are recovered from the flue gases. Magnesium oxide is recovered in a wet scrubber to give a slurry of magnesium hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Mg(OH)2. It occurs in nature as the mineral brucite. It is a white solid with low solubility in water (). Magnesium hydroxide is a common component of antacids, such as milk ...
.
:MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
This magnesium hydroxide slurry is then used in another scrubber to absorb sulfur dioxide from the flue gases
Flue gas is the gas exiting to the atmosphere via a flue, which is a pipe or channel for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, oven, furnace, boiler or steam generator. Quite often, the flue gas refers to the combustion exhaust gas produced ...
producing a magnesium bisulfite solution that is clarified, filtered and used as the pulping liquor.
:Mg(OH)2 + 2 SO2 → Mg(HSO3)2
;Sodium-based
Sodium-based processes use a recovery system similar to that used in the kraft recovery process, except that there is no "lime cycle".
Processes involved in sulfite pulping
The process is conducted in large pressure vessels called digesters. Sulfite pulping is carried out between pH 1.5 and 5. The pulp is in contact with the pulping chemicals for 4 to 14 hours and at temperatures ranging from 130 to 160°C
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The ...
(266 to 320 °F), again depending on the chemicals used.
Most of the intermediates involved in delignification in sulfite pulping are resonance-stabilized carbocations
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encount ...
formed either by protonation of carbon-carbon double bonds or acidic cleavage of ether bonds which connect many of the constituents of lignin. It is the latter reaction which is responsible for most lignin degradation in the sulfite process. The electrophilic carbocations react with bisulfite ions (HSO3−)to give sulfonates.
:R-O-R' + H+ → R+ + R'OH
:R+ + HSO3− → R-SO3H
The sulfite process does not degrade lignin to the same extent that the kraft process does and the lignosulfonates from the sulfite process are useful byproducts.
Chemical recovery
The spent cooking liquor from sulfite pulping is usually called brown liquor, but the terms red liquor, thick liquor and sulfite liquor are also used (compared to black liquor in the kraft process). Pulp washers, using countercurrent flow, remove the spent cooking chemicals and degraded lignin and hemicellulose. The extracted brown liquor is concentrated, in multiple effect evaporators. The concentrated brown liquor can be burned in the recovery boiler to generate steam and recover the inorganic chemicals for reuse in the pulping process or it can be neutralized to recover the useful byproducts of pulping. Recent developments in Chemrec'sblack liquor gasification
Gasification is a process that converts biomass- or fossil fuel-based carbonaceous materials into gases, including as the largest fractions: nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and carbon dioxide (). This is achieved by reactin ...
process, adapting the technology to use in the sulfite pulping process, could make second generation biofuels production an alternative to the conventional recovery boiler technology. Around 1906 Gösta Ekström a Swedish engineer patented a process of ethanol generation from the residual 2-2.5% fermentable hexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
sugars in the spent liquor.
The sulfite process can use calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
, ammonium, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
or sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
as a base.
Applications
The sulfite process isacidic
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a ...
and one of the drawbacks is that the acidic conditions hydrolyze
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
some of the cellulose, which means that sulfite pulp fibers are not as strong as kraft pulp fibers. The yield of pulp (based on wood used) is higher than for kraft pulping and sulfite pulp is easier to bleach.
Commodity
Sulfite pulp remains an important commodity, especially for specialty papers and as a source of cellulose for non-paper applications. It is used to make fine paper, tissue,glassine
Glassine is a smooth and glossy paper that is air, water, and grease resistant. It is usually available in densities between . It is translucent unless dyes are added to color it or make it opaque. It is manufactured by supercalendering: after ...
, and to add strength to newsprint.
Dissolving pulp
A special grade of bleached sulfite pulp is known as ''dissolving pulp'' which is the raw material for a wide variety of cellulose derivatives, for examplerayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose f ...
, cellophane
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coated ...
, cellulose acetate
In biochemistry, cellulose acetate refers to any acetate ester of cellulose, usually cellulose diacetate. It was first prepared in 1865. A bioplastic, cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and ...
and methylcellulose
Methyl cellulose (or methylcellulose) is a compound derived from cellulose. It is sold under a variety of trade names and is used as a thickener and emulsifier in various food and cosmetic products, and also as a bulk-forming laxative. Like cell ...
.
Rayon is a reconstituted cellulose fiber used to make many fabrics.
Cellophane is a clear reconstituted cellulose film used in wrapping and windows in envelopes.
Cellulose acetate was used to make flexible films for photographic use, computer tapes and so on and also to make fibers.
Methylcellulose and other cellulose ether derivatives are used in a wide range of everyday products from adhesives
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
to baked goods
Baking is a method of preparing food that uses dry heat, typically in an oven, but can also be done in hot ashes, or on hot stones. The most common baked item is bread but many other types of foods can be baked. Heat is gradually transferred ...
to pharmaceuticals.
Byproducts
Sulfite pulping is generally less destructive than kraft pulping, so there are more usable byproducts.Lignosulfonates
Chief among sulfite process byproducts arelignosulfonates
Lignosulfonates (LS) are water-soluble anionic polyelectrolyte polymers: they are byproducts from the production of wood pulp using sulfite pulping. Most delignification in sulfite pulping involves acidic cleavage of ether bonds, which connect ma ...
, which find a wide variety of uses where a relatively inexpensive agent is needed to make a water dispersion of a water-insoluble material. Lignosulfonates are used in tanning
Tanning may refer to:
*Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather
*Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin
**Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun
**Sunless tanning, application of a stain or dye t ...
leather, making concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
, drilling mud, drywall
Drywall (also called plasterboard, dry lining, wallboard, sheet rock, gypsum board, buster board, custard board, and gypsum panel) is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or without additives, typically extruded between thic ...
and so on.
Oxidation of lignosulfonates was used to produce vanillin
Vanillin is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a phenolic aldehyde. Its functional groups include aldehyde, hydroxyl, and ether. It is the primary component of the extract of the vanilla bean. Synthetic vanillin is now u ...
(artificial vanilla), and this process is still used by one supplier (Borregaard
Borregaard is a Norwegian company, established in 1889 in the southeastern town of Sarpsborg in Østfold county. Its main products were traditionally pulp and paper. The company later started producing chemicals based on timber as a raw materi ...
, Norway) while all North American production by this route ceased in the 1990s.
Other byproducts
Acid hydrolysis of hemicelluloses during sulfite pulping producesmonosaccharides
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units ( monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
They are usually colorless, water ...
, predominantly mannose
Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation ...
for softwoods and xylose
Xylose ( grc, ξύλον, , "wood") is a sugar first isolated from wood, and named for it. Xylose is classified as a monosaccharide of the aldopentose type, which means that it contains five carbon atoms and includes an aldehyde functional g ...
for hardwoods, which can be fermented to produce ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
.
See also
* Pulp millReferences
{{Authority control Papermaking Pulp and paper industry Chemical processes