Suction Filtration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
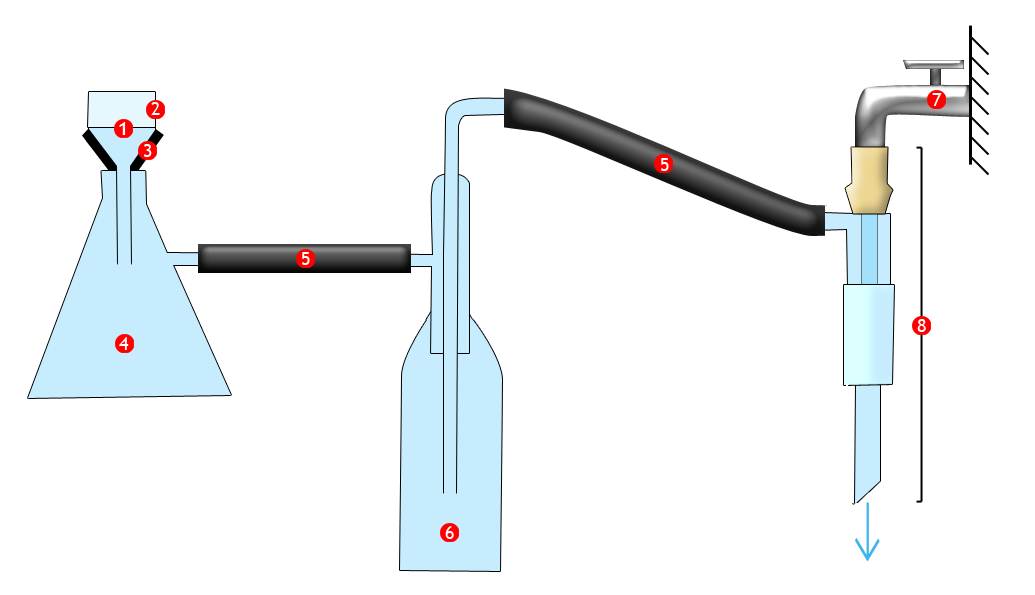 By flowing through the aspirator,
By flowing through the aspirator,
Vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often dis ...
filtration is a fast filtration
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a ''filter medium'' that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter ...
technique used to separate solid
Solid is one of the State of matter#Four fundamental states, four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and Plasma (physics), plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount o ...
s from liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
s.
Principle
 By flowing through the aspirator,
By flowing through the aspirator, water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
will suck out the air contained in the vacuum flask and the Büchner flask
A Büchner flask, also known as a vacuum flask,The use of the term ''vacuum flask'' sometimes causes confusion with the Thermos flask filter flask, suction flask, side-arm flask, Kitasato flask or Bunsen flask, is a thick-walled Erlenmeyer flas ...
. There is therefore a difference in pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
between the exterior and the interior of the flasks : the contents of the Büchner funnel
A Büchner funnel is a piece of laboratory equipment used in filtration. It is traditionally made of porcelain, but glass and plastic funnels are also available. On top of the funnel-shaped part there is a cylinder with a fritted glass disc/perf ...
are sucked towards the vacuum flask. The filter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
, which is placed at the bottom of the Büchner funnel, separates the solids from the liquids.
The solid residue
Residue may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
* An amino acid, within a peptide chain
* Crop residue, materials left after agricultural processes
* Pesticide residue, refers to the pesticides that may remain on or in food after they are applied ...
, which remains at the top of the Büchner funnel, is therefore recovered more efficiently: it is much drier than it would be with a simple filtration.
The rubber conical seal ensures the apparatus is hermetically closed, preventing the passage of air between the Büchner funnel and the vacuum flask. It maintains the vacuum in the apparatus and also avoids physical points of stress (glass against glass.)
Diagram annotations
#Filter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
# Büchner funnel
A Büchner funnel is a piece of laboratory equipment used in filtration. It is traditionally made of porcelain, but glass and plastic funnels are also available. On top of the funnel-shaped part there is a cylinder with a fritted glass disc/perf ...
# Conic seal
# Büchner flask
A Büchner flask, also known as a vacuum flask,The use of the term ''vacuum flask'' sometimes causes confusion with the Thermos flask filter flask, suction flask, side-arm flask, Kitasato flask or Bunsen flask, is a thick-walled Erlenmeyer flas ...
# Air tube
# Vacuum flask
# Water tap
# Aspirator
Uses
Filtration is a unit operation that is commonly used both in laboratory and production conditions. This apparatus, adapted for laboratory work, is often used to isolate the product ofsynthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
** Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organ ...
of a reaction when the product is a solid in suspension. The product of synthesis is then recovered faster, and the solid is drier than in the case of a simple filtration. Other than isolating a solid, filtration is also a stage of purification: the soluble impurities in the solvent are eliminated in the filtrate (liquid).
This apparatus is often used to purify a liquid. When a synthesised product is filtered, the insolubles (catalysers, impurities, sub-products of the reaction, salts, ...) remain in the filter. In this case, vacuum filtration is also more efficient that a simple filtration: there is more liquid recovered, and the yield is therefore better.
Practical aspects
It is often necessary to maintain the Büchner flask and, incidentally, the vacuum flask. The rigidity of the vacuum pipes and the difference in height between the different parts of the apparatus (as visible in the diagram) make such an apparatus relatively unstable. Therefore, a three-pronged clamp should be used to maintain the Büchner flask. This clamp should be placed such that the two prongs surround the part of the flask connected to the vacuum tube, the lasting prong resting on the other side. If it is also necessary to maintain the vacuum flask we use either a mandible clamp, or a three-pronged clamp, depending on the apparatus and its stability. The clamp to use is left to the judgement of the operator. Before closing the tap, it is necessary to "break the vacuum" (letting in the air in through any area in the apparatus, by removing the funnel for example), otherwise water goes up the apparatus from the aspirator. The vacuum flask prevents the water from going up the Büchner flask.Sources
{{Citation , title = Vacuum Filtration , url = http://orgchemboulder.com/Technique/Procedures/Filtration/Filtration.shtml , accessdate = 2017-01-14 Laboratory techniques Analytical chemistry Filters