Suakin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Suakin or Sawakin ( ar, سواكن, Sawákin, Beja: ''Oosook'') is a port city in northeastern
Suakin: Time and Tide
. ''Saudi Aramco World.'' The spelling on Admiralty charts in the late 19th century was "Sauakin", but in the popular press "Suakim" was predominant.
 One of Suakin's rulers, Ala al-Din al-Asba'ani, angered the
One of Suakin's rulers, Ala al-Din al-Asba'ani, angered the
"Precolonial Beja: A Periphery at the Crossroads."
''Nordic Journal of African Studies'' 15(4): 473–498 (2006). The Beja were originally Christian. Despite the town's formal submission to the
Chapter 5: "Australian naval defence", Edited: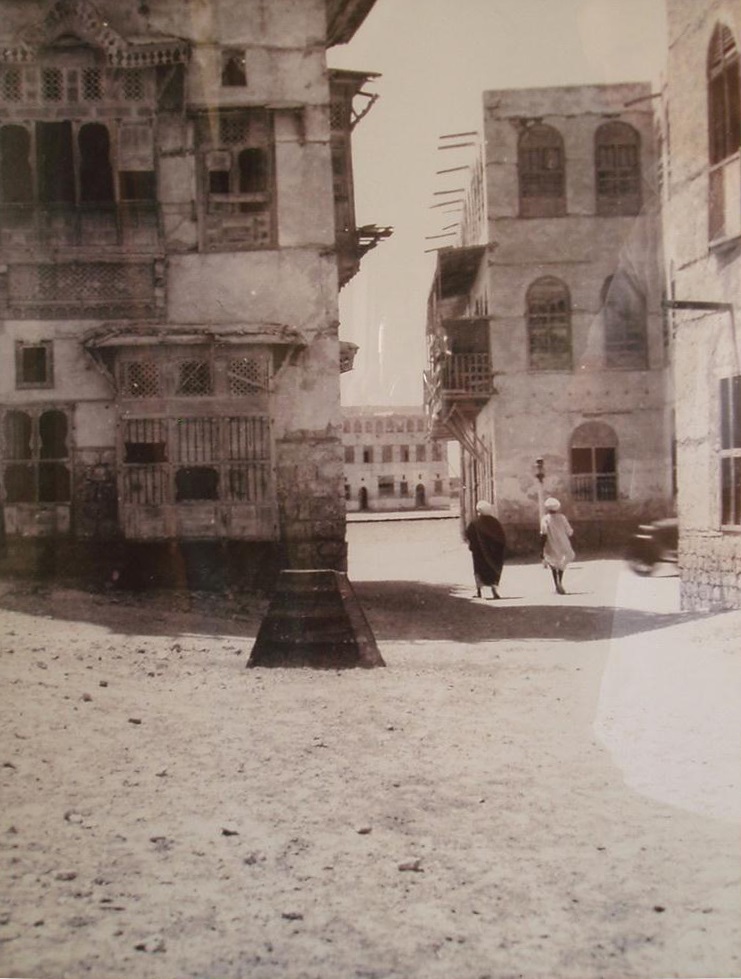
Monthly rainfall for Suakin
/ref>
"Greenlaw's Suakin: the limits of architectural representation and the continuing lives of buildings in Coastal Sudan." ''African Arts'', vol. 44, no. 4, 2011, p. 36+.
''Gale Literature Resource Center'' *Cooke, B. Kennedy, and B. Kennedy-Cooke. “The Red Sea coast in 1540.” ''Sudan Notes and Records'', vol. 16, no. 2, 1933, pp. 151–59,http://www.jstor.org/stable/41716059 . Accessed 11 Apr. 2022.
* Livro de Lisuarte de Abreu: ''fac-simile''. Comissão Nacional para as Comemorações dos Descobrimentos Portugueses. Lisboa, 1992. Vasco Graça Moura
* Couto, Diogo do; ''Observações sobre as principais causas da decadência dos portugueses na Ásia''
Comparative Vocabularies of the Languages Spoken at Suakin: Arabic, Hadendoa, Beni-AmerPictures of Suakin on Atlas ObscuraSuakin Island - A Virtual Experience
A 3D reconstruction of the Island *https://observador.pt/2016/12/16/diogo-do-couto-o-portugues-da-india-ha-500-anos/ {{Authority control Populated places in Red Sea (state) Port cities and towns of the Red Sea Ramsar sites in Sudan Cities in Sudan
Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, on the west coast of the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
. It was formerly the region's chief port, but is now secondary to Port Sudan
Port Sudan ( ar, بور سودان, Būr Sūdān) is a port city in eastern Sudan, and the capital of the state of Red Sea. , it has 489,725 residents. Located on the Red Sea, Port Sudan is recognized as Sudan's main seaport and the source of 90% ...
, about north.
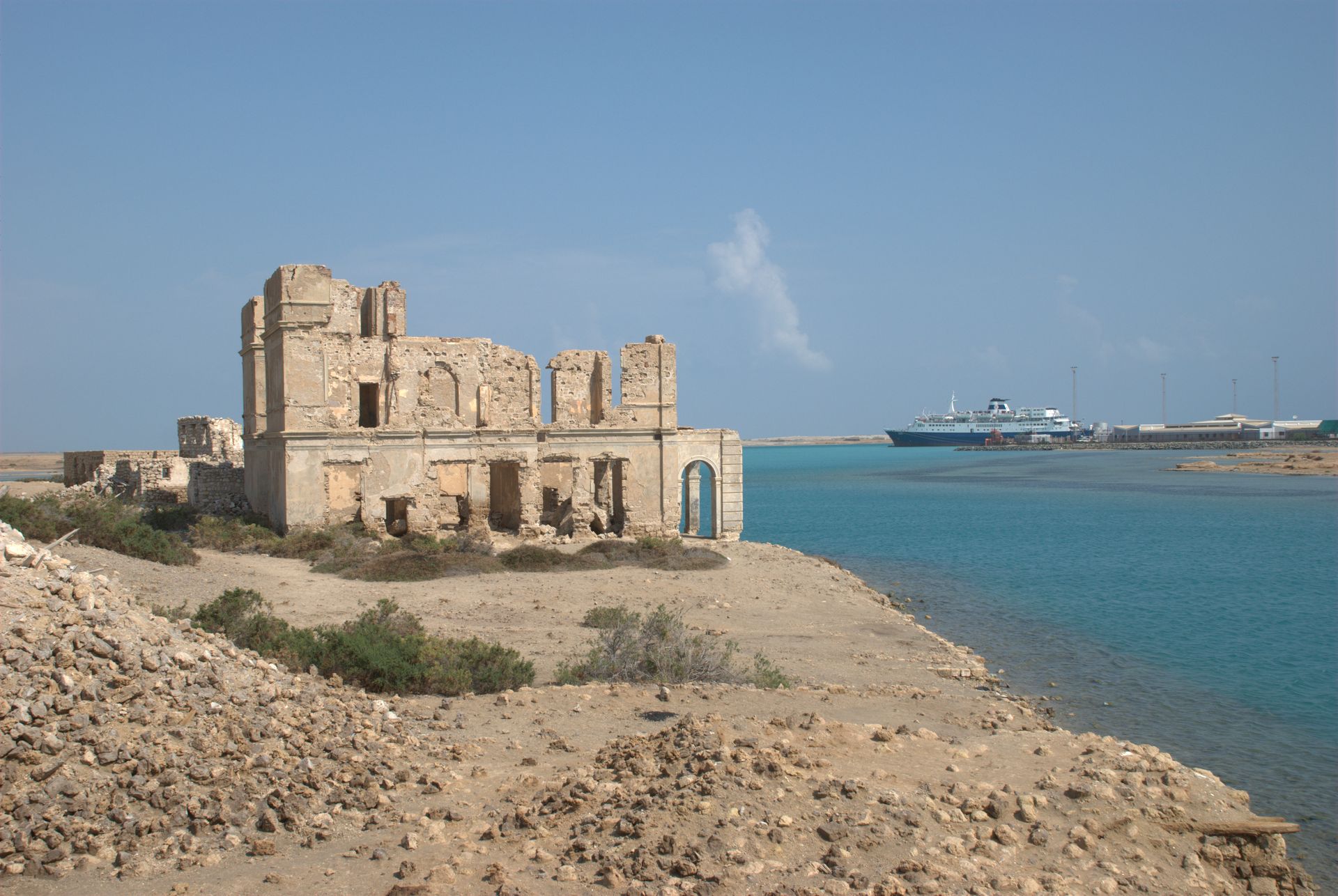
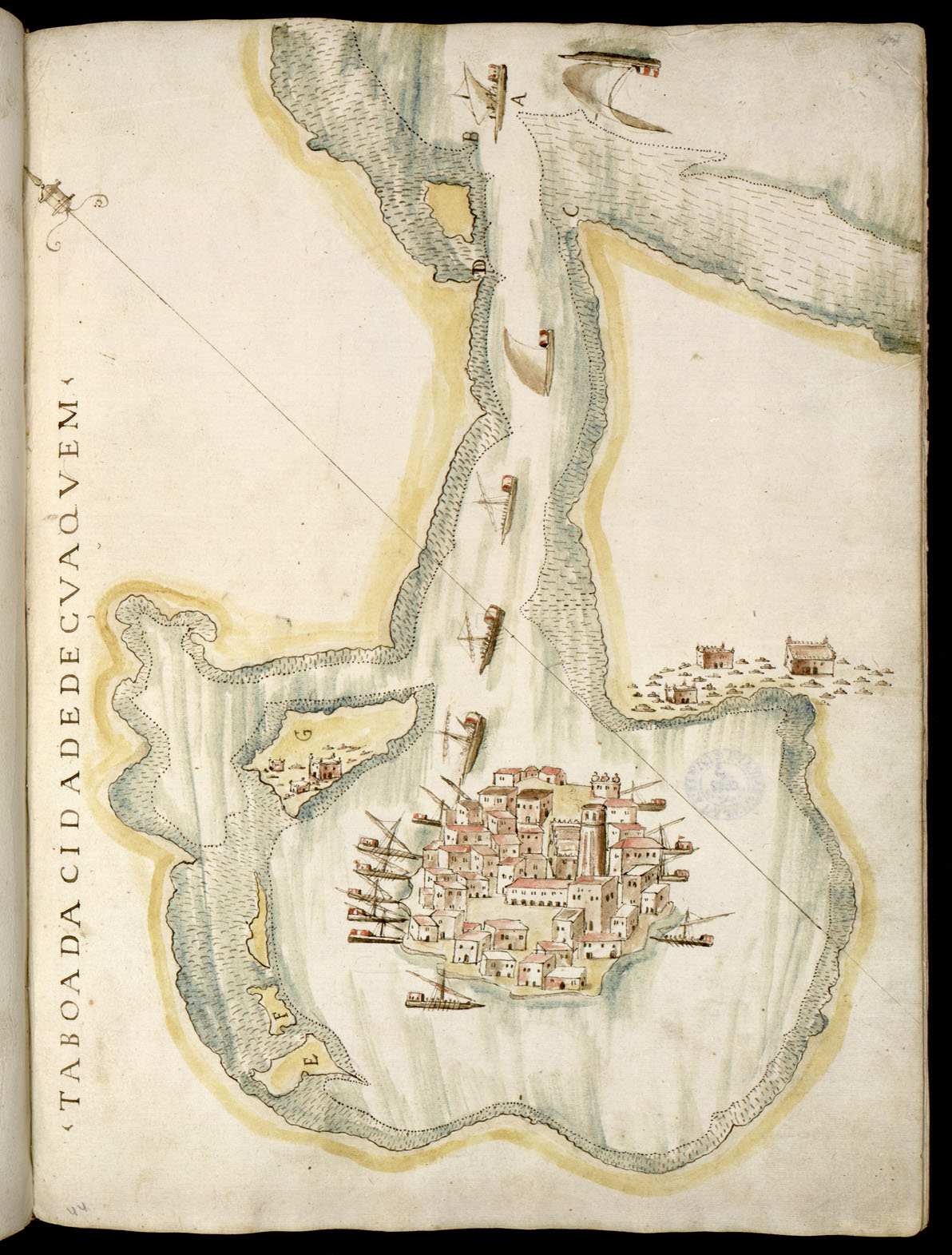
Suakin used to be considered the height of medieval luxury on the Red Sea, but the old city built of coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
is now in ruins. In 1983, the adjacent historic mainland town, known as the Geyf, had a population of 18,030 and the 2009 estimate is 43,337. Ferries run daily from Suakin to Jeddah
Jeddah ( ), also spelled Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; ar, , Jidda, ), is a city in the Hejaz region of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) and the country's commercial center. Established in the 6th century BC as a fishing village, Jeddah's pro ...
in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
.
Etymology
The Beja name for Suakin is Oosook. This is possibly from the Arabic word ''suq'', meaning market. In Beja, thelocative
In grammar, the locative case (abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which indicates a location. It corresponds vaguely to the English prepositions "in", "on", "at", and "by". The locative case belongs to the general local cases, together with the ...
case for this is ''isukib'', whence Suakin might have derived.Berg, RobertSuakin: Time and Tide
. ''Saudi Aramco World.'' The spelling on Admiralty charts in the late 19th century was "Sauakin", but in the popular press "Suakim" was predominant.
History
Ancient
Suakin was likelyPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's Port of Good Hope, Limen Evangelis, which is similarly described as lying on a circular island at the end of a long inlet. Under the Ptolemies and Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, though, the Red Sea's major port was Berenice
Berenice ( grc, Βερενίκη, ''Bereníkē'') is the Ancient Macedonian form of the Attic Greek name ''Pherenikē'', which means "bearer of victory" . Berenika, priestess of Demeter in Lete ca. 350 BC, is the oldest epigraphical evidence. ...
to the north. The growth of the Muslim caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
shifted trade first to the Hijaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provinc ...
and then to the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), me ...
.
Medieval
The collapse of theAbbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
s and growth of Fatimid Egypt changed this and Al-Qusayr and Aydhab became important emporia, trading with India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and ferrying African pilgrims to Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
. Suakin was first mentioned by name in the 10th century by al-Hamdani, who says it was already an ancient town. At that time, Suakin was a small Beja settlement, but it began to expand after the abandonment of the port of Badi to its south. The Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
and Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
drove more trade into the region: there are a number of references to Venetian merchants residing at Suakin and Massawa as early as the 14th century.
 One of Suakin's rulers, Ala al-Din al-Asba'ani, angered the
One of Suakin's rulers, Ala al-Din al-Asba'ani, angered the Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
sultan Baybars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak ...
by seizing the goods of merchants who died at sea nearby. In 1264, the governor of Qus and his general Ikhmin Ala al-Din attacked with the support of Aydhab. Al-Asba'ani was forced to flee the city. The continuing enmity between the two towns is testified to by reports that after the destruction of Aydhab by Sultan Barsbay in 1426, the refugees, who fled to Suakin instead of Dongola
Dongola ( ar, دنقلا, Dunqulā), also spelled ''Dunqulah'', is the capital of the state of Northern Sudan, on the banks of the Nile, and a former Latin Catholic bishopric (14th century). It should not be confused with Old Dongola, an ancien ...
, were all slaughtered.Dahl, Gudrun & al"Precolonial Beja: A Periphery at the Crossroads."
''Nordic Journal of African Studies'' 15(4): 473–498 (2006). The Beja were originally Christian. Despite the town's formal submission to the
Mamluks
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') i ...
in 1317, O. G. S. Crawford
Osbert Guy Stanhope Crawford (28 October 1886 – 28 November 1957) was a British archaeologist who specialised in the archaeology of prehistoric Britain and Sudan. A keen proponent of aerial archaeology, he spent most of his career as th ...
believed that the city remained a center of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
into the 13th century. Muslim immigrants such as the Banu Kanz Banu Kanz (), also known as Awlad Kanz, was a semi-nomadic Muslim dynasty of Arab descent that ruled the border region between Upper Egypt and Nubia between the 10th and 15th centuries. They were descended from the sons of sheikhs of the Arab Banu ...
gradually transformed this: Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
records that in 1332, there was a Muslim "sultan" of Suakin, al-Sharif Zaid ibn-Abi Numayy ibn-'Ajlan, who was the son of a Meccan sharif
Sharīf ( ar, شريف, 'noble', 'highborn'), also spelled shareef or sherif, feminine sharīfa (), plural ashrāf (), shurafāʾ (), or (in the Maghreb) shurfāʾ, is a title used to designate a person descended, or claiming to be descended, fr ...
. Following the region's inheritance laws, he had inherited the local leadership from his Bejan maternal uncles. In the fifteenth century, Suakin was briefly part of the Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din ...
. Suakin was sieged by the Portuguese in 1513 and captured briefly in 1541.
Ottoman

Ottoman sultan
The sultans of the Ottoman Empire ( tr, Osmanlı padişahları), who were all members of the Ottoman dynasty (House of Osman), ruled over the transcontinental empire from its perceived inception in 1299 to its dissolution in 1922. At its hei ...
Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite last ...
nominally added the port to the territory of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in 1517, though it was only loosely controlled, until the Ottoman province of Habesh was established in 1555 with the residence of its pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, gener ...
in Suakin. The Ottomans restored the two main mosques - Shafi'i
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
and Hanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named aft ...
, strengthened the walls of the fort and built new roads and buildings. As the Portuguese explorers
Portuguese maritime exploration resulted in the numerous territories and maritime routes recorded by the Portuguese as a result of their intensive maritime journeys during the 15th and 16th centuries. Portuguese sailors were at the vanguard of Eu ...
discovered and perfected the sea route around Africa and the Ottomans were unable to stop this trade, the local merchants began to abandon the town.
Some trade was kept up with the Sultanate of Sennar
The Funj Sultanate, also known as Funjistan, Sultanate of Sennar (after its capital Sennar) or Blue Sultanate due to the traditional Sudanese convention of referring to black people as blue () was a monarchy in what is now Sudan, northwestern E ...
, but by the 18th and 19th centuries, the Swiss traveler Johann Ludwig Burckhardt
Johann Ludwig (also known as John Lewis, Jean Louis) Burckhardt (24 November 1784 – 15 October 1817) was a Swiss traveller, geographer and Orientalist. Burckhardt assumed the alias ''Sheikh Ibrahim Ibn Abdallah'' during his travels in Arabia ...
found two-thirds of the homes in ruin. The Khedive
Khedive (, ota, خدیو, hıdiv; ar, خديوي, khudaywī) was an honorific title of Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.Adam Mestyan"Kh ...
Isma'il
Ismail ( ar, إِسْمَاعِيْل, ʾIsmāʿīl) is regarded as a prophet and messenger and the ancestor to the Ishmaelites in Islam. He is the son of Ibrahim (Abraham), born to Hajar (Hagar). Ismail is also associated with Mecca and th ...
received Suakin from the Ottomans in 1865 and attempted to revitalize it: Egypt built new houses, mills, mosques, hospitals, and a church for immigrant Copt
Copts ( cop, ⲛⲓⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ; ar, الْقِبْط ) are a Christians, Christian ethnoreligious group indigenous to North Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt and Sudan since Ancient history, antiqui ...
s.
British rule
The British Army was involved at Suakin in 1883 –1885 and Lord Kitchener was there in this period leading the Egyptian Army contingent. Suakin was his headquarters and his force survived a lengthy siege there. The Australian colonial forces ofVictoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
offered their torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of se ...
HMVS Childers
HMVS ''Childers'' was a torpedo boat of the Victorian Naval Forces, Commonwealth Naval Forces and the Royal Australian Navy.
Construction and acquisition
''Childers'', a first-class torpedo boat, was constructed for the colony of Victoria by Tho ...
and gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.
History Pre-steam ...
s HMVS Victoria HMVS ''Victoria'' is the name of two ships serving in the Victorian Naval Forces, the colonial navy of the colony of Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British ...
and HMVS Albert
HMVS ''Albert'' was a gunboat of the Victorian Naval Forces which was requisitioned for service with the Royal Australian Navy during World War I.
Operational history
HMVS ''Albert'' was built by Armstrong, Mitchell and Co. of Elswick, United K ...
, which arrived in Suakin on 19 March 1884 on their delivery voyage from Britain, only to be released as fighting had moved inland. They departed on 23 March, arriving in Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
on 25 June 1884. An essentially civilian military force of 770 men from New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, including some of the Naval Brigade, arrived in Suakin in March 1885 and served until mid-May.Before the Anzac Dawn: A military history of Australia before 1915Chapter 5: "Australian naval defence", Edited:
Craig Stockings
Craig Anthony John Stockings (born 1974) is an Australian historian with research interests in military and defence history. Since 2016, Stockings has been Official Historian and general editor of the '' Official History of Australian Operations ...
, John Connor (2013), accessed 23 June 2016
After the defeat of the Mahdist State
The Mahdist State, also known as Mahdist Sudan or the Sudanese Mahdiyya, was a state based on a religious and political movement launched in 1881 by Muhammad Ahmad bin Abdullah (later Muhammad al-Mahdi) against the Khedivate of Egypt, which had ...
, the British preferred to develop the new Port Sudan
Port Sudan ( ar, بور سودان, Būr Sūdān) is a port city in eastern Sudan, and the capital of the state of Red Sea. , it has 489,725 residents. Located on the Red Sea, Port Sudan is recognized as Sudan's main seaport and the source of 90% ...
, rather than engage in the extensive rebuilding and expansion that would have been necessary to make Suakin comparable. By 1922, the last of the British had left.21st century
SInce 2000, Sudan’s National Corporation for Antiquities and Museums has undertaken research and documented the history of Suakin, and in 2022, the online project Sudan Memory published historical photographs, architectural drawings and a3D reconstruction
In computer vision and computer graphics, 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance of real objects.
This process can be accomplished either by active or passive methods. If the model is allowed to change its shape i ...
of the town on its website.
On 17 January 2018, as part of a rapprochement with Sudan, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
was granted a 99-year lease over Suakin island. Turkey plans to restore the ruined Ottoman port city on the island.
Buildings of Suakin
A detailed description of the buildings of Suakin, including measured plans and detailed sketches, can be found in ''The Coral Buildings of Suakin: Islamic Architecture, Planning, Design and Domestic Arrangements in a Red Sea Port'' by Jean-Pierre Greenlaw,Kegan Paul
Charles Kegan Paul (8 March 1828 – 19 July 1902) was an English clergyman, publisher and author. He began his adult life as a clergyman of the Church of England, and served the Church for more than 20 years. His religious orientation moved fr ...
International, 1995, .
Climate
Suakin has a very hotdesert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
BWh) with brutally hot and humid, though dry, summers and very warm winters. Rainfall is minimal except from October to December, when easterly winds can give occasional downpours: in November 1965 as much as fell, but in the whole year from July 1981 to June 1982 no more than was recorded./ref>
References
Further reading
* Greenlaw, Jean-Pierre (1995) ''The Coral Buildings of Suakin: Islamic Architecture, Planning, Design and Domestic Arrangements in a Red Sea Port''.Kegan Paul
Charles Kegan Paul (8 March 1828 – 19 July 1902) was an English clergyman, publisher and author. He began his adult life as a clergyman of the Church of England, and served the Church for more than 20 years. His religious orientation moved fr ...
International,
*Um, Nancy"Greenlaw's Suakin: the limits of architectural representation and the continuing lives of buildings in Coastal Sudan." ''African Arts'', vol. 44, no. 4, 2011, p. 36+.
''Gale Literature Resource Center'' *Cooke, B. Kennedy, and B. Kennedy-Cooke. “The Red Sea coast in 1540.” ''Sudan Notes and Records'', vol. 16, no. 2, 1933, pp. 151–59,
External links
Comparative Vocabularies of the Languages Spoken at Suakin: Arabic, Hadendoa, Beni-Amer
A 3D reconstruction of the Island *https://observador.pt/2016/12/16/diogo-do-couto-o-portugues-da-india-ha-500-anos/ {{Authority control Populated places in Red Sea (state) Port cities and towns of the Red Sea Ramsar sites in Sudan Cities in Sudan