Stis Tris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) is a
The Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) is a
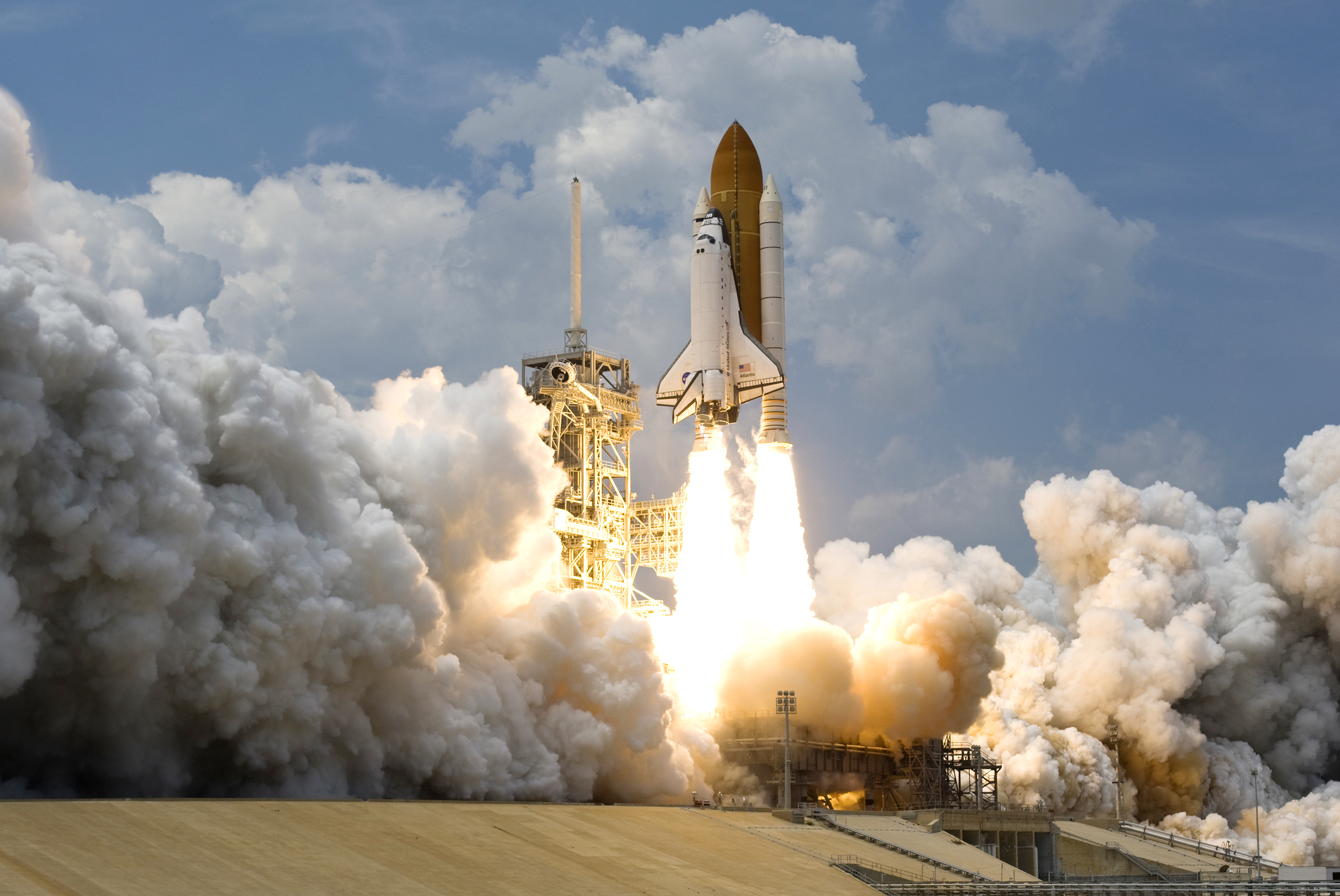 *February 14, 1997- STIS installed (
*February 14, 1997- STIS installed (
/ref> *August 3, 2004- STIS goes offline due to side-2 power-failure *2009- STIS repaired (
ESA/HubbleThe Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph
{{Use American English, date=January 2014 Hubble Space Telescope instruments Space science experiments Space imagers


 The Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) is a
The Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) is a spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
, also with a camera mode, installed on the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
. Aerospace engineer
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is si ...
Bruce Woodgate Bruce E. Woodgate (1939 – April 28, 2014) was a British-born American aerospace engineer, inventor and astronomer, who worked at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center for forty years.
He was the principal investigator of the Space Telescope Imagi ...
of the Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
was the principal investigator and creator of the STIS. It operated continuously from 1997 until a power supply failure in August 2004. After repairs, it began operating again in 2009. The spectrograph has made many important observations, including the first spectrum of the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
of an extrasolar planet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
, HD 209458b
HD 209458 b, which is also nicknamed Osiris after the Egyptian god, is an exoplanet that orbits the solar analog HD 209458 in the constellation Pegasus, some from the Solar System. The radius of the planet's orbit is , or one-eighth the radius ...
.
The STIS was installed on Hubble in 1997 during its second servicing mission (STS-82
STS-82 was the 22nd flight of the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' and the 82nd mission of the Space Shuttle program. It was NASA's second mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope, during which ''Discovery's'' crew repaired and upgraded the tel ...
) by Mark Lee and Steven Smith, replacing the High Resolution Spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
and the Faint Object Spectrograph
The Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS) was a spectrograph installed on the Hubble Space Telescope. It was replaced by the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph in 1997, and is now on display in the National Air and Space Museum in Washington DC.
FO ...
. It was designed to operate for five years. On August 3, 2004, an electronic failure rendered STIS inoperable, ending its use 2 years beyond its predicted lifespan. In order to bring it back to operational status, the instrument was repaired by space shuttle astronauts during STS-125
STS-125, or HST-SM4 (Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission 4), was the fifth and final Space Shuttle mission to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the last solo flight of the Space Shuttle Atlantis, Space Shuttle ''Atlantis''.
The launch of ...
, Servicing Mission 4, launched on May 11, 2009. The crew did a long (many hour) EVA to repair the instrument.
Design
STIS is both a spectrograph and an imaging camera, and is focused on ultraviolet light. The STIS has three 1024×1024 detector arrays. The first is acharge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
with a 52×52 arc-second field of view, covering the visible and near-infrared spectrum from 200 nm to 1030 nm.
The other two detectors are Multi-Anode Multichannel Arrays, each with a 25×25 arc-second field of view. One is Cs2Te, and covers the near-UV between 160 nm and 310 nm. The other is CsI and covers the far-UV between 115 nm and 170 nm.
Timeline
 *February 14, 1997- STIS installed (
*February 14, 1997- STIS installed (STS-82
STS-82 was the 22nd flight of the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' and the 82nd mission of the Space Shuttle program. It was NASA's second mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope, during which ''Discovery's'' crew repaired and upgraded the tel ...
)
* 2001, Switches to Side-2 electronics after a failure in side-1.''About STIS''/ref> *August 3, 2004- STIS goes offline due to side-2 power-failure *2009- STIS repaired (
STS-125
STS-125, or HST-SM4 (Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission 4), was the fifth and final Space Shuttle mission to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the last solo flight of the Space Shuttle Atlantis, Space Shuttle ''Atlantis''.
The launch of ...
)
* Operating on side-2 electronics with all optical and UV channels.
Selected discoveries and observations
On its 20th anniversary (1997-2017) NASA noted a selection of discoveries and/or observations conducted with STIS: *Survey of 20 galaxies to look for black holes *Study of theIntergalactic Medium
Intergalactic may refer to:
* "Intergalactic" (song), a song by the Beastie Boys
* ''Intergalactic'' (TV series), a 2021 UK science fiction TV series
* Intergalactic space
* Intergalactic travel, travel between galaxies in science fiction and sp ...
*Study of the Galactic Halo
A galactic halo is an extended, roughly spherical component of a galaxy which extends beyond the main, visible component. Several distinct components of galaxies comprise the halo:
* the stellar halo
* the galactic corona (hot gas, i.e. a plasma)
...
*Study of Interstellar Medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
*Chemical analysis of an atmosphere of an exoplanet
*Observations of a Dust Disk around Beta Pictoris
Beta Pictoris (abbreviated β Pictoris or β Pic) is the second brightest star in the constellation Pictor. It is located from the Solar System, and is 1.75 times as massive and 8.7 times as luminous as the Sun. The Beta Pictoris sy ...
*Study of massive stars in R136 (in the Tarantula Nebula
The Tarantula Nebula (also known as 30 Doradus) is a large H II region in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), forming its south-east corner (from Earth's perspective).
Discovery
The Tarantula Nebula was observed by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille durin ...
)
*Study of the star Eta Carinae
Eta Carinae (η Carinae, abbreviated to η Car), formerly known as Eta Argus, is a stellar system containing at least two stars with a combined luminosity greater than five million times that of the Sun, located around distant in t ...
*Study of Supernova 1987A
SN 1987A was a type II supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It occurred approximately from Earth and was the closest observed supernova since Kepler's Supernova. 1987A's light reached Earth on Febr ...
*Study of flows from an Active Galaxy
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that has a much-higher-than-normal luminosity over at least some portion of the electromagnetic spectrum with characteristics indicating that the luminosity is not prod ...
See also
Other Hubble instruments : *Advanced Camera for Surveys
The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) is a third-generation axial instrument aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The initial design and scientific capabilities of ACS were defined by a team based at Johns Hopkins University. ACS was assembl ...
*Cosmic Origins Spectrograph
The Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) is a science instrument that was installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during Servicing Mission 4 (STS-125) in May 2009. It is designed for ultraviolet (90–320 nm) spectroscopy of faint point sources w ...
*Faint Object Camera
The Faint Object Camera (FOC) was a camera installed on the Hubble Space Telescope from launch in 1990 until 2002. It was replaced by the Advanced Camera for Surveys. In December 1993, Hubble's vision was corrected on STS-61 by installing COSTAR ...
*Faint Object Spectrograph
The Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS) was a spectrograph installed on the Hubble Space Telescope. It was replaced by the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph in 1997, and is now on display in the National Air and Space Museum in Washington DC.
FO ...
*Goddard High Resolution Spectrograph
The Goddard High Resolution Spectrograph (GHRS or HRS) was an ultraviolet spectrograph installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during its original construction, and it was launched into space as part of that space telescope aboard the Space Shuttl ...
*Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer
The Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) is a scientific instrument for infrared astronomy, installed on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), operating from 1997 to 1999, and from 2002 to 2008. Images produced by NICMOS contain ...
*Wide Field and Planetary Camera
The Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WFPC) (pronounced as wiffpick (Operators of the WFPC1 were known as "whiff-pickers")) was a camera installed on the Hubble Space Telescope launched in April 1990 and operated until December 1993. It was one of ...
*Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2
The Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) is a camera formerly installed on the Hubble Space Telescope. The camera was built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and is roughly the size of a baby grand piano. It was installed by servicing mission ...
*Wide Field Camera 3
The Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) is the Hubble Space Telescope's last and most technologically advanced instrument to take images in the visible spectrum. It was installed as a replacement for the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 during the first s ...
References
External links
ESA/Hubble
{{Use American English, date=January 2014 Hubble Space Telescope instruments Space science experiments Space imagers