Sterling Crisis (1976) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
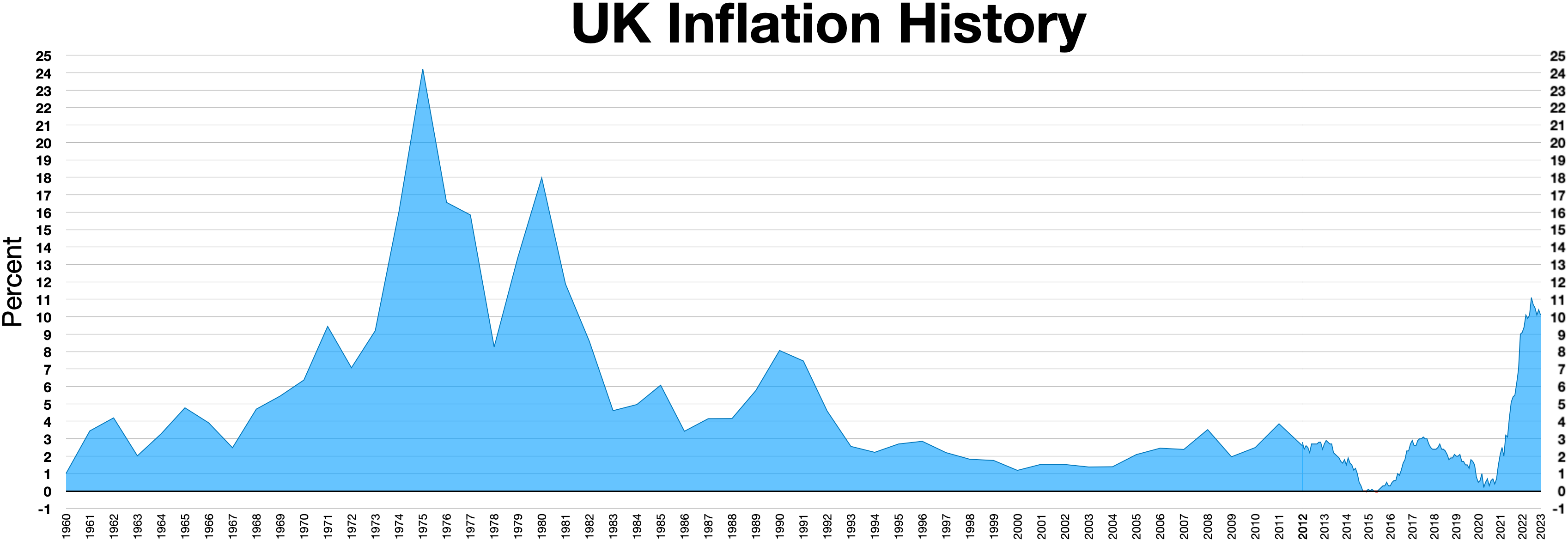
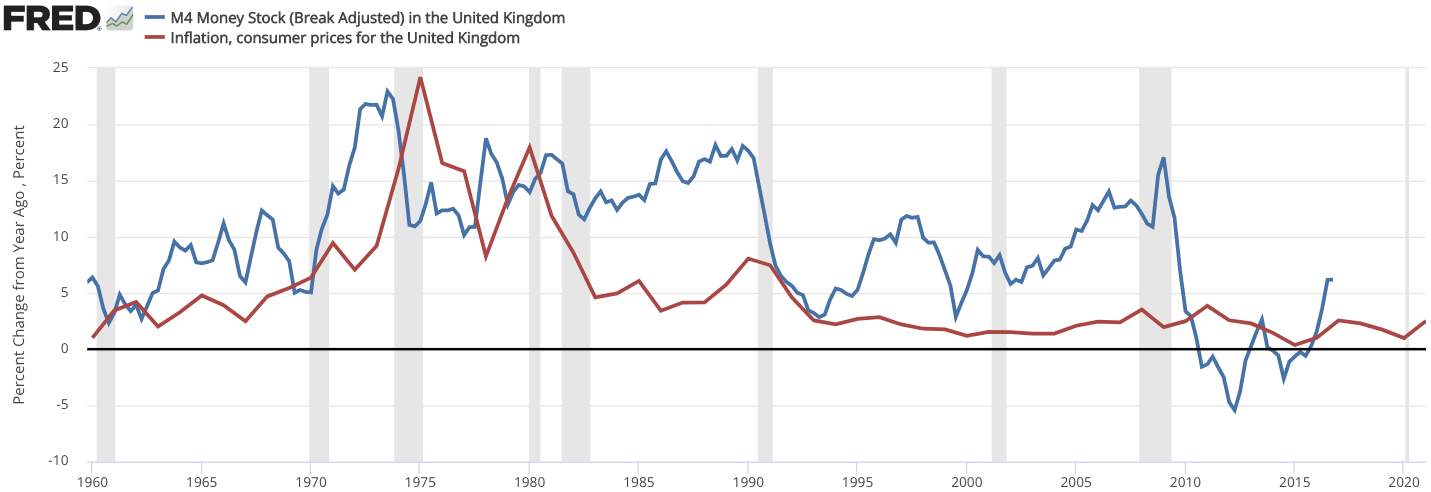
 The 1976 sterling crisis was a currency crisis in the United Kingdom. Inflation (at close to 25% in 1975, causing high bond yields and borrowing costs), a
The 1976 sterling crisis was a currency crisis in the United Kingdom. Inflation (at close to 25% in 1975, causing high bond yields and borrowing costs), a

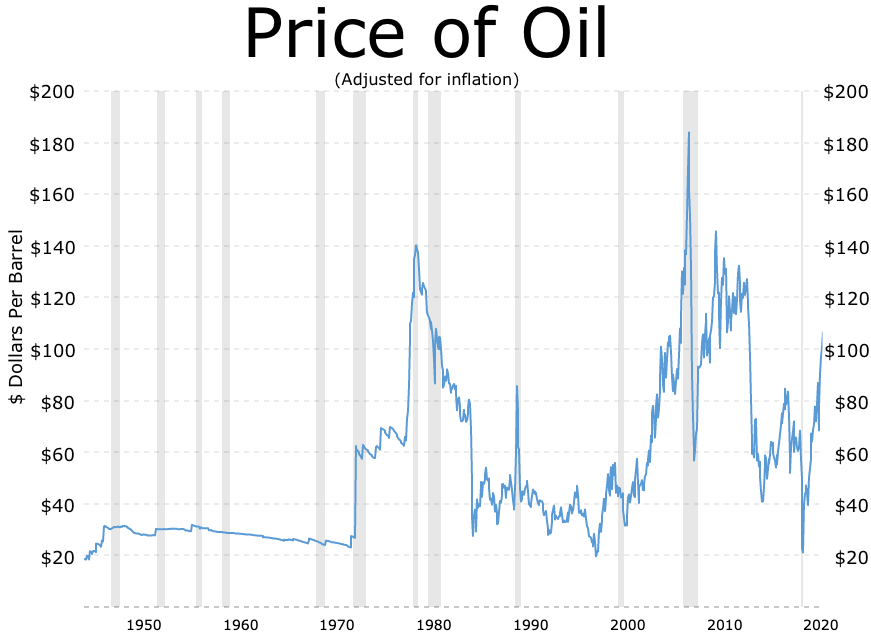 Initiation of the inflationary cycle is traced to
Initiation of the inflationary cycle is traced to


 The 1976 sterling crisis was a currency crisis in the United Kingdom. Inflation (at close to 25% in 1975, causing high bond yields and borrowing costs), a
The 1976 sterling crisis was a currency crisis in the United Kingdom. Inflation (at close to 25% in 1975, causing high bond yields and borrowing costs), a balance of payments
In international economics, the balance of payments (also known as balance of international payments and abbreviated BOP or BoP) of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time (e.g., a ...
deficit, a public spending deficit, and the 1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
were contributors.
The origins of the crisis are traced to the 1972 Conservative "spend for growth" budget that initiated the inflation cycle.
James Callaghan
Leonard James Callaghan, Baron Callaghan of Cardiff, ( ; 27 March 191226 March 2005), commonly known as Jim Callaghan, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1976 to 1979 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1976 to 1980. Callaghan is ...
's Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
government had to borrow $3.9 billion from the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
(IMF), with the intention of maintaining the value of sterling. At the time this was the largest loan ever to have been requested from the IMF.
History

 Initiation of the inflationary cycle is traced to
Initiation of the inflationary cycle is traced to Anthony Barber
Anthony Perrinott Lysberg Barber, Baron Barber, (4 July 1920 – 16 December 2005) was a British Conservative politician who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1970 to 1974.
After serving in both the Territorial Army and the Royal A ...
's 1972 budget which was designed to return the Conservatives to power in an election expected in 1974 or 1975. This budget led to a brief period growth known as "The Barber Boom," followed by a wage-price spiral, high inflation and currency depreciation, culminating in the 1976 sterling crisis. Barber was forced to introduce anti-inflation measures, along with a Price Commission
The Price Commission was set up in the UK under the Counter-Inflation Act 1973, alongside the Pay Board, in an attempt to control inflation. The Conservative government of Edward Heath, elected at the 1970 general election, had previously aboli ...
and a Pay Board
The Price Commission was set up in the UK under the Counter-Inflation Act 1973, alongside the Pay Board, in an attempt to control inflation. The Conservative government of Edward Heath, elected at the 1970 general election, had previously aboli ...
. The Conservatives lost the 1974 general election to Harold Wilson
James Harold Wilson, Baron Wilson of Rievaulx, (11 March 1916 – 24 May 1995) was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from October 1964 to June 1970, and again from March 1974 to April 1976. He ...
's Labour Party.
The crisis came to a head during James Callaghan
Leonard James Callaghan, Baron Callaghan of Cardiff, ( ; 27 March 191226 March 2005), commonly known as Jim Callaghan, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1976 to 1979 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1976 to 1980. Callaghan is ...
's term as Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
, and caused the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
to withdraw temporarily from the foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspec ...
. After the defeat of the public expenditure
Public expenditure is spending made by the government of a country on collective needs and wants, such as pension, provisions, security, infrastructure, etc. Until the 19th century, public expenditure was limited as laissez faire philosophies be ...
white paper
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. A white paper ...
in the House of Commons in March 1976 and the resignation of Harold Wilson
James Harold Wilson, Baron Wilson of Rievaulx, (11 March 1916 – 24 May 1995) was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from October 1964 to June 1970, and again from March 1974 to April 1976. He ...
, many investors became convinced sterling would soon lose value due to inflation. By June 1976, the pound had reached a record low against the dollar.
British ally to Israel during Arab-Israeli Conflicts
In 1967, theSuez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
closed down for eight years following the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
of that year, when Israel took and occupied the Sinai Peninsula for 15 years. That triggered the 1967 Oil Embargo
The 1967 Oil Embargo began on June 6, 1967, the second day of the Six-Day War, with a joint Arab decision to deter any countries from supporting Israel militarily. Several Middle Eastern countries eventually limited their oil shipments, some emba ...
, which only lasted a few months. In 1966, the year before it closed, 20% of all world oil cargo tonnage passed through the canal, with most of it heading north for Europe.
In 1973, the Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was an armed conflict fought from October 6 to 25, 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egy ...
was fought, with Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
crossing the Suez Canal aiming to take back the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a l ...
from Israel. This triggered the 1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
and embargo. Britain was an ally to Israel during the Arab–Israeli conflict
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by the ...
. The oil crisis presented a severe economic shock to Britain, which it was ill-placed to withstand.
Outcome
Only half of the loan was actually drawn by the British government and it was repaid by 4 May 1979, the day after the general election.Denis Healey
Denis Winston Healey, Baron Healey, (30 August 1917 – 3 October 2015) was a British Labour Party (UK), Labour politician who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1974 to 1979 and as Secretary of State for Defence from 1964 to 1970; he ...
, the Chancellor of the Exchequer at the time, went on to state that the main reason the loan had to be requested was that public sector borrowing requirement figures provided by the Treasury
A treasury is either
*A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry.
*A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be state or royal property, church treasure or in p ...
were grossly overstated.
The IMF loan meant that the United Kingdom's economy could be stabilised whilst drastic budget cuts were implemented. Despite the security provided by the loan, the Labour Party had already begun separating into social democratic
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote soci ...
and more socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
camps, causing bitter rows inside the party and with the trades unions
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
. Some believe the sterling crisis and IMF bailout may have contributed significantly to Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of the Conservative Party from 1975 to 1990. S ...
's 1979 Conservative victory.
See also
* * * * * Sterling crisis, other currency crises in British history * *Closure of the Suez Canal (1967–1975)
On 6 June 1967 the Suez Canal was closed shortly after the start of the Six-Day War or Third Arab–Israeli War. Israel bombed most of Egypt's airfields and then entered and occupied the Sinai Peninsula, all the way to the Suez Canal, for 15 yea ...
shortly after the start of the "Six-Day War" or Third Arab–Israeli War
*
*
Notes
References
Further reading
* Burk, Kathleen. "1976 IMF Crisis." (1989): 39–45. *Ludlam, Steve. "The gnomes of Washington: Four myths of the 1976 IMF crisis." Political Studies 40.4 (1992): 713–727. *Wass, Douglas. Decline to Fall: The Making of British Macro-economic Policy and the 1976 IMF Crisis. Oxford University Press, 2008. * * * {{James Callaghan, state=collapsed 1976 in economics 1976 in the United KingdomIMF crisis
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
Economic history of the United Kingdom
International Monetary Fund
History of pound sterling