Statute Miles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

and is thus also known as the "geographical mile", although the geographical mile is now a separate standard unit.
 The Scots mile was longer than the English mile, as mentioned by
The Scots mile was longer than the English mile, as mentioned by
(16 June 1685). ''APS'' viii: 494, c.59. '' RPS'' 1685/4/83. again by the 1707
 The Irish mile (' or ') measured 2,240 yards: approximately 1.27 statute miles or 2.048 kilometres. It was used in Ireland from the 16th century plantations until the 19th century, with residual use into the 20th century. The units were based on " English measure" but used a
The Irish mile (' or ') measured 2,240 yards: approximately 1.27 statute miles or 2.048 kilometres. It was used in Ireland from the 16th century plantations until the 19th century, with residual use into the 20th century. The units were based on " English measure" but used a
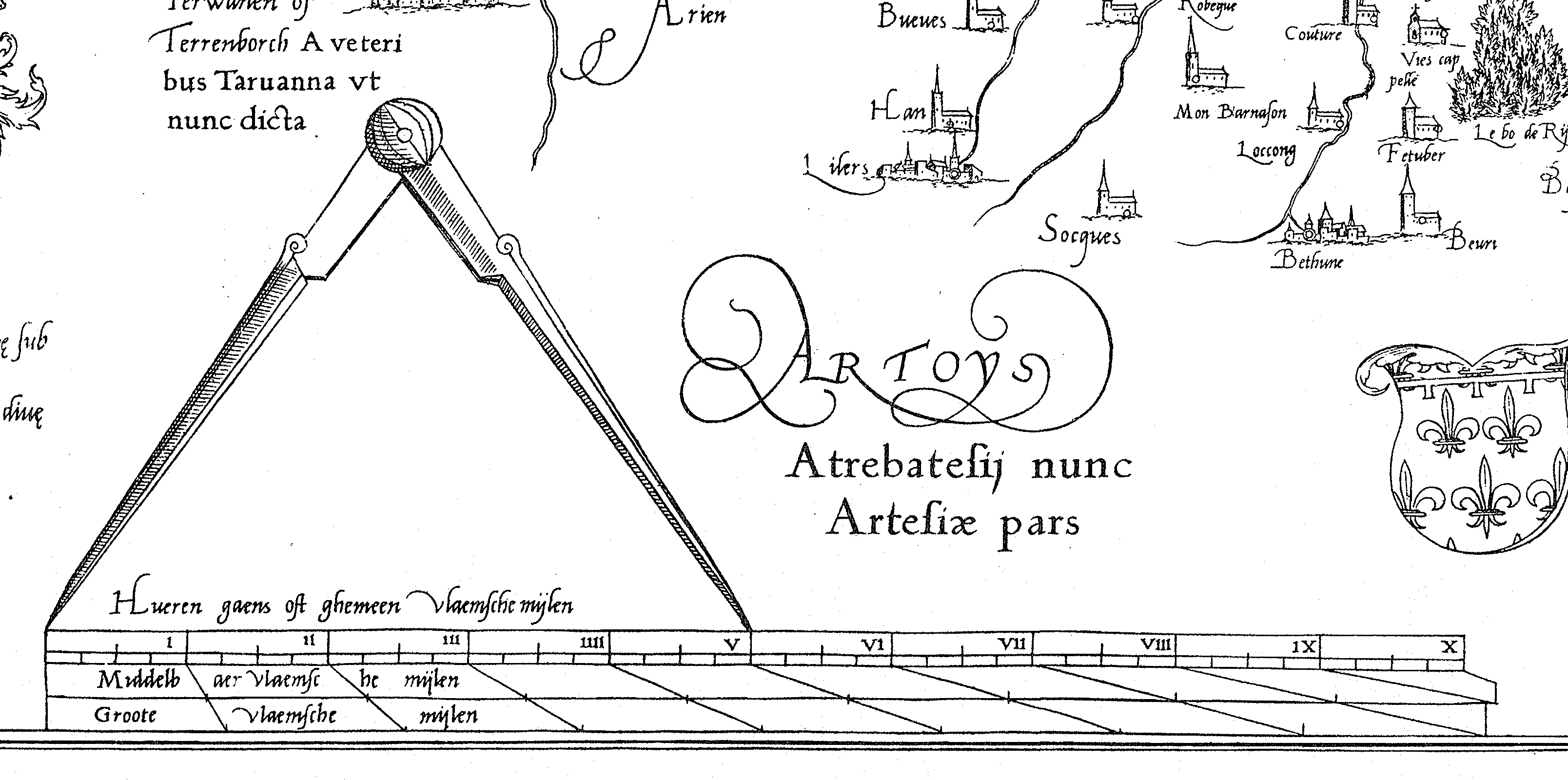 The Dutch mile () has had different definitions throughout history. One of the older definitions was 5,600 ells. But the length of an ell was not standardised, so that the length of a mile could range between 3,280 m and 4,280 m. The Dutch mile also has had historical definitions of one hour's walking (), which meant around 5 km, or 20,000 Amsterdam or Rhineland feet (respectively 5,660 m or 6,280 m). Besides the common Dutch mile, there is also the geographical mile. 15 geographical Dutch miles equal one degree of
The Dutch mile () has had different definitions throughout history. One of the older definitions was 5,600 ells. But the length of an ell was not standardised, so that the length of a mile could range between 3,280 m and 4,280 m. The Dutch mile also has had historical definitions of one hour's walking (), which meant around 5 km, or 20,000 Amsterdam or Rhineland feet (respectively 5,660 m or 6,280 m). Besides the common Dutch mile, there is also the geographical mile. 15 geographical Dutch miles equal one degree of
 The German mile () was 24,000 German feet. The standardised Austrian mile used in southern Germany and the
The German mile () was 24,000 German feet. The standardised Austrian mile used in southern Germany and the
 The ''nautical mile'' was originally defined as one
The ''nautical mile'' was originally defined as one
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and
style holds that "there is no acceptable abbreviation for 'miles'" and so it should be spelled out when used in describing areas.
United States customary unit
United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and U.S. territories since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system (USCS or USC) developed from English units ...
of distance; both are based on the older English unit
English units are the units of measurement used in England up to 1826 (when they were replaced by Imperial units), which evolved as a combination of the Anglo-Saxon and Roman systems of units. Various standards have applied to English units at d ...
of length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the Interna ...
equal to 5,280 English feet
The foot ( feet), standard symbol: ft, is a unit of length in the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. The prime symbol, , is a customarily used alternative symbol. Since the International Yard and Po ...
, or 1,760 yards
The yard (symbol: yd) is an English unit of length in both the British imperial and US customary systems of measurement equalling 3 feet or 36 inches. Since 1959 it has been by international agreement standardized as exactly 0.914 ...
. The statute mile was standardised between the British Commonwealth and the United States by an international agreement in 1959, when it was formally redefined with respect to SI units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes Pleonasm#Acronyms and initialisms, pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most wid ...
as exactly .
With qualifiers, ''mile'' is also used to describe or translate a wide range of units derived from or roughly equivalent to the Roman mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 Engli ...
, such as the nautical mile
A nautical mile is a unit of length used in air, marine, and space navigation, and for the definition of territorial waters. Historically, it was defined as the meridian arc length corresponding to one minute ( of a degree) of latitude. Today ...
(now exactly), the Italian mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
(roughly ), and the Chinese mile
''Li'' (, ''lǐ'', or , ''shìlǐ''), also known as the Chinese mile, is a traditional Chinese unit of distance. The li has varied considerably over time but was usually about one third of an English mile and now has a standardized length of ...
(now exactly). The Romans divided their mile into 5,000 Roman feet
The ancient Roman units of measurement were primarily founded on the Hellenic system, which in turn was influenced by the Egyptian system and the Mesopotamian system. The Roman units were comparatively consistent and well documented.
Length
...
but the greater importance of furlongs in Elizabethan-era England meant that the statute mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 Engli ...
was made equivalent to or in 1593. This form of the mile then spread across the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, some successor states of which continue to employ the mile. The US Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, an ...
now employs the metre for official purposes, but legacy data from its 1927 geodetic datum has meant that a separate US survey mile continues to see some use, although it was officially phased out in 2022. While most countries replaced the mile with the kilometre when switching to the International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
(SI), the international mile continues to be used in some countries, such as Liberia, the United Kingdom, the United States, and a number of countries with fewer than one million inhabitants, most of which are UK or US territories or have close historical ties with the UK or US.
Name
The modern English word ''mile'' derives fromMiddle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
' and Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
', which was cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
with all other Germanic terms for ''miles''. These derived from the nominal ellipsis form of ' 'mile' or ' 'miles', the Roman mile of one thousand pace
Pace or paces may refer to:
Business
*Pace (transit), a bus operator in the suburbs of Chicago, US
* Pace Airlines, an American charter airline
*Pace Foods, a maker of a popular brand of salsa sold in North America, owned by Campbell Soup Compan ...
s.
The present international mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
is usually what is understood by the unqualified term ''mile''. When this distance needs to be distinguished from the nautical mile, the international mile may also be described as a land mile or statute mile. In British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
, ''statute mile'' may refer to the present international mile or to any other form of English mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
since the 1593 Act of Parliament, which set it as a distance of . Under American law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the most important is the nation's Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the federal government of the United States, as well as va ...
, however, ''statute mile'' refers to the US survey mile. Foreign and historical units translated into English as ''miles'' usually employ a qualifier to describe the kind of mile being used but this may be omitted if it is obvious from the context, such as a discussion of the 2nd-century Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary ( la, Itinerarium Antonini Augusti, "The Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is a famous ''itinerarium'', a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly ...
describing its distances in terms of ''miles'' rather than ''Roman miles''.
Abbreviation
The mile has been variously abbreviated in English—with and without a trailing period—as "mi", "M", "ml", and "m". The AmericanNational Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
now uses and recommends "mi" to avoid confusion with the SI metre (m) and millilitre (ml). However, derived units such as miles per hour
Miles per hour (mph, m.p.h., MPH, or mi/h) is a British imperial and United States customary unit of speed expressing the number of miles travelled in one hour. It is used in the United Kingdom, the United States, and a number of smaller cou ...
or miles per gallon
The fuel economy of an Car, automobile relates distance traveled by a vehicle and the amount of fuel consumption, fuel consumed. Consumption can be expressed in terms of volume of fuel to travel a distance, or the distance traveled per unit volu ...
continue to be abbreviated as "mph" and "mpg" rather than "mi/h" and "mi/gal". In the United Kingdom, road signs
Traffic signs or road signs are signs erected at the side of or above roads to give instructions or provide information to road users. The earliest signs were simple wooden or stone milestones. Later, signs with directional arms were introduce ...
use "m" as the abbreviation for mile though height and width restrictions also use "m" as the symbol for the metre, which may be displayed alongside feet and inches. The BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Historical
Roman
TheRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
mile (', "thousand paces"; m.p.; also ' and ') consisted of a thousand pace
Pace or paces may refer to:
Business
*Pace (transit), a bus operator in the suburbs of Chicago, US
* Pace Airlines, an American charter airline
*Pace Foods, a maker of a popular brand of salsa sold in North America, owned by Campbell Soup Compan ...
s as measured by every other step—as in the total distance of the left foot hitting the ground 1,000 times. The ancient Roman
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
s, marching their armies through uncharted territory, would often push a carved stick in the ground after each 1,000 paces. Well-fed and harshly driven Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of ...
aries in good weather thus created longer miles. The distance was indirectly standardised by Agrippa Agrippa may refer to:
People Antiquity
* Agrippa (mythology), semi-mythological king of Alba Longa
* Agrippa (astronomer), Greek astronomer from the late 1st century
* Agrippa the Skeptic, Skeptic philosopher at the end of the 1st century
* Agri ...
's establishment of a standard Roman foot
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
(Agrippa's own) in 29 BC, and the definition of a pace as 5 feet. An Imperial Roman mile thus denoted 5,000 Roman feet
The ancient Roman units of measurement were primarily founded on the Hellenic system, which in turn was influenced by the Egyptian system and the Mesopotamian system. The Roman units were comparatively consistent and well documented.
Length
...
. Surveyors and specialised equipment such as the decempeda
A measuring rod is a tool used to physically measure lengths and survey areas of various sizes. Most measuring rods are round or square sectioned; however, they can also be flat boards. Some have markings at regular intervals. It is likely tha ...
and dioptra
A dioptra (sometimes also named dioptre or diopter, from el, διόπτρα) is a classical astronomical and surveying instrument, dating from the 3rd century BC. The dioptra was a sighting tube or, alternatively, a rod with a sight at ...
then spread its use.
In modern times, Agrippa's Imperial Roman mile was empirically estimated to have been about in length, slightly less than the of the modern international mile.
In Hellenic areas of the Empire, the Roman mile ( grc-gre, μίλιον, ''mílion'') was used beside the native Greek units Ancient Greek units of measurement varied according to location and epoch. Systems of ancient weights and measures evolved as needs changed; Solon and other lawgivers also reformed them ''en bloc''. Some units of measurement were found to be conveni ...
as equivalent to 8 stadia
Stadia may refer to:
* One of the plurals of stadium, along with "stadiums"
* The plural of stadion, an ancient Greek unit of distance, which equals to 600 Greek feet (''podes'').
* Stadia (Caria), a town of ancient Caria, now in Turkey
* Stadi ...
of 600 Greek feet
The pous ( podes; grc-gre, ποῦς, ''poûs'') or Greek foot ( feet) was a Greek unit of length. It had various subdivisions whose lengths varied by place and over time. 100 podes made up one plethron, 600 podes made up a stade (the ...
. The ''mílion'' continued to be used as a Byzantine unit and was also used as the name of the zero mile marker
In many countries, kilometre zero (also written ''km 0'') or similar terms in other languages (also known as zero mile marker, zero milepost, control stations or control points) denote a particular location (usually in the nation's capital cit ...
for the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, the Milion
The Milion ( grc-gre, Μίλιον or , ''Míllion''; tr, Milyon taşı) was a monument erected in the early 4th century AD in Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, Turkey). It was the Byzantine zero-mile marker, the starting-place for the measu ...
, located at the head of the Mese near Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
.
The Roman mile also spread throughout Europe, with its local variations giving rise to the different units below.
Also arising from the Roman mile is the milestone
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway line, canal or boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks; or they can give their position on the route relative to so ...
. All roads radiated out from the Roman Forum
The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum ( it, Foro Romano), is a rectangular forum (plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancient ...
throughout the Empire – 50,000 (Roman) miles of stone-paved roads. At every mile was placed a shaped stone. Originally these were obelisks
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by An ...
made from granite, marble, or whatever local stone was available. On these was carved a Roman numeral
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ...
, indicating the number of miles from the centre of Rome – the Forum. Hence, one always knew how far one was from Rome.
Italian
TheItalian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
mile (', ') was traditionally considered a direct continuation of the Roman mile, equal to 1000 paces, although its actual value over time or between regions could vary greatly. It was often used in international contexts from the Middle Ages into the 17th century1and is thus also known as the "geographical mile", although the geographical mile is now a separate standard unit.
Arabic
TheArabic mile
The Arab, Arabic, or Arabian mile ( ar, الميل, ''al-mīl'') was a historical Arabic unit of length. Its precise length is disputed, lying between 1.8 and 2.0 km. It was used by medieval Arab geographers and astronomers. The predecessor of ...
(, ''al-mīl'') was not the common Arabic unit The Ancient Arabic unit of measurements were a system of using units to associate with physical quantities. Arabic symbols are used to represent the values. The measurements were based on body measurements and common natural items. The length of for ...
of length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the Interna ...
; instead, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
and Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
traditionally used the longer parasang
The parasang is a historical Iranian unit of walking distance, the length of which varied according to terrain and speed of travel. The European equivalent is the league. In modern terms the distance is about 3 or 3½ miles (4.8 or 5.6 km).
His ...
or "Arabic league
League or The League may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Leagues'' (band), an American rock band
* ''The League'', an American sitcom broadcast on FX and FXX about fantasy football
Sports
* Sports league
* Rugby league, full contact footba ...
". The Arabic mile was, however, used by medieval geographers
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire an ...
and scientists and constituted a kind of precursor to the nautical
Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."
It involves topics a ...
or geographical mile. It extended the Roman mile to fit an astronomical
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies ...
approximation of 1 arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
measured directly north-and-south along a meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
. Although the precise value of the approximation remains disputed, it was somewhere between 1.8 and 2.0 km.
English
The "oldEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
mile" of the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
and early modern periods varied but seems to have measured about 1.3 international miles (2.1 km). The old English mile varied over time and location within England. The old English mile has also been defined as 79,200 or 79,320 inches (1.25 or 1.2519 statute miles). The English long continued the Roman computations of the mile as 5000 feet, 1000 paces
A pace is a unit of length consisting either of one normal walking step (approximately ), or of a double step, returning to the same foot (approximately ). The normal pace length decreases with age and some health conditions. The word "pace" is al ...
, or 8 longer divisions, which they equated with their "furrow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
's length" or furlong
A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one eighth of a mile, equivalent to 660 feet, 220 yards, 40 rods, 10 chains or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in hors ...
.
The origins of English units are "extremely vague and uncertain", but seem to have been a combination of the Roman system with native British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and Germanic systems both derived from multiples of the barleycorn. Probably by the reign of Edgar
Edgar is a commonly used English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Eadgar'' (composed of '' ead'' "rich, prosperous" and ''gar'' "spear").
Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the later medieval period; it was, however, rev ...
in the 10th century, the nominal prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
physical standard of English length was an arm-length iron bar (a yardstick) held by the king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
at Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
; the foot was then one-third of its length. Henry I was said to have made a new standard in 1101 based on his own arm. Following the issuance of Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
, the baron
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than a lord or knig ...
s of Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
directed John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
and his son to keep the king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
's standard measure (') and weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a Euclidean vector, vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weigh ...
at the Exchequer
In the civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty’s Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's ''current account'' (i.e., money held from taxation and other government reven ...
, which thereafter verified local standards until its abolition in the 19th century. New brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other with ...
standards are known to have been constructed under Henry VII and Elizabeth I.
Arnold's ''Customs of London'' recorded a mile shorter than previous ones, coming to 0.947 international miles (5000 feet) or 1.524 km.
Statute
The English statute mile was established by aWeights and Measures
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multi ...
Act of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of ...
in 1593 during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I. The act on the Composition of Yards and Perches
The Composition of Yards and Perches ( la, Compositio Ulnarum et Perticarum) or the Statute of Ells and Perches was a medieval English statute defining the length of the barleycorn, inch, foot, yard, and perch, as well as the area of the acre. It ...
had shortened the length of the foot and its associated measures, causing the two methods of determining the mile to diverge. Owing to the importance of the surveyor's rod in deeds and surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ca ...
undertaken under Henry VIII, decreasing the length of the rod by would have amounted to a significant tax
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or n ...
increase. Parliament instead opted to maintain the mile of 8 furlongs
A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one eighth of a mile, equivalent to 660 feet, 220 yards, 40 rods, 10 chains or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in hors ...
(which were derived from the rod) and to increase the number of feet per mile from the old Roman value. The applicable passage of the statute reads: "A Mile shall contain eight Furlongs, every Furlong forty Poles, and every Pole shall contain sixteen Foot and half." The statute mile therefore contained 5,280 feet or 1,760 yards. The distance was not uniformly adopted. Robert Morden
Robert Morden (c. 1650 – 1703) was an English bookseller, publisher, and mapmaker, globemaker and engraver.
He was among the first successful commercial map makers.
Between about 1675 and his death in 1703, he was based under the sign of the ...
had multiple scales on his 17th-century maps which included continuing local values: his map of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English citi ...
, for example, bore two different "miles" with a ratio of and his map of Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset (unitary authority), Dors ...
had three scales with a ratio of . In both cases, the traditional local units remained longer than the statute mile. The English statute mile was superseded in 1959 by the international mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
by international agreement.
Welsh
TheWelsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
mile (' or ') was 3 mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
s and 1,470 yards long (6.17 km). It comprised 9,000 pace
Pace or paces may refer to:
Business
*Pace (transit), a bus operator in the suburbs of Chicago, US
* Pace Airlines, an American charter airline
*Pace Foods, a maker of a popular brand of salsa sold in North America, owned by Campbell Soup Compan ...
s ('), each of 3 Welsh feet
Welsh units of measurement are those in use in Wales between the Sub-Roman period (prior to which the Britons used Roman units) and the 13th-century Edwardian conquest (after which English units were imposed). Modern Wales no longer employs these ...
(') of 9 inches ('). (The Welsh inch is usually reckoned as equivalent to the English inch.) Along with other Welsh units
Welsh units of measurement are those in use in Wales between the Sub-Roman period (prior to which the Britons used Roman units) and the 13th-century Edwardian conquest (after which English units were imposed). Modern Wales no longer employs the ...
, it was said to have been codified under Dyfnwal the Bald and Silent and retained unchanged by Hywel the Good
Hywel Dda, sometimes anglicised as Howel the Good, or Hywel ap Cadell (died 949/950) was a king of Deheubarth who eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubarth ...
. Along with other Welsh units, it was discontinued following the conquest
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
by the English under Edward I in the 13th century.
Scots
Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 175921 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the best known of the poets who hav ...
in the first verse of his poem " Tam o' Shanter". It comprised 8 (Scots) furlongs divided into 320 fall
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September (Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Southe ...
s or faws (Scots rods). It varied from place to place but the most accepted equivalencies are 1,976 Imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texa ...
yards (1.123 statute mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 Engli ...
s or 1.81 km).
It was legally abolished three times: first by a 1685 act of the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
,Act for a standard of miles(16 June 1685). ''APS'' viii: 494, c.59. '' RPS'' 1685/4/83. again by the 1707
Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new state of Great Britain, stating that the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland were to be "United i ...
with England, and finally by the Weights and Measures Act 1824
Weights and measures acts are acts of the British Parliament determining the regulation of weights and measures. It also refers to similar royal and parliamentary acts of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland and the medieval Welsh states. ...
. It had continued in use as a customary unit through the 18th century but had become obsolete by its final abolition.
Irish
 The Irish mile (' or ') measured 2,240 yards: approximately 1.27 statute miles or 2.048 kilometres. It was used in Ireland from the 16th century plantations until the 19th century, with residual use into the 20th century. The units were based on " English measure" but used a
The Irish mile (' or ') measured 2,240 yards: approximately 1.27 statute miles or 2.048 kilometres. It was used in Ireland from the 16th century plantations until the 19th century, with residual use into the 20th century. The units were based on " English measure" but used a linear perch
The rod, perch, or pole (sometimes also lug) is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions, often between approximately 3 and 8 meters (9 ft 10 in and 26 ft 2 in). In modern US customary units ...
measuring as opposed to the English rod of .
Dutch
 The Dutch mile () has had different definitions throughout history. One of the older definitions was 5,600 ells. But the length of an ell was not standardised, so that the length of a mile could range between 3,280 m and 4,280 m. The Dutch mile also has had historical definitions of one hour's walking (), which meant around 5 km, or 20,000 Amsterdam or Rhineland feet (respectively 5,660 m or 6,280 m). Besides the common Dutch mile, there is also the geographical mile. 15 geographical Dutch miles equal one degree of
The Dutch mile () has had different definitions throughout history. One of the older definitions was 5,600 ells. But the length of an ell was not standardised, so that the length of a mile could range between 3,280 m and 4,280 m. The Dutch mile also has had historical definitions of one hour's walking (), which meant around 5 km, or 20,000 Amsterdam or Rhineland feet (respectively 5,660 m or 6,280 m). Besides the common Dutch mile, there is also the geographical mile. 15 geographical Dutch miles equal one degree of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter l ...
on the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
. Its value changed as the circumference of the earth was estimated to a better precision. But at the time of usage, it was around 7,157 m. The metric system was introduced in the Netherlands in 1816, and the metric mile became a synonym for the kilometre, being exactly 1,000 m. Since 1870, the term was replaced by the equivalent . Today, the word is no longer used, except as part of certain proverbs and compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struct ...
terms like ("miles away").
German
 The German mile () was 24,000 German feet. The standardised Austrian mile used in southern Germany and the
The German mile () was 24,000 German feet. The standardised Austrian mile used in southern Germany and the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
was 7.586 km; the Prussian mile used in northern Germany was 7.5325 km. Following its standardisation by Ole Rømer
Ole Christensen Rømer (; 25 September 1644 – 19 September 1710) was a Danish astronomer who, in 1676, made the first measurement of the speed of light.
Rømer also invented the modern thermometer showing the temperature between two fix ...
in the late 17th century, the Danish mile (') was precisely equal to the Prussian mile and likewise divided into 24,000 feet. These were sometimes treated as equivalent to 7.5 km. Earlier values had varied: the , for instance, had been 11.13 km. The Germans also used a longer version of the geographical mile.
Breslau
The Breslau mile, used in Breslau, and from 1630 officially in all ofSilesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, equal to 11,250 ells, or about 6,700 meters. The mile equaled the distance from the Piaskowa Gate all the way to Psie Pole (Hundsfeld
Psie Pole () ( polish: ''Dog Field'') is one of the five administrative districts of Wrocław, Poland. Before 1928, it was an independent city. Its functions were largely taken over on 8 March 1990 by the Municipal Office of the newly establishe ...
). By rolling a circle with a radius of 5 ells through Piaskowa Island, Ostrów Tumski and suburban tracts, passing eight bridges on the way, the standard Breslau mile was determined.
Saxon
The Saxon post mile (' or ', introduced on occasion of a survey of the Saxon roads in the 1700s, corresponded to 2,000 Dresden rods, equivalent to 9.062 kilometres.Hungarian
The Hungarian mile (' or ') varied from 8.3790 km to 8.9374 km before being standardised as 8.3536 km.Portuguese
The Portuguese mile (') used in Portugal and Brazil was 2.0873 km prior to metrication.Russian
TheRussian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
mile ( or , ) was 7.468 km, divided into 7 verst
A verst (russian: верста, ) is an obsolete Russian unit of length defined as 500 sazhen. This makes a verst equal to .
Plurals and variants
In the English language, ''verst'' is singular with the normal plural ''versts''. In Russian, the no ...
s.
Croatian
The Croatian mile ('), first devised by theJesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
Stjepan Glavač on a 1673 map, is the length of an arc of the equator subtended by ° or 11.13 km exactly. The previous Croatian mile, now known as the " ban mile" ('), had been the Austrian mile given above.
Ottoman
The Ottoman mile was 1,894.35 m (1.17709 mi), which was equal to 5,000 Ottoman foot. After 1933, the Ottoman mile was replaced with the modern Turkish mile (1,853.181 m).International
The international mile is precisely equal to (or km as a fraction). It was established as part of the 1959international yard and pound
The international yard and pound are two units of measurement that were the subject of an agreement among representatives of six nations signed on 1 July 1959: the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. T ...
agreement reached by the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and the Union of South Africa
The Union of South Africa ( nl, Unie van Zuid-Afrika; af, Unie van Suid-Afrika; ) was the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into existence on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape, Natal, Trans ...
, which resolved small but measurable differences that had arisen from separate physical standards each country had maintained for the yard. As with the earlier statute mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 Engli ...
, it continues to comprise 1,760 yards or 5,280 feet.
The old Imperial value of the yard was used in converting measurements to metric values in India in a 1976 Act of the Indian Parliament. However, the current National Topographic Database of the Survey of India
The Survey of India is India's central engineering agency in charge of Cartography, mapping and surveying.
is based on the metric WGS-84
The World Geodetic System (WGS) is a standard used in cartography, geodesy, and satellite navigation including GPS. The current version, WGS 84, defines an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system and a geodetic datum, and also descr ...
datum
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. ...
, which is also used by the Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
.
The difference from the previous standards was 2 ppm, or about 3.2 millimetres ( inch) per mile. The U.S. standard was slightly longer and the old Imperial standards had been slightly shorter than the international mile. When the international mile was introduced in English-speaking countries, the basic geodetic datum
A geodetic datum or geodetic system (also: geodetic reference datum, geodetic reference system, or geodetic reference frame) is a global datum reference or reference frame for precisely representing the position of locations on Earth or other plan ...
in America was the North American Datum
The North American Datum (NAD) is the horizontal datum now used to define the geodetic network in North America. A datum is a formal description of the shape of the Earth along with an "anchor" point for the coordinate system. In surveying, ca ...
of 1927 (NAD27). This had been constructed by triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points.
Applications
In surveying
Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle me ...
based on the definition of the foot in the Mendenhall Order
The Mendenhall Order marked a decision to change the fundamental standards of length and mass of the United States from the customary standards based on those of England to metric standards. It was issued on April 5, 1893, by Thomas Corwin Mend ...
of 1893, with 1 foot = (≈0.304800609601) metres and the definition was retained for data derived from NAD27, but renamed the ''U.S. survey foot'' to distinguish it from the international foot.When reading the document it helps to bear in mind that 999,998 = 3,937 × 254. Thus a survey mile = × 5280 (≈1609.347218694) metres. An international mile = 1609.344 / ( × 5280) (=0.999998) survey miles.
The exact length of the land mile varied slightly among English-speaking countries until the international yard and pound
The international yard and pound are two units of measurement that were the subject of an agreement among representatives of six nations signed on 1 July 1959: the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. T ...
agreement in 1959 established the yard as exactly 0.9144 metres, giving a mile of exactly 1,609.344 metres. The U.S. adopted this international mile for most purposes, but retained the pre-1959 mile for some land-survey data, terming it the ''U. S. survey mile''. In the United States, ''statute mile'' normally refers to the survey mile, about 3.219 mm ( inch) longer than the international mile (the international mile is exactly 0.0002% less than the U.S. survey mile).
While most countries abandoned the mile when switching to the metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the Decimal, decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in French Revolution, France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the d ...
, the international mile continues to be used in some countries, such as Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
, Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
, the United Kingdom and the United States. It is also used in a number of territories with less than a million inhabitants, most of which are U.K. or U.S. territories, or have close historical ties with the U.K. or U.S.: American Samoa, Bahamas, Belize, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Falkland Islands, Grenada, Guam, The N. Mariana Islands, Samoa, St. Lucia, St. Vincent & The Grenadines, St. Helena, St. Kitts & Nevis, the Turks & Caicos Islands, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The mile is even encountered in Canada, though this is predominantly in rail transport and horse racing, as the roadways have been metricated since 1977. The Republic of Ireland gradually replaced miles with kilometres, including in speed measurements; the process was completed in 2005.
U.S. survey
The U.S. survey mile is 5,280 U.S. survey feet, or 1,609.347 metres and 0.30480061 metres respectively. Both are very slightly longer than theinternational mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
and international foot
The foot ( feet), standard symbol: ft, is a unit of length in the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. The prime symbol, , is a customarily used alternative symbol. Since the International Yard and P ...
. In the United States, the term ''statute mile'' formally refers to the survey mile, but for most purposes, the difference of less than between the survey mile and the international mile (1609.344 metres exactly) is insignificant—one international mile is U.S. survey miles—so ''statute mile'' can be used for either. But in some cases, such as in the U.S. State Plane Coordinate Systems (SPCSs), which can stretch over hundreds of miles, the accumulated difference can be significant, so it is important to note that the reference is to the U.S. survey mile.
The United States redefined its yard in 1893, and this resulted in U.S. and Imperial measures of distance having very slightly different lengths.
The North American Datum of 1983 (NAD83), which replaced the NAD27, is defined in metres. State Plane Coordinate Systems were then updated, but the National Geodetic Survey
The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a List of federal agencies in the United States, United States federal agency that defines and manages a national coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication; mapping an ...
left individual states to decide which (if any) definition of the foot they would use. All State Plane Coordinate Systems are defined in metres, and 42 of the 50 states only use the metre-based State Plane Coordinate Systems. However, eight states also have State Plane Coordinate Systems defined in feet, seven of them in U.S. survey feet and one in international feet.
State legislation in the U.S. is important for determining which conversion factor from the metric datum is to be used for land surveying and real estate transactions, even though the difference (2 ppm) is hardly significant, given the precision of normal surveying measurements over short distances (usually much less than a mile). Twenty-four states have legislated that surveying measures be based on the U.S. survey foot, eight have legislated that they be based on the international foot, and eighteen have not specified which conversion factor to use.
SPCS 83 legislation refers to state legislation that has been passed or updated using the newer 1983 NAD data. Most states have done so. Two states (AK, MO) and two jurisdictions (GU, PR) do not specify which foot to use. Additionally, two states (AL, HI) and four jurisdictions (DC, VI, AS, MP) do not have SPCS 83 legislation.
In October 2019, U.S. National Geodetic Survey
The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a United States federal agency that defines and manages a national coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication; mapping and charting; and a large number of applications ...
and National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
announced their joint intent to retire the U.S. survey foot and U.S. survey mile, as permitted by their 1959 decision, with effect on January 1, 2023.
Nautical
minute of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
along a meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
of the Earth. Navigators use dividers to step off the distance between two points on the navigational chart, then place the open dividers against the minutes-of-latitude scale at the edge of the chart, and read off the distance in nautical miles. The Earth is not perfectly spherical but an oblate spheroid, so the length of a minute of latitude increases by 1% from the equator to the poles. Using the WGS84 ellipsoid, the commonly accepted Earth model for many purposes today, one minute of latitude at the WGS84 equator is 6,046 feet and at the poles is 6,107.5 feet. The average is about 6,076 feet (about 1,852 metres or 1.15 statute miles).
In the United States, the nautical mile was defined in the 19th century as 6,080.2 feet (1,853.249 m), whereas in the United Kingdom, the ''Admiralty nautical mile'' was defined as 6,080 feet (1,853.184 m) and was about one minute of latitude in the latitudes of the south of the UK. Other nations had different definitions of the nautical mile, but it is now internationally defined to be exactly .
Related units
The nautical mile per hour is known as theknot
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ' ...
. Nautical miles and knots are almost universally used for aeronautical and maritime navigation, because of their relationship with degrees and minutes of latitude and the convenience of using the latitude scale on a map for distance measuring.
The data mile
In radar-related subjects and in JTIDS, a data mile is a unit of distance equal to 6000 feet (1.8288 kilometres or 0.987 nautical miles). An international mile is exactly 0.88 of a data mile.
The speed of light is 983571056 ft/s, or about one f ...
is used in radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
-related subjects and is equal to 6,000 feet (1.8288 kilometres). The radar mile Radar mile or radar nautical mile is an auxiliary constant for converting a (delay) time to the corresponding scale distance on the radar display.
Radar timing is usually expressed in microseconds. To relate radar timing to distances traveled by ra ...
is a unit of time (in the same way that the light year is a unit of distance), equal to the time required for a radar pulse to travel a distance of two miles (one mile each way). Thus, the radar statute mile is 10.8 μs and the radar nautical mile is 12.4 μs.
Geographical
The geographical mile is based upon the length of ameridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
. The German geographical mile () was previously ° of latitude (7.4127 km).
Grid system
Cities in the continental United States often have streets laid out by miles. Detroit,Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
, Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
, and Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a East Coast of the United States, coastal metropolis and the County seat, county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade C ...
, are several examples. Typically the largest streets are about a mile apart, with others at smaller intervals. In the Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
borough of New York City "streets" are close to 20 per mile, while the major numbered "avenues" are about six per mile. (Centerline to centerline, 42nd Street to 22nd Street is supposed to be 5,250 feet while 42nd Street to 62nd Street is supposed to be 5,276 ft 8 in.)
Metric
The informal term "metric mile" is used in some countries, in sports such astrack and field athletics
Track and field is a sport that includes Competition#Sports, athletic contests based on running, jumping, and throwing skills. The name is derived from where the sport takes place, a running track and a grass field for the throwing and some of ...
and speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors racing, race each other in travelling a certain distance on Ice skate, skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marath ...
, to denote a distance of . The 1500 meters is the premier middle distance running
Middle-distance running events are track races longer than sprints, up to 3000 metres. The standard middle distances are the 800 metres, 1500 metres and mile run, although the 3000 metres may also be classified as a middle-distance event. The 1 ...
event in Olympic sports
Olympic sports are contested in the Summer Olympic Games and Winter Olympic Games. The 2020 Summer Olympics included 33 sports; the 2022 Winter Olympics included seven sports. Each Olympic sport is represented by an Sports governing body, inter ...
. In United States high-school competition, the term is sometimes used for a race of .
Scandinavian
The Scandinavian mile (') remains in common use in Norway and Sweden, where it has meant precisely 10 km since metrication in 1889. It is used in informal situations and in measurements of fuel consumption, which are often given as litres per '. In formal situations (such as official road signs) and where confusion may occur withinternational mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
s, it is avoided in favour of kilometres.
The Swedish mile was standardised as 36,000 Swedish feet or 10.6884 km in 1649; before that it varied by province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
from about 6 to 14.485 km.
Before metrication, the Norwegian mile was 11.298 km.
The traditional Finnish ' was translated as ' in Swedish and also set equal to 10 km during metrication in 1887, but is much less commonly used.
Comparison table
A comparison of the different lengths for a "mile", in different countries and at different times in history, is given in the table below.League
League or The League may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Leagues'' (band), an American rock band
* ''The League'', an American sitcom broadcast on FX and FXX about fantasy football
Sports
* Sports league
* Rugby league, full contact footba ...
s are also included in this list because, in terms of length, they fall in between the short West European miles and the long North, Central and Eastern European miles.
Similar units:
* 1,066.8 m – verst
A verst (russian: верста, ) is an obsolete Russian unit of length defined as 500 sazhen. This makes a verst equal to .
Plurals and variants
In the English language, ''verst'' is singular with the normal plural ''versts''. In Russian, the no ...
, see also Obsolete Russian units of measurement
A native system of weights and measures was used in Imperial Russia and after the Russian Revolution, but it was abandoned after 21 July 1925, when the Soviet Union adopted the metric system, per the order of the Council of People's Commissars.
T ...
Idioms
Even in English-speaking countries that have moved from the Imperial to the metric system (for example, Australia, Canada, or New Zealand), the mile is still used in a variety ofidioms
An idiom is a phrase or expression that typically presents a figurative, non-literal meaning attached to the phrase; but some phrases become figurative idioms while retaining the literal meaning of the phrase. Categorized as formulaic language, ...
. These include:
* A '' country mile'' is used colloquially
Colloquialism (), also called colloquial language, everyday language or general parlance, is the style (sociolinguistics), linguistic style used for casual (informal) communication. It is the most common functional style of speech, the idiom norm ...
to denote a very long distance.
* ''"A miss is as good as a mile"'' (failure by a narrow margin is no better than any other failure)
* ''"Give him an inch and he'll take a mile"'' – a corruption of ''"Give him an inch and he'll take an ell"''''Concise Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Concise Oxford English Dictionary'' (officially titled ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary'' until 2002, and widely abbreviated ''COD'' or ''COED'') is probably the best-known of the 'smaller' Oxford dictionaries. The latest edition contains ...
'' (5th edition; 1964). Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. (the person in question will become greedy if shown generosity)
* ''"Missed by a mile"'' (missed by a wide margin)
* ''"Go a mile a minute"'' (move very quickly)
* ''"Talk a mile a minute"'' (speak at a rapid rate)
* ''"To go the extra mile"'' (to put in extra effort)
* ''"Miles away"'' (lost in thought, or daydreaming)
* ''"Milestone
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway line, canal or boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks; or they can give their position on the route relative to so ...
"'' (an event indicating significant progress)
See also
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * * * . * . * . * . * . * . * . & * . * . * . * . * . * . * . * .Further reading
* * (Item notes: Sammlung5-6 (1856–57) Original from Harvard University Digitized 9 January 2008) * * {{Authority control Ancient Roman geography Customary units of measurement in the United States Imperial units Obsolete Scottish units of measurement Surveying Units of length Croatian mile