Stator Bixae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
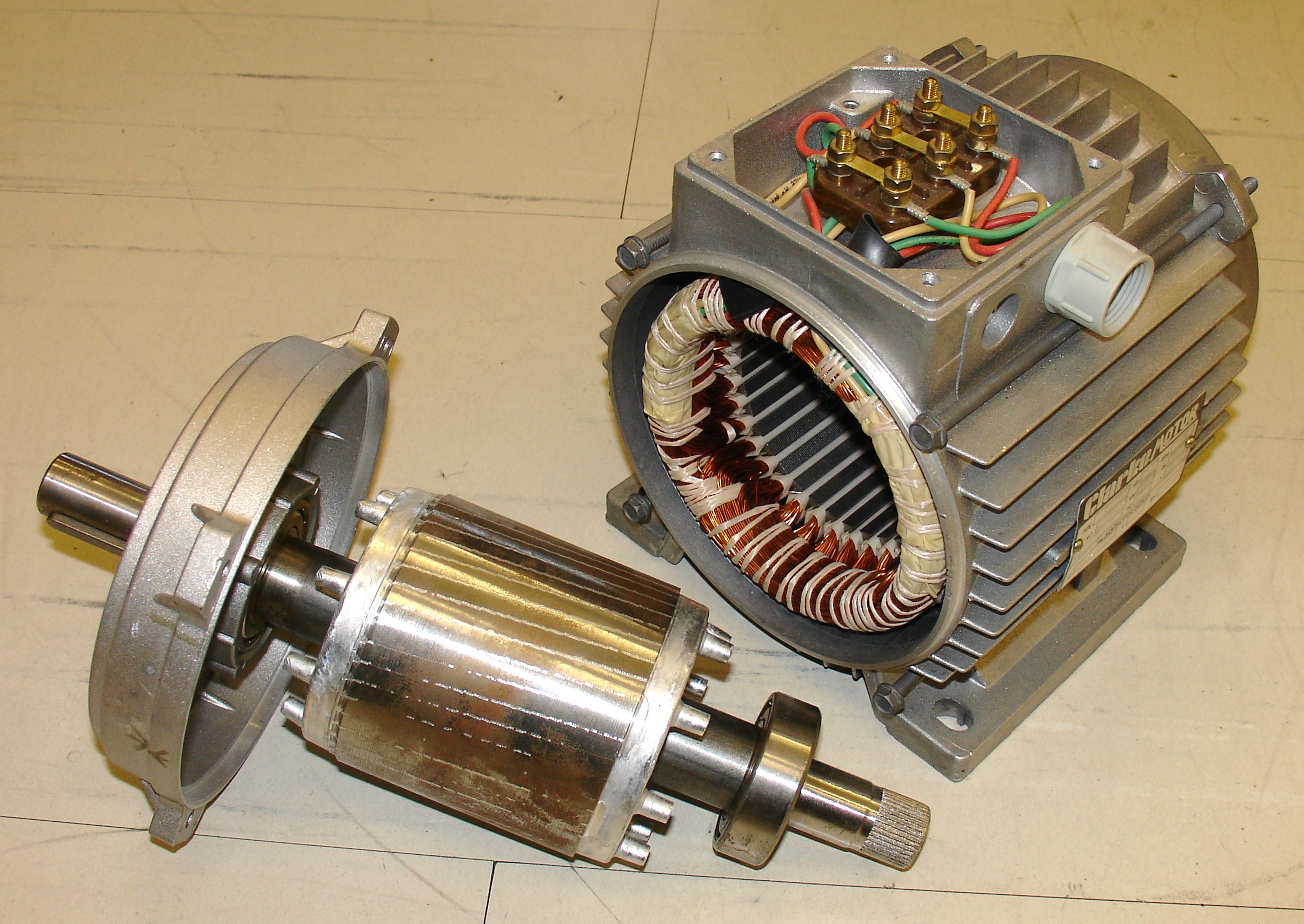

 The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in
 The stator of these devices may be either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet.
An AC alternator produces power across multiple high-current power generation coils connected in parallel, eliminating the commutator.
The stator of these devices may be either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet.
An AC alternator produces power across multiple high-current power generation coils connected in parallel, eliminating the commutator.


 The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in
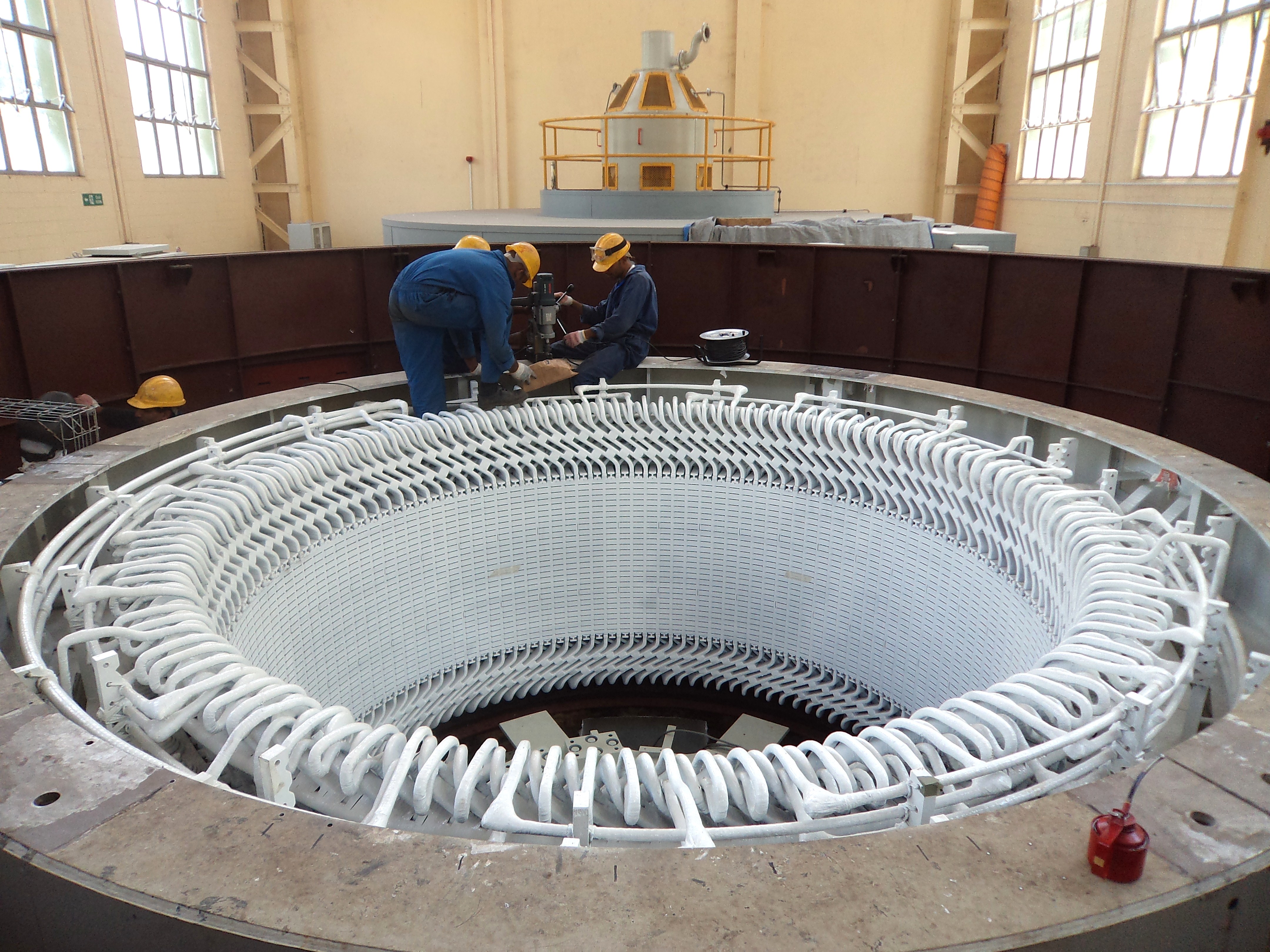
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas ...
s, electric motors, sirens, mud motors or biological rotors. Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system.
Design
Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from aprinted circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
(PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy.
One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core, saving space and weight, and allowing a smaller air gap.
Motors
Depending on the configuration of a spinning electromotive device the stator may act as the ''field magnet'', interacting with the armature to create motion, or it may act as the ''armature'', receiving its influence from moving field coils on the rotor. The first DC generators (known as dynamos) and DC motors put the field coils on the stator, and the power generation or motive reaction coils on the rotor. This is necessary because a continuously moving power switch known as thecommutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.
Group theory
The commutator of two elements, a ...
is needed to keep the field correctly aligned across the spinning rotor. The commutator must become larger and more robust as the current increases.

Fluid devices
In a turbine, the stator element contains blades or ports used to redirect the flow of fluid. Such devices include thesteam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
and the torque converter. In a mechanical siren, the stator contains one or more rows of holes that admit air into the rotor; by controlling the flow of air through the holes, the sound of the siren can be altered. A stator can reduce the turbulence and rotational energy introduced by an axial turbine fan, creating a steady column of air with a lower Reynolds number
In fluid mechanics, the Reynolds number () is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be domi ...
.
References
External links
{{Authority control Electric motors Sirens