States Of United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the

 The Supremacy Clause ( Article VI, Clause 2) establishes that the
The Supremacy Clause ( Article VI, Clause 2) establishes that the

 Article IV also grants to Congress the authority to admit new states into the Union. Since the establishment of the United States in 1776, the number of states has expanded from the original 13 to 50. Each new state has been admitted on an equal footing with the existing states. Article IV also forbids the creation of new states from parts of existing states without the consent of both the affected states and Congress. This caveat was designed to give Eastern states that still had Western land claims (including Georgia, North Carolina, and Virginia), to have a
Article IV also grants to Congress the authority to admit new states into the Union. Since the establishment of the United States in 1776, the number of states has expanded from the original 13 to 50. Each new state has been admitted on an equal footing with the existing states. Article IV also forbids the creation of new states from parts of existing states without the consent of both the affected states and Congress. This caveat was designed to give Eastern states that still had Western land claims (including Georgia, North Carolina, and Virginia), to have a
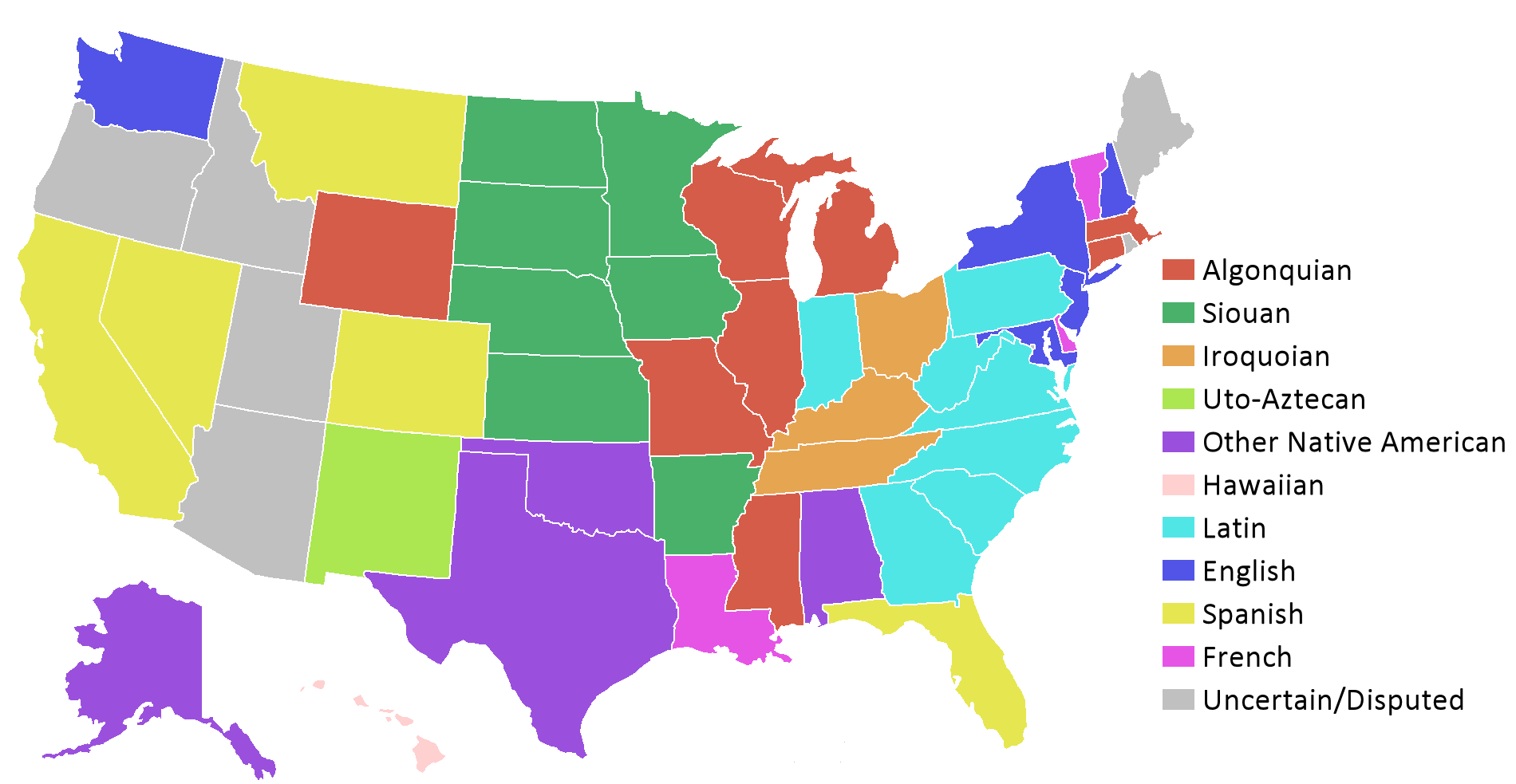 The 50 states have taken their names from a wide variety of languages. Twenty-four state names originate from Native American languages. Of these, eight are from
The 50 states have taken their names from a wide variety of languages. Twenty-four state names originate from Native American languages. Of these, eight are from
Food and Culture
',
Information about All States
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
State Resource Guides, from the Library of Congress
* [http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20090403030000/http://factfinder.census.gov/bf/_lang=en_vt_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_GCTPH1_US9_geo_id=01000US.html Tables with areas, populations, densities and more (alphabetical)]
State and Territorial Governments on USA.gov
StateMaster – statistical database for U.S. states
50states.com – States and Capitals
{{DEFAULTSORT:U.S. State United States 1 States, United States State States, United S
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, a state is a constituent
Constituent or constituency may refer to:
Politics
* An individual voter within an electoral district, state, community, or organization
* Advocacy group or constituency
* Constituent assembly
* Constituencies of Namibia
Other meanings
* Const ...
political entity
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union
A political union is a type of polity, political entity which is composed of, or created from, smaller polities, or the process which achieves this. These administrative subdivision, smaller polities are usually called federated states and federal ...
, each state holds government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
al jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
with the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
. Due to this shared sovereignty, Americans are citizens
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
both of the federal republic
A federal republic is a federation of states with a republican form of government. At its core, the literal meaning of the word republic when used to reference a form of government means: "a country that is governed by elected representatives ...
and of the state in which they reside. State citizenship and residency are flexible, and no government approval is required to move between states, except for persons restricted by certain types of court orders (such as paroled
Parole (also known as provisional release or supervised release) is a form of early release of a prison inmate where the prisoner agrees to abide by certain behavioral conditions, including checking-in with their designated parole officers, or ...
convicts and children of divorced spouses who share child custody
Child custody is a legal term regarding '' guardianship'' which is used to describe the legal and practical relationship between a parent or guardian and a child in that person's care. Child custody consists of ''legal custody'', which is the righ ...
).
State governments in the U.S. are allocated power by the people (of each respective state) through their individual state constitutions. All are grounded in republican principles (this being required by the federal constitution), and each provides for a government, consisting of three branches, each with separate and independent powers: executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dire ...
, legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as p ...
, and judicial. States are divided into counties or county-equivalents, which may be assigned some local governmental authority but are not sovereign. County or county-equivalent structure varies widely by state, and states also create other local governments
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
.
States, unlike U.S. territories, possess many powers and rights under the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
. States and their citizens are represented in the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
, a bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
legislature consisting of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and the House of Representatives. Each state is also entitled to select a number of electors (equal to the total number of representatives and senators from that state) to vote in the Electoral College, the body that directly elects the president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
. Additionally, each state has the opportunity to ratify constitutional amendments, and, with the consent of Congress, two or more states may enter into interstate compacts with one another. The police power of each state is also recognized.
Historically, the tasks of local law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by discovering, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term en ...
, public education
State schools (in England, Wales, Australia and New Zealand) or public schools (Scottish English and North American English) are generally primary or secondary schools that educate all students without charge. They are funded in whole or in pa ...
, public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
, intrastate commerce regulation, and local transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
and infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
, in addition to local, state, and federal elections, have generally been considered primarily state responsibilities, although all of these now have significant federal funding and regulation as well. Over time, the Constitution has been amended, and the interpretation and application of its provisions have changed. The general tendency has been toward centralization and incorporation
Incorporation may refer to:
* Incorporation (business), the creation of a corporation
* Incorporation of a place, creation of municipal corporation such as a city or county
* Incorporation (academic), awarding a degree based on the student having ...
, with the federal government playing a much larger role than it once did. There is a continuing debate over states' rights, which concerns the extent and nature of the states' powers and sovereignty in relation to the federal government and the rights of individuals.
The Constitution grants to Congress the authority to admit new states into the Union. Since the establishment of the United States in 1776 by the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
, the number of states has expanded from the original 13 to 50. Each new state has been admitted on an equal footing with the existing states. While the Constitution does not explicitly discuss the issue of whether states have the power to secede from the Union, shortly after the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, the U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
, in ''Texas v. White
''Texas v. White'', 74 U.S. (7 Wall.) 700 (1869), was a case argued before the United States Supreme Court in 1869. The case involved a claim by the Reconstruction government of Texas that United States bonds owned by Texas since 1850 had been ill ...
'', held that a state cannot unilaterally do so.
List
The 50 U.S. states, in alphabetical order, along with each state's flag:Background
The 13 original states came into existence in July 1776 during theAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
(1775–1783), as the successors of the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
, upon agreeing to the Lee Resolution and signing the United States Declaration of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House ...
. Prior to these events each state had been a British colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolit ...
; each then joined the first Union of states between 1777 and 1781, upon ratifying the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
, the first U.S. constitution. Also during this period, the newly independent states developed their own individual state constitutions, among the earliest written constitutions in the world. Although different in detail, these state constitutions shared features that would be important in the American constitutional order: they were republican in form, and separated power among three branches, most had bicameral legislatures, and contained statements of, or a bill of rights. Later, from 1787 to 1790, each of the states also ratified a new federal frame of government in the Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
. In relation to the states, the U.S. Constitution elaborated concepts of federalism
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments (Province, provincial, State (sub-national), state, Canton (administrative division), can ...
.
Governments
Under U.S. constitutional law, the 50 individual states and the United States as a whole are each sovereign jurisdictions. Radan, 2007, p. 12 The states are ''not'' administrative divisions of the country; theTenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Tenth Amendment (Amendment X) to the United States Constitution, a part of the Bill of Rights, was ratified on December 15, 1791. It expresses the principle of federalism, also known as states' rights, by stating that the federal governmen ...
reserves to the states or to the people all powers of government not delegated to the federal government.
Consequently, each of the 50 states reserves the right to organize its individual government in any way (within the broad parameters set by the U.S. Constitution and the Republican Guarantee The Guarantee Clause, also known as the Republican Form of Government Clause, is in Article IV, Section 4 of the United States Constitution, and requires the United States to guarantee every state a republican form of government and provide protect ...
enforced by Congress) deemed appropriate by its people, and to exercise all powers of government not delegated to the federal government by the Constitution. A state, unlike the federal government, has un-enumerated police power, that is the right to generally make all necessary laws for the welfare of its people. As a result, while the governments of the various states share many similar features, they often vary greatly with regard to form and substance. No two state governments are identical.
Constitutions
The government of each state is structured in accordance with its individual constitution. Many of these documents are more detailed and more elaborate than their federal counterpart. The Constitution of Alabama, for example, contains 310,296 words – more than 40 times as many as the U.S. Constitution. In practice, each state has adopted a three-branch frame of government: executive, legislative, and judicial (even though doing so has never been required). Early on in American history, four state governments differentiated themselves from the others in their first constitutions by choosing to self-identify asCommonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
s rather than as states: Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, in 1776; Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, in 1777; Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, in 1780; and Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, in 1792. Consequently, while these four are states like the other states, each is formally a commonwealth because the term is contained in its constitution. The term, ''commonwealth'', which refers to ''a state in which the supreme power is vested in the people'', was first used in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
during the Interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
, the 1649–60 period between the reigns of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
and Charles II during which parliament's Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Ki ...
as Lord Protector
Lord Protector (plural: ''Lords Protector'') was a title that has been used in British constitutional law for the head of state. It was also a particular title for the British heads of state in respect to the established church. It was sometimes ...
established a republican government known as the Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when England and Wales, later along with Ireland and Scotland, were governed as a republic after the end of the Second English Civil War and the trial and execut ...
. Virginia became a royal colony again in 1660, and the word was dropped from the full title; it went unused until reintroduced in 1776.
Executive
In each state, the chief executive is called the governor, who serves as bothhead of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a gro ...
. All governors are chosen by direct election
Direct election is a system of choosing political officeholders in which the voters directly cast ballots for the persons or political party that they desire to see elected. The method by which the winner or winners of a direct election are cho ...
. The governor may approve or veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto ...
bills passed by the state legislature, as well as recommend and work for the passage of bills, usually supported by their political party. In 44 states, governors have line item veto power. Most states have a plural executive
The unitary executive theory is a theory of United States constitutional law which holds that the President of the United States possesses the power to control the entire federal executive branch. The doctrine is rooted in Article Two of the Un ...
, meaning that the governor is not the only government official in the state responsible for its executive branch
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a State (polity), state.
In poli ...
. In these states, executive power is distributed amongst other officials, elected by the people independently of the governor—such as the lieutenant governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
, attorney general
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
, comptroller
A comptroller (pronounced either the same as ''controller'' or as ) is a management-level position responsible for supervising the quality of accounting and financial reporting of an organization. A financial comptroller is a senior-level executi ...
, secretary of state, and others.
Elections of officials in the United States are generally for a fixed term of office. The constitutions of 19 states allow for citizens to remove and replace an elected public official before the end of their term of office through a recall election
A recall election (also called a recall referendum, recall petition or representative recall) is a procedure by which, in certain polities, voters can remove an elected official from office through a referendum before that official's term of offi ...
. Each state follows its own procedures for recall elections, and sets its own restrictions on how often, and how soon after a general election
A general election is a political voting election where generally all or most members of a given political body are chosen. These are usually held for a nation, state, or territory's primary legislative body, and are different from by-elections ( ...
, they may be held. In all states, the legislatures can remove state executive branch officials, including governors, who have committed serious abuses of their power from office. The process of doing so includes impeachment
Impeachment is the process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In ...
(the bringing of specific charges), and a trial, in which legislators act as a jury.
Legislative
The primary responsibilities of state legislatures are to enact state laws and appropriate money for the administration of public policy. In all states, if the governor vetoes a bill (or a portion of one), it can still become law if the legislature overrides the veto (repasses the bill), which in most states requires atwo-thirds vote
A supermajority, supra-majority, qualified majority, or special majority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority r ...
in each chamber. In 49 of the 50 states the legislature consists of two chambers: a lower house (variously called the House of Representatives, State Assembly, General Assembly or House of Delegates) and a smaller upper house, in all states called the Senate. The exception is the unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multic ...
Nebraska Legislature, which has only a single chamber. Most states have a part-time
Part-time can refer to:
* Part-time job, a job that has fewer hours a week than a full-time job
* Part-time student, a student, usually in higher education, who takes fewer course credits than a full-time student
* Part Time
Part Time (styliz ...
legislature (traditionally called a citizen legislature). Ten state legislatures are considered full-time
Full-time or Full Time may refer to:
* Full-time job, employment in which a person works a minimum number of hours defined as such by their employer
* Full-time mother, a woman whose work is running or managing her family's home
* Full-time fat ...
; these bodies are more similar to the U.S. Congress than are the others.
Members of each state's legislature are chosen by direct election. In ''Baker v. Carr
''Baker v. Carr'', 369 U.S. 186 (1962), was a landmark United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that redistricting qualifies as a justiciable question under the Fourteenth Amendment, thus enabling federal courts to hear Fourteen ...
'' (1962) and ''Reynolds v. Sims
''Reynolds v. Sims'', 377 U.S. 533 (1964), was a landmark United States Supreme Court case in which the Court ruled that the electoral districts of state legislative chambers must be roughly equal in population. Along with ''Baker v. Carr'' (196 ...
'' (1964), the U.S. Supreme Court held that all states are required to elect their legislatures in such a way as to afford each citizen the same degree of representation (the one person, one vote standard). In practice, most states elect legislators from single-member district
A single-member district is an electoral district represented by a single officeholder. It contrasts with a multi-member district, which is represented by multiple officeholders. Single-member districts are also sometimes called single-winner vo ...
s, each of which has approximately the same population. Some states, such as Maryland and Vermont, divide the state into single- and multi-member districts. In this case, multi-member districts must have proportionately larger populations, e.g., a district electing two representatives must have approximately twice the population of a district electing just one. The voting systems used across the nation are: first-past-the-post
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast their ...
in single-member districts, and multiple non-transferable vote
The multiple non-transferable vote (MNTV) is a group of voting system, in which voters elect several representatives at once, with each voter having more than one vote. MNTV uses multi-member electoral districts or only one district, which conta ...
in multi-member districts.
In 2013, there were a total of 7,383 legislators in the 50 state legislative bodies. They earned from $0 annually (New Mexico) to $90,526 (California). There were various per diem and mileage compensation.
Judicial
States can also organize their judicial systems differently from the federal judiciary, as long as they protect the federal constitutional right of their citizens to proceduraldue process
Due process of law is application by state of all legal rules and principles pertaining to the case so all legal rights that are owed to the person are respected. Due process balances the power of law of the land and protects the individual pers ...
. Most have a trial-level court, generally called a District Court, Superior Court
In common law systems, a superior court is a court of general jurisdiction over civil and criminal legal cases. A superior court is "superior" in relation to a court with limited jurisdiction (see small claims court), which is restricted to civil ...
or Circuit Court, a first-level appellate court
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of ...
, generally called a Court of Appeal (or Appeals), and a Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
. Oklahoma and Texas have separate highest courts for criminal appeals. Uniquely, in New York State, the trial court is called the Supreme Court; appeals go up first to the Supreme Court's Appellate Division, and from there to the Court of Appeals.
State court systems exercise broad, plenary, and general jurisdiction, in contrast to the federal courts, which are courts of limited jurisdiction. The overwhelming majority of criminal and civil cases in the United States are heard in state courts. Each year, roughly 30 million new cases are filed in state courts and the total number of judges across all state courts is about 30,000—for comparison, 1 million new cases are filed each year in federal courts, which have about 1,700 judges.
Most states base their legal system on English common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
(with substantial indigenous changes and incorporation of certain civil law innovations), with the notable exception of Louisiana, a former French colony, which draws large parts of its legal system from French civil law.
Only a few states choose to have the judges on the state's courts serve for life terms. In most states, the judges, including the justices of the highest court in the state, are either elected or appointed for terms of a limited number of years and are usually eligible for re-election or reappointment.
Unitarism
All states areunitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only th ...
s, not federations or aggregates of local governments
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
. Local governments within them are created by and exist by virtue of state law, and local governments within each state are subject to the central authority of that particular state. State governments commonly delegate some authority to local units and channel policy decisions down to them for implementation. In a few states, local units of government are permitted a degree of home rule
Home rule is government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governance wit ...
over various matters. The prevailing legal theory of state preeminence over local governments, referred to as Dillon's Rule
John Forrest Dillon (December 25, 1831 – May 6, 1914) was an attorney in Iowa and New York, a justice of the Iowa Supreme Court and a United States circuit judge of the United States Circuit Court for the Eighth Circuit. He authored a highly ...
, holds that,
Each state defines for itself what powers it will allow local governments. Generally, four categories of power may be given to local jurisdictions:
Relationships
Interstate
Each state admitted to the Union by Congress since 1789 has entered it on an equal footing with the original states in all respects. With the growth of states' rights advocacy during the antebellum period, the Supreme Court asserted, in ''Lessee of Pollard v. Hagan'' (1845), that the Constitution mandated admission of new states on the basis of equality. With the consent of Congress, states may enter into interstate compacts, agreements between two or more states. Compacts are frequently used to manage a shared resource, such as transportation infrastructure or water rights. Under Article IV of the Constitution, which outlines the relationship between the states, each state is required to givefull faith and credit
Article IV, Section 1 of the United States Constitution, the Full Faith and Credit Clause, addresses the duty that states within the United States have to respect the "public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state." Accor ...
to the acts of each other's legislatures and courts, which is generally held to include the recognition of most contracts and criminal judgments, and before 1865, slavery status. Under the Extradition Clause The Extradition Clause or Interstate Rendition Clause of the United States Constitution is Article Four of the United States Constitution, Article IV, Article Four of the United States Constitution#Section 2: Rights of state citizens; rights of extr ...
, a state must extradite people located there who have fled charges of "treason, felony, or other crimes" in another state if the other state so demands. The principle of hot pursuit of a presumed felon and arrest by the law officers of one state in another state are often permitted by a state.
The full faith and credit expectation does have exceptions, some legal arrangements, such as professional licensure and marriages, may be state-specific, and until recently states have not been found by the courts to be required to honor such arrangements from other states. Such legal acts are nevertheless often recognized state-to-state according to the common practice of comity
In law, comity is "a practice among different political entities (as countries, states, or courts of different jurisdictions)" involving the "mutual recognition of legislative, executive, and judicial
The judiciary (also known as the judicial s ...
. States are prohibited from discriminating against citizens of other states with respect to their basic rights, under the Privileges and Immunities Clause.
With the federal government
Under Article IV, each state is guaranteed a form of government that is grounded in republican principles, such as the consent of the governed. This guarantee has long been at the forefront of the debate about the rights of citizens vis-à-vis the government. States are also guaranteed protection from invasion, and, upon the application of the state legislature (or executive, if the legislature cannot be convened), from domestic violence. This provision was discussed during the1967 Detroit riot
The 1967 Detroit Riot, also known as the 12th Street Riot or Detroit Rebellion, was the bloodiest of the urban riots in the United States during the "Long, hot summer of 1967". Composed mainly of confrontations between Black residents and the De ...
but was not invoked.
 The Supremacy Clause ( Article VI, Clause 2) establishes that the
The Supremacy Clause ( Article VI, Clause 2) establishes that the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
, federal laws
Federal law is the body of law created by the federal government of a country. A federal government is formed when a group of political units, such as states or provinces join in a federation, delegating their individual sovereignty and many pow ...
made pursuant to it, and treaties
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
made under its authority, constitute the supreme law of the land. It provides that state courts are bound by the supreme law; in case of conflict between federal and state law, the federal law must be applied. Even state constitutions are subordinate to federal law.
States' rights are understood mainly with reference to the Tenth Amendment
The Tenth Amendment (Amendment X) to the United States Constitution, a part of the Bill of Rights, was ratified on December 15, 1791. It expresses the principle of federalism, also known as states' rights, by stating that the federal governmen ...
. The Constitution delegates some powers to the national government, and it forbids some powers to the states. The Tenth Amendment reserves all other powers to the states, or to the people. Powers of the U.S. Congress are enumerated in Article I, Section 8, for example, the power to declare war. Making treaties is one power forbidden to the states, being listed among other such powers in Article I, Section 10.
Among the Article I enumerated powers of Congress is the power to regulate commerce. Since the early 20th century, the Supreme Court's interpretation of this " Commerce Clause" has, over time, greatly expanded the scope of federal power
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments ( provincial, state, cantonal, territorial, or other sub-unit governments) in a single p ...
, at the expense of powers formerly considered purely states' matters. The ''Cambridge Economic History of the United States'' says, "On the whole, especially after the mid-1880s, the Court construed the Commerce Clause in favor of increased federal power." In 1941, the Supreme Court in ''U.S. v. Darby
''United States v. Darby Lumber Co.'', 312 U.S. 100 (1941), was a case in which the United States Supreme Court upheld the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938, holding that the U.S. Congress had the power under the Commerce Clause to regulate employm ...
'' upheld the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938
The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 (FLSA) is a United States labor law that creates the right to a minimum wage, and "time-and-a-half" overtime pay when people work over forty hours a week. It also prohibits employment of minors in "oppres ...
, holding that Congress had the power under the Commerce Clause to regulate employment conditions. Then, one year later, in '' Wickard v. Filburn'', the Court expanded federal power to regulate the economy by holding that federal authority under the commerce clause extends to activities which may appear to be local in nature but in reality effect the entire national economy and are therefore of national concern. For example, Congress can regulate railway traffic across state lines, but it may also regulate rail traffic solely within a state, based on the reality that intrastate traffic still affects interstate commerce. Through such decisions, argues law professor David F. Forte, "the Court turned the commerce power into the equivalent of a general regulatory power and undid the Framers' original structure of limited and delegated powers." Subsequently, Congress invoked the Commerce Clause to expand federal criminal legislation, as well as for social reforms such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
. Only within the past couple of decades, through decisions in cases such as those in ''U.S. v. Lopez
''United States v. Alfonso D. Lopez, Jr.'', 514 U.S. 549 (1995), was a landmark case of the United States Supreme Court concerning the Commerce Clause. It was the first case since 1937 in which the Court held that Congress had exceeded its power t ...
'' (1995) and ''U.S. v. Morrison
''United States v. Morrison'', 529 U.S. 598 (2000), is a U.S. Supreme Court decision that held that parts of the Violence Against Women Act of 1994 were unconstitutional because they exceeded the powers granted to the US Congress under the Comme ...
'' (2000), has the Court tried to limit the Commerce Clause power of Congress.
Another enumerated congressional power is its taxing and spending power. An example of this is the system of federal aid for highways, which include the Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
. The system is mandated and largely funded by the federal government and serves the interests of the states. By threatening to withhold federal highway funds, Congress has been able to pressure state legislatures to pass various laws. An example is the nationwide legal drinking age of 21, enacted by each state, brought about by the National Minimum Drinking Age Act. Although some objected that this infringes on states' rights, the Supreme Court upheld the practice as a permissible use of the Constitution's Spending Clause in ''South Dakota v. Dole
''South Dakota v. Dole'', 483 U.S. 203 (1987), was a case in which the United States Supreme Court considered the limitations that the Constitution places on the authority of the United States Congress when Congress uses its authority to influence ...
'' .
As prescribed by Article I of the Constitution, which establishes the U.S. Congress, each state is represented in the Senate (irrespective of population size) by two senators, and each is guaranteed at least one representative in the House. Both senators and representatives are chosen in direct popular elections in the various states. (Prior to 1913, senators were elected by state legislatures.) There are presently 100 senators, who are elected at-large
At large (''before a noun'': at-large) is a description for members of a governing body who are elected or appointed to represent a whole membership or population (notably a city, county, state, province, nation, club or association), rather than ...
to staggered terms
Staggered elections are elections where only some of the places in an elected body are up for election at the same time. For example, United States senators have a six-year term, but they are not all elected at the same time. Rather, elections a ...
of six years, with one-third of them being chosen every two years. Representatives are elected at large or from single-member district
A single-member district is an electoral district represented by a single officeholder. It contrasts with a multi-member district, which is represented by multiple officeholders. Single-member districts are also sometimes called single-winner vo ...
s to terms of two years (not staggered). The size of the House—presently 435 voting members—is set by federal statute
In the law of the United States, the Code of Laws of the United States of America (variously abbreviated to Code of Laws of the United States, United States Code, U.S. Code, U.S.C., or USC) is the official compilation and codification of the ...
. Seats in the House are distributed among the states in proportion to the most recent constitutionally mandated decennial census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses incl ...
. The borders of these districts are established by the states individually through a process called redistricting
Redistribution (re-districting in the United States and in the Philippines) is the process by which electoral districts are added, removed, or otherwise changed. Redistribution is a form of boundary delimitation that changes electoral dist ...
, and within each state all districts are required to have approximately equal populations.
Citizens in each state plus those in the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
indirectly elect
An indirect election or ''hierarchical voting'' is an election in which voters do not choose directly among candidates or parties for an office (direct voting system), but elect people who in turn choose candidates or parties. It is one of the old ...
the president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
and vice president
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on t ...
. When casting ballots in presidential elections
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pr ...
they are voting for presidential electors
The United States Electoral College is the group of presidential electors required by the Constitution to form every four years for the sole purpose of appointing the president and vice president. Each state and the District of Columbia appo ...
, who then, using procedures provided in the 12th amendment, elect the president and vice president. There were 538 electors for the most recent presidential election in 2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, social and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, COVID- ...
; the allocation of electoral votes was based on the 2010 census. Each state is entitled to a number of electors equal to the total number of representatives and senators from that state; the District of Columbia is entitled to three electors.
While the Constitution does set parameters for the election of federal officials, state law, not federal, regulates most aspects of elections in the U.S., including primaries, the eligibility of voters (beyond the basic constitutional definition), the running of each state's electoral college, as well as the running of state and local elections. All elections—federal, state, and local—are administered by the individual states, and some voting rules and procedures may differ among them.
Article V of the Constitution accords states a key role in the process of amending the U.S. Constitution. Amendments may be proposed either by Congress with a two-thirds vote
A supermajority, supra-majority, qualified majority, or special majority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority r ...
in both the House and the Senate, or by a constitutional convention Constitutional convention may refer to:
* Constitutional convention (political custom), an informal and uncodified procedural agreement
*Constitutional convention (political meeting), a meeting of delegates to adopt a new constitution or revise an e ...
called for by two-thirds of the state legislatures. To become part of the Constitution, an amendment must be ratified by either—as determined by Congress—the legislatures of three-quarters of the states or state ratifying conventions
State ratifying conventions are one of the two methods established by Article V of the United States Constitution for '' ratifying'' proposed constitutional amendments. The only amendment that has been ratified through this method thus far is th ...
in three-quarters of the states. The vote in each state (to either ratify or reject a proposed amendment) carries equal weight, regardless of a state's population or length of time in the Union.
With other countries
U.S. states are not sovereign in the Westphalian sense ininternational law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
which says that each State has sovereignty over its territory and domestic affairs, to the exclusion of all external powers, on the principle of non-interference in another State's domestic affairs, and that each State (no matter how large or small) is equal in international law. Additionally, the 50 U.S. states do not possess international legal sovereignty, meaning that they are not recognized by other sovereign States such as, for example, France, Germany or the United Kingdom. The federal government is responsible for international relations
International relations (IR), sometimes referred to as international studies and international affairs, is the scientific study of interactions between sovereign states. In a broader sense, it concerns all activities between states—such as ...
, but state and local government leaders do occasionally travel to other countries and form economic and cultural relationships.
Admission into the Union
 Article IV also grants to Congress the authority to admit new states into the Union. Since the establishment of the United States in 1776, the number of states has expanded from the original 13 to 50. Each new state has been admitted on an equal footing with the existing states. Article IV also forbids the creation of new states from parts of existing states without the consent of both the affected states and Congress. This caveat was designed to give Eastern states that still had Western land claims (including Georgia, North Carolina, and Virginia), to have a
Article IV also grants to Congress the authority to admit new states into the Union. Since the establishment of the United States in 1776, the number of states has expanded from the original 13 to 50. Each new state has been admitted on an equal footing with the existing states. Article IV also forbids the creation of new states from parts of existing states without the consent of both the affected states and Congress. This caveat was designed to give Eastern states that still had Western land claims (including Georgia, North Carolina, and Virginia), to have a veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto ...
over whether their western counties could become states, and has served this same function since, whenever a proposal to partition an existing state or states in order that a region within might either join another state or to create a new state has come before Congress.
Most of the states admitted to the Union after the original 13 were formed from an organized territory
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sover ...
established and governed by Congress in accord with its plenary power under Article IV, Section 3, Clause 2. The outline for this process was established by the Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Co ...
(1787), which predates the ratification of the Constitution. In some cases, an entire territory has become a state; in others some part of a territory has.
When the people of a territory make their desire for statehood known to the federal government, Congress may pass an enabling act
An enabling act is a piece of legislation by which a legislative body grants an entity which depends on it (for authorization or legitimacy) the power to take certain actions. For example, enabling acts often establish government agencies to car ...
authorizing the people of that territory to organize a constitutional convention Constitutional convention may refer to:
* Constitutional convention (political custom), an informal and uncodified procedural agreement
*Constitutional convention (political meeting), a meeting of delegates to adopt a new constitution or revise an e ...
to write a state constitution as a step toward admission to the Union. Each act details the mechanism by which the territory will be admitted as a state following ratification of their constitution and election of state officers. Although the use of an enabling act is a traditional historic practice, a number of territories have drafted constitutions for submission to Congress absent an enabling act and were subsequently admitted. Upon acceptance of that constitution and meeting any additional Congressional stipulations, Congress has always admitted that territory as a state.
In addition to the original 13, six subsequent states were never an organized territory of the federal government, or part of one, before being admitted to the Union. Three were set off from an already existing state, two entered the Union after having been sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
s, and one was established from unorganized territory Unorganized territory may refer to:
* An unincorporated area in any number of countries
* One of the current or former territories of the United States that has not had a government "organized" with an "organic act" by the U.S. Congress
* Unorganize ...
:
* California, 1850, from land ceded
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdictio ...
to the United States by Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
in 1848 under the terms of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
.
* Kentucky, 1792, from Virginia (District of Kentucky: Fayette, Jefferson Jefferson may refer to:
Names
* Jefferson (surname)
* Jefferson (given name)
People
* Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), third president of the United States
* Jefferson (footballer, born 1970), full name Jefferson Tomaz de Souza, Brazilian foo ...
, and Lincoln counties)
* Maine, 1820, from Massachusetts (District of Maine
The District of Maine was the governmental designation for what is now the U.S. state of Maine from October 25, 1780 to March 15, 1820, when it was admitted to the Union as the 23rd state. The district was a part of the Commonwealth of Massachuse ...
)
* Texas, 1845, previously the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
* Vermont, 1791, previously the Vermont Republic
The Vermont Republic ( French: ''République du Vermont''), officially known at the time as the State of Vermont ( French: ''État du Vermont''), was an independent state in New England that existed from January 15, 1777, to March 4, 1791. The ...
(also known as the New Hampshire Grants and claimed by New York)
* West Virginia, 1863, from Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
(Trans- Allegheny region counties) during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
Congress is under no obligation to admit states, even in those areas whose population expresses a desire for statehood. Such has been the case numerous times during the nation's history. In one instance, Mormon pioneers
The Mormon pioneers were members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), also known as Latter Day Saints, who migrated beginning in the mid-1840s until the late-1860s across the United States from the Midwest to the S ...
in Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Utah, most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the county seat, seat of Salt Lake County, Utah, Sal ...
sought to establish the state of Deseret in 1849. It existed for slightly over two years and was never approved by the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
. In another, leaders of the Five Civilized Tribes (Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek, and Seminole) in Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United St ...
proposed to establish the state of Sequoyah
Sequoyah (Cherokee language, Cherokee: ᏍᏏᏉᏯ, ''Ssiquoya'', or ᏎᏉᏯ, ''Se-quo-ya''; 1770 – August 1843), also known as George Gist or George Guess, was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American polymath of the Ch ...
in 1905, as a means to retain control of their lands. The proposed constitution ultimately failed in the U.S. Congress. Instead, the Indian Territory and Oklahoma Territory
The Territory of Oklahoma was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 2, 1890, until November 16, 1907, when it was joined with the Indian Territory under a new constitution and admitted to the Union as th ...
were both incorporated into the new state of Oklahoma in 1907. The first instance occurred while the nation still operated under the Articles of Confederation. The State of Franklin
The State of Franklin (also the Free Republic of Franklin or the State of Frankland)Landrum, refers to the proposed state as "the proposed republic of Franklin; while Wheeler has it as ''Frankland''." In ''That's Not in My American History Boo ...
existed for several years, not long after the end of the American Revolution, but was never recognized by the Confederation Congress, which ultimately recognized North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
's claim of sovereignty over the area. The territory comprising Franklin later became part of the Southwest Territory, and ultimately of the state of Tennessee.
Additionally, the entry of several states into the Union was delayed due to distinctive complicating factors. Among them, Michigan Territory
The Territory of Michigan was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805, until January 26, 1837, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Michigan. Detroit w ...
, which petitioned Congress for statehood in 1835, was not admitted to the Union until 1837, due to a boundary dispute
A territorial dispute or boundary dispute is a disagreement over the possession or control of land between two or more political entities.
Context and definitions
Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of natural resources s ...
with the adjoining state of Ohio. The Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
requested annexation to the United States in 1837, but fears about potential conflict with Mexico delayed the admission of Texas for nine years. Statehood for Kansas Territory
The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the Slave and ...
was held up for several years (1854–61) due to a series of internal violent conflicts involving anti-slavery and pro-slavery factions. West Virginia's bid for statehood was also delayed over slavery and was settled when it agreed to adopt a gradual abolition plan.
Proposed additions
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
, an unincorporated U.S. territory, refers to itself as the "Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
of Puerto Rico" in the English version of its constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
, and as "Estado Libre Asociado" (literally, Associated Free State) in the Spanish version. As with all U.S. territories, its residents do not have full representation in the United States Congress. Puerto Rico has limited representation in the U.S. House of Representatives in the form of a Resident Commissioner
Resident commissioner was or is an official title of several different types of commissioners, who were or are representatives of any level of government. Historically, they were appointed by the British Crown in overseas protectorates (such ...
, a delegate with limited voting rights in the Committee of the Whole House on the State of the Union
In the United States House of Representatives, a Committee of the Whole House is a congressional committee that includes all members of the House. In modern practice there is only one such committee, the Committee of the Whole House on the State o ...
, but no voting rights otherwise.
A non-binding referendum on statehood, independence, or a new option for an associated territory (different from the current status) was held on November 6, 2012. Sixty one percent (61%) of voters chose the statehood option, while one third of the ballots were submitted blank.
On December 11, 2012, the Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico enacted a concurrent resolution requesting the President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
and the Congress of the United States to respond to the referendum of the people of Puerto Rico, held on November 6, 2012, to end its current form of territorial status and to begin the process to admit Puerto Rico as a state.
Another status referendum was held on June 11, 2017, in which 97% percent of voters chose statehood. Turnout was low, as only 23% of voters went to the polls, with advocates of both continued territorial status and independence urging voters to boycott it.
On June 27, 2018, the H.R. 6246 Act was introduced on the U.S. House
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they c ...
with the purpose of responding to, and comply with, the democratic will of the United States citizens residing in Puerto Rico as expressed in the plebiscites held on November 6, 2012, and June 11, 2017, by setting forth the terms for the admission of the territory of Puerto Rico as a state of the Union. The act has 37 original cosponsors between Republicans and Democrats in the U.S. House of Representatives.
On November 3, 2020, Puerto Rico held another referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
. In the non-binding referendum, Puerto Ricans voted in favor of becoming a state. They also voted for a pro-statehood governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
, Pedro Pierluisi.
Washington, D.C.
The intention of theFounding Fathers
The following list of national founding figures is a record, by country, of people who were credited with establishing a state. National founders are typically those who played an influential role in setting up the systems of governance, (i.e. ...
was that the United States capital should be at a neutral site, not giving favor to any existing state; as a result, the District of Columbia was created in 1800 to serve as the seat of government
The seat of government is (as defined by ''Brewer's Politics'') "the building, complex of buildings or the city from which a government exercises its authority".
In most countries, the nation’s capital is also seat of its government, thus that ...
. As it is not a state, the district does not have representation in the Senate and has a non-voting delegate in the House; neither does it have a sovereign elected government. Additionally, before ratification
Ratification is a principal's approval of an act of its agent that lacked the authority to bind the principal legally. Ratification defines the international act in which a state indicates its consent to be bound to a treaty if the parties inten ...
of the 23rd Amendment in 1961, district citizens did not get the right to vote
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
in presidential elections.
The strong majority of residents of the District support statehood of some form for that jurisdiction – either statehood for the whole district or for the inhabited part, with the remainder remaining under federal jurisdiction
Federal jurisdiction is the jurisdiction of the federal government in any country that uses federalism. Such a country is known as a Federation.
Federal jurisdiction by country
All federations, by definition, must have some form of federal juri ...
. In November 2016, Washington, D.C. residents voted in a statehood referendum in which 86% of voters supported statehood for Washington, D.C. For statehood to be achieved, it must be approved by Congress.
Secession from the Union
The Constitution is silent on the issue of whether a state can secede from the Union. Its predecessor, theArticles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
, stated that the United States "shall be perpetual
Perpetual, meaning "eternal", may refer to:
Christianity
* Perpetual curacy, a type of Christian priesthood in Anglicanism
* Perpetual virginity of Mary, one of the four Marian dogmas in Catholicism
Finance
*Perpetual bond, a bond that pays ...
." The question of whether or not individual states held the unilateral right to secession was a passionately debated feature of the nations' political discourse from early in its history and remained a difficult and divisive topic until the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
. In 1860 and 1861, 11 southern states each declared secession from the United States and joined to form the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
(CSA). Following the defeat of Confederate forces by Union armies in 1865, those states were brought back into the Union during the ensuing Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in American history following the American Civil War (1861–1865) and lasting until approximately the Compromise of 1877. During Reconstruction, attempts were made to rebuild the country after the bloo ...
. The federal government never recognized the sovereignty of the CSA, nor the validity of the ordinances of secession
Ordinance may refer to:
Law
* Ordinance (Belgium), a law adopted by the Brussels Parliament or the Common Community Commission
* Ordinance (India), a temporary law promulgated by the President of India on recommendation of the Union Cabinet
* ...
adopted by the seceding states.
Following the war, the United States Supreme Court, in ''Texas v. White
''Texas v. White'', 74 U.S. (7 Wall.) 700 (1869), was a case argued before the United States Supreme Court in 1869. The case involved a claim by the Reconstruction government of Texas that United States bonds owned by Texas since 1850 had been ill ...
'' (1869), held that states did not have the right to secede and that any act of secession was legally void. Drawing on the Preamble to the Constitution, which states that the Constitution was intended to "form a more perfect union" and speaks of the people of the United States in effect as a single body politic, as well as the language of the Articles of Confederation, the Supreme Court maintained that states did not have a right to secede. The court's reference in the same decision to the possibility of such changes occurring "through revolution, or through consent of the States," essentially means that this decision holds that no state has a right to unilaterally decide to leave the Union.
Name origins
 The 50 states have taken their names from a wide variety of languages. Twenty-four state names originate from Native American languages. Of these, eight are from
The 50 states have taken their names from a wide variety of languages. Twenty-four state names originate from Native American languages. Of these, eight are from Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic languages, Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language f ...
, seven are from Siouan languages
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
, three are from Iroquoian languages
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian la ...
, one is from Uto-Aztecan languages
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
and five others are from other indigenous languages. Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
's name is derived from the Polynesian Hawaiian language
Hawaiian (', ) is a Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaii, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language o ...
.
Of the remaining names, 22 are from European languages. Seven are from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
(mainly Latinized forms of English names) and the rest are from English, Spanish and French. Eleven states are named after individual people, including seven named for royalty and one named after a President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
. The origins of six state names are unknown or disputed. Several of the states that derive their names from names used for Native peoples have retained the plural ending of "s".
Geography
Borders
The borders of the 13 original states were largely determined by colonial charters. Their western boundaries were subsequently modified as the states ceded their western land claims to the Federal government during the 1780s and 1790s. Many state borders beyond those of the original 13 were set by Congress as it created territories, divided them, and over time, created states within them. Territorial and new state lines often followed various geographic features (such asrivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
or mountain range peaks), and were influenced by settlement or transportation patterns. At various times, national borders with territories formerly controlled by other countries ( British North America, New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
, New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
including Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, ...
, and Russian America) became institutionalized as the borders of U.S. states. In the West, relatively arbitrary straight lines following latitude and longitude often prevail due to the sparseness of settlement west of the Mississippi River.
Once established, most state borders have, with few exceptions, been generally stable. Only two states, Missouri (Platte Purchase
The Platte Purchase was a land acquisition in 1836 by the United States government from American Indian tribes of the region. It comprised lands along the east bank of the Missouri River and added to the northwest corner of the state of Miss ...
) and Nevada grew appreciably after statehood. Several of the original states ceded land, over a several-year period, to the Federal government, which in turn became the Northwest Territory, Southwest Territory, and Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. T ...
. In 1791, Maryland and Virginia ceded land to create the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
(Virginia's portion was returned in 1847). In 1850, Texas ceded a large swath of land to the federal government. Additionally, Massachusetts and Virginia (on two occasions), have lost land, in each instance to form a new state.
There have been numerous other minor adjustments to state boundaries over the years due to improved surveys, resolution of ambiguous or disputed boundary definitions, or minor mutually agreed boundary adjustments for administrative convenience or other purposes. Occasionally, either Congress or the U.S. Supreme Court has had to settle state border disputes. One notable example is the case ''New Jersey v. New York
''New Jersey v. New York'', 523 U.S. 767 (1998), was a U.S. Supreme Court case that determined that roughly 83% of Ellis Island was part of New Jersey, rather than New York State.
Because the New Jersey's original 1664 land grant was unclear, t ...
'', in which New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
won roughly 90% of Ellis Island from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
in 1998.
Once a territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
is admitted by Congress as a state of the Union, the state must consent to any changes pertaining to the jurisdiction of that state and Congress. The only potential violation of this occurred when the legislature of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
declared the secession of Virginia from the United States at the start of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
and a newly formed alternative Virginia legislature, recognized by the federal government, consented to have West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
secede from Virginia.
Regional grouping
States may be grouped in regions; there are many variations and possible groupings. Many are defined in law or regulations by the federal government. For example, the United States Census Bureau defines four statistical regions, with nine divisions. The Census Bureau region definition (Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
, Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
, South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
, and West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
) is "widely used ... for data collection and analysis,""The National Energy Modeling System: An Overview 2003" (Report #:DOE/EIA-0581, October 2009). United States Department of Energy, Energy Information Administration
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and publ ...
. and is the most commonly used classification system."(M)ost demographic and food consumption data are presented in this four-region format." Pamela Goyan Kittler, Kathryn P. Sucher, Food and Culture
',
Cengage Learning
Cengage Group is an American educational content, technology, and services company for the higher education, K-12, professional, and library markets. It operates in more than 20 countries around the world.(Jun 27, 2014Global Publishing Leaders ...
(2008): p.475. Other multi-state regions are unofficial, and defined by geography or cultural affinity rather than by state lines.
See also
*Insular area
In the law of the United States, an insular area is a U.S.-associated jurisdiction that is not part of the 50 states or the District of Columbia. This includes fourteen U.S. territories administered under U.S. sovereignty, as well as three sov ...
* ISO 3166-2:US
* Local government in the United States
Local government in the United States refers to governmental jurisdictions below the level of the state. Most states and territories have at least two tiers of local government: counties and municipalities. Louisiana uses the term parish and Alas ...
References
Further reading
* Stein, Mark, ''How the States Got Their Shapes'', New York : Smithsonian Books/Collins, 2008.External links
Information about All States
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
State Resource Guides, from the Library of Congress
* [http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20090403030000/http://factfinder.census.gov/bf/_lang=en_vt_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U_GCTPH1_US9_geo_id=01000US.html Tables with areas, populations, densities and more (alphabetical)]
State and Territorial Governments on USA.gov
StateMaster – statistical database for U.S. states
50states.com – States and Capitals
{{DEFAULTSORT:U.S. State United States 1 States, United States State States, United S