Square root of 3 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The square root of 3 is the positive

 The square root of 3 can be found as the
The square root of 3 can be found as the
Theodorus' Constant
at
Kevin Brown
E. B. Davis
{{DEFAULTSORT:Square root of three Quadratic irrational numbers Mathematical constants
real number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every real ...
that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number 3. It is denoted mathematically as or . It is more precisely called the principal square root of 3 to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. The square root
In mathematics, a square root of a number is a number such that ; in other words, a number whose ''square'' (the result of multiplying the number by itself, or ⋅ ) is . For example, 4 and −4 are square roots of 16, because .
E ...
of 3 is an irrational number
In mathematics, the irrational numbers (from in- prefix assimilated to ir- (negative prefix, privative) + rational) are all the real numbers that are not rational numbers. That is, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integ ...
. It is also known as Theodorus' constant, after Theodorus of Cyrene
Theodorus of Cyrene ( el, Θεόδωρος ὁ Κυρηναῖος) was an ancient Greek mathematician who lived during the 5th century BC. The only first-hand accounts of him that survive are in three of Plato's dialogues: the ''Theaetetus'', th ...
, who proved its irrationality.
, its numerical value in decimal notation had been computed to at least ten billion digits. Its decimal expansion
A decimal representation of a non-negative real number is its expression as a sequence of symbols consisting of decimal digits traditionally written with a single separator:
r = b_k b_\ldots b_0.a_1a_2\ldots
Here is the decimal separator, i ...
, written here to 65 decimal places, is given by :
:
The fraction (...) can be used as a good approximation. Despite having a denominator
A fraction (from la, fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole or, more generally, any number of equal parts. When spoken in everyday English, a fraction describes how many parts of a certain size there are, for example, one-half, eight ...
of only 56, it differs from the correct value by less than (approximately , with a relative error of ). The rounded value of is correct to within 0.01% of the actual value.
The fraction (...) is accurate to .
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
reported a range for its value: .
The lower limit is an accurate approximation for to (six decimal places, relative error ) and the upper limit to (four decimal places, relative error ).
Expressions
It can be expressed as thecontinued fraction
In mathematics, a continued fraction is an expression obtained through an iterative process of representing a number as the sum of its integer part and the reciprocal of another number, then writing this other number as the sum of its integer ...
.
So it is true to say:
:
then when :
:
It can also be expressed by generalized continued fraction In complex analysis, a branch of mathematics, a generalized continued fraction is a generalization of regular continued fractions in canonical form, in which the partial numerators and partial denominators can assume arbitrary complex values.
A ge ...
s such as
:
which is evaluated at every second term.
Geometry and trigonometry
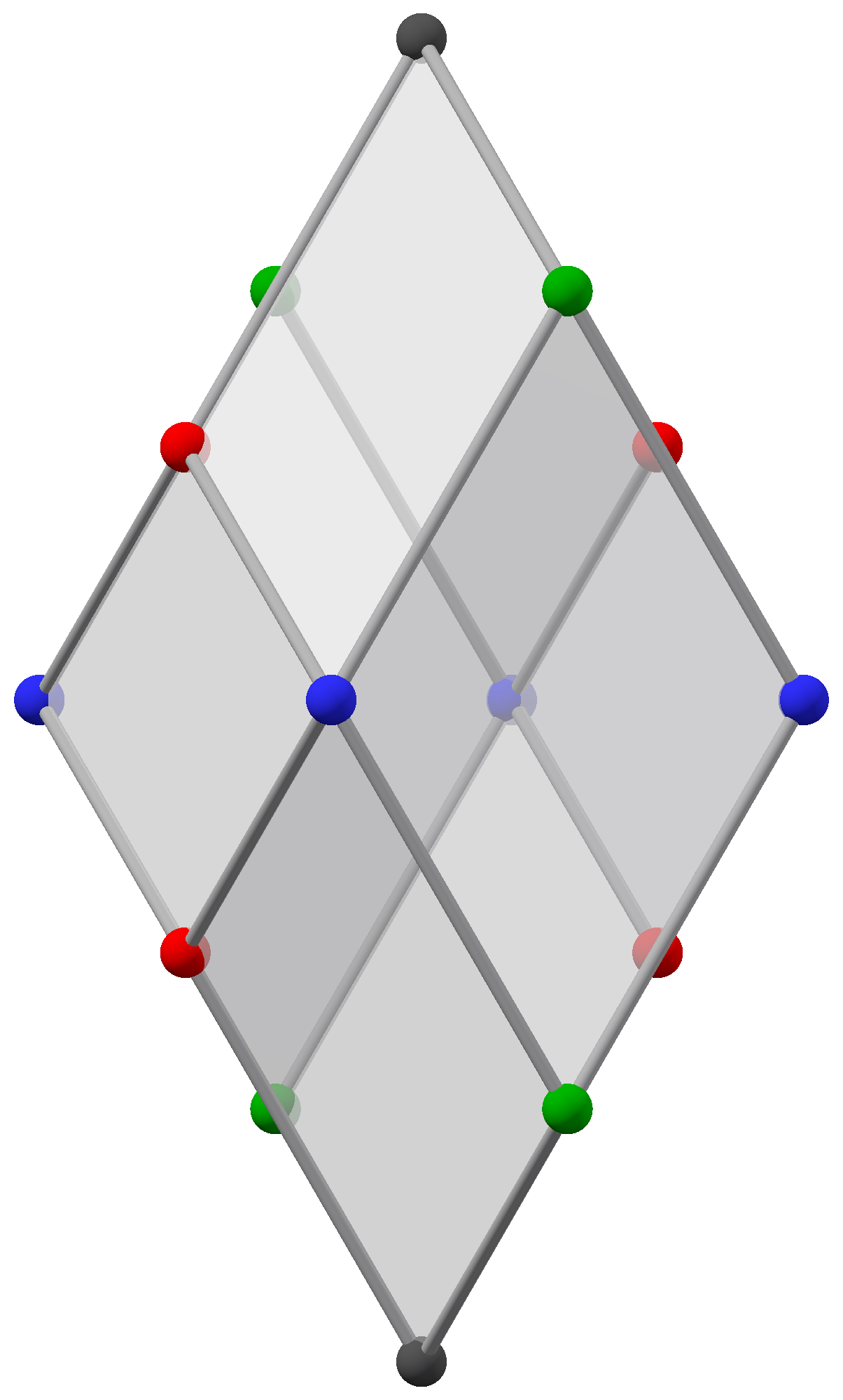
 The square root of 3 can be found as the
The square root of 3 can be found as the leg
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element ca ...
length of an equilateral triangle that encompasses a circle with a diameter of 1.
If an equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each othe ...
with sides of length 1 is cut into two equal halves, by bisecting an internal angle across to make a right angle with one side, the right angle triangle's hypotenuse
In geometry, a hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle. The length of the hypotenuse can be found using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse e ...
is length one, and the sides are of length and . From this, , , and .
The square root of 3 also appears in algebraic expressions for various other trigonometric constants, including the sines of 3°, 12°, 15°, 21°, 24°, 33°, 39°, 48°, 51°, 57°, 66°, 69°, 75°, 78°, 84°, and 87°.
It is the distance between parallel sides of a regular hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexa ...
with sides of length 1.
It is the length of the space diagonal
In geometry, a space diagonal (also interior diagonal or body diagonal) of a polyhedron is a line connecting two vertices that are not on the same face. Space diagonals contrast with '' face diagonals'', which connect vertices on the same face (bu ...
of a unit cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the only r ...
.
The vesica piscis
The vesica piscis is a type of lens, a mathematical shape formed by the intersection of two disks with the same radius, intersecting in such a way that the center of each disk lies on the perimeter of the other. In Latin, "vesica piscis" litera ...
has a major axis to minor axis ratio equal to . This can be shown by constructing two equilateral triangles within it.
Other uses
Power engineering
Inpower engineering
Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of electrical engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electric power, and the electrical apparatus connected to such sy ...
, the voltage between two phases in a three-phase system equals times the line to neutral voltage. This is because any two phases are 120° apart, and two points on a circle 120 degrees apart are separated by times the radius (see geometry examples above).
See also
*Square root of 2
The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is a positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as \sqrt or 2^, and is an algebraic number. Technically, it should be called the princip ...
* Square root of 5
The square root of 5 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the prime number 5. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 5, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. This numbe ...
Other references
* * *References
External links
Theodorus' Constant
at
MathWorld
''MathWorld'' is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Dig ...
Kevin Brown
E. B. Davis
{{DEFAULTSORT:Square root of three Quadratic irrational numbers Mathematical constants