Spin Angular Momentum Of Light on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The spin angular momentum of light (SAM) is the component of angular momentum of light that is associated with the quantum spin and the rotation between the polarization degrees of freedom of the photon.
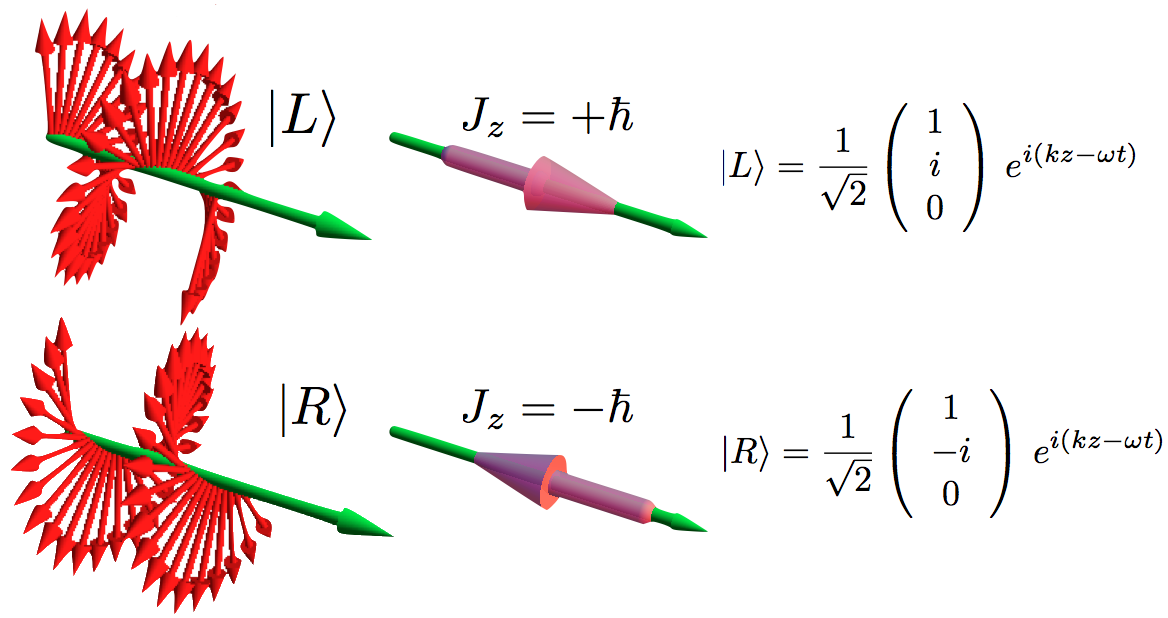 An
An
Introduction
Spin is the fundamental property that distinguishes the two types of elementary particles:fermions
In particle physics, a fermion is a subatomic particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-integer spin ( spin , spin , etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles include all quarks and leptons and ...
, with half-integer spins; and bosons
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0, 1, 2, ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have half odd-integer ...
, with integer spins. Photons
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that ...
, which are the quanta of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
, have been long recognized as spin-1 gauge bosons. The polarization of the light is commonly accepted as its “intrinsic” spin degree of freedom
In many scientific fields, the degrees of freedom of a system is the number of parameters of the system that may vary independently. For example, a point in the plane has two degrees of freedom for translation: its two coordinates; a non-infinites ...
. However, in free space, only two transverse polarizations are allowed. Thus, the photon spin is always only connected to the two circular polarizations. To construct the full quantum spin operator of light, longitudinal polarized photon modes have to be introduced.
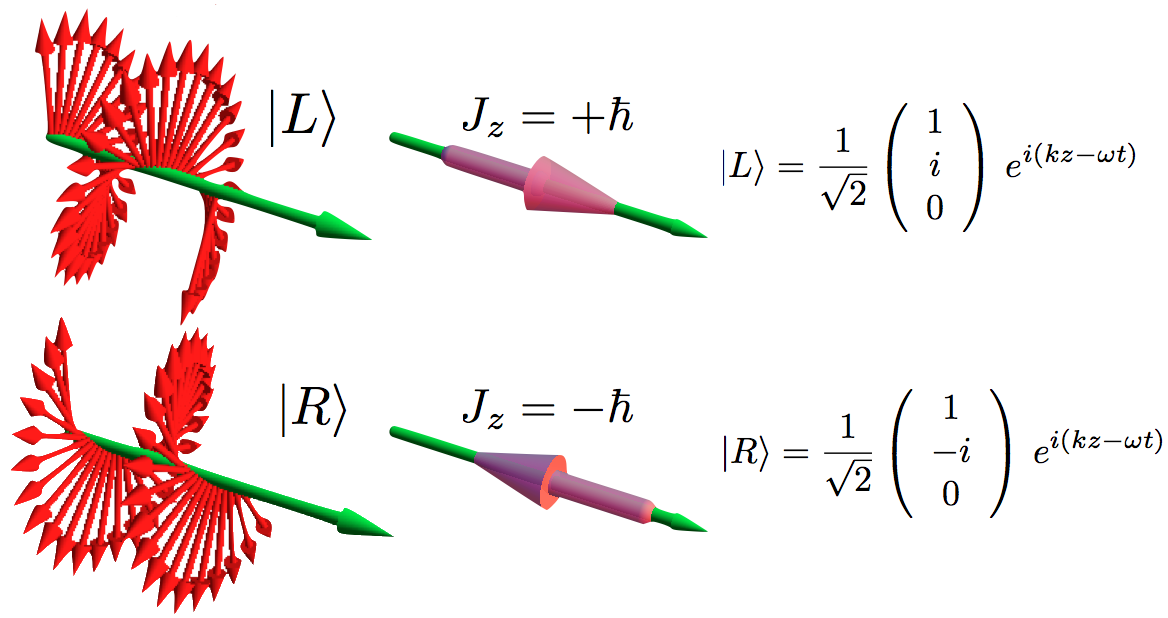 An
An electromagnetic wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ...
is said to have circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to ...
when its electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
and magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s rotate continuously around the beam axis during propagation. The circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to ...
is left () or right () depending on the field rotation direction and, according to the convention used: either from the point of view of the source, or the receiver. Both conventions are used in science, depending on the context.
When a light beam is circularly polarized, each of its photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s carries a spin angular momentum (SAM) of , where is the reduced Planck constant
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, denoted by h, is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics: a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant, and the wavelength of a ...
and the sign is positive for left and negative for right circular polarizations (this is adopting the convention from the point of view of the receiver most commonly used in optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
). This SAM is directed along the beam axis (parallel if positive, antiparallel if negative).
The above figure shows the instantaneous structure of the electric field of left () and right () circularly polarized light in space. The green arrows indicate the propagation direction.
The mathematical expressions reported under the figures give the three electric-field components of a circularly polarized plane wave propagating in the direction, in complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
notation.
Mathematical expression
The general expression for the spin angular momentum is where is the speed of light in free space and is the conjugate canonical momentum of thevector potential
In vector calculus, a vector potential is a vector field whose curl is a given vector field. This is analogous to a ''scalar potential'', which is a scalar field whose gradient is a given vector field.
Formally, given a vector field \mathbf, a ' ...
. The general expression for the orbital angular momentum of light is
where denotes four indices of the spacetime
In physics, spacetime, also called the space-time continuum, is a mathematical model that fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum. Spacetime diagrams are useful in visualiz ...
and Einstein's summation convention has been applied.
To quantize light, the basic equal-time commutation relations have to be postulated,
where is the reduced Planck constant
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, denoted by h, is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics: a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant, and the wavelength of a ...
and is the metric tensor of the Minkowski space
In physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is the main mathematical description of spacetime in the absence of gravitation. It combines inertial space and time manifolds into a four-dimensional model.
The model helps show how a ...
.
Then, one can verify that both and satisfy the canonical angular momentum commutation relations
and they commute with each other .
After the plane-wave expansion
In physics, the plane-wave expansion expresses a plane wave as a linear combination of spherical waves:
e^ = \sum_^\infty (2 \ell + 1) i^\ell j_\ell(k r) P_\ell(\hat \cdot \hat),
where
* is the imaginary unit,
* is a wave vector of length ,
* i ...
, the photon spin can be re-expressed in a simple and intuitive form in the wave-vector space
where the vector is the field operator of the photon in wave-vector space and the matrix
is the spin-1 operator of the photon with the SO(3) rotation generators
and the two unit vectors denote the two transverse polarizations of light in free space and unit vector denotes the longitudinal polarization.
Due to the longitudinal polarized photon and scalar photon have been involved, both and are not gauge invariant. To incorporate the gauge invariance into the photon angular momenta, a re-decomposition of the total QED angular momentum and the Lorenz gauge condition have to be enforced. Finally, the direct observable part of spin and orbital angular momenta of light are given by
and
which recover the angular momenta of classical transverse light. Here, () is the transverse part of the electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
(vector potential
In vector calculus, a vector potential is a vector field whose curl is a given vector field. This is analogous to a ''scalar potential'', which is a scalar field whose gradient is a given vector field.
Formally, given a vector field \mathbf, a ' ...
), is the vacuum permittivity
Vacuum permittivity, commonly denoted (pronounced "epsilon nought" or "epsilon zero"), is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It may also be referred to as the permittivity of free space, the electric const ...
, and we are using SI units
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official st ...
.
We can define the annihilation operators for circularly polarized transverse photons:
with polarization unit vectors
Then, the transverse-field photon spin can be re-expressed as
For a single plane-wave photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
, the spin can only have two values , which are eigenvalues
In linear algebra, an eigenvector ( ) or characteristic vector is a vector that has its direction unchanged (or reversed) by a given linear transformation. More precisely, an eigenvector \mathbf v of a linear transformation T is scaled by a ...
of the spin operator . The corresponding eigenfunctions describing photons with well defined values of SAM are described as circularly polarized waves:
See also
*Helmholtz equation
In mathematics, the Helmholtz equation is the eigenvalue problem for the Laplace operator. It corresponds to the elliptic partial differential equation:
\nabla^2 f = -k^2 f,
where is the Laplace operator, is the eigenvalue, and is the (eigen)fun ...
* Orbital angular momentum of light
* Polarization (physics)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polariz ...
* Photon polarization
* Spin polarization
In particle physics, spin polarization is the degree to which the spin, i.e., the intrinsic angular momentum of elementary particles, is aligned with a given direction. This property may pertain to the spin, hence to the magnetic moment, of co ...
References
Further reading
* * * {{refend Angular momentum of light Light Physical quantities