Sperm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sperm is the
Sperm is the

 The mammalian sperm cell can be divided in 2 parts:
* Head: contains the
The mammalian sperm cell can be divided in 2 parts:
* Head: contains the
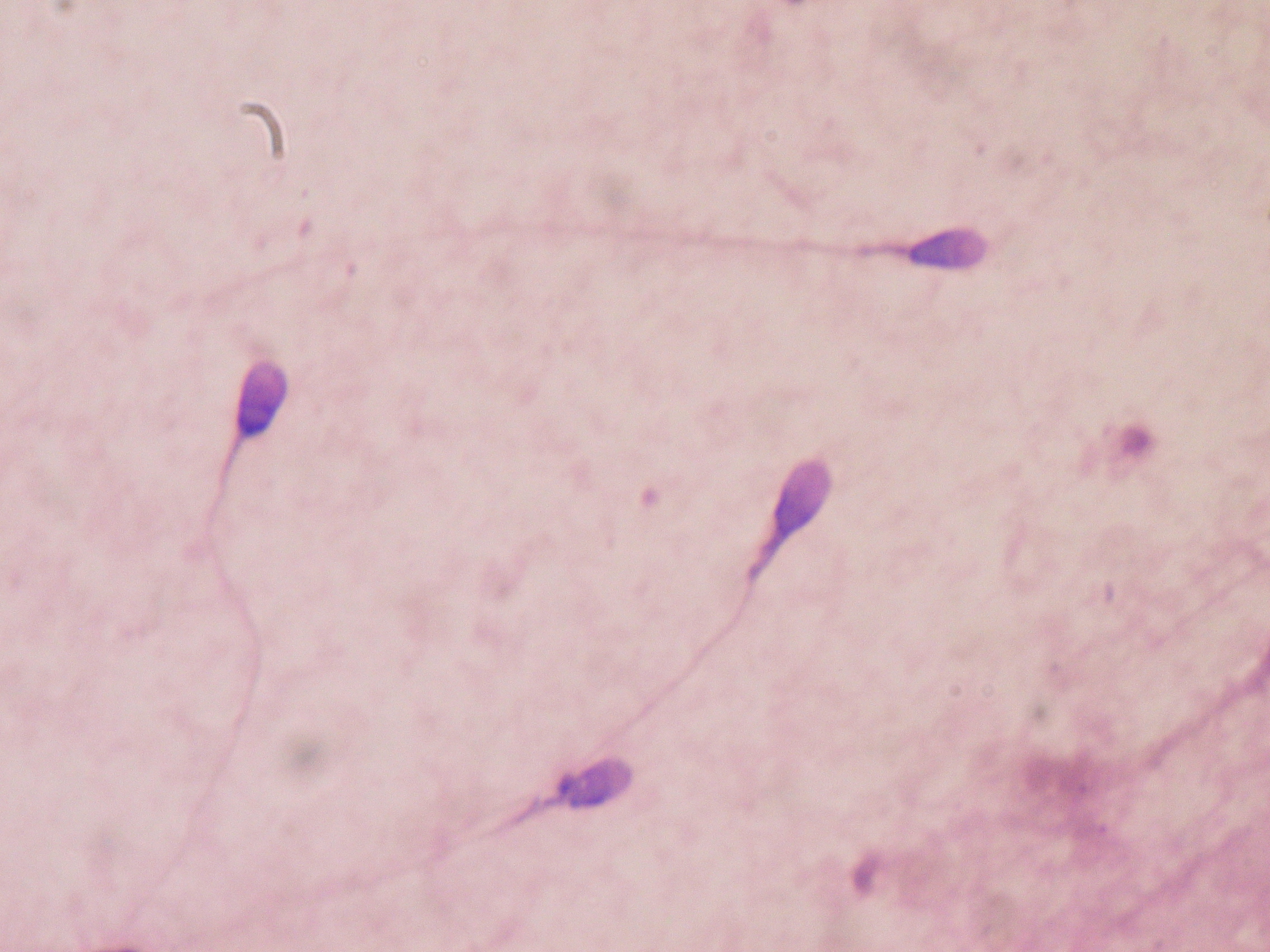 Sperm quantity and quality are the main parameters in semen quality, which is a measure of the ability of semen to accomplish
Sperm quantity and quality are the main parameters in semen quality, which is a measure of the ability of semen to accomplish
ncbio.org Furthermore, Nordic sperm donors tend to be tall and highly educated
Posted Aug 13, 08 7:37 AM CDT in World, Science & Health and have altruistic motives for their donations, partly due to the relatively low monetary compensation in Nordic countries. More than 50 countries worldwide are importers of Danish sperm, including
 Motile sperm cells typically move via flagella and require a water medium in order to swim toward the egg for fertilization. In animals most of the energy for sperm motility is derived from the metabolism of fructose carried in the seminal fluid. This takes place in the mitochondria located in the sperm's midpiece (at the base of the sperm head). These cells cannot swim backwards due to the nature of their propulsion. The uniflagellated sperm cells (with one flagellum) of
Motile sperm cells typically move via flagella and require a water medium in order to swim toward the egg for fertilization. In animals most of the energy for sperm motility is derived from the metabolism of fructose carried in the seminal fluid. This takes place in the mitochondria located in the sperm's midpiece (at the base of the sperm head). These cells cannot swim backwards due to the nature of their propulsion. The uniflagellated sperm cells (with one flagellum) of
''The Cell'', 2nd ed
. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company
pp. 604–640
. . . * Lehti, M. S. and A. Sironen (October 2017)
"Formation and function of sperm tail structures in association with sperm motility defects"
''Biol Reprod'' 97(4): 522–536. .
Human Sperm Under a Microscope
{{Authority control Fertility Germ cells Reproductive system Mammal male reproductive system Semen Human male reproductive system Articles containing video clips Microscopic discoveries by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
male
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to ...
reproductive cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
, or gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce t ...
, in anisogamous
Different forms of anisogamy: A) anisogamy of motile cells, B) egg_cell.html"_;"title="oogamy_(egg_cell">oogamy_(egg_cell_and_sperm_cell),_C)_anisogamy_of_non-motile_cells_(egg_cell_and_spermatia)..html" ;"title="egg_cell_and_sperm_cell.html" ;" ...
forms of sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
(forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
sperm with a tail known as a flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
, which are known as spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromos ...
, while some red algae and fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s contain non-motile sperm inside pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
, while some more basal plants like ferns
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except th ...
and some gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
s have motile sperm.
Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes ( reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubule
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testes, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa. Structure
The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells known ...
s of the testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans:
...
, which differentiate into spermatocyte
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and ...
s. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately r ...
, reducing their chromosome number
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectivel ...
by half, which produces spermatid
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are co ...
s. The spermatids then mature and, in animals, construct a tail, or flagellum, which gives rise to the mature, motile sperm cell. This whole process occurs constantly and takes around 3 months from start to finish.
Sperm cells cannot divide and have a limited lifespan, but after fusion with egg cells during fertilisation, a new organism begins developing, starting as a totipotent Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicellula ...
. The human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
sperm cell is haploid, so that its 23 chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
s can join the 23 chromosomes of the female egg to form a diploid cell with 46 paired chromosomes. In mammals, sperm is stored in the epididymis and is released from the penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
during ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the male reproductory tract as a result of an orgasm. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential componen ...
in a fluid known as semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Sem ...
.
The word ''sperm'' is derived from the Greek word σπέρμα, ''sperma'', meaning "seed".
Evolution
It is generally accepted thatisogamy
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves gametes of the same morphology (indistinguishable in shape and size), found in most unicellular eukaryotes. Because both gametes look alike, they generally cannot be classified as male or ...
is the ancestor to sperm and eggs. However, there are no fossil records for the evolution of sperm and eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
from isogamy leading there to be a strong emphasis on mathematical models to understand the evolution of sperm.
A widespread hypothesis states that sperm evolved rapidly, but there is no direct evidence that sperm evolved at a fast rate or before other male characteristics.
Sperm in animals
Function
The main sperm function is to reach the ovum and fuse with it to deliver two sub-cellular structures: (i) the malepronucleus
A pronucleus () is the nucleus of a sperm or egg cell during the process of fertilization. The sperm cell becomes a pronucleus after the sperm enters the ovum, but before the genetic material of the sperm and egg fuse. Contrary to the sperm cell, ...
that contains the genetic material and (ii) the centrioles that are structures that help organize the microtubule cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is com ...
.
Anatomy

 The mammalian sperm cell can be divided in 2 parts:
* Head: contains the
The mammalian sperm cell can be divided in 2 parts:
* Head: contains the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
with densely coiled chromatin fibers, surrounded anteriorly by a thin, flattened sac called the acrosome The acrosome is an organelle that develops over the anterior (front) half of the head in the spermatozoa (sperm cells) of many animals including humans. It is a cap-like structure derived from the Golgi apparatus. In placental mammals the acrosome ...
, which contains enzymes used for penetrating the female egg. It also contains vacuoles.
* Tail: also called the flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
, is the longest part and capable of wave-like motion that propels sperm for swimming and aids in the penetration of the egg. The tail was formerly thought to move symmetrically in a helical shape.
The neck or connecting piece contains one typical centriole and one atypical centriole such as the proximal centriole-like The proximal centriole-like or PCL is an atypical type of centriole found in the sperm cells of insects. The PCL name is due to some similarity to the Proximal centriole found in Vertebrates sperm and the hypothesis that the two structures are Homol ...
. The midpiece has a central filamentous core with many mitochondria spiralled around it, used for ATP production for the journey through the female cervix, uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
, and uterine tubes
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ot ...
.
During fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
, the sperm provides three essential parts to the oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The femal ...
: (1) a signalling or activating factor, which causes the metabolically
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
dormant oocyte to activate; (2) the haploid paternal genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
; (3) the centriole, which is responsible for forming the centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle prog ...
and microtubule system.
Origin
The spermatozoa ofanimal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s are produced through spermatogenesis inside the male gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
s (testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
s) via meiotic
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately res ...
division. The initial spermatozoon process takes around 70 days to complete. The process starts with the production of spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans:
...
from germ cell
Germ or germs may refer to:
Science
* Germ (microorganism), an informal word for a pathogen
* Germ cell, cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually
* Germ layer, a primary layer of cells that forms during emb ...
precursors. These divide and differentiate into spermatocytes
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and s ...
, which undergo meiosis to form spermatid
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are co ...
s. In the spermatid stage, the sperm develops the familiar tail. The next stage where it becomes fully mature takes around 60 days when it is called a spermatozoan. Sperm cells are carried out of the male body in a fluid known as semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Sem ...
. Human sperm cells can survive within the female reproductive tract for more than 5 days post coitus. Semen is produced in the seminal vesicles
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands, or seminal glands) are a pair of two convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of some male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.
The vesicles are 5� ...
, prostate gland
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physio ...
and urethral gland
The urethral or periurethral glands (also Littré glands after Alexis Littré) are glands that branch off the wall of the urethra of mammals. The glands secrete mucus and are most numerous in the section of the urethra that runs through the peni ...
s.
In 2016, scientists at Nanjing Medical University
Nanjing Medical University (NMU; ) is a university in Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China. It was established in 1934 in Zhenjiang, but subsequently relocated to Nanjing in 1957. The university has two main campuses: Wutai and Jiangning, both of which ...
claimed they had produced cells resembling mouse spermatids from mouse embryonic stem cells
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre- implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist ...
artificially. They injected these spermatids into mouse eggs and produced pups.
Sperm quality
fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
. Thus, in humans, it is a measure of fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
in a man
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromo ...
. The genetic quality of sperm, as well as its volume and motility, all typically decrease with age.
DNA damages present in sperm cells in the period after meiosis but before fertilization may be repaired in the fertilized egg, but if not repaired, can have serious deleterious effects on fertility and the developing embryo. Human sperm cells are particularly vulnerable to free radical attack and the generation of oxidative DNA damage, such as that from 8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine
8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) is an oxidized derivative of deoxyguanosine. 8-Oxo-dG is one of the major products of DNA oxidation. Concentrations of 8-oxo-dG within a cell are a measurement of oxidative stress.
In DNA
Steady-state leve ...
.
The postmeiotic phase of mouse spermatogenesis is very sensitive to environmental genotoxic agents, because as male germ cells form mature sperm they progressively lose the ability to repair DNA damage. Irradiation of male mice during late spermatogenesis can induce damage that persists for at least 7 days in the fertilizing sperm cells, and disruption of maternal DNA double-strand break repair pathways increases sperm cell-derived chromosomal aberrations. Treatment of male mice with melphalan
Melphalan, sold under the brand name Alkeran among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, melanoma, and AL amyloidosis. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
Common side effects incl ...
, a bifunctional alkylating agent frequently employed in chemotherapy, induces DNA lesions during meiosis that may persist in an unrepaired state as germ cells progress through DNA repair-competent phases of spermatogenic development. Such unrepaired DNA damages in sperm cells, after fertilization, can lead to offspring with various abnormalities.
Sperm size
Related to sperm quality is sperm size, at least in some animals. For instance, the sperm of some species of fruit fly (''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
'') are up to 5.8 cm long—about 20 times as long as the fly itself. Longer sperm cells are better than their shorter counterparts at displacing competitors from the female's seminal receptacle. The benefit to females is that only healthy males carry "good" genes that can produce long sperm in sufficient quantities to outcompete their competitors.
Market for human sperm
Some sperm banks hold up to of sperm. In addition toejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the male reproductory tract as a result of an orgasm. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential componen ...
, it is possible to extract sperm through testicular sperm extraction
Testicular sperm extraction (TESE) is a surgical procedure in which a small portion of tissue is removed from the testicle and any viable sperm cells from that tissue are extracted for use in further procedures, most commonly intracytoplasmic sperm ...
.
On the global market, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
has a well-developed system of human sperm export. This success mainly comes from the reputation of Danish sperm donors for being of high quality and, in contrast with the law in the other Nordic countries, gives donors the choice of being either anonymous or non-anonymous to the receiving couple.Assisted Reproduction in the Nordic Countriesncbio.org Furthermore, Nordic sperm donors tend to be tall and highly educated
Posted Aug 13, 08 7:37 AM CDT in World, Science & Health and have altruistic motives for their donations, partly due to the relatively low monetary compensation in Nordic countries. More than 50 countries worldwide are importers of Danish sperm, including
Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, and Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delt ...
. However, the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) of the US has banned import of any sperm, motivated by a risk of transmission of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), also known as subacute spongiform encephalopathy or neurocognitive disorder due to prion disease, is an invariably fatal degenerative brain disorder. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes ...
, although such a risk is insignificant, since artificial insemination is very different from the route of transmission of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. The prevalence of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease for donors is at most one in a million, and if the donor was a carrier, the infectious proteins would still have to cross the blood-testis barrier to make transmission possible.
History
Sperm were first observed in 1677 by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek using amicroscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
. He described them as being animalcule
Animalcule ('little animal', from Latin ''animal'' + the diminutive suffix ''-culum'') is an old term for microscopic organisms that included bacteria, protozoans, and very small animals. The word was invented by 17th-century Dutch scientist A ...
s (little animals), probably due to his belief in preformationism
In the history of biology, preformationism (or preformism) is a formerly popular theory that organisms develop from miniature versions of themselves. Instead of assembly from parts, preformationists believed that the form of living things exist, ...
, which thought that each sperm contained a fully formed but small human.
Forensic analysis
Ejaculated fluids are detected byultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
, irrespective of the structure or colour of the surface. Sperm heads, e.g. from vaginal swabs, are still detected by microscopy using the "Christmas Tree Stain" method, i.e., Kernechtrot-Picroindigocarmine (KPIC) staining.
Sperm in plants
Sperm cells in algal and many plantgametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the ...
s are produced in male gametangia
A gametangium (plural: gametangia) is an organ or cell in which gametes are produced that is found in many multicellular protists, algae, fungi, and the gametophytes of plants. In contrast to gametogenesis in animals, a gametangium is a haploi ...
(antheridia
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also ...
) via mitotic
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintai ...
division. In flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s, sperm nuclei are produced inside pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
.
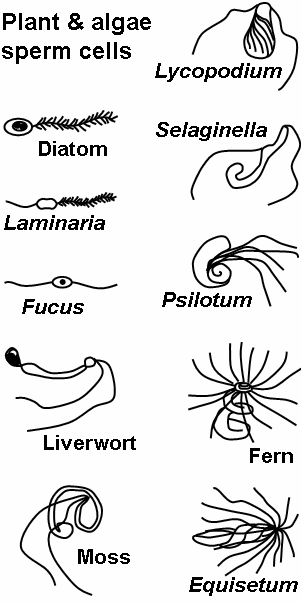
Motile sperm cells
 Motile sperm cells typically move via flagella and require a water medium in order to swim toward the egg for fertilization. In animals most of the energy for sperm motility is derived from the metabolism of fructose carried in the seminal fluid. This takes place in the mitochondria located in the sperm's midpiece (at the base of the sperm head). These cells cannot swim backwards due to the nature of their propulsion. The uniflagellated sperm cells (with one flagellum) of
Motile sperm cells typically move via flagella and require a water medium in order to swim toward the egg for fertilization. In animals most of the energy for sperm motility is derived from the metabolism of fructose carried in the seminal fluid. This takes place in the mitochondria located in the sperm's midpiece (at the base of the sperm head). These cells cannot swim backwards due to the nature of their propulsion. The uniflagellated sperm cells (with one flagellum) of animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s are referred to as spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromos ...
, and are known to vary in size.
Motile sperm are also produced by many protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s and the gametophytes of bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in s ...
s, fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
s and some gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
s such as cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male o ...
s and ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and is now the only living genus with ...
. The sperm cells are the only flagellated cells in the life cycle of these plants. In many ferns and lycophyte
The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a vascular plant (tracheophyte) subgroup of the kingdom Plantae. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldes ...
s, cycads and ginkgo they are multi-flagellated (carrying more than one flagellum).
In nematodes, the sperm cells are amoeboid
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopo ...
and crawl, rather than swim, towards the egg cell.
Non-motile sperm cells
Non-motile sperm cells called spermatia lack flagella and therefore cannot swim. Spermatia are produced in a spermatangium. Because spermatia cannot swim, they depend on their environment to carry them to the egg cell. Somered alga
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
e, such as ''Polysiphonia
''Polysiphonia'' is a genus of filamentous red algae with about 19 species on the coasts of the British Isles and about 200 species worldwide, including Crete in Greece, Antarctica and Greenland. Its members are known by a number of common names ...
'', produce non-motile spermatia that are spread by water currents after their release. The spermatia of rust fungi
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales).
An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently a ...
are covered with a sticky substance. They are produced in flask-shaped structures containing nectar, which attract flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced m ...
that transfer the spermatia to nearby hyphae for fertilization in a mechanism similar to insect pollination
Entomophily or insect pollination is a form of pollination whereby pollen of plants, especially but not only of flowering plants, is distributed by insects. Flowers pollinated by insects typically advertise themselves with bright colours, some ...
in flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s.
Fungal spermatia (also called pycniospores, especially in the Uredinales) may be confused with conidia. Conidia are spores that germinate independently of fertilization, whereas spermatia are gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce t ...
s that are required for fertilization. In some fungi, such as ''Neurospora crassa
''Neurospora crassa'' is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" in Greek, refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation ...
'', spermatia are identical to microconidia as they can perform both functions of fertilization as well as giving rise to new organisms without fertilization.
Sperm nuclei
In almost allembryophyte
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as si ...
s, including most gymnosperms and all angiosperms, the male gametophytes (pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
grains) are the primary mode of dispersal, for example via wind or insect pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds ...
, eliminating the need for water to bridge the gap between male and female. Each pollen grain contains a spermatogenous (generative) cell. Once the pollen lands on the stigma of a receptive flower, it germinates and starts growing a pollen tube
A pollen tube is a tubular structure produced by the male gametophyte of seed plants when it germinates. Pollen tube elongation is an integral stage in the plant life cycle. The pollen tube acts as a conduit to transport the male gamete cells fro ...
through the carpel
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) '' pistils' ...
. Before the tube reaches the ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the '' integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the ...
, the nucleus of the generative cell in the pollen grain divides and gives rise to two sperm nuclei, which are then discharged through the tube into the ovule for fertilization.
In some protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s, fertilization also involves sperm nuclei, rather than cells, migrating toward the egg cell through a fertilization tube. Oomycete
Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oomycetes (). They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore is the resul ...
s form sperm nuclei in a syncytical antheridium surrounding the egg cells. The sperm nuclei reach the eggs through fertilization tubes, similar to the pollen tube mechanism in plants.
Sperm centrioles
Most sperm cells have centrioles in the sperm neck. Sperm of many animals has two typical centrioles, known as the proximal centriole and distal centriole. Some animals (including humans and bovines) have a single typical centriole, the proximal centriole, as well as a second centriole with atypical structure. Mice and rats have no recognizable sperm centrioles. The fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the " vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with ...
'' has a single centriole and an atypical centriole named the proximal centriole-like.
Sperm tail formation
The sperm tail is a specialized type ofcilium
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike project ...
(aka flagella). In many animals the sperm tail is formed through the unique process of cytosolic ciliogenesis
Cytosolic ciliogenesis, otherwise cytoplasmic ciliogenesis, is a type of ciliogenesis where the cilium axoneme is formed in the cytoplasm or becomes exposed to the cytoplasm.
Cytosolic ciliogenesis is divided into three types: Primary cytosolic ci ...
, in which all or part of the sperm tail's axoneme
An axoneme, also called an axial filament is the microtubule-based cytoskeletal structure that forms the core of a cilium or flagellum. Cilia and flagella are found on many cells, organisms, and microorganisms, to provide motility. The axo ...
is formed in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
or gets exposed to the cytoplasm.
See also
*Female sperm Female sperm can refer to either:
#A sperm which contains an X chromosome, produced in the usual way in the testicles, referring to the occurrence of such a sperm fertilizing an egg and giving birth to a female.
#A sperm which artificially contains ...
* Female sperm storage
Female sperm storage is a biological process and often a type of sexual selection in which sperm cells transferred to a female during mating are temporarily retained within a specific part of the reproductive tract before the oocyte, or egg, is fe ...
* Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later popularize ...
* Polyspermy
In biology, polyspermy describes the fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm. Diploid organisms normally contain two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. The cell resulting from polyspermy, on the other hand, contains three or ...
* Sperm competition
Sperm competition is the competitive process between spermatozoa of two or more different males to fertilize the same egg during sexual reproduction. Competition can occur when females have multiple potential mating partners. Greater choice and ...
* Sperm granuloma
A sperm granuloma is a lump of leaked sperm that appears along the vasa deferentia or epididymides in vasectomized individuals. While majority of sperm granulomas are present along the vas deferens, the rest of them form at the epididymis. Sper ...
* Sperm theft
Sperm theft, also known as unauthorized use of sperm, forced fatherhood, spermjacking or (a portmanteau of sperm and burgling), occurs when a man's semen is used, against his will or without his knowledge or consent, to inseminate a woman. It ...
Citations
General and cited sources
* Fawcett, D. W. (1981). "Sperm Flagellum". In: D. W. Fawcett''The Cell'', 2nd ed
. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company
pp. 604–640
. . . * Lehti, M. S. and A. Sironen (October 2017)
"Formation and function of sperm tail structures in association with sperm motility defects"
''Biol Reprod'' 97(4): 522–536. .
External links
Human Sperm Under a Microscope
{{Authority control Fertility Germ cells Reproductive system Mammal male reproductive system Semen Human male reproductive system Articles containing video clips Microscopic discoveries by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek