Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a
Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European languages, I ...
of the
Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial
Latin spoken on the
Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a
global language
In sociolinguistics, a world language (sometimes global language, rarely international language) is a language that is geographically widespread and makes it possible for members of different language communities to communicate. The term may also b ...
with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
and
Spain. Spanish is the official language of
20 countries. It is the world's
second-most spoken native language after
Mandarin Chinese;
the world's
fourth-most spoken language overall after
English, Mandarin Chinese, and
Hindustani
Hindustani may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Hindustan (another name of India)
* Hindustani language, an Indo-Aryan language, whose two official norms are Hindi and Urdu
* Fiji Hindi, a variety of Eastern Hindi spoken in Fiji, and ...
(Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken
Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European languages, I ...
. The largest population of native speakers is in
Mexico.
Spanish is part of the
Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
in Iberia after the collapse of the
Western Roman Empire in the 5th century. The oldest
Latin texts with traces of Spanish come from mid-northern Iberia in the 9th century, and the first systematic written use of the language happened in
Toledo
Toledo most commonly refers to:
* Toledo, Spain, a city in Spain
* Province of Toledo, Spain
* Toledo, Ohio, a city in the United States
Toledo may also refer to:
Places Belize
* Toledo District
* Toledo Settlement
Bolivia
* Toledo, Orur ...
, a prominent city of the
Kingdom of Castile, in the 13th century. Spanish colonialism in the Early Modern Period spurred on the introduction of the language to overseas locations, most notably to the Americas.
As a Romance language, Spanish is a descendant of Latin, and has one of the smaller degrees of difference from it (about 20%) alongside
Sardinian and
Italian. Around 75% of modern Spanish vocabulary is derived from Latin, including Latin borrowings from Ancient Greek. Alongside English and
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, it is also one of the most taught foreign languages throughout the world. Spanish does not feature prominently as a scientific language; however, it is better represented in areas like
humanities and
social sciences. Spanish is also the third most used language on internet websites after English and Chinese.
Spanish is one of the
six official languages of the
United Nations, and it is also used as an official language by the
European Union, the
Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 April ...
, the
Union of South American Nations, the
Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, the
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
and
many other international organizations.
Name of the language and etymology

Name of the language
In Spain and in some other parts of the Spanish-speaking world, Spanish is called not only but also (Castilian), the language from the
Kingdom of Castile, contrasting it with other
languages spoken in Spain such as
Galician,
Basque,
Asturian,
Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
,
Aragonese and
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
.
The
Spanish Constitution of 1978 uses the term to define the
official language of the whole Spanish State, in contrast to (lit. "the other
Spanish languages
The languages of Spain ( es, lenguas de España), or Spanish languages ( es, lenguas españolas, link=no), are the languages spoken in Spain.
Most languages spoken in Spain belong to the Romance language family, of which Spanish is the only ...
"). Article III reads as follows:
The
Royal Spanish Academy
The Royal Spanish Academy ( es, Real Academia Española, generally abbreviated as RAE) is Spain's official royal institution with a mission to ensure the stability of the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, Spain, and is affiliated with ...
(''Real Academia Española''), on the other hand, currently uses the term in its publications. However, from 1713 to 1923, it called the language .
The (a language guide published by the Royal Spanish Academy) states that, although the Royal Spanish Academy prefers to use the term in its publications when referring to the Spanish language, both terms— and —are regarded as synonymous and equally valid.
Etymology
The term is related to
Castile ( or archaically ), the kingdom where the language was originally spoken. The name of Castile, in turn, is usually assumed to be derived from ('castle').
In the Middle Ages, the language spoken in Castile was generically referred to as and later also as .
Later in the period, it gained geographical specification as ("romanz castellano", "romanz de Castiella"), "lenguaje de Castiella", and ultimately simply as (noun).
Different etymologies have been suggested for the term (Spanish). According to the Royal Spanish Academy, derives from the
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
word and that, in turn, derives from the
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
('from Hispania').
Hispania was the Roman name for the
Iberian Peninsula.
There are other hypotheses apart from the one suggested by the Royal Spanish Academy. Spanish philologist
Ramón Menéndez Pidal
Ramón Menéndez Pidal (; 13 March 1869 – 14 November 1968) was a Spanish philologist and historian."Ramon Menendez Pidal", ''Almanac of Famous People'' (2011) ''Biography in Context'', Gale, Detroit He worked extensively on the history of t ...
suggested that the classic or took the suffix from
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
, as it happened with other words such as (Breton) or (Saxon). The word evolved into the
Old Spanish
Old Spanish, also known as Old Castilian ( es, castellano antiguo; osp, romance castellano ), or Medieval Spanish ( es, español medieval), was originally a dialect of Vulgar Latin spoken in the former provinces of the Roman Empire that provided ...
, eventually becoming .
History

Like the other
Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European languages, I ...
s, the Spanish language evolved from
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
, which here was brought to the
Iberian Peninsula by the
Romans during the
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
, beginning in 210 BC. Several pre-Roman languages (also called
Paleohispanic languages
The paleo-Hispanic languages were the languages of the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, excluding languages of foreign colonies, such as Greek in Emporion and Phoenician in Qart Hadast. After the Roman conquest of Hispania the Paleoh ...
)—some distantly related to Latin as
Indo-European language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
s, and some that are not related at all—were previously spoken in the Iberian Peninsula. These languages included
Proto-Basque
Proto-Basque ( eu, aitzineuskara; es, protoeuskera, protovasco; french: proto-basque), or Pre-Basque, is the reconstructed predecessor of the Basque language before the Roman conquests in the Western Pyrenees.
Background
The first linguist wh ...
,
Iberian,
Lusitanian,
Celtiberian and
Gallaecian
Gallaecian, or Northwestern Hispano-Celtic, is an extinct Celtic language of a Hispano-Celtic group. It was spoken by the Gallaeci at the beginning of the 1st millennium in the northwest corner of the Iberian Peninsula that became the Roman ...
.
The first documents to show traces of what is today regarded as the precursor of modern Spanish are from the 9th century. Throughout the
Middle Ages and into the
modern era
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is applie ...
, the most important
influences on the Spanish lexicon came from neighboring
Romance languages—
Mozarabic (
Andalusi Romance
Mozarabic, also called Andalusi Romance, refers to the medieval Romance languages, Romance varieties spoken in the Iberian Peninsula in territories controlled by the Islamic Emirate of Córdoba and its successors. They were the common tongue fo ...
),
Navarro-Aragonese
Navarro-Aragonese is a Romance language once spoken in a large part of the Ebro River basin, south of the middle Pyrenees, although it is only currently spoken in a small portion of its original territory. The areas where it was spoken might have ...
,
Leonese,
Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
,
Portuguese,
Galician,
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
, and later,
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and
Italian. Spanish also
borrowed a considerable number of words from
Arabic, as well as a minor influence from the Germanic
Gothic language through the migration of tribes and a period of
Visigoth rule in Iberia. In addition, many more words were borrowed from
Latin through the influence of written language and the liturgical language of the Church. The loanwords were taken from both
Classical Latin and
Renaissance Latin
Renaissance Latin is a name given to the distinctive form of Literary Latin style developed during the European Renaissance of the fourteenth to fifteenth centuries, particularly by the Renaissance humanism movement.
Ad fontes
''Ad fontes' ...
, the form of Latin in use at that time.
According to the theories of
Ramón Menéndez Pidal
Ramón Menéndez Pidal (; 13 March 1869 – 14 November 1968) was a Spanish philologist and historian."Ramon Menendez Pidal", ''Almanac of Famous People'' (2011) ''Biography in Context'', Gale, Detroit He worked extensively on the history of t ...
, local
sociolects of Vulgar Latin evolved into Spanish, in the north of Iberia, in an area centered in the city of
Burgos, and this dialect was later brought to the city of
Toledo
Toledo most commonly refers to:
* Toledo, Spain, a city in Spain
* Province of Toledo, Spain
* Toledo, Ohio, a city in the United States
Toledo may also refer to:
Places Belize
* Toledo District
* Toledo Settlement
Bolivia
* Toledo, Orur ...
, where the written standard of Spanish was first developed, in the 13th century.
In this formative stage, Spanish developed a strongly differing variant from its close cousin,
Leonese, and, according to some authors, was distinguished by a heavy Basque influence (see
Iberian Romance languages
The Iberian Romance, Ibero-Romance or sometimes Iberian languagesIberian languages is also used as a more inclusive term for all languages spoken on the Iberian Peninsula, which in antiquity included the non-Indo-European Iberian language. are a ...
). This distinctive dialect spread to southern Spain with the advance of the , and meanwhile gathered a sizable lexical influence from the
Arabic of
Al-Andalus, much of it indirectly, through the Romance
Mozarabic dialects (some 4,000
Arabic-derived words, make up around 8% of the language today). The written standard for this new language was developed in the cities of
Toledo
Toledo most commonly refers to:
* Toledo, Spain, a city in Spain
* Province of Toledo, Spain
* Toledo, Ohio, a city in the United States
Toledo may also refer to:
Places Belize
* Toledo District
* Toledo Settlement
Bolivia
* Toledo, Orur ...
, in the 13th to 16th centuries, and
Madrid, from the 1570s.
The development of the
Spanish sound system from that of
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
exhibits most of the changes that are typical of
Western Romance languages, including
lenition of intervocalic consonants (thus Latin > Spanish ). The
diphthongization of Latin stressed short and —which occurred in
open syllables
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds typically made up of a syllable nucleus (most often a vowel) with optional initial and final margins (typically, consonants). Syllables are often considered the phonological "bu ...
in French and Italian, but not at all in Catalan or Portuguese—is found in both open and closed syllables in Spanish, as shown in the following table:

Spanish is marked by
palatalization
Palatalization may refer to:
*Palatalization (phonetics), the phonetic feature of palatal secondary articulation
*Palatalization (sound change)
Palatalization is a historical-linguistic sound change that results in a palatalized articulation ...
of the Latin double consonants (
geminates) and (thus Latin
> Spanish , and Latin > Spanish
).
The consonant written or in Latin and pronounced in Classical Latin had probably "
fortified
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
" to a bilabial fricative in Vulgar Latin. In early Spanish (but not in Catalan or Portuguese) it merged with the consonant written ''b'' (a bilabial with plosive and fricative allophones). In modern Spanish, there is
no difference between the pronunciation of orthographic and .
Typical of Spanish (as also of neighboring
Gascon extending as far north as the
Gironde estuary
The Gironde estuary ( , US usually ; french: estuaire de la Gironde, ; oc, estuari de aGironda, ) is a navigable estuary (though often referred to as a river) in southwest France and is formed from the meeting of the rivers Dordogne and Gar ...
, and found in a small area of
Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
), attributed by some scholars to a Basque
substratum
In linguistics, a stratum (Latin for "layer") or strate is a language that influences or is influenced by another through contact. A substratum or substrate is a language that has lower power or prestige than another, while a superstratum or sup ...
was the mutation of Latin initial into whenever it was followed by a vowel that did not diphthongize. The , still preserved in spelling, is now silent in most varieties of the language, although in some Andalusian and Caribbean dialects it is still aspirated in some words. Because of borrowings from Latin and from neighboring Romance languages, there are many -/-
doublet
Doublet is a word derived from the Latin ''duplus'', "twofold, twice as much",

In the 15th and 16th centuries, Spanish underwent a dramatic change in the pronunciation of its
sibilant consonants
Sibilants are fricative consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words ''sip'', ''zip'', ''ship'', and ...
, known in Spanish as the , which resulted in the distinctive
velar pronunciation of the letter and—in a large part of Spain—the characteristic
interdental ("th-sound") for the letter (and for before or ). See
History of Spanish (Modern development of the Old Spanish sibilants) for details.
The , written in
Salamanca in 1492 by
Elio Antonio de Nebrija, was the first grammar written for a modern European language. According to a popular anecdote, when Nebrija presented it to
Queen Isabella I, she asked him what was the use of such a work, and he answered that language is the instrument of empire. In his introduction to the grammar, dated 18 August 1492, Nebrija wrote that "... language was always the companion of empire."
From the 16th century onwards, the language was taken to the Spanish-discovered
America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and the
Spanish East Indies via
Spanish colonization of America.
Miguel de Cervantes, author of ''
Don Quixote'', is such a well-known reference in the world that Spanish is often called ("the language of Cervantes").
In the 20th century, Spanish was introduced to
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
and the
Western Sahara, and to areas of the United States that had not been part of the Spanish Empire, such as
Spanish Harlem in
New York City. For details on borrowed words and other external influences upon Spanish, see
Influences on the Spanish language.
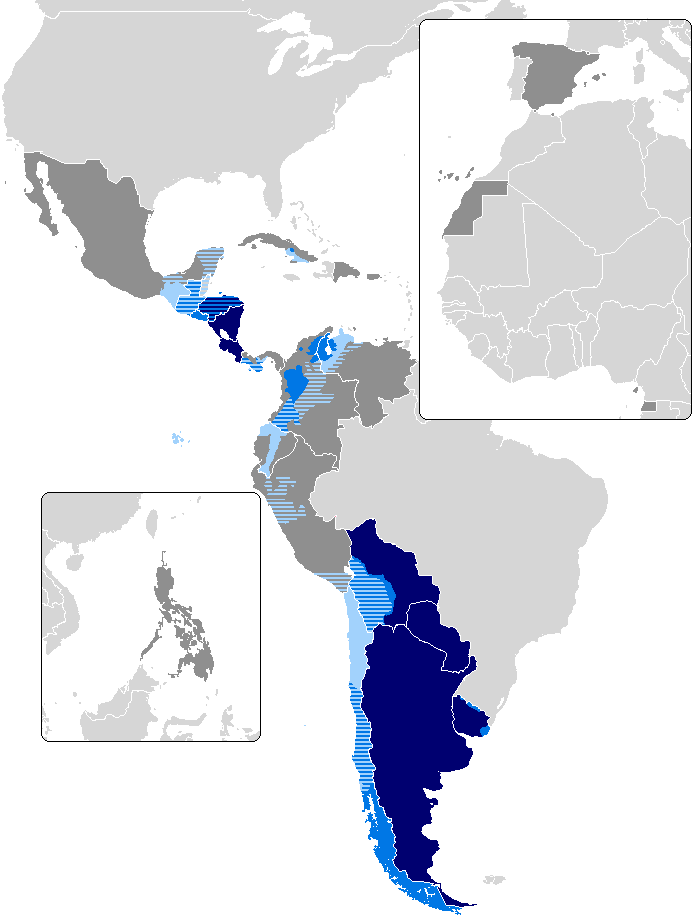
Geographical distribution

Spanish is the primary language in 20 countries worldwide. As of 2020, it is estimated that about 463 million people speak Spanish as a
native language, making it the second
most spoken language by number of native speakers. An additional 75 million speak Spanish as a second or
foreign language, making it the fourth most spoken language in the world overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindi with a total number of 538 million speakers. Spanish is also the third
most used language on the Internet, after English and Chinese.
Europe

Spanish is the official language of
Spain, the country after which it is named and from which it originated. Other European territories in which it is also widely spoken include
Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
and
Andorra.
Spanish is also spoken by immigrant communities in other European countries, such as the
United Kingdom,
France,
Italy, and
Germany. Spanish is an official language of the
European Union.
Americas
Hispanic America
Today, the majority of the Spanish speakers live in
Hispanic America. Nationally, Spanish is the official language—either ''
de facto'' or ''
de jure''—of
Argentina,
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
(co-official with 36 indigenous languages),
Chile,
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
,
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
,
Cuba,
Dominican Republic,
Ecuador,
El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south b ...
,
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
,
Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
,
Mexico (co-official with 63 indigenous languages),
Nicaragua,
Panama,
Paraguay (co-official with
Guaraní),
Peru (co-official with
Quechua,
Aymara, and "the other indigenous languages"),
Puerto Rico (co-official with English),
Uruguay, and
Venezuela.
United States

According to the 2020 census, over 60 million people of the U.S. population were of
Hispanic or
Hispanic American by origin. In turn, 41.8 million people in the United States aged five or older speak Spanish at home, or about 13% of the population. The Spanish language has a long history of presence in the United States due to early Spanish and, later, Mexican administration over territories now forming the
southwestern states, also
Louisiana ruled by Spain from 1762 to 1802, as well as
Florida, which was Spanish territory until 1821, and
Puerto Rico which was Spanish until 1898.
Spanish is by far the most common second language in the country, with over 50 million total speakers if non-native or second-language speakers are included.
[ (in Spanish)] While English is the de facto national language of the country, Spanish is often used in public services and notices at the federal and state levels. Spanish is also used in administration in the state of
New Mexico. The language has a strong influence in major metropolitan areas such as those of
Los Angeles,
Miami,
San Antonio,
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
,
San Francisco,
Dallas,
Tucson and
Phoenix of the
Arizona Sun Corridor, as well as more recently,
Chicago,
Las Vegas,
Boston,
Denver,
Houston,
Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion ...
,
Philadelphia,
Cleveland,
Salt Lake City,
Atlanta,
Nashville
Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the seat of Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the most populous city in the state, 21st most-populous city in the U.S., and the ...
,
Orlando,
Tampa
Tampa () is a city on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The city's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and the seat of Hillsborough County ...
,
Raleigh and
Baltimore-Washington, D.C. due to 20th- and 21st-century immigration.
Rest of the Americas
Although Spanish has no official recognition in the former
British colony
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Bri ...
of
Belize (known until 1973 as
British Honduras) where English is the sole official language, according to the 2010 census it was then spoken natively by 45% of the population and 56.6% of the total population were able to speak the language.
Due to their proximity to Spanish-speaking countries,
Trinidad and Tobago has implemented Spanish language teaching into its education system. The Trinidad government launched the ''Spanish as a First Foreign Language'' (SAFFL) initiative in March 2005.
In addition to sharing most of its borders with Spanish-speaking countries, the creation of
Mercosur in the early 1990s induced a favorable situation for the promotion of Spanish language teaching in
Brazil.
In 2005, the
National Congress of Brazil approved a bill, signed into law by the
President, making it mandatory for
schools to offer Spanish as an alternative foreign language course in both public and private secondary schools in Brazil. In September 2016 this law was revoked by
Michel Temer after
impeachment of Dilma Rousseff. In many border towns and villages along Paraguay and Uruguay, a
mixed language
A mixed language is a language that arises among a bilingual group combining aspects of two or more languages but not clearly deriving primarily from any single language. It differs from a creole language, creole or pidgin, pidgin language in that ...
known as
Portuñol
Portuñol (Spanish spelling) or Portunhol (Portuguese spelling) () is a portmanteau of the words portugués/português ("Portuguese") and español/espanhol ("Spanish"), and is the name often given to any non-systematic mixture of Portuguese and ...
is spoken.
Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa

Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
is the only Spanish-speaking country located entirely in Africa, with the language introduced during the
Spanish colonial period
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
. Enshrined in the constitution as an official language (alongside French and Portuguese), Spanish features prominently in the Equatoguinean education system and is the primary language used in government and business. Whereas it is not the mother tongue of virtually any of its speakers, the vast majority of the population is proficient in Spanish. The
Instituto Cervantes estimates that 87.7% of the population is fluent in Spanish. This figure highlights Equatorial Guinea as having a higher proportion of proficient speakers of a colonial language relative to the respective metropolitan languages in other West and Central African nations.
Spanish is spoken by very small communities in
Angola due to Cuban influence from the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
and in
South Sudan among South Sudanese natives that relocated to Cuba during the Sudanese wars and returned for their country's independence.
North Africa and Macaronesia
Spanish is also spoken in the integral territories of Spain in Africa, namely the cities of
Ceuta and
Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
and the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, located in the Atlantic Ocean some off the northwest of the African mainland. The
Spanish spoken in the Canary Islands, traces its origins back to the
Castilian conquest in the 15th century, and, in addition to a resemblance to Western Andalusian speech patterns, it also features strong influence from the Spanish varieties spoken in the Americas, which in turn have also been influenced historically by Canarian Spanish.
While far from the heyday of the
Spanish protectorate in Morocco, there are some presence of the Spanish language in the north of
Morocco, stemming for example from the availability of certain Spanish-language media. Many northern Moroccans have rudimentary knowledge of Spanish. Spanish has also presence in the education system of the country (either by means of selected education centres running the Spain's education system, primarily located in the North, and the availability of Spanish as foreign language subject in secondary education).
In
Western Sahara, formerly
Spanish Sahara, a primarily
Hassaniya Arabic
Hassānīya ( ar, حسانية '; also known as , , , , and ''Maure'') is a variety of Maghrebi Arabic spoken by Mauritanian Arabs and the Sahrawi. It was spoken by the Beni Ḥassān Bedouin tribes, who extended their authority over most of M ...
-speaking territory, Spanish was officially spoken as the language of the colonial administration during the late 19th and 20th centuries. Today, Spanish is present in the partially-recognized
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic and in the
Sahrawi refugee camps in Tindouf (
Algeria), where the Spanish-language teaching is largely preserved by Cuban educators. The number of Spanish speakers is unknown.
Spanish is also an official language of the
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
.
Asia
Spanish was an official language of the
Philippines from the beginning of Spanish administration in 1565 to a constitutional change in 1973. During
Spanish colonization (1565–1898), it was the language of government, trade, and education, and was spoken as a first language by Spaniards and educated Filipinos. In the mid-19th century, the colonial government set up a free public education system with Spanish as the medium of instruction. While this increased the use of Spanish throughout the islands and led to the formation of a class of Spanish-speaking intellectuals called the ''
Ilustrados'', only populations in urban areas or with places with a significant Spanish presence used the language on a daily basis or learned it as a second or third language. By the end of Spanish rule in 1898, only about 10% of the population had knowledge of Spanish, mostly those of Spanish descent or elite standing.
Despite
American administration of the Philippines after the defeat of Spain in the
Spanish–American War, Spanish continued to be used in Philippine literature and press during the early years of American administration. Gradually however, the American government began promoting the use of English at the expense of Spanish, characterizing it as a negative influence of the past. Eventually, by the 1920s, English became the primary language of administration and education. Nevertheless, despite a significant decrease in influence and speakers, Spanish remained an official language of the Philippines upon independence in 1946, alongside English and
Filipino, a standardized version of
Tagalog.

Spanish was briefly removed from official status in 1973 under the administration of
Ferdinand Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. ( , , ; September 11, 1917 – September 28, 1989) was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial ...
, but regained official status two months later under Presidential Decree No. 155, dated 15 March 1973. It remained an official language until 1987, with the ratification of the present constitution, in which it was re-designated as a voluntary and optional auxiliary language. In 2010, President
Gloria Macapagal Arroyo encouraged the reintroduction of Spanish-language teaching in the Philippine education system. However, the initiative failed to gain any traction, with the number of secondary schools at which the language is either a compulsory subject or offered as an elective remaining very limited. Today, the actual number of proficient Spanish speakers is around 400,000, or under 0.5% of the population. There are some 20,000 students studying the language every year.
Aside from standard Spanish, a Spanish-based creole language called
Chavacano developed in the southern Philippines. However, it is not mutually intelligible with Spanish. The number of Chavacano-speakers was estimated at 1.2 million in 1996. The local
languages of the Philippines also retain significant Spanish influence, with many words derived from
Mexican Spanish, owing to the administration of the islands by Spain through
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
until 1821, until direct governance from Madrid afterwards to 1898.
Oceania

Spanish is the official and most spoken language on
Easter Island, which is geographically part of
Polynesia in Oceania and politically part of
Chile. However, Easter Island's traditional language is
Rapa Nui, an
Eastern Polynesian language.
As a legacy of comprising the former
Spanish East Indies, Spanish loan words are present in the local languages of
Guam,
Northern Mariana Islands,
Palau,
Marshall Islands and
Micronesia.
In addition, in Australia and New Zealand, there are native Spanish communities, resulting from emigration from Spanish-speaking countries. Mainly from the
Southern Cone
The Southern Cone ( es, Cono Sur, pt, Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bou ...
.
Spanish speakers by country
The following table shows the number of Spanish speakers in some 79 countries.
Grammar

Most of the grammatical and
typological
Typology is the study of types or the systematic classification of the types of something according to their common characteristics. Typology is the act of finding, counting and classification facts with the help of eyes, other senses and logic. Ty ...
features of Spanish are shared with the other
Romance languages. Spanish is a
fusional language. The
noun and
adjective systems exhibit two
genders
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most cultures u ...
and two
numbers. In addition, articles and some
pronouns
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts o ...
and
determiners
A determiner, also called determinative (abbreviated ), is a word, phrase, or affix that occurs together with a noun or noun phrase and generally serves to express the reference of that noun or noun phrase in the context. That is, a determiner m ...
have a neuter gender in their singular form. There are about fifty
conjugated forms per
verb, with 3 tenses: past, present, future; 2
aspects for past:
perfective,
imperfective
The imperfective (abbreviated or more ambiguously ) is a grammatical aspect used to describe ongoing, habitual, repeated, or similar semantic roles, whether that situation occurs in the past, present, or future. Although many languages have a gen ...
; 4
moods: indicative, subjunctive, conditional, imperative; 3 persons: first, second, third; 2 numbers: singular, plural; 3
verboid
According to some linguistics theories, a stative verb is a verb that describes a state of being, in contrast to a dynamic verb, which describes an action. The difference can be categorized by saying that stative verbs describe situations that are ...
forms: infinitive, gerund, and past participle. The indicative mood is the
unmarked one, while the subjunctive mood expresses uncertainty or indetermination, and is commonly paired with the conditional, which is a mood used to express "would" (as in, "I would eat if I had food); the imperative is a mood to express a command, commonly a one word phrase – "¡Di!", "¡Talk!".
Verbs express
T-V distinction by using different persons for formal and informal addresses. (For a detailed overview of verbs, see
Spanish verbs and
Spanish irregular verbs
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
.)
Spanish
syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency) ...
is considered
right-branching, meaning that subordinate or
modifying constituents tend to be placed after head words. The language uses
prepositions (rather than postpositions or inflection of nouns for
case
Case or CASE may refer to:
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of related merchandise
* Cartridge case or casing, a firearm cartridge component
* Bookcase, a piece of furniture used to store books
* Briefcase or attaché case, a narrow box to c ...
), and usually—though not always—places
adjectives after
nouns, as do most other Romance languages.
Spanish is classified as a
subject–verb–object language; however, as in most Romance languages, constituent order is highly variable and governed mainly by
topicalization and
focus rather than by syntax. It is a "
pro-drop
A pro-drop language (from "pronoun-dropping") is a language where certain classes of pronouns may be omitted when they can be pragmatically or grammatically inferable. The precise conditions vary from language to language, and can be quite int ...
", or "
null-subject" language—that is, it allows the deletion of subject pronouns when they are
pragmatically unnecessary. Spanish is described as a "
verb-framed" language, meaning that the ''direction'' of motion is expressed in the verb while the ''mode'' of locomotion is expressed adverbially (e.g. ''subir corriendo'' or ''salir volando''; the respective English equivalents of these examples—'to run up' and 'to fly out'—show that English is, by contrast, "satellite-framed", with mode of locomotion expressed in the verb and direction in an adverbial modifier).
Phonology
The Spanish phonological system evolved from that of
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
. Its development exhibits some traits in common with other
Western Romance languages, others with the neighboring Hispanic varieties—especially
Leonese and
Aragonese—as well as other features unique to Spanish. Spanish is alone among its immediate neighbors in having undergone frequent aspiration and eventual loss of the Latin initial sound (e.g. Cast. vs. Leon. and Arag. ). The Latin initial consonant sequences , , and in Spanish typically merge as (originally pronounced ), while in Aragonese they are preserved in most dialects, and in Leonese they present a variety of outcomes, including , , and . Where Latin had before a vowel (e.g. ) or the ending , (e.g. ), Old Spanish produced , that in Modern Spanish became the velar fricative (, ), whereas neighboring languages have the palatal lateral (e.g. Portuguese , ; Catalan , ).
Segmental phonology

The Spanish
phonemic inventory consists of five vowel phonemes (, , , , ) and 17 to 19 consonant phonemes (the exact number depending on the dialect). The main
allophonic variation among vowels is the reduction of the high vowels and to glides— and respectively—when unstressed and adjacent to another vowel. Some instances of the mid vowels and , determined lexically, alternate with the diphthongs and respectively when stressed, in a process that is better described as
morphophonemic
Morphophonology (also morphophonemics or morphonology) is the branch of linguistics that studies the interaction between morphology (linguistics), morphological and phonology, phonological or phonetic processes. Its chief focus is the sound chan ...
rather than phonological, as it is not predictable from phonology alone.
The Spanish consonant system is characterized by (1) three
nasal
Nasal is an adjective referring to the nose, part of human or animal anatomy. It may also be shorthand for the following uses in combination:
* With reference to the human nose:
** Nasal administration, a method of pharmaceutical drug delivery
** ...
phonemes, and one or two (depending on the dialect) lateral consonant, lateral phoneme(s), which in syllable-final position Archiphonemic, lose their contrast and are subject to Assimilation (linguistics), assimilation to a following consonant; (2) three Voicelessness, voiceless Plosive, stops and the Affricate consonant, affricate ; (3) three or four (depending on the dialect) Voicelessness, voiceless Fricative consonant, fricatives; (4) a set of voiced obstruents—, , , and sometimes —which alternate between Approximant consonant, approximant and plosive allophones depending on the environment; and (5) a phonemic distinction between the "Flap consonant, tapped" and "Trill consonant, trilled" ''r''-sounds (single and double in orthography).
In the following table of consonant phonemes, is marked with an asterisk (*) to indicate that it is preserved only in some dialects. In most dialects it has been merged with in the merger called . Similarly, is also marked with an asterisk to indicate that most dialects do not distinguish it from (see ), although this is not a true merger but an outcome of different evolution of sibilants in Southern Spain.
The phoneme is in parentheses () to indicate that it appears only in loanwords. Each of the voiced obstruent phonemes , , , and appears to the right of a ''pair'' of voiceless phonemes, to indicate that, while the ''voiceless'' phonemes maintain a phonemic contrast between plosive (or affricate) and fricative, the ''voiced'' ones alternate Allophone, allophonically (i.e. without phonemic contrast) between plosive and approximant pronunciations.
Prosody
Spanish is classified by its Isochrony, rhythm as a isochrony#syllable timing, syllable-timed language: each syllable has approximately the same duration regardless of stress.
Spanish intonation (linguistics), intonation varies significantly according to dialect but generally conforms to a pattern of falling tone for declarative sentences and wh-questions (who, what, why, etc.) and rising tone for Yes–no question, yes/no questions. There are no syntactic markers to distinguish between questions and statements and thus, the recognition of declarative or interrogative depends entirely on intonation.
Stress most often occurs on any of the last three syllables of a word, with some rare exceptions at the fourth-to-last or earlier syllables. Stress tends to occur as follows:
* in words that end with a monophthong, on the penultimate syllable
* when the word ends in a diphthong, on the final syllable.
* in words that end with a consonant, on the last syllable, with the exception of two grammatical endings: , for third-person-plural of verbs, and , for plural of nouns and adjectives or for second-person-singular of verbs. However, even though a significant number of nouns and adjectives ending with are also stressed on the penult (, , ), the great majority of nouns and adjectives ending with are stressed on their last syllable (, , , ).
* Preantepenultimate stress (stress on the fourth-to-last syllable) occurs rarely, only on verbs with clitic pronouns attached (e.g. 'saving them for him/her/them/you').
In addition to the many exceptions to these tendencies, there are numerous minimal pairs that contrast solely on stress such as ('sheet') and ('savannah'); ('boundary'), ('he/she limits') and ('I limited'); ('liquid'), ('I sell off') and ('he/she sold off').
The orthographic system unambiguously reflects where the stress occurs: in the absence of an accent mark, the stress falls on the last syllable unless the last letter is , , or a vowel, in which cases the stress falls on the next-to-last (penultimate) syllable. Exceptions to those rules are indicated by an acute accent mark over the vowel of the stressed syllable. (See Spanish orthography.)
Speaker population
Spanish is the official, or national language in Hispanic America, 18 countries and one territory in the Americas,
Spain, and
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
. With a population of over 410 million, Spanish language in the Americas, Hispanophone America accounts for the vast majority of Spanish speakers, of which
Mexico is the most populous Spanish-speaking country. In the
European Union, Spanish is the First language, mother tongue of 8% of the population, with an additional 7% speaking it as a second language. Additionally, Spanish is the second most spoken language in the United States and is by far the most popular foreign language among students. In 2015, it was estimated that over 50 million Americans spoke Spanish, about 41 million of whom were native speakers. With continued immigration and increased use of the language domestically in public spheres and media, the number of Spanish speakers in the United States is expected to continue growing over the forthcoming decades.
Dialectal variation

While being mutually intelligible, there are important variations (Phonology, phonological, Grammar, grammatical, and Lexicon, lexical) in the spoken Spanish of the various regions of Spain and throughout the Spanish-speaking areas of the Americas.
The variety with the most speakers is
Mexican Spanish. It is spoken by more than twenty percent of the world's Spanish speakers (more than 112 million of the total of more than 500 million, according to the table above). One of its main features is the vowel reduction, reduction or loss of unstressed vowels, mainly when they are in contact with the sound /s/.
In Spain, northern dialects are popularly thought of as closer to the standard, although positive attitudes toward southern dialects have increased significantly in the last 50 years. The speech from the educated classes of Madrid is the standard variety for use on radio and television in Spain and it is indicated by many as the one that has most influenced the written standard for Spanish. Central (European) Spanish speech patterns have been noted to be in the process of merging with more innovative southern varieties (including Eastern Andalusian and Murcian), as an emerging interdialectal levelled ''koine'' buffered between the Madrid's traditional national standard and the Seville speech trends.
Phonology
The four main phonological divisions are based respectively on (1) the phoneme Voiceless dental fricative, ("theta"), (2) the debuccalization of syllable-final , (3) the sound of the spelled , (4) and the phoneme Palatal lateral approximant, ("turned ''y''"),
* The phoneme (spelled before or and spelled elsewhere), a voiceless dental fricative as in English ''thing'', is maintained by a majority of Spain's population, especially in the northern and central parts of the country. In other areas (some parts of southern Spain, the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, and the Americas), does not exist and occurs instead. The maintenance of phonemic contrast is called in Spanish, while the merger is generally called (in reference to the usual realization of the merged phoneme as ) or, occasionally, (referring to its interdental realization, , in some parts of southern Spain). In most of Hispanic America, the spelled before or , and spelled is always pronounced as a Voiceless alveolar sibilant#Dentalized laminal alveolar, voiceless dental sibilant.
* The debuccalization (pronunciation as , or loss) of syllable-final is associated with the southern half of Spain and lowland Americas: Central America (except central Costa Rica and Guatemala), the Caribbean, coastal areas of southern Mexico, and South America except Andean highlands. Debuccalization is frequently called "aspiration" in English, and in Spanish. When there is no debuccalization, the syllable-final is pronounced as Voiceless alveolar sibilant#Retracted alveolar, voiceless "apico-alveolar" sibilant or as a Voiceless alveolar sibilant#Dentalized laminal alveolar, voiceless dental sibilant in the same fashion as in the next paragraph.
* The sound that corresponds to the letter is pronounced in northern and central Spain as a Voiceless alveolar sibilant#Retracted alveolar, voiceless "apico-alveolar" sibilant (also described acoustically as "Grave and acute, grave" and articulatorily as "retracted"), with a weak "hushing" sound reminiscent of fricatives. In Andalusia,
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
and most of Hispanic America (except in the Colombian Spanish#Paisa dialect, Paisa region of Colombia) it is pronounced as a Voiceless alveolar sibilant#Dentalized laminal alveolar, voiceless dental sibilant , much like the most frequent pronunciation of the /s/ of English. Because /s/ is one of the most frequent phonemes in Spanish, the difference of pronunciation is one of the first to be noted by a Spanish-speaking person to differentiate Spaniards from Spanish-speakers of the Americas.
* The phoneme , spelled , a Palatal lateral approximant, palatal lateral consonant that can be approximated by the sound of the of English ''million'', tends to be maintained in less-urbanized areas of northern Spain and in Andean Spanish, highland areas of South America. Meanwhile, in the speech of most other Spanish-speakers, it is merged with ("curly-tail ''j''"), a non-lateral, usually voiced, usually fricative, palatal consonant, sometimes compared to English (''yod'') as in ''yacht'' and spelled in Spanish. As with other forms of allophony across world languages, the small difference of the spelled and the spelled is usually not perceived (the difference is not heard) by people who do not produce them as different phonemes. Such a phonemic merger is called in Spanish. In Rioplatense Spanish, the merged phoneme is generally pronounced as a postalveolar fricative, either voiced (as in English ''measure'' or the French ) in the central and western parts of the dialectal region (), or voiceless (as in the French or Portuguese ) in and around Buenos Aires and Montevideo ().
Morphology
The main Morphology (linguistics), morphological variations between dialects of Spanish involve differing uses of pronouns, especially those of the second Grammatical person, person and, to a lesser extent, the object pronouns of the third Grammatical person, person.
Voseo
Virtually all dialects of Spanish make the T–V distinction, distinction between a formal and a familiar register (sociolinguistics), register in the Grammatical person, second-person Grammatical number, singular and thus have two different pronouns meaning "you": in the formal and either or in the familiar (and each of these three pronouns has its associated verb forms), with the choice of or varying from one dialect to another. The use of (and/or its verb forms) is called . In a few dialects, all three pronouns are used, with , , and denoting respectively formality, familiarity, and intimacy.
In , is the Subject (grammar), subject form (, "you say") and the form for the object of a Preposition and postposition, preposition (, "I am going with you"), while the direct and indirect Object (grammar), object forms, and the Possessive adjective, possessives, are the same as those associated with : ("You know your friends respect you").
The verb forms of ''general voseo'' are the same as those used with except in the present grammatical tense, tense (indicative and imperative mood, imperative) verbs. The forms for generally can be derived from those of (the traditional second-person familiar ''plural'') by deleting the semivowel, glide , or , where it appears in the ending: > ; > , () > (), () > ().
In Chilean on the other hand, almost all verb forms are distinct from their standard -forms.
The use of the pronoun with the verb forms of () is called "pronominal ". Conversely, the use of the verb forms of with the pronoun ( or ) is called "verbal ".
In Chile, for example, ''verbal voseo'' is much more common than the actual use of the pronoun ''vos'', which is usually reserved for highly informal situations.
And in Central American , one can see even further distinction.
= Distribution in Spanish-speaking regions of the Americas
=
Although is not used in Spain, it occurs in many Spanish-speaking regions of the Americas as the primary spoken form of the second-person singular familiar pronoun, with wide differences in social consideration. Generally, it can be said that there are zones of exclusive use of (the use of ) in the following areas: almost all of
Mexico, the West Indies,
Panama, most of
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
,
Peru,
Venezuela and coastal
Ecuador.
as a cultured form alternates with as a popular or rural form in
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
, in the north and south of Peru, in Andean Ecuador, in small zones of the Venezuelan Andes (and most notably in the Venezuelan state of Zulia), and in a large part of Colombia. Some researchers maintain that can be heard in some parts of eastern Cuba, and others assert that it is absent from the island.
exists as the second-person usage with an intermediate degree of formality alongside the more familiar in
Chile, in the Venezuelan state of Zulia, on the Caribbean coast of
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, in the Azuero Peninsula in Panama, in the Mexican state of Chiapas, and in parts of Guatemala.
Areas of generalized include
Argentina,
Nicaragua, eastern
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
,
El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south b ...
,
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
,
Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
,
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
,
Paraguay,
Uruguay and the Colombian departments of Antioquia Department, Antioquia, Caldas Department, Caldas, Risaralda Department, Risaralda, Quindio and Valle del Cauca.
Ustedes
functions as formal and informal second-person plural in all of Hispanic America, the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, and parts of Andalusia. It agrees with verbs in the 3rd person plural. Most of Spain maintains the T-V distinction, formal/familiar distinction with and respectively. The use of with the second person plural is sometimes heard in Andalusia, but it's non-standard.
Usted
is the usual second-person singular pronoun in a formal context, but it is used jointly with the third-person singular voice of the verb. It is used to convey respect toward someone who is a generation older or is of higher authority ("you, sir"/"you, ma'am"). It is also used in a ''familiar'' context by many speakers in Colombia and Costa Rica and in parts of Ecuador and Panama, to the exclusion of or . This usage is sometimes called in Spanish.
In Central America, especially in Honduras, is often used as a formal pronoun to convey respect between the members of a romantic couple. is also used that way between parents and children in the Andean regions of Ecuador, Colombia and Venezuela.
Third-person object pronouns
Most speakers use (and the prefers) the pronouns and for Direct object#The object in linguistics, ''direct'' objects (masculine and feminine respectively, regardless of animacy, meaning "him", "her", or "it"), and for Direct object#The object in linguistics, ''indirect'' objects (regardless of Grammatical gender, gender or animacy, meaning "to him", "to her", or "to it"). The usage is sometimes called "etymological", as these direct and indirect object pronouns are a continuation, respectively, of the Accusative case, accusative and Dative case, dative pronouns of Latin, the ancestor language of Spanish.
Deviations from this norm (more common in Spain than in the Americas) are called "", "", or "", according to which respective pronoun, , , or , has expanded beyond the etymological usage ( as a direct object, or or as an indirect object).
Vocabulary
Some words can be significantly different in different Hispanophone countries. Most Spanish speakers can recognize other Spanish forms even in places where they are not commonly used, but Spaniards generally do not recognize specifically American usages. For example, Spanish , and (respectively, 'butter', 'avocado', 'apricot') correspond to (word used for lard in Peninsular Spanish), , and , respectively, in Argentina, Chile (except ), Paraguay, Peru (except and ), and Uruguay.
Relation to other languages
Spanish is closely related to the other West Iberian languages, West Iberian Romance languages, including
Asturian,
Aragonese,
Galician, Ladino language, Ladino,
Leonese, Mirandese language, Mirandese and
Portuguese.
It is generally acknowledged that Portuguese and Spanish speakers can communicate in written form, with varying degrees of mutual intelligibility. Mutual intelligibility of the ''written'' Spanish and Portuguese languages is remarkably high, and the difficulties of the spoken forms are based more on phonology than on grammatical and lexical dissimilarities. ''Ethnologue'' gives estimates of the lexical similarity between related languages in terms of precise percentages. For Spanish and Portuguese, that figure is 89%. Italian, on the other hand is phonologically similar to Spanish, but has a lower lexical similarity of 82%. Mutual intelligibility between Spanish and
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
or between Spanish and Romanian language, Romanian is lower still, given lexical similarity ratings of 75% and 71% respectively.
Comprehension of Spanish by French speakers who have not studied the language is much lower, at an estimated 45%. In general, thanks to the common features of the writing systems of the Romance languages, interlingual comprehension of the written word is greater than that of oral communication.
The Spanish vocabulary has been influenced by several languages: As in other European languages, Classical Greek words (Hellenisms) are abundant in several fields, mainly in Art, Science, Politics, Nature, etc. Its vocabulary has also been Arabic language influence on the Spanish language, influenced by Arabic, having developed during the
Al-Andalus era in the
Iberian Peninsula, with around 8% of its vocabulary having
Arabic lexical roots.
[,,] It has also been influenced by
Basque,
Iberian,
Celtiberian, Gothic language, Visigothic, and other neighboring Ibero-Romance languages.
Additionally, it has absorbed vocabulary from other languages, particularly other Romance languages such as
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
,
Italian,
Mozarabic,
Portuguese,
Galician,
Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
,
Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
, and
Sardinian, as well as from
Quechua, Nahuatl language, Nahuatl, and List of Spanish words of Indigenous American Indian origin, other indigenous languages of the Americas.
The following table compares the forms of some common words in several Romance languages:
1. In Romance etymology, Latin terms are given in the Accusative since most forms derive from this case.
2. As in "us very selves", an emphatic expression.
3. Also in early modern Portuguese (e.g. ''The Lusiads''), and in Galician.
4. Alternatively in French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
.
5. in many Southern List of languages of Italy, Italian dialects and languages.
6. Medieval Catalan (e.g. ''Llibre dels fets'').
7. Modified with the learned suffix ''-ción''.
8. Depending on the written norm used (see Reintegrationism).
9. From Basque ''esku'', "hand" + ''erdi'', "half, incomplete". Notice that this negative meaning also applies for Latin ''sinistra(m)'' ("dark, unfortunate").
10. Romanian ''caș'' (from Latin ) means a type of cheese. The universal term for cheese in Romanian is ''brânză'' (from unknown etymology).
Judaeo-Spanish

Judaeo-Spanish, also known as Ladino,
is a variety of Spanish which preserves many features of medieval Spanish and Portuguese and is spoken by descendants of the Sephardi Jews who were Alhambra decree, expelled from Spain in the 15th century.
Conversely, in Portugal the vast majority of the Portuguese Jews converted and became 'New Christians'. Therefore, its relationship to Spanish is comparable with that of the Yiddish language to German language, German. Ladino speakers today are almost exclusively Sephardim, Sephardi Jews, with family roots in Turkey, Greece, or the Balkans, and living mostly in Israel, Turkey, and the United States, with a few communities in Hispanic America.
Judaeo-Spanish lacks the Amerindian languages, Native American vocabulary which was acquired by standard Spanish during the Spanish Empire, Spanish colonial period, and it retains many archaic features which have since been lost in standard Spanish. It contains, however, other vocabulary which is not found in standard Spanish, including vocabulary from Hebrew language, Hebrew, French, Greek and Turkish language, Turkish, and other languages spoken where the Sephardim settled.
Judaeo-Spanish is in serious danger of extinction because many native speakers today are elderly as well as elderly ''olim'' (immigrants to Israel) who have not transmitted the language to their children or grandchildren. However, it is experiencing a minor revival among Sephardi communities, especially in music. In Latin American communities, the danger of extinction is also due to assimilation by modern Spanish.
A related dialect is Haketia, the Judaeo-Spanish of northern Morocco. This too tended to assimilate with modern Spanish, during the Spanish occupation of the region.
Writing system
Spanish is written in the Latin script, with the addition of the character (, representing the phoneme , a letter distinct from , although typographically composed of an with a tilde). Formerly the digraph (orthography), digraphs (, representing the phoneme ) and (, representing the phoneme or ), were also considered single letters. However, the digraph (, 'strong r', , 'double r', or simply ), which also represents a distinct phoneme , was not similarly regarded as a single letter. Since 1994 and have been treated as letter pairs for collation purposes, though they remained a part of the alphabet until 2010. Words with are now alphabetically sorted between those with and , instead of following as they used to. The situation is similar for .
Thus, the Spanish alphabet has the following 27 letters:
:
Since 2010, none of the digraphs () are considered letters by the Royal Spanish Academy.
The letters and are used only in words and names coming from foreign languages (, etc.).
With the exclusion of a very small number of regional terms such as (see Toponymy of Mexico#Phonetic evolution, Toponymy of Mexico), pronunciation can be entirely determined from spelling. Under the orthographic conventions, a typical Spanish word is stressed on the syllable before the last if it ends with a vowel (not including ) or with a vowel followed by or an ; it is stressed on the last syllable otherwise. Exceptions to this rule are indicated by placing an acute accent on the stress (linguistics), stressed vowel.
The acute accent is used, in addition, to distinguish between certain homophones, especially when one of them is a stressed word and the other one is a clitic: compare ('the', masculine singular definite article) with ('he' or 'it'), or ('you', object pronoun) with ('tea'), (preposition 'of') versus ('give' [formal imperative/third-person present subjunctive]), and (reflexive pronoun) versus ('I know' or imperative 'be').
The interrogative pronouns (, , , , etc.) also receive accents in direct or indirect questions, and some demonstratives (, , , etc.) can be accented when used as pronouns. Accent marks used to be omitted on capital letters (a widespread practice in the days of typewriters and the early days of computers when only lowercase vowels were available with accents), although the advises against this and the orthographic conventions taught at schools enforce the use of the accent.
When is written between and a front vowel or , it indicates a "Hard and soft G, hard g" pronunciation. A Diaeresis (diacritic), diaeresis indicates that it is not silent as it normally would be (e.g., , 'stork', is pronounced ; if it were written *, it would be pronounced *).
Interrogative and exclamatory clauses are introduced with inverted question and exclamation marks ( and , respectively) and closed by the usual question and exclamation marks.
Organizations


Royal Spanish Academy
The Royal Spanish Academy ( es, Real Academia Española), founded in 1713, together with the 21 other national ones (see Association of Spanish Language Academies), exercises a standardizing influence through its publication of dictionaries and widely respected grammar and style guides.
Because of influence and for other sociohistorical reasons, a standardized form of the language (Standard Spanish) is widely acknowledged for use in literature, academic contexts and the media.
Association of Spanish Language Academies

The Association of Spanish Language Academies (, or ) is the entity which regulates the Spanish language. It was created in Mexico in 1951 and represents the union of all the separate academies in the Spanish-speaking world. It comprises the academies of 23 countries, ordered by date of academy foundation: Real Academia Española, Spain (1713), Academia Colombiana de la Lengua, Colombia (1871), Academia Ecuatoriana de la Lengua, Ecuador (1874), Academia Mexicana de la Lengua, Mexico (1875), Academia Salvadoreña de la Lengua, El Salvador (1876), Academia Venezolana de la Lengua, Venezuela (1883), Academia Chilena de la Lengua, Chile (1885), Academia Peruana de la Lengua, Peru (1887), Academia Guatemalteca de la Lengua, Guatemala (1887), Academia Costarricense de la Lengua, Costa Rica (1923), Academia Filipina de la Lengua Española, Philippines (1924), Academia Panameña de la Lengua, Panama (1926), Academia Cubana de la Lengua, Cuba (1926),
Academia Paraguaya de la Lengua Española, Paraguay (1927), Academia Dominicana de la Lengua, Dominican Republic (1927), Academia Boliviana de la Lengua, Bolivia (1927), Academia Nicaragüense de la Lengua, Nicaragua (1928), Academia Argentina de Letras, Argentina (1931), Academia Nacional de Letras, del Uruguay, Uruguay (1943), Academia Hondureña de la Lengua, Honduras (1949), Academia Puertorriqueña de la Lengua Española, Puerto Rico (1955), North American Academy of the Spanish Language, United States (1973) and Academia Ecuatoguineana de la Lengua Española, Equatorial Guinea (2016).
Cervantes Institute

The (Cervantes Institute) is a worldwide nonprofit organization created by the Spanish government in 1991. This organization has branches in 45 countries, with 88 centers devoted to the Spanish and Hispanic American cultures and Spanish language. The goals of the Institute are to promote universally the education, the study, and the use of Spanish as a second language, to support methods and activities that help the process of Spanish-language education, and to contribute to the advancement of the Spanish and Hispanic American cultures in non-Spanish-speaking countries. The institute's 2015 report "El español, una lengua viva" (Spanish, a living language) estimated that there were 559 million Spanish speakers worldwide. Its latest annual report
El español en el mundo 2018 (Spanish in the world 2018) counts 577 million Spanish speakers worldwide. Among the sources cited in the report is the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau, which estimates that the U.S. will have 138 million Spanish speakers by 2050, making it the biggest Spanish-speaking nation on earth, with Spanish the mother tongue of almost a third of its citizens.
Official use by international organizations
Spanish is one of the official languages of the
United Nations, the
European Union, the World Trade Organization, the
Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 April ...
, the Organization of Ibero-American States, the
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
, the
Union of South American Nations, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, the Latin Union, the Caricom, the North American Free Trade Agreement, the Inter-American Development Bank, and numerous other international organizations.
Sample text
Article 1 of the ''Universal Declaration of Human Rights'' in Spanish:
:
Article 1 of the ''Universal Declaration of Human Rights'' in English:
:''All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.''
See also
* Fundéu BBVA
* List of Spanish-language poets
* Spanish as a second or foreign language
* Spanish-language literature
* Spanish-language music
Spanish words and phrases
* Cuento
* List of English–Spanish interlingual homographs
* Longest word in Spanish
* Most common words in Spanish
* Spanish profanity
* Spanish proverbs
Spanish-speaking world
* List of countries where Spanish is an official language, Countries where Spanish is an official language
* Hispanic culture
* Hispanicization
* Hispanidad
* Hispanism
* Panhispanism
Influences on the Spanish language
* Arabic influence on the Spanish language
* List of Spanish words of Germanic origin
* List of Spanish words of Philippine origin
Dialects and languages influenced by Spanish
* Caló language, Caló
* Chamorro language, Chamorro
* Frespañol
* Llanito
* Palenquero
* Papiamento
* Philippine languages
*
Chavacano
* Portuñol
* Spanglish
* Media Lengua
* List of English words of Spanish origin
Spanish dialects and varieties
* Spanish dialects and varieties
* European Spanish
** Andalusian Spanish
*** Andalusian language movement
** Canarian Spanish
** Castrapo (Galician Spanish)
** Castúo (Extremaduran Spanish)
** Murcian Spanish
* Spanish in the Americas
** North American Spanish
** Central American Spanish
** Caribbean Spanish
** Spanish language in South America, South American Spanish
** Spanish language in the United States, Spanish in the United States
* Spanish in Africa
** Equatoguinean Spanish
** Saharan Spanish
* Spanish in Asia
** Spanish language in the Philippines, Spanish in the Philippines
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
; Organizations
Real Academia Española (RAE) Royal Spanish Academy. Spain's official institution, with a mission to ensure the stability of the Spanish language
Cervantes Institute. A Spanish government agency, responsible for promoting the study and the teaching of the Spanish language and culture.
FundéuRAE Foundation of Emerging Spanish. A non-profit organization with collaboration of the RAE which mission is to clarify doubts and ambiguities of Spanish.
; Educational websites
ProfeDeEle Exercises targeted toward Spanish language teachers (ELE)
AprenderEspanol Spanish activities and material
{{DEFAULTSORT:Spanish Language
Spanish language,
Fusional languages
Languages of Argentina
Languages of Bolivia
Languages of Chile
Languages of Colombia
Languages of Costa Rica
Languages of Cuba
Languages of the Dominican Republic
Languages of Ecuador
Languages of El Salvador
Languages of Equatorial Guinea
Languages of Guatemala
Languages of Honduras
Languages of Mexico
Languages of Nicaragua
Languages of Panama
Languages of Paraguay
Languages of Peru
Languages of Puerto Rico
Languages of Spain
Languages of the United States
Languages of Uruguay
Languages of Venezuela
Lingua francas
Subject–verb–object languages

 Like the other
Like the other  Spanish is marked by
Spanish is marked by  In the 15th and 16th centuries, Spanish underwent a dramatic change in the pronunciation of its
In the 15th and 16th centuries, Spanish underwent a dramatic change in the pronunciation of its  Spanish is the primary language in 20 countries worldwide. As of 2020, it is estimated that about 463 million people speak Spanish as a native language, making it the second most spoken language by number of native speakers. An additional 75 million speak Spanish as a second or foreign language, making it the fourth most spoken language in the world overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindi with a total number of 538 million speakers. Spanish is also the third most used language on the Internet, after English and Chinese.
Spanish is the primary language in 20 countries worldwide. As of 2020, it is estimated that about 463 million people speak Spanish as a native language, making it the second most spoken language by number of native speakers. An additional 75 million speak Spanish as a second or foreign language, making it the fourth most spoken language in the world overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindi with a total number of 538 million speakers. Spanish is also the third most used language on the Internet, after English and Chinese.
 Spanish was briefly removed from official status in 1973 under the administration of
Spanish was briefly removed from official status in 1973 under the administration of  Spanish is the official and most spoken language on Easter Island, which is geographically part of Polynesia in Oceania and politically part of Chile. However, Easter Island's traditional language is Rapa Nui, an Eastern Polynesian language.
As a legacy of comprising the former Spanish East Indies, Spanish loan words are present in the local languages of Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Palau, Marshall Islands and Micronesia.
In addition, in Australia and New Zealand, there are native Spanish communities, resulting from emigration from Spanish-speaking countries. Mainly from the
Spanish is the official and most spoken language on Easter Island, which is geographically part of Polynesia in Oceania and politically part of Chile. However, Easter Island's traditional language is Rapa Nui, an Eastern Polynesian language.
As a legacy of comprising the former Spanish East Indies, Spanish loan words are present in the local languages of Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Palau, Marshall Islands and Micronesia.
In addition, in Australia and New Zealand, there are native Spanish communities, resulting from emigration from Spanish-speaking countries. Mainly from the  Most of the grammatical and
Most of the grammatical and  While being mutually intelligible, there are important variations (Phonology, phonological, Grammar, grammatical, and Lexicon, lexical) in the spoken Spanish of the various regions of Spain and throughout the Spanish-speaking areas of the Americas.
The variety with the most speakers is Mexican Spanish. It is spoken by more than twenty percent of the world's Spanish speakers (more than 112 million of the total of more than 500 million, according to the table above). One of its main features is the vowel reduction, reduction or loss of unstressed vowels, mainly when they are in contact with the sound /s/.
In Spain, northern dialects are popularly thought of as closer to the standard, although positive attitudes toward southern dialects have increased significantly in the last 50 years. The speech from the educated classes of Madrid is the standard variety for use on radio and television in Spain and it is indicated by many as the one that has most influenced the written standard for Spanish. Central (European) Spanish speech patterns have been noted to be in the process of merging with more innovative southern varieties (including Eastern Andalusian and Murcian), as an emerging interdialectal levelled ''koine'' buffered between the Madrid's traditional national standard and the Seville speech trends.
While being mutually intelligible, there are important variations (Phonology, phonological, Grammar, grammatical, and Lexicon, lexical) in the spoken Spanish of the various regions of Spain and throughout the Spanish-speaking areas of the Americas.
The variety with the most speakers is Mexican Spanish. It is spoken by more than twenty percent of the world's Spanish speakers (more than 112 million of the total of more than 500 million, according to the table above). One of its main features is the vowel reduction, reduction or loss of unstressed vowels, mainly when they are in contact with the sound /s/.
In Spain, northern dialects are popularly thought of as closer to the standard, although positive attitudes toward southern dialects have increased significantly in the last 50 years. The speech from the educated classes of Madrid is the standard variety for use on radio and television in Spain and it is indicated by many as the one that has most influenced the written standard for Spanish. Central (European) Spanish speech patterns have been noted to be in the process of merging with more innovative southern varieties (including Eastern Andalusian and Murcian), as an emerging interdialectal levelled ''koine'' buffered between the Madrid's traditional national standard and the Seville speech trends.
 Judaeo-Spanish, also known as Ladino, is a variety of Spanish which preserves many features of medieval Spanish and Portuguese and is spoken by descendants of the Sephardi Jews who were Alhambra decree, expelled from Spain in the 15th century. Conversely, in Portugal the vast majority of the Portuguese Jews converted and became 'New Christians'. Therefore, its relationship to Spanish is comparable with that of the Yiddish language to German language, German. Ladino speakers today are almost exclusively Sephardim, Sephardi Jews, with family roots in Turkey, Greece, or the Balkans, and living mostly in Israel, Turkey, and the United States, with a few communities in Hispanic America. Judaeo-Spanish lacks the Amerindian languages, Native American vocabulary which was acquired by standard Spanish during the Spanish Empire, Spanish colonial period, and it retains many archaic features which have since been lost in standard Spanish. It contains, however, other vocabulary which is not found in standard Spanish, including vocabulary from Hebrew language, Hebrew, French, Greek and Turkish language, Turkish, and other languages spoken where the Sephardim settled.
Judaeo-Spanish is in serious danger of extinction because many native speakers today are elderly as well as elderly ''olim'' (immigrants to Israel) who have not transmitted the language to their children or grandchildren. However, it is experiencing a minor revival among Sephardi communities, especially in music. In Latin American communities, the danger of extinction is also due to assimilation by modern Spanish.
A related dialect is Haketia, the Judaeo-Spanish of northern Morocco. This too tended to assimilate with modern Spanish, during the Spanish occupation of the region.
Judaeo-Spanish, also known as Ladino, is a variety of Spanish which preserves many features of medieval Spanish and Portuguese and is spoken by descendants of the Sephardi Jews who were Alhambra decree, expelled from Spain in the 15th century. Conversely, in Portugal the vast majority of the Portuguese Jews converted and became 'New Christians'. Therefore, its relationship to Spanish is comparable with that of the Yiddish language to German language, German. Ladino speakers today are almost exclusively Sephardim, Sephardi Jews, with family roots in Turkey, Greece, or the Balkans, and living mostly in Israel, Turkey, and the United States, with a few communities in Hispanic America. Judaeo-Spanish lacks the Amerindian languages, Native American vocabulary which was acquired by standard Spanish during the Spanish Empire, Spanish colonial period, and it retains many archaic features which have since been lost in standard Spanish. It contains, however, other vocabulary which is not found in standard Spanish, including vocabulary from Hebrew language, Hebrew, French, Greek and Turkish language, Turkish, and other languages spoken where the Sephardim settled.
Judaeo-Spanish is in serious danger of extinction because many native speakers today are elderly as well as elderly ''olim'' (immigrants to Israel) who have not transmitted the language to their children or grandchildren. However, it is experiencing a minor revival among Sephardi communities, especially in music. In Latin American communities, the danger of extinction is also due to assimilation by modern Spanish.
A related dialect is Haketia, the Judaeo-Spanish of northern Morocco. This too tended to assimilate with modern Spanish, during the Spanish occupation of the region.

 The (Cervantes Institute) is a worldwide nonprofit organization created by the Spanish government in 1991. This organization has branches in 45 countries, with 88 centers devoted to the Spanish and Hispanic American cultures and Spanish language. The goals of the Institute are to promote universally the education, the study, and the use of Spanish as a second language, to support methods and activities that help the process of Spanish-language education, and to contribute to the advancement of the Spanish and Hispanic American cultures in non-Spanish-speaking countries. The institute's 2015 report "El español, una lengua viva" (Spanish, a living language) estimated that there were 559 million Spanish speakers worldwide. Its latest annual report
The (Cervantes Institute) is a worldwide nonprofit organization created by the Spanish government in 1991. This organization has branches in 45 countries, with 88 centers devoted to the Spanish and Hispanic American cultures and Spanish language. The goals of the Institute are to promote universally the education, the study, and the use of Spanish as a second language, to support methods and activities that help the process of Spanish-language education, and to contribute to the advancement of the Spanish and Hispanic American cultures in non-Spanish-speaking countries. The institute's 2015 report "El español, una lengua viva" (Spanish, a living language) estimated that there were 559 million Spanish speakers worldwide. Its latest annual report