Soviet Classical Violinists on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a transcontinental country that spanned much of
 The Supreme Soviet (successor of the
The Supreme Soviet (successor of the



 During his rule, Stalin always made the final policy decisions. Otherwise, Soviet foreign policy was set by the commission on the Foreign Policy of the Central Committee of the
During his rule, Stalin always made the final policy decisions. Otherwise, Soviet foreign policy was set by the commission on the Foreign Policy of the Central Committee of the
 The Marxist-Leninist leadership of the Soviet Union intensely debated foreign policy issues and changed directions several times. Even after Stalin assumed dictatorial control in the late 1920s, there were debates, and he frequently changed positions.
During the country's early period, it was assumed that Communist revolutions would break out soon in every major industrial country, and it was the Russian responsibility to assist them. The
The Marxist-Leninist leadership of the Soviet Union intensely debated foreign policy issues and changed directions several times. Even after Stalin assumed dictatorial control in the late 1920s, there were debates, and he frequently changed positions.
During the country's early period, it was assumed that Communist revolutions would break out soon in every major industrial country, and it was the Russian responsibility to assist them. The
 Under the Military Law of September 1925, the
Under the Military Law of September 1925, the
 The Soviet Union adopted a
The Soviet Union adopted a  By the early 1940s, the Soviet economy had become relatively Autarky, self-sufficient; for most of the period until the creation of
By the early 1940s, the Soviet economy had become relatively Autarky, self-sufficient; for most of the period until the creation of  From the 1930s until its dissolution in late 1991, the way the Soviet economy operated remained essentially unchanged. The economy was formally directed by economic planning, central planning, carried out by Gosplan and organized in Five-year plans for the national economy of the Soviet Union, five-year plans. However, in practice, the plans were highly aggregated and provisional, subject to ''ad hoc'' intervention by superiors. All critical economic decisions were taken by the political leadership. Allocated resources and plan targets were usually denominated in Soviet ruble, rubles rather than in physical goods. Credit was discouraged, but widespread. The final allocation of output was achieved through relatively decentralized, unplanned contracting. Although in theory prices were legally set from above, in practice they were often negotiated, and informal horizontal links (e.g. between producer factories) were widespread.
A number of basic Service (economics), services were state-funded, such as education in the Soviet Union, education and health care. In the manufacturing sector, heavy industry and defence were prioritized over Consumer goods in the Soviet Union, consumer goods. Consumer goods, particularly outside large cities, were often scarce, of poor quality and limited variety. Under the command economy, consumers had almost no influence on production, and the changing demands of a population with growing incomes could not be satisfied by supplies at rigidly fixed prices.Hanson, Philip. ''The Rise and Fall of the Soviet Economy: An Economic History of the USSR from 1945''. London: Longman, 2003. A massive unplanned second economy grew up at low levels alongside the planned one, providing some of the goods and services that the planners could not. The legalization of some elements of the decentralized economy was attempted with the 1965 Soviet economic reform, reform of 1965.
From the 1930s until its dissolution in late 1991, the way the Soviet economy operated remained essentially unchanged. The economy was formally directed by economic planning, central planning, carried out by Gosplan and organized in Five-year plans for the national economy of the Soviet Union, five-year plans. However, in practice, the plans were highly aggregated and provisional, subject to ''ad hoc'' intervention by superiors. All critical economic decisions were taken by the political leadership. Allocated resources and plan targets were usually denominated in Soviet ruble, rubles rather than in physical goods. Credit was discouraged, but widespread. The final allocation of output was achieved through relatively decentralized, unplanned contracting. Although in theory prices were legally set from above, in practice they were often negotiated, and informal horizontal links (e.g. between producer factories) were widespread.
A number of basic Service (economics), services were state-funded, such as education in the Soviet Union, education and health care. In the manufacturing sector, heavy industry and defence were prioritized over Consumer goods in the Soviet Union, consumer goods. Consumer goods, particularly outside large cities, were often scarce, of poor quality and limited variety. Under the command economy, consumers had almost no influence on production, and the changing demands of a population with growing incomes could not be satisfied by supplies at rigidly fixed prices.Hanson, Philip. ''The Rise and Fall of the Soviet Economy: An Economic History of the USSR from 1945''. London: Longman, 2003. A massive unplanned second economy grew up at low levels alongside the planned one, providing some of the goods and services that the planners could not. The legalization of some elements of the decentralized economy was attempted with the 1965 Soviet economic reform, reform of 1965.
 Although statistics of the Soviet economy are notoriously unreliable and its economic growth difficult to estimate precisely, by most accounts, the economy continued to expand until the mid-1980s. During the 1950s and 1960s, it had comparatively high growth and was catching up to the West. However, after 1970, the growth, while still positive, Era of Stagnation, steadily declined much more quickly and consistently than in other countries, despite a rapid increase in the capital stock (the rate of capital increase was only surpassed by Japan).
Overall, the growth rate of per capita income in the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1989 was slightly above the world average (based on 102 countries). A 1986 study published in the ''American Journal of Public Health'' claimed that, citing World Bank data, the Soviet model provided a better quality of life and Human development (economics), human development than market economies at the same level of economic development in most cases. According to Stanley Fischer and William Easterly, growth could have been faster. By their calculation, per capita income in 1989 should have been twice higher than it was, considering the amount of investment, education and population. The authors attribute this poor performance to the low productivity of capital. Steven Rosefielde states that the standard of living declined due to Stalin's despotism. While there was a brief improvement after his death, it lapsed into stagnation.
In 1987,
Although statistics of the Soviet economy are notoriously unreliable and its economic growth difficult to estimate precisely, by most accounts, the economy continued to expand until the mid-1980s. During the 1950s and 1960s, it had comparatively high growth and was catching up to the West. However, after 1970, the growth, while still positive, Era of Stagnation, steadily declined much more quickly and consistently than in other countries, despite a rapid increase in the capital stock (the rate of capital increase was only surpassed by Japan).
Overall, the growth rate of per capita income in the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1989 was slightly above the world average (based on 102 countries). A 1986 study published in the ''American Journal of Public Health'' claimed that, citing World Bank data, the Soviet model provided a better quality of life and Human development (economics), human development than market economies at the same level of economic development in most cases. According to Stanley Fischer and William Easterly, growth could have been faster. By their calculation, per capita income in 1989 should have been twice higher than it was, considering the amount of investment, education and population. The authors attribute this poor performance to the low productivity of capital. Steven Rosefielde states that the standard of living declined due to Stalin's despotism. While there was a brief improvement after his death, it lapsed into stagnation.
In 1987,
 The need for fuel declined in the Soviet Union from the 1970s to the 1980s, both per ruble of gross social product and per ruble of industrial product. At the start, this decline grew very rapidly but gradually slowed down between 1970 and 1975. From 1975 and 1980, it grew even slower, only 2.6%. David Wilson, a historian, believed that the gas industry would account for 40% of Soviet fuel production by the end of the century. His theory did not come to fruition because of the USSR's collapse. The USSR, in theory, would have continued to have an economic growth rate of 2–2.5% during the 1990s because of Soviet energy fields. However, the energy sector faced many difficulties, among them the country's high military expenditure and hostile relations with the First World.
In 1991, the Soviet Union had a pipeline network of for crude oil and another for natural gas. Petroleum and petroleum-based products, natural gas, metals, wood, agricultural products, and a variety of manufactured goods, primarily machinery, arms and military equipment, were exported. In the 1970s and 1980s, the USSR heavily relied on fossil fuel exports to earn hard currency. At its peak in 1988, it was the largest producer and second-largest exporter of crude oil, surpassed only by Saudi Arabia.
The need for fuel declined in the Soviet Union from the 1970s to the 1980s, both per ruble of gross social product and per ruble of industrial product. At the start, this decline grew very rapidly but gradually slowed down between 1970 and 1975. From 1975 and 1980, it grew even slower, only 2.6%. David Wilson, a historian, believed that the gas industry would account for 40% of Soviet fuel production by the end of the century. His theory did not come to fruition because of the USSR's collapse. The USSR, in theory, would have continued to have an economic growth rate of 2–2.5% during the 1990s because of Soviet energy fields. However, the energy sector faced many difficulties, among them the country's high military expenditure and hostile relations with the First World.
In 1991, the Soviet Union had a pipeline network of for crude oil and another for natural gas. Petroleum and petroleum-based products, natural gas, metals, wood, agricultural products, and a variety of manufactured goods, primarily machinery, arms and military equipment, were exported. In the 1970s and 1980s, the USSR heavily relied on fossil fuel exports to earn hard currency. At its peak in 1988, it was the largest producer and second-largest exporter of crude oil, surpassed only by Saudi Arabia.
 The Soviet Union placed great emphasis on Science and technology in the Soviet Union, science and technology. Lenin believed the USSR would never overtake the developed world if it remained as technologically backward as it was upon its founding. Soviet authorities proved their commitment to Lenin's belief by developing massive networks and research and development organizations. In the early 1960s, 40% of chemistry PhDs in the Soviet Union were attained by women, compared with only 5% in the United States. By 1989, Soviet scientists were among the world's best-trained specialists in several areas, such as energy physics, selected areas of medicine, mathematics, welding, space technology, and military technologies. However, due to rigid state planning and Nomenklatura, bureaucracy, the Soviets remained far behind the First World in chemistry, biology, and computer science. Under Stalin, the Soviet government persecuted geneticists in favour of Lysenkoism, a pseudoscience rejected by the scientific community in the Soviet Union and abroad but supported by Stalin's inner circles. Implemented in the USSR and China, it resulted in reduced crop yields and is widely believed to have contributed to the Great Chinese Famine. In the 1980s, the Soviet Union had more scientists and engineers relative to the world's population than any other major country, owing to strong levels of state support. Some of its most remarkable technological achievements, such as launching the Sputnik 1, world's first space satellite, were achieved through military research.
Under the Reagan administration, Project Socrates determined that the Soviet Union addressed the acquisition of science and technology in a manner radically different to the United States. The US prioritized indigenous research and development in both the public and private sectors. In contrast, the USSR placed greater emphasis on acquiring foreign technology, which it did through both Industrial espionage, covert and overt means. However, centralized state planning kept Soviet technological development greatly inflexible. This was exploited by the US to undermine the strength of the Soviet Union and thus foster its reform.
The Soviet Union placed great emphasis on Science and technology in the Soviet Union, science and technology. Lenin believed the USSR would never overtake the developed world if it remained as technologically backward as it was upon its founding. Soviet authorities proved their commitment to Lenin's belief by developing massive networks and research and development organizations. In the early 1960s, 40% of chemistry PhDs in the Soviet Union were attained by women, compared with only 5% in the United States. By 1989, Soviet scientists were among the world's best-trained specialists in several areas, such as energy physics, selected areas of medicine, mathematics, welding, space technology, and military technologies. However, due to rigid state planning and Nomenklatura, bureaucracy, the Soviets remained far behind the First World in chemistry, biology, and computer science. Under Stalin, the Soviet government persecuted geneticists in favour of Lysenkoism, a pseudoscience rejected by the scientific community in the Soviet Union and abroad but supported by Stalin's inner circles. Implemented in the USSR and China, it resulted in reduced crop yields and is widely believed to have contributed to the Great Chinese Famine. In the 1980s, the Soviet Union had more scientists and engineers relative to the world's population than any other major country, owing to strong levels of state support. Some of its most remarkable technological achievements, such as launching the Sputnik 1, world's first space satellite, were achieved through military research.
Under the Reagan administration, Project Socrates determined that the Soviet Union addressed the acquisition of science and technology in a manner radically different to the United States. The US prioritized indigenous research and development in both the public and private sectors. In contrast, the USSR placed greater emphasis on acquiring foreign technology, which it did through both Industrial espionage, covert and overt means. However, centralized state planning kept Soviet technological development greatly inflexible. This was exploited by the US to undermine the strength of the Soviet Union and thus foster its reform.

 Transport was a vital component of the country's economy. The First five-year plan (Soviet Union), economic centralization of the late 1920s and 1930s led to the development of infrastructure on a massive scale, most notably the establishment of Aeroflot, an aviation enterprise. The country had a wide variety of modes of transport by land, water and air. However, due to inadequate maintenance, much of the road, water and Soviet civil aviation transport were outdated and technologically backward compared to the First World.
Soviet rail transport was the largest and most intensively used in the world; it was also better developed than most of its Western counterparts. By the late 1970s and early 1980s, Soviet economists were calling for the construction of more roads to alleviate some of the burdens from the railways and to improve the Soviet
Transport was a vital component of the country's economy. The First five-year plan (Soviet Union), economic centralization of the late 1920s and 1930s led to the development of infrastructure on a massive scale, most notably the establishment of Aeroflot, an aviation enterprise. The country had a wide variety of modes of transport by land, water and air. However, due to inadequate maintenance, much of the road, water and Soviet civil aviation transport were outdated and technologically backward compared to the First World.
Soviet rail transport was the largest and most intensively used in the world; it was also better developed than most of its Western counterparts. By the late 1970s and early 1980s, Soviet economists were calling for the construction of more roads to alleviate some of the burdens from the railways and to improve the Soviet
 Excess deaths throughout World War I and the
Excess deaths throughout World War I and the
 The Soviet Union imposed heavy control on city growth, preventing some cities from reaching their full potential while promoting others.
For the entirety of its existence, the most populous cities were
The Soviet Union imposed heavy control on city growth, preventing some cities from reaching their full potential while promoting others.
For the entirety of its existence, the most populous cities were
 Under Lenin, the state made explicit commitments to promote the equality of men and women. Many early Russian feminists and ordinary Russian working women actively participated in the Revolution, and many more were affected by the events of that period and the new policies. Beginning in October 1918, Lenin's government liberalized divorce and abortion laws, decriminalized homosexuality (re-criminalized in 1932), permitted cohabitation, and ushered in a host of reforms. However, without birth control, the new system produced many broken marriages, as well as countless out-of-wedlock children. The epidemic of divorces and extramarital affairs created social hardships when Soviet leaders wanted people to concentrate their efforts on growing the economy. Giving women control over their fertility also led to a precipitous decline in the birth rate, perceived as a threat to their country's military power. By 1936, Stalin reversed most of the liberal laws, ushering in a Natalism, pronatalist era that lasted for decades.
By 1917, Russia became the first great power to grant women the right to vote. After heavy casualties in World Wars I and II, women outnumbered men in Russia by a 4:3 ratio; this contributed to the larger role women played in Russian society compared to other great powers at the time.
Under Lenin, the state made explicit commitments to promote the equality of men and women. Many early Russian feminists and ordinary Russian working women actively participated in the Revolution, and many more were affected by the events of that period and the new policies. Beginning in October 1918, Lenin's government liberalized divorce and abortion laws, decriminalized homosexuality (re-criminalized in 1932), permitted cohabitation, and ushered in a host of reforms. However, without birth control, the new system produced many broken marriages, as well as countless out-of-wedlock children. The epidemic of divorces and extramarital affairs created social hardships when Soviet leaders wanted people to concentrate their efforts on growing the economy. Giving women control over their fertility also led to a precipitous decline in the birth rate, perceived as a threat to their country's military power. By 1936, Stalin reversed most of the liberal laws, ushering in a Natalism, pronatalist era that lasted for decades.
By 1917, Russia became the first great power to grant women the right to vote. After heavy casualties in World Wars I and II, women outnumbered men in Russia by a 4:3 ratio; this contributed to the larger role women played in Russian society compared to other great powers at the time.
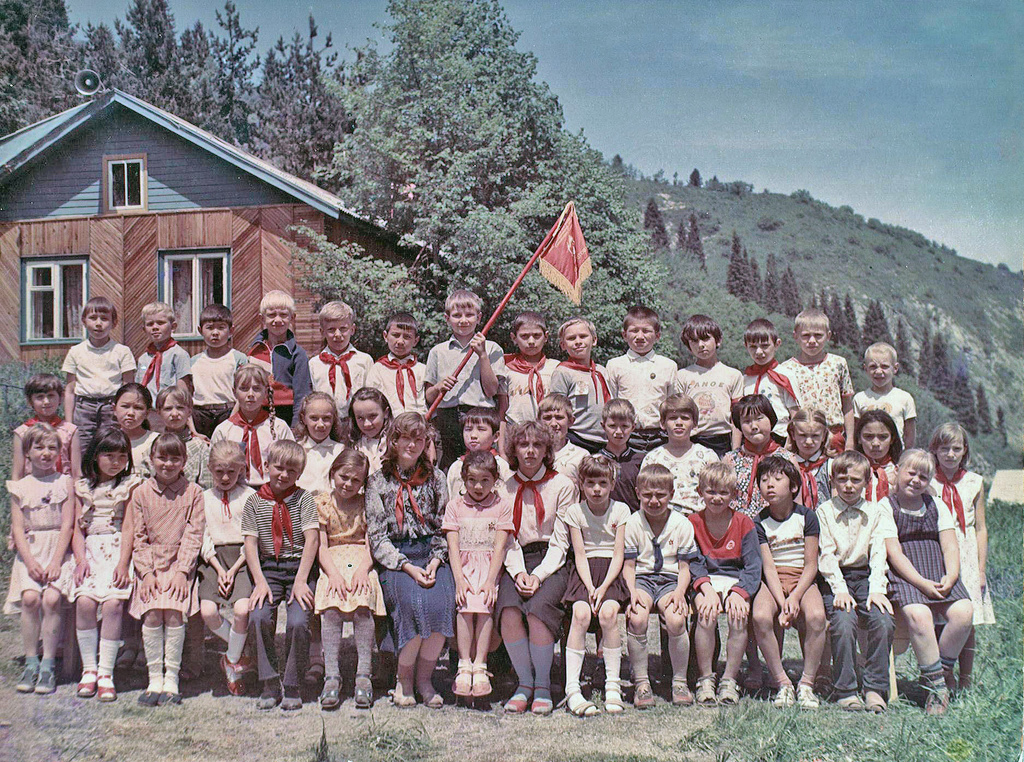 Anatoly Lunacharsky became the first People's Commissar for Education of Soviet Russia. In the beginning, the Soviet authorities placed great emphasis on the Likbez, elimination of illiteracy. All left-handed children were forced to write with their right hand in the Soviet school system. Literate people were automatically hired as teachers. For a short period, quality was sacrificed for quantity. By 1940, Stalin could announce that illiteracy had been eliminated. Throughout the 1930s, social mobility rose sharply, which has been attributed to reforms in education. In the aftermath of World War II, the country's educational system expanded dramatically, which had a tremendous effect. In the 1960s, nearly all children had access to education, the only exception being those living in remote areas.
Anatoly Lunacharsky became the first People's Commissar for Education of Soviet Russia. In the beginning, the Soviet authorities placed great emphasis on the Likbez, elimination of illiteracy. All left-handed children were forced to write with their right hand in the Soviet school system. Literate people were automatically hired as teachers. For a short period, quality was sacrificed for quantity. By 1940, Stalin could announce that illiteracy had been eliminated. Throughout the 1930s, social mobility rose sharply, which has been attributed to reforms in education. In the aftermath of World War II, the country's educational system expanded dramatically, which had a tremendous effect. In the 1960s, nearly all children had access to education, the only exception being those living in remote areas.
 The Soviet Union was an ethnically diverse country, with more than 100 distinct ethnic groups. The total population of the country was estimated at 293 million in 1991. According to a 1990 estimate, the majority of the population were
The Soviet Union was an ethnically diverse country, with more than 100 distinct ethnic groups. The total population of the country was estimated at 293 million in 1991. According to a 1990 estimate, the majority of the population were
File:Ethnic map USSR 1930.jpg, Ethnographic map of the USSR, 1930
File:European Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) Ethnic Groups (Before 1939) - DPLA - 9820cc06b72e7b131366b861f5ee351a.jpg, European Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) Ethnic Groups, before 1939
File:Ethnic map USSR 1941.jpg, Ethnographic map of the Soviet Union, 1941
File:U.S. S.R. - Ethnic Compositions - DPLA - 754227d4ec980a6b169104b656de499a.jpg, Ethnic composition of the Soviet Union in 1949
File:Map of the ethnic groups of the Soviet Union.png, Ethnographic map of the Soviet Union, 1970
File:French map of the ethnic groups living in USSR.png, Map of the ethnic groups living in USSR, 1970
File:Ethnic Groups in the Soviet Union - DPLA - d7a6475bd436c74e2b67e621a6b2afad.jpg, Ethnic Groups in the Soviet Union, 1979
File:Comparative Soviet Nationalities by Republic, 1989 - DPLA - 23930ee870e66bd2efa5417463128b28.jpg, Comparative Soviet Nationalities by Republic, 1989
 In 1917, before the revolution, health conditions were significantly behind those of developed countries. As Lenin later noted, "Either the lice will defeat socialism, or socialism will defeat the lice". The Soviet health care system was conceived by the People's Commissariat for Health in 1918. Under the Semashko model, health care was to be controlled by the state and would be provided to its citizens free of charge, a revolutionary concept at the time. Article 42 of the 1977 Soviet Constitution gave all citizens the right to health protection and free access to any health institutions in the USSR. Before
In 1917, before the revolution, health conditions were significantly behind those of developed countries. As Lenin later noted, "Either the lice will defeat socialism, or socialism will defeat the lice". The Soviet health care system was conceived by the People's Commissariat for Health in 1918. Under the Semashko model, health care was to be controlled by the state and would be provided to its citizens free of charge, a revolutionary concept at the time. Article 42 of the 1977 Soviet Constitution gave all citizens the right to health protection and free access to any health institutions in the USSR. Before
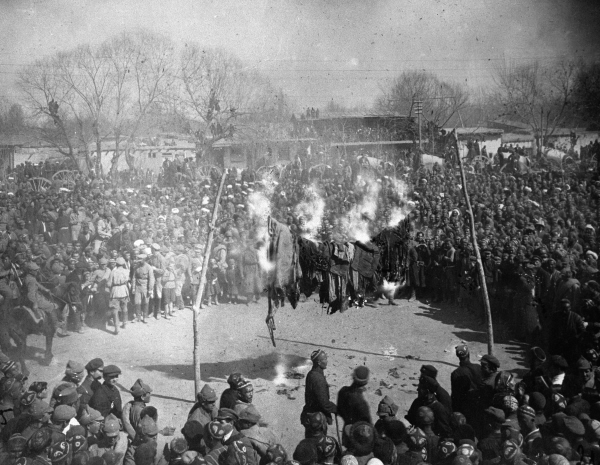



 Christianity and Islam had the highest number of adherents among the religious citizens. Eastern Christianity predominated among Christians, with Russia's traditional Russian Orthodox Church being the largest Christian denomination. About 90% of the Soviet Union's Muslims were Sunnis, with Shias being concentrated in the Azerbaijan SSR. Smaller groups included Roman Catholics, Jews, Buddhists, and a variety of Protestant denominations (especially Baptists and Lutherans).
Religious influence had been strong in the Russian Empire. The Russian Orthodox Church enjoyed a privileged status as the church of the monarchy and took part in carrying out official state functions. The immediate period following the establishment of the Soviet state included a struggle against the Orthodox Church, which the revolutionaries considered an ally of the former ruling classes.
In Soviet law, the 'freedom to hold religious services' was constitutionally guaranteed, although the ruling Communist Party regarded religion as incompatible with the Marxist spirit of scientific materialism. In practice, the Soviet system subscribed to a narrow interpretation of this right, and in fact used a range of official measures to discourage religion and curb the activities of religious groups.
The 1918 Council of People's Commissars decree establishing the Russian SFSR as a secular state also decreed that 'the teaching of religion in all [places] where subjects of general instruction are taught, is forbidden. Citizens may teach and may be taught religion privately.' Among further restrictions, those adopted in 1929 included express prohibitions on a range of church activities, including meetings for organized Bible study (Christian), Bible study. Both Christian and non-Christian establishments were shut down by the thousands in the 1920s and 1930s. By 1940, as many as 90% of the churches, synagogues, and mosques that had been operating in 1917 were closed; the majority of them were demolished or re-purposed for state needs with little concern for their historic and cultural value.
More than 85,000 Orthodox priests were shot in 1937 alone. Only a twelfth of the Russian Orthodox Church's priests were left functioning in their parishes by 1941. In the period between 1927 and 1940, the number of Orthodox Churches in Russia fell from 29,584 to less than 500 (1.7%).
The Soviet Union was officially a secular state, but a 'government-sponsored program of forced conversion to Marxist-Leninist atheism, atheism' was conducted under the doctrine of state atheism. The government targeted religions based on state interests, and while most organized religions were never outlawed, religious property was confiscated, believers were harassed, and religion was ridiculed while atheism was propagated in schools. In 1925, the government founded the League of Militant Atheists to intensify the propaganda campaign. Accordingly, although personal expressions of religious faith were not explicitly banned, a strong sense of social stigma was imposed on them by the formal structures and mass media, and it was generally considered unacceptable for members of certain professions (teachers, state bureaucrats, soldiers) to be openly religious. While persecution accelerated following Stalin's rise to power, a revival of Orthodoxy was fostered by the government during World War II and the Soviet authorities sought to control the Russian Orthodox Church rather than liquidate it. During the first five years of Soviet power, the Bolsheviks executed 28 Russian Orthodox bishops and over 1,200 Russian Orthodox priests. Many others were imprisoned or exiled. Believers were harassed and persecuted. Most seminaries were closed, and the publication of most religious material was prohibited. By 1941, only 500 churches remained open out of about 54,000 in existence before World War I.
Convinced that religious anti-Sovietism had become a thing of the past, and with the looming threat of war, the Stalin administration began shifting to a more moderate religion policy in the late 1930s. Soviet religious establishments overwhelmingly rallied to support the war effort during World War II. Amid other accommodations to religious faith after the German invasion, churches were reopened. Radio Moscow began broadcasting a religious hour, and a historic meeting between Stalin and Orthodox Church leader Patriarch Sergius of Moscow was held in 1943. Stalin had the support of the majority of the religious people in the USSR even through the late 1980s. The general tendency of this period was an increase in religious activity among believers of all faiths.
Under
Christianity and Islam had the highest number of adherents among the religious citizens. Eastern Christianity predominated among Christians, with Russia's traditional Russian Orthodox Church being the largest Christian denomination. About 90% of the Soviet Union's Muslims were Sunnis, with Shias being concentrated in the Azerbaijan SSR. Smaller groups included Roman Catholics, Jews, Buddhists, and a variety of Protestant denominations (especially Baptists and Lutherans).
Religious influence had been strong in the Russian Empire. The Russian Orthodox Church enjoyed a privileged status as the church of the monarchy and took part in carrying out official state functions. The immediate period following the establishment of the Soviet state included a struggle against the Orthodox Church, which the revolutionaries considered an ally of the former ruling classes.
In Soviet law, the 'freedom to hold religious services' was constitutionally guaranteed, although the ruling Communist Party regarded religion as incompatible with the Marxist spirit of scientific materialism. In practice, the Soviet system subscribed to a narrow interpretation of this right, and in fact used a range of official measures to discourage religion and curb the activities of religious groups.
The 1918 Council of People's Commissars decree establishing the Russian SFSR as a secular state also decreed that 'the teaching of religion in all [places] where subjects of general instruction are taught, is forbidden. Citizens may teach and may be taught religion privately.' Among further restrictions, those adopted in 1929 included express prohibitions on a range of church activities, including meetings for organized Bible study (Christian), Bible study. Both Christian and non-Christian establishments were shut down by the thousands in the 1920s and 1930s. By 1940, as many as 90% of the churches, synagogues, and mosques that had been operating in 1917 were closed; the majority of them were demolished or re-purposed for state needs with little concern for their historic and cultural value.
More than 85,000 Orthodox priests were shot in 1937 alone. Only a twelfth of the Russian Orthodox Church's priests were left functioning in their parishes by 1941. In the period between 1927 and 1940, the number of Orthodox Churches in Russia fell from 29,584 to less than 500 (1.7%).
The Soviet Union was officially a secular state, but a 'government-sponsored program of forced conversion to Marxist-Leninist atheism, atheism' was conducted under the doctrine of state atheism. The government targeted religions based on state interests, and while most organized religions were never outlawed, religious property was confiscated, believers were harassed, and religion was ridiculed while atheism was propagated in schools. In 1925, the government founded the League of Militant Atheists to intensify the propaganda campaign. Accordingly, although personal expressions of religious faith were not explicitly banned, a strong sense of social stigma was imposed on them by the formal structures and mass media, and it was generally considered unacceptable for members of certain professions (teachers, state bureaucrats, soldiers) to be openly religious. While persecution accelerated following Stalin's rise to power, a revival of Orthodoxy was fostered by the government during World War II and the Soviet authorities sought to control the Russian Orthodox Church rather than liquidate it. During the first five years of Soviet power, the Bolsheviks executed 28 Russian Orthodox bishops and over 1,200 Russian Orthodox priests. Many others were imprisoned or exiled. Believers were harassed and persecuted. Most seminaries were closed, and the publication of most religious material was prohibited. By 1941, only 500 churches remained open out of about 54,000 in existence before World War I.
Convinced that religious anti-Sovietism had become a thing of the past, and with the looming threat of war, the Stalin administration began shifting to a more moderate religion policy in the late 1930s. Soviet religious establishments overwhelmingly rallied to support the war effort during World War II. Amid other accommodations to religious faith after the German invasion, churches were reopened. Radio Moscow began broadcasting a religious hour, and a historic meeting between Stalin and Orthodox Church leader Patriarch Sergius of Moscow was held in 1943. Stalin had the support of the majority of the religious people in the USSR even through the late 1980s. The general tendency of this period was an increase in religious activity among believers of all faiths.
Under
 In summer of 1923 in Moscow was established the Dynamo Sports Club, Proletarian Sports Society "Dynamo" as a sports organization of Soviet secret police Cheka.
On 13 July 1925 the Central Committee of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks) adopted a statement "About the party's tasks in sphere of physical culture". In the statement was determined the role of physical culture in Soviet society and the party's tasks in political leadership of physical culture movement in the country.
The Soviet Olympic Committee formed on 21 April 1951, and the IOC recognized the new body in its List of IOC meetings, 45th session. In the same year, when the Soviet representative Konstantin Andrianov became an IOC member, the USSR officially joined the Olympic Movement. The 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki thus became first Olympic Games for Soviet athletes. The Soviet Union was the biggest rival to the United States at the Summer Olympics, winning Soviet Union at the Olympics#Medals by Summer Games, six of its nine appearances at the games and also topping the medal tally at the Winter Olympics six times. The Soviet Union's Olympics success has been attributed to its large investment in sports to demonstrate its superpower image and political influence on a global stage.
The Soviet Union national ice hockey team won nearly every Ice Hockey World Championships, world championship and Ice hockey at the Olympic Games, Olympic tournament between 1954 and 1991 and never failed to medal in any International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) tournament in which they competed.
Soviet Olympic team was notorious for skirting the edge of amateur rules. All Soviet athletes held some nominal jobs, but were in fact state-sponsored and trained full-time. According to many experts, that gave the Soviet Union a huge advantage over the
In summer of 1923 in Moscow was established the Dynamo Sports Club, Proletarian Sports Society "Dynamo" as a sports organization of Soviet secret police Cheka.
On 13 July 1925 the Central Committee of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks) adopted a statement "About the party's tasks in sphere of physical culture". In the statement was determined the role of physical culture in Soviet society and the party's tasks in political leadership of physical culture movement in the country.
The Soviet Olympic Committee formed on 21 April 1951, and the IOC recognized the new body in its List of IOC meetings, 45th session. In the same year, when the Soviet representative Konstantin Andrianov became an IOC member, the USSR officially joined the Olympic Movement. The 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki thus became first Olympic Games for Soviet athletes. The Soviet Union was the biggest rival to the United States at the Summer Olympics, winning Soviet Union at the Olympics#Medals by Summer Games, six of its nine appearances at the games and also topping the medal tally at the Winter Olympics six times. The Soviet Union's Olympics success has been attributed to its large investment in sports to demonstrate its superpower image and political influence on a global stage.
The Soviet Union national ice hockey team won nearly every Ice Hockey World Championships, world championship and Ice hockey at the Olympic Games, Olympic tournament between 1954 and 1991 and never failed to medal in any International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) tournament in which they competed.
Soviet Olympic team was notorious for skirting the edge of amateur rules. All Soviet athletes held some nominal jobs, but were in fact state-sponsored and trained full-time. According to many experts, that gave the Soviet Union a huge advantage over the
 The legacy of the USSR remains a controversial topic. The socio-economic nature of
The legacy of the USSR remains a controversial topic. The socio-economic nature of  Western academicians published various analyses of the post-Soviet states' development, claiming that the dissolution was followed by a severe drop in economic and social conditions in these countries, including a rapid increase in poverty, crime, corruption, unemployment, homelessness, rates of disease, infant mortality and domestic violence, as well as demographic losses, income inequality and the rise of an Russian oligarchs, oligarchical class, along with decreases in calorie intake, life expectancy, adult literacy, and income. Between 1988 and 1989 and 1993–1995, the Gini ratio increased by an average of 9 points for all former Soviet republics. According to Western analysis, the economic shocks that accompanied wholesale privatization were associated with sharp increases in mortality, Russia, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia saw a tripling of unemployment and a 42% increase in male death rates between 1991 and 1994, and in the following decades, only five or six of the post-communist states are on a path to joining the wealthy capitalist West while most are falling behind, some to such an extent that it will take over fifty years to catch up to where they were before the fall of the Soviet Bloc. However, virtually all the former Soviet republics were able to turn their economies around and increase GDP to multiple times what it was under the USSR, though with large wealth disparities, and many post-soviet economies described as oligarchic.
Since the
Western academicians published various analyses of the post-Soviet states' development, claiming that the dissolution was followed by a severe drop in economic and social conditions in these countries, including a rapid increase in poverty, crime, corruption, unemployment, homelessness, rates of disease, infant mortality and domestic violence, as well as demographic losses, income inequality and the rise of an Russian oligarchs, oligarchical class, along with decreases in calorie intake, life expectancy, adult literacy, and income. Between 1988 and 1989 and 1993–1995, the Gini ratio increased by an average of 9 points for all former Soviet republics. According to Western analysis, the economic shocks that accompanied wholesale privatization were associated with sharp increases in mortality, Russia, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia saw a tripling of unemployment and a 42% increase in male death rates between 1991 and 1994, and in the following decades, only five or six of the post-communist states are on a path to joining the wealthy capitalist West while most are falling behind, some to such an extent that it will take over fifty years to catch up to where they were before the fall of the Soviet Bloc. However, virtually all the former Soviet republics were able to turn their economies around and increase GDP to multiple times what it was under the USSR, though with large wealth disparities, and many post-soviet economies described as oligarchic.
Since the
Impressions of Soviet Russia
by John Dewey
A Country Study: Soviet Union
(PDF) {{Authority control Soviet Union, States and territories established in 1922 States and territories disestablished in 1991 20th century in Russia Early Soviet republics, Communism in Russia Former countries in Europe Former countries in West Asia Former countries in Central Asia Former socialist republics Historical transcontinental empires Countries and territories where Russian is an official language
Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
from 1922 until it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the largest country by area, extending across eleven time zones and sharing borders with twelve countries, and the third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, it was nominally organized as a federal union of national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
. In practice, its government and economy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
were highly centralized. As a one-party state
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a governance structure in which only a single political party controls the ruling system. In a one-party state, all opposition parties are either outlawed or en ...
governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
(CPSU), it was a flagship communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of Marxism–Leninism, a branch of the communist ideology. Marxism–Leninism was ...
. Its capital and largest city was Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
.
The Soviet Union's roots lay in the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
of 1917. The new government, led by Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
, established the Russian SFSR, the world's first constitutionally communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of Marxism–Leninism, a branch of the communist ideology. Marxism–Leninism was ...
. The revolution was not accepted by all within the Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federative Republic in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
, resulting in the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
. The Russian SFSR and its subordinate republics were merged into the Soviet Union in 1922. Following Lenin's death in 1924, Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
came to power, inaugurating rapid industrialization and forced collectivization that led to significant economic growth but contributed to a famine between 1930 and 1933 that killed millions. The Soviet forced labour camp system of the Gulag
The Gulag was a system of Labor camp, forced labor camps in the Soviet Union. The word ''Gulag'' originally referred only to the division of the Chronology of Soviet secret police agencies, Soviet secret police that was in charge of runnin ...
was expanded. During the late 1930s, Stalin's government conducted the Great Purge
The Great Purge, or the Great Terror (), also known as the Year of '37 () and the Yezhovshchina ( , ), was a political purge in the Soviet Union that took place from 1936 to 1938. After the Assassination of Sergei Kirov, assassination of ...
to remove opponents, resulting in mass death, imprisonment, and deportation. In 1939, the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
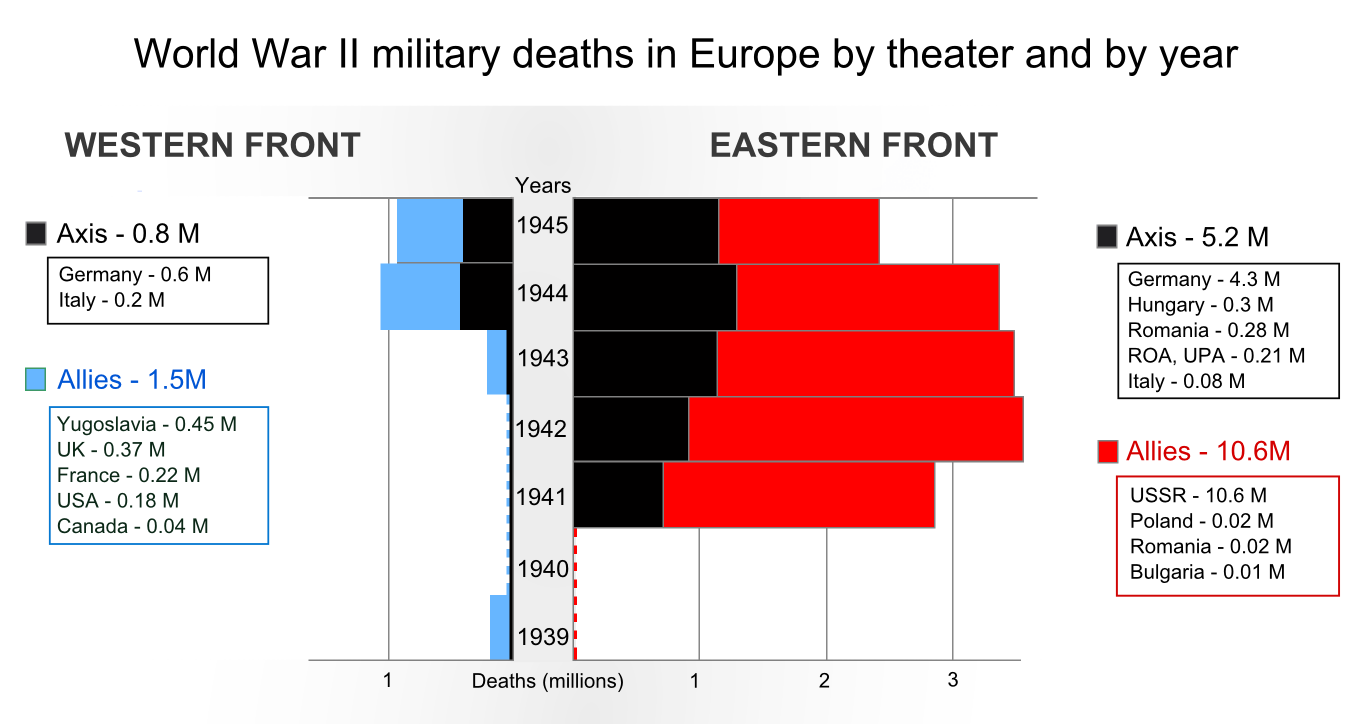
signed a non-aggression pact, but in 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in the largest land invasion in history, opening the Eastern Front of World War II. The Soviets played a decisive role in defeating the Axis powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
, suffering an estimated 27 million casualties, which accounted for most Allied losses. In the aftermath of the war, the Soviet Union consolidated the territory occupied by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
, forming satellite states, and undertook rapid economic development which cemented its status as a superpower
Superpower describes a sovereign state or supranational union that holds a dominant position characterized by the ability to Sphere of influence, exert influence and Power projection, project power on a global scale. This is done through the comb ...
.
Geopolitical tensions with the United States led to the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
. The American-led Western Bloc coalesced into NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
in 1949, prompting the Soviet Union to form its own military alliance, the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
, in 1955. Neither side engaged in direct military confrontation, and instead fought on an ideological basis and through proxy war
In political science, a proxy war is an armed conflict where at least one of the belligerents is directed or supported by an external third-party power. In the term ''proxy war'', a belligerent with external support is the ''proxy''; both bel ...
s. In 1953, following Stalin's death, the Soviet Union undertook a campaign of de-Stalinization
De-Stalinization () comprised a series of political reforms in the Soviet Union after Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, the death of long-time leader Joseph Stalin in 1953, and Khrushchev Thaw, the thaw brought about by ascension of Nik ...
under Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
, which saw reversals and rejections of Stalinist policies. This campaign caused tensions with Communist China. During the 1950s, the Soviet Union expanded its efforts in space exploration and took a lead in the Space Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
with the first artificial satellite, the first human spaceflight, the first space station, and the first probe to land on another planet. In 1985, the last Soviet leader, Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
, sought to reform the country through his policies of ''glasnost
''Glasnost'' ( ; , ) is a concept relating to openness and transparency. It has several general and specific meanings, including a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information and the inadmissi ...
'' and ''perestroika
''Perestroika'' ( ; rus, перестройка, r=perestrojka, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg, links=no) was a political reform movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s, widely associ ...
''. In 1989, various countries of the Warsaw Pact overthrew their Soviet-backed regimes, and nationalist
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation,Anthony D. Smith, Smith, A ...
and separatist
Separatism is the advocacy of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, regional, governmental, or gender separation from the larger group. As with secession, separatism conventionally refers to full political separation. Groups simply seekin ...
movements erupted across the Soviet Union. In 1991, amid efforts to preserve the country as a renewed federation, an attempted coup against Gorbachev by hardline communists prompted the largest republics—Ukraine, Russia, and Belarus—to secede. On 26 December, Gorbachev officially recognized the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
. Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin (1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician and statesman who served as President of Russia from 1991 to 1999. He was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) from 1961 to ...
, the leader of the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
, oversaw its reconstitution into the Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, which became the Soviet Union's successor state; all other republics emerged as fully independent post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they ...
.
During its existence, the Soviet Union produced many significant social and technological achievements and innovations. It had the world's second-largest economy and largest standing military. An NPT-designated state, it wielded the largest arsenal of nuclear weapons in the world. As an Allied nation, it was a founding member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
as well as one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
. Before its dissolution, the Soviet Union was one of the world's two superpowers through its hegemony in Eastern Europe, global diplomatic and ideological influence (particularly in the Global South
Global North and Global South are terms that denote a method of grouping countries based on their defining characteristics with regard to socioeconomics and politics. According to UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the Global South broadly com ...
), military and economic strengths, and scientific
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
accomplishments.
Etymology
The word ''soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
'' is derived from the Russian word (), meaning 'council', 'assembly', 'advice', ultimately deriving from the proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th ...
verbal stem of ('to inform'), related to Slavic ('news'), English ''wise''. The word ''sovietnik'' means 'councillor'. Some organizations in Russian history were called ''council'' (). In the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, the State Council, which functioned from 1810 to 1917, was referred to as a Council of Ministers.
The soviets as workers' councils first appeared during the 1905 Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905, also known as the First Russian Revolution, was a revolution in the Russian Empire which began on 22 January 1905 and led to the establishment of a constitutional monarchy under the Russian Constitution of 1906, th ...
. Although they were quickly suppressed by the Imperial army, after the February Revolution of 1917, workers' and soldiers' soviets emerged throughout the country and shared power with the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
. The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
, demanded that all power be transferred to the soviets, and gained support from the workers and soldiers. After the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
, in which the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
seized power from the Provisional Government in the name of the soviets, Lenin proclaimed the formation of the Russian Socialist Federal Soviet Republic (RSFSR).
During the Georgian Affair of 1922, Lenin called for the Russian SFSR and other national soviet republics to form a greater union which he initially named as the Union of Soviet Republics of Europe and Asia (). Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
initially resisted Lenin's proposal but ultimately accepted it, and with Lenin's agreement he changed the name to the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), although all republics began as ''socialist soviet'' and did not change to the other order until 1936
Events January–February
* January 20 – The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King Edward VIII, following the death of his father, George V, at Sandringham House.
* January 28 – Death and state funer ...
. In addition, in the regional languages of several republics, the word ''council'' or ''conciliar'' in the respective language was only quite late changed to an adaptation of the Russian ''soviet'' and never in others, e.g. Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
.
(in the Latin alphabet: ''SSSR'') is the abbreviation of the Russian-language cognate of USSR, as written in Cyrillic letters
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Easte ...
. The soviets used this abbreviation so frequently that audiences worldwide became familiar with its meaning. After this, the most common Russian initialization is (transliteration: ) which essentially translates to ''Union of SSRs'' in English. In addition, the Russian short form name (transliteration: , which literally means ''Soviet Union'') is also commonly used, but only in its unabbreviated form. Since the start of the Great Patriotic War
The Eastern Front, also known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union and its successor states, and the German–Soviet War in modern Germany and Ukraine, was a Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II ...
at the latest, abbreviating the Russian name of the Soviet Union as has been taboo, the reason being that as a Russian Cyrillic abbreviation is associated with the infamous of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, as ''SS'' is in English.
In English-language media, the state was referred to as the Soviet Union or the USSR. The Russian SFSR dominated the Soviet Union to such an extent that, for most of the Soviet Union's existence, it was colloquially, but incorrectly, referred to as Russia.
History
The history of the Soviet Union began with the ideals of the Bolshevik Revolution and ended in dissolution amidst economic collapse and political disintegration. Established in 1922 following theRussian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
, the Soviet Union quickly became a one-party state under the Communist Party. Its early years under Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
were marked by the implementation of socialist policies and the New Economic Policy (NEP), which allowed for market-oriented reforms.
The rise of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
in the late 1920s ushered in an era of intense centralization and totalitarianism. Stalin's rule was characterized by the forced collectivization of agriculture, rapid industrialization
Industrialisation (British English, UK) American and British English spelling differences, or industrialization (American English, US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an i ...
, and the Great Purge
The Great Purge, or the Great Terror (), also known as the Year of '37 () and the Yezhovshchina ( , ), was a political purge in the Soviet Union that took place from 1936 to 1938. After the Assassination of Sergei Kirov, assassination of ...
, which eliminated perceived enemies of the state. The Soviet Union played a crucial role in the Allied victory in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, but at a tremendous human cost, with millions of Soviet citizens perishing in the conflict.
The Soviet Union emerged as one of the world's two superpowers, leading the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
in opposition to the Western Bloc during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
. This period saw the USSR engage in an arms race, the Space Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
, and proxy wars
In political science, a proxy war is an armed conflict where at least one of the belligerents is directed or supported by an external third-party power. In the term ''proxy war'', a belligerent with external support is the ''proxy''; both bel ...
around the globe. The post-Stalin leadership, particularly under Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
, initiated a de-Stalinization
De-Stalinization () comprised a series of political reforms in the Soviet Union after Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, the death of long-time leader Joseph Stalin in 1953, and Khrushchev Thaw, the thaw brought about by ascension of Nik ...
process, leading to a period of liberalization and relative openness known as the Khrushchev Thaw
The Khrushchev Thaw (, or simply ''ottepel'')William Taubman, Khrushchev: The Man and His Era, London: Free Press, 2004 is the period from the mid-1950s to the mid-1960s when Political repression in the Soviet Union, repression and Censorship in ...
. However, the subsequent era under Leonid Brezhnev
Leonid Ilyich Brezhnev (19 December 190610 November 1982) was a Soviet politician who served as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1964 until Death and state funeral of Leonid Brezhnev, his death in 1982 as w ...
, referred to as the Era of Stagnation
The "Era of Stagnation" (, or ) is a term coined by Mikhail Gorbachev in order to describe the negative way in which he viewed the economic, political, and social policies of the Soviet Union that began during the rule of Leonid Brezhnev (1964 ...
, was marked by economic decline, political corruption, and a rigid gerontocracy
A gerontocracy is a form of rule in which an entity is ruled by leaders who are substantially older than most of the adult population.
In many political structures, power within the ruling class accumulates with age, making the oldest individu ...
. Despite efforts to maintain the Soviet Union's superpower status, the economy struggled due to its centralized nature, technological backwardness, and inefficiencies. The vast military expenditures and burdens of maintaining the Eastern Bloc, further strained the Soviet economy.
In the 1980s, Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
's policies of Glasnost
''Glasnost'' ( ; , ) is a concept relating to openness and transparency. It has several general and specific meanings, including a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information and the inadmissi ...
(openness) and Perestroika
''Perestroika'' ( ; rus, перестройка, r=perestrojka, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg, links=no) was a political reform movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s, widely associ ...
(restructuring) aimed to revitalize the Soviet system but instead accelerated its unraveling. Nationalist movements gained momentum across the Soviet republics, and the control of the Communist Party weakened. The failed coup attempt in August 1991 against Gorbachev by hardline communists hastened the end of the Soviet Union, which formally dissolved on 26 December 1991, ending nearly seven decades of Soviet rule.
Geography
With an area of , the Soviet Union was the world's largest country, a status that is retained by theRussian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Covering a sixth of Earth's land surface, its size was comparable to that of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
. Two other successor states, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, rank among the top 10 countries by land area, and the largest country entirely in Europe, respectively. The Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an portion accounted for a quarter of the country's area and was the cultural and economic center. The eastern part in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
extended to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
to the east and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
to the south, and, except some areas in Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, was much less populous. It spanned over east to west across 11 time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of ...
s, and over north to south. It had five climate zones: tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
, taiga
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. In North A ...
, steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
s, desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
and mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
s.
The USSR, like Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, had the world's longest border
Borders are generally defined as geography, geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by polity, political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other administrative divisio ...
, measuring over , or circumferences of Earth. Two-thirds of it was a coast
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
line. The country bordered Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
, and Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
from 1945 to 1991. The Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
separated the USSR from the United States.
The country's highest mountain was Communism Peak (now Ismoil Somoni Peak) in Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, at . The USSR also included most of the world's largest lakes; the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
(shared with Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
), and Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
, the world's largest (by volume) and deepest freshwater lake that is also an internal body of water in Russia.
Neighbouring countries were aware of the high levels of pollution in the Soviet Union but after the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
it was discovered that its environmental problems were greater than what the Soviet authorities admitted. The Soviet Union was the world's second largest producer of harmful emissions. In 1988, total emissions in the Soviet Union were about 79% of those in the United States. But since the Soviet GNP was only 54% of that of the United States, this means that the Soviet Union generated 1.5 times more pollution than the United States per unit of GNP.
The Soviet Chernobyl disaster
On 26 April 1986, the no. 4 reactor of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, located near Pripyat, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union (now Ukraine), exploded. With dozens of direct casualties, it is one of only ...
in 1986 was the first major accident at a civilian nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power st ...
. Unparalleled in the world, it resulted in a large number of radioactive isotopes being released into the atmosphere. Radioactive doses were scattered relatively far. Although long-term effects of the accident were unknown, 4,000 new cases of thyroid cancer which resulted from the accident's contamination were reported at the time of the accident, but this led to a relatively low number of deaths (WHO data, 2005). Another major radioactive accident was the Kyshtym disaster.
The Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula (; ) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk of the territory of Murmansk Oblast, it lies almost completely inside the Arctic Circle and is border ...
was one of the places with major problems. Around the industrial cities of Monchegorsk and Norilsk
Norilsk ( rus, Нори́льск, p=nɐˈrʲilʲsk) is a closed city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located south of the western Taymyr Peninsula, around 90 km east of the Yenisei, Yenisey River and 1,500 km north of Krasnoyarsk. Norilsk is 300 ...
, where nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, for example, is mined, all forests have been destroyed by contamination, while the northern and other parts of Russia have been affected by emissions. During the 1990s, people in the West were also interested in the radioactive hazards of nuclear facilities, decommissioned nuclear submarine
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor, but not necessarily nuclear-armed.
Nuclear submarines have considerable performance advantages over "conventional" (typically diesel-electric) submarines. Nuclear propulsion ...
s, and the processing of nuclear waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear ...
or spent nuclear fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor (usually at a nuclear power plant). It is no longer useful in sustaining a nuclear reaction in an ordinary thermal reactor and ...
. It was also known in the early 1990s that the USSR had transported radioactive material to the Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; , ; ) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters.World Wildlife Fund, 2008. It was known earlier among Russi ...
and Kara Sea
The Kara Sea is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. Ultimately the Kara, Barents and Laptev Seas are all ...
, which was later confirmed by the Russian parliament. The crash of the K-141 Kursk submarine in 2000 in the west further raised concerns. In the past, there were accidents involving submarines K-19 K19 may refer to:
* K-19 (Kansas highway)
* ''K-19: The Widowmaker'', an American historical drama film
* K19 pipe, a diatreme in Northern Alberta, Canada
* Albany Municipal Airport (Missouri)
* Keratin 19, a human protein
* , a Soviet submarine
* S ...
, K-8, a K-129, K-27, K-219 and K-278 Komsomolets.
Government and politics
The Sovietcommunist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of Marxism–Leninism, a branch of the communist ideology. Marxism–Leninism was ...
system was based on unified state power and democratic centralism
Democratic centralism is the organisational principle of most communist parties, in which decisions are made by a process of vigorous and open debate amongst party membership, and are subsequently binding upon all members of the party. The co ...
. The highest organ of state authority, the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, stood above all other state organs and worked under the leadership of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
. The executive organ of the state (synonymous with government), the Council of Ministers
Council of Ministers is a traditional name given to the supreme Executive (government), executive organ in some governments. It is usually equivalent to the term Cabinet (government), cabinet. The term Council of State is a similar name that also m ...
, was an internal organ of the All-Union Supreme Soviet.Sakwa, Richard. ''Soviet Politics in Perspective''. 2nd ed. London – N.Y.: Routledge, 1998.
Communist Party
At the top of the Communist Party was the Central Committee, elected at Party Congresses and Conferences. In turn, the Central Committee voted for aPolitburo
A politburo () or political bureau is the highest organ of the central committee in communist parties. The term is also sometimes used to refer to similar organs in socialist and Islamist parties, such as the UK Labour Party's NEC or the Poli ...
(called the Presidium between 1952 and 1966), Secretariat and the general secretary
Secretary is a title often used in organizations to indicate a person having a certain amount of authority, Power (social and political), power, or importance in the organization. Secretaries announce important events and communicate to the org ...
(First Secretary from 1953 to 1966), the ''de facto'' highest office in the Soviet Union. Depending on the degree of power consolidation, it was either the Politburo as a collective body or the General Secretary, who always was one of the Politburo members, that effectively led the party and the country (except for the period of the highly personalized authority of Stalin, exercised directly through his position in the Council of Ministers rather than the Politburo after 1941). They were not controlled by the general party membership, as the key principle of the party organization was democratic centralism
Democratic centralism is the organisational principle of most communist parties, in which decisions are made by a process of vigorous and open debate amongst party membership, and are subsequently binding upon all members of the party. The co ...
, demanding strict subordination to higher bodies, and elections went uncontested, endorsing the candidates proposed from above.
The Communist Party maintained its dominance over the state mainly through its control over the system of appointments. All senior government officials and most deputies of the Supreme Soviet were members of the CPSU. Of the party heads themselves, Stalin (1941–1953) and Khrushchev (1958–1964) were Premiers. Upon the forced retirement of Khrushchev, the party leader was prohibited from this kind of double membership, but the later General Secretaries for at least some part of their tenure occupied the mostly ceremonial position of Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet, the nominal head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
. The institutions at lower levels were overseen and at times supplanted by primary party organizations.
However, in practice the degree of control the party was able to exercise over the state bureaucracy, particularly after the death of Stalin, was far from total, with the bureaucracy pursuing different interests that were at times in conflict with the party, nor was the party itself monolithic from top to bottom, although factions were officially banned.
Highest organ of state authority
 The Supreme Soviet (successor of the
The Supreme Soviet (successor of the Congress of Soviets
The Congress of Soviets was the supreme governing body of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and several other Soviet republics and national autonomies in the Soviet Russia and the Soviet Union from 1917 to 1936 and a somewhat simil ...
) was nominally the highest organ of state authority for most of the Soviet history, at first acting as a rubber stamp institution, approving and implementing all decisions made by the party. However, its powers and functions were extended in the late 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, including the creation of new state commissions and committees. It gained additional powers relating to the approval of the Five-Year Plans and the government budget
A government budget is a projection of the government's revenues and expenditure for a particular period, often referred to as a financial or fiscal year, which may or may not correspond with the calendar year. Government revenues mostly incl ...
. The Supreme Soviet elected a Presidium (successor of the Central Executive Committee) to wield its power between plenary sessions, ordinarily held twice a year, and appointed the Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
, the Procurator General and the Council of Ministers
Council of Ministers is a traditional name given to the supreme Executive (government), executive organ in some governments. It is usually equivalent to the term Cabinet (government), cabinet. The term Council of State is a similar name that also m ...
(known before 1946 as the Council of People's Commissars
The Council of People's Commissars (CPC) (), commonly known as the ''Sovnarkom'' (), were the highest executive (government), executive authorities of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), the Soviet Union (USSR), and the Sovi ...
), headed by the Chairman
The chair, also chairman, chairwoman, or chairperson, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the gro ...
(Premier) and managing an enormous bureaucracy responsible for the administration of the economy and society. State and party structures of the constituent republics largely emulated the structure of the central institutions, although the Russian SFSR, unlike the other constituent republics, for most of its history had no republican branch of the CPSU, being ruled directly by the union-wide party until 1990. Local authorities were organized likewise into party committees, local Soviets and executive committees. While the state system was nominally federal, the party was unitary.
The state security police (the KGB
The Committee for State Security (, ), abbreviated as KGB (, ; ) was the main security agency of the Soviet Union from 1954 to 1991. It was the direct successor of preceding Soviet secret police agencies including the Cheka, Joint State Polit ...
and its predecessor agencies) played an important role in Soviet politics. It was instrumental in the Red Terror
The Red Terror () was a campaign of political repression and Mass killing, executions in Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Russia which was carried out by the Bolsheviks, chiefly through the Cheka, the Bolshevik secret police ...
and Great Purge
The Great Purge, or the Great Terror (), also known as the Year of '37 () and the Yezhovshchina ( , ), was a political purge in the Soviet Union that took place from 1936 to 1938. After the Assassination of Sergei Kirov, assassination of ...
, but was brought under strict party control after Stalin's death. Under Yuri Andropov
Yuri Vladimirovich Andropov ( – 9 February 1984) was a Soviet politician who served as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from late 1982 until his death in 1984. He previously served as the List of Chairmen of t ...
, the KGB engaged in the suppression of political dissent and maintained an extensive network of informers, reasserting itself as a political actor to some extent independent of the party-state structure, culminating in the anti-corruption campaign targeting high-ranking party officials in the late 1970s and early 1980s.
Unified power and reform
Theconstitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, which was promulgated in 1924, 1936
Events January–February
* January 20 – The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King Edward VIII, following the death of his father, George V, at Sandringham House.
* January 28 – Death and state funer ...
and 1977
Events January
* January 8 – 1977 Moscow bombings, Three bombs explode in Moscow within 37 minutes, killing seven. The bombings are attributed to an Armenian separatist group.
* January 10 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in eastern Zaire (no ...
, did not limit state power. No separation of powers
The separation of powers principle functionally differentiates several types of state (polity), state power (usually Legislature#Legislation, law-making, adjudication, and Executive (government)#Function, execution) and requires these operat ...
existed in the Soviet Union, as the state system was based on the unified state power of the highest organ of state authority, that is, the All-Union Supreme Soviet which worked under the party's leadership. The system was governed less by statute than by informal conventions, and no settled mechanism of leadership succession existed. Bitter and at times deadly power struggles took place in the Politburo after the deaths of Lenin and Stalin, as well as after Khrushchev's dismissal, itself due to a decision by both the Politburo and the Central Committee. All leaders of the Communist Party before Gorbachev died in office, except Georgy Malenkov and Khrushchev, both dismissed from the party leadership amid internal struggle within the party.
Between 1988 and 1990, facing considerable opposition, Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
enacted reforms shifting power away from the highest bodies of the party and making the Supreme Soviet less dependent on them. The Congress of People's Deputies was established, the majority of whose members were directly elected in competitive elections held in March 1989, the first in Soviet history. The Congress now elected the Supreme Soviet, which became a full-time parliament, and much stronger than before. For the first time since the 1920s, it refused to rubber stamp proposals from the party and Council of Ministers. In 1990, Gorbachev introduced and assumed the position of the President of the Soviet Union
The president of the Soviet Union (), officially the president of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (), abbreviated as president of the USSR (), was the executive head of state of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics from 15 March ...
, concentrated power in his executive office, independent of the party, and subordinated the government, now renamed the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR, to himself.
Tensions grew between the Union-wide authorities under Gorbachev, reformists led in Russia by Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin (1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician and statesman who served as President of Russia from 1991 to 1999. He was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) from 1961 to ...
and controlling the newly elected Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR, and communist hardliners. On 19–21 August 1991, a group of hardliners staged a coup attempt. The coup failed, and the State Council of the Soviet Union became the highest organ of state power 'in the period of transition'. Gorbachev resigned as General Secretary, only remaining President for the final months of the existence of the USSR.
Judicial system
The judiciary was not independent of the other branches of government. The Supreme Court supervised the lower courts ( People's Court) and applied the law as established by the constitution or as interpreted by the Supreme Soviet. The Constitutional Oversight Committee reviewed the constitutionality of laws and acts. The Soviet Union used theinquisitorial system
An inquisitorial system is a legal system in which the court, or a part of the court, is actively involved in investigating the facts of the case. This is distinct from an adversarial system, in which the role of the court is primarily that of an ...
of Roman law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (), to the (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I.
Roman law also den ...
, where the judge, procurator, and defence attorney collaborate to "establish the truth".
Human rights
Human rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
in the Soviet Union were severely limited. The Soviet Union was a totalitarian state from 1927 until 1953 and a one-party state until 1990. Freedom of speech
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The rights, right to freedom of expression has been r ...
was suppressed and dissent was punished. Independent political activities were not tolerated, whether these involved participation in free labour union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
s, private corporation
A corporation or body corporate is an individual or a group of people, such as an association or company, that has been authorized by the State (polity), state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law as ...
s, independent churches or opposition political parties
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
. The freedom of movement
Freedom of movement, mobility rights, or the right to travel is a human rights concept encompassing the right of individuals to travel from place to place within the territory of a country,Jérémiee Gilbert, ''Nomadic Peoples and Human Rights'' ...
within and especially outside the country was limited. The state restricted rights of citizens to private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Capacity (law), legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property, which is owned by a state entity, and from Collective ownership ...
.
Foreign relations



 During his rule, Stalin always made the final policy decisions. Otherwise, Soviet foreign policy was set by the commission on the Foreign Policy of the Central Committee of the
During his rule, Stalin always made the final policy decisions. Otherwise, Soviet foreign policy was set by the commission on the Foreign Policy of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
, or by the party's highest body the Politburo
A politburo () or political bureau is the highest organ of the central committee in communist parties. The term is also sometimes used to refer to similar organs in socialist and Islamist parties, such as the UK Labour Party's NEC or the Poli ...
. Operations were handled by the separate Ministry of Foreign Affairs
In many countries, the ministry of foreign affairs (abbreviated as MFA or MOFA) is the highest government department exclusively or primarily responsible for the state's foreign policy and relations, diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral r ...
. It was known as the People's Commissariat for Foreign Affairs (or Narkomindel), until 1946. The most influential spokesmen were Georgy Chicherin, Maxim Litvinov, Vyacheslav Molotov, Andrey Vyshinsky
Andrey Yanuaryevich Vyshinsky (; ) ( – 22 November 1954) was a Soviet politician, jurist and diplomat.
He is best known as a Procurator General of the Soviet Union, state prosecutor of Joseph Stalin's Moscow Trials and in the Nuremberg trial ...
, and Andrei Gromyko. Intellectuals were based in the Moscow State Institute of International Relations
Moscow State Institute of International Relations (MGIMO) (, also known as MGIMO University) is an higher education, institute of higher education located in Moscow, Russia. The institute is run by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Russia), Russian ...
.
* Comintern (1919–1943), or Communist International
The Communist International, abbreviated as Comintern and also known as the Third International, was a political international which existed from 1919 to 1943 and advocated world communism. Emerging from the collapse of the Second Internationa ...
, was an international communist organization based in the Kremlin that advocated world communism
World communism, also known as global communism or international communism, is a form of communism placing emphasis on an international scope rather than being individual communist states. The long-term goal of world communism is an unlimited ...
. The Comintern intended to 'struggle by all available means, including armed force, for the overthrow of the international bourgeoisie and the creation of an international Soviet republic as a transition stage to the complete abolition of the state'. It was abolished as a conciliatory measure toward Britain and the United States.
* Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, often abbreviated as Comecon ( ) or CMEA, was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc#List of states, Easter ...
, the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (, , , ) was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under Soviet control that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc along with several communist states elsewhere in the world. Moscow was concerned about the Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
, and Comecon was meant to prevent countries in the Soviets' sphere of influence from moving towards that of the Americans and Southeast Asia. Comecon was the Eastern Bloc's reply to the formation in Western Europe of the Organization for European Economic Co-Operation (OEEC),
* The Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
was a collective defence alliance formed in 1955 among the USSR and its satellite state
A satellite state or dependent state is a country that is formally independent but under heavy political, economic, and military influence or control from another country. The term was coined by analogy to planetary objects orbiting a larger ob ...
s in Eastern Europe during the Cold War. The Warsaw Pact was the military complement to the Comecon, the regional economic organization for the socialist state
A socialist state, socialist republic, or socialist country is a sovereign state constitutionally dedicated to the establishment of socialism. This article is about states that refer to themselves as socialist states, and not specifically ...
s of Central and Eastern Europe. The Warsaw Pact was created in reaction to the integration of West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
into NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
. Although nominally a "defensive" alliance, the Pact's primary function was to safeguard the Soviet Union's hegemony over its Eastern European
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountains, and ...
satellites, with the Pact's only direct military actions having been the invasions of its own member states to keep them from breaking away.
* The Cominform (1947–1956), informally the Communist Information Bureau and officially the Information Bureau of the Communist and Workers' Parties, was the first official agency of the international Marxist-Leninist movement since the dissolution of the Comintern in 1943. Its role was to coordinate actions between Marxist-Leninist parties under Soviet direction. Stalin used it to order Western European communist parties to abandon their exclusively parliamentarian line and instead concentrate on politically impeding the operations of the Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
, the U.S. program of rebuilding Europe after the war and developing its economy. It also coordinated international aid to Marxist-Leninist insurgents during the Greek Civil War in 1947–1949. It expelled Yugoslavia in 1948 after Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito ( ; , ), was a Yugoslavia, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and politician who served in various positions of national leadership from 1943 unti ...
insisted on an independent program. Its newspaper, ''For a Lasting Peace, for a People's Democracy!'', promoted Stalin's positions. The Cominform's concentration on Europe meant a deemphasis on world revolution in Soviet foreign policy. By enunciating a uniform ideology, it allowed the constituent parties to focus on personalities rather than issues.
Early policies (1919–1939)
 The Marxist-Leninist leadership of the Soviet Union intensely debated foreign policy issues and changed directions several times. Even after Stalin assumed dictatorial control in the late 1920s, there were debates, and he frequently changed positions.
During the country's early period, it was assumed that Communist revolutions would break out soon in every major industrial country, and it was the Russian responsibility to assist them. The
The Marxist-Leninist leadership of the Soviet Union intensely debated foreign policy issues and changed directions several times. Even after Stalin assumed dictatorial control in the late 1920s, there were debates, and he frequently changed positions.
During the country's early period, it was assumed that Communist revolutions would break out soon in every major industrial country, and it was the Russian responsibility to assist them. The Comintern
The Communist International, abbreviated as Comintern and also known as the Third International, was a political international which existed from 1919 to 1943 and advocated world communism. Emerging from the collapse of the Second Internatio ...
was the weapon of choice. A few revolutions did break out, but they were quickly suppressed (the longest lasting one was in Hungary)—the Hungarian Soviet Republic—lasted only from 21 March 1919 to 1 August 1919. The Russian Bolsheviks were in no position to give any help.
By 1921, Lenin, Trotsky, and Stalin realized that capitalism had stabilized itself in Europe and there would not be any widespread revolutions anytime soon. It became the duty of the Russian Bolsheviks to protect what they had in Russia, and avoid military confrontations that might destroy their bridgehead. Russia was now a pariah state, along with Germany. The two came to terms in 1922 with the Treaty of Rapallo that settled long-standing grievances. At the same time, the two countries secretly set up training programs for the illegal German army and air force operations at hidden camps in the USSR.
Moscow eventually stopped threatening other states, and instead worked to open peaceful relationships in terms of trade, and diplomatic recognition. The United Kingdom dismissed the warnings of Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
and a few others about a continuing Marxist-Leninist threat, and opened trade relations and ''de facto'' diplomatic recognition in 1922. There was hope for a settlement of the pre-war Tsarist debts, but it was repeatedly postponed. Formal recognition came when the new Labour Party came to power in 1924. All the other countries followed suit in opening trade relations. Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialist and business magnate. As the founder of the Ford Motor Company, he is credited as a pioneer in making automob ...
opened large-scale business relations with the Soviets in the late 1920s, hoping that it would lead to long-term peace. Finally, in 1933, the United States officially recognized the USSR, a decision backed by the public opinion and especially by US business interests that expected an opening of a new profitable market.
In the late 1920s and early 1930s, Stalin ordered Marxist-Leninist parties across the world to strongly oppose non-Marxist political parties, labour unions or other organizations on the left, which they labelled social fascists. In the usage of the Soviet Union, and of the Comintern and its affiliated parties in this period, the epithet ''fascist
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural soci ...
'' was used to describe capitalist society in general and virtually any anti-Soviet
Anti-Sovietism or anti-Soviet sentiment are activities that were actually or allegedly aimed against the Soviet Union or government power within the Soviet Union.
Three common uses of the term include the following:
* Anti-Sovietism in inter ...
or anti-Stalinist activity or opinion. Stalin reversed himself in 1934 with the Popular Front program that called on all Marxist parties to join with all anti-Fascist
Anti-fascism is a political movement in opposition to fascist ideologies, groups and individuals. Beginning in European countries in the 1920s, it was at its most significant shortly before and during World War II, where the Axis powers were op ...
political, labour, and organizational forces that were opposed to fascism
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural social hie ...
, especially of the Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
variety.
The rapid growth of power in Nazi Germany encouraged both Paris and Moscow to form a military alliance, and the Franco-Soviet Treaty of Mutual Assistance
The Franco-Soviet Treaty of Mutual Assistance was a bilateral treaty between France and the Soviet Union with the aim of enveloping Nazi Germany in 1935 to reduce the threat from Central Europe. It was pursued by Maxim Litvinov, the Soviet forei ...
was signed in May 1935. A firm believer in collective security, Stalin's foreign minister Maxim Litvinov worked very hard to form a closer relationship with France and Britain.
In 1939, half a year after the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement was reached in Munich on 30 September 1938, by Nazi Germany, the United Kingdom, the French Third Republic, French Republic, and the Kingdom of Italy. The agreement provided for the Occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–194 ...
, the USSR attempted to form an anti-Nazi alliance with France and Britain. Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
proposed a better deal, which would give the USSR control over much of Eastern Europe through the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. In September, Germany invaded Poland, and the USSR also invaded later that month, resulting in the partition of Poland. In response, Britain and France declared war on Germany, marking the beginning of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
World War II (1939–1945)
Up until his death in 1953,Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
controlled all foreign relations of the Soviet Union during the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
. Despite the increasing build-up of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
's war machine and the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was fought between the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the Empire of Japan between 1937 and 1945, following a period of war localized to Manchuria that started in 1931. It is considered part ...
, the Soviet Union did not cooperate with any other nation, choosing to follow its own path. However, after Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along ...
, the Soviet Union's priorities changed. Despite previous conflict with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Vyacheslav Molotov dropped his post war border demands.
Cold War (1945–1991)
TheCold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
was a period of geopolitical
Geopolitics () is the study of the effects of Earth's geography on politics and international relations. Geopolitics usually refers to countries and relations between them, it may also focus on two other kinds of states: ''de facto'' independen ...
tension between the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
, which began following World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in 1945. The term ''cold war
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
'' is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy war
In political science, a proxy war is an armed conflict where at least one of the belligerents is directed or supported by an external third-party power. In the term ''proxy war'', a belligerent with external support is the ''proxy''; both bel ...
s. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or sovereign state, states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an a ...
and victory
The term victory (from ) originally applied to warfare, and denotes success achieved in personal duel, combat, after military operations in general or, by extension, in any competition. Success in a military campaign constitutes a strategic vi ...
against Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare
Psychological warfare (PSYWAR), or the basic aspects of modern psychological operations (PsyOp), has been known by many other names or terms, including Military Information Support Operations ( MISO), Psy Ops, political warfare, "Hearts and Mi ...
, propaganda campaigns, espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering, as a subfield of the intelligence field, is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence). A person who commits espionage on a mission-specific contract is called an ...
, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events
Sport is a physical activity or game, often Competition, competitive and organization, organized, that maintains or improves physical ability and skills. Sport may provide enjoyment to participants and entertainment to spectators. The numbe ...
and technological competitions such as the Space Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
.
Administrative divisions
Constitutionally, the USSR was a federation of constituent Union Republics, which were either unitary states, such asUkraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
or Byelorussia (SSRs), or federations, such as Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
or Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
(SFSRs), all four being the founding republics who signed the Treaty on the Creation of the USSR
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, conventio ...
in December 1922. In 1924, during the national delimitation in Central Asia, Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
were formed from parts of Russia's Turkestan ASSR and two Soviet dependencies, the Khorezm and Bukharan PSPs. In 1929, Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
was split off from the Uzbekistan SSR. With the constitution of 1936, the Transcaucasian SFSR was dissolved, resulting in its constituent republics of Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
being elevated to Union Republics, while Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
and Kirghizia were split off from the Russian SFSR, resulting in the same status. In August 1940, Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
was formed from parts of Ukraine and Soviet-occupied Bessarabia, and Ukrainian SSR. Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
were also annexed by the Soviet Union and turned into SSRs, which was not recognized by most of the international community and was considered an illegal occupation. After the Soviet invasion of Finland, the Karelo-Finnish SSR
The Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic (Karelo-Finnish SSR), also called Soviet Karelia or simply known as Karelia, was a republic of the Soviet Union. It existed from 31 March 1940 until it was made part of the Russian SFSR on 16 July 1956 ...
was formed on annexed territory as a Union Republic in March 1940 and then incorporated into Russia as the Karelian ASSR in 1956. Between July 1956 and September 1991, there were 15 union republics (see map below).
While nominally a union of equals, in practice the Soviet Union was dominated by Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
. The domination was so absolute that for most of its existence, the country was commonly (but incorrectly) referred to as 'Russia'. While the Russian SFSR was technically only one republic within the larger union, it was by far the largest (both in terms of population and area), most powerful, and most highly developed. The Russian SFSR was also the industrial center of the Soviet Union. Historian Matthew White wrote that it was an open secret that the country's federal structure was 'window dressing' for Russian dominance. For that reason, the people of the USSR were usually called 'Russians', not 'Soviets', since 'everyone knew who really ran the show'.
Military
 Under the Military Law of September 1925, the
Under the Military Law of September 1925, the Soviet Armed Forces
The Armed Forces of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, also known as the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union, the Red Army (1918–1946) and the Soviet Army (1946–1991), were the armed forces of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republi ...
consisted of the Land Forces, the Air Force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
, the Navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
, Joint State Political Directorate
The Joint State Political Directorate ( rus, Объединённое государственное политическое управление, p=ɐbjɪdʲɪˈnʲɵn(ː)əjə ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)əjə pəlʲɪˈtʲitɕɪskəjə ʊprɐˈv ...
(OGPU) and the Internal Troops. The OGPU later became independent and in 1934 joined the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (, ), abbreviated as NKVD (; ), was the interior ministry and secret police of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) se ...
secret police, and so its internal troops were under the joint leadership of the defense and internal commissariats. After World War II, Strategic Missile Forces (1959), Air Defense Forces (1948) and National Civil Defense Forces (1970) were formed, which ranked first, third, and sixth in the official Soviet system of importance (ground forces were second, Air Force fourth, and Navy fifth).
The army had the greatest political influence. In 1989, there served two million soldiers divided between 150 motorized and 52 armored divisions. Until the early 1960s, the Soviet navy was a rather small military branch, but after the Caribbean crisis, under the leadership of Sergei Gorshkov, it expanded significantly. It became known for battlecruisers and submarines. In 1989, there served 500 000 men. The Soviet Air Force focused on a fleet of strategic bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range Penetrator (aircraft), penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unl ...
s and during war situation was to eradicate enemy infrastructure and nuclear capacity. The air force also had a number of fighters and tactical bombers to support the army in the war. Strategic missile forces had more than 1,400 intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conven ...
s (ICBMs), deployed between 28 bases and 300 command centers.
In the post-war period, the Soviet Army was directly involved in several military operations abroad. These included the suppression of the uprising in East Germany (1953), Hungarian revolution (1956) and the invasion of Czechoslovakia (1968). The Soviet Union also participated in the war in Afghanistan between 1979 and 1989.
In the Soviet Union, general conscription
Conscription, also known as the draft in the United States and Israel, is the practice in which the compulsory enlistment in a national service, mainly a military service, is enforced by law. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it conti ...
applied, meaning all able-bodied males aged 18 and older were drafted in the armed forces.
Economy
 The Soviet Union adopted a
The Soviet Union adopted a command economy
A planned economy is a type of economic system where investment, production and the allocation of capital goods takes place according to economy-wide economic plans and production plans. A planned economy may use centralized, decentralized, ...
, whereby production and distribution of goods were centralized and directed by the government. For the overwhelming majority of its existence, the USSR did not use GDP or GNP to measure its economy, instead relying on the Material Product System. The first Bolshevik experience with a command economy was the policy of war communism, which involved the nationalization of industry, centralized distribution of output, coercive or forced requisition of agricultural production, and attempts to eliminate money circulation, private enterprises and free trade. The barrier troops were also used to enforce Bolshevik control over food supplies in areas controlled by the Red Army, a role which soon earned them the hatred of the Russian civilian population. After the severe economic collapse, Lenin replaced war communism by the New Economic Policy (NEP) in 1921, legalizing free trade and private ownership of small businesses. The economy steadily recovered as a result.
After a long debate among the members of the Politburo about the course of economic development, by 1928–1929, upon gaining control of the country, Stalin abandoned the NEP and pushed for full central planning, starting Collectivization in the Soviet Union, forced collectivization of agriculture and enacting draconian labour legislation. Resources were mobilized for History of the Soviet Union (1927–53)#Industrialization in practice, rapid industrialization, which significantly expanded Soviet capacity in heavy industry and capital goods during the 1930s. The primary motivation for industrialization was preparation for war, mostly due to distrust of the outside capitalist world. As a result, the USSR was transformed from a largely agrarian economy into a great industrial power, leading the way for its emergence as a superpower after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The war caused extensive devastation of the Soviet economy and infrastructure, which required massive reconstruction.
Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, often abbreviated as Comecon ( ) or CMEA, was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc#List of states, Easter ...
, only a tiny share of domestic products was traded internationally. After the creation of the Eastern Bloc, external trade rose rapidly. However, the influence of the world economy on the USSR was limited by fixed domestic prices and a state monopoly on Foreign trade of the Soviet Union, foreign trade. Grain and sophisticated consumer manufactures became major import articles from around the 1960s. During the arms race of the Cold War, the Soviet economy was burdened by military expenditures, heavily lobbied for by a powerful bureaucracy dependent on the arms industry. At the same time, the USSR became the largest arms exporter to the Third World. A portion of Soviet resources during the Cold War were International relations within the Comecon, allocated in aid to the Soviet-aligned states. The Soviet Union's military budget in the 1970s was gigantic, forming 40–60% of the entire federal budget and accounting to 15% of the USSR's GDP (13% in the 1980s).
 From the 1930s until its dissolution in late 1991, the way the Soviet economy operated remained essentially unchanged. The economy was formally directed by economic planning, central planning, carried out by Gosplan and organized in Five-year plans for the national economy of the Soviet Union, five-year plans. However, in practice, the plans were highly aggregated and provisional, subject to ''ad hoc'' intervention by superiors. All critical economic decisions were taken by the political leadership. Allocated resources and plan targets were usually denominated in Soviet ruble, rubles rather than in physical goods. Credit was discouraged, but widespread. The final allocation of output was achieved through relatively decentralized, unplanned contracting. Although in theory prices were legally set from above, in practice they were often negotiated, and informal horizontal links (e.g. between producer factories) were widespread.
A number of basic Service (economics), services were state-funded, such as education in the Soviet Union, education and health care. In the manufacturing sector, heavy industry and defence were prioritized over Consumer goods in the Soviet Union, consumer goods. Consumer goods, particularly outside large cities, were often scarce, of poor quality and limited variety. Under the command economy, consumers had almost no influence on production, and the changing demands of a population with growing incomes could not be satisfied by supplies at rigidly fixed prices.Hanson, Philip. ''The Rise and Fall of the Soviet Economy: An Economic History of the USSR from 1945''. London: Longman, 2003. A massive unplanned second economy grew up at low levels alongside the planned one, providing some of the goods and services that the planners could not. The legalization of some elements of the decentralized economy was attempted with the 1965 Soviet economic reform, reform of 1965.
From the 1930s until its dissolution in late 1991, the way the Soviet economy operated remained essentially unchanged. The economy was formally directed by economic planning, central planning, carried out by Gosplan and organized in Five-year plans for the national economy of the Soviet Union, five-year plans. However, in practice, the plans were highly aggregated and provisional, subject to ''ad hoc'' intervention by superiors. All critical economic decisions were taken by the political leadership. Allocated resources and plan targets were usually denominated in Soviet ruble, rubles rather than in physical goods. Credit was discouraged, but widespread. The final allocation of output was achieved through relatively decentralized, unplanned contracting. Although in theory prices were legally set from above, in practice they were often negotiated, and informal horizontal links (e.g. between producer factories) were widespread.
A number of basic Service (economics), services were state-funded, such as education in the Soviet Union, education and health care. In the manufacturing sector, heavy industry and defence were prioritized over Consumer goods in the Soviet Union, consumer goods. Consumer goods, particularly outside large cities, were often scarce, of poor quality and limited variety. Under the command economy, consumers had almost no influence on production, and the changing demands of a population with growing incomes could not be satisfied by supplies at rigidly fixed prices.Hanson, Philip. ''The Rise and Fall of the Soviet Economy: An Economic History of the USSR from 1945''. London: Longman, 2003. A massive unplanned second economy grew up at low levels alongside the planned one, providing some of the goods and services that the planners could not. The legalization of some elements of the decentralized economy was attempted with the 1965 Soviet economic reform, reform of 1965.
 Although statistics of the Soviet economy are notoriously unreliable and its economic growth difficult to estimate precisely, by most accounts, the economy continued to expand until the mid-1980s. During the 1950s and 1960s, it had comparatively high growth and was catching up to the West. However, after 1970, the growth, while still positive, Era of Stagnation, steadily declined much more quickly and consistently than in other countries, despite a rapid increase in the capital stock (the rate of capital increase was only surpassed by Japan).
Overall, the growth rate of per capita income in the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1989 was slightly above the world average (based on 102 countries). A 1986 study published in the ''American Journal of Public Health'' claimed that, citing World Bank data, the Soviet model provided a better quality of life and Human development (economics), human development than market economies at the same level of economic development in most cases. According to Stanley Fischer and William Easterly, growth could have been faster. By their calculation, per capita income in 1989 should have been twice higher than it was, considering the amount of investment, education and population. The authors attribute this poor performance to the low productivity of capital. Steven Rosefielde states that the standard of living declined due to Stalin's despotism. While there was a brief improvement after his death, it lapsed into stagnation.
In 1987,
Although statistics of the Soviet economy are notoriously unreliable and its economic growth difficult to estimate precisely, by most accounts, the economy continued to expand until the mid-1980s. During the 1950s and 1960s, it had comparatively high growth and was catching up to the West. However, after 1970, the growth, while still positive, Era of Stagnation, steadily declined much more quickly and consistently than in other countries, despite a rapid increase in the capital stock (the rate of capital increase was only surpassed by Japan).
Overall, the growth rate of per capita income in the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1989 was slightly above the world average (based on 102 countries). A 1986 study published in the ''American Journal of Public Health'' claimed that, citing World Bank data, the Soviet model provided a better quality of life and Human development (economics), human development than market economies at the same level of economic development in most cases. According to Stanley Fischer and William Easterly, growth could have been faster. By their calculation, per capita income in 1989 should have been twice higher than it was, considering the amount of investment, education and population. The authors attribute this poor performance to the low productivity of capital. Steven Rosefielde states that the standard of living declined due to Stalin's despotism. While there was a brief improvement after his death, it lapsed into stagnation.
In 1987, Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
attempted to reform and revitalize the economy with his program of ''perestroika
''Perestroika'' ( ; rus, перестройка, r=perestrojka, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg, links=no) was a political reform movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s, widely associ ...
''. His policies relaxed state control over enterprises but did not replace it by market incentives, resulting in a sharp decline in output. The economy, already suffering from 1980s oil glut, reduced petroleum export revenues, started to collapse. Prices were still fixed, and the property was still largely state-owned until after the country's dissolution. For most of the period after World War II until its collapse, Soviet GDP (Purchasing power parity, PPP) was List of regions by past GDP (PPP), the second-largest in the world, and third during the second half of the 1980s, although on a List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, per-capita basis, it was behind that of First World countries. Compared to countries with similar per-capita GDP in 1928, the Soviet Union experienced significant growth.
In 1990, the country had a Human Development Index of 0.920, placing it in the 'high' category of human development. It was the third-highest in the Eastern Bloc, behind Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
and East Germany, and the 25th in the world of 130 countries.
Energy
 The need for fuel declined in the Soviet Union from the 1970s to the 1980s, both per ruble of gross social product and per ruble of industrial product. At the start, this decline grew very rapidly but gradually slowed down between 1970 and 1975. From 1975 and 1980, it grew even slower, only 2.6%. David Wilson, a historian, believed that the gas industry would account for 40% of Soviet fuel production by the end of the century. His theory did not come to fruition because of the USSR's collapse. The USSR, in theory, would have continued to have an economic growth rate of 2–2.5% during the 1990s because of Soviet energy fields. However, the energy sector faced many difficulties, among them the country's high military expenditure and hostile relations with the First World.
In 1991, the Soviet Union had a pipeline network of for crude oil and another for natural gas. Petroleum and petroleum-based products, natural gas, metals, wood, agricultural products, and a variety of manufactured goods, primarily machinery, arms and military equipment, were exported. In the 1970s and 1980s, the USSR heavily relied on fossil fuel exports to earn hard currency. At its peak in 1988, it was the largest producer and second-largest exporter of crude oil, surpassed only by Saudi Arabia.
The need for fuel declined in the Soviet Union from the 1970s to the 1980s, both per ruble of gross social product and per ruble of industrial product. At the start, this decline grew very rapidly but gradually slowed down between 1970 and 1975. From 1975 and 1980, it grew even slower, only 2.6%. David Wilson, a historian, believed that the gas industry would account for 40% of Soviet fuel production by the end of the century. His theory did not come to fruition because of the USSR's collapse. The USSR, in theory, would have continued to have an economic growth rate of 2–2.5% during the 1990s because of Soviet energy fields. However, the energy sector faced many difficulties, among them the country's high military expenditure and hostile relations with the First World.
In 1991, the Soviet Union had a pipeline network of for crude oil and another for natural gas. Petroleum and petroleum-based products, natural gas, metals, wood, agricultural products, and a variety of manufactured goods, primarily machinery, arms and military equipment, were exported. In the 1970s and 1980s, the USSR heavily relied on fossil fuel exports to earn hard currency. At its peak in 1988, it was the largest producer and second-largest exporter of crude oil, surpassed only by Saudi Arabia.
Science and technology
 The Soviet Union placed great emphasis on Science and technology in the Soviet Union, science and technology. Lenin believed the USSR would never overtake the developed world if it remained as technologically backward as it was upon its founding. Soviet authorities proved their commitment to Lenin's belief by developing massive networks and research and development organizations. In the early 1960s, 40% of chemistry PhDs in the Soviet Union were attained by women, compared with only 5% in the United States. By 1989, Soviet scientists were among the world's best-trained specialists in several areas, such as energy physics, selected areas of medicine, mathematics, welding, space technology, and military technologies. However, due to rigid state planning and Nomenklatura, bureaucracy, the Soviets remained far behind the First World in chemistry, biology, and computer science. Under Stalin, the Soviet government persecuted geneticists in favour of Lysenkoism, a pseudoscience rejected by the scientific community in the Soviet Union and abroad but supported by Stalin's inner circles. Implemented in the USSR and China, it resulted in reduced crop yields and is widely believed to have contributed to the Great Chinese Famine. In the 1980s, the Soviet Union had more scientists and engineers relative to the world's population than any other major country, owing to strong levels of state support. Some of its most remarkable technological achievements, such as launching the Sputnik 1, world's first space satellite, were achieved through military research.
Under the Reagan administration, Project Socrates determined that the Soviet Union addressed the acquisition of science and technology in a manner radically different to the United States. The US prioritized indigenous research and development in both the public and private sectors. In contrast, the USSR placed greater emphasis on acquiring foreign technology, which it did through both Industrial espionage, covert and overt means. However, centralized state planning kept Soviet technological development greatly inflexible. This was exploited by the US to undermine the strength of the Soviet Union and thus foster its reform.
The Soviet Union placed great emphasis on Science and technology in the Soviet Union, science and technology. Lenin believed the USSR would never overtake the developed world if it remained as technologically backward as it was upon its founding. Soviet authorities proved their commitment to Lenin's belief by developing massive networks and research and development organizations. In the early 1960s, 40% of chemistry PhDs in the Soviet Union were attained by women, compared with only 5% in the United States. By 1989, Soviet scientists were among the world's best-trained specialists in several areas, such as energy physics, selected areas of medicine, mathematics, welding, space technology, and military technologies. However, due to rigid state planning and Nomenklatura, bureaucracy, the Soviets remained far behind the First World in chemistry, biology, and computer science. Under Stalin, the Soviet government persecuted geneticists in favour of Lysenkoism, a pseudoscience rejected by the scientific community in the Soviet Union and abroad but supported by Stalin's inner circles. Implemented in the USSR and China, it resulted in reduced crop yields and is widely believed to have contributed to the Great Chinese Famine. In the 1980s, the Soviet Union had more scientists and engineers relative to the world's population than any other major country, owing to strong levels of state support. Some of its most remarkable technological achievements, such as launching the Sputnik 1, world's first space satellite, were achieved through military research.
Under the Reagan administration, Project Socrates determined that the Soviet Union addressed the acquisition of science and technology in a manner radically different to the United States. The US prioritized indigenous research and development in both the public and private sectors. In contrast, the USSR placed greater emphasis on acquiring foreign technology, which it did through both Industrial espionage, covert and overt means. However, centralized state planning kept Soviet technological development greatly inflexible. This was exploited by the US to undermine the strength of the Soviet Union and thus foster its reform.
Space program
At the end of the 1950s, the USSR constructed the first satellite—Sputnik 1, which marked the beginning of theSpace Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
—a competition to achieve superior spaceflight capability with the United States. This was followed by other successful satellites, most notably Sputnik 5, where test dogs were sent to space. On 12 April 1961, the USSR launched Vostok 1, which carried Yuri Gagarin, making him the first human to ever be launched into space and complete a space journey. The first plans for spaceplane, space shuttles and orbital stations were drawn up in Soviet design offices, but personal disputes between designers and management prevented their development.
In terms of the Luna program, the USSR only had automated spacecraft launches with no crewed spacecraft, passing on the 'Moon' part of Space Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
, which was Apollo 11, won by the Americans. The Soviet public's reaction to the American moon-landing was mixed. The Soviet government limited the release of information about it, which affected the reaction. A portion of the populace did not give it attention, and another portion was angered.
In the 1970s, specific proposals for the design of a space shuttle emerged, but shortcomings, especially in the electronics industry (rapid overheating of electronics), postponed it till the end of the 1980s. The first shuttle, the Buran (spacecraft), Buran, flew in 1988, but without a human crew. Another, ''Ptichka'', endured prolonged construction and was canceled in 1991. For their launch into space, there is today an unused superpower rocket, Energia (rocket), Energia, which is the most powerful in the world.
In the late 1980s, the Soviet Union built the ''Mir'' orbital station. It was built on the construction of Salyut programme, ''Salyut'' stations and its only role was civilian-grade research tasks. Mir was the only orbital station in operation from 1986 to 1998. Gradually, other modules were added to it, including American modules. However, the station deteriorated rapidly after a fire on board, so in 2001 it was decided to bring it into the atmosphere where it burned down.
Transport
 Transport was a vital component of the country's economy. The First five-year plan (Soviet Union), economic centralization of the late 1920s and 1930s led to the development of infrastructure on a massive scale, most notably the establishment of Aeroflot, an aviation enterprise. The country had a wide variety of modes of transport by land, water and air. However, due to inadequate maintenance, much of the road, water and Soviet civil aviation transport were outdated and technologically backward compared to the First World.
Soviet rail transport was the largest and most intensively used in the world; it was also better developed than most of its Western counterparts. By the late 1970s and early 1980s, Soviet economists were calling for the construction of more roads to alleviate some of the burdens from the railways and to improve the Soviet
Transport was a vital component of the country's economy. The First five-year plan (Soviet Union), economic centralization of the late 1920s and 1930s led to the development of infrastructure on a massive scale, most notably the establishment of Aeroflot, an aviation enterprise. The country had a wide variety of modes of transport by land, water and air. However, due to inadequate maintenance, much of the road, water and Soviet civil aviation transport were outdated and technologically backward compared to the First World.
Soviet rail transport was the largest and most intensively used in the world; it was also better developed than most of its Western counterparts. By the late 1970s and early 1980s, Soviet economists were calling for the construction of more roads to alleviate some of the burdens from the railways and to improve the Soviet government budget
A government budget is a projection of the government's revenues and expenditure for a particular period, often referred to as a financial or fiscal year, which may or may not correspond with the calendar year. Government revenues mostly incl ...
. The street network and Automotive industry in the Soviet Union, automotive industry remained underdeveloped, and dirt roads were common outside major cities. Soviet maintenance projects proved unable to take care of even the few roads the country had. By the early-to-mid-1980s, the Soviet authorities tried to solve the road problem by ordering the construction of new ones. Meanwhile, the automobile industry was growing at a faster rate than road construction. The underdeveloped road network led to a growing demand for public transport.
Despite improvements, several aspects of the transport sector were still riddled with problems due to outdated infrastructure, lack of investment, corruption and bad decision-making. Soviet authorities were unable to meet the growing demand for transport infrastructure and services.
The Soviet merchant navy was one of the largest in the world.
Demographics
Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
(including the Russian famine of 1921–1922, famine of 1921–1922 that was triggered by Lenin's war communism policies) amounted to a combined total of 18 million, some 10 million in the 1930s, and more than 20 million in 1941–1945. The postwar Population of the Soviet Union, Soviet population was 45 to 50 million smaller than it would have been if pre-war demographic growth had continued. According to Catherine Merridale, '...reasonable estimate would place the total number of excess deaths for the whole period somewhere around 60 million.'
The birth rate of the USSR decreased from 44.0 per thousand in 1926 to 18.0 in 1974, mainly due to increasing urbanization and the rising average age of marriages. The mortality rate demonstrated a gradual decrease as well—from 23.7 per thousand in 1926 to 8.7 in 1974. In general, the birth rates of the southern republics in Transcaucasia and Central Asia were considerably higher than those in the northern parts of the Soviet Union, and in some cases even increased in the post–World War II period, a phenomenon partly attributed to slower rates of urbanization and traditionally earlier marriages in the southern republics. Soviet Europe moved towards sub-replacement fertility, while Soviet Central Asia continued to exhibit population growth well above replacement-level fertility.
The late 1960s and the 1970s witnessed a reversal of the declining trajectory of the rate of mortality in the USSR, and was especially notable among men of working age, but was also prevalent in Russia and other predominantly Slavic areas of the country. An analysis of the official data from the late 1980s showed that after worsening in the late-1970s and the early 1980s, adult mortality began to improve again. The infant mortality rate increased from 24.7 in 1970 to 27.9 in 1974. Some researchers regarded the rise as mostly real, a consequence of worsening health conditions and services. The rises in both adult and infant mortality were not explained or defended by Soviet officials, and the Soviet government stopped publishing all mortality statistics for ten years. Soviet demographers and health specialists remained silent about the mortality increases until the late-1980s, when the publication of mortality data resumed, and researchers could delve into the real causes.
Urbanism
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
and Leningrad (both in Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
), with the third far place taken by Kiev (Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
). At its inception, the Top 5 was completed by Kharkov (Ukrainian SSR) and Baku (Azerbaijan SSR), but, by the end of the century, Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), which had assumed the position of capital of Soviet Central Asia, had risen to fourth place. Another city worth mentioning is Minsk (Byelorussian SSR), which saw rapid growth during the 20th century, rising from the 32nd most populous in the union to the 7th.
Women and fertility
 Under Lenin, the state made explicit commitments to promote the equality of men and women. Many early Russian feminists and ordinary Russian working women actively participated in the Revolution, and many more were affected by the events of that period and the new policies. Beginning in October 1918, Lenin's government liberalized divorce and abortion laws, decriminalized homosexuality (re-criminalized in 1932), permitted cohabitation, and ushered in a host of reforms. However, without birth control, the new system produced many broken marriages, as well as countless out-of-wedlock children. The epidemic of divorces and extramarital affairs created social hardships when Soviet leaders wanted people to concentrate their efforts on growing the economy. Giving women control over their fertility also led to a precipitous decline in the birth rate, perceived as a threat to their country's military power. By 1936, Stalin reversed most of the liberal laws, ushering in a Natalism, pronatalist era that lasted for decades.
By 1917, Russia became the first great power to grant women the right to vote. After heavy casualties in World Wars I and II, women outnumbered men in Russia by a 4:3 ratio; this contributed to the larger role women played in Russian society compared to other great powers at the time.
Under Lenin, the state made explicit commitments to promote the equality of men and women. Many early Russian feminists and ordinary Russian working women actively participated in the Revolution, and many more were affected by the events of that period and the new policies. Beginning in October 1918, Lenin's government liberalized divorce and abortion laws, decriminalized homosexuality (re-criminalized in 1932), permitted cohabitation, and ushered in a host of reforms. However, without birth control, the new system produced many broken marriages, as well as countless out-of-wedlock children. The epidemic of divorces and extramarital affairs created social hardships when Soviet leaders wanted people to concentrate their efforts on growing the economy. Giving women control over their fertility also led to a precipitous decline in the birth rate, perceived as a threat to their country's military power. By 1936, Stalin reversed most of the liberal laws, ushering in a Natalism, pronatalist era that lasted for decades.
By 1917, Russia became the first great power to grant women the right to vote. After heavy casualties in World Wars I and II, women outnumbered men in Russia by a 4:3 ratio; this contributed to the larger role women played in Russian society compared to other great powers at the time.
LGBT rights
The Soviet Union repressed homosexuality. Even during the period when homosexuality was officially legal after the abolition of the Tsarist penal code criminalising it, Soviet courts attempted to repress non-traditional forms of sexuality, which were widely viewed by Russian revolutionaries as a form of capitalist decadence despite more liberal views on homosexuality from Soviet academic sexologists. After Stalin's consolidation of power, homosexuality became officially recriminalised in 1934 and remained a criminal offence throughout the remainder of the Soviet Union's existence.Education
 Anatoly Lunacharsky became the first People's Commissar for Education of Soviet Russia. In the beginning, the Soviet authorities placed great emphasis on the Likbez, elimination of illiteracy. All left-handed children were forced to write with their right hand in the Soviet school system. Literate people were automatically hired as teachers. For a short period, quality was sacrificed for quantity. By 1940, Stalin could announce that illiteracy had been eliminated. Throughout the 1930s, social mobility rose sharply, which has been attributed to reforms in education. In the aftermath of World War II, the country's educational system expanded dramatically, which had a tremendous effect. In the 1960s, nearly all children had access to education, the only exception being those living in remote areas.
Anatoly Lunacharsky became the first People's Commissar for Education of Soviet Russia. In the beginning, the Soviet authorities placed great emphasis on the Likbez, elimination of illiteracy. All left-handed children were forced to write with their right hand in the Soviet school system. Literate people were automatically hired as teachers. For a short period, quality was sacrificed for quantity. By 1940, Stalin could announce that illiteracy had been eliminated. Throughout the 1930s, social mobility rose sharply, which has been attributed to reforms in education. In the aftermath of World War II, the country's educational system expanded dramatically, which had a tremendous effect. In the 1960s, nearly all children had access to education, the only exception being those living in remote areas. Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
tried to make education more accessible, making it clear to children that education was closely linked to the needs of society. Education also became important in giving rise to the New Soviet man, New Man. Citizens directly entering the workforce had the constitutional right to a job and to free Vocational-technical school, vocational training.
The Education in the Soviet Union, education system was highly centralized and universally accessible to all citizens, with affirmative action for applicants from nations associated with cultural backwardness. However, as part of a general Antisemitism in the Soviet Union, antisemitic policy, an unofficial Jewish quota was applied in the leading institutions of higher education by subjecting Jewish applicants to harsher entrance examinations. The Brezhnev era also introduced a rule that required all university applicants to present a reference from the local Komsomol party secretary. According to statistics from 1986, the number of higher education students per the population of 10,000 was 181 for the USSR, compared to 517 for the US.
Nationalities and ethnic groups
Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
(50.78%), followed by Ukrainians (15.45%) and Uzbeks (5.84%). Overall, in 1989 the ethnic demography of the country showed that 69.8% was East Slavs, East Slavic, 17.5% was Turkic peoples, Turkic, 1.6% were Armenians, 1.6% were Balts, 1.5% were Uralic peoples, Uralic, 1.5% were Tajiks, Tajik, 1.4% were Georgians, Georgian, 1.2% were Moldovans, Moldovan and 4.1% were of other various ethnic groups.
All citizens of the USSR had their own ethnic affiliation. The ethnicity of a person was chosen at the age of sixteen by the child's parents. If the parents did not agree, the child was automatically assigned the ethnicity of the father. Partly due to Soviet policies, some of the smaller minority ethnic groups were considered part of larger ones, such as the Mingrelians of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, who were classified with the linguistically related Georgians. Some ethnic groups voluntarily assimilated, while others were brought in by force. Russians, Belarusians, and Ukrainians, who were all East Slavic and Orthodox, shared close cultural, ethnic, and religious ties, while other groups did not. With multiple nationalities living in the same territory, Ethnic conflicts in the Soviet Union, ethnic antagonisms developed over the years.
Members of various ethnicities participated in legislative bodies. Organs of power like the Politburo, the Secretariat of the Central Committee etc., were formally ethnically neutral, but in reality, ethnic Russians were overrepresented, although there were also non-Russian leaders in the List of leaders of the Soviet Union, Soviet leadership, such as Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
, Grigory Zinoviev, Nikolai Podgorny or Andrei Gromyko. During the Soviet era, a significant number of ethnic Russians and Ukrainians migrated to other Soviet republics, and many of them settled there. According to the last census in 1989, the Russian 'diaspora' in the Soviet republics had reached 25 million.
Health
 In 1917, before the revolution, health conditions were significantly behind those of developed countries. As Lenin later noted, "Either the lice will defeat socialism, or socialism will defeat the lice". The Soviet health care system was conceived by the People's Commissariat for Health in 1918. Under the Semashko model, health care was to be controlled by the state and would be provided to its citizens free of charge, a revolutionary concept at the time. Article 42 of the 1977 Soviet Constitution gave all citizens the right to health protection and free access to any health institutions in the USSR. Before
In 1917, before the revolution, health conditions were significantly behind those of developed countries. As Lenin later noted, "Either the lice will defeat socialism, or socialism will defeat the lice". The Soviet health care system was conceived by the People's Commissariat for Health in 1918. Under the Semashko model, health care was to be controlled by the state and would be provided to its citizens free of charge, a revolutionary concept at the time. Article 42 of the 1977 Soviet Constitution gave all citizens the right to health protection and free access to any health institutions in the USSR. Before Leonid Brezhnev
Leonid Ilyich Brezhnev (19 December 190610 November 1982) was a Soviet politician who served as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1964 until Death and state funeral of Leonid Brezhnev, his death in 1982 as w ...
became general secretary, the Soviet healthcare system was held in high esteem by many foreign specialists. This changed, however, from Brezhnev's accession and Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
's tenure as leader, during which the health care system was heavily criticized for many basic faults, such as the quality of service and the unevenness in its provision. Ministry of Health (Soviet Union), Minister of Health Yevgeniy Chazov, during the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, while highlighting such successes as having the most doctors and hospitals in the world, recognized the system's areas for improvement and felt that billions of Soviet ruble, rubles were squandered.
After the revolution, life expectancy for all age groups went up. This statistic in itself was seen by some that the Socialist mode of production, socialist system was superior to the capitalist system. These improvements continued into the 1960s when statistics indicated that the life expectancy briefly surpassed that of the United States. Life expectancy started to decline in the 1970s, possibly because of Alcohol consumption in Russia, alcohol abuse. At the same time, infant mortality began to rise. After 1974, the government stopped publishing statistics on the matter. This trend can be partly explained by the number of pregnancies rising drastically in the Asian part of the country where infant mortality was the highest while declining markedly in the more developed European part of the Soviet Union.
Dentistry
Soviet dental technology and dental health were considered notoriously bad. In 1991, the average 35-year-old had 12 to 14 cavities, fillings or missing teeth. Toothpaste was often not available, and toothbrushes did not conform to standards of modern dentistry.Language
Under Lenin, the government gave small language groups their own writing systems. The development of these writing systems was highly successful, even though some flaws were detected. During the later days of the USSR, countries with the same multilingual situation implemented similar policies. A serious problem when creating these writing systems was that the languages differed dialectally greatly from each other. When a language had been given a writing system and appeared in a notable publication, it would attain 'official language' status. There were many minority languages which never received their own writing system; therefore, their speakers were forced to have a second language. There are examples where the government retreated from this policy, most notably under Stalin where education was discontinued in languages that were not widespread. These languages were then assimilated into another language, mostly Russian. During World War II, some minority languages were banned, and their speakers accused of collaborating with the enemy. As the most widely spoken of the Soviet Union's many languages, Russian ''de facto'' functioned as an official language, as the 'language of interethnic communication' (), but only assumed the ''de jure'' status as the official national language in 1990.Religion



 Christianity and Islam had the highest number of adherents among the religious citizens. Eastern Christianity predominated among Christians, with Russia's traditional Russian Orthodox Church being the largest Christian denomination. About 90% of the Soviet Union's Muslims were Sunnis, with Shias being concentrated in the Azerbaijan SSR. Smaller groups included Roman Catholics, Jews, Buddhists, and a variety of Protestant denominations (especially Baptists and Lutherans).
Religious influence had been strong in the Russian Empire. The Russian Orthodox Church enjoyed a privileged status as the church of the monarchy and took part in carrying out official state functions. The immediate period following the establishment of the Soviet state included a struggle against the Orthodox Church, which the revolutionaries considered an ally of the former ruling classes.
In Soviet law, the 'freedom to hold religious services' was constitutionally guaranteed, although the ruling Communist Party regarded religion as incompatible with the Marxist spirit of scientific materialism. In practice, the Soviet system subscribed to a narrow interpretation of this right, and in fact used a range of official measures to discourage religion and curb the activities of religious groups.
The 1918 Council of People's Commissars decree establishing the Russian SFSR as a secular state also decreed that 'the teaching of religion in all [places] where subjects of general instruction are taught, is forbidden. Citizens may teach and may be taught religion privately.' Among further restrictions, those adopted in 1929 included express prohibitions on a range of church activities, including meetings for organized Bible study (Christian), Bible study. Both Christian and non-Christian establishments were shut down by the thousands in the 1920s and 1930s. By 1940, as many as 90% of the churches, synagogues, and mosques that had been operating in 1917 were closed; the majority of them were demolished or re-purposed for state needs with little concern for their historic and cultural value.
More than 85,000 Orthodox priests were shot in 1937 alone. Only a twelfth of the Russian Orthodox Church's priests were left functioning in their parishes by 1941. In the period between 1927 and 1940, the number of Orthodox Churches in Russia fell from 29,584 to less than 500 (1.7%).
The Soviet Union was officially a secular state, but a 'government-sponsored program of forced conversion to Marxist-Leninist atheism, atheism' was conducted under the doctrine of state atheism. The government targeted religions based on state interests, and while most organized religions were never outlawed, religious property was confiscated, believers were harassed, and religion was ridiculed while atheism was propagated in schools. In 1925, the government founded the League of Militant Atheists to intensify the propaganda campaign. Accordingly, although personal expressions of religious faith were not explicitly banned, a strong sense of social stigma was imposed on them by the formal structures and mass media, and it was generally considered unacceptable for members of certain professions (teachers, state bureaucrats, soldiers) to be openly religious. While persecution accelerated following Stalin's rise to power, a revival of Orthodoxy was fostered by the government during World War II and the Soviet authorities sought to control the Russian Orthodox Church rather than liquidate it. During the first five years of Soviet power, the Bolsheviks executed 28 Russian Orthodox bishops and over 1,200 Russian Orthodox priests. Many others were imprisoned or exiled. Believers were harassed and persecuted. Most seminaries were closed, and the publication of most religious material was prohibited. By 1941, only 500 churches remained open out of about 54,000 in existence before World War I.
Convinced that religious anti-Sovietism had become a thing of the past, and with the looming threat of war, the Stalin administration began shifting to a more moderate religion policy in the late 1930s. Soviet religious establishments overwhelmingly rallied to support the war effort during World War II. Amid other accommodations to religious faith after the German invasion, churches were reopened. Radio Moscow began broadcasting a religious hour, and a historic meeting between Stalin and Orthodox Church leader Patriarch Sergius of Moscow was held in 1943. Stalin had the support of the majority of the religious people in the USSR even through the late 1980s. The general tendency of this period was an increase in religious activity among believers of all faiths.
Under
Christianity and Islam had the highest number of adherents among the religious citizens. Eastern Christianity predominated among Christians, with Russia's traditional Russian Orthodox Church being the largest Christian denomination. About 90% of the Soviet Union's Muslims were Sunnis, with Shias being concentrated in the Azerbaijan SSR. Smaller groups included Roman Catholics, Jews, Buddhists, and a variety of Protestant denominations (especially Baptists and Lutherans).
Religious influence had been strong in the Russian Empire. The Russian Orthodox Church enjoyed a privileged status as the church of the monarchy and took part in carrying out official state functions. The immediate period following the establishment of the Soviet state included a struggle against the Orthodox Church, which the revolutionaries considered an ally of the former ruling classes.
In Soviet law, the 'freedom to hold religious services' was constitutionally guaranteed, although the ruling Communist Party regarded religion as incompatible with the Marxist spirit of scientific materialism. In practice, the Soviet system subscribed to a narrow interpretation of this right, and in fact used a range of official measures to discourage religion and curb the activities of religious groups.
The 1918 Council of People's Commissars decree establishing the Russian SFSR as a secular state also decreed that 'the teaching of religion in all [places] where subjects of general instruction are taught, is forbidden. Citizens may teach and may be taught religion privately.' Among further restrictions, those adopted in 1929 included express prohibitions on a range of church activities, including meetings for organized Bible study (Christian), Bible study. Both Christian and non-Christian establishments were shut down by the thousands in the 1920s and 1930s. By 1940, as many as 90% of the churches, synagogues, and mosques that had been operating in 1917 were closed; the majority of them were demolished or re-purposed for state needs with little concern for their historic and cultural value.
More than 85,000 Orthodox priests were shot in 1937 alone. Only a twelfth of the Russian Orthodox Church's priests were left functioning in their parishes by 1941. In the period between 1927 and 1940, the number of Orthodox Churches in Russia fell from 29,584 to less than 500 (1.7%).
The Soviet Union was officially a secular state, but a 'government-sponsored program of forced conversion to Marxist-Leninist atheism, atheism' was conducted under the doctrine of state atheism. The government targeted religions based on state interests, and while most organized religions were never outlawed, religious property was confiscated, believers were harassed, and religion was ridiculed while atheism was propagated in schools. In 1925, the government founded the League of Militant Atheists to intensify the propaganda campaign. Accordingly, although personal expressions of religious faith were not explicitly banned, a strong sense of social stigma was imposed on them by the formal structures and mass media, and it was generally considered unacceptable for members of certain professions (teachers, state bureaucrats, soldiers) to be openly religious. While persecution accelerated following Stalin's rise to power, a revival of Orthodoxy was fostered by the government during World War II and the Soviet authorities sought to control the Russian Orthodox Church rather than liquidate it. During the first five years of Soviet power, the Bolsheviks executed 28 Russian Orthodox bishops and over 1,200 Russian Orthodox priests. Many others were imprisoned or exiled. Believers were harassed and persecuted. Most seminaries were closed, and the publication of most religious material was prohibited. By 1941, only 500 churches remained open out of about 54,000 in existence before World War I.
Convinced that religious anti-Sovietism had become a thing of the past, and with the looming threat of war, the Stalin administration began shifting to a more moderate religion policy in the late 1930s. Soviet religious establishments overwhelmingly rallied to support the war effort during World War II. Amid other accommodations to religious faith after the German invasion, churches were reopened. Radio Moscow began broadcasting a religious hour, and a historic meeting between Stalin and Orthodox Church leader Patriarch Sergius of Moscow was held in 1943. Stalin had the support of the majority of the religious people in the USSR even through the late 1980s. The general tendency of this period was an increase in religious activity among believers of all faiths.
Under Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
, the state leadership clashed with the churches in 1958–1964, a period when atheism was emphasized in the educational curriculum, and numerous state publications promoted atheistic views. During this period, the number of churches fell from 20,000 to 10,000 from 1959 to 1965, and the number of synagogues dropped from 500 to 97. The number of working mosques also declined, falling from 1,500 to 500 within a decade.
Religious institutions remained monitored by the Soviet government, but churches, synagogues, temples, and mosques were all given more leeway in the Brezhnev era. Official relations between the Orthodox Church and the government again warmed to the point that the Brezhnev government twice honored Orthodox Patriarch Alexy I with the Order of the Red Banner of Labour. A poll conducted by Soviet authorities in 1982 recorded 20% of the Soviet population as 'active religious believers.'
Culture
The culture of the Soviet Union evolved through several stages during its existence. During the first decade following the revolution, there was relative freedom and artists experimented with several different styles to find a distinctive Soviet style of art. Lenin wanted art to be accessible to the Russian people. On the other hand, hundreds of intellectuals, writers, and artists were exiled or executed, and their work banned, such as Nikolay Gumilyov who was shot for alleged conspiracy against the Bolsheviks, and Yevgeny Zamyatin. The government encouraged a variety of trends. In art and literature, numerous schools, some traditional and others radically experimental, proliferated. Communist writers Maxim Gorky and Vladimir Mayakovsky were active during this time. As a means of influencing a largely illiterate society, films received encouragement from the state, and much of director Sergei Eisenstein's best work dates from this period. During Stalin's rule, the Soviet culture was characterized by the rise and domination of the government-imposed style of socialist realism, with all other trends being severely repressed, with rare exceptions, such as Mikhail Bulgakov's works. Many writers were imprisoned and killed. Following theKhrushchev Thaw
The Khrushchev Thaw (, or simply ''ottepel'')William Taubman, Khrushchev: The Man and His Era, London: Free Press, 2004 is the period from the mid-1950s to the mid-1960s when Political repression in the Soviet Union, repression and Censorship in ...
, censorship was diminished. During this time, a distinctive period of Soviet culture developed, characterized by conformist public life and an intense focus on personal life. Greater experimentation in art forms was again permissible, resulting in the production of more sophisticated and subtly critical work. The government loosened its emphasis on socialist realism; thus, for instance, many protagonists of the novels of author Yury Trifonov concerned themselves with problems of daily life rather than with building socialism. Underground dissident literature, known as ''samizdat'', developed during this late period. In architecture, the Khrushchev era mostly focused on functional design as opposed to the highly decorated style of Stalin's epoch. In music, in response to the increasing popularity of forms of popular music like jazz in the West, many jazz orchestras were permitted throughout the USSR, notably the Melodiya Ensemble, named after the principle record label in the USSR.
In the second half of the 1980s, Gorbachev's policies of ''perestroika
''Perestroika'' ( ; rus, перестройка, r=perestrojka, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg, links=no) was a political reform movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s, widely associ ...
'' and ''glasnost
''Glasnost'' ( ; , ) is a concept relating to openness and transparency. It has several general and specific meanings, including a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information and the inadmissi ...
'' significantly expanded freedom of expression throughout the country in the media and the press.
Sport
 In summer of 1923 in Moscow was established the Dynamo Sports Club, Proletarian Sports Society "Dynamo" as a sports organization of Soviet secret police Cheka.
On 13 July 1925 the Central Committee of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks) adopted a statement "About the party's tasks in sphere of physical culture". In the statement was determined the role of physical culture in Soviet society and the party's tasks in political leadership of physical culture movement in the country.
The Soviet Olympic Committee formed on 21 April 1951, and the IOC recognized the new body in its List of IOC meetings, 45th session. In the same year, when the Soviet representative Konstantin Andrianov became an IOC member, the USSR officially joined the Olympic Movement. The 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki thus became first Olympic Games for Soviet athletes. The Soviet Union was the biggest rival to the United States at the Summer Olympics, winning Soviet Union at the Olympics#Medals by Summer Games, six of its nine appearances at the games and also topping the medal tally at the Winter Olympics six times. The Soviet Union's Olympics success has been attributed to its large investment in sports to demonstrate its superpower image and political influence on a global stage.
The Soviet Union national ice hockey team won nearly every Ice Hockey World Championships, world championship and Ice hockey at the Olympic Games, Olympic tournament between 1954 and 1991 and never failed to medal in any International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) tournament in which they competed.
Soviet Olympic team was notorious for skirting the edge of amateur rules. All Soviet athletes held some nominal jobs, but were in fact state-sponsored and trained full-time. According to many experts, that gave the Soviet Union a huge advantage over the
In summer of 1923 in Moscow was established the Dynamo Sports Club, Proletarian Sports Society "Dynamo" as a sports organization of Soviet secret police Cheka.
On 13 July 1925 the Central Committee of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks) adopted a statement "About the party's tasks in sphere of physical culture". In the statement was determined the role of physical culture in Soviet society and the party's tasks in political leadership of physical culture movement in the country.
The Soviet Olympic Committee formed on 21 April 1951, and the IOC recognized the new body in its List of IOC meetings, 45th session. In the same year, when the Soviet representative Konstantin Andrianov became an IOC member, the USSR officially joined the Olympic Movement. The 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki thus became first Olympic Games for Soviet athletes. The Soviet Union was the biggest rival to the United States at the Summer Olympics, winning Soviet Union at the Olympics#Medals by Summer Games, six of its nine appearances at the games and also topping the medal tally at the Winter Olympics six times. The Soviet Union's Olympics success has been attributed to its large investment in sports to demonstrate its superpower image and political influence on a global stage.
The Soviet Union national ice hockey team won nearly every Ice Hockey World Championships, world championship and Ice hockey at the Olympic Games, Olympic tournament between 1954 and 1991 and never failed to medal in any International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) tournament in which they competed.
Soviet Olympic team was notorious for skirting the edge of amateur rules. All Soviet athletes held some nominal jobs, but were in fact state-sponsored and trained full-time. According to many experts, that gave the Soviet Union a huge advantage over the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and other Western countries, whose athletes were students or real amateurs. Indeed, the Soviet Union monopolized the top place in the medal standings after 1968, and, until its collapse, placed second only once, in the 1984 Winter Olympics, 1984 Winter games, after another Eastern bloc nation, the GDR. Amateur rules were relaxed only in the late 1980s and were almost completely abolished in the 1990s, after the fall of the USSR.
According to British journalist Andrew Jennings, a KGB
The Committee for State Security (, ), abbreviated as KGB (, ; ) was the main security agency of the Soviet Union from 1954 to 1991. It was the direct successor of preceding Soviet secret police agencies including the Cheka, Joint State Polit ...
colonel stated that the agency's officers had posed as anti-doping authorities from the International Olympic Committee (IOC) to undermine doping tests and that Soviet athletes were "rescued with [these] tremendous efforts". Documents obtained in 2016 revealed the Soviet Union's plans for a statewide doping system in track and field in preparation for the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. Dated prior to the country's decision to boycott the Games, the document detailed the existing steroids operations of the program, along with suggestions for further enhancements.
Legacy
 The legacy of the USSR remains a controversial topic. The socio-economic nature of
The legacy of the USSR remains a controversial topic. The socio-economic nature of communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state in which the totality of the power belongs to a party adhering to some form of Marxism–Leninism, a branch of the communist ideology. Marxism–Leninism was ...
s such as the USSR, especially under Stalin, has also been much debated, varyingly being labelled a form of bureaucratic collectivism, state capitalism, state socialism, or a totally unique mode of production. The USSR implemented a broad range of policies over a long period of time, with a large amount of conflicting policies being implemented by different leaders. Some have a positive view of it whilst others are critical towards the country, calling it a repressive oligarchy. The opinions on the USSR are complex and have changed over time, with different generations having different views on the matter as well as on Soviet policies corresponding to separate time periods during its history.
 Western academicians published various analyses of the post-Soviet states' development, claiming that the dissolution was followed by a severe drop in economic and social conditions in these countries, including a rapid increase in poverty, crime, corruption, unemployment, homelessness, rates of disease, infant mortality and domestic violence, as well as demographic losses, income inequality and the rise of an Russian oligarchs, oligarchical class, along with decreases in calorie intake, life expectancy, adult literacy, and income. Between 1988 and 1989 and 1993–1995, the Gini ratio increased by an average of 9 points for all former Soviet republics. According to Western analysis, the economic shocks that accompanied wholesale privatization were associated with sharp increases in mortality, Russia, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia saw a tripling of unemployment and a 42% increase in male death rates between 1991 and 1994, and in the following decades, only five or six of the post-communist states are on a path to joining the wealthy capitalist West while most are falling behind, some to such an extent that it will take over fifty years to catch up to where they were before the fall of the Soviet Bloc. However, virtually all the former Soviet republics were able to turn their economies around and increase GDP to multiple times what it was under the USSR, though with large wealth disparities, and many post-soviet economies described as oligarchic.
Since the
Western academicians published various analyses of the post-Soviet states' development, claiming that the dissolution was followed by a severe drop in economic and social conditions in these countries, including a rapid increase in poverty, crime, corruption, unemployment, homelessness, rates of disease, infant mortality and domestic violence, as well as demographic losses, income inequality and the rise of an Russian oligarchs, oligarchical class, along with decreases in calorie intake, life expectancy, adult literacy, and income. Between 1988 and 1989 and 1993–1995, the Gini ratio increased by an average of 9 points for all former Soviet republics. According to Western analysis, the economic shocks that accompanied wholesale privatization were associated with sharp increases in mortality, Russia, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia saw a tripling of unemployment and a 42% increase in male death rates between 1991 and 1994, and in the following decades, only five or six of the post-communist states are on a path to joining the wealthy capitalist West while most are falling behind, some to such an extent that it will take over fifty years to catch up to where they were before the fall of the Soviet Bloc. However, virtually all the former Soviet republics were able to turn their economies around and increase GDP to multiple times what it was under the USSR, though with large wealth disparities, and many post-soviet economies described as oligarchic.
Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of ...
, annual polling by the Levada Center has shown that over 50% of Russia's population regretted this event, with the only exception to this being in 2012 when support for the Soviet Union dipped below 50 percent. A 2018 poll showed that 66% of Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
regretted the fall of the Soviet Union, setting a 15-year record, and the majority of these regretting opinions came from people older than 55. In 2020, polls conducted by the Levada Center found that 75% of Russians agreed that the Soviet era was the greatest era in their country's history.
According to the New Russia Barometer (NRB) polls by the Centre for the Study of Public Policy, 50% of Russian respondents reported a positive impression of the Soviet Union in 1991. This increased to about 75% of NRB respondents in 2000, dropping slightly to 71% in 2009. Throughout the 2000s, an average of 32% of NRB respondents supported the restoration of the Soviet Union.
In a 2021 poll, a record 70% of Russians indicated they had a mostly/very favourable view of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
. In Armenia, 12% of respondents said the USSR collapse did good, while 66% said it did harm. In Kyrgyzstan, 16% of respondents said the collapse of the USSR did good, while 61% said it did harm. In a 2018 Sociological group "RATING", Rating Sociological Group poll, 47% of Ukrainians, Ukrainian respondents had a positive opinion of Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev
Leonid Ilyich Brezhnev (19 December 190610 November 1982) was a Soviet politician who served as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1964 until Death and state funeral of Leonid Brezhnev, his death in 1982 as w ...
, who ruled the Soviet Union from 1964 to 1982, while viewing Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
, Stalin, and Gorbachev very negatively. A 2021 poll conducted by the Levada Center found that 49% of Russians prefer the USSR's political system, while 18% prefer the current political system and 16% would prefer a Western democracy. A further 62% of people polled preferred the Soviet system of central planning, while 24% prefer a market-based system. According to the Levada Center's polls, the primary reasons cited for Soviet nostalgia are the advantages of the shared economic union between the Soviet republics, including perceived financial stability. This was referenced by up to 53% of respondents in 2016. At least 43% also lamented the loss of the Soviet Union's global political superpower status. About 31% cited the loss of social trust and capital. The remainder of the respondents cited a mix of reasons ranging from practical travel difficulties to a sense of national displacement.
The 1941–1945 period of World War II is still known in Russia as the 'Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War'. The war became a topic of great importance in cinema, literature, history lessons at school, the mass media, and the arts. As a result of the World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, massive losses suffered by the military and civilians during the conflict, Victory Day (9 May), Victory Day celebrated on 9 May is still one of the most important and emotional dates in Russia. Catherine Wanner asserts that Victory Day commemorations are a vehicle for Soviet nostalgia, as they "kept alive a mythology of Soviet grandeur, of solidarity among the ''Sovietskii narod'', and of a sense of self as citizen of a superpower state".
Russian Victory Day parades are organized annually in most cities, with the central military parade taking place in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
(just as during the Soviet times). Additionally, the recently introduced Immortal Regiment on 9 May sees millions of Russians carry the portraits of their relatives who fought in the war. Russia also Public holidays in Russia, retains other Soviet holidays, such as the Defender of the Fatherland Day (23 February), International Women's Day (8 March), and International Workers' Day#Russia, International Workers' Day.
In the former Soviet republics
In some post-Soviet republics, there is a more negative view of the USSR, although there is no unanimity on the matter. In large part due to the Holodomor, ethnic Ukrainians have a negative view of the Soviet Union. Russian language in Ukraine, Russian-speaking Ukrainians of Ukraine's southern and eastern regions have a more positive view of the USSR. In some countries with internal conflict, there is also nostalgia for the USSR, especially for refugees of the post-Soviet conflicts who have been forced to flee their homes and have been displaced. The many Russian enclaves in the former USSR republics such as Transnistria have in a general a positive remembrance of it.By the political left
The left's view of the USSR is complex. While some leftists regard the USSR as an example of state capitalism or that it was an oligarchical state, other leftists admireVladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
and the Russian Revolution. Council communists generally view the USSR as failing to create class consciousness, turning into a corrupt state in which the elite controlled society.
Trotskyists believe that the ascendancy of the Stalinist bureaucracy ensured a degenerated workers' state, degenerated or deformed workers' state, where the capitalist elite have been replaced by an unaccountable bureaucratic elite and there is no true democracy or workers' control of industry. In particular, American Trotskyist David North (socialist), David North noted that the generation of nomenklatura, bureaucrats that rose to power under Stalin's tutelage presided over the Stagnation of the Soviet Union, stagnation and Dissolution of the Soviet Union, breakdown of the Soviet Union.
Many anti-Stalinist leftists such as anarchists are extremely critical of Soviet authoritarianism and Nabat#Decline, repression. Much of the criticism it receives is centered around List of massacres in the Soviet Union, massacres in the Soviet Union, the centralized hierarchy present in the USSR and mass Political repression in the Soviet Union, political repression as well as violence towards government critics and Soviet dissidents, political dissidents such as other leftists. Critics also point towards its failure to implement any substantial worker cooperatives or implementing worker liberation, as well as corruption and the Soviet authoritarian nature.
Anarchists are also critical of the country, labeling the Soviet system as ''red fascism''. Factors contributing to the anarchist animosity towards the USSR included the Soviet destruction of the Makhnovist movement after an initial alliance, the suppression of the anarchist Kronstadt rebellion, and the defeat of the rival anarchist factions by the Soviet-supported Communist faction during the Spanish Civil War.
Maoists also have a mixed opinion on the USSR, viewing it negatively during the Sino-Soviet Split and denouncing it as revisionist and reverted to capitalism. The Chinese government in 1963 articulated its criticism of the USSR's system and promoted China's ideological line as an alternative.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Japanese Communist Party (JCP) released a press statement titled "We welcome the end of a party which embodied the historical evil of great power chauvinism and hegemonism".
Noam Chomsky called the collapse of the Soviet Union "a small victory for socialism, not only because of the fall of one of the most anti-socialist states in the world, where working people had fewer rights than in the West, but also because it freed the term 'socialism' from the burden of being associated in the propaganda systems of East and West with Soviet tyranny—for the East, in order to benefit from the aura of authentic socialism, for the West, in order to demonize the concept." Some scholars on the left have posited that the end of the Soviet Union and communism as a global force allowed neoliberal capitalism to become a global system, which has resulted in rising economic inequality.
See also
*Succession, continuity and legacy of the Soviet Union *Baltic states under Soviet rule (1944–1991) *Ideocracy *Index of Soviet Union–related articles *Neo-Stalinism *Orphans in the Soviet Union *Russification *Second Cold War *Sovietization *Soviet patriotismNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Impressions of Soviet Russia
by John Dewey
A Country Study: Soviet Union
(PDF) {{Authority control Soviet Union, States and territories established in 1922 States and territories disestablished in 1991 20th century in Russia Early Soviet republics, Communism in Russia Former countries in Europe Former countries in West Asia Former countries in Central Asia Former socialist republics Historical transcontinental empires Countries and territories where Russian is an official language