Southwest Territory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Territory South of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Southwest Territory, was an
/ref> In 1784, North Carolina ceded control of the Overmountain settlements following a hotly contested vote. The cession was rescinded later that year, but not before some of the settlers had organized the State of Franklin, which sought statehood.
 The new territory was essentially governed under the same provisions as the Northwest Ordinance, a 1787 act enacted for the creation of the Northwest Territory north of the Ohio River. The Northwest Ordinance's provision outlawing
The new territory was essentially governed under the same provisions as the Northwest Ordinance, a 1787 act enacted for the creation of the Northwest Territory north of the Ohio River. The Northwest Ordinance's provision outlawing
 Residents of the Southwest Territory initially welcomed federal control, believing the federal government would provide better protection from hostile Indians than North Carolina's distant government to the east. However, the Federal government was already more focused on critical affairs in the old Northwest Territory. Most of the land in the " Old Southwest" was still either Indian territory or had already been claimed by speculators or settlers, and thus there was little money to be made from land sales. President Washington issued a proclamation forbidding the violation of the
Residents of the Southwest Territory initially welcomed federal control, believing the federal government would provide better protection from hostile Indians than North Carolina's distant government to the east. However, the Federal government was already more focused on critical affairs in the old Northwest Territory. Most of the land in the " Old Southwest" was still either Indian territory or had already been claimed by speculators or settlers, and thus there was little money to be made from land sales. President Washington issued a proclamation forbidding the violation of the 
 A census in the summer of 1791 showed the territory's population to be 35,691. There were 6,271 free adult white males, more than the 5,000 needed for the territory to organize a legislature. Blount, however, waited until 1793 to call for elections. Members of the territorial House of Representatives (the lower chamber of the legislature) were elected in December 1793, and the first House session convened on February 24, 1794. The representatives nominated ten individuals for appointment to the territorial council (the legislature's upper chamber), five of whom—
A census in the summer of 1791 showed the territory's population to be 35,691. There were 6,271 free adult white males, more than the 5,000 needed for the territory to organize a legislature. Blount, however, waited until 1793 to call for elections. Members of the territorial House of Representatives (the lower chamber of the legislature) were elected in December 1793, and the first House session convened on February 24, 1794. The representatives nominated ten individuals for appointment to the territorial council (the legislature's upper chamber), five of whom—
 Legislative power in the Southwest Territory initially rested with the governor, who consulted with the three territorial judges on new laws. After the territory's population of white males reached 5,000, the territory could form a legislative assembly (the power to summon the assembly rested with the governor). The assembly consisted of an upper chamber, the Territorial Council (the role of which was similar to that of a state senate), and a lower chamber, the House of Representatives. While the assembly could propose new laws, the governor could still veto any bill. To serve on the council, an individual had to own at least of land in the territory.
The territorial House of Representatives consisted of thirteen popularly elected members. These members elected a
Legislative power in the Southwest Territory initially rested with the governor, who consulted with the three territorial judges on new laws. After the territory's population of white males reached 5,000, the territory could form a legislative assembly (the power to summon the assembly rested with the governor). The assembly consisted of an upper chamber, the Territorial Council (the role of which was similar to that of a state senate), and a lower chamber, the House of Representatives. While the assembly could propose new laws, the governor could still veto any bill. To serve on the council, an individual had to own at least of land in the territory.
The territorial House of Representatives consisted of thirteen popularly elected members. These members elected a
Tennessee Blue Book
'' (2012), p. 566. Hopkins Lacy was elected clerk.William Robertson Garrett and Albert Virgil Goodpasture,
History of Tennessee
' (Brandon Printing Company, 1903), p. 109. Members of the territorial council were appointed by the President from a list of candidates submitted by the territorial House of Representatives. At its first session in February 1794, the House submitted ten candidates for the council: James Winchester, William Fort, Stockley Donelson, Richard Gammon, David Russell,
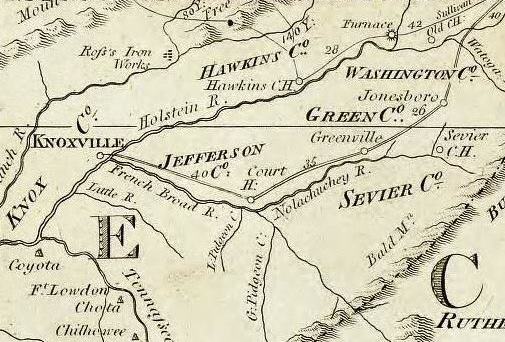 The Southwest Territory covered , consisting of what is now Tennessee, with the exception of a few minor boundary changes resulting from later surveys. To its north was Virginia's
The Southwest Territory covered , consisting of what is now Tennessee, with the exception of a few minor boundary changes resulting from later surveys. To its north was Virginia's  The Washington District initially included lands north of the
The Washington District initially included lands north of the
Fort Blount
" ''Tennessee Encyclopedia of History and Culture''. Retrieved: 10 November 2013. The population of the Southwest Territory in 1791 was 35,691. This included 3,417 slaves and 361 free persons of color. The population of the Washington District was 28,649, while the population of Mero was 7,042. The territory's 1795 census showed a total population of 77,262 inhabitants, including 10,613 slaves and 973 free persons of color. The population of the Washington and Hamilton districts was 65,338, and the population of Mero was 11,924.
Southwest Ordinance of 1790
at Tennessee GenWeb.com *
"Journal of the proceedings of the Legislative council of the territory of the United States of America, South of the river Ohio: begun and held at Knoxville, the 25th day of August, 1794"
at archives.org. {{Tennessee 1790 establishments in the United States 1796 disestablishments in the United States Pre-statehood history of Tennessee
organized incorporated territory of the United States
The territory of the United States and its overseas possessions has evolved over time, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, internationa ...
that existed from May 26, 1790, until June 1, 1796, when it was admitted to the United States as the State of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
. The Southwest Territory was created by the Southwest Ordinance from lands of the Washington District
The Washington District is a Norfolk Southern Railway line in the U.S. state of Virginia that connects Alexandria, Virginia, Alexandria and Lynchburg, Virginia, Lynchburg. Most of the line was originally built from 1850 to 1860 by the Orange and ...
that had been ceded
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdictio ...
to the U.S. federal government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fed ...
by North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. The territory's lone governor was William Blount
William Blount (March 26, 1749March 21, 1800) was an American Founding Father, statesman, farmer and land speculator who signed the United States Constitution. He was a member of the North Carolina delegation at the Constitutional Convention o ...
.
The establishment of the Southwest Territory followed a series of efforts by North Carolina's trans-Appalachia
The area in United States west of the Appalachian Mountains and extending vaguely to the Mississippi River, spanning the lower Great Lakes to the upper south, is a region known as trans-Appalachia, particularly when referring to frontier times. It ...
n residents to form a separate political entity, initially with the Watauga Association
The Watauga Association (sometimes referred to as the Republic of Watauga) was a semi-autonomous government created in 1772 by frontier settlers living along the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. Although it lasted only a few ...
, and later with the failed State of Franklin. North Carolina ceded these lands in April 1790 as payment of obligations owed to the federal government. The territory's residents welcomed the cession, believing the federal government would provide better protection from Indian hostilities. The federal government paid relatively little attention to the territory, however, increasing its residents' desire for full statehood.
Along with Blount, a number of individuals who played prominent roles in early Tennessee history served in the Southwest Territory's administration. These included John Sevier
John Sevier (September 23, 1745 September 24, 1815) was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennes ...
, James Robertson, Griffith Rutherford
Griffith Rutherford (c. 1721 – August 10, 1805) was an American military officer in the Revolutionary War, a political leader in North Carolina, and an important figure in the early history of the Southwest Territory and the state of Ten ...
, James Winchester, Archibald Roane
Archibald Roane (1759/60 – January 18, 1819) was the second Governor of Tennessee, serving from 1801 to 1803. He won the office after the state's first governor, John Sevier, was prevented by constitutional restrictions from seeking a fourth ...
, John McNairy
John McNairy (March 30, 1762 – November 12, 1837) was a British-American federal judge of the United States District Court for the District of Tennessee, the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Tennessee and the United Sta ...
, Joseph McMinn
Joseph McMinn (June 22, 1758October 17, 1824) was an American politician who served as the fourth Governor of Tennessee from 1815 to 1821. A veteran of the American Revolution, he had previously served in the legislature of the Southwest Territo ...
and Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
.
Background
During the colonial period, land that would become the Southwest Territory was part ofNorth Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
's land patent
A land patent is a form of letters patent assigning official ownership of a particular tract of land that has gone through various legally-prescribed processes like surveying and documentation, followed by the letter's signing, sealing, and publi ...
. The Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virgin ...
, which rise along the modern Tennessee-North Carolina border, hindered North Carolina from pursuing any lasting interest in the territory. Initially trade, political interest, and settlement came mostly from Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
and South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, though refugees from the Regulator War began arriving from North Carolina in the early 1770s.
The Watauga Association
The Watauga Association (sometimes referred to as the Republic of Watauga) was a semi-autonomous government created in 1772 by frontier settlers living along the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. Although it lasted only a few ...
was a semi-autonomous government created in 1772 by frontier settlers living along the Watauga River
The Watauga River () is a large stream of western North Carolina and East Tennessee. It is long with its headwaters in Linville Gap to the South Fork Holston River at Boone Lake.
Course
The Watauga River rises from a spring near the base ...
in what is present day Elizabethton, Tennessee
Elizabethton is a city in, and the county seat of Carter County, Tennessee, United States. Elizabethton is the historical site of the first independent American government (known as the Watauga Association, created in 1772) located west of both t ...
. The colony was established on Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
-owned land in which the Watauga and Nolichucky settlers had negotiated a 10-year lease directly with the Indians. Fort Watauga
Fort Watauga, more properly Fort Caswell, was an American Revolutionary War fort that once stood at the Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. The fort was originally built in 1775–1776 by the area's front ...
was established on the Watauga River at Sycamore Shoals
The Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, usually shortened to Sycamore Shoals, is a rocky stretch of river rapids along the Watauga River in Elizabethton, Tennessee. Archeological excavations have found Native Americans lived near the shoals s ...
as a trade center of the settlements.
In March 1775, land speculator and North Carolina judge Richard Henderson met with more than 1,200 Cherokees at Sycamore Shoals. Included at the gathering were Cherokee leaders such as Attacullaculla
Attakullakulla (Cherokee”Tsalagi”, (ᎠᏔᎫᎧᎷ) ''Atagukalu''; also spelled Attacullaculla and often called Little Carpenter by the English) (c. 1715 – c. 1777) was an influential Cherokee leader and the tribe's First Belove ...
, Oconostota
Oconostota (c. 1710–1783) was a Cherokee '' skiagusta'' (war chief) of Chota, which was for nearly four decades the primary town in the Overhill territory, and within what is now Monroe County, Tennessee. He served as the First Beloved Man of C ...
, and Dragging Canoe
Dragging Canoe (ᏥᏳ ᎦᏅᏏᏂ, pronounced ''Tsiyu Gansini'', "he is dragging his canoe") (c. 1738 – February 29, 1792) was a Cherokee war chief who led a band of Cherokee warriors who resisted colonists and United States settlers in the ...
. The meeting resulted in the "Treaty of Sycamore Shoals
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
", in which Henderson purchased from the Cherokee all the land situated south of the Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
and lying between the Cumberland River
The Cumberland River is a major waterway of the Southern United States. The U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 8, 2011 river drains almost of southern Kentucky and ...
, the Cumberland Mountains
The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in western Virginia, southwestern West Virginia, the eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the ...
, and the Kentucky River
The Kentucky River is a tributary of the Ohio River, long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed June 13, 2011 in the U.S. Commonwealth of Kentucky. The river and its tri ...
. This land, which encompassed roughly 20 million acres (80,000 km²), became known as the Transylvania Purchase
The Transylvania Colony, also referred to as the Transylvania Purchase, was a short-lived, extra-legal colony founded in early 1775 by North Carolina land speculator Richard Henderson, who formed and controlled the Transylvania Company. Henders ...
. Henderson's land deal was found to be in violation of North Carolina and Virginia law, as well as the Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Procla ...
, which had prohibited the private purchase of American Indian land.
Both North Carolina and Virginia considered the trans-Appalachian settlements illegal, and refused to annex them. Nevertheless, at the onset of the American War for Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
in 1776, the settlers, who vigorously supported the Patriot cause, organized themselves into the "Washington District" and formed a committee of safety to govern it. In July 1776, Dragging Canoe and the faction of the Cherokee opposed to the Transylvania Purchase (later called the Chickamaugas) aligned with the British and launched an invasion of the Watauga settlements, targeting Fort Watauga
Fort Watauga, more properly Fort Caswell, was an American Revolutionary War fort that once stood at the Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. The fort was originally built in 1775–1776 by the area's front ...
at modern Elizabethton and Eaton's Station near modern Kingsport. After the settlers thwarted the attacks, North Carolina agreed to annex the settlements as the Washington District
The Washington District is a Norfolk Southern Railway line in the U.S. state of Virginia that connects Alexandria, Virginia, Alexandria and Lynchburg, Virginia, Lynchburg. Most of the line was originally built from 1850 to 1860 by the Orange and ...
.
In September 1780, a large group of trans-Appalachian settlers, led by William Campbell, John Sevier
John Sevier (September 23, 1745 September 24, 1815) was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennes ...
and Isaac Shelby
Isaac Shelby (December 11, 1750 – July 18, 1826) was the first and fifth Governor of Kentucky and served in the state legislatures of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic an ...
, assembled at Sycamore Shoals in response to a British threat to attack frontier settlements. Known as the Overmountain Men
The Overmountain Men were American frontiersmen from west of the Blue Ridge Mountains which are the leading edge of the Appalachian Mountains, who took part in the American Revolutionary War. While they were present at multiple engagements in t ...
, the settlers marched across the mountains to South Carolina, where they engaged and defeated a loyalist force led by Patrick Ferguson
Patrick Ferguson (1744 – 7 October 1780) was a Scottish officer in the British Army, an early advocate of light infantry and the designer of the Ferguson rifle. He is best known for his service in the 1780 military campaign of Charles C ...
at the Battle of Kings Mountain
The Battle of Kings Mountain was a military engagement between Patriot and Loyalist militias in South Carolina during the Southern Campaign of the American Revolutionary War, resulting in a decisive victory for the Patriots. The battle took pla ...
. Overmountain Men would also take part in the Battle of Musgrove Mill
The Battle of Musgrove Mill, August 19, 1780, occurred near a ford of the Enoree River, near the present-day border between Spartanburg, Laurens and Union Counties in South Carolina. During the course of the battle, 200 Patriot militiamen defeate ...
and the Battle of Cowpens
The Battle of Cowpens was an engagement during the American Revolutionary War fought on January 17, 1781 near the town of Cowpens, South Carolina, between U.S. forces under Brigadier General Daniel Morgan and Kingdom of Great Britain, British for ...
.U.S. National Park Service./ref> In 1784, North Carolina ceded control of the Overmountain settlements following a hotly contested vote. The cession was rescinded later that year, but not before some of the settlers had organized the State of Franklin, which sought statehood.
John Sevier
John Sevier (September 23, 1745 September 24, 1815) was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennes ...
was named governor and the area began operating as an independent state not recognized by the Congress of the Confederation. Many Overmountain settlers, led by John Tipton
John Tipton (August 14, 1786 – April 5, 1839) was from Tennessee and became a farmer in Indiana; an officer in the 1811 Battle of Tippecanoe, and veteran officer of the War of 1812, in which he reached the rank of Brigadier General; and po ...
, remained loyal to North Carolina, and frequently quarreled with the Franklinites. Following Tipton's defeat of Sevier at the "Battle of Franklin" in early 1788, the State of Franklin movement declined. The Franklinites had agreed to rejoin North Carolina by early 1789.
Territory formation
North Carolina ratified theUnited States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
on November 21, 1789. On December 22, the state legislature voted to cede the Overmountain settlements as payment of its obligations to the new federal government.Walter T. Durham, "The Southwest Territory: Progression to Statehood," ''Journal of East Tennessee History'', Vol. 62 (1990), pp. 3–17. Congress accepted the cession during its first session on April 2, 1790, when it passed "An Act to Accept a Cession of the Claims of the State of North Carolina to a Certain District of Western Territory".Walter T. Durham, "The Territory of the United States South of the River Ohio," ''Before Tennessee: The Southwest Territory, 1790–1796'' (Rocky Mount Historical Association, 1990), pp. 31–46. On May 26, 1790, Congress passed an act organizing the new cession as the "Territory of the United States South of the River Ohio," which consisted of modern Tennessee, with the exception of later minor boundary changes. However, most of the new territory was under Indian control, with territorial administration initially covering two unconnected areas— the Washington District in what is now northeast Tennessee, and the Mero District around Nashville. The act also merged the office of territorial governor with the office of Superintendent of Indian Affairs for the Southern Department.
 The new territory was essentially governed under the same provisions as the Northwest Ordinance, a 1787 act enacted for the creation of the Northwest Territory north of the Ohio River. The Northwest Ordinance's provision outlawing
The new territory was essentially governed under the same provisions as the Northwest Ordinance, a 1787 act enacted for the creation of the Northwest Territory north of the Ohio River. The Northwest Ordinance's provision outlawing slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
was not applied to the Southwest Territory, however. Along with rules of governance, the Ordinance outlined steps a territory could take to gain admission to the Union. The first step involved the organization of a territorial government. The next step, which would take place when the territory had at least 5,000 adult males, was to organize a territorial legislature, with a popularly elected lower chamber and an upper chamber appointed by the president. The final step, which would take place when the territory had a population of at least 60,000, was to write a state constitution and elect a state government, at which time the territory would be admitted to the Union.
Several candidates were put forth for governor of the new territory. William Blount (1749–1800), a Constitutional Convention delegate and former state legislator who had championed the causes of western settlers, was supported by key North Carolina politicians such as Hugh Williamson
Hugh Williamson (December 5, 1735 – May 22, 1819) was an American Founding Father, physician, and politician. He is best known as a signatory to the U.S. Constitution, and for representing North Carolina at the Constitutional Convention.
Wi ...
, Timothy Bloodworth
Timothy James Bloodworth (1736August 24, 1814) was a slave owner, ardent patriot in the American Revolution, member of the Confederation Congress, vigorous anti-Federalist, U.S. congressman and senator, and collector of customs for the Port of Wi ...
, John B. Ashe and Benjamin Hawkins
Benjamin Hawkins (August 15, 1754June 6, 1816) was an American planter, statesman and a U.S. Indian agent He was a delegate to the Continental Congress and a United States Senator from North Carolina, having grown up among the planter elite ...
. An aggressive land speculator, Blount had extensive land holdings in the new territory. Virginia's Patrick Henry
Patrick Henry (May 29, 1736June 6, 1799) was an American attorney, planter, politician and orator known for declaring to the Second Virginia Convention (1775): " Give me liberty, or give me death!" A Founding Father, he served as the first an ...
called for his friend, General Joseph Martin, to be appointed governor. A small group of ex-Franklinites convened in Greeneville to push for the appointment of John Sevier.
On June 8, 1790, President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
chose Blount as the territory's new governor. He also appointed Daniel Smith (1748–1818) the territory's Secretary, and named two of the territory's three judges, John McNairy
John McNairy (March 30, 1762 – November 12, 1837) was a British-American federal judge of the United States District Court for the District of Tennessee, the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Tennessee and the United Sta ...
and David Campbell (Joseph Anderson
Joseph Inslee Anderson (November 5, 1757 – April 17, 1837) was an American soldier, judge, and politician, who served as a United States Senator from Tennessee from 1797 to 1815, and later as the First Comptroller of the United States Treasur ...
would eventually be chosen as the third judge). John Sevier was appointed brigadier general of the Washington District militia, and James Robertson was appointed brigadier general of the Mero District militia.
In September 1790, Blount visited Washington at Mount Vernon
Mount Vernon is an American landmark and former plantation of Founding Father, commander of the Continental Army in the Revolutionary War, and the first president of the United States George Washington and his wife, Martha. The estate is on ...
, and was sworn in by Supreme Court justice James Iredell
James Iredell (October 5, 1751 – October 20, 1799) was one of the first Justices of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was appointed by President George Washington and served from 1790 until his death in 1799. His son, James Iredel ...
. He then moved to the new territory, where he set up a temporary capital at Rocky Mount, the home of William Cobb in Sullivan County. He recruited North Carolina publisher George Roulstone to establish a newspaper, the ''Knoxville Gazette
The ''Knoxville Gazette'' was the first newspaper published in the U.S. state of Tennessee and the third published west of the Appalachian Mountains. Established by George Roulstone (1767–1804) at the urging of Southwest Territory governor W ...
'' (initially published at Rogersville). He spent most of October and November issuing appointments to lower-level administrative and militia positions. In December, he made the dangerous trip across Indian territory to the Mero District, where he likewise issued appointments, before returning to Rocky Mount by the end of the year.
Blount initially wanted the permanent territorial capital to be located at the confluence of the Clinch
Clinch may refer to:
* Nail (fastener) or device to hold in this way
* Clinching, in metalworking
* Clinch fighting or the clinch, a grappling position in boxing or wrestling, a stand-up embrace
* Clinch County, Georgia, USA
* Clinch River, near T ...
and Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
rivers (in the vicinity of modern Kingston), where he had extensive land claims, but was unable to convince the Cherokee to relinquish ownership of these lands. He therefore chose James White's Fort
James White's Fort, also known as White's Fort, was an 18th-century settlement that became Knoxville, Tennessee, in the United States. The name also refers to the fort, itself.
The settlement of White's Fort began in 1786 by James White, a mil ...
, an outpost located further upstream along the Tennessee. In 1791, White's son-in-law, Charles McClung
Charles McClung (May 13, 1761 – August 9, 1835) was an American pioneer, politician, and surveyor best known for drawing up the original plat of Knoxville, Tennessee, in 1791. While Knoxville has since expanded to many times its original s ...
, platted the new city, and lots were sold in October of that year. Blount named the new city "Knoxville" after his superior in the War Department, Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
.
In the 1790 United States census, 7 counties in the Southwest Territory reported the following population counts:
Indian hostilities
 Residents of the Southwest Territory initially welcomed federal control, believing the federal government would provide better protection from hostile Indians than North Carolina's distant government to the east. However, the Federal government was already more focused on critical affairs in the old Northwest Territory. Most of the land in the " Old Southwest" was still either Indian territory or had already been claimed by speculators or settlers, and thus there was little money to be made from land sales. President Washington issued a proclamation forbidding the violation of the
Residents of the Southwest Territory initially welcomed federal control, believing the federal government would provide better protection from hostile Indians than North Carolina's distant government to the east. However, the Federal government was already more focused on critical affairs in the old Northwest Territory. Most of the land in the " Old Southwest" was still either Indian territory or had already been claimed by speculators or settlers, and thus there was little money to be made from land sales. President Washington issued a proclamation forbidding the violation of the Treaty of Hopewell
Three agreements, each known as the Treaty of Hopewell, were signed between representatives of the Congress of the United States and the Cherokee, Choctaw, and Chickasaw peoples, were negotiated and signed at the Hopewell plantation in South Car ...
(which had set Indian boundaries), and Secretary of War Knox frequently accused settlers of illegally encroaching on Indian lands. Blount was consistently torn between placating angry frontiersmen and appeasing his superiors in the Federal government.
In the Summer of 1791, Blount negotiated the Treaty of Holston
The Treaty of Holston (or Treaty of the Holston) was a treaty between the United States government and the Cherokee signed on July 2, 1791, and proclaimed on February 7, 1792. It was negotiated and signed by William Blount, governor of the South ...
with the Cherokee at the future site of Knoxville. The Treaty brought lands south of the French Broad River
The French Broad River is a river in the U.S. states of North Carolina and Tennessee. It flows from near the town of Rosman in Transylvania County, North Carolina, into Tennessee, where its confluence with the Holston River at Knoxville form ...
and east of the divide between Little River
Little River may refer to several places:
Australia Streams New South Wales
*Little River (Dubbo), source in the Dubbo region, a tributary of the Macquarie River
* Little River (Oberon), source in the Oberon Shire, a tributary of Coxs River (Haw ...
and the Little Tennessee River
The Little Tennessee River is a tributary of the Tennessee River that flows through the Blue Ridge Mountains from Georgia, into North Carolina, and then into Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. It drains portions of three national ...
(essentially modern Cocke Cocke is a surname (pronounced ''cock'', ''cox'' or ''coke'') and may refer to:
* Charles Lewis Cocke (1940- ) Professor of Physics at Kansas State University, winner of 2006 Davisson–Germer Prize in Atomic or Surface Physics
* Erle Cocke Jr. ...
, Sevier and Blount counties) under U.S. control, and guaranteed the Territory use of a road between the Washington and Mero districts, as well as the Tennessee River. The following year, Blount negotiated an agreement clarifying land boundaries with the Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as ...
, who controlled what is now West Tennessee
West Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of the U.S. state of Tennessee that roughly comprises the western quarter of the state. The region includes 21 counties between the Tennessee and Mississippi rivers, delineated by state law. Its ...
.
In spite of these agreements, continued encroachment by settlers onto Indian lands prompted reprisals, which primarily came from hostile Chickamauga Cherokee
The Chickamauga Cherokee refers to a group that separated from the greater body of the Cherokee during the American Revolutionary War. The majority of the Cherokee people wished to make peace with the Americans near the end of 1776, following se ...
and Creek Indians
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsSpanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, who controlled Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
along the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
coast and still disputed the southern borders of the United States, fifteen years after the end of the Revolutionary War, encouraged and armed the southern tribes. These attacks persisted throughout 1792 and 1793, with the Mero settlements bearing the brunt of the hostilities. Ziegler's Station near modern Hendersonville was destroyed, and Mero defenders had to rally to thwart a large invasion at Buchanan's Station
Buchanan's Station was a fortified stockade featuring a bunkhouse, a way station, and a surrounding settlement established about 1784 in Davidson County on Mill Creek by Major John Buchanan in what is today the Donelson neighborhood of Nashv ...
near Nashville. In spite of growing impatience from frontiersmen, Secretary of War Knox refused to authorize an invasion of Indian territory.
In September 1793, while Blount was away in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, a large group of Cherokee invaders overran Cavet's Station west of Knoxville, and was planning to march on Knoxville before the invading force dissolved due to infighting among chiefs. Territorial Secretary Daniel Smith, who was Acting Governor
An acting governor is a person who acts in the role of governor. In Commonwealth jurisdictions where the governor is a vice-regal position, the role of "acting governor" may be filled by a lieutenant governor (as in most Australian states) or an ...
in Blount's absence, summoned the militia and ordered an invasion of Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
territory. Militia General Sevier led the militia south and destroyed several Chickamauga villages. While Blount supported Smith's decision, the invasion angered Knox, who refused to issue pay for the militiamen. In September 1794, Robertson, without authorization from Knox, dispatched a mounted American force under James Ore
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
which destroyed the Chickamauga towns of Nickajack and Running Water. Robertson resigned as brigadier general shortly afterward.
The defeat of northern tribes at the Battle of Fallen Timbers
The Battle of Fallen Timbers (20 August 1794) was the final battle of the Northwest Indian War, a struggle between Native American tribes affiliated with the Northwestern Confederacy and their British allies, against the nascent United State ...
in August 1794, the destruction of Nickajack and Running Water, and the resolving of boundary disputes between the United States and Spain led to a decline in hostile Indian attacks. In November 1794, Blount negotiated an end to the Cherokee–American wars
The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1794 between the Cherokee and American se ...
at the Tellico Blockhouse
The Tellico Blockhouse was an early American outpost located along the Little Tennessee River in what developed as Vonore, Monroe County, Tennessee. Completed in 1794, the blockhouse was a US military outpost that operated until 1807; the garrison ...
, a federal outpost south of Knoxville.

Statehood
 A census in the summer of 1791 showed the territory's population to be 35,691. There were 6,271 free adult white males, more than the 5,000 needed for the territory to organize a legislature. Blount, however, waited until 1793 to call for elections. Members of the territorial House of Representatives (the lower chamber of the legislature) were elected in December 1793, and the first House session convened on February 24, 1794. The representatives nominated ten individuals for appointment to the territorial council (the legislature's upper chamber), five of whom—
A census in the summer of 1791 showed the territory's population to be 35,691. There were 6,271 free adult white males, more than the 5,000 needed for the territory to organize a legislature. Blount, however, waited until 1793 to call for elections. Members of the territorial House of Representatives (the lower chamber of the legislature) were elected in December 1793, and the first House session convened on February 24, 1794. The representatives nominated ten individuals for appointment to the territorial council (the legislature's upper chamber), five of whom— Griffith Rutherford
Griffith Rutherford (c. 1721 – August 10, 1805) was an American military officer in the Revolutionary War, a political leader in North Carolina, and an important figure in the early history of the Southwest Territory and the state of Ten ...
, John Sevier, James Winchester, Stockley Donelson and Parmenas Taylor— were eventually appointed by President Washington. Rutherford was chosen as the council's president.
The assembly first convened on August 26, 1794, and called for immediate steps to be taken to achieve full statehood. The assembly appointed Dr. James White (not to be confused with Knoxville's founder) as its non-voting representative in Congress, making the Southwest Territory one of the first U.S. territories to make use of this power. A special session of the assembly on June 29, 1795, called for a census to be taken the following month to determine if the territory's population had reached the 60,000 threshold required for statehood. The census revealed a population of 77,262 inhabitants.
After the census, the territory moved swiftly to form a state government. In December 1795, counties elected delegates for the state constitutional convention. This convention met in Knoxville in January 1796, and drafted a new state constitution. The name "Tennessee," which had been in common use since 1793 when Secretary Smith published his "Short Description of the Tennassee Government," was chosen as the new name for the state.
The Northwest Ordinance was vague on the final steps to be taken for a state to be fully admitted to the Union, so Tennessee's leaders proceeded to organize a state government. John Sevier was elected governor, the first Tennessee General Assembly convened in March 1796, and Blount notified the Secretary of State, Timothy Pickering
Timothy Pickering (July 17, 1745January 29, 1829) was the third United States Secretary of State under Presidents George Washington and John Adams. He also represented Massachusetts in both houses of Congress as a member of the Federalist Party ...
, that the territorial government had been terminated. A copy of the state constitution was delivered to Pickering by future governor Joseph McMinn
Joseph McMinn (June 22, 1758October 17, 1824) was an American politician who served as the fourth Governor of Tennessee from 1815 to 1821. A veteran of the American Revolution, he had previously served in the legislature of the Southwest Territo ...
. Blount and William Cocke
William Cocke (1748August 22, 1828) was an American lawyer, pioneer, and statesman. He has the distinction of having served in the state legislatures of four different states: Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Mississippi, and was one of t ...
were chosen as the state's U.S. Senators, and Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
was elected the state's representative. As the Southwest Territory was the first federal territory to petition to join the Union, there was confusion in Congress about how to proceed. Nonetheless, Tennessee was admitted to the Union on June 1, 1796, as the 16th state.
Government and law
The Southwest Territory was governed under an act of Congress, "An Act for the Government of the Territory of the United States, South of the River Ohio" (Southwest Ordinance), passed May 26, 1790. This act essentially mirrored the earlier Northwest Ordinance, the key difference being over slavery, which was prohibited by the Northwest Ordinance, but not the Southwest Ordinance. Both ordinances provided for freedom of religion and the sanctity of contracts, barred legal primogeniture, and encouraged the establishment of schools and respect for the liberty of the Indians. The supreme power in the territory rested in the governor, who was appointed by the President of the United States. He was assisted by the Secretary, also appointed by the President. Legislative powers rested in a bicameral territorial assembly consisting of the House of Representatives (lower chamber) and the Territorial Council (upper chamber). Representatives were popularly elected, whereas councilors were appointed by the President. Judicial power rested in three judges appointed by the President. Brigadier generals of the territorial militia were also appointed by the President. Lower administrative, judicial and military officers were appointed by the governor.Executive
The Governor of the Southwest Territory had supreme authority in the territory. The governor could decree ordinances, propose and enact new laws, create towns and counties, and license lawyers. Though the territorial assembly held legislative powers, the governor held veto power over all proposed laws. The governor was responsible for appointing the lower territorial administrative officers, including attorneys general, justices of the peace, registers, and court clerks. He recommended candidates for brigadier general to the President, and appointed lower militia officers. The governor also served as the Superintendent of Indian Affairs for the Southern Department, the federal government's chief diplomat to the Southern tribes. To serve as governor, an individual had to own at least of land in the territory.William Blount
William Blount (March 26, 1749March 21, 1800) was an American Founding Father, statesman, farmer and land speculator who signed the United States Constitution. He was a member of the North Carolina delegation at the Constitutional Convention o ...
(1749–1800) served as Governor of the Southwest Territory throughout the territory's existence.
The Secretary of the Southwest Territory was the official record-keeper of the territory. The Secretary also served as acting governor
An acting governor is a person who acts in the role of governor. In Commonwealth jurisdictions where the governor is a vice-regal position, the role of "acting governor" may be filled by a lieutenant governor (as in most Australian states) or an ...
if the governor was absent or incapacitated. To serve as Secretary, an individual had to own at least of land in the territory. Daniel Smith (1748–1818) served as Secretary throughout the territory's existence.
Legislature
speaker
Speaker may refer to:
Society and politics
* Speaker (politics), the presiding officer in a legislative assembly
* Public speaker, one who gives a speech or lecture
* A person producing speech: the producer of a given utterance, especially:
** I ...
from their own ranks. The House first convened at Knoxville on February 24, 1794. Its members were John Tipton
John Tipton (August 14, 1786 – April 5, 1839) was from Tennessee and became a farmer in Indiana; an officer in the 1811 Battle of Tippecanoe, and veteran officer of the War of 1812, in which he reached the rank of Brigadier General; and po ...
(Washington), George Rutledge (Sullivan), Joseph Hardin (Greene), William Cocke
William Cocke (1748August 22, 1828) was an American lawyer, pioneer, and statesman. He has the distinction of having served in the state legislatures of four different states: Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Mississippi, and was one of t ...
(Hawkins), Joseph McMinn
Joseph McMinn (June 22, 1758October 17, 1824) was an American politician who served as the fourth Governor of Tennessee from 1815 to 1821. A veteran of the American Revolution, he had previously served in the legislature of the Southwest Territo ...
(Hawkins), Alexander Kelly (Knox), John Beard (Knox), Samuel Wear (Jefferson), George Doharty (Jefferson), David Wilson (Sumner), Dr. James White (Davidson) and James Ford (Tennessee County). Wilson, of Sumner County, served as Speaker from 1794 to 1795. Hardin, of Greene, served as Speaker from 1795 to 1796.Tennessee Blue Book
'' (2012), p. 566. Hopkins Lacy was elected clerk.William Robertson Garrett and Albert Virgil Goodpasture,
History of Tennessee
' (Brandon Printing Company, 1903), p. 109. Members of the territorial council were appointed by the President from a list of candidates submitted by the territorial House of Representatives. At its first session in February 1794, the House submitted ten candidates for the council: James Winchester, William Fort, Stockley Donelson, Richard Gammon, David Russell,
John Sevier
John Sevier (September 23, 1745 September 24, 1815) was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennes ...
, Adam Meek, John Adair, Griffith Rutherford
Griffith Rutherford (c. 1721 – August 10, 1805) was an American military officer in the Revolutionary War, a political leader in North Carolina, and an important figure in the early history of the Southwest Territory and the state of Ten ...
and Parmenas Taylor. From this list, President Washington appointed Winchester, Donelson, Sevier, Rutherford and Taylor. Rutherford was chosen as council president (a role similar to speaker).
The Northwest Ordinance allowed a territory's assembly to elect a representative to the United States Congress. This representative could consult with congressmen on legislation, but could not vote. In 1794, the Southwest Territory's assembly chose Dr. James White as its non-voting representative to Congress. The Southwest Territory was the first U.S. territory to exercise this power, and White's efforts in Congress set a precedent for future territorial delegates.
Judiciary
The territory's supreme judicial power rested in three judges, each appointed by the President. The governor appointed court clerks, attorneys general and lower judicial offices, as well as justices of the peace. Along with their judicial powers, the judges could consult with the governor on new legislation, though the governor held final veto power over any proposed laws. To serve as a judge, an individual had to own at least of land in the territory. The judges appointed by President Washington in 1790 wereJohn McNairy
John McNairy (March 30, 1762 – November 12, 1837) was a British-American federal judge of the United States District Court for the District of Tennessee, the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Tennessee and the United Sta ...
(1762–1837), David Campbell (1750–1812), and Joseph Anderson
Joseph Inslee Anderson (November 5, 1757 – April 17, 1837) was an American soldier, judge, and politician, who served as a United States Senator from Tennessee from 1797 to 1815, and later as the First Comptroller of the United States Treasur ...
(1757–1837). Blount appointed Francis Alexander Ramsey clerk of the Washington District's superior court of law, Andrew Russell clerk of the Washington District's court of equity, David Allison clerk of Mero's superior court of law, and Joseph Sitgreaves clerk of Mero's court of equity.
The courts of the Southwest Territory were generally more highly regarded than other branches of government. Frontiersmen had for years relied on county courts to settle disputes, and upon being appointed governor, Blount left the existing county courts largely intact. These courts generally followed old North Carolina laws when rendering decisions, relying heavily on James Iredell
James Iredell (October 5, 1751 – October 20, 1799) was one of the first Justices of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was appointed by President George Washington and served from 1790 until his death in 1799. His son, James Iredel ...
's ''Revisal of the Laws of North Carolina'' (1791). Along with hearing criminal and civil cases, courts were responsible for licensing ferries
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water tax ...
, regulating taverns, and designating public gristmill
A gristmill (also: grist mill, corn mill, flour mill, feed mill or feedmill) grinds cereal grain into flour and middlings. The term can refer to either the grinding mechanism or the building that holds it. Grist is grain that has been separat ...
s. Courts occasionally rendered financial assistance for internal improvements
Internal improvements is the term used historically in the United States for public works from the end of the American Revolution through much of the 19th century, mainly for the creation of a transportation infrastructure: roads, turnpikes, canal ...
and relief for the destitute. County sheriffs were responsible for collecting taxes.
Lawyers were licensed by the governor to practice in the territory's courts. Notable individuals licensed to practice in the territory included future president Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, future governor Archibald Roane
Archibald Roane (1759/60 – January 18, 1819) was the second Governor of Tennessee, serving from 1801 to 1803. He won the office after the state's first governor, John Sevier, was prevented by constitutional restrictions from seeking a fourth ...
, future congressman John Rhea
John Rhea (pronounced ) (1753May 27, 1832) was an American soldier and politician of the early 19th century who represented Tennessee in the United States House of Representatives. Rhea County, Tennessee and Rheatown, a community and former ...
, and Blount's younger half-brother, future governor Willie Blount
Willie Blount (April 18, 1768September 10, 1835) was an American politician who served as the third Governor of Tennessee from 1809 to 1815. Blount's efforts to raise funds and soldiers during the War of 1812 earned Tennessee the nickname, "Volu ...
. Jackson served as a district attorney for the territory.
Land details
 The Southwest Territory covered , consisting of what is now Tennessee, with the exception of a few minor boundary changes resulting from later surveys. To its north was Virginia's
The Southwest Territory covered , consisting of what is now Tennessee, with the exception of a few minor boundary changes resulting from later surveys. To its north was Virginia's District of Kentucky
Kentucky County (then alternately spelled Kentucke County) was formed by the Commonwealth of Virginia from the western portion (beyond the Cumberland Mountains) of Fincastle County effective December 31, 1776. The name of the county was taken ...
, which became the 15th U.S. state in 1792. The lands to the territory's south were at the time either still claimed by Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, or disputed with Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, but subsequently consolidated into the Mississippi Territory.
At its creation in 1790, the Southwest Territory's administration oversaw two unconnected districts— the Washington District in the northeast, and the Mero District in the area around and north of Nashville. The remainder of the territory remained under Indian control, with the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
being the dominant tribe in the east, and the Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as ...
controlling the western part of the territory. Other important tribes included the Creeks and Choctaw.
 The Washington District initially included lands north of the
The Washington District initially included lands north of the French Broad River
The French Broad River is a river in the U.S. states of North Carolina and Tennessee. It flows from near the town of Rosman in Transylvania County, North Carolina, into Tennessee, where its confluence with the Holston River at Knoxville form ...
and northeast of the confluence of the Clinch
Clinch may refer to:
* Nail (fastener) or device to hold in this way
* Clinching, in metalworking
* Clinch fighting or the clinch, a grappling position in boxing or wrestling, a stand-up embrace
* Clinch County, Georgia, USA
* Clinch River, near T ...
and Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
rivers (near modern Kingston). The 1791 Treaty of Holston pushed the boundary south of the French Broad and southeast to the divide between Little River and the Little Tennessee River (in what is now southern Blount County). The Washington District originally included Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Sullivan, Greene
Greene may refer to:
Places United States
*Greene, Indiana, an unincorporated community
*Greene, Iowa, a city
*Greene, Maine, a town
** Greene (CDP), Maine, in the town of Greene
*Greene (town), New York
** Greene (village), New York, in the town ...
and Hawkins counties. Knox and Jefferson Jefferson may refer to:
Names
* Jefferson (surname)
* Jefferson (given name)
People
* Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), third president of the United States
* Jefferson (footballer, born 1970), full name Jefferson Tomaz de Souza, Brazilian foo ...
were created by Governor Blount in 1792.Michael Toomey, "'Doing Justice to Suitors': The Role of County Courts in the Southwest Territory," ''Journal of East Tennessee History'', Vol. 62 (1990), pp. 33–53. In 1793, Blount organized these two new counties into a separate district, called the "Hamilton District."Stanley Folmsbee, Robert Corlew and Enoch Mitchell, ''Tennessee: A Short History'' (University of Tennessee Press, 1969), p. 100. Blount and Sevier counties would be added to this new district during territorial administration.
The Mero District included the lands around Nashville
Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the seat of Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the most populous city in the state, 21st most-populous city in the U.S., and the ...
and along the Cumberland River
The Cumberland River is a major waterway of the Southern United States. The U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 8, 2011 river drains almost of southern Kentucky and ...
, north to the modern Kentucky border. It included three counties— Davidson
Davidson may refer to:
* Davidson (name)
* Clan Davidson, a Highland Scottish clan
* Davidson Media Group
* Davidson Seamount, undersea mountain southwest of Monterey, California, USA
* Tyler Davidson Fountain, monument in Cincinnati, Ohio, USA
* ...
, Sumner and Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
. The Mero and Washington districts were connected by a road, generally known as Avery's Trace Avery's Trace was the principal road used by settlers travelling from the Knoxville area in East Tennessee to the Nashville area from 1788 to the mid-1830s.
In an effort to encourage settlers to move west into the new territory of Tennessee, in ...
, which traversed Indian lands.Benjamin Nance,Fort Blount
" ''Tennessee Encyclopedia of History and Culture''. Retrieved: 10 November 2013. The population of the Southwest Territory in 1791 was 35,691. This included 3,417 slaves and 361 free persons of color. The population of the Washington District was 28,649, while the population of Mero was 7,042. The territory's 1795 census showed a total population of 77,262 inhabitants, including 10,613 slaves and 973 free persons of color. The population of the Washington and Hamilton districts was 65,338, and the population of Mero was 11,924.
See also
*Indian Reserve (1763)
"Indian Reserve" is a historical term for the largely uncolonized land in North America that was claimed by France, ceded to Great Britain through the Treaty of Paris (1763) at the end of the Seven Years' War—also known as the French and Indian ...
* Overhill Cherokee
Overhill Cherokee was the term for the Cherokee people located in their historic settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Tennessee in the Southeastern United States, on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. This name was used by 1 ...
References
External links
Southwest Ordinance of 1790
at Tennessee GenWeb.com *
"Journal of the proceedings of the Legislative council of the territory of the United States of America, South of the river Ohio: begun and held at Knoxville, the 25th day of August, 1794"
at archives.org. {{Tennessee 1790 establishments in the United States 1796 disestablishments in the United States Pre-statehood history of Tennessee