Southern Cult on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
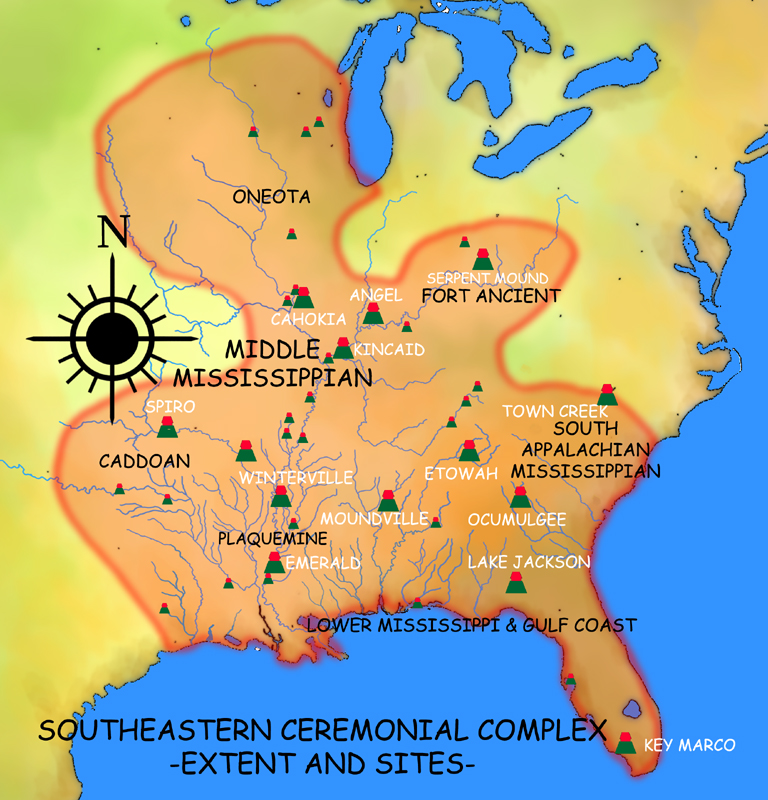 The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts,
The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts,
With the redefinition of the complex, some scholars have suggested choosing a new name to exemplify the new understanding of the large body of art symbols classified as the S.E.C.C. Participants of a decade-long series of conferences held at Texas State University have proposed the terms ''"Mississippian Ideological Interaction Sphere"'' or ''"M.I.I.S."'' and ''"Mississippian Art and Ceremonial Complex"'' or ''"M.A.C.C."'' Present theories suggest that the complex developed from pre-existing beliefs spread over the midwest and southeast by the Hopewell Interaction Sphere from 100 BCE to 500 CE. The major expression of the complex developed at the Cahokia site and is known as the Braden Style; it corresponds with the Southern Cult Period horizon defined by Muller. Other regional styles developed as a result of the fusion of ideas borrowed from the Braden Style and pre-existing local expressions of post-Hopewellian traditions.
 Most S.E.C.C. imagery focuses on
Most S.E.C.C. imagery focuses on
 The
The
File:Etowah Dancing Warrior plate HRoe 2013.jpg, Late Braden style Falcon dancer with wings-Mound C, Etowah
File:Rogan plate 1 birdman HRoe 2012.jpg, Classic Braden style warrior with wings- Mound C, Etowah
File:Castalian Springs Braden style Warrior gorget HRoe 2012.jpg, Club-wielding wingless warrior- Castalian Springs shell engraving
Image:Chromesun digital chunkeyplayer 01.jpg, Chunkey player
*Falcon Dancers with wings.
* Chunkey players / warriors with wings.
*Club-wielding wingless warriors.
*Dancing wingless warriors / chunkey players
Various motifs are associated with the Birdman, including the forked eye motif, columnella pendants, mace or club weapons, severed heads, chunkey play (including chunkey stones, striped and broken chunkey sticks), bellows-shaped aprons, and bi-lobed arrow motifs.
Image:Spiro red horn statue HRoe 2005.jpg
Image:S.E.C.C. red horn and friends HRoe 2008.jpg
Image:S.E.C.C. Hero Twins 5 HRoe 2006.jpg
Image:S.E.C.C. Hero Twins 4 HRoe 2006.jpg
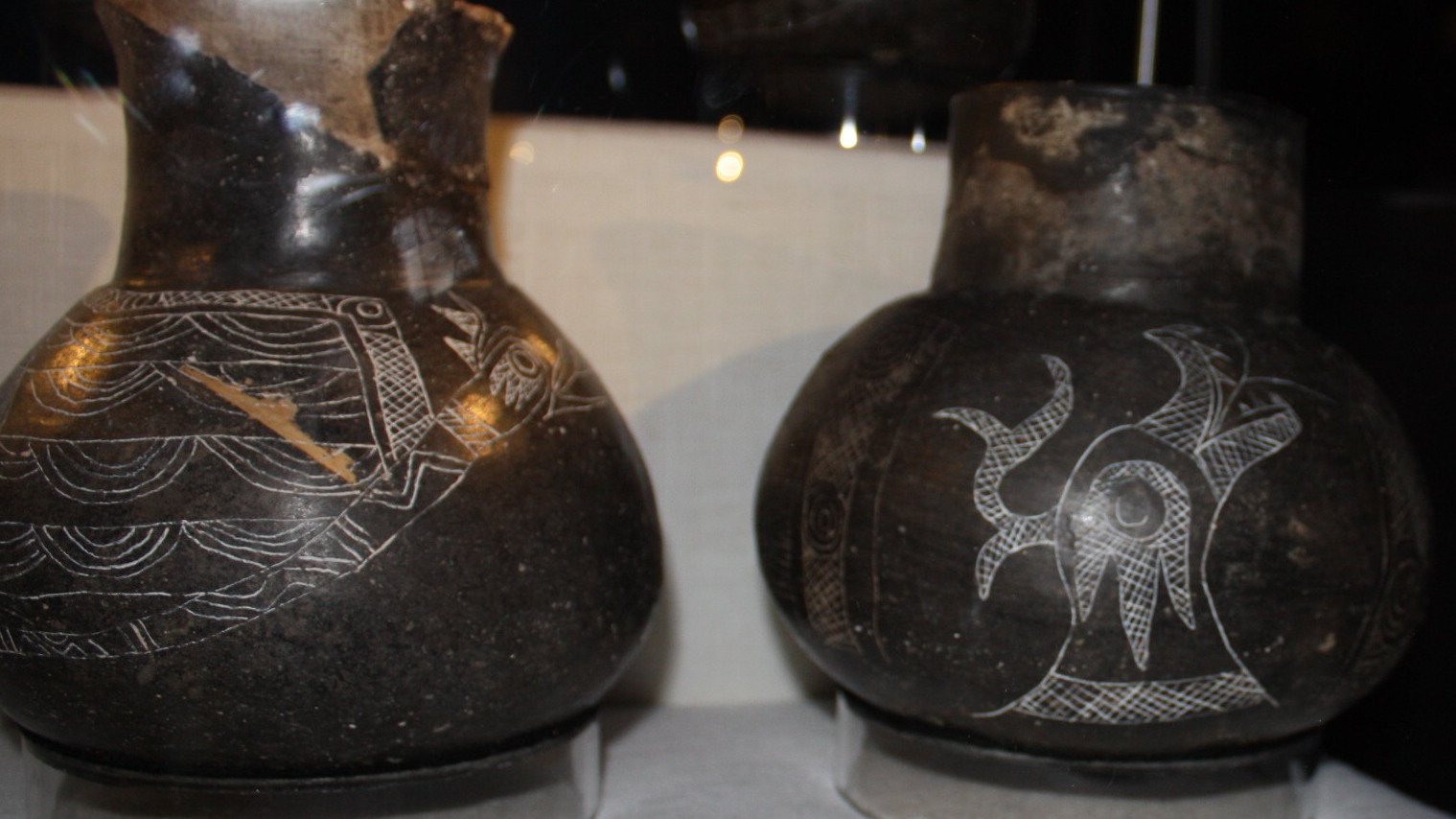
The Great Serpents, the great denizens of the Underworld, were described as powerful beings who were in constant antagonism with the forces of the Upper World, usually represented by the Thunderers (Birdmen or Falcon beings). Although men were to be careful of these beings, they could also be the source of great power. A Shawnee myth tells of the capture and dismemberment of ''Msi Kinepikwa''. The pieces were distributed to the five '' septs'' of the tribe, who kept them in their sacred "medicine bundles".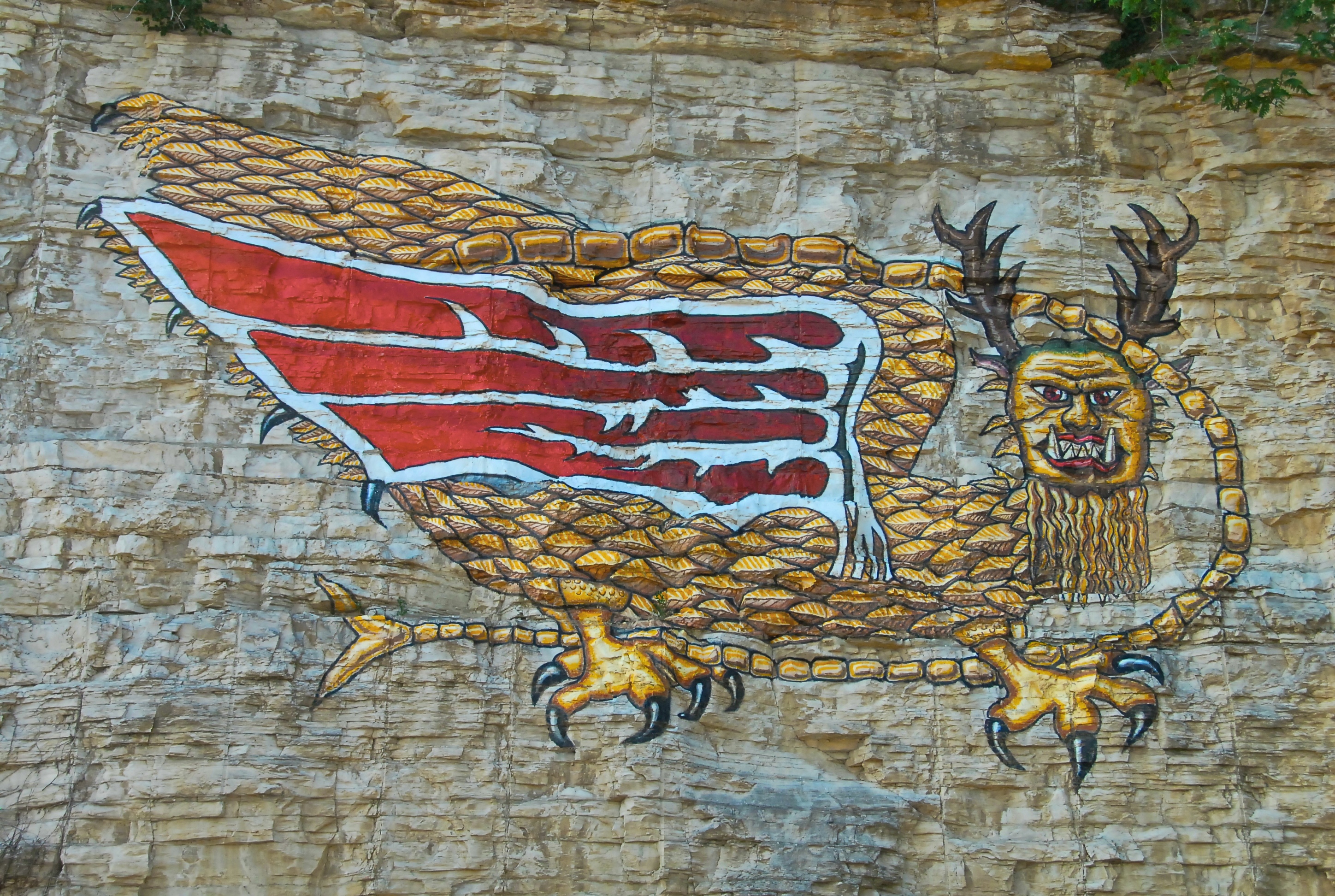
 *
*
archive.is
{{Visual arts by indigenous peoples of the Americas Mississippian culture History of indigenous peoples of North America Pre-Columbian art Native American art Indigenous culture of the Northeastern Woodlands Indigenous culture of the Southeastern Woodlands Native American religion Native American history Southeastern United States 13th-century establishments in North America 1650s disestablishments in North America
 The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts,
The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
, ceremonies
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan origin, via the Latin '' caerimonia''.
Church and civil (secular) ...
, and mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
of the Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
. It coincided with their adoption of maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures (i.e., artwork with similar aesthetics or motifs; maize-based agriculture; and the development of sophisticated cities with large pyramidal structures), scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations.
But, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that their civilizations developed independently.
Obsolete names for this ceremonial complex, found in some anthropological sources, include Buzzard Cult and Southern Death Cult.
Theories and names
The complex operated as an exchange network. This kind of network may be illustrated by a pair ofshell gorget
Shell gorgets are a Native American art form of polished, carved shell pendants worn around the neck. The gorgets are frequently engraved, and are sometimes highlighted with pigments, or fenestrated (pierced with openings).
Shell gorgets were mos ...
s whose representation is so similar as to suggest that they were made by the same artist. One is found in southeast Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
and the other in Spiro Mounds
Spiro Mounds ( 34 LF 40) is an archaeological site located in present-day eastern Oklahoma that remains from an indigenous Indian culture that was part of the major northern Caddoan Mississippian culture. The 80-acre site is located within a flo ...
in Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
. Numerous other pairs of extremely similar gorgets serve to link sites across the entire Southeast. The social organization of the Mississippian culture was based on warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
, which was represented by an array of motifs and symbols in articles made from costly raw materials, such as conch
Conch () is a common name of a number of different medium-to-large-sized sea snails. Conch shells typically have a high spire and a noticeable siphonal canal (in other words, the shell comes to a noticeable point at both ends).
In North Am ...
es from Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
from the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
area and Appalachian Mountains, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
from northern Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
and Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
, pottery from Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, and stone tools sourced from Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, and southern Illinois
Southern Illinois, also known as Little Egypt, is the southern third of Illinois, principally along and south of Interstate 64. Although part of a Midwestern United States, Midwestern state, this region is aligned in culture more with that of th ...
. Such objects occur in elite burials, together with war axes, maces
Mace may refer to:
Spices
* Mace (spice), a spice derived from the aril of nutmeg
* '' Achillea ageratum'', known as English mace, a flowering plant once used as a herb
Weapons
* Mace (bludgeon), a weapon with a heavy head on a solid shaft used ...
, and other weapons. These warrior symbols occur alongside other artifacts, which bear cosmic imagery depicting animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s, human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s, and legendary creature
A legendary creature (also mythical or mythological creature) is a type of fictional entity, typically a hybrid, that has not been proven and that is described in folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses ...
s. This symbolic imagery bound together warfare, cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount (lexicographer), Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in ...
, and nobility into a coherent whole. Some of these categories of artifacts were used as markers of chiefly office, which varied from one location to another. The term Southeast Ceremonial Complex refers to a complex, highly variable set of religious mechanisms that supported the authority of local chiefs.
The ''S.E.C.C.'' was first defined in 1945 by the archaeologists Antonio Waring and Preston Holder
Preston Holder (September 10, 1907, Wabash, Indiana – June 3, 1980, Lincoln, Nebraska) was an American archaeologist and photographer.
In 1930 he entered the University of California, Berkeley, to study anthropology. While there he met photograp ...
as a series of four lists of traits, which they categorized as the ''Southeastern (centered) Ceremonial Complex''. Their concept was of a complex of a specific cult manifestation that originated with Muskogean-speaking peoples in the southern United States. Since then scholars have expanded the original definition, while using its trait lists as a foundation for critical analysis of the entire concept.
In 1989 scholars proposed a more archaeologically based definition for the Mississippian artistic tradition. Jon Muller of Southern Illinois University proposes the classification of the complex into five horizons, with each as a discrete tradition defined by the origin of specific motifs and ritual objects, and the specific developments in long-distance exchange and political structures.
''Mississippian Ideological Interaction Sphere'' horizons
With the redefinition of the complex, some scholars have suggested choosing a new name to exemplify the new understanding of the large body of art symbols classified as the S.E.C.C. Participants of a decade-long series of conferences held at Texas State University have proposed the terms ''"Mississippian Ideological Interaction Sphere"'' or ''"M.I.I.S."'' and ''"Mississippian Art and Ceremonial Complex"'' or ''"M.A.C.C."'' Present theories suggest that the complex developed from pre-existing beliefs spread over the midwest and southeast by the Hopewell Interaction Sphere from 100 BCE to 500 CE. The major expression of the complex developed at the Cahokia site and is known as the Braden Style; it corresponds with the Southern Cult Period horizon defined by Muller. Other regional styles developed as a result of the fusion of ideas borrowed from the Braden Style and pre-existing local expressions of post-Hopewellian traditions.
Projected development
Projected development of Mississippian Art and Ceremonial Complex (M.A.C.C.) styles As the major centers, such as Cahokia, collapsed and the trade networks broke down, the regional styles diverged more from the ''Braden Style'' and from each other. During the ensuing centuries, the local traditions diverged into the religious beliefs and cosmologies of the different historic tribes known to exist at the time of European contact.Cosmology

 Most S.E.C.C. imagery focuses on
Most S.E.C.C. imagery focuses on cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount (lexicographer), Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in ...
and the supernatural beings who inhabit the cosmos. The cosmological map encompassed real, knowable locations, whether in this world or the supernatural reality of the Otherworld. S.E.C.C. iconography portrayed the cosmos in three levels. The Above World or Overworld, was the home of the Thunderers, the Sun, Moon, and Morning Star or Red Horn
Red Horn is a culture hero in Siouan oral traditions, specifically of the Ioway and Hocąk (Winnebago) nations.
He has different names. Only in Hocąk literature is he known as "Red Horn" (''Hešucka''), but among the Ioway and Hocągara both, ...
/ ''"He Who Wears Human Heads For Earrings"'' and represented Order and Stability. The Middle World was the Earth that humans live in. The Beneath World or Under World was a cold, dark place of Chaos that was home to the Underwater Panther and Corn Mother or "Old Woman Who Never Dies".
These three worlds were connected by an ''axis mundi
In astronomy, axis mundi is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles.
In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere.
Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the '' ...
'', usually portrayed as a cedar tree or a striped pole reaching from the Under World to the Over World. Each of the three levels also was believed to have its own sub-levels. Deeply ingrained in the world view was the concept of duality
Duality may refer to:
Mathematics
* Duality (mathematics), a mathematical concept
** Dual (category theory), a formalization of mathematical duality
** Duality (optimization)
** Duality (order theory), a concept regarding binary relations
** Dual ...
and opposition. The beings of the Upper and Under realms were in constant opposition to each other. Ritual and ceremony were the means by which these powerful forces could be accessed and harnessed.
Motifs
Many common motifs in S.E.C.C. artwork are locative symbols that help determine where the action takes place and where the beings originated:Birdman
 The
The falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene.
Adult falcons ...
is one of the most conspicuous symbols of the S.E.C.C. It was simultaneously an avatar
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appearanc ...
of warriors and an object of supplication for a lengthy life, healthy family, and a long line of descendants. Its supernatural origin is placed in the Upper World with a pantheon including the Sun, Moon, and Four Stars. He is most often represented on precious materials, sometimes shell, most often on beaten copper. He dances, costumed with great ground-sweeping wings and a raptor-beaked mask. In his raised right hand he holds a club, prepared to strike. In his left he holds rattles fashioned from human skulls.
At Cahokia, the falcon imagery was elaborated in figural expression. It is associated with warfare, high-stakes gaming, and possibly family dynastic ambitions, symbolized by arrow flights and the rising of the pre-dawn morning star
Morning Star, morning star, or Morningstar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Morning star, most commonly used as a name for the planet Venus when it appears in the east before sunrise
** See also Venus in culture
* Morning star, a name for the star Siri ...
as metaphors for the succession of descendants into the future. Raptor imagery gained prominence during the Hopewell period, but attained its peak in the Braden Style of the early Mississippian period. It survived afterward in the Red Horn
Red Horn is a culture hero in Siouan oral traditions, specifically of the Ioway and Hocąk (Winnebago) nations.
He has different names. Only in Hocąk literature is he known as "Red Horn" (''Hešucka''), but among the Ioway and Hocągara both, ...
mythological cycle and native religion of the Ho-Chunk
The Ho-Chunk, also known as Hoocągra or Winnebago (referred to as ''Hotúŋe'' in the neighboring indigenous Iowa-Otoe language), are a Siouan-speaking Native American people whose historic territory includes parts of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iow ...
(Winnebagos), Osage The Osage Nation, a Native American tribe in the United States, is the source of most other terms containing the word "osage".
Osage can also refer to:
* Osage language, a Dhaegin language traditionally spoken by the Osage Nation
* Osage (Unicode b ...
, Ioway
The Iowa, also known as Ioway, and the Bah-Kho-Je or Báxoje (English: grey snow; Chiwere: Báxoje ich'é) are a Native American Siouan people. Today, they are enrolled in either of two federally recognized tribes, the Iowa Tribe of Oklahoma and ...
, and other plains Siouan
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
peoples. In the Braden Style, the Birdman is divided into four categories.
Red Horn and his sons
TheRed Horn
Red Horn is a culture hero in Siouan oral traditions, specifically of the Ioway and Hocąk (Winnebago) nations.
He has different names. Only in Hocąk literature is he known as "Red Horn" (''Hešucka''), but among the Ioway and Hocągara both, ...
Mythic Cycle is from the Ho Chunk
The Ho-Chunk, also known as Hoocągra or Winnebago (referred to as ''Hotúŋe'' in the neighboring indigenous Iowa-Otoe language), are a Siouan-speaking Native American people whose historic territory includes parts of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iow ...
, or Winnebago people. The mythic cycle of Red Horn and his sons has certain analogies with the Hero Twins mythic cycle of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
. Redhorn was known by many names, including "Morning Star
Morning Star, morning star, or Morningstar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Morning star, most commonly used as a name for the planet Venus when it appears in the east before sunrise
** See also Venus in culture
* Morning star, a name for the star Siri ...
", a reference to his celestial origin, and ''"He who is Struck with Deer Lungs,"'' a possible reference to the Bi-Lobed Arrow Motif. In the episode associated with this name, Red Horn turns into an arrow to win a race. After winning the race, Redhorn creates heads on his earlobes and makes his hair into a long red braid. Thus he becomes known as ''"Redhorn"'' and as ''"He who has Human Heads as Earlobes"''.
In another episode, Redhorn and his friends are challenged by the Giants to play ball
A ball is a round object (usually spherical, but can sometimes be ovoid) with several uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used f ...
(or possibly chunkey) with their lives staked on the outcome. The best Giant player was a woman with long red hair identical to Redhorn's. The little heads on Redhorn's ears caused her to laugh so much that it interfered with her game and the Giants lost. The Giants lost all the other contests as well. Then they challenged Redhorn and his friends to a wrestling match in which they threw all but Red Horn's friend Turtle. Since Redhorn and his fellow spirits lost two out of the three matches, they were all slain. The two wives of Redhorn were pregnant at the time of his death. The sons born to each have red hair, with the older one having heads where his earlobes should be, and the younger one having heads in place of his nipples. The older brother discovers where the Giants keep the heads of Redhorn and his friends. The two boys use their powers to steal the heads from the Giants, whom they wipe out almost completely. The boys bring back to life Redhorn, Storms as He Walks, and Turtle. In honor of this feat, Turtle and "Storms as He Walks" promise the boys special weapons.
In another episode, the sons of Redhorn decide to go on the warpath. The older brother asks "Storms as He Walks" for the Thunderbird War bundle. After some effort, it is produced, but the Thunderbirds demand that it have a case. A friend of the sons of Redhorn offers his own body as its case. The boys take the Thunderbird War bundle and with their followers go on a raid to the other side of the sky.
Many S.E.C.C. images seem to be of Red Horn, his companions, and his sons. The characters in the myth seem to be tied integrally to the pipe ceremony, and its association with kinship and adoption. In fact, the Bi-Lobed Arrow Motif may be a graphic depiction of the calumet. Other images found in S.E.C.C. art show figures with long-nosed god maskette
Long-nosed god maskettes are artifacts made from bone, copper and marine shells (Lightning whelk) associated with the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE) and found in archaeological sites in the Midwestern United States and the Southeastern Uni ...
s on their ears and in place of their nipples.
Great Serpent
The Great Serpent (or Horned Serpent) is the most well-known mythological figure from the S.E.C.C. Its roots go back to Hopewell times, if not earlier. It usually is described as horned and winged, although the wings are more an indicator of its celestial origin than an essential form of the creature. In some versions ofShawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
myths, the serpent is described as a multi-headed monster with one green and one red horn, horns being a manifestation or marker of its power. In other myths, it is described as a one-eyed buffalo with one green and one red horn. The Piasa
The Piasa ( ) or Piasa Bird is a creature from Native American mythology depicted in one of two murals painted by Native Americans on cliffsides above the Mississippi River. Its original location was at the end of a chain of limestone bluffs in ...
figure of the Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a East Coast of the United States, coastal metropolis and the County seat, county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade C ...
was painted on a bluff near present-day Alton, Illinois. It was described as having the body of a panther, four legs, a human head, an impossibly long tail and horns.
''Mishibizhiw'', the Ojibwa
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
underwater panther, was a combination of rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small anim ...
, cougar
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large Felidae, cat native to the Americas. Its Species distribution, range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mamm ...
, deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
, and hawk
Hawks are bird of prey, birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. Th ...
. Other native peoples also gave descriptions of the being, sometimes now referred to as the ''Spirit Otter'', with the majority seeming to belong to one of two extremes, and a multitude in between.
Distribution of belief
The Great Serpents, the great denizens of the Underworld, were described as powerful beings who were in constant antagonism with the forces of the Upper World, usually represented by the Thunderers (Birdmen or Falcon beings). Although men were to be careful of these beings, they could also be the source of great power. A Shawnee myth tells of the capture and dismemberment of ''Msi Kinepikwa''. The pieces were distributed to the five '' septs'' of the tribe, who kept them in their sacred "medicine bundles".

Artifacts
S.E.C.C. motifs have been found on a variety of non-perishable materials, including marine shell, ceramics,chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a prec ...
(Duck River cache
The Duck River cache is the archaeological collection of 46 Mississippian culture artifacts discovered by a worker on at the Link Farm site in Middle Tennessee in December 1894.
Chert objects
The cache has been called "perhaps the most specta ...
), carved stone
Stone carving is an activity where pieces of rough natural stone are shaped by the controlled removal of stone. Owing to the permanence of the material, stone work has survived which was created during our prehistory or past time.
Work carried ...
, and copper (Wulfing cache
The Wulfing cache, or Malden plates, are eight Mississippian copper plates crafted by peoples of the Mississippian culture. They were discovered in Dunklin County, Missouri in 1906 by Ray Grooms, a farmer, while plowing a field south of Malden. ...
and Etowah plates
The Etowah plates, including the Rogan Plates, are a collection of Mississippian copper plates discovered in Mound C at the Etowah Indian Mounds near Cartersville, Georgia. Many of the plates display iconography that archaeologists have classified ...
). Undoubtedly many other materials also were used, but haven't survived the intervening centuries. It may be judged by looking at the remaining artifacts that S.E.C.C. practitioners worked with feathers and designs woven into cloth, practiced body painting, and possibly tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several Process of tatt ...
ing, as well as having pierced ears. One surviving painting found on a baked clay floor at the Wickliffe Mounds
Wickliffe Mounds ( 15 BA 4) is a prehistoric, Mississippian culture archaeological site located in Ballard County, Kentucky, just outside the town of Wickliffe, about from the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi rivers. Archaeological inve ...
site suggests they also painted designs in and on their dwellings. Paintings displaying S.E.C.C. imagery also have been found in caves, most notably Mud Glyph Cave in Tennessee. Animal images, serpents, and warrior figures occur, as well as winged warriors, horned snakes, stylized birds, maces, and arrows. Their location underneath the Earth probably reflect aspects of Mississippian myth and cosmology concerning the (perhaps sacred) precincts beneath the earth.
Sites
Alligator Effigy Mound
The Alligator Effigy Mound is an effigy mound in Granville, Ohio, United States. The mound is believed to have been built between AD 800 and 1200 by people of the Fort Ancient culture. The mound was likely a ceremonial site, as it was not use ...
* Angel Mounds
* Cahokia
* Castalian Springs Mound Site
The Castalian Springs Mound State Historic Site ( 40SU14) (also known as Bledsoe's Lick Mound and Cheskiki Mound) is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located near the small unincorporated community of Castalian Springs in Sumner County ...
* Etowah Indian Mounds
* Hiwassee Island
Hiwassee Island, also known as Jollys Island and Benham Island, is located in Meigs County, Tennessee, at the confluence of the Tennessee and Hiwassee Rivers. It is about northeast of Chattanooga. The island was the second largest land mass on the ...
* Kincaid Mounds State Historic Site
* Kolomoki Mounds
The Kolomoki Mounds is one of the largest and earliest Woodland period earthwork mound complexes in the Southeastern United States and is the largest in Georgia. Constructed from 350CE to 600CE, the mound complex is located in southwest Georgi ...
* Lake Jackson Mounds Archaeological State Park
* Mangum Mound Site
* Moundville Archaeological Site
Moundville Archaeological Site, also known as the Moundville Archaeological Park, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site on the Black Warrior River in Hale County, near the modern city of Tuscaloosa, Alabama. Extensive archaeological inv ...
* Ocmulgee National Monument
Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park (formerly Ocmulgee National Monument) in Macon, Georgia, United States preserves traces of over ten millennia of culture from the Native Americans in the Southeastern Woodlands. Its chief remains are majo ...
* Serpent Mound
* Spiro Mounds
Spiro Mounds ( 34 LF 40) is an archaeological site located in present-day eastern Oklahoma that remains from an indigenous Indian culture that was part of the major northern Caddoan Mississippian culture. The 80-acre site is located within a flo ...
* Town Creek Indian Mound
Town Creek Indian Mound ( 31 MG 2) is a prehistoric Native American archaeological site located near present-day Mount Gilead, Montgomery County, North Carolina, in the United States. The site, whose main features are a platform mound with a su ...
* Wickliffe Mounds
Wickliffe Mounds ( 15 BA 4) is a prehistoric, Mississippian culture archaeological site located in Ballard County, Kentucky, just outside the town of Wickliffe, about from the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi rivers. Archaeological inve ...
* Winterville site
The Winterville site (Smithsonian trinomial, 22 WS 500) is a major archaeological site in unincorporated area, unincorporated Washington County, Mississippi, north of Greenville, Mississippi, Greenville and along the river. It consists of major ...
References
External links
archive.is
{{Visual arts by indigenous peoples of the Americas Mississippian culture History of indigenous peoples of North America Pre-Columbian art Native American art Indigenous culture of the Northeastern Woodlands Indigenous culture of the Southeastern Woodlands Native American religion Native American history Southeastern United States 13th-century establishments in North America 1650s disestablishments in North America