Soul Blazer Box Art on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or
 In the
In the
 According to some
According to some
 The "origin of the soul" has provided a vexing question in Christianity. The major theories put forward include soul creationism,
The "origin of the soul" has provided a vexing question in Christianity. The major theories put forward include soul creationism,
 ;Protestantism
Protestants generally believe in the soul's existence and immortality, but fall into two major camps about what this means in terms of an
;Protestantism
Protestants generally believe in the soul's existence and immortality, but fall into two major camps about what this means in terms of an
Is The Buddhist ‘No-Self’ Doctrine Compatible With Pursuing Nirvana?
, Philosophy Now In
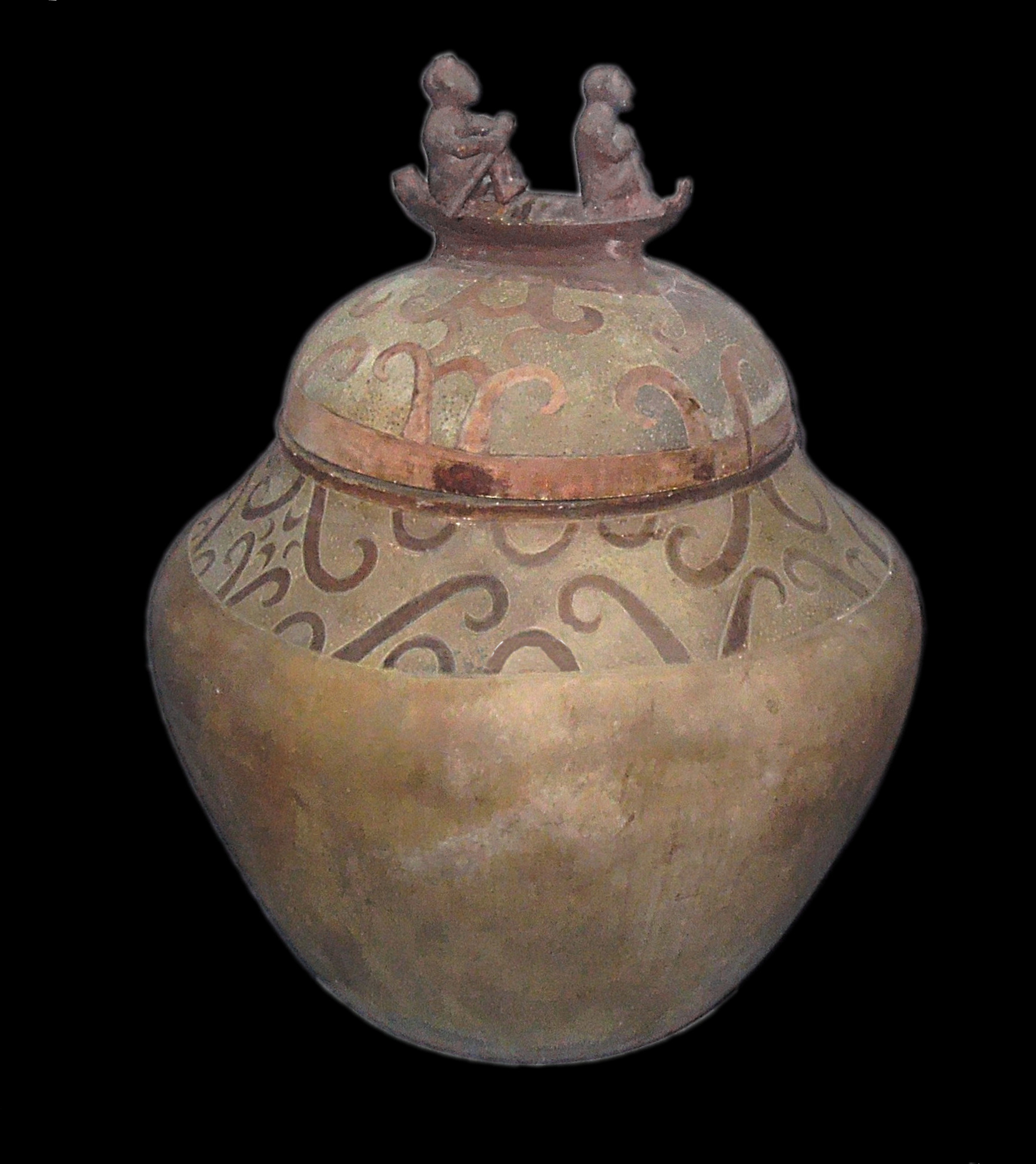 Soul dualism (also called "multiple souls" or "dualistic pluralism") is a common belief in Shamanism, and is essential in the universal and central concept of "soul flight" (also called "soul journey", "out-of-body experience", "Religious ecstasy, ecstasy", or "astral projection"). It is the belief that humans have two or more souls, generally termed the "body soul" (or "life soul") and the "free soul". The former is linked to bodily functions and awareness when awake, while the latter can freely wander during sleep or trance states. In some cases, there are a plethora of soul types with different functions.
Soul dualism and multiple souls are prominent in the traditional animistic beliefs of the Austronesian peoples, the Hun and po, Chinese people (Hun and po, ''hún'' and ''pò''), the Tibetan people, most Ethnic groups of Africa, African peoples, most Indigenous peoples of the Americas#North America, Native North Americans, ancient South Asian peoples, Northern Eurasian peoples, and in Ancient Egyptians (the Ancient Egyptian conception of the soul, ''ka'' and ''ba'').
The belief in soul dualism is found throughout most Austronesian people, Austronesian shamanistic traditions. The reconstructed Proto-Austronesian word for the "body soul" is ''*nawa'' ("breath", "life", or "vital spirit"). It is located somewhere in the abdominal cavity, often in the liver or the heart (Proto-Austronesian ''*qaCay''). The "free soul" is located in the head. Its names are usually derived from Proto-Austronesian ''*qaNiCu'' ("ghost", "spirit [of the dead]"), which also apply to other non-human nature spirits. The "free soul" is also referred to in names that literally mean "twin" or "double", from Proto-Austronesian ''*duSa'' ("two"). A virtuous person is said to be one whose souls are in harmony with each other, while an evil person is one whose souls are in conflict.
The "free soul" is said to leave the body and journey to the Spirit world (spiritualism), spirit world during sleep, trance, trance-like states, delirium, insanity, and death. The duality is also seen in the healing traditions of Austronesian shamans, where illnesses are regarded as a "soul loss" and thus to heal the sick, one must "return" the "free soul" (which may have been stolen by an evil spirit or got lost in the spirit world) into the body. If the "free soul" can not be returned, the afflicted person dies or goes permanently insane.
In some ethnic groups, there can also be more than two souls. Like among the Tagbanwa people, where a person is said to have six souls – the "free soul" (which is regarded as the "true" soul) and five secondary souls with various functions.
Several Inuit groups believe that a person has more than one type of soul. One is associated with respiration, the other can accompany the body as a shadow. In some cases, it is connected to Inuit religion, shamanistic beliefs among the various Inuit groups. Also Caribou Inuit groups believed in several types of souls.
The shaman heals within the spiritual dimension by returning 'lost' parts of the human soul from wherever they have gone. The shaman also cleanses excess negative energies, which confuse or pollute the soul.
Soul dualism (also called "multiple souls" or "dualistic pluralism") is a common belief in Shamanism, and is essential in the universal and central concept of "soul flight" (also called "soul journey", "out-of-body experience", "Religious ecstasy, ecstasy", or "astral projection"). It is the belief that humans have two or more souls, generally termed the "body soul" (or "life soul") and the "free soul". The former is linked to bodily functions and awareness when awake, while the latter can freely wander during sleep or trance states. In some cases, there are a plethora of soul types with different functions.
Soul dualism and multiple souls are prominent in the traditional animistic beliefs of the Austronesian peoples, the Hun and po, Chinese people (Hun and po, ''hún'' and ''pò''), the Tibetan people, most Ethnic groups of Africa, African peoples, most Indigenous peoples of the Americas#North America, Native North Americans, ancient South Asian peoples, Northern Eurasian peoples, and in Ancient Egyptians (the Ancient Egyptian conception of the soul, ''ka'' and ''ba'').
The belief in soul dualism is found throughout most Austronesian people, Austronesian shamanistic traditions. The reconstructed Proto-Austronesian word for the "body soul" is ''*nawa'' ("breath", "life", or "vital spirit"). It is located somewhere in the abdominal cavity, often in the liver or the heart (Proto-Austronesian ''*qaCay''). The "free soul" is located in the head. Its names are usually derived from Proto-Austronesian ''*qaNiCu'' ("ghost", "spirit [of the dead]"), which also apply to other non-human nature spirits. The "free soul" is also referred to in names that literally mean "twin" or "double", from Proto-Austronesian ''*duSa'' ("two"). A virtuous person is said to be one whose souls are in harmony with each other, while an evil person is one whose souls are in conflict.
The "free soul" is said to leave the body and journey to the Spirit world (spiritualism), spirit world during sleep, trance, trance-like states, delirium, insanity, and death. The duality is also seen in the healing traditions of Austronesian shamans, where illnesses are regarded as a "soul loss" and thus to heal the sick, one must "return" the "free soul" (which may have been stolen by an evil spirit or got lost in the spirit world) into the body. If the "free soul" can not be returned, the afflicted person dies or goes permanently insane.
In some ethnic groups, there can also be more than two souls. Like among the Tagbanwa people, where a person is said to have six souls – the "free soul" (which is regarded as the "true" soul) and five secondary souls with various functions.
Several Inuit groups believe that a person has more than one type of soul. One is associated with respiration, the other can accompany the body as a shadow. In some cases, it is connected to Inuit religion, shamanistic beliefs among the various Inuit groups. Also Caribou Inuit groups believed in several types of souls.
The shaman heals within the spiritual dimension by returning 'lost' parts of the human soul from wherever they have gone. The shaman also cleanses excess negative energies, which confuse or pollute the soul.
 In theological reference to the soul, the terms "life" and "death" are viewed as emphatically more definitive than the common concepts of "life, biological life" and "biological death". Because the soul is said to be transcendent of the ''matter, material existence,'' and is said to have (potentially) immortality, eternal life, the death of the soul is likewise said to be an ''eternal death''. Thus, in the concept of divine judgment, God is commonly said to have options with regard to the dispensation of souls, ranging from Heaven (i.e., angels) to
In theological reference to the soul, the terms "life" and "death" are viewed as emphatically more definitive than the common concepts of "life, biological life" and "biological death". Because the soul is said to be transcendent of the ''matter, material existence,'' and is said to have (potentially) immortality, eternal life, the death of the soul is likewise said to be an ''eternal death''. Thus, in the concept of divine judgment, God is commonly said to have options with regard to the dispensation of souls, ranging from Heaven (i.e., angels) to
 Drawing on the words of his teacher Socrates, Plato considered the psyche to be the
Drawing on the words of his teacher Socrates, Plato considered the psyche to be the
 Aristotle (384–322 BCE) defined the soul, or ''Psūchê'' (ψυχή), as the "first actuality" of a naturally organized body, and argued against its separate existence from the physical body. In Aristotle's view, the primary activity, or full actualization, of a living thing constitutes its soul. For example, the full actualization of an eye, as an independent organism, is to see (its purpose or final cause). Another example is that the full actualization of a human being would be living a fully functional human life in accordance with reason (which he considered to be a faculty unique to humanity). For Aristotle, the soul is the organization of the form and matter of a natural being which allows it to strive for its full actualization. This organization between form and matter is necessary for any activity, or functionality, to be possible in a natural being. Using an artifact (non-natural being) as an example, a house is a building for human habituation, but for a house to be actualized requires the material (wood, nails, bricks, etc.) necessary for its actuality (i.e. being a fully functional house). However, this does not imply that a house has a soul. In regards to artifacts, the source of motion that is required for their full actualization is outside of themselves (for example, a builder builds a house). In natural beings, this source of motion is contained within the being itself. Aristotle elaborates on this point when he addresses the faculties of the soul.
The various faculties of the soul, such as nutrition, movement (peculiar to animals), reason (peculiar to humans), sensation (special, common, and incidental) and so forth, when exercised, constitute the "second" actuality, or fulfillment, of the capacity to be alive. For example, someone who falls asleep, as opposed to someone who falls dead, can wake up and live their life, while the latter can no longer do so.
Aristotle identified three hierarchical levels of natural beings: plants, animals, and people, having three different degrees of soul: ''Bios'' (life), ''Zoë'' (animate life), and ''Psuchë'' (self-conscious life). For these groups, he identified three corresponding levels of soul, or biological activity: the nutritive activity of growth, sustenance and reproduction which all life shares (''Bios''); the self-willed motive activity and sensory faculties, which only animals and people have in common (''Zoë''); and finally "reason", of which people alone are capable (''Pseuchë'').
Aristotle's discussion of the soul is in his work, ''De Anima'' (''
Aristotle (384–322 BCE) defined the soul, or ''Psūchê'' (ψυχή), as the "first actuality" of a naturally organized body, and argued against its separate existence from the physical body. In Aristotle's view, the primary activity, or full actualization, of a living thing constitutes its soul. For example, the full actualization of an eye, as an independent organism, is to see (its purpose or final cause). Another example is that the full actualization of a human being would be living a fully functional human life in accordance with reason (which he considered to be a faculty unique to humanity). For Aristotle, the soul is the organization of the form and matter of a natural being which allows it to strive for its full actualization. This organization between form and matter is necessary for any activity, or functionality, to be possible in a natural being. Using an artifact (non-natural being) as an example, a house is a building for human habituation, but for a house to be actualized requires the material (wood, nails, bricks, etc.) necessary for its actuality (i.e. being a fully functional house). However, this does not imply that a house has a soul. In regards to artifacts, the source of motion that is required for their full actualization is outside of themselves (for example, a builder builds a house). In natural beings, this source of motion is contained within the being itself. Aristotle elaborates on this point when he addresses the faculties of the soul.
The various faculties of the soul, such as nutrition, movement (peculiar to animals), reason (peculiar to humans), sensation (special, common, and incidental) and so forth, when exercised, constitute the "second" actuality, or fulfillment, of the capacity to be alive. For example, someone who falls asleep, as opposed to someone who falls dead, can wake up and live their life, while the latter can no longer do so.
Aristotle identified three hierarchical levels of natural beings: plants, animals, and people, having three different degrees of soul: ''Bios'' (life), ''Zoë'' (animate life), and ''Psuchë'' (self-conscious life). For these groups, he identified three corresponding levels of soul, or biological activity: the nutritive activity of growth, sustenance and reproduction which all life shares (''Bios''); the self-willed motive activity and sensory faculties, which only animals and people have in common (''Zoë''); and finally "reason", of which people alone are capable (''Pseuchë'').
Aristotle's discussion of the soul is in his work, ''De Anima'' (''
''The Myth of an Afterlife: The Case against Life After Death''
Rowman & Littlefield. * Robert L. Park, Park, Robert L. (2009). ''Superstition: Belief in the Age of Science''. Princeton University Press. * Erwin Rohde, Rohde, Erwin. (1925)
''Psyche: The Cult of Souls and Belief in Immortality Among the Greeks''
London: Routledge, Kegan Paul, Trench, Trübner & Co., Ltd. * Ryle, Gilbert. (1949) ''The Concept of Mind'', London: Hutchinson. * Spenard, Michael (2011
"Dueling with Dualism: the forlorn quest for the immaterial soul"
essay. An historical account of mind-body duality and a comprehensive conceptual and empirical critique on the position. * Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, Richard. (1997). ''The Evolution of the Soul''. Oxford: Oxford University Press. * Leibowitz, Aryeh. (2018). The Neshama: A Study of the Human Soul. Feldheim Publishers. * * Translation of the original:
Quantum Theory Won’t Save The Soul
What Science Really Says About the Soul
by Stephen Cave
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy entry on Ancient Theories of the Soul
The soul in Judaism
at Chabad.org
The Old Testament Concept of the Soul
by Heinrich J. Vogel]
Body, Soul and Spirit
Article in th
Journal of Biblical Accuracy
Is Another Human Living Inside You?
*
"The Soul"
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Richard Sorabji, Ruth Padel and Martin Palmer (''In Our Time'', 6 June 2002) {{Authority control Conceptions of self Concepts in metaphysics Dualism (philosophy of mind) Ghosts Metaphysics of religion Mind Religious philosophical concepts Religious belief and doctrine Vitalism
essence
Essence ( la, essentia) is a polysemic term, used in philosophy and theology as a designation for the property or set of properties that make an entity or substance what it fundamentally is, and which it has by necessity, and without which it ...
of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun ''soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun ''soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest attes ...
'' is derived from Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest attestations reported in the ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a com ...
'' are from the 8th century. In King Alfred
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bot ...
's translation of ''De Consolatione Philosophiae
''On the Consolation of Philosophy'' ('' la, De consolatione philosophiae'')'','' often titled as ''The Consolation of Philosophy'' or simply the ''Consolation,'' is a philosophical work by the Roman statesman Boethius. Written in 523 while he ...
'', it is used to refer to the immaterial, spiritual, or thinking aspect of a person, as contrasted with the person's physical body; in the Vespasian Psalter
The Vespasian Psalter (London, British Library, Cotton Vespasian A I) is an Anglo-Saxon illuminated psalter decorated in a partly Insular style produced in the second or third quarter of the 8th century. It contains an interlinear gloss in Old En ...
77.50, it means "life" or "animate existence".
The Old English word is cognate with other historical Germanic terms for the same idea, including Old Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries along the North Sea coast, roughly between the mouths of the Rhine and Weser rivers. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland (today's Northern Friesl ...
''sēle, sēl'' (which could also mean "salvation", or "solemn oath"), Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
''saiwala'', Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
''sēula, sēla'', Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It i ...
''sēola'', and Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and t ...
''sāla''. Present-day cognates include Dutch ''ziel'' and German ''Seele''.
Religious views
InJudaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
and in some Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
denominations, only human beings have immortal souls (although immortality is disputed within Judaism and the concept of immortality was most likely influenced by Plato). For example, Thomas Aquinas, borrowing directly from Aristotle's ''On the Soul
''On the Soul'' (Greek: , ''Peri Psychēs''; Latin: ''De Anima'') is a major treatise written by Aristotle c. 350 BC. His discussion centres on the kinds of souls possessed by different kinds of living things, distinguished by their different op ...
'', attributed "soul" (''anima
Anima may refer to:
Animation
* Ánima (company), a Mexican animation studio founded in 2002
* Córdoba International Animation Festival – ANIMA, in Argentina
Religion and philosophy
* Animism, the belief that objects, places, and creatures ...
'') to all organisms but argued that only human souls are immortal. Other religions (most notably Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current ...
) believe that all living things from the smallest bacterium to the largest of mammals are the souls themselves (Atman Atman or Ātman may refer to:
Film
* ''Ātman'' (1975 film), a Japanese experimental short film directed by Toshio Matsumoto
* ''Atman'' (1997 film), a documentary film directed by Pirjo Honkasalo
People
* Pavel Atman (born 1987), Russian hand ...
, jiva
''Jiva'' ( sa, जीव, IAST: ) is a living being or any entity imbued with a life force in Hinduism and Jīva (Jainism), Jainism. The word itself originates from the Sanskrit verb-root ''jīv'', which translates as 'to breathe' or 'to live'. ...
) and have their physical representative (the body) in the world. The actual self
The self is an individual as the object of that individual’s own reflective consciousness. Since the ''self'' is a reference by a subject to the same subject, this reference is necessarily subjective. The sense of having a self—or ''selfhood ...
is the soul, while the body is only a mechanism to experience the karma of that life. Thus if one sees a tiger then there is a self-conscious identity residing in it (the soul), and a physical representative (the whole body of the tiger, which is observable) in the world. Some teach that even non-biological entities (such as rivers and mountains) possess souls. This belief is called animism
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—Animal, animals, Plant, plants, Ro ...
.
Ancient Near East
 In the
In the ancient Egyptian religion
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with many deities believed to be present in, and in control ...
, an individual was believed to be made up of various elements, some physical and some spiritual. Similar ideas are found in ancient Assyrian and Babylonian religion. The Kuttamuwa stele
The Kuttamuwa stele is an 800-pound basalt funerary stele with an Aramaic inscription referring to Kuttamuwa, an 8th-century BC royal official. It was found in Sam'al, in southeastern Turkey, in 2008, by the Neubauer Expedition of the Oriental ...
, a funeral stele for an 8th-century BCE royal official from Sam'al, describes Kuttamuwa Kuttamuwa was an 8th-century BC royal official from Aramean city Sam'al named on the Kuttamuwa stele, that was to be erected upon his death. The inscription in Aramaic requested that his mourners commemorate his life and his afterlife with feasts " ...
requesting that his mourners commemorate his life and his afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving ess ...
with feasts "for my soul that is in this stele". It is one of the earliest references to a soul as a separate entity from the body. The basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
stele is tall and wide. It was uncovered in the third season of excavations by the Neubauer Expedition of the Oriental Institute in Chicago, Illinois.
Baháʼí Faith
TheBaháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
affirms that "the soul is a sign of God, a heavenly gem whose reality the most learned of men hath failed to grasp, and whose mystery no mind, however acute, can ever hope to unravel". Bahá'u'lláh stated that the soul not only continues to live after the physical death of the human body, but is, in fact, immortal. Heaven can be seen partly as the soul's state of nearness to God; and hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
as a state of remoteness from God. Each state follows as a natural consequence of individual efforts, or the lack thereof, to develop spiritually. Bahá'u'lláh taught that individuals have no existence prior to their life here on earth and the soul's evolution is always towards God and away from the material world.
Christianity
 According to some
According to some Christian eschatology
Christian eschatology, a major branch of study within Christian theology, deals with "last things". Such eschatology – the word derives from two Greek roots meaning "last" () and "study" (-) – involves the study of "end things", whether of ...
, when people die, their souls will be judged by God and determined to go to Heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
or to Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
awaiting a resurrection or the resurrection
Resurrection or anastasis is the concept of coming back to life after death. In a number of religions, a dying-and-rising god is a deity which dies and is resurrected. Reincarnation is a similar process hypothesized by other religions, which ...
. The oldest existing branches of Christianity, the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and the Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
and Oriental
The Orient is a term for the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of ''Occident'', the Western World. In English, it is largely a metonym for, and coterminous with, the ...
Orthodox churches, adhere to this view, as well as many Protestant denominations. Some Protestant Christians understand the soul as "life,” and believe that the dead have no conscious existence until after the resurrection (Christian conditionalism
In Christian theology, conditionalism or conditional immortality is a concept in which the gift of immortality is attached to (conditional upon) belief in Jesus Christ. This doctrine is based in part upon another biblical argument, that the human ...
). Some Protestant Christians believe that the souls and bodies of the unrighteous will be destroyed in Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
rather than suffering eternally (annihilationism
In Christianity, annihilationism (also known as extinctionism or destructionism) is the belief that after the Last Judgment, all unsaved human beings, all fallen angels (all of the damned) and Satan himself will be totally destroyed so as to no ...
). Believers will inherit eternal life either in Heaven, or in a Kingdom of God
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms Kingdom of God and Kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" b ...
on earth, and enjoy eternal fellowship with God. Other Christians reject the punishment of the soul.
Origin of the soul
 The "origin of the soul" has provided a vexing question in Christianity. The major theories put forward include soul creationism,
The "origin of the soul" has provided a vexing question in Christianity. The major theories put forward include soul creationism, traducianism
In Christian theology, traducianism is a doctrine about the origin of the soul holding that this immaterial aspect is transmitted through natural generation along with the body, the material aspect of human beings. That is, human propagation is of ...
, and pre-existence
Pre-existence, preexistence, beforelife, or premortal existence, is the belief that each individual human soul existed before mortal conception, and at some point before birth enters or is placed into the body. Concepts of pre-existence can enco ...
. According to soul creationism, God creates each individual soul directly, either at the moment of conception or some later time. According to traducianism, the soul comes from the parents by natural generation. According to the preexistence theory, the soul exists before the moment of conception. There have been differing thoughts regarding whether human embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
s have souls from conception, or whether there is a point between conception and birth where the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal deve ...
acquires a soul, consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
, and/or personhood
Personhood or personality is the status of being a person. Defining personhood is a controversial topic in philosophy and law and is closely tied with legal and political concepts of citizenship, equality, and liberty. According to law, only a leg ...
. Stances in this question might play a role in judgements on the morality of abortion
The abortion debate is a longstanding, ongoing controversy that touches on the moral, legal, medical, and religious aspects of induced abortion. In English-speaking countries, the debate most visibly polarizes around adherents of the self-describ ...
.
Trichotomy of the soul
Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berbers, Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia (Roman pr ...
(354-430), one of western Christianity's most influential early Christian thinkers, described the soul as "a special substance, endowed with reason, adapted to rule the body". Some Christians espouse a trichotomic view of humans, which characterizes humans as consisting of a body (''soma''), soul (''psyche''), and spirit (''pneuma''). However, the majority of modern Bible scholars point out how the concepts of "spirit" and of "soul" are used interchangeably in many biblical passages, and so hold to dichotomy: the view that each human comprises a body and a soul. Paul said that the "body wars against" the soul, "For the word of God is living and active and sharper than any two-edged sword, and piercing as far as the division of soul and spirit" (Heb 4:12 NASB), and that "I buffet my body", to keep it under control.
Views of various denominations
; Roman Catholicism The presentCatechism of the Catholic Church
The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' ( la, Catechismus Catholicae Ecclesiae; commonly called the ''Catechism'' or the ''CCC'') is a catechism promulgated for the Catholic Church by Pope John Paul II in 1992. It aims to summarize, in book for ...
states that the term soul
: “refers to the innermost aspect of ersons that which is of greatest value in hem
A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the ga ...
that by which hey are
Hey or Hey! may refer to:
Music
* Hey (band), a Polish rock band
Albums
* Hey (Andreas Bourani album), ''Hey'' (Andreas Bourani album) or the title song (see below), 2014
* Hey! (Julio Iglesias album), ''Hey!'' (Julio Iglesias album) or the ti ...
most especially in God's image: ‘soul’ signifies the spiritual principle in umanity��.
All souls living and dead will be judged by Jesus Christ when he comes back to earth. The Catholic Church teaches that the existence of each individual soul is dependent wholly upon God:
: "The doctrine of the faith affirms that the spiritual and immortal soul is created immediately by God."
afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving ess ...
. Some, following John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
, believe that the soul persists as consciousness after death. Others, following Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Reformation, Protestant Refo ...
, believe that the soul dies with the body, and is unconscious ("sleeps") until the resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead ( Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died ...
.
;Adventism:
Various new religious movement
A new religious movement (NRM), also known as alternative spirituality or a new religion, is a religious or spiritual group that has modern origins and is peripheral to its society's dominant religious culture. NRMs can be novel in origin or th ...
s deriving from Adventism
Adventism is a branch of Protestant Christianity that believes in the imminent Second Coming (or the "Second Advent") of Jesus Christ. It originated in the 1830s in the United States during the Second Great Awakening when Baptist preacher Wil ...
— including Christadelphians
The Christadelphians () or Christadelphianism are a restorationist and millenarian Christian group who hold a view of biblical unitarianism. There are approximately 50,000 Christadelphians in around 120 countries. The movement developed in the U ...
, Seventh-day Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventism, Adventist Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the Names of the days of the week#Numbered days of the week, seventh day of the ...
, and Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
— similarly believe that the dead do not possess a soul separate from the body and are unconscious until the resurrection.
;Latter-day Saints (‘Mormonism’):
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
teaches that the spirit and body together constitute the Soul of Man (Mankind). "The spirit and the body are the soul of man." Latter-day Saints believe that the soul is the union of a pre-existing, God-made spirit and a temporal body, which is formed by physical conception on earth.
After death, the spirit continues to live and progress in the Spirit world until the resurrection
Resurrection or anastasis is the concept of coming back to life after death. In a number of religions, a dying-and-rising god is a deity which dies and is resurrected. Reincarnation is a similar process hypothesized by other religions, which ...
, when it is reunited with the body that once housed it. This reuniting of body and spirit results in a perfect soul that is immortal, and eternal, and capable of receiving a fulness of joy.
Latter-day Saint cosmology also describes "intelligences" as the essence of consciousness or agency. These are co-eternal with God, and animate the spirits. The union of a newly-created spirit body with an eternally-existing intelligence constitutes a "spirit birth" and justifies God's title "Father of our spirits".
Confucianism
Some Confucian traditions contrast a spiritual soul with a corporeal soul.Hinduism
''Ātman'' is aSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
word that means inner self
The self is an individual as the object of that individual’s own reflective consciousness. Since the ''self'' is a reference by a subject to the same subject, this reference is necessarily subjective. The sense of having a self—or ''selfhood ...
or soul.David Lorenzen
David N. Lorenzen is a British–American historian, scholar of Religious studies, essayist, and emeritus professor of South Asian history at the Centre for Asian and African studies, El Colegio de México in Mexico City.
He is chiefly notable ...
(2004), The Hindu World (Editors: Sushil Mittal and Gene Thursby), Routledge, , pp. 208–09, Quote: "Advaita and nirguni movements, on the other hand, stress an interior mysticism in which the devotee seeks to discover the identity of individual soul (atman) with the universal ground of being (brahman) or to find god within himself". In Hindu philosophy
Hindu philosophy encompasses the philosophies, world views and teachings of Hinduism that emerged in Ancient India which include six systems ('' shad-darśana'') – Samkhya, Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Mimamsa and Vedanta.Andrew Nicholson (20 ...
, especially in the Vedanta
''Vedanta'' (; sa, वेदान्त, ), also ''Uttara Mīmāṃsā'', is one of the six (''āstika'') schools of Hindu philosophy. Literally meaning "end of the Vedas", Vedanta reflects ideas that emerged from, or were aligned with, t ...
school of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Ātman is the first principle
In philosophy and science, a first principle is a basic proposition or assumption that cannot be deduced from any other proposition or assumption.
First principles in philosophy are from First Cause attitudes and taught by Aristotelians, and nuanc ...
, the ''true'' self of an individual beyond identification with phenomena, the essence of an individual. In order to attain liberation (moksha), a human being must acquire self-knowledge (atma jnana), which is to realize that one's true self (Ātman) is identical with the transcendent self Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' ( sa, ब्रह्मन्) connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality in the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part X ...
according to Advaita Vedanta
''Advaita Vedanta'' (; sa, अद्वैत वेदान्त, ) is a Hinduism, Hindu sādhanā, a path of spiritual discipline and experience, and the oldest extant tradition of the Āstika and nāstika, orthodox Hindu school Ved ...
.
The six orthodox schools of Hinduism believe that there is Ātman (self, essence) in every being.K. N. Jayatilleke
Kulatissa Nanda Jayatilleke (1 November 1920 – 23 July 1970) was an internationally recognised authority on Buddhist philosophy whose book ''Early Buddhist Theory of Knowledge'' has been described as "an outstanding philosophical interpretatio ...
(2010), Early Buddhist Theory of Knowledge, , pp. 246–49, from note 385 onwards; Steven Collins (1994), Religion and Practical Reason (Editors: Frank Reynolds, David Tracy), State Univ of New York Press, , p. 64; "Central to Buddhist soteriology is the doctrine of not-self (Pali: anattā, Sanskrit: anātman, the opposed doctrine of ātman is central to Brahmanical thought). Put very briefly, this is the uddhistdoctrine that human beings have no soul, no self, no unchanging essence."; Edward Roer (Translator), to ''Brihad Aranyaka Upanishad'', pp. 2–4; Katie Javanaud (2013)Is The Buddhist ‘No-Self’ Doctrine Compatible With Pursuing Nirvana?
, Philosophy Now In
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current ...
, a ''jiva'' ( sa, जीव, , alternative spelling ''jiwa''; hi, जीव, , alternative spelling ''jeev'') is a living being, or any entity imbued with a life force.
The concept of ''jiva'' in Jainism is similar to ''atman Atman or Ātman may refer to:
Film
* ''Ātman'' (1975 film), a Japanese experimental short film directed by Toshio Matsumoto
* ''Atman'' (1997 film), a documentary film directed by Pirjo Honkasalo
People
* Pavel Atman (born 1987), Russian hand ...
'' in Hinduism. However, some Hindu traditions differentiate between the two concepts, with ''jiva'' considered as individual self, while atman as that which is universal unchanging self that is present in all living beings and everything else as the metaphysical Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' ( sa, ब्रह्मन्) connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality in the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part X ...
. The latter is sometimes referred to as ''jiva-atman'' (a soul in a living body).
Islam
TheQuran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Classical Arabic, Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation in Islam, revelation from God in Islam, ...
, the holy book of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, uses two words to refer to the soul: ''rūḥ
The Holy Spirit ( ar, رُوحُ ٱلْقُدُسِ, ''ruh al-qudus'') is mentioned four times in the Quran, where it acts as an agent of divine action or communication. The Muslim interpretation of the Holy Spirit is generally consistent with o ...
'' (translated as spirit, consciousness, pneuma or "soul") and ''nafs
''Nafs'' () is an Arabic word occurring in the Quran, literally meaning "self", and has been translated as "psyche
Psyche (''Psyché'' in French) is the Greek term for "soul" (ψυχή).
Psyche may also refer to:
Psychology
* Psyche (psych ...
'' (translated as self, ego, psyche or "soul"), cognates of the Hebrew ''nefesh'' and ''ruach''. The two terms are frequently used interchangeably, though ''rūḥ'' is more often used to denote the divine spirit or "the breath of life", while ''nafs'' designates one's disposition or characteristics. In Islamic philosophy, the immortal rūḥ "drives" the mortal nafs, which comprises temporal desires and perceptions necessary for living.
Two of the passages in the Quran that mention the rûh occur in chapters 17 ("The Night Journey") and 39 ("The Troops"):
Jainism
In Jainism, every living being, from plant or bacterium to human, has a soul and the concept forms the very basis of Jainism. According to Jainism, there is no beginning or end to the existence of soul. It is eternal in nature and changes its form until it attains liberation. In Jainism, ''jiva'' is the immortal essence or soul of a living organism (human, animal, fish or plant etc.) which survives physical death. The concept of ''Ajiva'' in Jainism means "not soul", and represents matter (including body), time, space, non-motion and motion. In Jainism, a ''Jiva'' is either ''samsari'' (mundane, caught in cycle of rebirths) or ''mukta'' (liberated). According to this belief until the time the soul is liberated from the ''saṃsāra
''Saṃsāra'' (Devanagari: संसार) is a Pali/Sanskrit word that means "world". It is also the concept of rebirth and "cyclicality of all life, matter, existence", a fundamental belief of most Indian religions. Popularly, it is the c ...
'' (cycle of repeated birth and death), it gets attached to one of these bodies based on the karma
Karma (; sa, कर्म}, ; pi, kamma, italic=yes) in Sanskrit means an action, work, or deed, and its effect or consequences. In Indian religions, the term more specifically refers to a principle of cause and effect, often descriptivel ...
(actions) of the individual soul. Irrespective of which state the soul is in, it has got the same attributes and qualities. The difference between the liberated and non-liberated souls is that the qualities and attributes are manifested completely in case of ''siddha
''Siddha'' (Sanskrit: '; "perfected one") is a term that is used widely in Indian religions and culture. It means "one who is accomplished." It refers to perfected masters who have achieved a high degree of physical as well as spiritual ...
'' (liberated soul) as they have overcome all the karmic bondages whereas in case of non-liberated souls they are partially exhibited. Souls who rise victorious over wicked emotions while still remaining within physical bodies are referred to as arihants.
Concerning the Jain view of the soul, Virchand Gandhi
Virachand Raghavji Gandhi (25 August 1864 – 7 August 1901) was a Jain scholar who represented Jainism at the first World Parliament of Religions in 1893. A barrister by profession, he worked to defend the rights of Jains, and wrote and lecture ...
said
Judaism
TheHebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
terms ''nefesh
A nefesh (plural: ''nefashot'') is a Semitic monument placed near a grave so as to be seen from afar.
Nabataea
In a Nabataean votive inscription from Salkhad, an Aramaic heap of stones set up in memorial is described as "for Allat and her ''w ...
'' (literally "living being"), ''ruach
In Judaism, the Holy Spirit ( he, רוח הקודש, ''ruach ha-kodesh'') refers to the divine force, quality, and influence of God over the universe or over God's creatures, in given contexts.Maimonides, Moses. Part II, Ch. 45: "The various cla ...
'' (literally "wind"), ''neshamah'' (literally "breath"), ''chayah'' (literally "life") and ''yechidah'' (literally "singularity") are used to describe the soul or spirit.
In Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
the soul is believed to be given by God to Adam as mentioned in Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
,
Judaism relates the quality of one's soul to one's performance of the commandments (''mitzvot
In its primary meaning, the Hebrew word (; he, מִצְוָה, ''mīṣvā'' , plural ''mīṣvōt'' ; "commandment") refers to a commandment commanded by God to be performed as a religious duty. Jewish law () in large part consists of discus ...
)'' and reaching higher levels of understanding, and thus closeness to God. A person with such closeness is called a ''tzadik
Tzadik ( he, צַדִּיק , "righteous ne, also ''zadik'', ''ṣaddîq'' or ''sadiq''; pl. ''tzadikim'' ''ṣadiqim'') is a title in Judaism given to people considered righteous, such as biblical figures and later spiritual masters. The ...
''. Therefore, Judaism embraces the commemoration of the day of one's death, '' nahala''/''Yahrtzeit'' and not the birthday
A birthday is the anniversary of the birth of a person, or figuratively of an institution. Birthdays of people are celebrated in numerous cultures, often with birthday gifts, birthday cards, a birthday party, or a rite of passage.
Many relig ...
as a festivity of remembrance, for only toward the end of life's struggles, tests and challenges could human souls be judged and credited for righteousness. Judaism places great importance on the study of the souls.
Kabbalah
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and Jewish theology, school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "rece ...
and other mystic traditions go into greater detail into the nature of the soul. Kabbalah separates the soul into five elements, corresponding to the five worlds
The Four Worlds ( he, עולמות ''Olamot'', singular: ''Olam'' עולם), sometimes counted with a prior stage to make Five Worlds, are the comprehensive categories of spiritual realms in Kabbalah in the descending chain of Existence.
The c ...
:
# Nephesh, Nefesh, related to natural instinct.
# Ruach, related to intellect and the awareness of God.
# Neshamah, related to emotion and morality.
# Chayah, considered a part of God, as it were.
# Yechidah. This aspect is essentially one with God.
Kabbalah also proposed a concept of reincarnation, the ''gilgul''. (See also ''nefesh habehamit'' the "animal soul".)
Some Jewish traditions assert that the soul is housed in the ''Luz (bone), luz'' bone, though traditions disagree as to whether it is the Atlas (anatomy), atlas at the top of the spine, or the sacrum at bottom of the spine.
Scientology
The Scientology view is that a person does not have a soul, it is a soul. It is the belief of the religion that they do not have the power to force adherents' conclusions. Therefore, a person is immortal, and may be reincarnated if they wish. Scientologists view that one's future happiness and immortality, as guided by their spirituality, is influenced by how they live and act during their time on earth. The Scientology term for the soul is "thetan", derived from the Greek word "theta", symbolizing thought. Scientology counselling (called Auditing (Scientology), auditing) addresses the soul to improve abilities, both worldly and spiritual. The ideologies surrounding this understanding align with those of the five major world religions.Shamanism
 Soul dualism (also called "multiple souls" or "dualistic pluralism") is a common belief in Shamanism, and is essential in the universal and central concept of "soul flight" (also called "soul journey", "out-of-body experience", "Religious ecstasy, ecstasy", or "astral projection"). It is the belief that humans have two or more souls, generally termed the "body soul" (or "life soul") and the "free soul". The former is linked to bodily functions and awareness when awake, while the latter can freely wander during sleep or trance states. In some cases, there are a plethora of soul types with different functions.
Soul dualism and multiple souls are prominent in the traditional animistic beliefs of the Austronesian peoples, the Hun and po, Chinese people (Hun and po, ''hún'' and ''pò''), the Tibetan people, most Ethnic groups of Africa, African peoples, most Indigenous peoples of the Americas#North America, Native North Americans, ancient South Asian peoples, Northern Eurasian peoples, and in Ancient Egyptians (the Ancient Egyptian conception of the soul, ''ka'' and ''ba'').
The belief in soul dualism is found throughout most Austronesian people, Austronesian shamanistic traditions. The reconstructed Proto-Austronesian word for the "body soul" is ''*nawa'' ("breath", "life", or "vital spirit"). It is located somewhere in the abdominal cavity, often in the liver or the heart (Proto-Austronesian ''*qaCay''). The "free soul" is located in the head. Its names are usually derived from Proto-Austronesian ''*qaNiCu'' ("ghost", "spirit [of the dead]"), which also apply to other non-human nature spirits. The "free soul" is also referred to in names that literally mean "twin" or "double", from Proto-Austronesian ''*duSa'' ("two"). A virtuous person is said to be one whose souls are in harmony with each other, while an evil person is one whose souls are in conflict.
The "free soul" is said to leave the body and journey to the Spirit world (spiritualism), spirit world during sleep, trance, trance-like states, delirium, insanity, and death. The duality is also seen in the healing traditions of Austronesian shamans, where illnesses are regarded as a "soul loss" and thus to heal the sick, one must "return" the "free soul" (which may have been stolen by an evil spirit or got lost in the spirit world) into the body. If the "free soul" can not be returned, the afflicted person dies or goes permanently insane.
In some ethnic groups, there can also be more than two souls. Like among the Tagbanwa people, where a person is said to have six souls – the "free soul" (which is regarded as the "true" soul) and five secondary souls with various functions.
Several Inuit groups believe that a person has more than one type of soul. One is associated with respiration, the other can accompany the body as a shadow. In some cases, it is connected to Inuit religion, shamanistic beliefs among the various Inuit groups. Also Caribou Inuit groups believed in several types of souls.
The shaman heals within the spiritual dimension by returning 'lost' parts of the human soul from wherever they have gone. The shaman also cleanses excess negative energies, which confuse or pollute the soul.
Soul dualism (also called "multiple souls" or "dualistic pluralism") is a common belief in Shamanism, and is essential in the universal and central concept of "soul flight" (also called "soul journey", "out-of-body experience", "Religious ecstasy, ecstasy", or "astral projection"). It is the belief that humans have two or more souls, generally termed the "body soul" (or "life soul") and the "free soul". The former is linked to bodily functions and awareness when awake, while the latter can freely wander during sleep or trance states. In some cases, there are a plethora of soul types with different functions.
Soul dualism and multiple souls are prominent in the traditional animistic beliefs of the Austronesian peoples, the Hun and po, Chinese people (Hun and po, ''hún'' and ''pò''), the Tibetan people, most Ethnic groups of Africa, African peoples, most Indigenous peoples of the Americas#North America, Native North Americans, ancient South Asian peoples, Northern Eurasian peoples, and in Ancient Egyptians (the Ancient Egyptian conception of the soul, ''ka'' and ''ba'').
The belief in soul dualism is found throughout most Austronesian people, Austronesian shamanistic traditions. The reconstructed Proto-Austronesian word for the "body soul" is ''*nawa'' ("breath", "life", or "vital spirit"). It is located somewhere in the abdominal cavity, often in the liver or the heart (Proto-Austronesian ''*qaCay''). The "free soul" is located in the head. Its names are usually derived from Proto-Austronesian ''*qaNiCu'' ("ghost", "spirit [of the dead]"), which also apply to other non-human nature spirits. The "free soul" is also referred to in names that literally mean "twin" or "double", from Proto-Austronesian ''*duSa'' ("two"). A virtuous person is said to be one whose souls are in harmony with each other, while an evil person is one whose souls are in conflict.
The "free soul" is said to leave the body and journey to the Spirit world (spiritualism), spirit world during sleep, trance, trance-like states, delirium, insanity, and death. The duality is also seen in the healing traditions of Austronesian shamans, where illnesses are regarded as a "soul loss" and thus to heal the sick, one must "return" the "free soul" (which may have been stolen by an evil spirit or got lost in the spirit world) into the body. If the "free soul" can not be returned, the afflicted person dies or goes permanently insane.
In some ethnic groups, there can also be more than two souls. Like among the Tagbanwa people, where a person is said to have six souls – the "free soul" (which is regarded as the "true" soul) and five secondary souls with various functions.
Several Inuit groups believe that a person has more than one type of soul. One is associated with respiration, the other can accompany the body as a shadow. In some cases, it is connected to Inuit religion, shamanistic beliefs among the various Inuit groups. Also Caribou Inuit groups believed in several types of souls.
The shaman heals within the spiritual dimension by returning 'lost' parts of the human soul from wherever they have gone. The shaman also cleanses excess negative energies, which confuse or pollute the soul.
Shinto
Shinto distinguishes between the souls of living persons (''tamashii'') and those of dead persons (''mitama''), each of which may have different aspects or sub-souls.Sikhism
Sikhism considers soul (''atma'') to be part of God (Waheguru). Various hymns are cited from the holy book Guru Granth Sahib (SGGS) that suggests this belief. "God is in the Soul and the Soul is in the God." The same concept is repeated at various pages of the SGGS. For example: "The soul is divine; divine is the soul. Worship Him with love." and "The soul is the Lord, and the Lord is the soul; contemplating the Shabad, the Lord is found." The ''atma'' or soul according to Sikhism is an entity or "spiritual spark" or "light" in the human body - because of which the body can sustain life. On the departure of this entity from the body, the body becomes lifeless – no amount of manipulations to the body can make the person make any physical actions. The soul is the "driver" in the body. It is the ''roohu'' or spirit or ''atma'', the presence of which makes the physical body alive. Many religious and philosophical traditions support the view that the soul is the ethereal substance – a spirit; a non-material spark – particular to a unique living being. Such traditions often consider the soul both immortal and innately aware of its immortal nature, as well as the true basis for sentience in each living being. The concept of the soul has strong links with notions of an afterlife, but opinions may vary wildly even within a given religion as to what happens to the soul after death. Many within these religions and philosophies see the soul as immaterial, while others consider it possibly material.Taoism
According to Chinese traditions, every person has two types of soul called hun and po (魂 and 魄), which are respectively yin and yang, yang and yin. Taoism believes in ten souls, ''sanhunqipo'' (:zh:三魂七魄, 三魂七魄) "three ''hun'' and seven ''po''". A living being that loses any of them is said to have mental illness or unconsciousness, while a dead soul may reincarnate to a disability, lower desire realms, or may even be unable to reincarnate.Zoroastrianism
Other religious beliefs and views
 In theological reference to the soul, the terms "life" and "death" are viewed as emphatically more definitive than the common concepts of "life, biological life" and "biological death". Because the soul is said to be transcendent of the ''matter, material existence,'' and is said to have (potentially) immortality, eternal life, the death of the soul is likewise said to be an ''eternal death''. Thus, in the concept of divine judgment, God is commonly said to have options with regard to the dispensation of souls, ranging from Heaven (i.e., angels) to
In theological reference to the soul, the terms "life" and "death" are viewed as emphatically more definitive than the common concepts of "life, biological life" and "biological death". Because the soul is said to be transcendent of the ''matter, material existence,'' and is said to have (potentially) immortality, eternal life, the death of the soul is likewise said to be an ''eternal death''. Thus, in the concept of divine judgment, God is commonly said to have options with regard to the dispensation of souls, ranging from Heaven (i.e., angels) to hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
(i.e., demons), with various concepts in between. Typically both Heaven and hell are said to be eternal, or at least far beyond a typical human concept of life expectancy, lifespan and time.
According to Louis Ginzberg, the soul of Adam is the image of God. Every soul of human also escapes from the body every night, rises up to heaven, and fetches new life thence for the body of man.
Spirituality, New Age, and new religions
Brahma Kumaris
In Brahma Kumaris, human souls are believed to be incorporeal and eternity, eternal. God is considered to be the Supreme Soul, with maximum degrees of spiritual qualities, such as peace, love and purity.Theosophy
In Helena Blavatsky's Theosophy (Blavatskian), Theosophy, the soul is the field of our psychological activity (thinking, emotions, memory, desires, will, and so on) as well as of the so-called paranormal or psychic phenomena (extrasensory perception, out-of-body experiences, etc.). However, the soul is not the highest, but a middle dimension of human beings. Higher than the soul is the spirit, which is considered to be the real self; the source of everything we call "good"—happiness, wisdom, love, compassion, harmony, peace, etc. While the spirit is eternal and incorruptible, the soul is not. The soul acts as a link between the material body and the spiritual self, and therefore shares some characteristics of both. The soul can be attracted either towards the spiritual or towards the material realm, being thus the "battlefield" of good and evil. It is only when the soul is attracted towards the spiritual and merges with the Self that it becomes eternal and divine.Anthroposophy
Rudolf Steiner claimed classical trichotomic stages of soul development, which interpenetrated one another in consciousness: * The "sentient soul", centering on sensations, drives, and passions, with strong conatus, conative (will) and emotional components; * The "intellectual" or "mind soul", internalizing and reflecting on outer experience, with strong affective (feeling) and cognitive (thinking) components; and * The "consciousness soul", in search of universal, objective truths.Miscellaneous
In Surat Shabd Yoga, Surat Shabda Yoga, the soul is considered to be an exact replica and spark of the Divine. The purpose of Surat Shabd Yoga is to realize one's True Self as soul (Self-Realisation), True Essence (Spirit-Realisation) and True Divinity (God-Realisation) while living in the physical body. Similarly, the spiritual teacher Meher Baba held that "Atma, or the soul, is in reality identical with Paramatma the Oversoul – which is one, infinite, and eternal...[and] [t]he sole purpose of creation is for the soul to enjoy the infinite state of the Oversoul consciously." Eckankar, founded by Paul Twitchell in 1965, defines Soul as the true self; the inner, most sacred part of each person. George Gurdjieff, G.I. Gurdjieff taught that humans are not born with immortal souls but could develop them through certain efforts.Philosophical views
Greek philosophers, such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, understood that the soul (ψυχή ''wikt:ψυχή#Ancient Greek, psykhḗ'') must have a logical faculty, the exercise of which was the most divine of human actions. At his defense trial, Socrates even summarized his teachings as nothing other than an exhortation for his fellow Athenians to excel in matters of the psyche since all bodily goods are dependent on such excellence (''Apology (Plato), Apology'' 30a–b). Aristotle reasoned that a man's body and soul were his matter and form respectively: the body is a collection of elements and the soul is the essence. Soul or Psyche (psychology), psyche (Ancient Greek: ψυχή ''psykhḗ'', of ψύχειν ''psýkhein'', "to breathe", cf. Latin 'anima') comprises the mental abilities of a living being: reason, character, free will, feeling,consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
, qualia, memory, perception, thinking, etc. Depending on the philosophical system, a soul can either be Mortality of the soul, mortal or immortality of the soul, immortal. The ancient Greece, ancient Greeks used the word "Ensoulment, ensouled" to represent the concept of being "alive", indicating that the earliest surviving western philosophy, western philosophical view believed that the soul was that which gave the body life. The soul was considered the incorporeal or spiritual "breath" that animates (from the Latin, '':wikt:anima, anima'', cf. "animal") the living organism.
F. M. Cornford, Francis M. Cornford quotes Pindar by saying that the soul sleeps while the limbs are active, but when one is sleeping, the soul is active and reveals "an award of joy or sorrow drawing near" in dreams.
Erwin Rohde writes that an early pre-Pythagoreanism, Pythagorean belief presented the soul as lifeless when it departed the body, and that it retired into Hades with no hope of returning to a body.
Plato was the first thinker in antiquity to combine the various functions of the soul into one coherent conception: the soul is that which moves things (i.e., that which gives life, on the view that life is self-motion) by means of its thoughts, requiring that it be both a mover and a thinker.Campbell, Douglas (2021). "Self‐Motion and Cognition: Plato's Theory of the Soul". ''The Southern Journal of Philosophy''. 59: 523–544.
Socrates and Plato
 Drawing on the words of his teacher Socrates, Plato considered the psyche to be the
Drawing on the words of his teacher Socrates, Plato considered the psyche to be the essence
Essence ( la, essentia) is a polysemic term, used in philosophy and theology as a designation for the property or set of properties that make an entity or substance what it fundamentally is, and which it has by necessity, and without which it ...
of a person, being that which decides how we behave. He considered this essence to be an incorporeal, eternal occupant of our being. Plato said that even after death, the soul exists and is able to think. He believed that as bodies die, the soul is continually reborn (metempsychosis) in subsequent bodies. However, Aristotle believed that only one part of the soul was immortal, namely the intellect (''Logos#Ancient Greek philosophy, logos''). The Platonic soul consists of three parts:
# the ''logos'', or ''logistikon'' (mind, nous, or reason)
# the ''Thumos, thymos'', or ''thumetikon'' (emotion, spiritedness, or masculine)
# the ''Eros (concept), eros'', or ''epithumetikon'' (appetitive, motivation, desire, or feminine)
The parts are located in different regions of the body:
# ''logos'' is located in the head, is related to reason and regulates the other part.
# ''thymos'' is located near the chest region and is related to anger.
# ''eros'' is located in the stomach and is related to one's desires.
Plato also compares the three parts of the soul or psyche to a societal Plato's tripartite theory of soul, caste system. According to Plato's theory, the three-part soul is essentially the same thing as a state's class system because, to function well, each part must contribute so that the whole functions well. Logos keeps the other functions of the soul regulated.
The soul is at the heart of Plato's philosophy. Francis Cornford described the twin pillars of Platonism as being the theory of the Forms, on the one hand, and, on the other hand, the doctrine of the immortality of the soul. Indeed, Plato was the first person in the history of philosophy to believe that the soul was both the source of life and the mind. In Plato's dialogues, we find the soul playing many disparate roles. Among other things, Plato believes that the soul is what gives life to the body (which was articulated most of all in the ''Laws'' and ''Phaedrus'') in terms of self-motion: to be alive is to be capable of moving yourself; the soul is a self-mover. He also thinks that the soul is the bearer of moral properties (i.e., when I am virtuous, it is my soul that is virtuous as opposed to, say, my body). The soul is also the mind: it is that which thinks in us.
We see this casual oscillation between different roles of the soul in many dialogues. First of all, in the ''Republic'':Is there any function of the soul that you could not accomplish with anything else, such as taking care of something (''epimeleisthai''), ruling, and deliberating, and other such things? Could we correctly assign these things to anything besides the soul, and say that they are characteristic (''idia'') of it? No, to nothing else. What about living? Will we deny that this is a function of the soul? That absolutely is.The ''Phaedo'' most famously caused problems to scholars who were trying to make sense of this aspect of Plato's theory of the soul, such as Sarah Broadie and Dorothea Frede. More-recent scholarship has overturned this accusation by arguing that part of the novelty of Plato's theory of the soul is that it was the first to unite the different features and powers of the soul that became commonplace in later ancient and medieval philosophy. For Plato, the soul moves things by means of its thoughts, as one scholar puts it, and accordingly, the soul is both a mover (i.e., the principle of life, where life is conceived of as ''self-motion'') and a thinker.
Aristotle
 Aristotle (384–322 BCE) defined the soul, or ''Psūchê'' (ψυχή), as the "first actuality" of a naturally organized body, and argued against its separate existence from the physical body. In Aristotle's view, the primary activity, or full actualization, of a living thing constitutes its soul. For example, the full actualization of an eye, as an independent organism, is to see (its purpose or final cause). Another example is that the full actualization of a human being would be living a fully functional human life in accordance with reason (which he considered to be a faculty unique to humanity). For Aristotle, the soul is the organization of the form and matter of a natural being which allows it to strive for its full actualization. This organization between form and matter is necessary for any activity, or functionality, to be possible in a natural being. Using an artifact (non-natural being) as an example, a house is a building for human habituation, but for a house to be actualized requires the material (wood, nails, bricks, etc.) necessary for its actuality (i.e. being a fully functional house). However, this does not imply that a house has a soul. In regards to artifacts, the source of motion that is required for their full actualization is outside of themselves (for example, a builder builds a house). In natural beings, this source of motion is contained within the being itself. Aristotle elaborates on this point when he addresses the faculties of the soul.
The various faculties of the soul, such as nutrition, movement (peculiar to animals), reason (peculiar to humans), sensation (special, common, and incidental) and so forth, when exercised, constitute the "second" actuality, or fulfillment, of the capacity to be alive. For example, someone who falls asleep, as opposed to someone who falls dead, can wake up and live their life, while the latter can no longer do so.
Aristotle identified three hierarchical levels of natural beings: plants, animals, and people, having three different degrees of soul: ''Bios'' (life), ''Zoë'' (animate life), and ''Psuchë'' (self-conscious life). For these groups, he identified three corresponding levels of soul, or biological activity: the nutritive activity of growth, sustenance and reproduction which all life shares (''Bios''); the self-willed motive activity and sensory faculties, which only animals and people have in common (''Zoë''); and finally "reason", of which people alone are capable (''Pseuchë'').
Aristotle's discussion of the soul is in his work, ''De Anima'' (''
Aristotle (384–322 BCE) defined the soul, or ''Psūchê'' (ψυχή), as the "first actuality" of a naturally organized body, and argued against its separate existence from the physical body. In Aristotle's view, the primary activity, or full actualization, of a living thing constitutes its soul. For example, the full actualization of an eye, as an independent organism, is to see (its purpose or final cause). Another example is that the full actualization of a human being would be living a fully functional human life in accordance with reason (which he considered to be a faculty unique to humanity). For Aristotle, the soul is the organization of the form and matter of a natural being which allows it to strive for its full actualization. This organization between form and matter is necessary for any activity, or functionality, to be possible in a natural being. Using an artifact (non-natural being) as an example, a house is a building for human habituation, but for a house to be actualized requires the material (wood, nails, bricks, etc.) necessary for its actuality (i.e. being a fully functional house). However, this does not imply that a house has a soul. In regards to artifacts, the source of motion that is required for their full actualization is outside of themselves (for example, a builder builds a house). In natural beings, this source of motion is contained within the being itself. Aristotle elaborates on this point when he addresses the faculties of the soul.
The various faculties of the soul, such as nutrition, movement (peculiar to animals), reason (peculiar to humans), sensation (special, common, and incidental) and so forth, when exercised, constitute the "second" actuality, or fulfillment, of the capacity to be alive. For example, someone who falls asleep, as opposed to someone who falls dead, can wake up and live their life, while the latter can no longer do so.
Aristotle identified three hierarchical levels of natural beings: plants, animals, and people, having three different degrees of soul: ''Bios'' (life), ''Zoë'' (animate life), and ''Psuchë'' (self-conscious life). For these groups, he identified three corresponding levels of soul, or biological activity: the nutritive activity of growth, sustenance and reproduction which all life shares (''Bios''); the self-willed motive activity and sensory faculties, which only animals and people have in common (''Zoë''); and finally "reason", of which people alone are capable (''Pseuchë'').
Aristotle's discussion of the soul is in his work, ''De Anima'' (''On the Soul
''On the Soul'' (Greek: , ''Peri Psychēs''; Latin: ''De Anima'') is a major treatise written by Aristotle c. 350 BC. His discussion centres on the kinds of souls possessed by different kinds of living things, distinguished by their different op ...
''). Although mostly seen as opposing Plato in regard to the immortality of the soul, a controversy can be found in relation to the fifth chapter of the third book: in this text both interpretations can be argued for, soul as a whole can be deemed mortal, and a part called "active intellect" or "active mind" is immortal and eternal. Advocates exist for both sides of the controversy, but it has been understood that there will be permanent disagreement about its final conclusions, as no other Aristotelianism, Aristotelian text contains this specific point, and this part of ''De Anima'' is obscure. Further, Aristotle states that the soul helps humans find the truth, and understanding the true purpose or role of the soul is extremely difficult.
Avicenna and Ibn al-Nafis
Following Aristotle, Avicenna (Ibn Sina) and Ibn al-Nafis, an Arab physician, further elaborated upon the Aristotelian understanding of the soul and developed their own theories on the soul. They both made a distinction between the soul and the spirit, and the Avicennism, Avicennian doctrine on the nature of the soul was influential among the Scholasticism, Scholastics. Some of Avicenna's views on the soul include the idea that the immortality of the soul is a consequence of its nature, and not a purpose for it to fulfill. In his theory of "The Ten Intellects", he viewed the human soul as the tenth and final intelligence, intellect. While he was imprisoned, Avicenna wrote his famous "Floating man" thought experiment to demonstrate human self-awareness and the substantial nature of the soul. He told his readers to imagine themselves suspended in the air, isolated from all sensations, which includes no sense, sensory contact with even their own bodies. He argues that in this scenario one would still have self-consciousness. He thus concludes that the idea of the self (philosophy), self is not logically dependent on any physical object (philosophy), thing, and that the soul should not be seen in relative terms, but as a primary given, a substance theory, substance. This argument was later refined and simplified by René Descartes in epistemology, epistemic terms, when he stated: "I can abstract from the supposition of all external things, but not from the supposition of my own consciousness." Avicenna generally supported Aristotle's idea of the soul originating from the heart, whereas Ibn al-Nafis rejected this idea and instead argued that the soul "is related to the entirety and not to one or a few organ (anatomy), organs". He further criticized Aristotle's idea whereby every unique soul requires the existence of a unique source, in this case the heart. Al-Nafis concluded that "the soul is related primarily neither to the spirit nor to any organ, but rather to the entire matter whose temperament is prepared to receive that soul," and he defined the soul as nothing other than "what a human indicates by saying "I (pronoun), I".Thomas Aquinas
Following Aristotle (whom he referred to as "the Philosopher") and Avicenna, Thomas Aquinas (1225–74) understood the soul to be the first actuality of the living body. Consequent to this, he distinguished three orders of life: plants, which feed and grow; animals, which add sensation to the operations of plants; and humans, which add intellect to the operations of animals. Concerning the human soul, his epistemological theory required that, since the knower becomes what he knows, the soul is definitely not corporeal—if it is corporeal when it knows what some corporeal thing is, that thing would come to be within it. Therefore, the soul has an operation which does not rely on a body organ, and therefore the soul can exist without a body. Furthermore, since the rational soul of human beings is a subsistent form and not something made of matter and form, it cannot be destroyed in any natural process. The full argument for the immortality of the soul and Aquinas' elaboration of Aristotelian theory is found in Question 75 of the First Part of the Summa Theologica. Aquinas affirmed in the doctrine of the divine effusion of the soul, the particular judgement of the soul after the separation from a dead body, and the final Resurrection of the flesh. He recalled two canons of the 4th-century ''Gennadius of Massilia#De Ecclesiasticis Dogmatibus, De Ecclesiasticis Dogmatibus'' for which "the rational soul is not engendered by coition" (canon XIV) and "is one and the same soul in man, that both gives life to the body by being united to it, and orders itself by its own reasoning." Moreover, he believed in a unique and tripartite soul, within which are distinctively present a nutritive, a sensitive and intellectual soul. The latter is created by God and is taken solely by human beings, includes the other two types of soul and makes the sensitive soul incorruptible.Immanuel Kant
In his discussions of rational psychology, Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) identified the soul as the "I" in the strictest sense, and argued that the existence of inner experience can neither be proved nor disproved. It is from the "I", or soul, that Kant proposes transcendental rationalization, but cautions that such rationalization can only determine the limits of knowledge if it is to remain practical.Philosophy of mind
Gilbert Ryle's ghost in the machine argument, which is a rejection of Descartes's mind–body dualism, can provide a contemporary understanding of the soul/mind, and the problem concerning its connection to the brain/body.Psychology
Soul belief prominently figues in Otto Rank's work recovering the importance of immortality in the psychology of primitive, classical and modern interest in life and death. Rank's work directly opposed the "scientific" psychology that concedes the possibility of the soul's existence and postulates it as an object of research without really admitting that it exists. "Just as religion represents a psychological commentary on the social evolution of man, various psychologies represent our current attitudes toward spiritual belief. In the animistic era, psychologizing was a ''creating'' of the soul; in the religious era, it was a ''representing'' of the soul to one's self; in our era of natural science it is a ''knowing'' of the individual soul." Rank's "Seelenglaube" translates to "Soul Belief". Rank's work had a significant influence on Ernest Becker's understanding of a universal interest in immortality. In Denial of Death, Becker describes "soul" in terms of Kierkegaard's use of "self" when he says, "what we call schizophrenia is an attempt by the symbolic self to deny the limitations of the finite body."Science
According to Julien Musolino, the vast majority of scientists hold that the mind is a complex machine that operates on the same physical laws as all other objects in the universe. According to Musolino, there is currently no scientific evidence whatsoever to support the existence of the soul. The search for the soul, however, is seen to have been instrumental in driving the understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the human body, particularly in the fields of cardiovascular and neurology. In the two dominant conflicting concepts of the soul – one seeing it to be spiritual and immortal, and the other seeing it to be material and mortal, both have described the soul as being located in a particular organ or as pervading the whole body.Neuroscience
Neuroscience as an interdisciplinary field, and its branch of cognitive neuroscience particularly, operates under the ontology, ontological assumption of physicalism. In other words, it assumes that only the fundamental phenomena studied by physics exist. Thus, neuroscience seeks to understand mental phenomena within the framework according to which human thought and behavior are caused solely by physical processes taking place inside the brain, and it operates by the way of reductionism by seeking an explanation for the mind in terms of brain activity. To study the mind in terms of the brain several methods of functional neuroimaging are used to study the neuroanatomical correlates of various cognition, cognitive processes that constitute the mind. The evidence from brain imaging indicates that all processes of the mind have physical correlates in brain function. However, such correlational studies cannot determine whether neural activity plays a causal role in the occurrence of these cognitive processes (correlation does not imply causation) and they cannot determine if the neural activity is either necessity and sufficiency, necessary or sufficient for such processes to occur. Identification of causality, causation, and of necessary and sufficient conditions requires explicit experimental manipulation of that activity. If manipulation of brain activity changes consciousness, then a causal role for that brain activity can be inferred. Two of the most common types of manipulation experiments are loss-of-function and gain-of-function experiments. In a loss-of-function (also called "necessity") experiment, a part of the nervous system is diminished or removed in an attempt to determine if it is necessary for a certain process to occur, and in a gain-of-function (also called "sufficiency") experiment, an aspect of the nervous system is increased relative to normal. Manipulations of brain activity can be performed with direct electrical brain stimulation, magnetic brain stimulation using transcranial magnetic stimulation, psychoactive drug, psychopharmacological manipulation, optogenetics, optogenetic manipulation, and by studying the symptoms of brain damage (case studies) and lesions. In addition, neuroscientists are also investigating how the mind develops with the development of the brain.Physics
Physicist Sean M. Carroll has written that the idea of a soul is incompatible with quantum field theory (QFT). He writes that for a soul to exist: "Not only is new physics required, but dramatically new physics. Within QFT, there can't be a new collection of 'spirit particles' and 'spirit forces' that interact with our regular atoms, because we would have detected them in existing experiments." Quantum indeterminacy, Quantum indeterminism has been invoked as an explanatory mechanism for possible soul/brain interaction, but neuroscientist Peter Clarke found errors with this viewpoint, noting there is no evidence that such processes play a role in brain function; Clarke concluded that a Cartesian dualism, Cartesian soul has no basis from quantum physics.Parapsychology
Some parapsychologists have attempted to establish, by scientific experiment, whether a soul separate from the brain exists, as is more commonly defined in religion rather than as a synonym of psyche or mind. Milbourne Christopher (1979) and Mary Roach (2010) have argued that none of the attempts by parapsychologists have yet succeeded.Weight of the soul
In 1901 Duncan MacDougall (doctor), Duncan MacDougall conducted 21 grams experiment, an experiment in which he made weight measurements of patients as they died. He claimed that there was weight loss of varying amounts at the time of death; he concluded the soul weighed 21 grams, based on measurements of a single patient and discarding conflicting results. The physicist Robert L. Park wrote that MacDougall's experiments "are not regarded today as having any scientific merit" and the psychologist Bruce Hood (psychologist), Bruce Hood wrote that "because the weight loss was not reliable or replicable, his findings were unscientific."Bruce Hood (psychologist), Hood, Bruce. (2009). ''Supersense: From Superstition to Religion – The Brain Science of Belief''. Constable. p. 165.See also
* Ancient Egyptian concept of the soul * Being * Chinese room * Ekam * History of the location of the soul * Kami * Knowledge argument * Metaphysical naturalism * Mind–body problem * Nafs in Islam * Nishimta in Mandaeism * The Over-Soul (essay) * Paramatman (or oversoul) * Philosophical zombie * Qualia * Self * Self-awareness * Shade (mythology) * Soul dualism * Soul flight * Substance dualism * VitalismReferences
Further reading
* Batchelor, Stephen. (1998). ''Buddhism Without Beliefs''. Bloomsbury Publishing. * * * Chalmers, David. J. (1996). ''The Conscious Mind: In Search of a Fundamental Theory'', New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press. * Milbourne Christopher, Christopher, Milbourne. (1979). ''Search for the Soul: An Insider's Report on the Continuing Quest By Psychics & Scientists For Evidence of Life After Death''. Thomas Y. Crowell, Publishers. * * Bruce Hood (psychologist), Hood, Bruce. (2009). ''Supersense: From Superstition to Religion – The Brain Science of Belief''. Constable. * McGraw, John J. (2004). ''Brain & Belief: An Exploration of the Human Soul''. Aegis Press. * Michael Martin (philosopher), Martin, Michael; Augustine, Keith. (2015)''The Myth of an Afterlife: The Case against Life After Death''
Rowman & Littlefield. * Robert L. Park, Park, Robert L. (2009). ''Superstition: Belief in the Age of Science''. Princeton University Press. * Erwin Rohde, Rohde, Erwin. (1925)
''Psyche: The Cult of Souls and Belief in Immortality Among the Greeks''
London: Routledge, Kegan Paul, Trench, Trübner & Co., Ltd. * Ryle, Gilbert. (1949) ''The Concept of Mind'', London: Hutchinson. * Spenard, Michael (2011
"Dueling with Dualism: the forlorn quest for the immaterial soul"
essay. An historical account of mind-body duality and a comprehensive conceptual and empirical critique on the position. * Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, Richard. (1997). ''The Evolution of the Soul''. Oxford: Oxford University Press. * Leibowitz, Aryeh. (2018). The Neshama: A Study of the Human Soul. Feldheim Publishers. * * Translation of the original:
External links
Quantum Theory Won’t Save The Soul
What Science Really Says About the Soul
by Stephen Cave
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy entry on Ancient Theories of the Soul
The soul in Judaism
at Chabad.org
The Old Testament Concept of the Soul
by Heinrich J. Vogel]
Body, Soul and Spirit
Article in th
Journal of Biblical Accuracy
Is Another Human Living Inside You?
*
"The Soul"
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Richard Sorabji, Ruth Padel and Martin Palmer (''In Our Time'', 6 June 2002) {{Authority control Conceptions of self Concepts in metaphysics Dualism (philosophy of mind) Ghosts Metaphysics of religion Mind Religious philosophical concepts Religious belief and doctrine Vitalism