Sofia - National Museum Of History on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the
 For a long time the city possessed a
For a long time the city possessed a

 When Emperor Diocletian divided the province of Dacia into Dacia Ripensis (on the banks of the Danube) and Dacia Mediterranea, Serdica became the capital of the latter.
Roman emperors Aurelian (215–275) and Galerius (260–311) were born in Serdica.
The city expanded and became a significant political and economical centre, more so as it became one of the first Roman cities where Christianity was recognised as an State religion, official religion (under Galerius). The Edict of Toleration by Galerius was issued in 311 in Serdica by the Roman emperor Galerius, officially ending the Diocletianic persecution of Christianity. The Edict implicitly granted Christianity the status of "religio licita", a worship recognised and accepted by the Roman Empire. It was the first edict legalising Christianity, preceding the Edict of Milan by two years.
Serdica was the capital of the Diocese of Dacia (337-602).
For Constantine the Great it was 'Sardica mea Roma est' (Serdica is my Rome). He considered making Serdica the capital of the Byzantine Empire instead of Constantinople. which was already not dissimilar to a Tetrarchy, tetrarchic capital of the Roman Empire. In 343 AD, the Council of Sardica was held in the city, in a church located where the current 6th century Hagia Sophia Church (Sofia), Church of Saint Sophia was later built.
The city was destroyed in the Theodosius II#Wars with the Huns, Vandals, and Persians, 447 invasion of the
When Emperor Diocletian divided the province of Dacia into Dacia Ripensis (on the banks of the Danube) and Dacia Mediterranea, Serdica became the capital of the latter.
Roman emperors Aurelian (215–275) and Galerius (260–311) were born in Serdica.
The city expanded and became a significant political and economical centre, more so as it became one of the first Roman cities where Christianity was recognised as an State religion, official religion (under Galerius). The Edict of Toleration by Galerius was issued in 311 in Serdica by the Roman emperor Galerius, officially ending the Diocletianic persecution of Christianity. The Edict implicitly granted Christianity the status of "religio licita", a worship recognised and accepted by the Roman Empire. It was the first edict legalising Christianity, preceding the Edict of Milan by two years.
Serdica was the capital of the Diocese of Dacia (337-602).
For Constantine the Great it was 'Sardica mea Roma est' (Serdica is my Rome). He considered making Serdica the capital of the Byzantine Empire instead of Constantinople. which was already not dissimilar to a Tetrarchy, tetrarchic capital of the Roman Empire. In 343 AD, the Council of Sardica was held in the city, in a church located where the current 6th century Hagia Sophia Church (Sofia), Church of Saint Sophia was later built.
The city was destroyed in the Theodosius II#Wars with the Huns, Vandals, and Persians, 447 invasion of the
 Serdica became part of the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Khan
Serdica became part of the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Khan
 When it comes to the cityscape, 16th century sources mention eight Jama Masjid, Friday mosques, three public libraries, numerous schools, 12 churches, three synagogues, and the largest bedesten (market) of the Balkans. Additionally, there were fountains and ''Turkish bath, hammams'' (bathhouses). Most prominent churches such as Saint Sofia and Saint George were converted into mosques, and a number of new ones were constructed, including
When it comes to the cityscape, 16th century sources mention eight Jama Masjid, Friday mosques, three public libraries, numerous schools, 12 churches, three synagogues, and the largest bedesten (market) of the Balkans. Additionally, there were fountains and ''Turkish bath, hammams'' (bathhouses). Most prominent churches such as Saint Sofia and Saint George were converted into mosques, and a number of new ones were constructed, including
 For a few decades after the liberation, Sofia experienced large population growth, mainly by migration from other regions of the Principality (Kingdom since 1908) of Bulgaria, and from the still Ottoman Macedonia (region), Macedonia and Thrace.
In 1900, the first electric lightbulb in the city was turned on.
In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria was fighting alone practically all of its neighbouring countries. When the Romanian Army entered Vrazhdebna in 1913, then a village from Sofia, now a suburb,Hall (2000), p. 97. this prompted the Kingdom of Bulgaria, Tsardom of Bulgaria to capitulate. During the war, Sofia was flown by the Romanian Air Corps, which engaged on photoreconnaissance operations and threw propaganda pamphlets to the city. Thus, Sofia became the first capital on the world to be overflown by enemy aircraft.Hall (2000), p. 118.
In 1925, a terrorist act of ultra-leftists failed their attempted assassination of the king but resulted in the destruction of the Saint Nedelya Church and many victims.
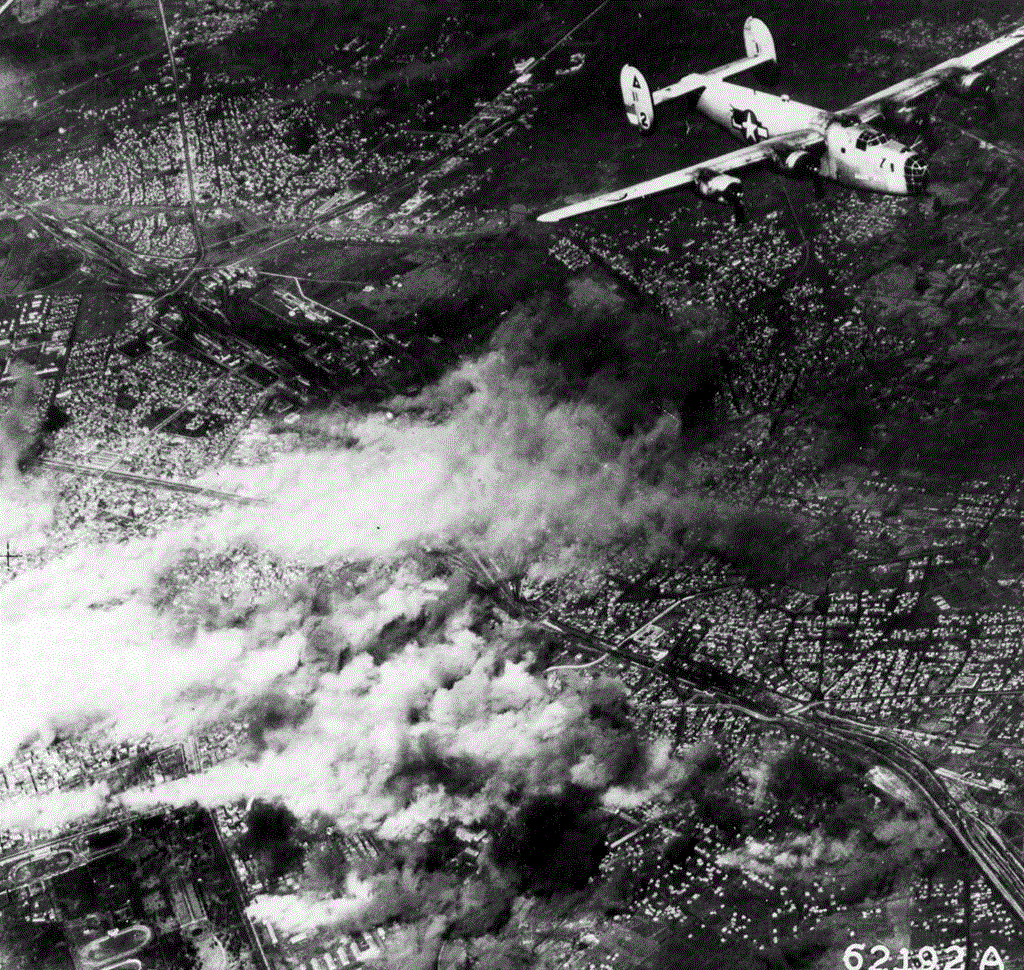
During the Military history of Bulgaria during World War II, Second World War, Bulgaria declared war on the US and UK on 13 December 1941 and in late 1943 and early 1944 the Bombing of Sofia in World War II, US and UK Air forces conducted bombings over Sofia. As a consequence of the bombings thousands of buildings were destroyed or damaged including the Capital Library and thousands of books. In 1944 Sofia and the rest of Bulgaria was occupied by the Soviet Red Army and within days of the Soviet invasion Bulgaria declared war on Nazi Germany.
In 1945, the communist Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power. The transformations of Bulgaria into the People's Republic of Bulgaria in 1946 and into the Republic of Bulgaria in 1990 marked significant changes in the city's appearance. The population of Sofia expanded rapidly due to migration from rural regions. New residential areas were built in the outskirts of the city, like Druzhba, Mladost and Lyulin.
During the Bulgarian Communist Party, Communist Party rule, a number of the city's most emblematic streets and squares were renamed for ideological reasons, with the original names restored after 1989.
The Georgi Dimitrov Mausoleum, where Georgi Dimitrov, Dimitrov's body had been preserved in a similar way to the Lenin mausoleum, was demolished in 1999.
For a few decades after the liberation, Sofia experienced large population growth, mainly by migration from other regions of the Principality (Kingdom since 1908) of Bulgaria, and from the still Ottoman Macedonia (region), Macedonia and Thrace.
In 1900, the first electric lightbulb in the city was turned on.
In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria was fighting alone practically all of its neighbouring countries. When the Romanian Army entered Vrazhdebna in 1913, then a village from Sofia, now a suburb,Hall (2000), p. 97. this prompted the Kingdom of Bulgaria, Tsardom of Bulgaria to capitulate. During the war, Sofia was flown by the Romanian Air Corps, which engaged on photoreconnaissance operations and threw propaganda pamphlets to the city. Thus, Sofia became the first capital on the world to be overflown by enemy aircraft.Hall (2000), p. 118.
In 1925, a terrorist act of ultra-leftists failed their attempted assassination of the king but resulted in the destruction of the Saint Nedelya Church and many victims.
During the Military history of Bulgaria during World War II, Second World War, Bulgaria declared war on the US and UK on 13 December 1941 and in late 1943 and early 1944 the Bombing of Sofia in World War II, US and UK Air forces conducted bombings over Sofia. As a consequence of the bombings thousands of buildings were destroyed or damaged including the Capital Library and thousands of books. In 1944 Sofia and the rest of Bulgaria was occupied by the Soviet Red Army and within days of the Soviet invasion Bulgaria declared war on Nazi Germany.
In 1945, the communist Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power. The transformations of Bulgaria into the People's Republic of Bulgaria in 1946 and into the Republic of Bulgaria in 1990 marked significant changes in the city's appearance. The population of Sofia expanded rapidly due to migration from rural regions. New residential areas were built in the outskirts of the city, like Druzhba, Mladost and Lyulin.
During the Bulgarian Communist Party, Communist Party rule, a number of the city's most emblematic streets and squares were renamed for ideological reasons, with the original names restored after 1989.
The Georgi Dimitrov Mausoleum, where Georgi Dimitrov, Dimitrov's body had been preserved in a similar way to the Lenin mausoleum, was demolished in 1999.
 In Sofia there are 607,473 dwellings and 101,696 buildings. According to modern records, 39,551 dwellings were constructed until 1949, 119,943 between 1950 and 1969, 287,191 between 1970 and 1989, 57,916 in the 90s and 102,623 between 2000 and 2011. Until 1949, 13,114 buildings were constructed and between 10,000 and 20,000 in each following decade. Sofia's architecture combines a wide range of architectural styles, some of which are aesthetically incompatible. These vary from Christian Roman architecture and medieval Bulgarian fortresses to Neoclassicism and prefabricated Socialist-era apartment blocks. A number of ancient Roman, Byzantine and medieval Bulgarian buildings are preserved in the centre of the city. These include the 4th century Church of St. George, Sofia, Rotunda of St. George, the walls of the Serdica fortress and the partially preserved Amphitheatre of Serdica.
After the Liberation War, knyaz Alexander, Prince of Bulgaria, Alexander Battenberg invited architects from Austria-Hungary to shape the new capital's architectural appearance.
Among the architects invited to work in Bulgaria were Friedrich Grünanger, Adolf Václav Kolář, and Viktor Rumpelmayer, who designed the most important public buildings needed by the newly re-established Bulgarian government, as well as numerous houses for the country's elite. Later, many foreign-educated Bulgarian architects also contributed. The architecture of Sofia's centre is thus a combination of Baroque Revival architecture, Neo-Baroque, Neo-Rococo, Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance and Neoclassicism, with the Vienna Secession also later playing an important part, but it is most typically Central European.
After World War II and the establishment of a Communist state, Communist government in Bulgaria in 1944, the architectural style was substantially altered. Stalinist architecture, Stalinist Gothic public buildings emerged in the centre, notably the spacious government complex around Largo, Sofia, The Largo, Vasil Levski Stadium, the Cyril and Methodius National Library and others. As the city grew outwards, the then-new neighbourhoods were dominated by many concrete tower blocks, prefabricated panel apartment buildings and examples of Brutalist architecture.
After the abolition of Communism in 1989, Sofia witnessed the construction of whole business districts and neighbourhoods, as well as modern skryscraper-like glass-fronted office buildings, but also top-class residential neighbourhoods. The Capital Fort Business Centre is the first skyscraper in Bulgaria, with its 36 floors. However, the end of the old administration and centrally planned system also paved the way for chaotic and unrestrained construction, which continues today.
In Sofia there are 607,473 dwellings and 101,696 buildings. According to modern records, 39,551 dwellings were constructed until 1949, 119,943 between 1950 and 1969, 287,191 between 1970 and 1989, 57,916 in the 90s and 102,623 between 2000 and 2011. Until 1949, 13,114 buildings were constructed and between 10,000 and 20,000 in each following decade. Sofia's architecture combines a wide range of architectural styles, some of which are aesthetically incompatible. These vary from Christian Roman architecture and medieval Bulgarian fortresses to Neoclassicism and prefabricated Socialist-era apartment blocks. A number of ancient Roman, Byzantine and medieval Bulgarian buildings are preserved in the centre of the city. These include the 4th century Church of St. George, Sofia, Rotunda of St. George, the walls of the Serdica fortress and the partially preserved Amphitheatre of Serdica.
After the Liberation War, knyaz Alexander, Prince of Bulgaria, Alexander Battenberg invited architects from Austria-Hungary to shape the new capital's architectural appearance.
Among the architects invited to work in Bulgaria were Friedrich Grünanger, Adolf Václav Kolář, and Viktor Rumpelmayer, who designed the most important public buildings needed by the newly re-established Bulgarian government, as well as numerous houses for the country's elite. Later, many foreign-educated Bulgarian architects also contributed. The architecture of Sofia's centre is thus a combination of Baroque Revival architecture, Neo-Baroque, Neo-Rococo, Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance and Neoclassicism, with the Vienna Secession also later playing an important part, but it is most typically Central European.
After World War II and the establishment of a Communist state, Communist government in Bulgaria in 1944, the architectural style was substantially altered. Stalinist architecture, Stalinist Gothic public buildings emerged in the centre, notably the spacious government complex around Largo, Sofia, The Largo, Vasil Levski Stadium, the Cyril and Methodius National Library and others. As the city grew outwards, the then-new neighbourhoods were dominated by many concrete tower blocks, prefabricated panel apartment buildings and examples of Brutalist architecture.
After the abolition of Communism in 1989, Sofia witnessed the construction of whole business districts and neighbourhoods, as well as modern skryscraper-like glass-fronted office buildings, but also top-class residential neighbourhoods. The Capital Fort Business Centre is the first skyscraper in Bulgaria, with its 36 floors. However, the end of the old administration and centrally planned system also paved the way for chaotic and unrestrained construction, which continues today.


 The city has an extensive green belt. Some of the neighbourhoods constructed after 2000 are densely built up and lack green spaces. There are four principal parks – Borisova gradina in the city centre and the ''Southern'', ''Western'' and ''Northern'' parks. Several smaller parks, among which the Vazrazhdane Park, Zaimov Park, City Garden (Sofia), City Garden and the Doctors' Garden, are located in central Sofia. The
The city has an extensive green belt. Some of the neighbourhoods constructed after 2000 are densely built up and lack green spaces. There are four principal parks – Borisova gradina in the city centre and the ''Southern'', ''Western'' and ''Northern'' parks. Several smaller parks, among which the Vazrazhdane Park, Zaimov Park, City Garden (Sofia), City Garden and the Doctors' Garden, are located in central Sofia. The
 Sofia Capital Municipality, Sofia Municipality is identical to
Sofia Capital Municipality, Sofia Municipality is identical to

 Under Bulgaria's centralised political system, Sofia concentrates much of the political and financial resources of the country. It is the only city in Bulgaria to host three electoral constituencies: the 23rd Multi-member Constituency, 23rd, 24th Multi-member Constituency, 24th and 25th Multi-member Constituency, 25th Multi-member Constituencies, which together field 42 mandates in the 240-member National Assembly.
Under Bulgaria's centralised political system, Sofia concentrates much of the political and financial resources of the country. It is the only city in Bulgaria to host three electoral constituencies: the 23rd Multi-member Constituency, 23rd, 24th Multi-member Constituency, 24th and 25th Multi-member Constituency, 25th Multi-member Constituencies, which together field 42 mandates in the 240-member National Assembly.
 Sofia concentrates the majority of Bulgaria's leading performing arts troupes. Theatre is by far the most popular form of performing art, and theatrical venues are among the most visited, second only to cinemas. There were 3,162 theatric performances with 570,568 people attending in 2014. The
Sofia concentrates the majority of Bulgaria's leading performing arts troupes. Theatre is by far the most popular form of performing art, and theatrical venues are among the most visited, second only to cinemas. There were 3,162 theatric performances with 570,568 people attending in 2014. The 
 The city houses many cultural institutes such as the Russian Cultural Institute, the Polish Cultural Institute, the Hungarian Institute, the Czech and the Slovak Cultural Institutes, the Italian Cultural Institute, Confucius Institute, Institut Français, Goethe-Institut, Goethe Institut, British Council and Instituto Cervantes which regularly organise temporary expositions of visual, sound and literary works by artists from their respective countries.
Some of the biggest telecommunications companies, TV and radio stations, newspapers, magazines, and web portals are based in Sofia, including the Bulgarian National Television, BTV (Bulgaria), bTV and Nova Television (Bulgaria), Nova TV. Top-circulation newspapers include ''24 Chasa'' and ''Dneven Trud, Trud''.
The
The city houses many cultural institutes such as the Russian Cultural Institute, the Polish Cultural Institute, the Hungarian Institute, the Czech and the Slovak Cultural Institutes, the Italian Cultural Institute, Confucius Institute, Institut Français, Goethe-Institut, Goethe Institut, British Council and Instituto Cervantes which regularly organise temporary expositions of visual, sound and literary works by artists from their respective countries.
Some of the biggest telecommunications companies, TV and radio stations, newspapers, magazines, and web portals are based in Sofia, including the Bulgarian National Television, BTV (Bulgaria), bTV and Nova Television (Bulgaria), Nova TV. Top-circulation newspapers include ''24 Chasa'' and ''Dneven Trud, Trud''.
The
 Sofia is one of the most visited tourist destinations in Bulgaria alongside coastal and mountain resorts. Among its highlights is the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Sofia, Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, one of the symbols of Bulgaria, constructed in the late 19th century. It occupies an area of and can hold 10,000 people.
The city center contains many remains of ancient Serdica that have been excavated and are on public display, including ''Complex Ancient Serdica'', eastern gate, western gate, city walls, thermal baths, 4th c. Church of St. George, Sofia, church of St. George Rotunda, amphitheatre of Serdica, the tombs and basilicas under the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, basilica of St. Sophia.
Vitosha Boulevard, also called ''Vitoshka'', is a pedestrian zone with numerous cafés, restaurants, fashion boutiques, and luxury goods stores. Sofia's geographic coordinate system, geographic location, in the foothills of the weekend retreat
Sofia is one of the most visited tourist destinations in Bulgaria alongside coastal and mountain resorts. Among its highlights is the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Sofia, Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, one of the symbols of Bulgaria, constructed in the late 19th century. It occupies an area of and can hold 10,000 people.
The city center contains many remains of ancient Serdica that have been excavated and are on public display, including ''Complex Ancient Serdica'', eastern gate, western gate, city walls, thermal baths, 4th c. Church of St. George, Sofia, church of St. George Rotunda, amphitheatre of Serdica, the tombs and basilicas under the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, basilica of St. Sophia.
Vitosha Boulevard, also called ''Vitoshka'', is a pedestrian zone with numerous cafés, restaurants, fashion boutiques, and luxury goods stores. Sofia's geographic coordinate system, geographic location, in the foothills of the weekend retreat
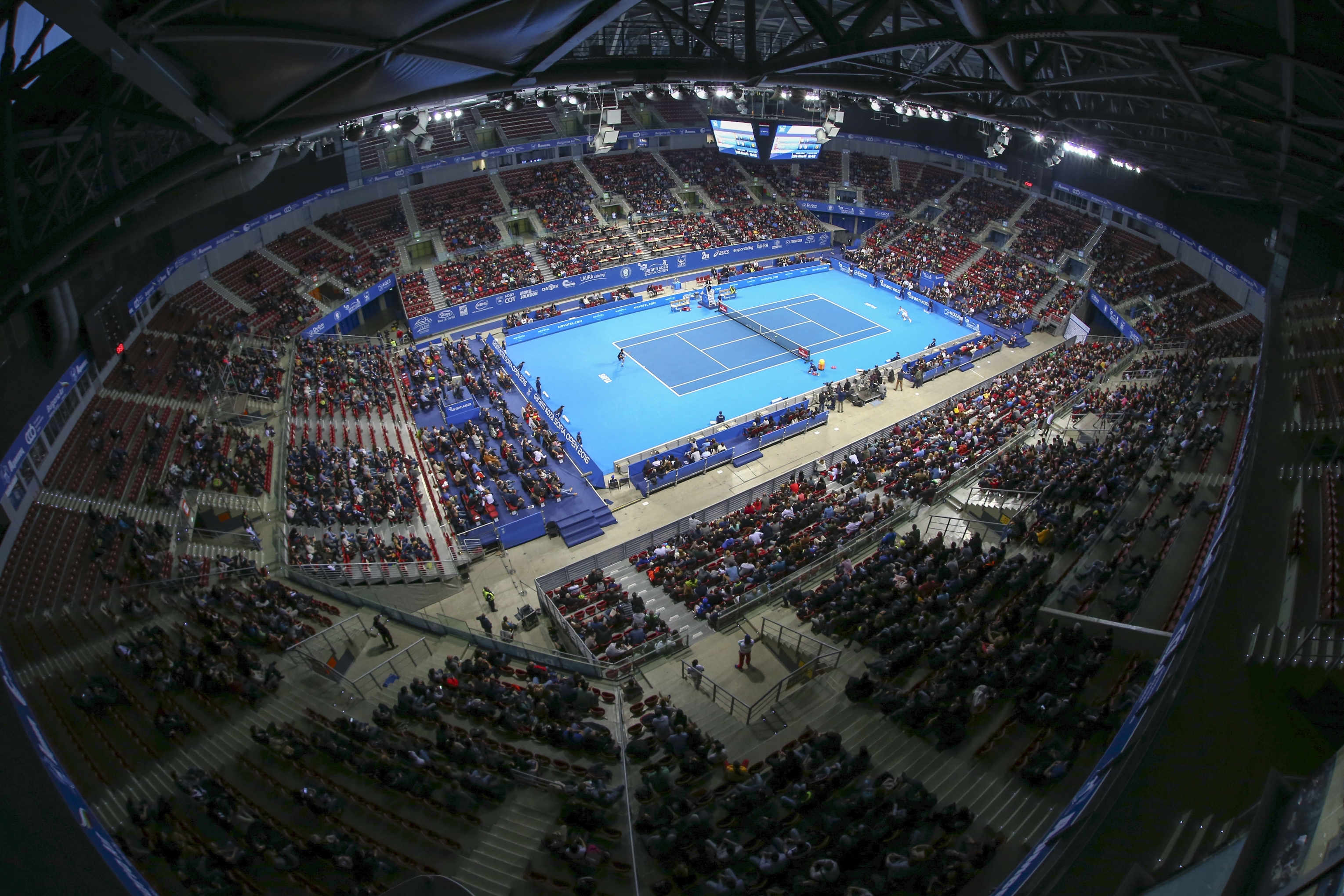 The city is home to a number of large sports venues, including the 43,000-seat
The city is home to a number of large sports venues, including the 43,000-seat
ImageSize = width:750 height:280
PlotArea = left:50 right:20 top:25 bottom:30
TimeAxis = orientation:vertical
AlignBars = late
Colors =
id:linegrey2 value:gray(0.9)
id:linegrey value:gray(0.7)
id:cobar value:rgb(0.2,0.7,0.8)
id:cobar2 value:rgb(0.6,0.9,0.6)
DateFormat = yyyy
Period = from:0 till:1500
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:100 start:0 gridcolor:linegrey
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:50 start:0 gridcolor:linegrey2
PlotData =
color:cobar width:19 align:left
bar:1700s from:0 till:70
bar:1870 from:0 till:19
bar:1880 from:0 till:20
bar:1887 from:0 till:30
bar:1892 from:0 till:46
bar:1900 from:0 till:68
bar:1905 from:0 till:82
bar:1910 from:0 till:102
bar:1920 from:0 till:154
bar:1926 from:0 till:213
bar:1934 from:0 till:287
bar:1939 from:0 till:401
bar:1946 from:0 till:435
bar:1956 from:0 till:639
bar:1965 from:0 till:802
bar:1975 from:0 till:965
bar:1985 from:0 till:1121
bar:1992 from:0 till:1114
bar:2001 from:0 till:1091
bar:2011 from:0 till:1202
bar:2015 from:0 till:1228
bar:2016 from:0 till:1236
bar:2018 from:0 till:1269
PlotData=
textcolor:black fontsize:S
bar:1700s at: 70 text: 70,0 shift:(-8,5)
bar:1870 at: 19 text: 19,0 shift:(-8,5)
bar:1880 at: 20 text: 20,5 shift:(-8,5)
bar:1887 at: 30 text: 30,5 shift:(-11,5)
bar:1892 at: 46 text: 46,6 shift:(-11,5)
bar:1900 at: 68 text: 68,0 shift:(-11,5)
bar:1905 at: 82 text: 82,6 shift:(-11,5)
bar:1910 at: 102 text: 102,8 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1920 at: 154 text: 154,0 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1926 at: 213 text: 213,0 shift:(-11,5)
bar:1934 at: 287 text: 287,1 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1939 at: 401 text: 401,0 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1946 at: 435 text: 435,0 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1956 at: 639 text: 639,9 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1965 at: 802 text: 802,4 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1975 at: 965 text: 965,7 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1985 at: 1121 text: 1122 shift:(-14,5)
bar:1992 at: 1114 text: 1115 shift:(-14,5)
bar:2001 at: 1091 text: 1092 shift:(-14,5)
bar:2011 at: 1202 text: 1203 shift:(-14,5)
bar:2015 at: 1228 text: 1228 shift:(-14,5)
bar:2016 at: 1236 text: 1236 shift:(-14,5)
bar:2018 at: 1269 text: 1269 shift:(-14,5)
 According to 2018 data, the city has a population of 1,400,384 and the whole Sofia Capital Municipality of 1,500,120. The first census carried out in February 1878 by the Russian Army recorded a population of 11,694 inhabitants including 6,560 Bulgarians, 3,538 Bulgarian Jews, Jews, 839 Turkish people, Turks and 737 Romani people, Romani.
The ratio of women per 1,000 men was 1,102. The birth rate per 1000 people was 12.3 per mile and steadily increasing in the last 5 years, the Mortality rate, death rate reaching 12.1 per mile and decreasing. The natural growth rate during 2009 was 0.2 per mile, the first positive growth rate in nearly 20 years. The considerable immigration to the capital from poorer regions of the country, as well as urbanisation, are among the other reasons for the increase in Sofia's population. The infant mortality rate was 5.6 per 1,000, down from 18.9 in 1980. According to the 2011 census, people aged 20–24 years are the most numerous group, numbering 133,170 individuals and accounting for 11% of the total 1,202,761 people. The median age is 38 though. According to the census, 1,056,738 citizens (87.9%) are recorded as ethnic Bulgarians, 17,550 (1.5%) as Romani people in Bulgaria, Romani, 6,149 (0.5%) as Turks in Bulgaria, Turks, 9,569 (0.8%) belonged to other ethnic groups, 6,993 (0.6%) do not self-identify and 105,762 (8.8%) remained with undeclared affiliation.
According to the 2011 census, throughout the whole municipality some 892,511 people (69.1%) are recorded as Eastern Orthodox Christians, 10,256 (0.8%) as Protestantism in Bulgaria, Protestant, 6,767 (0.5%) as Islam in Bulgaria, Muslim, 5,572 (0.4%) as Roman Catholicism in Bulgaria, Roman Catholic, 4,010 (0.3%) belonged to other faith and 372,475 (28.8%) declared themselves irreligious or did not mention any faith. The data says that roughly a third of the total population have already earned a university degree. Of the population aged 15–64 – 265,248 people within the municipality (28.5%) are not economically active, the unemployed being another group of 55,553 people (6%), a large share of whom have completed higher education. The largest group are occupied in trading, followed by those in manufacturing industry. Within the municipality, three-quarters, or 965,328 people are recorded as having access to television at home and 836,435 (64.8%) as having internet. Out of 464,865 homes – 432,847 have connection to the communal sanitary sewer, while 2,732 do not have any. Of these 864 do not have any water supply and 688 have other than communal. Over 99.6% of males and females aged over 9 are recorded as literacy, literate. The largest group of the population aged over 20 are recorded to live within marriage (46.3%), another 43.8% are recorded as single and another 9.9% as having other type of coexistence/partnership, whereas not married in total are a majority and among people aged up to 40 and over 70. The people with juridical status divorced or widowed are either part of the factual singles or those having another type of partnership, each of the two constitutes by around 10% of the population aged over 20. Only over 1% of the juridically married do not de facto live within marriage. The families that consist of two people are 46.8%, another 34.2% of the families are made up by three people, whereas most of the households (36.5%) consist of only one person.
Sofia was declared the national capital in 1879. One year later, in 1880, it was the fifth-largest city in the country after Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse and Shumen. Plovdiv remained the most populous Bulgarian town until 1892 when Sofia took the lead. The city is the hot spot of internal migration, the capital population is increasing and is around 17% of the national, thus a small number of people with local roots remain today, they dominate the surrounding Districts of Sofia, rural suburbs and are called Shopi. Shopi speak the Bulgarian dialects, Western Bulgarian dialects.
According to 2018 data, the city has a population of 1,400,384 and the whole Sofia Capital Municipality of 1,500,120. The first census carried out in February 1878 by the Russian Army recorded a population of 11,694 inhabitants including 6,560 Bulgarians, 3,538 Bulgarian Jews, Jews, 839 Turkish people, Turks and 737 Romani people, Romani.
The ratio of women per 1,000 men was 1,102. The birth rate per 1000 people was 12.3 per mile and steadily increasing in the last 5 years, the Mortality rate, death rate reaching 12.1 per mile and decreasing. The natural growth rate during 2009 was 0.2 per mile, the first positive growth rate in nearly 20 years. The considerable immigration to the capital from poorer regions of the country, as well as urbanisation, are among the other reasons for the increase in Sofia's population. The infant mortality rate was 5.6 per 1,000, down from 18.9 in 1980. According to the 2011 census, people aged 20–24 years are the most numerous group, numbering 133,170 individuals and accounting for 11% of the total 1,202,761 people. The median age is 38 though. According to the census, 1,056,738 citizens (87.9%) are recorded as ethnic Bulgarians, 17,550 (1.5%) as Romani people in Bulgaria, Romani, 6,149 (0.5%) as Turks in Bulgaria, Turks, 9,569 (0.8%) belonged to other ethnic groups, 6,993 (0.6%) do not self-identify and 105,762 (8.8%) remained with undeclared affiliation.
According to the 2011 census, throughout the whole municipality some 892,511 people (69.1%) are recorded as Eastern Orthodox Christians, 10,256 (0.8%) as Protestantism in Bulgaria, Protestant, 6,767 (0.5%) as Islam in Bulgaria, Muslim, 5,572 (0.4%) as Roman Catholicism in Bulgaria, Roman Catholic, 4,010 (0.3%) belonged to other faith and 372,475 (28.8%) declared themselves irreligious or did not mention any faith. The data says that roughly a third of the total population have already earned a university degree. Of the population aged 15–64 – 265,248 people within the municipality (28.5%) are not economically active, the unemployed being another group of 55,553 people (6%), a large share of whom have completed higher education. The largest group are occupied in trading, followed by those in manufacturing industry. Within the municipality, three-quarters, or 965,328 people are recorded as having access to television at home and 836,435 (64.8%) as having internet. Out of 464,865 homes – 432,847 have connection to the communal sanitary sewer, while 2,732 do not have any. Of these 864 do not have any water supply and 688 have other than communal. Over 99.6% of males and females aged over 9 are recorded as literacy, literate. The largest group of the population aged over 20 are recorded to live within marriage (46.3%), another 43.8% are recorded as single and another 9.9% as having other type of coexistence/partnership, whereas not married in total are a majority and among people aged up to 40 and over 70. The people with juridical status divorced or widowed are either part of the factual singles or those having another type of partnership, each of the two constitutes by around 10% of the population aged over 20. Only over 1% of the juridically married do not de facto live within marriage. The families that consist of two people are 46.8%, another 34.2% of the families are made up by three people, whereas most of the households (36.5%) consist of only one person.
Sofia was declared the national capital in 1879. One year later, in 1880, it was the fifth-largest city in the country after Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse and Shumen. Plovdiv remained the most populous Bulgarian town until 1892 when Sofia took the lead. The city is the hot spot of internal migration, the capital population is increasing and is around 17% of the national, thus a small number of people with local roots remain today, they dominate the surrounding Districts of Sofia, rural suburbs and are called Shopi. Shopi speak the Bulgarian dialects, Western Bulgarian dialects.
 The city's GDP (PPS) per capita stood at €29,600 ($33,760) in 2015, one of the highest in Southeast Europe and well above other cities in the country. The total nominal GDP in 2018 was 38.5 billion leva ($22.4 billion), or 33,437 leva ($19,454) per capita, and average monthly wages in March 2020 were $1,071, the highest nationally. Services dominate the economy, accounting for 88.6% of the gross value added, followed by industry 11.3% and agriculture 0.1%.
Historically, after World War II and the era of industrialisation under socialism, the city and its surrounding areas expanded rapidly and became the most heavily industrialised region of the country, with numerous factories producing steel, pig iron, machinery, industrial equipment, electronics, trams, chemicals, textiles, food. The influx of workers from other parts of the country became so intense that a restriction policy was imposed, and residing in the capital was only possible after obtaining Sofianite citizenship. However, after the political changes in 1989, this kind of citizenship was removed.
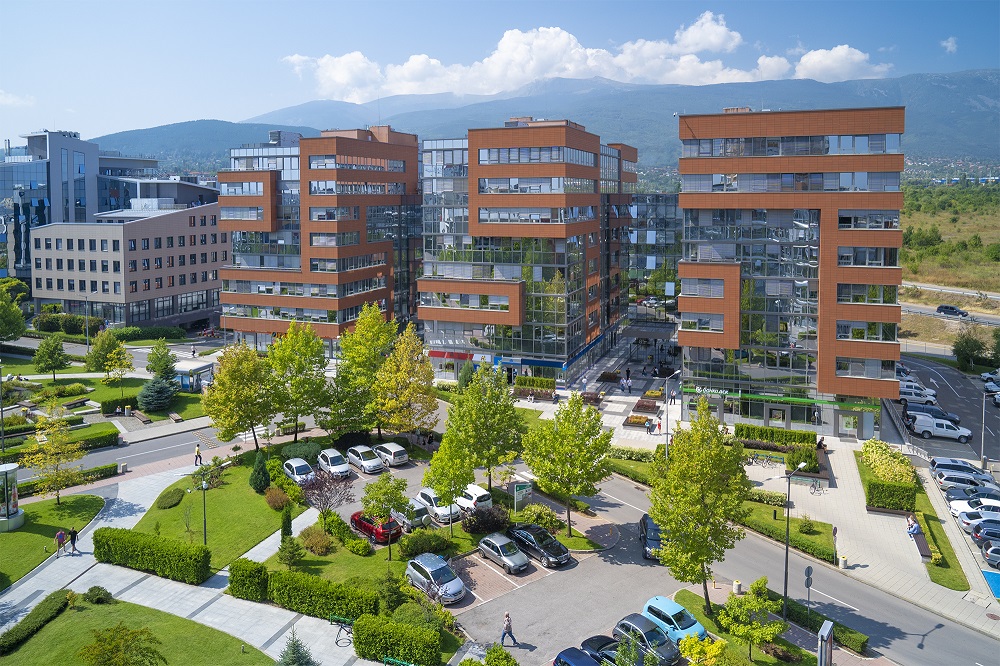
The most dynamic sectors include Information technology (IT) and manufacturing. Sofia is a regional IT hub, ranking second among the Top 10 fastest growing tech centers in Europe in terms of annual growth of active members. The sector employs about 50,000 professionals, 30% of them involved in programming, and contributes for 14% of the city's exports. The IT sector is highly diverse and includes both multinational corporations, local companies and start-ups. Multinationals with major research, development, innovation and engineering centers in Sofia include the second largest global IT center of Coca-Cola, Ubisoft Sofia, Ubisoft, Hewlett-Packard, VMware, Robert Bosch GmbH, Financial Times, Experian, etc. Several office and tech clusters have been established across the city, including Business Park Sofia, Sofia Tech Park, Capital Fort and others.
Manufacturing has registered a strong recovery since 2012, increasing the exports three-fold and the employment by 52% accounting for over 70,000 jobs. Supported by the city's R&D expertise, Sofia is shifting to high value-added manufacturing including electrical equipment, precision mechanics, pharmaceuticals. There are 16 industrial and logistics parks in Sofia, some sprawling to towns in neighbouring
The city's GDP (PPS) per capita stood at €29,600 ($33,760) in 2015, one of the highest in Southeast Europe and well above other cities in the country. The total nominal GDP in 2018 was 38.5 billion leva ($22.4 billion), or 33,437 leva ($19,454) per capita, and average monthly wages in March 2020 were $1,071, the highest nationally. Services dominate the economy, accounting for 88.6% of the gross value added, followed by industry 11.3% and agriculture 0.1%.
Historically, after World War II and the era of industrialisation under socialism, the city and its surrounding areas expanded rapidly and became the most heavily industrialised region of the country, with numerous factories producing steel, pig iron, machinery, industrial equipment, electronics, trams, chemicals, textiles, food. The influx of workers from other parts of the country became so intense that a restriction policy was imposed, and residing in the capital was only possible after obtaining Sofianite citizenship. However, after the political changes in 1989, this kind of citizenship was removed.
The most dynamic sectors include Information technology (IT) and manufacturing. Sofia is a regional IT hub, ranking second among the Top 10 fastest growing tech centers in Europe in terms of annual growth of active members. The sector employs about 50,000 professionals, 30% of them involved in programming, and contributes for 14% of the city's exports. The IT sector is highly diverse and includes both multinational corporations, local companies and start-ups. Multinationals with major research, development, innovation and engineering centers in Sofia include the second largest global IT center of Coca-Cola, Ubisoft Sofia, Ubisoft, Hewlett-Packard, VMware, Robert Bosch GmbH, Financial Times, Experian, etc. Several office and tech clusters have been established across the city, including Business Park Sofia, Sofia Tech Park, Capital Fort and others.
Manufacturing has registered a strong recovery since 2012, increasing the exports three-fold and the employment by 52% accounting for over 70,000 jobs. Supported by the city's R&D expertise, Sofia is shifting to high value-added manufacturing including electrical equipment, precision mechanics, pharmaceuticals. There are 16 industrial and logistics parks in Sofia, some sprawling to towns in neighbouring
All major types of transport (except Ship transport, water) are represented in the city. The Central Railway Station, Sofia, Central Railway Station is the primary hub for domestic and international rail transport, carried out by Bulgarian State Railways (BDZ), the national rail company headquartered in the city. It is one of the main stations along BDZ Line 1, and a hub of Lines BDZ Line 2, 2, BDZ Line 5, 5 and BDZ Line 13, 13. Line 1 provides a connection to Plovdiv, the second-largest city in Bulgaria, while Line 2 is the longest national railway and connects Sofia and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, the largest coastal city. Lines 5 and 13 are shorter and provide connections to Kulata and Bankya, respectively. Overall, Sofia has of railway lines.
The Central Railway Station, Sofia, Central Railway Station is the primary hub for domestic and international rail transport, carried out by Bulgarian State Railways (BDZ), the national rail company headquartered in the city. It is one of the main stations along BDZ Line 1, and a hub of Lines BDZ Line 2, 2, BDZ Line 5, 5 and BDZ Line 13, 13. Line 1 provides a connection to Plovdiv, the second-largest city in Bulgaria, while Line 2 is the longest national railway and connects Sofia and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, the largest coastal city. Lines 5 and 13 are shorter and provide connections to Kulata and Bankya, respectively. Overall, Sofia has of railway lines.
 Private automobile ownership has grown rapidly in the 1990s; more than 1,000,000 cars were registered in Sofia after 2002. The city has the 4th-highest number of automobiles per capita in the European Union at 546.4 vehicles per 1,000 people. The municipality was known for minor and cosmetic repairs and many streets are in a poor condition. This is noticeably changing in the past years. There are different boulevards and streets in the city with a higher amount of traffic than others. These include Tsarigradsko shose, Cherni Vrah, Bulgaria, Slivnitsa and Todor Aleksandrov boulevards, as well as the city's ring road. Consequently, traffic and air pollution problems have become more severe and receive regular criticism in local media. The extension of the underground system is hoped to alleviate the city's immense traffic problems.
Sofia has an extensive Toplofikatsiya Sofia, district heating system that draws on four cogeneration, combined heat and power (CHP) plants and heat-only boiler station, boiler stations. Virtually the entire city (900,000 households and 5,900 companies) is centrally heated, using residual heat from electricity generation (3,000 MW) and gas- and oil-fired heating furnaces; total Thermal mass, heat capacity is 4,640 MW. The heat distribution piping network is long and comprises 14,000 substations and 10,000 heated buildings.
Private automobile ownership has grown rapidly in the 1990s; more than 1,000,000 cars were registered in Sofia after 2002. The city has the 4th-highest number of automobiles per capita in the European Union at 546.4 vehicles per 1,000 people. The municipality was known for minor and cosmetic repairs and many streets are in a poor condition. This is noticeably changing in the past years. There are different boulevards and streets in the city with a higher amount of traffic than others. These include Tsarigradsko shose, Cherni Vrah, Bulgaria, Slivnitsa and Todor Aleksandrov boulevards, as well as the city's ring road. Consequently, traffic and air pollution problems have become more severe and receive regular criticism in local media. The extension of the underground system is hoped to alleviate the city's immense traffic problems.
Sofia has an extensive Toplofikatsiya Sofia, district heating system that draws on four cogeneration, combined heat and power (CHP) plants and heat-only boiler station, boiler stations. Virtually the entire city (900,000 households and 5,900 companies) is centrally heated, using residual heat from electricity generation (3,000 MW) and gas- and oil-fired heating furnaces; total Thermal mass, heat capacity is 4,640 MW. The heat distribution piping network is long and comprises 14,000 substations and 10,000 heated buildings.
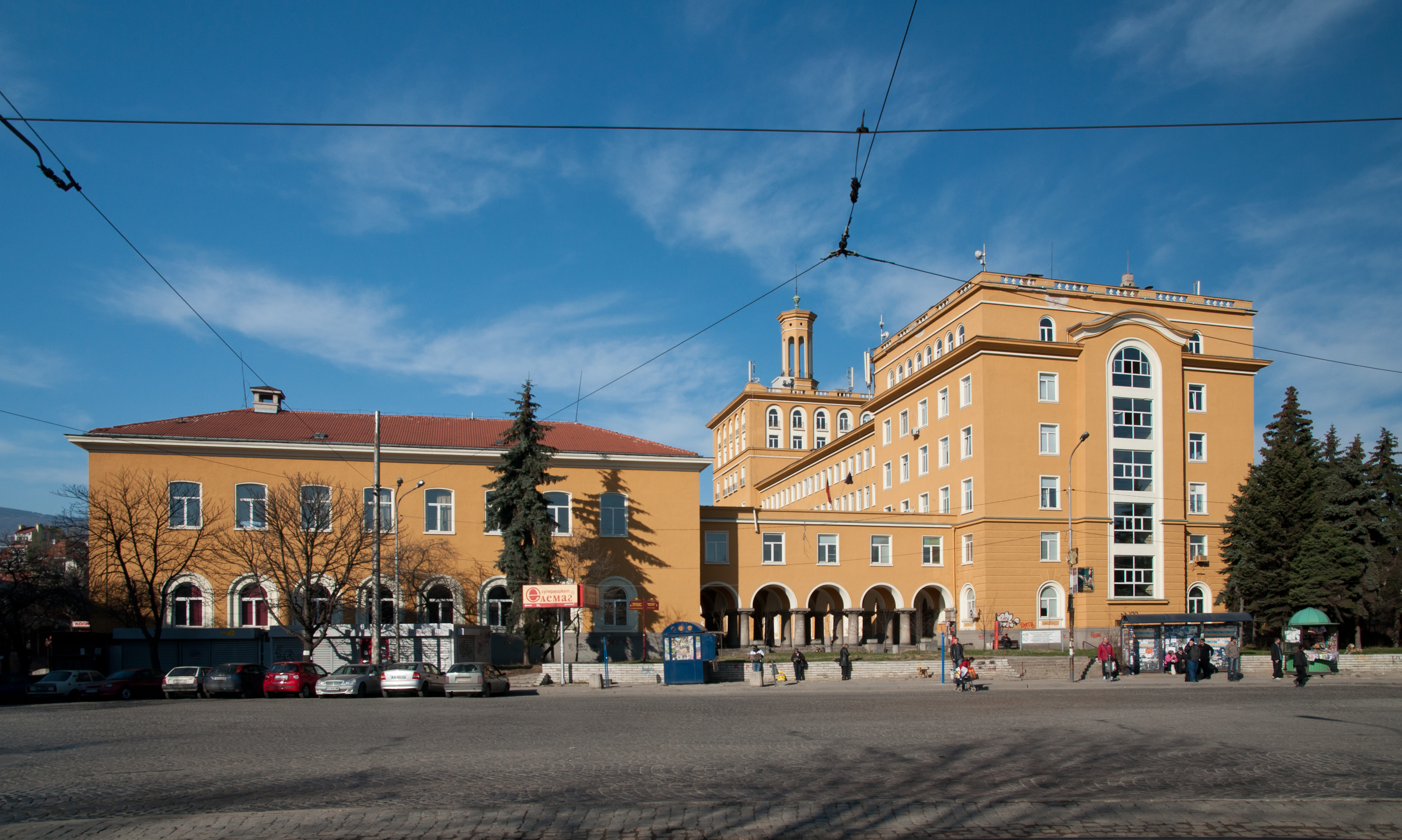 Much of Bulgaria's educational capacity is concentrated in Sofia. There are 221 general, 11 special and seven arts or sports schools, 56 vocational gymnasiums and colleges, and four independent colleges. The city also hosts 23 of Bulgaria's 51 higher education establishments and more than 105,000 university students. The American College of Sofia, a private secondary school with roots in a school founded by American missionaries in 1860, is among the oldest American educational institutions outside of the United States.
A number of secondary language schools provide education in a selected foreign language. These include the First English Language School, 91st German Language School, 164 GPIE "Miguel de Cervantes", 164th Spanish Language School, and the Lycée Français de Sofia, Lycée Français. These are among the most sought-after secondary schools, along with Vladislav the Grammarian 73rd Secondary School and the Sofia High School of Mathematics, High School of Mathematics, which topped the 2018 preference list for high school candidates.
Higher education includes four of the five highest-ranking national universities – Sofia University (SU), the Technical University of Sofia, New Bulgarian University and the Medical University of Sofia. Sofia University was founded in 1888. More than 20,000 students study in its 16 faculties. A number of research and cultural departments operate within SU, including its own publishing house, botanical gardens, a space research centre, a quantum electronics department, and a Confucius Institute. Rakovski Defence and Staff College, the National Academy of Arts, the University of Architecture, Civil Engineering and Geodesy, the University of National and World Economy and the University of Mining and Geology are other major higher education establishments in the city.
Other institutions of national significance, such as the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (BAS) and the SS. Cyril and Methodius National Library are located in Sofia. BAS is the centrepiece of scientific research in Bulgaria, employing more than 4,500 scientists in various institutes. Its Institute of Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy will operate the largest cyclotron in the country. All five of Bulgaria's supercomputers and supercomputing clusters are located in Sofia as well. Three of those are operated by the BAS; one by Sofia Tech Park and one by the Faculty of Physics at Sofia University.
Much of Bulgaria's educational capacity is concentrated in Sofia. There are 221 general, 11 special and seven arts or sports schools, 56 vocational gymnasiums and colleges, and four independent colleges. The city also hosts 23 of Bulgaria's 51 higher education establishments and more than 105,000 university students. The American College of Sofia, a private secondary school with roots in a school founded by American missionaries in 1860, is among the oldest American educational institutions outside of the United States.
A number of secondary language schools provide education in a selected foreign language. These include the First English Language School, 91st German Language School, 164 GPIE "Miguel de Cervantes", 164th Spanish Language School, and the Lycée Français de Sofia, Lycée Français. These are among the most sought-after secondary schools, along with Vladislav the Grammarian 73rd Secondary School and the Sofia High School of Mathematics, High School of Mathematics, which topped the 2018 preference list for high school candidates.
Higher education includes four of the five highest-ranking national universities – Sofia University (SU), the Technical University of Sofia, New Bulgarian University and the Medical University of Sofia. Sofia University was founded in 1888. More than 20,000 students study in its 16 faculties. A number of research and cultural departments operate within SU, including its own publishing house, botanical gardens, a space research centre, a quantum electronics department, and a Confucius Institute. Rakovski Defence and Staff College, the National Academy of Arts, the University of Architecture, Civil Engineering and Geodesy, the University of National and World Economy and the University of Mining and Geology are other major higher education establishments in the city.
Other institutions of national significance, such as the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (BAS) and the SS. Cyril and Methodius National Library are located in Sofia. BAS is the centrepiece of scientific research in Bulgaria, employing more than 4,500 scientists in various institutes. Its Institute of Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy will operate the largest cyclotron in the country. All five of Bulgaria's supercomputers and supercomputing clusters are located in Sofia as well. Three of those are operated by the BAS; one by Sofia Tech Park and one by the Faculty of Physics at Sofia University.
Online guide to Sofia
Official Site of Sofia Public Transport
*
Archival images of Sofia
Sofia by Night Light: A Photographic Exhibition
More than 25 live webcams from Sofia
Pictures from Vitosha mountain
{{Authority control Sofia, Populated places in Sofia City Province Capitals in Europe Roman towns and cities in Bulgaria Dacia Mediterranea Populated places established in the 7th millennium BC
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
. It is situated in the Sofia Valley
The Sofia Valley ( bg, Софийска котловина, Sofiyska kotlovina), or Sofia Field ( bg, Софийско поле, Sofiysko pole, link=no), is a valley in central western Bulgaria bordering Stara Planina to the northeast, the Viskya ...
at the foot of the Vitosha
Vitosha ( bg, Витоша ), the ancient ''Scomius'' or ''Scombrus'', is a mountain massif, on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. Vitosha is one of the symbols of Sofia and the closest site for hiking, alpinism and skiing. Conveni ...
mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and has many mineral springs, such as the Sofia Central Mineral Baths
The Central Mineral Baths (Централна минерална баня, ''Tsentralna mineralna banya'') is a landmark in the city center of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria, a city known for the mineral springs in the area. It was built in the ...
. It has a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
. Being in the centre of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, it is midway between the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
and the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
, and closest to the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
.
Known as Serdica in Antiquity and Sredets in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, Sofia has been an area of human habitation
Habitability refers to the adequacy of an environment for human living. Where housing is concerned, there are generally local ordinances which define habitability. If a residence complies with those laws it is said to be habitable. In extreme e ...
since at least 7000 BC. The recorded history of the city begins with the attestation of the conquest of Serdica by the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
in 29 BC from the Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
tribe Serdi
The Serdi were a Celtic tribe inhabiting Thrace. They were located around Serdica ( bg, Сердика, Serdika; ; el, Σαρδική o Σαρδῶν πόλις, Sardike o Sardon polis), now Sofia in Bulgaria, which reflects their ethnonym. They ...
. During the decline of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, the city was raided by Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
, Avars and Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
. In 809, Serdica was incorporated into the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
by Khan Krum
Krum ( bg, Крум, el, Κροῦμος/Kroumos), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome ( bg, Крум Страшни) was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territor ...
and became known as Sredets. In 1018, the Byzantines ended Bulgarian rule until 1194, when it was reincorporated by the reborn Bulgarian Empire. Sredets became a major administrative, economic, cultural and literary hub until its conquest by the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in 1382. From 1530 to 1836, Sofia was the regional capital of Rumelia Eyalet
The Eyalet of Rumeli, or Eyalet of Rumelia ( ota, ایالت روم ایلی, ), known as the Beylerbeylik of Rumeli until 1591, was a first-level province ('' beylerbeylik'' or ''eyalet'') of the Ottoman Empire encompassing most of the Balkans (" ...
, the Ottoman Empire's key province in Europe. Bulgarian rule was restored in 1878. Sofia was selected as the capital of the Third Bulgarian State
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hig ...
in the next year, ushering a period of intense demographic and economic growth.
Sofia is the 13th largest city in the European Union. It is surrounded by mountainsides, such as Vitosha
Vitosha ( bg, Витоша ), the ancient ''Scomius'' or ''Scombrus'', is a mountain massif, on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. Vitosha is one of the symbols of Sofia and the closest site for hiking, alpinism and skiing. Conveni ...
by the southern side, Lyulin by the western side, and the Balkan Mountains
The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border betw ...
by the north, which makes it the third highest European capital after Andorra la Vella
Andorra la Vella french: Andorre-la-Vieille is the capital (political), capital of the Andorra, Principality of Andorra. It is located high in the east Pyrenees, between France and Spain. It is also the name of the parishes of Andorra, parish ...
and Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
. Being Bulgaria's primate city
A primate city is a city that is the largest in its country, province, Federated state, state, or region, and disproportionately larger than any others in the urban hierarchy. A ''primate city distribution'' is a rank-size distribution that has on ...
, Sofia is home of many of the major local universities, cultural institutions and commercial companies. The city has been described as the "triangle of religious tolerance". This is due to the fact that three temples of three major world religions—Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
—are situated close together: Sveta Nedelya Church, Banya Bashi Mosque
Banya Bashi Mosque ( bg, Баня баши джамия, ; tr, Banya Başı Camii) is a mosque in Sofia, Bulgaria.
History
The mosque was designed by the famous Ottoman architect Mimar Sinan and completed in 1566, during the years the Otto ...
and Sofia Synagogue
The Sofia Synagogue ( bg, Софийска синагога, ''Sofiyska sinagoga'') is the largest synagogue in Southeastern Europe, one of two functioning in Bulgaria (with the other one in Plovdiv) and the third-largest in Europe.
. This triangle was recently expanded to a "square" and includes the Catholic Cathedral of St Joseph.
Sofia has been named one of the top ten best places for start-up businesses in the world, especially in information technologies. It was Europe's most affordable capital to visit in 2013. In 1979, the Boyana Church
The Boyana Church ( bg, Боянска църква, ''Boyanska tsărkva'') is a medieval Bulgarian Orthodox church situated on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria, in the Boyana quarter. In 1979, the building was added to the UNESCO W ...
in Sofia was included onto the World Heritage List
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNES ...
, and it was deconstructed in the Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1396. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II ...
, holding much patrimonial symbolism to the Bulgarian Orthodox Church
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
. With its cultural significance in Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (al ...
, Sofia is home to the National Opera and Ballet of Bulgaria
The National Opera and Ballet ( bg, Национална опера и балет) is a national cultural institution in Bulgaria that covers opera and ballet. It is based in an imposing building in Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria.
The first opera ...
, the National Palace of Culture
The National Palace of Culture (, ; abbreviated as , NDK), located in Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria, is the largest, multifunctional conference and exhibition centre in south-eastern Europe. It was opened in 1981 in celebration of Bulgaria's 130 ...
, the Vasil Levski National Stadium
Vasil Levski National Stadium ( bg, Национален стадион „Васил Левски“), named after Bulgarian national hero and revolutionary Vasil Levski (1837–1873), is the country's second largest stadium. The stadium has 43,2 ...
, the Ivan Vazov National Theatre
The Ivan Vazov National Theatre ( bg, Народен театър „Иван Вазов“, ') is Bulgaria's national theatre, as well as the oldest and most authoritative theatre in the country and one of the important landmarks of Sofia, the ...
, the National Archaeological Museum, and the Serdica Amphitheatre. The Museum of Socialist Art includes many sculptures and posters that educate visitors about the lifestyle in communist Bulgaria
The People's Republic of Bulgaria (PRB; bg, Народна Република България (НРБ), ''Narodna Republika Balgariya, NRB'') was the official name of Bulgaria, when it was a socialist republic from 1946 to 1990, ruled by the ...
.
The population of Sofia declined from 70,000 in the late 18th century, through 19,000 in 1870, to 11,649 in 1878, after which it began increasing. Sofia hosts some 1.24 million residents within a territory of 492 km2, a concentration of 17.9% of the country population within the 200th percentile of the country territory. The urban area of Sofia hosts some 1.54 million residents within 5723 km2, which comprises Sofia City Province
Sofia City Province ( bg, Област София-град, translit=Oblast Sofiya-grad) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. Its administrative center is the city of Sofia, the capital of the country.
The province borders on Sofia Provinc ...
and parts of Sofia Province
Sofia Province ( bg, Софийска област, translit=Sofiyska oblast) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. The province does not include Sofia in its territories, but Sofia remains its administrative center. The province borders on t ...
(Dragoman
A dragoman or Interpretation was an interpreter, translator, and official guide between Turkish-, Arabic-, and Persian-speaking countries and polities of the Middle East and European embassies, consulates, vice-consulates and trading posts. A ...
, Slivnitsa
Slivnitsa ( bg, Сливница ) is a town in western Bulgaria, 22 km away from Sofia, lying on the main road connecting the capital with the Bulgarian-Serbian border. Slivnitsa is part of Sofia Province and is close to the towns of Kostin ...
, Kostinbrod
Kostinbrod ( bg, Костинброд ) is a town in western Bulgaria. It is the seat of Kostinbrod Municipality. It is located 15 km west of the capital city of Sofia. It is located on two important transport corridors: Lom — Sofia — T ...
, Bozhurishte
Bozhurishte ( bg, Божурище ) is a town in western Bulgaria. It is the administrative center of Bozhurishte Municipality in Sofia Province; close to Kostinbrod and the capital Sofia. The old airport of Sofia, now a military one, is near th ...
, Svoge
Svoge ( bg, Своге, ) is a town in western Bulgaria, part of Sofia Province. It is located in the gorge of the Iskar River, at the place where the mountains Mala planina, Golema planina and Ponor meet, 40 km north of the capital Sofia. Svoge is ...
, Elin Pelin
Elin Pelin ( bg, Елин Пелин ) (8 July 1877 – 3 December 1949), born Dimitar Ivanov Stoyanov ( bg, Димитър Иванов Стоянов) is considered Bulgaria’s best narrator of the Bulgarian (Balkan) countryside and village.
...
, Gorna Malina
Gorna Malina ( bg, Горна Малина, ) is a village in western Bulgaria, part of Sofia Province. It is the administrative centre of Gorna Malina municipality, which lies in the central eastern part of Sofia Province, 20-30 kilometres east o ...
, Ihtiman
Ihtiman ( bg, Ихтиман ) is a town in western Bulgaria, part of Sofia Province. It is located in the Ihtimanska Sredna Gora mountains and lies in a valley 48 km from Sofia and 95 km from Plovdiv, close to the Trakiya motorway.
For ...
, Kostenets
Kostenets ( bg, Костенец ) is a town in Sofia Province in southwestern Bulgaria, and the administrative centre of the Kostenets Municipality (which also contains a separate village of Kostenets). The town is situated at the foot of Rila ...
) and Pernik Province
Pernik Province is a province in western Bulgaria, neighbouring Serbia. Its main city is Pernik, and other municipalities are Breznik, Kovachevtsi, Radomir, Tran, and Zemen.
Population
Pernik province had a population of 133,750 according ...
(Pernik
Pernik ( bg, Перник ) is a town in western Bulgaria (about south-west of Sofia) with a population of 70,285 . Pernik is the most populated town in western Bulgaria after Sofia. It is the main town of Pernik Province and lies on both banks ...
, Radomir), representing 5.16% of the country territory. The metropolitan area of Sofia is based upon one hour of car travel time, stretches internationally and includes Dimitrovgrad in Serbia. The metropolitan region of Sofia is inhabited by a population of 1.66 million.
Names
 For a long time the city possessed a
For a long time the city possessed a Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
name, Serdica (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
: , or ; Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
: or ), derived from the tribe ''Serdi
The Serdi were a Celtic tribe inhabiting Thrace. They were located around Serdica ( bg, Сердика, Serdika; ; el, Σαρδική o Σαρδῶν πόλις, Sardike o Sardon polis), now Sofia in Bulgaria, which reflects their ethnonym. They ...
'', who were either of Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
,"The Cambridge Ancient History", Volume 3, Part 2: ''The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC'' by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond, , 1992, p. 600: "In the place of the vanished Treres and Tilataei we find the Serdi for whom there is no evidence before the first century BC. It has for long been supposed on convincing linguistic and archeological grounds that this tribe was of Celtic origin" or mixed Thracian-Celtic origin. The emperor Marcus Ulpius Traianus (53–117 AD) gave the city the combinative name of '' Ulpia Serdica''; Ulpia may be derived from an Umbrian cognate of the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word ''lupus'', meaning "wolf" or from the Latin ''vulpes'' (fox).
It seems that the first written mention of ''Serdica'' was made during his reign and the last mention was in the 19th century in a Bulgarian text (Сардакіи, ''Sardaki''). Other names given to Sofia, such as ''Serdonpolis'' (Σερδών πόλις, "City of the Serdi" in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
) and ''Triaditza'' (Τριάδιτζα, "Trinity" in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
), were mentioned by Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
sources or coins. The Slavic name ''Sredets'' (Срѣдецъ), which is related to "middle" (среда, "sreda") and to the city's earliest name, first appeared on paper in an 11th-century text. The city was called ''Atralisa'' by the Arab traveller Idrisi
TerrSet (formerly IDRISI) is an integrated geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing software developed by Clark Labs at Clark University for the analysis and display of digital geospatial information. TerrSet is a PC grid-based syste ...
and ''Strelisa'', ''Stralitsa'' or ''Stralitsion'' by the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
.
The name ''Sofia'' comes from the Saint Sofia Church, as opposed to the prevailing Slavic origin of Bulgarian cities and towns. The origin is in the Greek word '' sophia'' (σοφία) "wisdom". The earliest works where this latest name is registered are the duplicate of the Gospel of Serdica, in a dialogue between two salesmen from Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterran ...
around 1359, in the 14th-century Vitosha Charter of Bulgarian tsar Ivan Shishman
Ivan Shishman ( bg, Иван Шишман) ruled as emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria in Tarnovo from 1371 to 3 June 1395. The authority of Ivan Shishman was limited to the central parts of the Bulgarian Empire.
In the wake of the death of Ivan Alexan ...
and in a Ragusan Ragusan may refer to:
* citizen of the Republic of Ragusa
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world"
, population_estimate ...
merchant's notes of 1376. In these documents the city is called ''Sofia'', but at the same time the region and the city's inhabitants are still called ''Sredecheski'' (срѣдечьскои, "of Sredets"), which continued until the 20th century. The Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
came to favour the name ''Sofya'' (صوفيه). In 1879 there was a dispute about what the name of the new Bulgarian capital should be, when the citizens created a committee of famous people, insisting for the Slavic name. Gradually, a compromise arose, officialisation of ''Sofia'' for the nationwide institutions, while legitimating the title ''Sredets'' for the administrative and church institutions, before the latter was abandoned through the years.
Geography
Sofia City Province
Sofia City Province ( bg, Област София-град, translit=Oblast Sofiya-grad) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. Its administrative center is the city of Sofia, the capital of the country.
The province borders on Sofia Provinc ...
has an area of 1344 km2, while the surrounding and much bigger Sofia Province
Sofia Province ( bg, Софийска област, translit=Sofiyska oblast) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. The province does not include Sofia in its territories, but Sofia remains its administrative center. The province borders on t ...
is 7,059 km2. Sofia's development as a significant settlement owes much to its central position in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. It is situated in western Bulgaria, at the northern foot of the Vitosha
Vitosha ( bg, Витоша ), the ancient ''Scomius'' or ''Scombrus'', is a mountain massif, on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. Vitosha is one of the symbols of Sofia and the closest site for hiking, alpinism and skiing. Conveni ...
mountain, in the Sofia Valley
The Sofia Valley ( bg, Софийска котловина, Sofiyska kotlovina), or Sofia Field ( bg, Софийско поле, Sofiysko pole, link=no), is a valley in central western Bulgaria bordering Stara Planina to the northeast, the Viskya ...
that is surrounded by the Balkan mountains
The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border betw ...
to the north. The valley has an average altitude of . Sofia is the second highest capital of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(after Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
) and the third highest capital of Europe (after Andorra la Vella
Andorra la Vella french: Andorre-la-Vieille is the capital (political), capital of the Andorra, Principality of Andorra. It is located high in the east Pyrenees, between France and Spain. It is also the name of the parishes of Andorra, parish ...
and Madrid). Unlike most European capitals, Sofia does not straddle any large river, but is surrounded by comparatively high mountains on all sides. Three mountain pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since many of the world's mountain ranges have presented formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human a ...
es lead to the city, which have been key roads since antiquity, Vitosha being the watershed between Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have o ...
and Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
s.
A number of shallow rivers cross the city, including the Boyanska, Vladayska and Perlovska
Perlovska river ( bg, Перловска река) is a small river in the Sofia Valley in western Bulgaria. The river is only long. It takes its source from the foothills of Vitosha, runs through Sofia's South Park, separates the two lanes of Evl ...
. The Iskar River
The Iskar ( bg, Искър, ; la, Oescus) is a right tributary of the Danube. With a length of 368 km it is the longest river that runs entirely within Bulgaria.Rila
Rila ( bg, Рила, ) is the highest mountain range of Bulgaria, the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula and Southeast Europe. It is situated in southwestern Bulgaria and forms part of the Rila–Rhodope Mountains, Rhodope Massif. The highest summit is Mus ...
, Bulgaria's highest mountain, and enters Sofia Valley near the village of German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
. The Iskar flows north toward the Balkan Mountains, passing between the eastern city suburbs, next to the main building and below the runways of Sofia Airport
Sofia Airport ( bg, Летище София, translit=Letishte Sofiya) is the main international airport of Bulgaria, located east of the centre of the capital Sofia. In 2019 the airport surpassed 7 million passengers for the first time. The ai ...
, and flows out of the Sofia Valley at the town of Novi Iskar
Novi Iskar ( bg, Нови Искър ) is a town in Western Bulgaria, located in Sofia City Province, which is a part of the Municipality of Sofia (the capital of Bulgaria).
It is often regarded as a northern suburb of Bulgarian capital Sofia and ...
, where the scenic Iskar Gorge The Iskar Gorge is a gorge passing through the Balkan Mountains (Stara Planina) in Bulgaria. It is the chief pass through the Balkans, which otherwise cross northern Bulgaria in a solid line. The pass connects the capital of Sofia with other major ...
begins.
The city is known for its 49 mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
and thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
springs. Artificial and dam lakes were built in the twentieth century.
While the 1818 and 1858 earthquakes were intense and destructive, the 2012 Pernik earthquake
The 2012 Pernik earthquake was a 5.6 magnitude earthquake, which struck 24 km (15 miles) west of Bulgaria's capital Sofia and 9 km (6 miles) north-northwest of the provincial center Pernik on at 3:00 am local time (00:00 UTC) at ...
occurred west of Sofia with a moment magnitude
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 pape ...
of 5.6 and a much lower Mercalli intensity of VI (''Strong''). The 2014 Aegean Sea earthquake was also noticed in the city.
Climate
Sofia has ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfb''; ''Cfb'' if with −3 °C isotherm) with an average annual temperature of .
Winters are relatively cold and snowy. Weather can be very unstable and dynamic with sudden significant temperature amplitudes. In the coldest days temperatures can drop below , most notably in January. The lowest recorded temperature is (16 January 1893). Fog is not unusual, especially in the beginning of the season. On average, Sofia receives a total snowfall of and 57 days with snow cover. The snowiest recorded winter was 1995/1996 with a total snowfall of . The record snow depth is (25 December 2001). The coldest recorded year was 1893 with an average January temperature of and an annual temperature of .
Summers are quite warm and sunny. In summer, the city generally remains slightly cooler than other parts of Bulgaria, due to its higher altitude. However, the city is also subject to heat waves with high temperatures reaching or exceeding on the hottest days, particularly in July and August. The highest recorded temperature is (5 July 2000 and 24 July 2007). The hottest recorded month was July 2012 with an average temperature of . The warmest year on record was 2019 with an annual temperature of .
Springs and autumns in Sofia are usually short with variable and dynamic weather.
The city receives an average precipitation of a year, reaching its peak in late spring and early summer when thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are someti ...
are common. The driest recorded year was 2000 with a total precipitation of , while the wettest year on record was 2014 with a total precipitation of .
Environment
The geographic position of the Sofia Valley limits the flow of air masses, increasing the chances of air pollution by particulate matter and nitrogen oxide. Solid fuel used for heating and motor vehicle traffic are significant sources of pollutants. Smog thus persists over the city as Inversion (meteorology), temperature inversions and the mountains surrounding the city prevent the circulation of air masses. As a result, air pollution levels in Sofia are some of the highest in Europe. Particulate matter concentrations are consistently above the norm. During the October 2017 – March 2018 heating season, particulate levels exceeded the norm on 70 occasions; on 7 January 2018, PM10 levels reached 632 µg/m3, some twelve times the EU norm of 50 µg/m3. Even areas with few sources of air pollution, like Gorna Banya, had PM2.5 and PM10 levels above safe thresholds. In response to hazardous spikes in air pollution, the Municipal Council implemented a variety of measures in January 2018, like more frequent washing of streets. However, a report by the European Court of Auditors issued in September 2018 revealed that Sofia has not drafted any projects to reduce air pollution from heating. The report also noted that no industrial pollution monitoring stations operate in Sofia, even though industrial facilities are active in the city. A monitoring station on Eagles' Bridge, where some of the highest particulate matter values were measured, was moved away from the location and has measured sharply lower values since then. Particulates are now largely measured by a network of 300 sensors maintained by volunteers since 2017. The European Commission has taken Bulgaria to court over its failure to curb air pollution.History

Prehistory and antiquity
The area has a history of nearly 7000 years, with the great attraction of the hot water springs that still flow abundantly in the centre of the city. The neolithic village in Slatina, Sofia, Slatina dating to the 5th–6th millennium BC is documented. Remains from another neolithic settlement around the National Art Gallery (Bulgaria), National Art Gallery are traced to the 3rd–4th millennium BC, which has been the traditional centre of the city ever since. The earliest tribes who settled were theThracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
Tilataei.
In the 500s BC, the area became part of a Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
state union, the Odrysian kingdom from another Thracian tribe the Odrysses.
In 339 BC Philip II of Macedon destroyed and ravaged the town for the first time.
The Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
tribe Serdi
The Serdi were a Celtic tribe inhabiting Thrace. They were located around Serdica ( bg, Сердика, Serdika; ; el, Σαρδική o Σαρδῶν πόλις, Sardike o Sardon polis), now Sofia in Bulgaria, which reflects their ethnonym. They ...
gave their name to the city. The earliest mention of the city comes from an Athens, Athenian inscription from the 1st century BC, attesting ''Astiu ton Serdon'', i.e. city of the Serdi
The Serdi were a Celtic tribe inhabiting Thrace. They were located around Serdica ( bg, Сердика, Serdika; ; el, Σαρδική o Σαρδῶν πόλις, Sardike o Sardon polis), now Sofia in Bulgaria, which reflects their ethnonym. They ...
. The inscription and Dio Cassius told that the Roman general Crassus subdued the Serdi
The Serdi were a Celtic tribe inhabiting Thrace. They were located around Serdica ( bg, Сердика, Serdika; ; el, Σαρδική o Σαρδῶν πόλις, Sardike o Sardon polis), now Sofia in Bulgaria, which reflects their ethnonym. They ...
and behanded the captives.
In 27–29 BC, according do Dio Cassius, Pliny the Elder, Pliny and Ptolemy, the region "Segetike" was attacked by Crassus, which is assumed to be Serdica, or the city of the Serdi. The ancient city is located between TZUM (Sofia), TZUM, Sheraton Hotel and the Presidency. It gradually became the most important Roman city of the region. It became a ''municipium'' during the reign of Emperor Trajan (98–117). Serdica expanded, as Turret (architecture), turrets, protective walls, public bathing, public baths, administrative and cult buildings, a civic basilica, an amphitheatre, a circus, the City council (Boulé), a large forum, a big circus (theatre), etc. were built. Serdica was a significant city on the Roman road Via Militaris, connecting Singidunum and Byzantium. In the 3rd century, it became the capital of Dacia Aureliana, and when Emperor Diocletian divided the province of Dacia Aureliana into Dacia Ripensis (at the banks of the Danube) and Dacia (Roman province), Dacia Mediterranea, Serdica became the capital of the latter. Serdica's citizens of Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
descent were referred to as Illyrians probably because it was at some time the capital of Eastern Illyria (Second Illyria).
 When Emperor Diocletian divided the province of Dacia into Dacia Ripensis (on the banks of the Danube) and Dacia Mediterranea, Serdica became the capital of the latter.
Roman emperors Aurelian (215–275) and Galerius (260–311) were born in Serdica.
The city expanded and became a significant political and economical centre, more so as it became one of the first Roman cities where Christianity was recognised as an State religion, official religion (under Galerius). The Edict of Toleration by Galerius was issued in 311 in Serdica by the Roman emperor Galerius, officially ending the Diocletianic persecution of Christianity. The Edict implicitly granted Christianity the status of "religio licita", a worship recognised and accepted by the Roman Empire. It was the first edict legalising Christianity, preceding the Edict of Milan by two years.
Serdica was the capital of the Diocese of Dacia (337-602).
For Constantine the Great it was 'Sardica mea Roma est' (Serdica is my Rome). He considered making Serdica the capital of the Byzantine Empire instead of Constantinople. which was already not dissimilar to a Tetrarchy, tetrarchic capital of the Roman Empire. In 343 AD, the Council of Sardica was held in the city, in a church located where the current 6th century Hagia Sophia Church (Sofia), Church of Saint Sophia was later built.
The city was destroyed in the Theodosius II#Wars with the Huns, Vandals, and Persians, 447 invasion of the
When Emperor Diocletian divided the province of Dacia into Dacia Ripensis (on the banks of the Danube) and Dacia Mediterranea, Serdica became the capital of the latter.
Roman emperors Aurelian (215–275) and Galerius (260–311) were born in Serdica.
The city expanded and became a significant political and economical centre, more so as it became one of the first Roman cities where Christianity was recognised as an State religion, official religion (under Galerius). The Edict of Toleration by Galerius was issued in 311 in Serdica by the Roman emperor Galerius, officially ending the Diocletianic persecution of Christianity. The Edict implicitly granted Christianity the status of "religio licita", a worship recognised and accepted by the Roman Empire. It was the first edict legalising Christianity, preceding the Edict of Milan by two years.
Serdica was the capital of the Diocese of Dacia (337-602).
For Constantine the Great it was 'Sardica mea Roma est' (Serdica is my Rome). He considered making Serdica the capital of the Byzantine Empire instead of Constantinople. which was already not dissimilar to a Tetrarchy, tetrarchic capital of the Roman Empire. In 343 AD, the Council of Sardica was held in the city, in a church located where the current 6th century Hagia Sophia Church (Sofia), Church of Saint Sophia was later built.
The city was destroyed in the Theodosius II#Wars with the Huns, Vandals, and Persians, 447 invasion of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
and laid in ruins for a century It was rebuilt by List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine Emperor Justinian I. During the reign of Justinian it flourished, being surrounded with great fortress walls whose remnants can still be seen today.
Middle Ages
 Serdica became part of the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Khan
Serdica became part of the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Khan Krum
Krum ( bg, Крум, el, Κροῦμος/Kroumos), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome ( bg, Крум Страшни) was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territor ...
in 809, after a long Siege of Serdica (809), siege. The fall of the strategic city prompted a major and ultimately disastrous invasion of Bulgaria by the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
emperor Nikephoros I, which led to his demise at the hands of the Medieval Bulgarian army, Bulgarian army. In the aftermath of the war, the city was permanently integrated in Bulgaria and became known by the Slavic name of Sredets. It grew into an important fortress and administrative centre under Krum's successor Khan Omurtag of Bulgaria, Omurtag, who made it a centre of Sredets province (Sredetski komitat, Средецки комитат). The Bulgarian patron saint John of Rila was buried in Sredets by orders of Emperor Peter I of Bulgaria, Peter I in the mid 10th century. After the conquest of the Bulgarian capital Preslav by Sviatoslav I, Sviatoslav I of Kyiv and John I Tzimiskes' armies in 970–971, the Patriarch of All Bulgaria, Bulgarian Patriarch Damyan chose Sredets for his seat in the next year and the capital of Bulgaria was temporarily moved there. In the second half of 10th century the city was ruled by Nicholas (komes), Komit Nikola and his sons, known as the "Cometopuli dynasty, Komitopuli". One of them was Samuel of Bulgaria, Samuil, who was eventually crowned Emperor of Bulgaria in 997. In 986, the Byzantine Emperor Basil II laid siege to Sredets but after 20 days of fruitless assaults the garrison broke out and forced the Byzantines to abandon the campaign. On his way to Constantinople, Basil II was ambushed and soundly defeated by the Bulgarians in the battle of the Gates of Trajan.
The city eventually fell to the Byzantine Empire in 1018, following the Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria. Sredets joined the uprising of Peter Delyan in 1040–1041 in a failed attempt to restore Bulgarian independence and was the last stronghold of the rebels, led by the local commander Botko.
It was once again incorporated into the Second Bulgarian Empire, restored Bulgarian Empire in 1194 at the time of Emperor Ivan Asen I of Bulgaria, Ivan Asen I and became a major administrative and cultural centre. Several of the city's governors were members of the Bulgarian imperial family and held the title of ''sebastokrator'', the second highest at the time, after the tsar. Some known holders of the title were Kaloyan (sebastocrator), Kaloyan, Peter (sevastokrator), Peter and their relative Aleksandar Asen (d. after 1232), a son of Ivan Asen I of Bulgaria (). In the 13th and 14th centuries Sredets was an important spiritual and literary hub with a cluster of 14 monasteries in its vicinity, that were eventually destroyed by the Ottomans. The city produced multicolored sgraffito ceramics, jewelry and ironware.
In 1382/1383 or 1385, Sredets was seized by the Ottoman Empire in the course of the Bulgarian–Ottoman Wars, Bulgarian-Ottoman Wars by Lala Şahin Pasha, following a Siege of Sofia, three-month siege.Ivanova, Svetlana, "Ṣofya", in: Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition, Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W.P. Heinrichs. Consulted online on 23 January 2018. The Ottoman commander left the following description of the city garrison: "Inside the fortress [Sofia] there is a large and elite army, its soldiers are heavily built, moustached and look war-hardened, but are used to consume wine and rakia—in a word, jolly fellows."
Early modern history
From the 14th century till the 19th century Sofia was an important administrative center in the Ottoman Empire. It became the capital of the beylerbeylik of Rumelia (Rumelia Eyalet
The Eyalet of Rumeli, or Eyalet of Rumelia ( ota, ایالت روم ایلی, ), known as the Beylerbeylik of Rumeli until 1591, was a first-level province ('' beylerbeylik'' or ''eyalet'') of the Ottoman Empire encompassing most of the Balkans (" ...
), the Administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire, province that administered the Ottoman lands in Europe (the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
), one of the two together with the beylerbeylik of Anatolia. It was the capital of the important Sanjak of Sofia as well, including the whole of Thrace with Plovdiv and Edirne, and part of Macedonia (region), Macedonia with Thessaloniki and Skopje.
During the initial stages of the Crusade of Varna in 1443, it was occupied by Hungarian forces for a short time in 1443, and the Bulgarian population celebrated a mass Saint Sofia Church. Following the defeat of the crusader forces in 1444, the city's Christians faced persecution. In 1530 Sofia became the capital of the Subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman province (beylerbeylik) of Rumelia for about three centuries. During that time Sofia was the largest import-export-base in modern-day Bulgaria for the caravan trade with the Republic of Ragusa. In the 15th and 16th century, Sofia was expanded by Ottoman building activity. Public investments in infrastructure, education and local economy brought greater diversity to the city. Amongst others, the population consisted of Muslims, Bulgarian language, Bulgarian and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
speaking Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christians, Armenians, Georgians, Catholic Church, Catholic Ragusans, Jews (Romaniote Jews, Romaniote, Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi and Sephardi), and Romani people. The 16th century was marked by a wave of persecutions against the Bulgarian Christians, a total of nine became New Martyrs in Sofia and were sainted by the Orthodox Church, including George of Kratovo, George the New (1515), Sophronius of Sofia (1515), George the Newest (1530), St. Nicholas of Sofia, Nicholas of Sofia (1555) and Terapontius of Sofia (1555).
 When it comes to the cityscape, 16th century sources mention eight Jama Masjid, Friday mosques, three public libraries, numerous schools, 12 churches, three synagogues, and the largest bedesten (market) of the Balkans. Additionally, there were fountains and ''Turkish bath, hammams'' (bathhouses). Most prominent churches such as Saint Sofia and Saint George were converted into mosques, and a number of new ones were constructed, including
When it comes to the cityscape, 16th century sources mention eight Jama Masjid, Friday mosques, three public libraries, numerous schools, 12 churches, three synagogues, and the largest bedesten (market) of the Balkans. Additionally, there were fountains and ''Turkish bath, hammams'' (bathhouses). Most prominent churches such as Saint Sofia and Saint George were converted into mosques, and a number of new ones were constructed, including Banya Bashi Mosque
Banya Bashi Mosque ( bg, Баня баши джамия, ; tr, Banya Başı Camii) is a mosque in Sofia, Bulgaria.
History
The mosque was designed by the famous Ottoman architect Mimar Sinan and completed in 1566, during the years the Otto ...
built by the renowned Ottoman architect Mimar Sinan. In total there were 11 big and over 100 small mosques by the 17th century. In 1610 the Catholic Church, Vatican established the Roman Catholic Diocese of Sofia and Plovdiv, See of Sofia for Catholics of Rumelia, which existed until 1715 when most Catholics had emigrated. There was an important uprising against Ottoman rule in Sofia, Samokov and Western Bulgaria in 1737.
Sofia entered a period of economic and political decline in the 17th century, accelerated during the period of anarchy in the Ottoman Balkans of the late 18th and early 19th century, when local Ottoman warlords ravaged the countryside. Since the 18th century the ''beylerbeys'' of Rumelia often stayed in Bitola, which became the official capital of the province in 1826. Sofia remained the seat of a sanjak (district). By the 19th century the Bulgarian population had two schools and seven churches, contributing to the Bulgarian National Revival. In 1858 Nedelya Petkova created the first Bulgarian school for women in the city. In 1867 was inaugurated the first ''chitalishte'' in Sofia – a Bulgarian cultural institution. In 1870 the Bulgarian revolutionary Vasil Levski established a Internal Revolutionary Organization, revolutionary committee in the city and in the neighbouring villages. Following his capture in 1873, Vasil Levski was transferred and hanged in Sofia by the Ottomans.
Modern and contemporary history
During the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, Suleiman Pasha (Ottoman general), Suleiman Pasha threatened to burn the city in defence, but the foreign diplomats Leandre Legay, Vito Positano, Rabbi Gabriel Almosnino and Josef Valdhart refused to leave the city thus saving it. Many Bulgarian residents of Sofia armed themselves and sided with the Russian forces. Sofia was relieved (see Battle of Sofia) from Ottoman rule of Bulgaria, Ottoman rule by Imperial Russian Army, Russian forces under Gen. Iosif Gurko on 4 January 1878. It was proposed as a capital by Marin Drinov and was accepted as such on 3 April 1879. By the time of its liberation the population of the city was 11,649. Most mosques in Sofia were destroyed in that war, seven of them destroyed in one night in December 1878 when a thunderstorm masked the noise of the explosions arranged by Russian military engineers. Following the war, the great majority of the Muslim population left Sofia. For a few decades after the liberation, Sofia experienced large population growth, mainly by migration from other regions of the Principality (Kingdom since 1908) of Bulgaria, and from the still Ottoman Macedonia (region), Macedonia and Thrace.
In 1900, the first electric lightbulb in the city was turned on.
In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria was fighting alone practically all of its neighbouring countries. When the Romanian Army entered Vrazhdebna in 1913, then a village from Sofia, now a suburb,Hall (2000), p. 97. this prompted the Kingdom of Bulgaria, Tsardom of Bulgaria to capitulate. During the war, Sofia was flown by the Romanian Air Corps, which engaged on photoreconnaissance operations and threw propaganda pamphlets to the city. Thus, Sofia became the first capital on the world to be overflown by enemy aircraft.Hall (2000), p. 118.
In 1925, a terrorist act of ultra-leftists failed their attempted assassination of the king but resulted in the destruction of the Saint Nedelya Church and many victims.
During the Military history of Bulgaria during World War II, Second World War, Bulgaria declared war on the US and UK on 13 December 1941 and in late 1943 and early 1944 the Bombing of Sofia in World War II, US and UK Air forces conducted bombings over Sofia. As a consequence of the bombings thousands of buildings were destroyed or damaged including the Capital Library and thousands of books. In 1944 Sofia and the rest of Bulgaria was occupied by the Soviet Red Army and within days of the Soviet invasion Bulgaria declared war on Nazi Germany.
In 1945, the communist Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power. The transformations of Bulgaria into the People's Republic of Bulgaria in 1946 and into the Republic of Bulgaria in 1990 marked significant changes in the city's appearance. The population of Sofia expanded rapidly due to migration from rural regions. New residential areas were built in the outskirts of the city, like Druzhba, Mladost and Lyulin.
During the Bulgarian Communist Party, Communist Party rule, a number of the city's most emblematic streets and squares were renamed for ideological reasons, with the original names restored after 1989.
The Georgi Dimitrov Mausoleum, where Georgi Dimitrov, Dimitrov's body had been preserved in a similar way to the Lenin mausoleum, was demolished in 1999.
For a few decades after the liberation, Sofia experienced large population growth, mainly by migration from other regions of the Principality (Kingdom since 1908) of Bulgaria, and from the still Ottoman Macedonia (region), Macedonia and Thrace.
In 1900, the first electric lightbulb in the city was turned on.
In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria was fighting alone practically all of its neighbouring countries. When the Romanian Army entered Vrazhdebna in 1913, then a village from Sofia, now a suburb,Hall (2000), p. 97. this prompted the Kingdom of Bulgaria, Tsardom of Bulgaria to capitulate. During the war, Sofia was flown by the Romanian Air Corps, which engaged on photoreconnaissance operations and threw propaganda pamphlets to the city. Thus, Sofia became the first capital on the world to be overflown by enemy aircraft.Hall (2000), p. 118.
In 1925, a terrorist act of ultra-leftists failed their attempted assassination of the king but resulted in the destruction of the Saint Nedelya Church and many victims.
During the Military history of Bulgaria during World War II, Second World War, Bulgaria declared war on the US and UK on 13 December 1941 and in late 1943 and early 1944 the Bombing of Sofia in World War II, US and UK Air forces conducted bombings over Sofia. As a consequence of the bombings thousands of buildings were destroyed or damaged including the Capital Library and thousands of books. In 1944 Sofia and the rest of Bulgaria was occupied by the Soviet Red Army and within days of the Soviet invasion Bulgaria declared war on Nazi Germany.
In 1945, the communist Fatherland Front (Bulgaria), Fatherland Front took power. The transformations of Bulgaria into the People's Republic of Bulgaria in 1946 and into the Republic of Bulgaria in 1990 marked significant changes in the city's appearance. The population of Sofia expanded rapidly due to migration from rural regions. New residential areas were built in the outskirts of the city, like Druzhba, Mladost and Lyulin.
During the Bulgarian Communist Party, Communist Party rule, a number of the city's most emblematic streets and squares were renamed for ideological reasons, with the original names restored after 1989.
The Georgi Dimitrov Mausoleum, where Georgi Dimitrov, Dimitrov's body had been preserved in a similar way to the Lenin mausoleum, was demolished in 1999.
Cityscape
 In Sofia there are 607,473 dwellings and 101,696 buildings. According to modern records, 39,551 dwellings were constructed until 1949, 119,943 between 1950 and 1969, 287,191 between 1970 and 1989, 57,916 in the 90s and 102,623 between 2000 and 2011. Until 1949, 13,114 buildings were constructed and between 10,000 and 20,000 in each following decade. Sofia's architecture combines a wide range of architectural styles, some of which are aesthetically incompatible. These vary from Christian Roman architecture and medieval Bulgarian fortresses to Neoclassicism and prefabricated Socialist-era apartment blocks. A number of ancient Roman, Byzantine and medieval Bulgarian buildings are preserved in the centre of the city. These include the 4th century Church of St. George, Sofia, Rotunda of St. George, the walls of the Serdica fortress and the partially preserved Amphitheatre of Serdica.
After the Liberation War, knyaz Alexander, Prince of Bulgaria, Alexander Battenberg invited architects from Austria-Hungary to shape the new capital's architectural appearance.
Among the architects invited to work in Bulgaria were Friedrich Grünanger, Adolf Václav Kolář, and Viktor Rumpelmayer, who designed the most important public buildings needed by the newly re-established Bulgarian government, as well as numerous houses for the country's elite. Later, many foreign-educated Bulgarian architects also contributed. The architecture of Sofia's centre is thus a combination of Baroque Revival architecture, Neo-Baroque, Neo-Rococo, Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance and Neoclassicism, with the Vienna Secession also later playing an important part, but it is most typically Central European.
After World War II and the establishment of a Communist state, Communist government in Bulgaria in 1944, the architectural style was substantially altered. Stalinist architecture, Stalinist Gothic public buildings emerged in the centre, notably the spacious government complex around Largo, Sofia, The Largo, Vasil Levski Stadium, the Cyril and Methodius National Library and others. As the city grew outwards, the then-new neighbourhoods were dominated by many concrete tower blocks, prefabricated panel apartment buildings and examples of Brutalist architecture.
After the abolition of Communism in 1989, Sofia witnessed the construction of whole business districts and neighbourhoods, as well as modern skryscraper-like glass-fronted office buildings, but also top-class residential neighbourhoods. The Capital Fort Business Centre is the first skyscraper in Bulgaria, with its 36 floors. However, the end of the old administration and centrally planned system also paved the way for chaotic and unrestrained construction, which continues today.
In Sofia there are 607,473 dwellings and 101,696 buildings. According to modern records, 39,551 dwellings were constructed until 1949, 119,943 between 1950 and 1969, 287,191 between 1970 and 1989, 57,916 in the 90s and 102,623 between 2000 and 2011. Until 1949, 13,114 buildings were constructed and between 10,000 and 20,000 in each following decade. Sofia's architecture combines a wide range of architectural styles, some of which are aesthetically incompatible. These vary from Christian Roman architecture and medieval Bulgarian fortresses to Neoclassicism and prefabricated Socialist-era apartment blocks. A number of ancient Roman, Byzantine and medieval Bulgarian buildings are preserved in the centre of the city. These include the 4th century Church of St. George, Sofia, Rotunda of St. George, the walls of the Serdica fortress and the partially preserved Amphitheatre of Serdica.
After the Liberation War, knyaz Alexander, Prince of Bulgaria, Alexander Battenberg invited architects from Austria-Hungary to shape the new capital's architectural appearance.
Among the architects invited to work in Bulgaria were Friedrich Grünanger, Adolf Václav Kolář, and Viktor Rumpelmayer, who designed the most important public buildings needed by the newly re-established Bulgarian government, as well as numerous houses for the country's elite. Later, many foreign-educated Bulgarian architects also contributed. The architecture of Sofia's centre is thus a combination of Baroque Revival architecture, Neo-Baroque, Neo-Rococo, Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance and Neoclassicism, with the Vienna Secession also later playing an important part, but it is most typically Central European.
After World War II and the establishment of a Communist state, Communist government in Bulgaria in 1944, the architectural style was substantially altered. Stalinist architecture, Stalinist Gothic public buildings emerged in the centre, notably the spacious government complex around Largo, Sofia, The Largo, Vasil Levski Stadium, the Cyril and Methodius National Library and others. As the city grew outwards, the then-new neighbourhoods were dominated by many concrete tower blocks, prefabricated panel apartment buildings and examples of Brutalist architecture.
After the abolition of Communism in 1989, Sofia witnessed the construction of whole business districts and neighbourhoods, as well as modern skryscraper-like glass-fronted office buildings, but also top-class residential neighbourhoods. The Capital Fort Business Centre is the first skyscraper in Bulgaria, with its 36 floors. However, the end of the old administration and centrally planned system also paved the way for chaotic and unrestrained construction, which continues today.


Green areas
 The city has an extensive green belt. Some of the neighbourhoods constructed after 2000 are densely built up and lack green spaces. There are four principal parks – Borisova gradina in the city centre and the ''Southern'', ''Western'' and ''Northern'' parks. Several smaller parks, among which the Vazrazhdane Park, Zaimov Park, City Garden (Sofia), City Garden and the Doctors' Garden, are located in central Sofia. The
The city has an extensive green belt. Some of the neighbourhoods constructed after 2000 are densely built up and lack green spaces. There are four principal parks – Borisova gradina in the city centre and the ''Southern'', ''Western'' and ''Northern'' parks. Several smaller parks, among which the Vazrazhdane Park, Zaimov Park, City Garden (Sofia), City Garden and the Doctors' Garden, are located in central Sofia. The Vitosha
Vitosha ( bg, Витоша ), the ancient ''Scomius'' or ''Scombrus'', is a mountain massif, on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. Vitosha is one of the symbols of Sofia and the closest site for hiking, alpinism and skiing. Conveni ...
Nature Park (the oldest national park in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
) includes most of Vitosha
Vitosha ( bg, Витоша ), the ancient ''Scomius'' or ''Scombrus'', is a mountain massif, on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. Vitosha is one of the symbols of Sofia and the closest site for hiking, alpinism and skiing. Conveni ...
mountain and covers an area of , with roughly half of it lying within the municipality of Sofia. Vitosha mountain is a popular hiking destination due to its proximity and ease of access via car and public transport. Two functioning cable cars provide year long access from the outskirts of the city. The mountain offers favourable skiing conditions during the winter. During the 1970s and the 1980s multiple ski slopes of varying difficulty were made available. Skiing equipment can be rented and skiing lessons are available. However, due to the bad communication between the private offshore company that runs the resort and Sofia municipality, most of the ski areas have been left to decay in the last 10 years, so that only one chairlift and one slope work.
Government and law
Local government
Sofia City Province
Sofia City Province ( bg, Област София-град, translit=Oblast Sofiya-grad) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. Its administrative center is the city of Sofia, the capital of the country.
The province borders on Sofia Provinc ...
, which is distinct from Sofia Province
Sofia Province ( bg, Софийска област, translit=Sofiyska oblast) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. The province does not include Sofia in its territories, but Sofia remains its administrative center. The province borders on t ...
, which surrounds but does not include the capital itself. Besides the city proper, the 24 districts of Sofia Municipality encompass three other towns and 34 villages. Districts and settlements have their own governor who is elected in a popular election. The assembly members are chosen every four years. The common head of Sofia Municipality and all the 38 settlements is the List of mayors of Sofia, mayor of Sofia. The mayor Yordanka Fandakova is serving a third consecutive term, having won the 2015 election at first round with 238,500 votes, or 60.2% of the vote, when Reformist Bloc opponent Vili Lilkov was second with 9.6%; the turnout was 41.25%. Some party leaders claimed that ballots were falsified and called for annulment of the election. A precedent happened, due to the suspicion, as a preventative action between 300 and 5000 people and counters had been locked inside Arena Armeets against their will for two days, following which the director of the Electoral Commission of Sofia resigned at the request of Prime Minister Boyko Borisov.
National government
Sofia is the seat of the executive (Government of Bulgaria, Council of Ministers), legislative (National Assembly (Bulgaria), National Assembly) and judiciary (Supreme Court of Bulgaria, Supreme Court and Constitutional Court of Bulgaria, Constitutional Court) bodies of Bulgaria, as well as all government agencies, ministries, the Bulgarian National Bank, National Bank, and the delegation of the European Commission. The President of Bulgaria, President, along with the Council of Ministers, is located on Largo, Sofia, Independence Square, also known as The Largo or ''The Triangle of Power''. One of the three buildings in the architectural ensemble, the former Bulgarian Communist Party headquarters, is due to become the seat of the Parliament. A refurbishment project is due to be completed in mid-2019, while the Bulgaria National Assembly Building, old National Assembly building will become a museum or will only host ceremonial political events.
Crime
With a murder rate of 1.7/per 100.000 people () Sofia is a quite safe capital city. Nevertheless, in the 21st century, crimes, including Bulgarian mafia killings, caused problems in the city, where authorities had difficulties convicting the actors, which had caused the European Commission to warn the Bulgarian government that the country would not be able to join the EU unless it curbed crime (Bulgaria eventually joined in 2007). Many of the most severe crimes are contract killings that are connected to organised crime, but these had dropped in recent years after several arrests of gang members. Crime in Bulgaria#Corruption, Corruption in Bulgaria also affects Sofia's authorities. According to the director of Sofia District Police Directorate, the largest share of the crimes are thefts, making up 62.4% of all crimes in the capital city. Increasing are frauds, drug-related crimes, petty theft and vandalism. According to a survey, almost a third of Sofia's residents say that they never feel safe in the Bulgarian capital, while 20% always feel safe. , the consumer-reported perceived crime risk on the Numbeo database was "high" for theft and vandalism and "low" for violent crimes; safety while walking during daylight was rated "very high", and "moderate" during the night. With 1,600 prisoners, the incarceration rate is above 0.1%; however, roughly 70% of all prisoners are part of the Romani people in Bulgaria, Romani minority.Culture
Arts and entertainment
 Sofia concentrates the majority of Bulgaria's leading performing arts troupes. Theatre is by far the most popular form of performing art, and theatrical venues are among the most visited, second only to cinemas. There were 3,162 theatric performances with 570,568 people attending in 2014. The
Sofia concentrates the majority of Bulgaria's leading performing arts troupes. Theatre is by far the most popular form of performing art, and theatrical venues are among the most visited, second only to cinemas. There were 3,162 theatric performances with 570,568 people attending in 2014. The Ivan Vazov National Theatre
The Ivan Vazov National Theatre ( bg, Народен театър „Иван Вазов“, ') is Bulgaria's national theatre, as well as the oldest and most authoritative theatre in the country and one of the important landmarks of Sofia, the ...
, which performs mainly classical plays and is situated in the very centre of the city, is the most prominent theatre. The National Opera and Ballet of Bulgaria
The National Opera and Ballet ( bg, Национална опера и балет) is a national cultural institution in Bulgaria that covers opera and ballet. It is based in an imposing building in Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria.
The first opera ...
is a combined opera and ballet collective established in 1891. Regular performances began in 1909. Some of Bulgaria's most famous operatic singers, such as Nicolai Ghiaurov and Ghena Dimitrova, made their first appearances on the stage of the National Opera and Ballet.
Cinema is the most popular form of entertainment: there were more than 141,000 film shows with a total attendance exceeding 2,700,000 in 2014. Over the past two decades, numerous independent cinemas have closed and most shows are in shopping centre Multiplex (movie theater), multiplexes. ''Odeon'' (not part of the Odeon Cinemas chain) shows exclusively European and independent American films, as well as 20th century classics. The Boyana Film studios was at the centre of a once-thriving domestic film industry, which declined significantly after 1990. Nu Image acquired the studios to upgrade them into Nu Boyana Film Studios, used to shoot scenes for a number of action movies like ''The Expendables 2'', ''Rambo: Last Blood'' and ''London Has Fallen''.
Bulgaria's largest art museums are located in the central areas of the city. Since 2015, the National Art Gallery (Bulgaria), National Art Gallery, the National Gallery for Foreign Art (NGFA) and the Museum of Contemporary Art – Sofia Arsenal were merged to form the National Gallery. Its largest branch is Kvadrat 500, located on the NFGA premises, where some 2,000 works are on display in twenty eight exhibition halls. The collections encompass diverse cultural items, from Ashanti Empire sculptures and Buddhism, Buddhist art to Dutch Golden Age painting, works by Albrecht Dürer, Jean-Baptiste Greuze and Auguste Rodin. The crypt of the Alexander Nevsky cathedral is another branch of the National Gallery. It holds a collection of Eastern Orthodox icons from the 9th to the 19th century.
The National Historical Museum (Bulgaria), National History Museum, located in Boyana, it has a vast collection of more than 650,000 historical items dating from Prehistory to the modern era, although only 10,000 of them are permanently displayed due to the lack of space. Smaller collections of historical items are displayed in the National Archaeological Museum (Bulgaria), National Archaeological Museum, a former mosque located between the edifices of the National Bank and the Presidency. Two natural sciences museums—the National Museum of Natural History (Bulgaria), Natural History Museum and Earth and Man National Museum, Earth and Man—display minerals, animal species (alive and Taxidermy, taxidermic) and rare materials. The Ethnographic Museum and the National Museum of Military History (Bulgaria), Museum of Military History hold large collections of Bulgarian folk costumes and armaments, respectively. The National Polytechnical Museum, Polytechnical Museum has more than 1,000 technological items on display. The SS. Cyril and Methodius National Library, the foremost information repository in the country, holds some 1,800,000 books and more than 7,000,000 documents, manuscripts, maps and other items.

 The city houses many cultural institutes such as the Russian Cultural Institute, the Polish Cultural Institute, the Hungarian Institute, the Czech and the Slovak Cultural Institutes, the Italian Cultural Institute, Confucius Institute, Institut Français, Goethe-Institut, Goethe Institut, British Council and Instituto Cervantes which regularly organise temporary expositions of visual, sound and literary works by artists from their respective countries.
Some of the biggest telecommunications companies, TV and radio stations, newspapers, magazines, and web portals are based in Sofia, including the Bulgarian National Television, BTV (Bulgaria), bTV and Nova Television (Bulgaria), Nova TV. Top-circulation newspapers include ''24 Chasa'' and ''Dneven Trud, Trud''.
The
The city houses many cultural institutes such as the Russian Cultural Institute, the Polish Cultural Institute, the Hungarian Institute, the Czech and the Slovak Cultural Institutes, the Italian Cultural Institute, Confucius Institute, Institut Français, Goethe-Institut, Goethe Institut, British Council and Instituto Cervantes which regularly organise temporary expositions of visual, sound and literary works by artists from their respective countries.
Some of the biggest telecommunications companies, TV and radio stations, newspapers, magazines, and web portals are based in Sofia, including the Bulgarian National Television, BTV (Bulgaria), bTV and Nova Television (Bulgaria), Nova TV. Top-circulation newspapers include ''24 Chasa'' and ''Dneven Trud, Trud''.
The Boyana Church
The Boyana Church ( bg, Боянска църква, ''Boyanska tsărkva'') is a medieval Bulgarian Orthodox church situated on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria, in the Boyana quarter. In 1979, the building was added to the UNESCO W ...
, a UNESCO World Heritage site, contains realistic frescoes, depicting more than 240 human images and a total 89 scenes, were painted. With their vital, humanistic realism they are a Renaissance phenomenon at its culmination phase in the context of the common-European art.
Tourism
 Sofia is one of the most visited tourist destinations in Bulgaria alongside coastal and mountain resorts. Among its highlights is the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Sofia, Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, one of the symbols of Bulgaria, constructed in the late 19th century. It occupies an area of and can hold 10,000 people.
The city center contains many remains of ancient Serdica that have been excavated and are on public display, including ''Complex Ancient Serdica'', eastern gate, western gate, city walls, thermal baths, 4th c. Church of St. George, Sofia, church of St. George Rotunda, amphitheatre of Serdica, the tombs and basilicas under the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, basilica of St. Sophia.
Vitosha Boulevard, also called ''Vitoshka'', is a pedestrian zone with numerous cafés, restaurants, fashion boutiques, and luxury goods stores. Sofia's geographic coordinate system, geographic location, in the foothills of the weekend retreat
Sofia is one of the most visited tourist destinations in Bulgaria alongside coastal and mountain resorts. Among its highlights is the Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, Sofia, Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, one of the symbols of Bulgaria, constructed in the late 19th century. It occupies an area of and can hold 10,000 people.
The city center contains many remains of ancient Serdica that have been excavated and are on public display, including ''Complex Ancient Serdica'', eastern gate, western gate, city walls, thermal baths, 4th c. Church of St. George, Sofia, church of St. George Rotunda, amphitheatre of Serdica, the tombs and basilicas under the Saint Sophia Church, Sofia, basilica of St. Sophia.
Vitosha Boulevard, also called ''Vitoshka'', is a pedestrian zone with numerous cafés, restaurants, fashion boutiques, and luxury goods stores. Sofia's geographic coordinate system, geographic location, in the foothills of the weekend retreat Vitosha
Vitosha ( bg, Витоша ), the ancient ''Scomius'' or ''Scombrus'', is a mountain massif, on the outskirts of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. Vitosha is one of the symbols of Sofia and the closest site for hiking, alpinism and skiing. Conveni ...
mountain, further adds to the city's specific atmosphere.
Sports
A large number of sports clubs are based in the city. During the Communist era, most sports clubs concentrated on all-round sporting development, therefore USC CSKA Sofia, CSKA, Levski Sofia (sports club), Levski, PFC Lokomotiv Sofia, Lokomotiv and PFC Slavia Sofia, Slavia are dominant not only in football, but in many other team sports as well. Basketball and volleyball also have strong traditions in Sofia. A notable local basketball team is twice Euroleague#Champions 1958-2008, European Champions Cup finalist PBC Lukoil Academic, Lukoil Akademik. The Bulgarian Volleyball Federation is the world's second-oldest, and it was an exhibition tournament organised by the BVF in Sofia that convinced the International Olympic Committee to include volleyball as an Volleyball at the Summer Olympics#History, olympic sport in 1957. Tennis is increasingly popular in the city. There are some ten tennis court complexes within the city including the one founded by former Women's Tennis Association, WTA top-five athlete Magdalena Maleeva. Sofia applied to host the Winter Olympic Games in 1992 and in 1994, coming second and third respectively. The city was also an applicant for the 2014 Winter Olympics, but was not selected as candidate. In addition, Sofia hosted EuroBasket 1957 and the 1961 Summer Universiade, 1961 and 1977 Summer Universiades, as well as the 1983 Winter Universiade, 1983 and 1989 Winter Universiade, 1989 winter editions. In 2012, it hosted the FIVB World League finals. The city is home to a number of large sports venues, including the 43,000-seat
The city is home to a number of large sports venues, including the 43,000-seat Vasil Levski National Stadium
Vasil Levski National Stadium ( bg, Национален стадион „Васил Левски“), named after Bulgarian national hero and revolutionary Vasil Levski (1837–1873), is the country's second largest stadium. The stadium has 43,2 ...
which hosts international football matches, as well as Stadion Balgarska Armia, Balgarska Armia Stadium, Georgi Asparuhov Stadium and Lokomotiv Stadium (Sofia), Lokomotiv Stadium, the main venues for outdoor musical concerts. Armeets Arena holds many indoor events and has a capacity of up to 19,000 people depending on its use. The venue was inaugurated on 30 July 2011, and the first event it hosted was a friendly volleyball match between Bulgaria and Serbia. There are two ice skating complexes — the Winter Sports Palace with a capacity of 4,600 and the Slavia Winter Stadium with a capacity of 2,000, both containing two rinks each. A velodrome with 5,000 seats in the city's Borisova gradina, central park is undergoing renovation. There are also various other sports complexes in the city which belong to institutions other than football clubs, such as those of the National Sports Academy "Vasil Levski", National Sports Academy, the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, or those of different universities. There are more than fifteen swimming complexes in the city, most of them outdoor. Nearly all of these were constructed as competition venues and therefore have seating facilities for several hundred people.
There are two golf courses just to the east of Sofia — in Elin Pelin (St Sofia club) and in Ihtiman (Air Sofia club), and a horseriding club (St George club).
Sofia was designated as European Capital of Sport in 2018. The decision was announced in November 2014 by the Evaluation Committee of ACES Europe, on the grounds that "the city is a good example of sport for all, as means to improve healthy lifestyle, integration and education, which are the basis of the initiative."
Demographics
Population over the years (in thousands): According to 2018 data, the city has a population of 1,400,384 and the whole Sofia Capital Municipality of 1,500,120. The first census carried out in February 1878 by the Russian Army recorded a population of 11,694 inhabitants including 6,560 Bulgarians, 3,538 Bulgarian Jews, Jews, 839 Turkish people, Turks and 737 Romani people, Romani.
The ratio of women per 1,000 men was 1,102. The birth rate per 1000 people was 12.3 per mile and steadily increasing in the last 5 years, the Mortality rate, death rate reaching 12.1 per mile and decreasing. The natural growth rate during 2009 was 0.2 per mile, the first positive growth rate in nearly 20 years. The considerable immigration to the capital from poorer regions of the country, as well as urbanisation, are among the other reasons for the increase in Sofia's population. The infant mortality rate was 5.6 per 1,000, down from 18.9 in 1980. According to the 2011 census, people aged 20–24 years are the most numerous group, numbering 133,170 individuals and accounting for 11% of the total 1,202,761 people. The median age is 38 though. According to the census, 1,056,738 citizens (87.9%) are recorded as ethnic Bulgarians, 17,550 (1.5%) as Romani people in Bulgaria, Romani, 6,149 (0.5%) as Turks in Bulgaria, Turks, 9,569 (0.8%) belonged to other ethnic groups, 6,993 (0.6%) do not self-identify and 105,762 (8.8%) remained with undeclared affiliation.
According to the 2011 census, throughout the whole municipality some 892,511 people (69.1%) are recorded as Eastern Orthodox Christians, 10,256 (0.8%) as Protestantism in Bulgaria, Protestant, 6,767 (0.5%) as Islam in Bulgaria, Muslim, 5,572 (0.4%) as Roman Catholicism in Bulgaria, Roman Catholic, 4,010 (0.3%) belonged to other faith and 372,475 (28.8%) declared themselves irreligious or did not mention any faith. The data says that roughly a third of the total population have already earned a university degree. Of the population aged 15–64 – 265,248 people within the municipality (28.5%) are not economically active, the unemployed being another group of 55,553 people (6%), a large share of whom have completed higher education. The largest group are occupied in trading, followed by those in manufacturing industry. Within the municipality, three-quarters, or 965,328 people are recorded as having access to television at home and 836,435 (64.8%) as having internet. Out of 464,865 homes – 432,847 have connection to the communal sanitary sewer, while 2,732 do not have any. Of these 864 do not have any water supply and 688 have other than communal. Over 99.6% of males and females aged over 9 are recorded as literacy, literate. The largest group of the population aged over 20 are recorded to live within marriage (46.3%), another 43.8% are recorded as single and another 9.9% as having other type of coexistence/partnership, whereas not married in total are a majority and among people aged up to 40 and over 70. The people with juridical status divorced or widowed are either part of the factual singles or those having another type of partnership, each of the two constitutes by around 10% of the population aged over 20. Only over 1% of the juridically married do not de facto live within marriage. The families that consist of two people are 46.8%, another 34.2% of the families are made up by three people, whereas most of the households (36.5%) consist of only one person.
Sofia was declared the national capital in 1879. One year later, in 1880, it was the fifth-largest city in the country after Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse and Shumen. Plovdiv remained the most populous Bulgarian town until 1892 when Sofia took the lead. The city is the hot spot of internal migration, the capital population is increasing and is around 17% of the national, thus a small number of people with local roots remain today, they dominate the surrounding Districts of Sofia, rural suburbs and are called Shopi. Shopi speak the Bulgarian dialects, Western Bulgarian dialects.
According to 2018 data, the city has a population of 1,400,384 and the whole Sofia Capital Municipality of 1,500,120. The first census carried out in February 1878 by the Russian Army recorded a population of 11,694 inhabitants including 6,560 Bulgarians, 3,538 Bulgarian Jews, Jews, 839 Turkish people, Turks and 737 Romani people, Romani.
The ratio of women per 1,000 men was 1,102. The birth rate per 1000 people was 12.3 per mile and steadily increasing in the last 5 years, the Mortality rate, death rate reaching 12.1 per mile and decreasing. The natural growth rate during 2009 was 0.2 per mile, the first positive growth rate in nearly 20 years. The considerable immigration to the capital from poorer regions of the country, as well as urbanisation, are among the other reasons for the increase in Sofia's population. The infant mortality rate was 5.6 per 1,000, down from 18.9 in 1980. According to the 2011 census, people aged 20–24 years are the most numerous group, numbering 133,170 individuals and accounting for 11% of the total 1,202,761 people. The median age is 38 though. According to the census, 1,056,738 citizens (87.9%) are recorded as ethnic Bulgarians, 17,550 (1.5%) as Romani people in Bulgaria, Romani, 6,149 (0.5%) as Turks in Bulgaria, Turks, 9,569 (0.8%) belonged to other ethnic groups, 6,993 (0.6%) do not self-identify and 105,762 (8.8%) remained with undeclared affiliation.
According to the 2011 census, throughout the whole municipality some 892,511 people (69.1%) are recorded as Eastern Orthodox Christians, 10,256 (0.8%) as Protestantism in Bulgaria, Protestant, 6,767 (0.5%) as Islam in Bulgaria, Muslim, 5,572 (0.4%) as Roman Catholicism in Bulgaria, Roman Catholic, 4,010 (0.3%) belonged to other faith and 372,475 (28.8%) declared themselves irreligious or did not mention any faith. The data says that roughly a third of the total population have already earned a university degree. Of the population aged 15–64 – 265,248 people within the municipality (28.5%) are not economically active, the unemployed being another group of 55,553 people (6%), a large share of whom have completed higher education. The largest group are occupied in trading, followed by those in manufacturing industry. Within the municipality, three-quarters, or 965,328 people are recorded as having access to television at home and 836,435 (64.8%) as having internet. Out of 464,865 homes – 432,847 have connection to the communal sanitary sewer, while 2,732 do not have any. Of these 864 do not have any water supply and 688 have other than communal. Over 99.6% of males and females aged over 9 are recorded as literacy, literate. The largest group of the population aged over 20 are recorded to live within marriage (46.3%), another 43.8% are recorded as single and another 9.9% as having other type of coexistence/partnership, whereas not married in total are a majority and among people aged up to 40 and over 70. The people with juridical status divorced or widowed are either part of the factual singles or those having another type of partnership, each of the two constitutes by around 10% of the population aged over 20. Only over 1% of the juridically married do not de facto live within marriage. The families that consist of two people are 46.8%, another 34.2% of the families are made up by three people, whereas most of the households (36.5%) consist of only one person.
Sofia was declared the national capital in 1879. One year later, in 1880, it was the fifth-largest city in the country after Plovdiv, Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, Ruse, Bulgaria, Ruse and Shumen. Plovdiv remained the most populous Bulgarian town until 1892 when Sofia took the lead. The city is the hot spot of internal migration, the capital population is increasing and is around 17% of the national, thus a small number of people with local roots remain today, they dominate the surrounding Districts of Sofia, rural suburbs and are called Shopi. Shopi speak the Bulgarian dialects, Western Bulgarian dialects.
Economy
Sofia is ranked as Beta- global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. It is the economic hub of Bulgaria and home to most major Bulgarian and international companies operating in the country, as well as the Bulgarian National Bank and the Bulgarian Stock Exchange – Sofia, Bulgarian Stock Exchange. The city is ranked 62nd among financial centres worldwide. In 2015, Sofia was ranked 30th out of 300 global cities in terms of combined growth in employment and real gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, the highest one amongst cities in Southeast Europe. The real GDP (PPP) per capita growth at the time was 2.5% and the employment went up by 3.4% to 962,400. In 2015, Forbes listed Sofia as one of the top 10 places in the world to launch a startup business, because of the low corporate tax (10%), the fast internet connection speeds available – one of the fastest in the world, and the presence of several investment funds, including Eleven Startup Accelerator, LAUNCHub and Neveq. The city's GDP (PPS) per capita stood at €29,600 ($33,760) in 2015, one of the highest in Southeast Europe and well above other cities in the country. The total nominal GDP in 2018 was 38.5 billion leva ($22.4 billion), or 33,437 leva ($19,454) per capita, and average monthly wages in March 2020 were $1,071, the highest nationally. Services dominate the economy, accounting for 88.6% of the gross value added, followed by industry 11.3% and agriculture 0.1%.
Historically, after World War II and the era of industrialisation under socialism, the city and its surrounding areas expanded rapidly and became the most heavily industrialised region of the country, with numerous factories producing steel, pig iron, machinery, industrial equipment, electronics, trams, chemicals, textiles, food. The influx of workers from other parts of the country became so intense that a restriction policy was imposed, and residing in the capital was only possible after obtaining Sofianite citizenship. However, after the political changes in 1989, this kind of citizenship was removed.
The most dynamic sectors include Information technology (IT) and manufacturing. Sofia is a regional IT hub, ranking second among the Top 10 fastest growing tech centers in Europe in terms of annual growth of active members. The sector employs about 50,000 professionals, 30% of them involved in programming, and contributes for 14% of the city's exports. The IT sector is highly diverse and includes both multinational corporations, local companies and start-ups. Multinationals with major research, development, innovation and engineering centers in Sofia include the second largest global IT center of Coca-Cola, Ubisoft Sofia, Ubisoft, Hewlett-Packard, VMware, Robert Bosch GmbH, Financial Times, Experian, etc. Several office and tech clusters have been established across the city, including Business Park Sofia, Sofia Tech Park, Capital Fort and others.
Manufacturing has registered a strong recovery since 2012, increasing the exports three-fold and the employment by 52% accounting for over 70,000 jobs. Supported by the city's R&D expertise, Sofia is shifting to high value-added manufacturing including electrical equipment, precision mechanics, pharmaceuticals. There are 16 industrial and logistics parks in Sofia, some sprawling to towns in neighbouring
The city's GDP (PPS) per capita stood at €29,600 ($33,760) in 2015, one of the highest in Southeast Europe and well above other cities in the country. The total nominal GDP in 2018 was 38.5 billion leva ($22.4 billion), or 33,437 leva ($19,454) per capita, and average monthly wages in March 2020 were $1,071, the highest nationally. Services dominate the economy, accounting for 88.6% of the gross value added, followed by industry 11.3% and agriculture 0.1%.
Historically, after World War II and the era of industrialisation under socialism, the city and its surrounding areas expanded rapidly and became the most heavily industrialised region of the country, with numerous factories producing steel, pig iron, machinery, industrial equipment, electronics, trams, chemicals, textiles, food. The influx of workers from other parts of the country became so intense that a restriction policy was imposed, and residing in the capital was only possible after obtaining Sofianite citizenship. However, after the political changes in 1989, this kind of citizenship was removed.
The most dynamic sectors include Information technology (IT) and manufacturing. Sofia is a regional IT hub, ranking second among the Top 10 fastest growing tech centers in Europe in terms of annual growth of active members. The sector employs about 50,000 professionals, 30% of them involved in programming, and contributes for 14% of the city's exports. The IT sector is highly diverse and includes both multinational corporations, local companies and start-ups. Multinationals with major research, development, innovation and engineering centers in Sofia include the second largest global IT center of Coca-Cola, Ubisoft Sofia, Ubisoft, Hewlett-Packard, VMware, Robert Bosch GmbH, Financial Times, Experian, etc. Several office and tech clusters have been established across the city, including Business Park Sofia, Sofia Tech Park, Capital Fort and others.
Manufacturing has registered a strong recovery since 2012, increasing the exports three-fold and the employment by 52% accounting for over 70,000 jobs. Supported by the city's R&D expertise, Sofia is shifting to high value-added manufacturing including electrical equipment, precision mechanics, pharmaceuticals. There are 16 industrial and logistics parks in Sofia, some sprawling to towns in neighbouring Sofia Province
Sofia Province ( bg, Софийска област, translit=Sofiyska oblast) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. The province does not include Sofia in its territories, but Sofia remains its administrative center. The province borders on t ...
, such as Bozhurishte, Kostinbrod and Elin Pelin (town), Elin Pelin. Manufacturing companies include Woodward, Inc., producing airframe and industrial turbomachinery systems, Festo, producing microsensors, Visteon, development and engineering of instrument clusters, LCD displays and domain controllers, Melexis, producing micro-electronic semiconductor solutions in the automotive sector, Sopharma, producing pharmaceuticals, the largest Lufthansa Technik maintenance facilities outside Germany etc.
Transport and infrastructure
With its developing infrastructure and strategic location, Sofia is a major hub for international railway and automobile transport. Three of the ten Pan-European corridors, Pan-European Transport Corridors cross the city: Pan-European Corridor IV, IV, Pan-European Corridor VIII, VIII and Pan-European Corridor X, X.Sofia infrastructure from the official website of the MunicipalityAll major types of transport (except Ship transport, water) are represented in the city.
 The Central Railway Station, Sofia, Central Railway Station is the primary hub for domestic and international rail transport, carried out by Bulgarian State Railways (BDZ), the national rail company headquartered in the city. It is one of the main stations along BDZ Line 1, and a hub of Lines BDZ Line 2, 2, BDZ Line 5, 5 and BDZ Line 13, 13. Line 1 provides a connection to Plovdiv, the second-largest city in Bulgaria, while Line 2 is the longest national railway and connects Sofia and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, the largest coastal city. Lines 5 and 13 are shorter and provide connections to Kulata and Bankya, respectively. Overall, Sofia has of railway lines.
The Central Railway Station, Sofia, Central Railway Station is the primary hub for domestic and international rail transport, carried out by Bulgarian State Railways (BDZ), the national rail company headquartered in the city. It is one of the main stations along BDZ Line 1, and a hub of Lines BDZ Line 2, 2, BDZ Line 5, 5 and BDZ Line 13, 13. Line 1 provides a connection to Plovdiv, the second-largest city in Bulgaria, while Line 2 is the longest national railway and connects Sofia and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna, the largest coastal city. Lines 5 and 13 are shorter and provide connections to Kulata and Bankya, respectively. Overall, Sofia has of railway lines.
Sofia Airport
Sofia Airport ( bg, Летище София, translit=Letishte Sofiya) is the main international airport of Bulgaria, located east of the centre of the capital Sofia. In 2019 the airport surpassed 7 million passengers for the first time. The ai ...
handled 7,107,096 passengers in 2019.
Sofia Public Transport, Public transport is well-developed with Public buses in Sofia, bus (), Sofia tram system, tram () and Trolleybuses in Sofia, trolleybus ()) lines running in all areas of the city. The Sofia Metro became operational in 1998, and now has four lines and 47 stations.
, the system has of track. Six new stations were opened in 2009, two more in April 2012, and eleven more in August 2012. In 2015 seven new stations were opened and the underground extended to Sofia Airport
Sofia Airport ( bg, Летище София, translit=Letishte Sofiya) is the main international airport of Bulgaria, located east of the centre of the capital Sofia. In 2019 the airport surpassed 7 million passengers for the first time. The ai ...
on its Northern branch and to Business Park Sofia on its Southern branch. In July 2016 the Vitosha Metro Station was opened on the M2 main line. A third line was opened in August of 2020 and re-organisation of the previous lines lead to a 4th line being created. This line will complete the proposed underground system of three lines with about of lines. The master plan for the Sofia Metro includes three lines with a total of 63 stations. Marshrutkas provide an efficient and popular Mode of transport, means of transport by being faster than public transport, but cheaper than taxis. There are around 13,000 taxicab, taxi cabs operating in the city. Additionally, all-electric vehicles are available through carsharing company Spark (carsharing), Spark, which is set to increase its fleet to 300 cars by mid-2019.
 Private automobile ownership has grown rapidly in the 1990s; more than 1,000,000 cars were registered in Sofia after 2002. The city has the 4th-highest number of automobiles per capita in the European Union at 546.4 vehicles per 1,000 people. The municipality was known for minor and cosmetic repairs and many streets are in a poor condition. This is noticeably changing in the past years. There are different boulevards and streets in the city with a higher amount of traffic than others. These include Tsarigradsko shose, Cherni Vrah, Bulgaria, Slivnitsa and Todor Aleksandrov boulevards, as well as the city's ring road. Consequently, traffic and air pollution problems have become more severe and receive regular criticism in local media. The extension of the underground system is hoped to alleviate the city's immense traffic problems.
Sofia has an extensive Toplofikatsiya Sofia, district heating system that draws on four cogeneration, combined heat and power (CHP) plants and heat-only boiler station, boiler stations. Virtually the entire city (900,000 households and 5,900 companies) is centrally heated, using residual heat from electricity generation (3,000 MW) and gas- and oil-fired heating furnaces; total Thermal mass, heat capacity is 4,640 MW. The heat distribution piping network is long and comprises 14,000 substations and 10,000 heated buildings.
Private automobile ownership has grown rapidly in the 1990s; more than 1,000,000 cars were registered in Sofia after 2002. The city has the 4th-highest number of automobiles per capita in the European Union at 546.4 vehicles per 1,000 people. The municipality was known for minor and cosmetic repairs and many streets are in a poor condition. This is noticeably changing in the past years. There are different boulevards and streets in the city with a higher amount of traffic than others. These include Tsarigradsko shose, Cherni Vrah, Bulgaria, Slivnitsa and Todor Aleksandrov boulevards, as well as the city's ring road. Consequently, traffic and air pollution problems have become more severe and receive regular criticism in local media. The extension of the underground system is hoped to alleviate the city's immense traffic problems.
Sofia has an extensive Toplofikatsiya Sofia, district heating system that draws on four cogeneration, combined heat and power (CHP) plants and heat-only boiler station, boiler stations. Virtually the entire city (900,000 households and 5,900 companies) is centrally heated, using residual heat from electricity generation (3,000 MW) and gas- and oil-fired heating furnaces; total Thermal mass, heat capacity is 4,640 MW. The heat distribution piping network is long and comprises 14,000 substations and 10,000 heated buildings.
Education and science
 Much of Bulgaria's educational capacity is concentrated in Sofia. There are 221 general, 11 special and seven arts or sports schools, 56 vocational gymnasiums and colleges, and four independent colleges. The city also hosts 23 of Bulgaria's 51 higher education establishments and more than 105,000 university students. The American College of Sofia, a private secondary school with roots in a school founded by American missionaries in 1860, is among the oldest American educational institutions outside of the United States.
A number of secondary language schools provide education in a selected foreign language. These include the First English Language School, 91st German Language School, 164 GPIE "Miguel de Cervantes", 164th Spanish Language School, and the Lycée Français de Sofia, Lycée Français. These are among the most sought-after secondary schools, along with Vladislav the Grammarian 73rd Secondary School and the Sofia High School of Mathematics, High School of Mathematics, which topped the 2018 preference list for high school candidates.
Higher education includes four of the five highest-ranking national universities – Sofia University (SU), the Technical University of Sofia, New Bulgarian University and the Medical University of Sofia. Sofia University was founded in 1888. More than 20,000 students study in its 16 faculties. A number of research and cultural departments operate within SU, including its own publishing house, botanical gardens, a space research centre, a quantum electronics department, and a Confucius Institute. Rakovski Defence and Staff College, the National Academy of Arts, the University of Architecture, Civil Engineering and Geodesy, the University of National and World Economy and the University of Mining and Geology are other major higher education establishments in the city.
Other institutions of national significance, such as the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (BAS) and the SS. Cyril and Methodius National Library are located in Sofia. BAS is the centrepiece of scientific research in Bulgaria, employing more than 4,500 scientists in various institutes. Its Institute of Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy will operate the largest cyclotron in the country. All five of Bulgaria's supercomputers and supercomputing clusters are located in Sofia as well. Three of those are operated by the BAS; one by Sofia Tech Park and one by the Faculty of Physics at Sofia University.
Much of Bulgaria's educational capacity is concentrated in Sofia. There are 221 general, 11 special and seven arts or sports schools, 56 vocational gymnasiums and colleges, and four independent colleges. The city also hosts 23 of Bulgaria's 51 higher education establishments and more than 105,000 university students. The American College of Sofia, a private secondary school with roots in a school founded by American missionaries in 1860, is among the oldest American educational institutions outside of the United States.
A number of secondary language schools provide education in a selected foreign language. These include the First English Language School, 91st German Language School, 164 GPIE "Miguel de Cervantes", 164th Spanish Language School, and the Lycée Français de Sofia, Lycée Français. These are among the most sought-after secondary schools, along with Vladislav the Grammarian 73rd Secondary School and the Sofia High School of Mathematics, High School of Mathematics, which topped the 2018 preference list for high school candidates.
Higher education includes four of the five highest-ranking national universities – Sofia University (SU), the Technical University of Sofia, New Bulgarian University and the Medical University of Sofia. Sofia University was founded in 1888. More than 20,000 students study in its 16 faculties. A number of research and cultural departments operate within SU, including its own publishing house, botanical gardens, a space research centre, a quantum electronics department, and a Confucius Institute. Rakovski Defence and Staff College, the National Academy of Arts, the University of Architecture, Civil Engineering and Geodesy, the University of National and World Economy and the University of Mining and Geology are other major higher education establishments in the city.
Other institutions of national significance, such as the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (BAS) and the SS. Cyril and Methodius National Library are located in Sofia. BAS is the centrepiece of scientific research in Bulgaria, employing more than 4,500 scientists in various institutes. Its Institute of Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy will operate the largest cyclotron in the country. All five of Bulgaria's supercomputers and supercomputing clusters are located in Sofia as well. Three of those are operated by the BAS; one by Sofia Tech Park and one by the Faculty of Physics at Sofia University.
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Sofia is Sister city, twinned with: * Algiers, Algeria * Amman, Jordan * Ankara, Turkey * Bucharest, Romania * Doha, Qatar * Kyiv, Ukraine * Pittsburgh, United States * Salalah, Oman * Shanghai, China * Sidon, Lebanon * Tel Aviv, IsraelCooperation agreements
In addition Sofia cooperates with: * Budapest, Hungary * Paris, France * Lisbon, Portugal *Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
, Spain
* Yerevan, Armenia
Honour
Serdica Peak on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is named after Serdica.Media
*Graffitti Studio (1994), a broadcast media content localization companySee also
* List of churches in Sofia * List of shopping malls in Sofia * List of tallest buildings in Sofia *Sofia Province
Sofia Province ( bg, Софийска област, translit=Sofiyska oblast) is a province (''oblast'') of Bulgaria. The province does not include Sofia in its territories, but Sofia remains its administrative center. The province borders on t ...
* Monument to the Tsar Liberator
References
Bibliography
* * *Further reading
* The 110 footnotes provide a guide to the literature on the city * *External links
*Online guide to Sofia
Official Site of Sofia Public Transport
*
Archival images of Sofia
Sofia by Night Light: A Photographic Exhibition
More than 25 live webcams from Sofia
Pictures from Vitosha mountain
{{Authority control Sofia, Populated places in Sofia City Province Capitals in Europe Roman towns and cities in Bulgaria Dacia Mediterranea Populated places established in the 7th millennium BC