Société Anonyme Des Aéroplanes G. Voisin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Aéroplanes Voisin was a French aircraft manufacturing company established in 1905 by Gabriel Voisin and his brother
Aéroplanes Voisin was a French aircraft manufacturing company established in 1905 by Gabriel Voisin and his brother
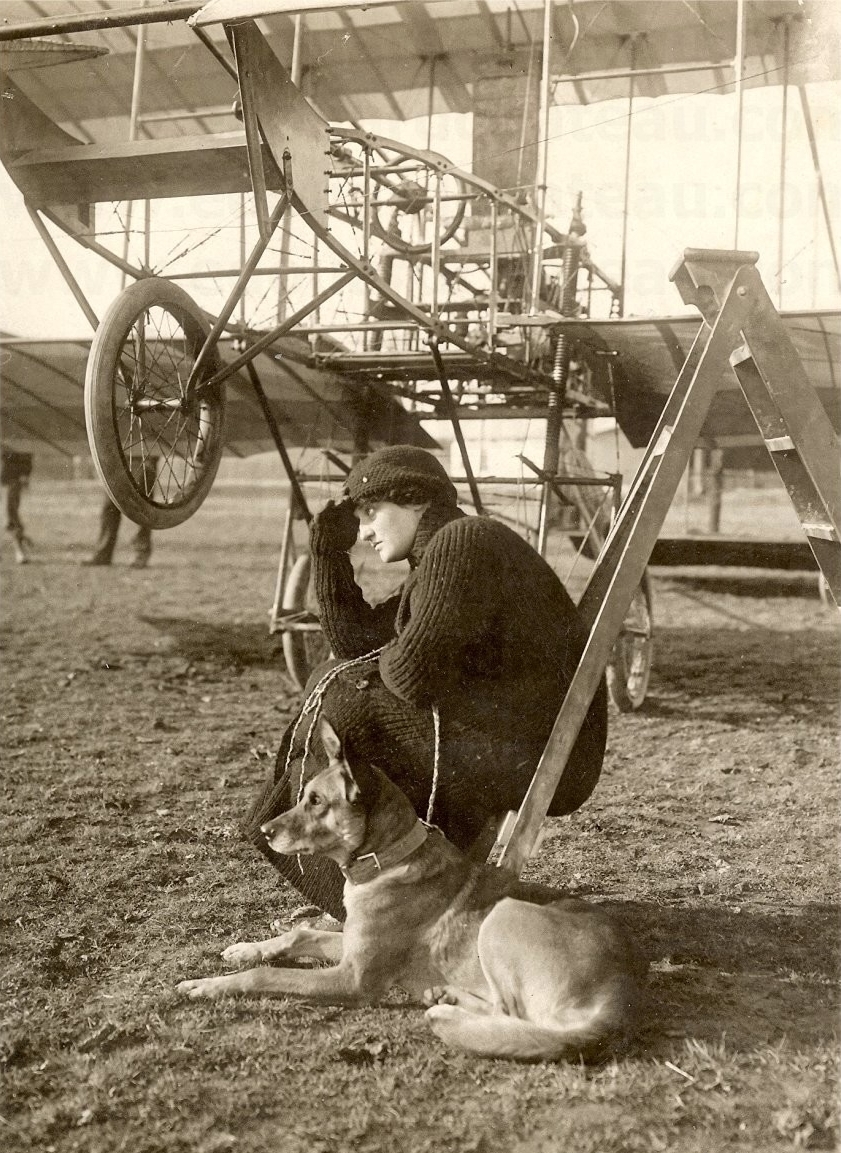 Gabriel Voisin had been employed by
Gabriel Voisin had been employed by

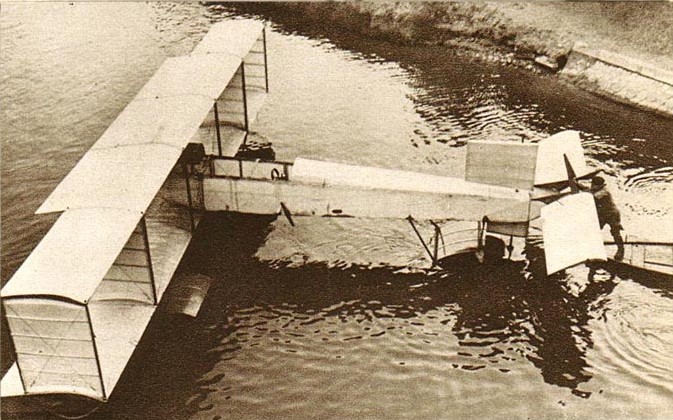 *1907 Voisin 1907 biplane
*1909 Voisin Tractor
::Only one built.
*1910
*1907 Voisin 1907 biplane
*1909 Voisin Tractor
::Only one built.
*1910
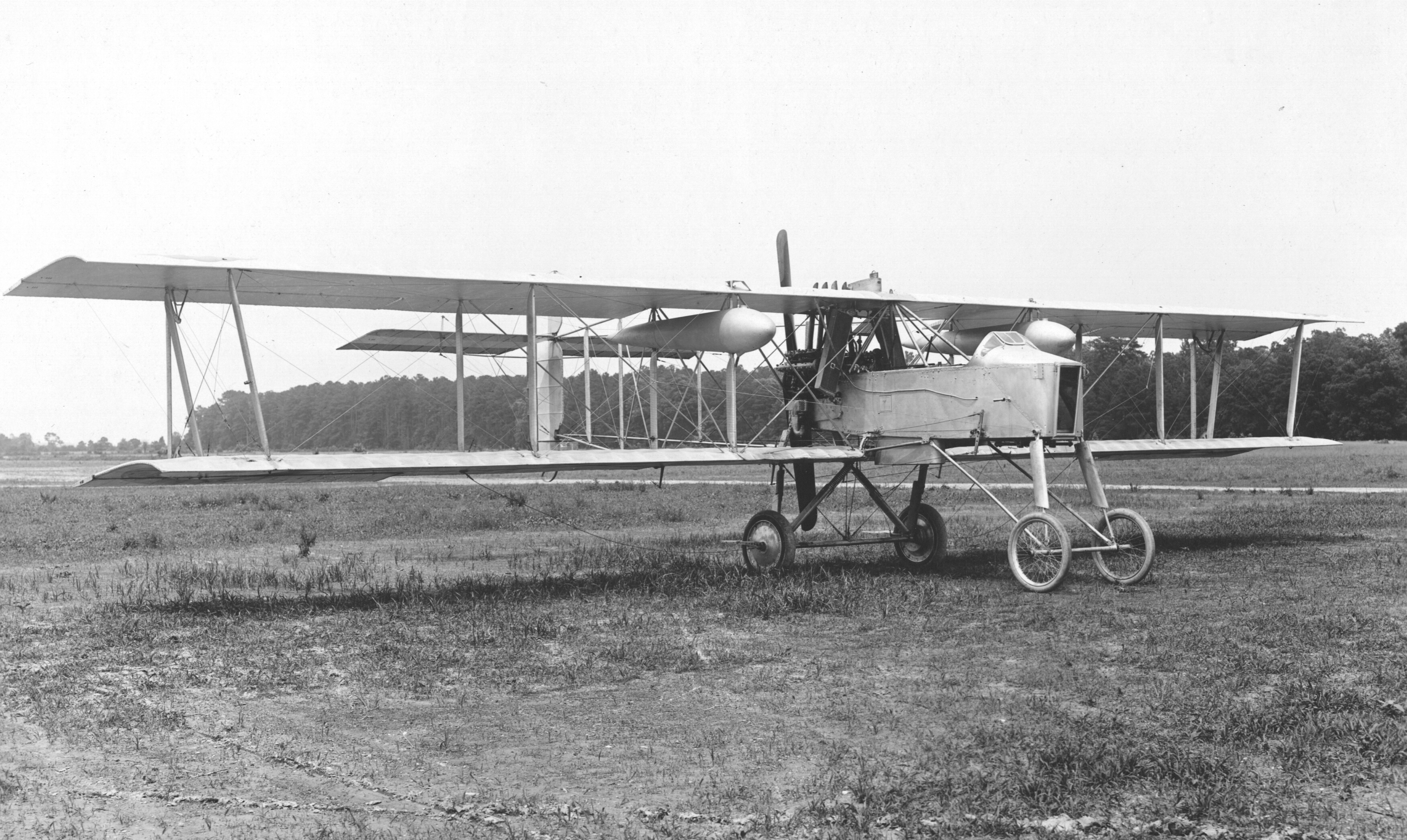



 Production of the Voisin III ''Type LA'' and ''LAS'' increased with the outbreak of the First World War, with examples being built under licence in Italy by S.I.T., in Russia by Anatra, Breshnev-Moller, Dux Lebedev and Schetinin, and in the UK by Savages of King's Lynn, with production exceeding 1,350 airframes. Examples would also be used by the Belgian and Romanian Air Services, and a few even survived the war to be used in the Ukraine, and in Russia. Soon after the outbreak of the First World War, it became apparent that the French aviation industry could not produce aircraft in sufficient numbers to meet military requirements. Manufacturers from various other fields became aviation subcontractors, and later license-builders as did many smaller aircraft manufacturers who had been unable to secure orders for their own designs. By 1918, Voisin was involved with the Voisin-Lafresnaye company, a major constructor of airframes, and the Voisin-Lefebvre company, a major builder of aircraft engines.
The Voisin III was followed by a small number of the 37mm cannon armed
Production of the Voisin III ''Type LA'' and ''LAS'' increased with the outbreak of the First World War, with examples being built under licence in Italy by S.I.T., in Russia by Anatra, Breshnev-Moller, Dux Lebedev and Schetinin, and in the UK by Savages of King's Lynn, with production exceeding 1,350 airframes. Examples would also be used by the Belgian and Romanian Air Services, and a few even survived the war to be used in the Ukraine, and in Russia. Soon after the outbreak of the First World War, it became apparent that the French aviation industry could not produce aircraft in sufficient numbers to meet military requirements. Manufacturers from various other fields became aviation subcontractors, and later license-builders as did many smaller aircraft manufacturers who had been unable to secure orders for their own designs. By 1918, Voisin was involved with the Voisin-Lafresnaye company, a major constructor of airframes, and the Voisin-Lefebvre company, a major builder of aircraft engines.
The Voisin III was followed by a small number of the 37mm cannon armed
 Aéroplanes Voisin was a French aircraft manufacturing company established in 1905 by Gabriel Voisin and his brother
Aéroplanes Voisin was a French aircraft manufacturing company established in 1905 by Gabriel Voisin and his brother Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
, and was continued by Gabriel after Charles died in an automobile accident in 1912; the full official company name then became ''Société Anonyme des Aéroplanes G. Voisin''Gunston, 1993, says the full name was "Aéroplanes G. Voisin". On the other hand the avions-voisin.org webpage specifies the name as "Société Aéroplanes Voisin, Société Anonyme". ( en, Aeroplanes Voisin public limited company).
During World War I, it was a major producer of military aircraft, notably the Voisin III. After the war Gabriel Voisin abandoned the aviation industry, and set up a company to design and produce luxury automobiles, called Avions Voisin.
Early History
 Gabriel Voisin had been employed by
Gabriel Voisin had been employed by Ernest Archdeacon
Ernest Archdeacon (23 March 1863 – 3 January 1950) was a French lawyer and aviation pioneer before the First World War. He made his first balloon flight at the age of 20. He commissioned a copy of the 1902 Wright No. 3 glider but ha ...
to work on the construction of gliders and then entered into partnership with Louis Blériot
Louis Charles Joseph Blériot ( , also , ; 1 July 1872 – 1 August 1936) was a French aviator, inventor, and engineer. He developed the first practical headlamp for cars and established a profitable business manufacturing them, using much of th ...
, to form the company ''Ateliers d' Aviation Edouard Surcouf, Blériot et Voisin'' in 1905. Following a disagreement, Gabriel Voisin bought out Blériot and on 5 November 1906 established the ''Appareils d'Aviation Les Frères Voisin'' with his brother Charles ( en, Flying Machines of Voisin Brothers). The company, based in the Parisian suburb of Billancourt, was the first commercial aircraft factory in the world.
It created Europe's first manned, heavier-than-air powered aircraft capable of a sustained (1 km), circular, controlled flight, including take-off and landing, the Voisin-Farman I
The 1907 Voisin biplane (designated the Voisin II by the 1913 edition of ''Jane's All the World's Aircraft''), was the first successful powered aircraft designed by aeronautical engineer and manufacturer Gabriel Voisin. It was used by the F ...
.
Having learned to fly with a Voisin, on 8 March 1910, Raymonde de Laroche became the first woman to receive a pilot licence when the Aéro-Club de France issued her licence #36.
In South Africa, on 28 December 1909, French aviator Albert Kimmerling made the first manned, heavier-than-air powered flight in Africa in a Voisin 1907 biplane.
Like many early aircraft companies, Voisin built machines to the designs of their customers which helped support their own experiments. The company's first customers were a M. Florencie, who commissioned them to build an ornithopter he had designed, and Henri Kapferer
Henri is an Estonian, Finnish, French, German and Luxembourgish form of the masculine given name Henry.
People with this given name
; French noblemen
:'' See the 'List of rulers named Henry' for Kings of France named Henri.''
* Henri I de Montm ...
, for whom they built a pusher biplane of their own design. The latter was underpowered, having a Buchet engine of only , and it failed to fly. However, Kapferer introduced them to Leon Delagrange, for whom they built a similar machine, powered by a Antoinette engine. This was first successfully flown by Charles Voisin on 30 March 1907, achieving a straight-line flight of . In turn Delagrange introduced them to Henri Farman, who ordered an identical aircraft. These two aircraft are often referred to by their owners' names as the Voisin-Delagrange No.1marked on the side-curtains of the tail unit as Léon Delagrange No. 1 and the Voisin-Farman No.1,marked on the side-curtains of the tail unit as Henri Farman No. 1 and were the foundation of the company's success. On 13 January 1908 Farman used his aircraft to win the "Grand Prix de l'aviation" offered by Ernest Archdeacon
Ernest Archdeacon (23 March 1863 – 3 January 1950) was a French lawyer and aviation pioneer before the First World War. He made his first balloon flight at the age of 20. He commissioned a copy of the 1902 Wright No. 3 glider but ha ...
and Henry Deutsch de la Meurthe for the first closed-circuit flight of over a kilometer. Since the Wright Brothers would provide no evidence of their own accomplishments, they were widely disbelieved at the time, so this was a major breakthrough in the conquest of the air, and brought Voisin many orders for similar aircraft. Around sixty would be built.
Major Designs of 1907-1914

 *1907 Voisin 1907 biplane
*1909 Voisin Tractor
::Only one built.
*1910
*1907 Voisin 1907 biplane
*1909 Voisin Tractor
::Only one built.
*1910 Voisin Type de Course
The Voisin Type de Course was an early French aircraft built by Voisin Frères. It was first flown early in 1910.
Design and development
The 1910 Type de Course was designed by Gabriel Voisin as a racing aircraft to take part in the many compet ...
*1910 Voisin Type Militaire
*1910 Type Bordeaux
*1911 Voisin Canard
::Tail first pusher design initially flown as a landplane but later fitted with floats. Examples were sold to the French and Russia Navies.
* 1911 Type Tourism
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* Ty ...
*1912 Type Monaco
::Smaller version of the Canard floatplane. Two were built to take part in the 1912 Monaco Aero Meeting.
*1912 Voisin Icare Aero-Yacht
The Voisin ''Icare'' Aero-yacht was an early flying boat built by Voisin Frères for the oil magnate and promoter of early aviation experimentation Henry Deutsch de la Meurthe. It first flew in 1912.
Design and development
It was initially bu ...
::Flying boat built for Henry Deutsch de la Meurthe with a six-wheeled boat hull suspended below the wings.
*1912 Voisin Type ''L'' or Voisin Type I & II
::A pod and boom pusher biplane developed for the French Army's 1912 trials. It performed successfully, and some seventy were built in France, and a small number in Russia
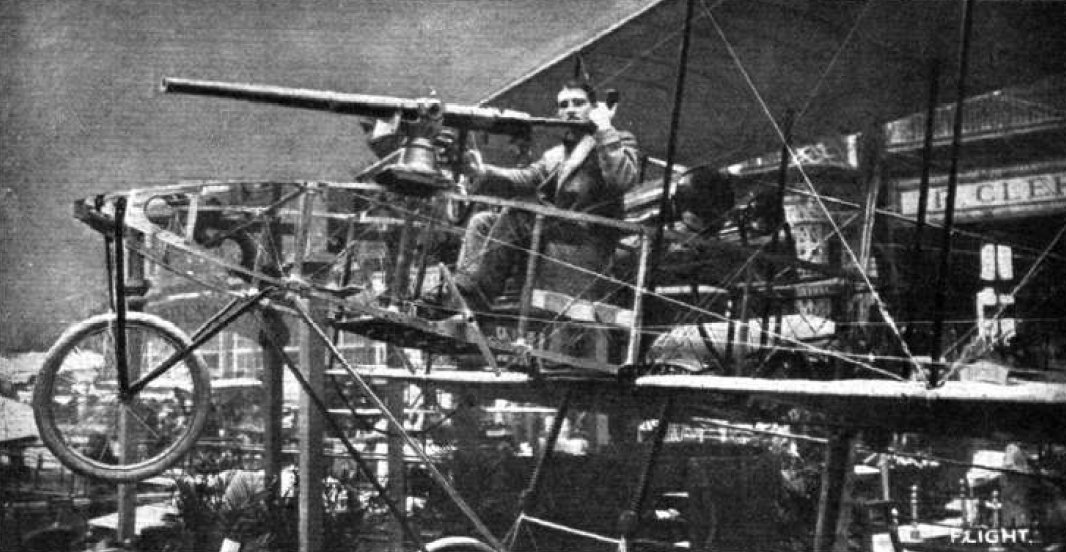
*1913 Voisin Canon Voisin (French for "neighbour") may refer to:
Companies
*Avions Voisin, the French automobile company
:*Voisin Laboratoire, a car manufactured by Avions Voisin
*Voisin (aircraft), the French aircraft manufacturer
* Voisin, a Lyon-based chocolat ...
::Six wheeled triple tailed pod and boom pusher armed with a 37mm Hotchkiss
Hotchkiss may refer to:
Places Canada
* Hotchkiss, Alberta
* Hotchkiss, Calgary
United States
* Hotchkiss, Colorado
* Hotchkiss, Virginia
* Hotchkiss, West Virginia
Business and industry
* Hotchkiss (car), a French automobile manufactu ...
cannon
*1914 Type ''LA'' or Voisin III
::Development of the ''L'' with detail improvements but of the same general configuration.
Voisin designs in World War I



 Production of the Voisin III ''Type LA'' and ''LAS'' increased with the outbreak of the First World War, with examples being built under licence in Italy by S.I.T., in Russia by Anatra, Breshnev-Moller, Dux Lebedev and Schetinin, and in the UK by Savages of King's Lynn, with production exceeding 1,350 airframes. Examples would also be used by the Belgian and Romanian Air Services, and a few even survived the war to be used in the Ukraine, and in Russia. Soon after the outbreak of the First World War, it became apparent that the French aviation industry could not produce aircraft in sufficient numbers to meet military requirements. Manufacturers from various other fields became aviation subcontractors, and later license-builders as did many smaller aircraft manufacturers who had been unable to secure orders for their own designs. By 1918, Voisin was involved with the Voisin-Lafresnaye company, a major constructor of airframes, and the Voisin-Lefebvre company, a major builder of aircraft engines.
The Voisin III was followed by a small number of the 37mm cannon armed
Production of the Voisin III ''Type LA'' and ''LAS'' increased with the outbreak of the First World War, with examples being built under licence in Italy by S.I.T., in Russia by Anatra, Breshnev-Moller, Dux Lebedev and Schetinin, and in the UK by Savages of King's Lynn, with production exceeding 1,350 airframes. Examples would also be used by the Belgian and Romanian Air Services, and a few even survived the war to be used in the Ukraine, and in Russia. Soon after the outbreak of the First World War, it became apparent that the French aviation industry could not produce aircraft in sufficient numbers to meet military requirements. Manufacturers from various other fields became aviation subcontractors, and later license-builders as did many smaller aircraft manufacturers who had been unable to secure orders for their own designs. By 1918, Voisin was involved with the Voisin-Lafresnaye company, a major constructor of airframes, and the Voisin-Lefebvre company, a major builder of aircraft engines.
The Voisin III was followed by a small number of the 37mm cannon armed Voisin IV
The Voisin IV was a French two-seat bomber and ground attack aircraft of World War I.
Design
The Voisin IV was a biplane with a single engine in a pusher configuration, developed by Voisin in 1915 with staggered wings. It differed from earlier V ...
''Type LB'' and ''Type LBS''. The ''B'' in the factory designations indicate that the airframe was equipped with a cannon, although some had it removed in service. The ''S'' indicates that the engine was raised (surélevé) compared to the original installation.
Three hundred of the improved Voisin V
The Voisin V was a French pusher-type bomber aircraft of World War I.
Development history
The Voisin III had proved a successful bomber, but its payload was limited by the Salmson M9 engine, which produced only 120-hp. With an already identif ...
''Type LAS'' aircraft followed.
The Voisin VI
The Voisin VI or Voisin Type 6 was a French pusher biplane bomber aircraft of World War I.
Development history
The first Voisin Type VI entered service in 1916 and replaced the Voisin III on the production lines. However, the Voisin (as they ...
''Type LAS'' was a development of the V fitted with a Salmson radial, of which only around 50 were built despite the improved performance as the basic type was considered to be obsolete.
The larger ''Type LC'', Voisin VII
The Voisin VII was a French reconnaissance pusher biplane aircraft of World War I.
Design
The Voisin VII was a biplane with a single engine in a pusher configuration, developed by Voisin in 1916 as an enlarged Voisin V with the engine cooling ...
, followed in 1916 with the engine cooling radiators moved to the nose, but was not a success as it was badly underpowered and only a hundred of these were built.
Voisin built a large Triplane powered by four Salmson water-cooled aero-engines in 1915 with twin superimposed fuselage booms, however it attracted no orders, but its wings were reused in 1916 for the E.28 triplane bomber which was now powered by four V8 Hispano-Suiza 8
The Hispano-Suiza 8 was a water-cooled V8 SOHC aero engine introduced by Hispano-Suiza in 1914, and was the most commonly used liquid-cooled engine in the aircraft of the Entente Powers during the First World War. The original Hispano-Suiza ...
B engines, which likewise failed to secure any orders.
Also in 1915, Voisin built the '' Type M'' in which the fuselage was below the lower wing, and the engine filled the gap between the wings, however neither it, nor the otherwise similar twin fuselage ''Type O
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes. For human blood transfusions, it is the most important of the 43 different blood type (or group) classification system ...
'' were successful.
Following the Voisin VII came the more powerful, and more successful Voisin VIII
The Voisin VIII was a French two-seat biplane pusher configuration, pusher which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37mm Hotchkiss cannon (the LBP or Ca.2), and the other as a conventional bomber (the LAP or Bn.2).Davilla, p.559 Probl ...
''Type LAP'' and ''Type LBP''. This was the French army's main night bomber in 1916 and 1917, with over one thousand built.
The Voisin IX
The Voisin VIII was a French two-seat biplane pusher which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37mm Hotchkiss cannon (the LBP or Ca.2), and the other as a conventional bomber (the LAP or Bn.2).Davilla, p.559 Problems with the Peugeot ...
, or ''Type LC'' (the designation was reused), was an unsuccessful lightened development of the VIII for a reconnaissance aeroplane, which lost out to the Salmson 2
The Salmson 2 A.2, (often shortened to Salmson 2) was a French biplane reconnaissance aircraft developed and produced by Salmson to a 1916 requirement. Along with the Breguet 14, it was the main reconnaissance aircraft of the French army in 1918 ...
and Breguet 14.
The Voisin X
The Voisin X (sometimes written as Voisin 10) was a French two-seat pusher biplane which was built in two versions, one fitted with a Hotchkiss cannon (the LBR or X Ca.2), and the other as a conventional night bomber (the LAR or X Bn.2). Probl ...
, ''Type LAR'' and ''Type LBR'', was the Voisin VIII with a more reliable, lighter and more powerful Renault 12Fe engine in place of the Peugeot 8Aa used on the VIII. Deliveries were severely delayed, but some nine hundred were built before the end of the war. In 1918, a Voisin X (No. 3500) was used to create the Voisin 'Aerochir' ('Ambulance'). The aircraft was capable of flying a surgeon, together with an operating table and support equipment, including an x-ray machine and autoclave, into the battlefield. Under-wing panniers could be carry of equipment. Another X was converted into a drone, and flown in 1918 and again in 1923.
The Voisin XI
The Voisin X (sometimes written as Voisin 10) was a French two-seat pusher biplane which was built in two versions, one fitted with a Hotchkiss cannon (the LBR or X Ca.2), and the other as a conventional night bomber (the LAR or X Bn.2). Prob ...
was a development of the X powered by a Panhard 12Bc, with a slightly longer wingspan and assorted detail changes. Only about 10 were built and it did not see service.
The final Voisin design, the Voisin XII
The Voisin XII was a prototype French two-seat four-engine biplane bomber built near the end of the First World War but which did not enter service.
Development
The Voisin XII was a long-range night bomber with four Hispano-Suiza 8
The Hisp ...
, was successful in trials in 1918 for the BN2 bomber competition, but with the end of the war, no production was ordered. The Voisin XII was a large, four-engined biplane night bomber. Several projects for heavy bombers for the next bomber specification (BN3/4) may have been based on the XII, but fitted with larger Salmson or Hispano-Suiza engines, but were not built.Davilla p.569
In the 1930s, a glider was built by a Louis Voisin, however he had no connection to Gabriel Voisin.
Post World War I
After 1918, Gabriel Voisin abandoned the aviation industry in favor of automobile construction under the name Avions Voisin.Notes
References
Bibliography
* Carlier, Claude, ''Sera Maître du Monde, qui sera Maître de l'Air: La Création de l'Aviation militaire française.'' Paris: Economica/ISC, 2004. * Davilla, James J., & Soltan, Arthur M., ''French Aircraft of the First World War.'' Stratford, Connecticut: Flying Machines Press, 1997. * Lacaze, Henri, ''Les Aéroplanes Voisin'', ''Collection Histoire de L'Aviation N°39.'' Paris:LELA PRESSE, 2018. * Opdycke, Leonard E ''French Aeroplanes Before the Great War'' Atglen, PA: Schiffer, 1999 * Voisin, Gabriel, ''Mes 10,000 Cerfs-volants'', Editions La Table Ronde, Paris, 1960. * ( Italy ) Grassani, Enrico "''Elisa Deroche alias Raymonde de Laroche. La presenza femminile negli anni pionieristici dell'aviazione''" Editoriale Delfino, Milano 2015. {{Authority control Defunct aircraft manufacturers of France Manufacturing companies established in 1906 Manufacturing companies disestablished in 1918 French companies established in 1906 1918 disestablishments in France