Small Carbonaceous Fossil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Small carbonaceous fossils (SCFs) are sub-millimetric organic remains of organisms preserved in sedimentary strata.
This category of fossils has traditionally included robust or thick-walled entities such as plant spores,
Small carbonaceous fossils (SCFs) are sub-millimetric organic remains of organisms preserved in sedimentary strata.
This category of fossils has traditionally included robust or thick-walled entities such as plant spores,
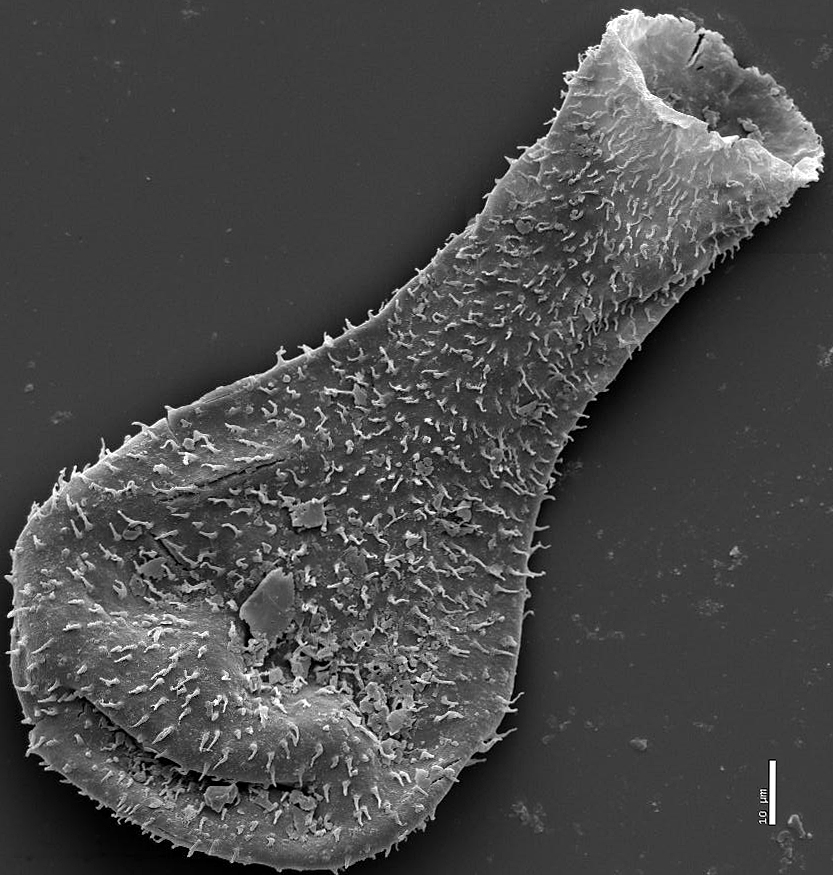 Traditional palynological methods are designed for extracting fossilized plant spores and other resistant organic microfossils such as
Traditional palynological methods are designed for extracting fossilized plant spores and other resistant organic microfossils such as
 Small carbonaceous fossils (SCFs) are sub-millimetric organic remains of organisms preserved in sedimentary strata.
This category of fossils has traditionally included robust or thick-walled entities such as plant spores,
Small carbonaceous fossils (SCFs) are sub-millimetric organic remains of organisms preserved in sedimentary strata.
This category of fossils has traditionally included robust or thick-walled entities such as plant spores, acritarch
Acritarchs are organic microfossils, known from approximately 1800 million years ago to the present. The classification is a catch all term used to refer to any organic microfossils that cannot be assigned to other groups. Their diversity refle ...
s and chitinozoa
Chitinozoa (singular: chitinozoan, plural: chitinozoans) are a group of flask-shaped, organic walled marine microfossils produced by an as yet unknown organism. Common from the Ordovician to Devonian periods (i.e. the mid-Paleozoic), the millimetr ...
, but the term 'SCFs' is usually applied to more fragile remnants of animals that can only be extracted through a delicate maceration technique. SCFs are relatively widespread and abundant, and can potentially preserve both mineralized and non-mineralized parts of organisms. Since SCFs can preserve the remains of non-biomineralized organisms, they have been viewed as a relatively untapped record of animal evolution, which has the potential to circumvent some of the biases of the shelly fossil record.
Extraction
SCFs are typically preserved in fine-grained siliciclastic rocks, and are too small to be fruitfully examined on bedding planes. Instead, they are extracted by dissolving the rock in acid. Traditional palynological preparations involve high-energy steps such as centrifuging that destroy large and fragile fossils. In the more delicate technique pioneered by Butterfield, individual microfossils are picked from sieved acid residues by hand. The sieving stage removes crystalline residue, making it easier to extract fossils, but introduces a filter: the smallest fossils (<~40 µm) pass through the sieve and are lost. Once extracted, fossils can be mounted for light or scanning electron microscopy: transmitted light illuminates internal microstructures, whereas SEM picks out surface features.Preservation
SCFs are best preserved in environments that had anoxic conditions and where the sediments have not been subject to high temperatures (limited thermal maturity); the presence of oxygen is particularly deleterious at high temperatures.Biota
 Traditional palynological methods are designed for extracting fossilized plant spores and other resistant organic microfossils such as
Traditional palynological methods are designed for extracting fossilized plant spores and other resistant organic microfossils such as acritarch
Acritarchs are organic microfossils, known from approximately 1800 million years ago to the present. The classification is a catch all term used to refer to any organic microfossils that cannot be assigned to other groups. Their diversity refle ...
s and chitinozoa
Chitinozoa (singular: chitinozoan, plural: chitinozoans) are a group of flask-shaped, organic walled marine microfossils produced by an as yet unknown organism. Common from the Ordovician to Devonian periods (i.e. the mid-Paleozoic), the millimetr ...
. By using the modified SCFs extraction technique, more delicate fossil structures can also be recovered, including fragments of animals. In particular, this technique has been applied to sediments deposited during the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
Period, since there is great interest in tracking how soft-bodied animals evolved during this time interval. Animal SCFs extracted from Cambrian sediments include the minute scales of priapulid
Priapulida (priapulid worms, from Gr. πριάπος, ''priāpos'' 'Priapus' + Lat. ''-ul-'', diminutive), sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility ...
worms, ''Wiwaxia
''Wiwaxia'' is a genus of soft-bodied animals that were covered in carbonaceous scales and spines that protected it from predators. ''Wiwaxia'' fossils – mainly isolated scales, but sometimes complete, articulated fossils – are known from ear ...
'' sclerites, and arthropod feeding parts, for example. These organisms are not represented in the conventional (shelly) fossil record, and so the SCFs record provides data on their distribution and evolution that would not otherwise be available. Lagerstätte
A Lagerstätte (, from ''Lager'' 'storage, lair' '' Stätte'' 'place'; plural ''Lagerstätten'') is a sedimentary deposit that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues. These for ...
n such as the Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest foss ...
provide isolated snapshots of Palaeozoic life, whereas SCFs provide a more continuous record, albeit blighted by the fragmentary (and consequently enigmatic) nature of many of its constituents. As such, SCFs can help to fill in some of the details of the fossil record outside the rare Lagerstätten sites: for instance, highlighting the rapid nature of the Cambrian explosion
The Cambrian explosion, Cambrian radiation, Cambrian diversification, or the Biological Big Bang refers to an interval of time approximately in the Cambrian Period when practically all major animal phyla started appearing in the fossil recor ...
.
References
{{reflist Fossils