Slotted Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Slotted lines are used for
Slotted lines are used for

 A typical test setup with a waveguide slotted line is shown in figure 2. Referring to this figure, power from a test equipment source (not shown) enters the apparatus through the co-axial cable on the left and is converted to waveguide format by means of a launcher (1). This is followed by a section of waveguide (2) providing a transition to a smaller size of guide. An important component in the setup is the isolator (3) which prevents power being reflected back into the source. Depending on the test conditions, such reflections can be large and a high-power source may be damaged by the returning wave. The power entering the slotted line is controlled by a rotary variable attenuator (4). This is followed by the slotted line itself (5) above which is the probe mounted on a movable carriage. The carriage also carries the probe adjustments: (6) is the probe depth adjustment, (7) is a length of co-axial section with tuning adjustments, and (8) is a ''detector'', which uses either a point contact ''crystal rectifier'' or a Schottky barrier diode.H. C. Torrey, C. A. Whitmer, ''Crystal Rectifiers'', New York: McGraw-Hill, 1948 The right-hand end of the slotted line is terminated in a matched load (9) which absorbs all the power exiting the end of the waveguide. The load can be replaced by the component or system that it is desired to test. It can also be replaced with a reference short-circuit (10) which is used to calibrate the slotted line. The carriage can be moved along the slotted line by means of a rotary knob (11) which simultaneously moves a vernier gauge (12) for accurate measurement of the probes position along the line.
The probe is connected to a detector and a display meter (not shown in figure 2). These can be, respectively, a
A typical test setup with a waveguide slotted line is shown in figure 2. Referring to this figure, power from a test equipment source (not shown) enters the apparatus through the co-axial cable on the left and is converted to waveguide format by means of a launcher (1). This is followed by a section of waveguide (2) providing a transition to a smaller size of guide. An important component in the setup is the isolator (3) which prevents power being reflected back into the source. Depending on the test conditions, such reflections can be large and a high-power source may be damaged by the returning wave. The power entering the slotted line is controlled by a rotary variable attenuator (4). This is followed by the slotted line itself (5) above which is the probe mounted on a movable carriage. The carriage also carries the probe adjustments: (6) is the probe depth adjustment, (7) is a length of co-axial section with tuning adjustments, and (8) is a ''detector'', which uses either a point contact ''crystal rectifier'' or a Schottky barrier diode.H. C. Torrey, C. A. Whitmer, ''Crystal Rectifiers'', New York: McGraw-Hill, 1948 The right-hand end of the slotted line is terminated in a matched load (9) which absorbs all the power exiting the end of the waveguide. The load can be replaced by the component or system that it is desired to test. It can also be replaced with a reference short-circuit (10) which is used to calibrate the slotted line. The carriage can be moved along the slotted line by means of a rotary knob (11) which simultaneously moves a vernier gauge (12) for accurate measurement of the probes position along the line.
The probe is connected to a detector and a display meter (not shown in figure 2). These can be, respectively, a
 When the slotted line is terminated with a precision matching load there is no variation in the detected power along the line, other than a very small decrease due to losses in the line. However, when this is replaced by a
When the slotted line is terminated with a precision matching load there is no variation in the detected power along the line, other than a very small decrease due to losses in the line. However, when this is replaced by a
''Microwave Engineering''
Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2009 . *Gupta, K. C., ''Microwaves'', New Age International, 1979 . * Lee, Thomas H.
''Planar Microwave Engineering''
Cambridge University Press, 2004 . *Voltmer, David Russell
''Fundamentals Of Electromagnetics 2: Quasistatics and Waves''
Morgan & Claypool, 2007 {{ISBN, 1-59829-172-6. Microwave technology Electronic test equipment Radio electronics Measuring instruments Laboratory equipment Electrical engineering
 Slotted lines are used for
Slotted lines are used for microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different fre ...
measurements and consist of a movable probe inserted into a slot in a transmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmi ...
. They are used in conjunction with a microwave power source and usually, in keeping with their low-cost application, a low cost Schottky diode
The Schottky diode (named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltag ...
detector and VSWR meter rather than an expensive microwave power meter
A microwave power meter is an instrument which measures the electrical power at microwave frequencies typically in the range 100 MHz to 40 GHz.
Usually a microwave power meter will consist of a measuring head which contains the actual ...
.
Slotted lines can measure standing wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect ...
s, wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
, and, with some calculation or plotting on Smith chart
The Smith chart, invented by Phillip H. Smith (1905–1987) and independently by Mizuhashi Tosaku, is a graphical calculator or nomogram designed for electrical and electronics engineers specializing in radio frequency (RF) engineering to assist ...
s, a number of other parameters including reflection coefficient
In physics and electrical engineering the reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of a wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity in the transmission medium. It is equal to the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected w ...
and electrical impedance
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit.
Quantitatively, the impedance of a two-terminal circuit element is the ratio of the comp ...
. A precision variable attenuator is often incorporated in the test setup to improve accuracy. This is used to make level measurements, while the detector and VSWR meter are retained only to mark a reference point for the attenuator to be set to, thus eliminating entirely the detector and meter measurement errors. The parameter most commonly measured by a slotted line is SWR. This serves as a measure of the accuracy of the impedance match to the item under test. This is especially important for transmitting antennas and their feed lines; high standing wave ratio
In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the tra ...
on a radio or TV antenna can distort the signal, increase transmission line loss and potentially damage components in the transmission path, possibly even the transmitter.
Slotted lines are no longer widely used, but can still be found in budget applications. Their main drawback is that they are labour-intensive to use and require calculation, tables, or plotting to make use of the results. They need to be made with mechanical precision and the probe and its detector need to be adjusted with care, but they can give very accurate results.
Description
The slotted line is one of the basic instruments used inradio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the uppe ...
test and measurement at microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different fre ...
frequencies. It consists of a precision transmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmi ...
, usually co-axial but waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave intensities de ...
implementations are also used, with a movable insulated probe inserted into a longitudinal slot cut into the line. In a co-axial slotted line, the slot is cut into the outer conductor of the line. The probe is inserted past the outer conductor, but not so far that it touches the inner conductor. In a rectangular waveguide, the slot is usually cut along the centre of the broad wall of the waveguide. Circular waveguide slotted lines are also possible.
Slotted lines are relatively cheap Thomas H. Lee even describes a microstrip
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated with any technology where a conductor is separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as the substrate. Microstrip lines are used to convey microwave-freque ...
slotted line for use up to that he claims can be made for less than $10. He calls this a " cost reduction" over the price of a network analyser. That is, its cost is 10,000 times less than an analyser costing $100,000 (Lee, pages xv, 268-271). and can perform many of the measurements done by more expensive equipment such as network analysers. However, slotted line measurement techniques are more labour-intensive and often do not directly output the desired parameter; some calculation or plotting is frequently required. In particular, they can only carry out a measurement at one spot frequency at a time so producing a plot of a parameter versus frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is ...
is very time consuming. This is to be compared to modern instruments like network and spectrum analysers which are intrinsically frequency swept and produce a plot instantly. Slotted lines have now largely been superseded, but are still found where capital cost
Capital costs are fixed, one-time expenses incurred on the purchase of land, buildings, construction, and equipment used in the production of goods or in the rendering of services. In other words, it is the total cost needed to bring a projec ...
s are an issue. Their remaining uses are mostly in the millimetre band, where modern test apparatus is either prohibitively expensive or not available at all, and with academic laboratories and hobbyists. They are also useful as a teaching aid as the user is more directly exposed to basic line phenomena than with more sophisticated instruments.
Operation
The slotted line works by sampling the electric field inside the transmission line with the probe. For accuracy, it is important that the probe disturbs the field as little as possible. For this reason the probe diameter and slot width are kept small (usually around ) and the probe is inserted in no further than necessary. It is also necessary in waveguide slotted lines to place the slot at a position where the current in the waveguide walls is parallel to the slot. The current will then not be disturbed by the presence of the slot as long as it is not too wide. For the dominant mode this is on the centre-line of the broad face of the waveguide, but for some other modes it may need to be off-centre. This is not an issue for the co-axial line because this operates in the TEM (transverse electromagnetic) mode and hence the current is everywhere parallel to the slot. The slot may be tapered at its ends to avoid discontinuities causing reflections. The disturbance to the field inside the line caused by the insertion of the probe is minimised as far as possible. There are two parts to this disturbance. The first part is due to the power the probe has extracted from the line and manifests as a lumped equivalent circuit of aresistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias activ ...
. This is minimised by limiting the distance the probe is inserted into the line so that only enough power is extracted for the detector to operate effectively. The second part of the disturbance is due to energy stored in the field around the probe and manifests as a lumped equivalent of a capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of a ...
. This capacitance
Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized a ...
can be cancelled out with an inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The flow of electric current creates a magnetic field around the conductor. The field strength depends on the magnitude of t ...
of equal and opposite impedance. Lumped inductors are not practical at microwave frequencies; instead, an adjustable stub
Stub or Stubb may refer to:
Shortened objects and entities
* Stub (stock), the portion of a corporation left over after most but not all of it has been bought out or spun out
* Stub, a tree cut and allowed to regrow from the trunk; see Pollardi ...
with an inductive equivalent circuit is used to "tune out" the probe capacitance. The result is an equivalent circuit of a high impedance in shunt across the line which has little effect on the transmitted power in the line. The probe is more sensitive as a result of this tuning and the distance it is inserted can be further limited as a result.
Test setup

 A typical test setup with a waveguide slotted line is shown in figure 2. Referring to this figure, power from a test equipment source (not shown) enters the apparatus through the co-axial cable on the left and is converted to waveguide format by means of a launcher (1). This is followed by a section of waveguide (2) providing a transition to a smaller size of guide. An important component in the setup is the isolator (3) which prevents power being reflected back into the source. Depending on the test conditions, such reflections can be large and a high-power source may be damaged by the returning wave. The power entering the slotted line is controlled by a rotary variable attenuator (4). This is followed by the slotted line itself (5) above which is the probe mounted on a movable carriage. The carriage also carries the probe adjustments: (6) is the probe depth adjustment, (7) is a length of co-axial section with tuning adjustments, and (8) is a ''detector'', which uses either a point contact ''crystal rectifier'' or a Schottky barrier diode.H. C. Torrey, C. A. Whitmer, ''Crystal Rectifiers'', New York: McGraw-Hill, 1948 The right-hand end of the slotted line is terminated in a matched load (9) which absorbs all the power exiting the end of the waveguide. The load can be replaced by the component or system that it is desired to test. It can also be replaced with a reference short-circuit (10) which is used to calibrate the slotted line. The carriage can be moved along the slotted line by means of a rotary knob (11) which simultaneously moves a vernier gauge (12) for accurate measurement of the probes position along the line.
The probe is connected to a detector and a display meter (not shown in figure 2). These can be, respectively, a
A typical test setup with a waveguide slotted line is shown in figure 2. Referring to this figure, power from a test equipment source (not shown) enters the apparatus through the co-axial cable on the left and is converted to waveguide format by means of a launcher (1). This is followed by a section of waveguide (2) providing a transition to a smaller size of guide. An important component in the setup is the isolator (3) which prevents power being reflected back into the source. Depending on the test conditions, such reflections can be large and a high-power source may be damaged by the returning wave. The power entering the slotted line is controlled by a rotary variable attenuator (4). This is followed by the slotted line itself (5) above which is the probe mounted on a movable carriage. The carriage also carries the probe adjustments: (6) is the probe depth adjustment, (7) is a length of co-axial section with tuning adjustments, and (8) is a ''detector'', which uses either a point contact ''crystal rectifier'' or a Schottky barrier diode.H. C. Torrey, C. A. Whitmer, ''Crystal Rectifiers'', New York: McGraw-Hill, 1948 The right-hand end of the slotted line is terminated in a matched load (9) which absorbs all the power exiting the end of the waveguide. The load can be replaced by the component or system that it is desired to test. It can also be replaced with a reference short-circuit (10) which is used to calibrate the slotted line. The carriage can be moved along the slotted line by means of a rotary knob (11) which simultaneously moves a vernier gauge (12) for accurate measurement of the probes position along the line.
The probe is connected to a detector and a display meter (not shown in figure 2). These can be, respectively, a thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''.
Thermistors are divided based on their conduction ...
and power meter, or an envelope detector
An envelope detector (sometimes called a peak detector) is an electronic circuit that takes a (relatively) high-frequency amplitude modulated signal as input and provides an output, which is the demodulated ''envelope'' of the original signal.
...
and VSWR meter. The detector can be a crystal detector or a Schottky barrier diode
The Schottky diode (named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltage d ...
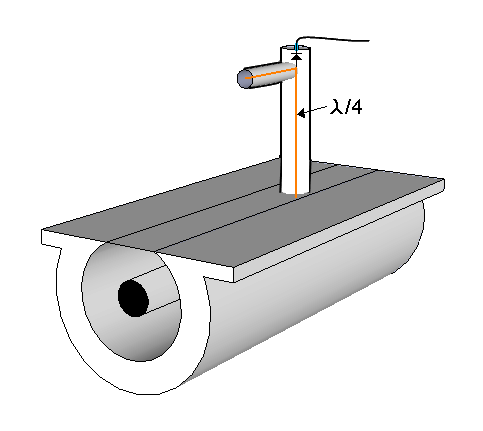
. The detector is mounted on the probe assembly, usually a distance λ/4λ, the customary symbol for wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
. It is usually most convenient to give distances on transmission lines in terms of wavelengths of the transmitted wave, or sometimes, when the distance involved is small or not an exact multiple of a quarter wavelength, in radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit (before tha ...
s where θ=2πλ radians. from the probe tip as shown in figure 3. This is because the detector looks almost like a short circuit to the transmission line, and this distance will convert it to an open circuit through the quarter-wave impedance transformer
A quarter-wave impedance transformer, often written as λ/4 impedance transformer, is a transmission line or waveguide used in electrical engineering of length one-quarter wavelength (λ), terminated with some known impedance.
It presents at its i ...
effect. Thus, the detector has minimal effect on loading the line. The probe tuning stub can be seen on figure 3 branching from the line linking the probe to the detector. Figure 2 has a slightly different arrangement; the main probe into the waveguide leads to a vertical co-axial tuning and adjustment section but the detector is on a horizontal side-section with a secondary probe into the upright co-axial section.
Measurements
Measurements of microwave power can be made directly, usually with a thermistor based detector and meter. However, these instruments are expensive and a common meter used in measurements with a slotted line is instead a cheaper low-frequency VSWR meter. The microwave power source isamplitude modulated
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude (signal strength) of the wave is varied in proportion to t ...
with, typically, a signal which is recovered by the envelope detector in the probe and sent to the VSWR meter. This scheme is preferred to simply detecting the unmodulated carrier
Carrier may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Carrier'' (album), a 2013 album by The Dodos
* ''Carrier'' (board game), a South Pacific World War II board game
* ''Carrier'' (TV series), a ten-part documentary miniseries that aired on PBS in April 20 ...
directly, which would result in a DC output, because a stable, narrowband, tuned amplifier
A tuned amplifier is an electronic amplifier which includes bandpass filtering components within the amplifier circuitry. They are widely used in a variety of wireless applications.
Schemes
There are several tuning schemes in use,
* Staggere ...
can be used to amplify the signal. A large amplification is required in the VSWR meter because the limit of the square law rangesquare law, of a detector diode, the range over which the demodulated output voltage is proportional to the square of the carrier voltage on the line. of the detector diode is no more than .
Maxima and minima
device under test A device under test (DUT), also known as equipment under test (EUT) and unit under test (UUT), is a manufactured product undergoing testing, either at first manufacture or later during its life cycle as part of ongoing functional testing and calibra ...
(DUT) which is not perfectly matched to the line there will be a reflection back towards the source. This causes a standing wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect ...
to be set up on the line with periodic maxima and minima
In mathematical analysis, the maxima and minima (the respective plurals of maximum and minimum) of a function, known collectively as extrema (the plural of extremum), are the largest and smallest value of the function, either within a given r ...
(collectively, ''extrema'') due to alternating constructive and destructive interference
Interference is the act of interfering, invading, or poaching. Interference may also refer to:
Communications
* Interference (communication), anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a message
* Adjacent-channel interference, caused by extra ...
. These extrema are found by moving the probe back and forth along the line and the level at that point can then be measured on the meter.
The extrema are not of any great interest in themselves, but are used in the calculation of several more useful parameters. Some of these parameters require the measurement of the exact position of the extremum. Either maxima or minima can equally be used, from a mathematical point of view, but minima are preferred because they are always much sharper than maxima, especially for large reflections, as shown in figure 4. Additionally, the probe causes less disturbance to the field near a minimum than it does near a maximum.
Wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
is determined by measuring the distance between two adjacent minima. This distance will be λ/2. There is no need for a DUT, better results are obtained with the reference short in position.
Standing wave ratio
Standing wave ratio
In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the tra ...
(SWR or VSWR) is a basic parameter and the one most commonly measured on a slotted line. This quantity is of particular importance for transmitter antennae. A high SWR indicates a poor match between the feed line and the antenna, which increases wasted power, can cause damage to components in the transmission path, possibly including the transmitter, and cause distortion to TV, FM stereo and digital signals. With the input power set so that the maxima are at 0 dBm
DBM or dbm may refer to:
Science and technology
* dBm, a unit for power measurement
* DBM (computing), family of key-value database engines including dbm, ndbm, gdbm, and Berkeley DB
* Database Manager (DBM), a component of 1987's ''Extended Edit ...
, a measurement of a minimum in decibels will directly give SWR (after discarding the minus sign).
Reflection coefficient
Thereflection coefficient
In physics and electrical engineering the reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of a wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity in the transmission medium. It is equal to the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected w ...
, ρ, is the ratio of the reflected wave to the incident wave. In general it is a complex number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the for ...
. The magnitude of the reflection coefficient can be calculated from the VSWR measurement by,
:
where VSWR is the standing wave ratio expressed as a voltage ratio (not in decibels). However, to completely characterise the reflection coefficient, the phase of ρ must also be found. This is done on a slotted line by measuring the distance of the first minimum from the DUT. Moving the probe right up to the DUT is not practicable so a different approach is usually adopted. The position of the first minimum when the reference short is in place is noted. The distance back along the line from this reference point to the next minimum when the DUT is in place will be the same as the distance from the DUT to the first minimum. This is so because the reference short guarantees a minimum at the DUT position.
The phase part of ρ is given by,
:
where λ is the wavelength and ''x'' is the distance to the first minimum as described earlier. The magnitude and phase representation of ρ can, if required, be expressed as real and imaginary parts instead by the usual manipulation of complex numbers.
Impedance
The impedance, ''Z'', of the DUT can be calculated from the reflection coefficient by, : where ''Z''0 is the characteristic impedance of the line. An alternative method is to plot the VSWR and distance to the node (in wavelengths) on aSmith chart
The Smith chart, invented by Phillip H. Smith (1905–1987) and independently by Mizuhashi Tosaku, is a graphical calculator or nomogram designed for electrical and electronics engineers specializing in radio frequency (RF) engineering to assist ...
. These quantities are directly measured by the slotted line. From this plot the DUT impedance (normalised to ''Z''0) can be read directly off the Smith chart.
Accuracy considerations
Good slotted lines are precision made instruments. They need to be because mechanical defects can affect accuracy. Some of the mechanical issues that are relevant to this includebacklash
Backlash may refer to:
Literature
* '' Backlash: The Undeclared War Against American Women'', a 1991 book by Susan Faludi
* ''Backlash'' (Star Wars novel), a 2010 novel by Aaron Allston
* Backlash (Marc Slayton), comic book character
* ''Backl ...
of the vernier, concentricity of the inner and outer conductor, circularity of the outer conductor, centrality and straightness of the inner conductor, variations in cross-section, and the ability of the carriage to maintain a constant probe depth. Issues with probe tuning and disturbances to the field have already been discussed, but the insulated spacers holding the centre conductor in place can also disturb the field. Consequently, these are made as discrete as is compatible with mechanical strength. However, the greatest source of inaccuracy is usually not the slotted line itself, but the characteristics of the detector diode.
The detected voltage signal output of the Schottky barrier diodes typically used in microwave detectors have a square law relationship to the power being measured and meters are calibrated accordingly. However, as the power increases, the diode deviates significantly from a square law and remains accurate up to an output voltage of only around . This can be improved a little by adding a load resistor to the detector output, but this also has the undesirable effect of decreasing sensitivity. Another technique is to reduce the range of power being measured (so that it is brought within the square law range of the detector) by measuring at a point other than a maximum. The maximum is then calculated from the known mathematical shape of the standing wave pattern. This has the objection that it adds significantly to the labour required to make the measurements, as does the technique of precisely calibrating the detector and adjusting the readings on the meter according to a calibration chart.
It is possible to completely eliminate errors in the detector and meter if a precision variable attenuator is used in the test setup. In this technique a minimum is first found and the attenuator adjusted so that the meter is indicating precisely some convenient mark. A maximum is then found and the attenuation increased until the meter is indicating the same mark. The amount the attenuation had to be increased is the VSWR of the standing wave. Accuracy here depends on the accuracy of the attenuator and not at all on the detector.Lee, page 253
Notes
References
Bibliography
*Connor, F. R., ''Wave Transmission'', Edward Arnold Ltd., 1972 . *Das, Annapurna; Das, Sisir K''Microwave Engineering''
Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2009 . *Gupta, K. C., ''Microwaves'', New Age International, 1979 . * Lee, Thomas H.
''Planar Microwave Engineering''
Cambridge University Press, 2004 . *Voltmer, David Russell
''Fundamentals Of Electromagnetics 2: Quasistatics and Waves''
Morgan & Claypool, 2007 {{ISBN, 1-59829-172-6. Microwave technology Electronic test equipment Radio electronics Measuring instruments Laboratory equipment Electrical engineering