Single Colour Reflectometry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Single colour reflectometry (SCORE), formerly known as imaging Reflectometric Interferometry (iRIf) and 1-lambda Reflectometry, is a physical method based on interference of monochromatic light at thin films, which is used to investigate (bio-)molecular interactions. The obtained binding curves using SCORE provide detailed information on 
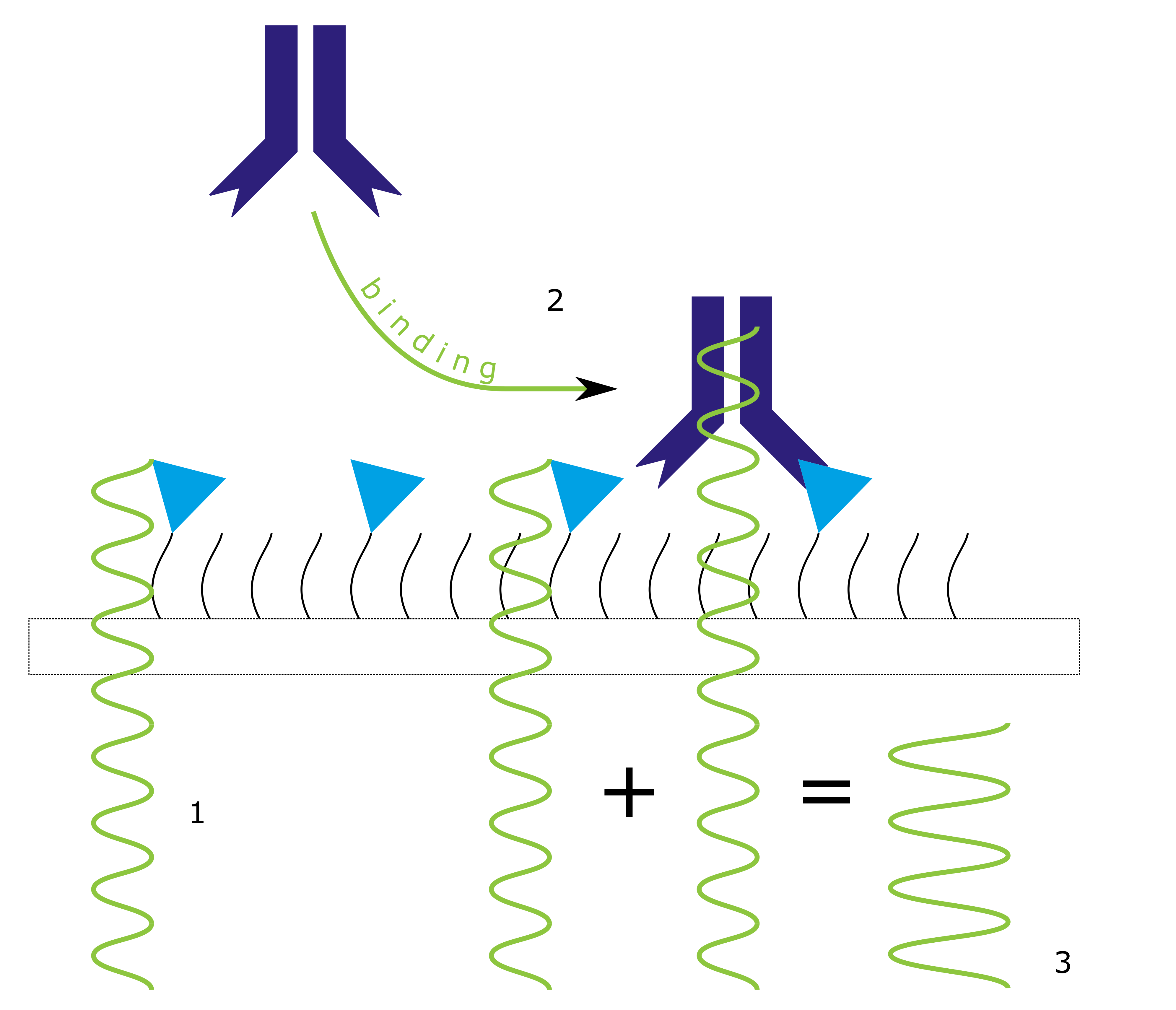 Monitoring the change of the reflected intensity of the used light over time results in binding curves that provide information on:
* concentration of used ligand
* binding kinetics (association and dissociation rate constants) between receptor and ligand
* binding strength (affinity) between receptor and ligand
* specificity of the interaction between receptor and ligand
Compared to
Monitoring the change of the reflected intensity of the used light over time results in binding curves that provide information on:
* concentration of used ligand
* binding kinetics (association and dissociation rate constants) between receptor and ligand
* binding strength (affinity) between receptor and ligand
* specificity of the interaction between receptor and ligand
Compared to 
SCORE Technology
Spectroscopy Biophysics Forensic techniques Nanotechnology Biochemistry methods Protein–protein interaction assays
kinetics
Kinetics ( grc, κίνησις, , kinesis, ''movement'' or ''to move'') may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Kinetics (physics), the study of motion and its causes
** Rigid body kinetics, the study of the motion of rigid bodies
* Chemical ki ...
and thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of the ...
of the observed interaction(s) as well as on concentrations of the used analytes. These data can be relevant for pharmaceutical screening and drug design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that acti ...
, biosensor
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector.
The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell recep ...
s and other biomedical applications, diagnostics, and cell-based assays.

Principle
The underlying principle corresponds to that of the Fabry-Pérot interferometer, which is also the underlying principle for the white-light interferometry.Realisation / setup
Monochromatic light is illuminated vertically on the rear side of a transparent multi-layer substrate. The partial beams of the monochromatic light are transmitted and reflected at each interphase of the multi-layer system. Superimposition of the reflected beams result in destructive or constructiveinterference
Interference is the act of interfering, invading, or poaching. Interference may also refer to:
Communications
* Interference (communication), anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a message
* Adjacent-channel interference, caused by extra ...
(depending on wavelength of the used light and the used substrate/multi-layer system materials) that can be detected in an intensity change of the reflected light using a photodiode
A photodiode is a light-sensitive semiconductor diode. It produces current when it absorbs photons.
The package of a photodiode allows light (or infrared or ultraviolet radiation, or X-rays) to reach the sensitive part of the device. The packag ...
, CCD, or CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFE ...
element.
The sensitive layer on top of the multi-layer system can be (bio-)chemically modified with receptor molecules, e.g. antibodies. Binding of specific ligands to the immobilised receptor molecules results in a change refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
n and physical thickness d of the sensitive layer. The product of n and d results in the optical thickness (n*d) of the sensitive layer.
 Monitoring the change of the reflected intensity of the used light over time results in binding curves that provide information on:
* concentration of used ligand
* binding kinetics (association and dissociation rate constants) between receptor and ligand
* binding strength (affinity) between receptor and ligand
* specificity of the interaction between receptor and ligand
Compared to
Monitoring the change of the reflected intensity of the used light over time results in binding curves that provide information on:
* concentration of used ligand
* binding kinetics (association and dissociation rate constants) between receptor and ligand
* binding strength (affinity) between receptor and ligand
* specificity of the interaction between receptor and ligand
Compared to bio-layer interferometry Bio-layer interferometry (BLI) is an optical biosensing technology that analyzes biomolecular interactions in real-time without the need for fluorescent labeling. Alongside Surface Plasmon Resonance, BLI is one of few widely available label-free bi ...
, which monitors the change of the interference pattern of reflected white light, SCORE only monitors the intensity change of the reflected light using a photodiode, CCD, or CMOS element. Thus, it is possible to analyse not only a single interaction but high-density arrays with up to 10,000 interactions per cm2.
Compared to surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material in a particle stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measu ...
, which penetration depth is limited by the evanescent field
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillati ...
, SCORE is limited by the coherence length
In physics, coherence length is the propagation distance over which a coherent wave (e.g. an electromagnetic wave) maintains a specified degree of coherence. Wave interference is strong when the paths taken by all of the interfering waves differ ...
of the light source, which is typically a few micrometers. This is especially relevant when investigating whole cell assays. Also, SCORE (as well as BLI) is not influenced by temperature fluctuations during the measurement, while SPR needs thermostabilisation.

Application
SCORE is especially used as detection method in bio- and chemosensors. It is a label-free technique like Reflectometric interference spectroscopy (RIfS), Bio-layer Interferometry (BLI) and Surface plasmon resonance (SPR), which allows time-resolved observation of binding events on the sensor surface without the use offluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
or radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
labels.
The SCORE technology was commercialised by Biametrics GmbH, a service provider and instrument manufacturer with headquarters in Tübingen
Tübingen (, , Swabian: ''Dibenga'') is a traditional university city in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, and developed on both sides of the Neckar and Ammer rivers. about one in thr ...
, Germany. In January 2020, Biametrics GmbH and its technology was acquired by BioCopy Holding AG, headquartered in Aadorf, Switzerland.
See also
* Reflectometric interference spectroscopy (RIfS) * Bio-layer Interferometry (BLI) *Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material in a particle stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measu ...
References
{{reflistLiterature
* Ewald, M., Fechner, P. & Gauglitz, G. Anal Bioanal Chem (2015) 407: 4005. doi:10.1007/s00216-015-8562-0 * Bleher, O., Schindler, A., Yin, MX. et al. Anal Bioanal Chem (2014) 406: 3305. doi:10.1007/s00216-013-7504-y * Schindler, A., Bleher, O., Thaler, M., et al. (2014). Diagnostic performance study of an antigen microarray for the detection of antiphospholipid antibodies in human serum. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 53(5), pp. 801–808. Retrieved 2 Mar. 2017, from doi:10.1515/cclm-2014-0569 * Ewald, M., Le Blanc, A.F., Gauglitz, G. et al. Anal Bioanal Chem (2013) 405: 6461. doi:10.1007/s00216-013-7040-9 * Rüdiger Frank ; Bernd Möhrle ; Dieter Fröhlich and Günter Gauglitz, "A transducer-independent optical sensor system for the detection of biochemical binding reactions", Proc. SPIE 5993, Advanced Environmental, Chemical, and Biological Sensing Technologies III, 59930A (November 8, 2005); doi:10.1117/12.633881; https://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.633881 * SLAS Technol. 2017 Aug;22(4):437-446. doi: 10.1177/2211068216657512. Low-Volume Label-Free Detection of Molecule-Protein Interactions on Microarrays by Imaging Reflectometric Interferometry. Burger J, Rath C, Woehrle J, Meyer PA, Ben Ammar N, Kilb N, Brandstetter T, Pröll F, Proll G, Urban G, Roth G.External links
SCORE Technology
Spectroscopy Biophysics Forensic techniques Nanotechnology Biochemistry methods Protein–protein interaction assays