single-phase generator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Single-phase generator (also known as single-phase alternator) is an
Single-phase generator (also known as single-phase alternator) is an

 More poles can also be added to single-phase generator to allow one rotation to produce more than one cycle of AC output. In an example on the left, the stator part is reconfigured to have 4 poles which are equally spaced. A north pole is adjacent to the two south poles. The shape of the armature at the rotor part is also changed. It is no longer a flat rectangle. The arm is bent 90 degrees. This allows one side of the armature to interact with a north pole while the other side interacts with a south pole similarly to the two-pole configuration. The current is still delivered out through the two sets of slip rings and brushes in the same fashion as in the two-pole configuration. The difference is that a cycle of AC output can be completed after a 180 degree rotation of the armature. In one rotation, the AC output will be two cycles. This increases the frequency of the output of the generator. More poles can be added to achieves higher frequency at the same rotation speed of the generator, or same frequency of output at the lower rotation speed of the generator depending on the applications.
This design also allows us to increase the output voltage by modifying the shape of the armature. We can add more rectangular loops to the armature as seen on the picture on the right. The additional loops at the armature arm are connected in series, which are actually additional windings of the same conductor wire to form a coil in rectangular shape. In this example, there are 4 windings in the coil. Since the shapes of all windings are the same, the amount of the lines of force will be cut at the same amount in the same direction at the same time in all windings. This creates
More poles can also be added to single-phase generator to allow one rotation to produce more than one cycle of AC output. In an example on the left, the stator part is reconfigured to have 4 poles which are equally spaced. A north pole is adjacent to the two south poles. The shape of the armature at the rotor part is also changed. It is no longer a flat rectangle. The arm is bent 90 degrees. This allows one side of the armature to interact with a north pole while the other side interacts with a south pole similarly to the two-pole configuration. The current is still delivered out through the two sets of slip rings and brushes in the same fashion as in the two-pole configuration. The difference is that a cycle of AC output can be completed after a 180 degree rotation of the armature. In one rotation, the AC output will be two cycles. This increases the frequency of the output of the generator. More poles can be added to achieves higher frequency at the same rotation speed of the generator, or same frequency of output at the lower rotation speed of the generator depending on the applications.
This design also allows us to increase the output voltage by modifying the shape of the armature. We can add more rectangular loops to the armature as seen on the picture on the right. The additional loops at the armature arm are connected in series, which are actually additional windings of the same conductor wire to form a coil in rectangular shape. In this example, there are 4 windings in the coil. Since the shapes of all windings are the same, the amount of the lines of force will be cut at the same amount in the same direction at the same time in all windings. This creates

 The design of revolving field generators is to have the armature part on stator and the magnetic field part on rotor. A basic design of revolving field single-phase generator is shown on the right. There are two magnetic poles, north and south, attached to a rotor and two coils which are connected in series and equally spaced on stator. The windings of the two coils are in reverse direction to have the current to flow in the same direction because the two coils always interact with opposing polarities. Since poles and coils are equally spaced and the locations of the poles match to the locations of the coils, the magnetic lines of force are cut at the same amount at any degree of the rotor. As a result, the voltages induced to all windings have the same value at any given time. The voltages from both coils are "
The design of revolving field generators is to have the armature part on stator and the magnetic field part on rotor. A basic design of revolving field single-phase generator is shown on the right. There are two magnetic poles, north and south, attached to a rotor and two coils which are connected in series and equally spaced on stator. The windings of the two coils are in reverse direction to have the current to flow in the same direction because the two coils always interact with opposing polarities. Since poles and coils are equally spaced and the locations of the poles match to the locations of the coils, the magnetic lines of force are cut at the same amount at any degree of the rotor. As a result, the voltages induced to all windings have the same value at any given time. The voltages from both coils are "
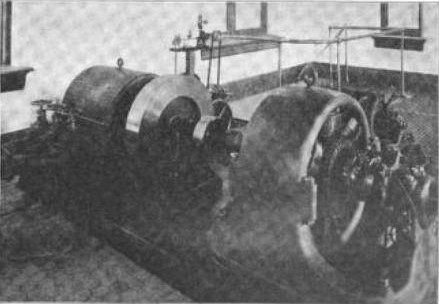


 In the very early days of
In the very early days of
alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
electrical generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an extern ...
that produces a single, continuously alternating voltage. Single-phase generators can be used to generate power in single-phase electric power
In electrical engineering, single-phase electric power (abbreviated 1φ) is the distribution of alternating current electric power using a system in which all the voltages of the supply vary in unison. Single-phase distribution is used when loads ...
systems. However, polyphase generators are generally used to deliver power in three-phase distribution system and the current is converted to single-phase near the single-phase loads instead. Therefore, single-phase generators are found in applications that are most often used when the loads being driven are relatively light, and not connected to a three-phase distribution, for instance, portable engine-generators. Larger single-phase generators are also used in special applications such as single-phase traction power for railway electrification system
Railway electrification is the use of electric power for the propulsion of rail transport. Electric railways use either electric locomotives (hauling passengers or freight in separate cars), electric multiple units ( passenger cars with their own ...
s.
Designs
Revolving armature
The design of revolving armature generators is to have the armature part on arotor
ROTOR was an elaborate air defence radar system built by the British Government in the early 1950s to counter possible attack by Soviet bombers. To get it operational as quickly as possible, it was initially made up primarily of WWII-era syst ...
and the magnetic field part on stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotat ...
. A basic design, called elementary generator, is to have a rectangular loop armature to cut the lines of force
In the history of physics, a line of force in Michael Faraday's extended sense is synonymous with James Clerk Maxwell's line of induction. According to J.J. Thomson, Faraday usually discusses ''lines of force'' as chains of polarized particles in ...
between the north and south poles. By cutting lines of force through rotation, it produces electric current. The current is sent out of the generator unit through two sets of slip ring
A slip ring is an electromechanical device that allows the transmission of Electric power, power and electrical Signal, signals from a stationary to a rotating structure. A slip ring can be used in any Electromechanics, electromechanical system ...
s and brushes
A brush is a common tool with bristles, wire or other filaments. It generally consists of a handle or block to which filaments are affixed in either a parallel or perpendicular orientation, depending on the way the brush is to be gripped during u ...
, one of which is used for each end of the armature. In this two-pole design, as the armature rotates one revolution, it generates one cycle of single phase
In electrical engineering, single-phase electric power (abbreviated 1φ) is the distribution of alternating current electric power using a system in which all the voltages of the supply vary in unison. Single-phase distribution is used when load ...
alternating current (AC). To generate an AC output, the armature is rotated at a constant speed having the number of rotations per second to match the desired frequency (in hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in ter ...
) of the AC output.
The relationship of armature rotation and the AC output can be seen in this series of pictures. Due to the circular motion of the armature against the straight lines of force, a variable number of lines of force will be cut even at a constant speed of the motion. At zero degrees, the rectangular arm of the armature does not cut any lines of force, giving zero voltage output. As the armature arm rotates at a constant speed toward the 90° position, more lines are cut. The lines of force are cut at most when the armature is at the 90° position, giving out the most current on one direction. As it turns toward the 180° position, lesser number of lines of force are cut, giving out lesser voltage until it becomes zero again at the 180° position. The voltage starts to increase again as the armature heads to the opposite pole at the 270° position. Toward this position, the current is generated on the opposite direction, giving out the maximum voltage on the opposite side. The voltage decrease again as it completes the full rotation. In one rotation, the AC output is produced with one complete cycle as represented in the sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic function, periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric function, trigonometric sine, sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is ''simple ...
.

 More poles can also be added to single-phase generator to allow one rotation to produce more than one cycle of AC output. In an example on the left, the stator part is reconfigured to have 4 poles which are equally spaced. A north pole is adjacent to the two south poles. The shape of the armature at the rotor part is also changed. It is no longer a flat rectangle. The arm is bent 90 degrees. This allows one side of the armature to interact with a north pole while the other side interacts with a south pole similarly to the two-pole configuration. The current is still delivered out through the two sets of slip rings and brushes in the same fashion as in the two-pole configuration. The difference is that a cycle of AC output can be completed after a 180 degree rotation of the armature. In one rotation, the AC output will be two cycles. This increases the frequency of the output of the generator. More poles can be added to achieves higher frequency at the same rotation speed of the generator, or same frequency of output at the lower rotation speed of the generator depending on the applications.
This design also allows us to increase the output voltage by modifying the shape of the armature. We can add more rectangular loops to the armature as seen on the picture on the right. The additional loops at the armature arm are connected in series, which are actually additional windings of the same conductor wire to form a coil in rectangular shape. In this example, there are 4 windings in the coil. Since the shapes of all windings are the same, the amount of the lines of force will be cut at the same amount in the same direction at the same time in all windings. This creates
More poles can also be added to single-phase generator to allow one rotation to produce more than one cycle of AC output. In an example on the left, the stator part is reconfigured to have 4 poles which are equally spaced. A north pole is adjacent to the two south poles. The shape of the armature at the rotor part is also changed. It is no longer a flat rectangle. The arm is bent 90 degrees. This allows one side of the armature to interact with a north pole while the other side interacts with a south pole similarly to the two-pole configuration. The current is still delivered out through the two sets of slip rings and brushes in the same fashion as in the two-pole configuration. The difference is that a cycle of AC output can be completed after a 180 degree rotation of the armature. In one rotation, the AC output will be two cycles. This increases the frequency of the output of the generator. More poles can be added to achieves higher frequency at the same rotation speed of the generator, or same frequency of output at the lower rotation speed of the generator depending on the applications.
This design also allows us to increase the output voltage by modifying the shape of the armature. We can add more rectangular loops to the armature as seen on the picture on the right. The additional loops at the armature arm are connected in series, which are actually additional windings of the same conductor wire to form a coil in rectangular shape. In this example, there are 4 windings in the coil. Since the shapes of all windings are the same, the amount of the lines of force will be cut at the same amount in the same direction at the same time in all windings. This creates in phase
In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is expressed in such a s ...
AC output for these 4 windings. As a result, the output voltage is increased 4 time as shown in the sine wave in the diagram.
Revolving field
in phase
In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is expressed in such a s ...
" to each other. Therefore, the total output voltage is two times the voltage induced in each winding. In the figure, at the position where pole number 1 and coil number 1 meet, the generator produces the highest output voltage on one direction. As the rotor turns 180 degrees, the output voltage is alternated to produce the highest voltage on the other direction. The frequency of the AC output in this case equals to the number of rotations of the rotor per second.
This design can also allow us to increase the output frequency by adding more poles. In this example on the right, we have 4 coils connected in series on the stator and the field rotor has 4 poles. Both coils and poles are equally spaced. Each pole has opposite polarity to its neighbors which are angled at 90 degrees. Each coils also have opposite winding to its neighbors. This configuration allows the lines of force at 4 poles to be cut by 4 coils at the same amount at a given time. At each 90-degree rotation, the voltage output polarity is switched from one direction to the other. Therefore, there are 4 cycles of the AC output in one rotation. As the 4 coils are wired in series and their outputs are "in phase", the AC output of this single-phase generator will have 4 times the voltage of that generated by each individual coil.
A benefit of the revolving field design is that if the poles are permanent magnets
Permanent may refer to:
Art and entertainment
* ''Permanent'' (film), a 2017 American film
* ''Permanent'' (Joy Division album)
* "Permanent" (song), by David Cook
*"Permanent", a song by Alex Lahey from '' The Answer Is Always Yes'', 2023
Other ...
, then there is no need to use any slip ring and brush to deliver electricity out of the generator as the coils are stationary and can be wired directly from the generator to the external loads.
Small generators
Single-phase generators that people are familiar with are usually small. The applications are forstandby generator
Standby generators
A standby generator is a back-up electrical system that operates automatically.Robert B. Hickey ''Electrical Construction Databook'', McGraw Hill, 2002 , Chapter 14 Within seconds of a utility outage an automatic transfer s ...
s in case of main power supply is interrupted and for supplying temporary power on construction sites.
Another application is in small wind technology. Although most of wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that wind power, converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. , hundreds of thousands of list of most powerful wind turbines, large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, were generating over ...
s use three-phase generators, single-phase generators are found in some of the small wind turbine models with rated power outputs of up with 55 kW. The single-phase models are available in the vertical axis wind turbines (VAWT) and Horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWT).
Power stations



 In the very early days of
In the very early days of electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utility, utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its Electricity delivery, delivery (Electric power transm ...
, the generators at power station
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electr ...
s had been single-phase AC or direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
. The direction of the power industry were changing in 1895 when more efficient polyphase generators were successfully implemented at Adams Hydroelectric Generating Plant which was the first large-scale polyphase power station. Newer power stations started to adopt the polyphase system. In the 1900s, many railways started the electrification
Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and, in many contexts, the introduction of such power by changing over from an earlier power source. In the context of history of technology and economic development, electrification refe ...
of their lines. During that time, the single-phase AC system had been widely used for their traction power networks beside the direct current system. The early generators for those single-phase traction networks are single-phase generators. Even with newer three-phase motors which were introduced to some modern trains, the single-phases transmission for traction networks survive their time and are still in use in many railways today. However, many traction power stations have replaced their generators over time to use three-phase generators and convert into single-phase for transmission.
Hydro
In the early development ofhydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
, single-phase generators played an important role in demonstrating the benefits of alternating current. In 1891, a 3,000 volts and 133 Hz single-phase generator of 100 horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are t ...
was installed at Ames Hydroelectric Generating Plant
The Ames Hydroelectric Generating Plant, constructed in 1890 near Ophir, Colorado, was one of the first (if not the first) commercial system to produce and transmit alternating current (AC) electricity for industrial use and one of the first AC hy ...
which was belt-connected with Pelton water wheel. The power was transmitted through cables to power an identical motor at the mill. The plant was the first to generate alternating current electric power for industrial application and it was a demonstration of the efficiency in AC transmission. This was a precedent to larger for much larger plants such as the Edward Dean Adams Power Plant in Niagara Falls, New York
Niagara Falls is a City (New York), city in Niagara County, New York, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a total population of 48,671. It is adjacent to the Niagara River, across from the city of Niagar ...
in 1895. However, the larger plants were operated using polyphase generators for greater efficiency. That left the applications for single-phase hydroelectricity generation to special cases such as in light loads.
An example of using single-phase in a special case was implemented in 1902 at St. Louis Municipal Electric Power Plant. A 20 kW single-phase generator was direct-connected to a Pelton water wheel to generate electricity enough to power light loads. This was an early demonstration of in-conduit hydro to capture energy from water flow in the public water pipeline
A pipeline is a system of Pipe (fluid conveyance), pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries ...
. The energy for the water main in this case was not created by gravity, but the water was pumped by a larger steam engine at a water pumping station to supply water to customers. The decision to have water pumped by a larger engine then take some of the energy from water flow to power a smaller generator using water wheel was based on the cost. At the time, steam engines were not efficient and cost effective for a 20 kW system. Therefore, they installed a steam water pump to have enough energy to maintain water pressure for customer and to drive a small generator at the same time.
The main usage of single-phase hydroelectricity generation today is to supply power for traction network for railways. Many electrical transmission networks for railways especially in Germany rely on single-phase generation and transmission which are still in use today. A notable power station is Walchensee Hydroelectric Power Station in Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
. The station takes water from elevated Lake Walchensee to drive eight turbines that drive the generators. Four of those are three-phase generators to supply the power grid
''Power Grid'' is the English-language version of the second edition of the multiplayer German-style board game ''Funkenschlag'', designed by Friedemann Friese and first released in 2004. ''Power Grid'' was released by Rio Grande Games.
I ...
. The other four are single-phase generators are connected to Pelton turbines which have combined capacity of 52 MW to supply the German 15 kV AC railway electrification
Railway electrification using at are used on transport railways in Rail transport in Germany, Germany, Rail transport in Austria, Austria, Rail transport in Switzerland, Switzerland, Rail transport in Sweden, Sweden, and Rail transport in No ...
.
Similar single-phase hydroelectricity generations are also used in another variance of railway electrification system in the United States. A power station at Safe Harbor Dam in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
provides power generation for both public utilities and for Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
railway. Two out of its 14 turbines are connected to two single-phase generators to supply Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system
The traction power network of Amtrak uses 25 Hz for the southern portion of the Northeast Corridor (NEC), the Keystone Corridor, and several branch lines between New York City and Washington D.C. The system was constructed by the Pennsylvania Rai ...
. The two turbines are of Kaplan type with 5 blades rated 42,500 horsepower.
Steam
In the early years, steam engines were used as prime movers of generators. An installation atSt. Louis
St. Louis ( , sometimes referred to as St. Louis City, Saint Louis or STL) is an independent city in the U.S. state of Missouri. It lies near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a populatio ...
Municipal Electric Power Plant in the 1900s was an example of using steam engines with single-phase generators. The St. Louis plant used compound steam engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages.
A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure (HP) cylinder, then having given up heat ...
to drive a 100 kW single-phase generator which produced current at rated power of 1,150 volts.
The steam engines were also used during the twentieth century in power stations for traction networks which had single-phase power distribution for specific railways. A special set of single-phase generators with steam turbines at Waterside Generating Station in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
in 1938 was an example of such generation and distribution systems. The single-phase generators were eventually retired in the late 1970s due to concerns of a turbine failure in another station. The generators were replaced by two transformers to reduce from another three-phase power source to existing single-phase catenary
In physics and geometry, a catenary ( , ) is the curve that an idealized hanging chain or wire rope, cable assumes under its own weight when supported only at its ends in a uniform gravitational field.
The catenary curve has a U-like shape, ...
power. Eventually, the transformers were replaced by two solid-state cycloconverter
A cycloconverter (CCV) or a cycloinverter converts a constant amplitude, constant frequency Alternating current, AC waveform to another AC waveform of a lower frequency by synthesizing the output waveform from segments of the AC supply without an ...
instead.
Nuclear
Normally,nuclear power plants
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power s ...
are used as base load
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants or dispatchable generation, depending on which approach has the best m ...
stations with very high capacities to supply power to the grids. Neckarwestheim I in Neckarwestheim is a unique nuclear power plant in that it is equipped with high-capacity single-phase generators to supply Deutsche Bahn
(, ; abbreviated as DB or DB AG ) is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG).
DB was fou ...
railway with specific AC voltage at frequency of 16 2/3 Hz. The pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada).
In a PWR, water is used both as ...
transport thermal energy to two turbines and generators which are rated for 187 MW and 152 MW.
See also
*Alternator
An alternator (or synchronous generator) is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field wit ...
* Polyphase coil
References
{{Electric motors Electrical generators AC power