Single-carrier Frequency-domain-equalization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Single-carrier FDMA (SC-FDMA) is a
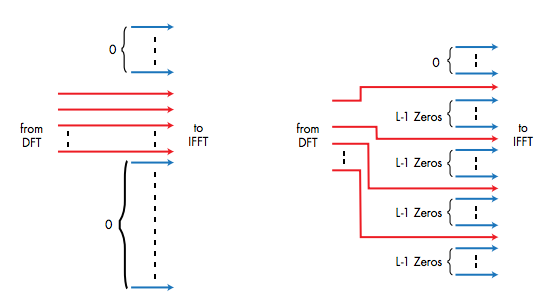 The distinguishing feature of SC-FDMA is that it leads to a single-carrier transmit signal, in contrast to OFDMA which is a multi-carrier transmission scheme. Subcarrier mapping can be classified into two types: localized mapping and distributed mapping. In localized mapping, the DFT outputs are mapped to a subset of consecutive subcarriers, thereby confining them to only a fraction of the system bandwidth. In distributed mapping, the DFT outputs of the input data are assigned to subcarriers over the entire bandwidth non-continuously, resulting in zero amplitude for the remaining subcarriers. A special case of distributed SC-FDMA is called interleaved SC-FDMA ( IFDMA), where the occupied subcarriers are equally spaced over the entire bandwidth.
Owing to its inherent single carrier structure, a prominent advantage of SC-FDMA over
The distinguishing feature of SC-FDMA is that it leads to a single-carrier transmit signal, in contrast to OFDMA which is a multi-carrier transmission scheme. Subcarrier mapping can be classified into two types: localized mapping and distributed mapping. In localized mapping, the DFT outputs are mapped to a subset of consecutive subcarriers, thereby confining them to only a fraction of the system bandwidth. In distributed mapping, the DFT outputs of the input data are assigned to subcarriers over the entire bandwidth non-continuously, resulting in zero amplitude for the remaining subcarriers. A special case of distributed SC-FDMA is called interleaved SC-FDMA ( IFDMA), where the occupied subcarriers are equally spaced over the entire bandwidth.
Owing to its inherent single carrier structure, a prominent advantage of SC-FDMA over
frequency-division multiple access
Frequency-division multiple access (FDMA) is a channel access method used in some multiple-access protocols. FDMA allows multiple users to send data through a single communication channel, such as a coaxial cable or microwave beam, by dividi ...
scheme. It is also called linearly precoded OFDMA (LP-OFDMA). Like other multiple access schemes (TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, OFDMA), it deals with the assignment of multiple users to a shared communication resource. SC-FDMA can be interpreted as a linearly precoded OFDMA
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarrier ...
scheme, in the sense that it has an additional DFT processing step preceding the conventional OFDMA processing.
SC-FDMA has drawn great attention as an attractive alternative to OFDMA
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarrier ...
, especially in the uplink communications where lower peak-to-average power ratio ( PAPR) greatly benefits the mobile terminal in terms of transmit power efficiency and reduced cost of the power amplifier. It has been adopted as the uplink multiple access scheme in 3GPP Long Term Evolution
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/ EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by ...
(LTE), or Evolved UTRA (E-UTRA).
The performance of SC-FDMA in relation to OFDMA has been the subject of various studies. Although the performance gap is small, SC-FDMA's advantage of low PAPR makes it desirable for uplink wireless transmission in mobile communication systems, where transmitter power efficiency is of paramount importance.
Transmitter and receiver structure
The transmission processing of SC-FDMA is very similar to that of OFDMA. For each user, the sequence of bits transmitted is mapped to a complex constellation of symbols (BPSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at ...
, QPSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at ...
, or M-quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message sig ...
). Then different transmitters (users) are assigned different Fourier coefficients. This assignment is carried out in the mapping and demapping blocks. The receiver side includes one demapping block, one IDFT block, and one detection block for each user signal to be received. Just like in OFDM
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission and a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital comm ...
, guard intervals (called cyclic prefixes) with cyclic repetition are introduced between blocks of symbols in view to efficiently eliminate inter-symbol interference from time spreading (caused by multi-path propagation) among the blocks.
In SC-FDMA, multiple access among users is made possible by assigning different users different sets of non-overlapping Fourier coefficients (sub-carriers). This is achieved at the transmitter by inserting (prior to IDFT) silent Fourier coefficients (at positions assigned to other users), and removing them on the receiver side after the DFT.
 The distinguishing feature of SC-FDMA is that it leads to a single-carrier transmit signal, in contrast to OFDMA which is a multi-carrier transmission scheme. Subcarrier mapping can be classified into two types: localized mapping and distributed mapping. In localized mapping, the DFT outputs are mapped to a subset of consecutive subcarriers, thereby confining them to only a fraction of the system bandwidth. In distributed mapping, the DFT outputs of the input data are assigned to subcarriers over the entire bandwidth non-continuously, resulting in zero amplitude for the remaining subcarriers. A special case of distributed SC-FDMA is called interleaved SC-FDMA ( IFDMA), where the occupied subcarriers are equally spaced over the entire bandwidth.
Owing to its inherent single carrier structure, a prominent advantage of SC-FDMA over
The distinguishing feature of SC-FDMA is that it leads to a single-carrier transmit signal, in contrast to OFDMA which is a multi-carrier transmission scheme. Subcarrier mapping can be classified into two types: localized mapping and distributed mapping. In localized mapping, the DFT outputs are mapped to a subset of consecutive subcarriers, thereby confining them to only a fraction of the system bandwidth. In distributed mapping, the DFT outputs of the input data are assigned to subcarriers over the entire bandwidth non-continuously, resulting in zero amplitude for the remaining subcarriers. A special case of distributed SC-FDMA is called interleaved SC-FDMA ( IFDMA), where the occupied subcarriers are equally spaced over the entire bandwidth.
Owing to its inherent single carrier structure, a prominent advantage of SC-FDMA over OFDM
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission and a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital comm ...
and OFDMA
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarrier ...
is that its transmit signal has a lower peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR), resulting in relaxed design parameters in the transmit path of a subscriber unit. Intuitively, the reason lies in the fact that where OFDM transmit symbols directly modulate multiple sub-carriers, SC-FDMA transmit symbols are first processed by an N-point DFT block.
In OFDM, as well as SC-FDMA, equalization is achieved on the receiver side, after the DFT calculation, by multiplying each Fourier coefficient by a complex number. Thus, frequency-selective fading
In wireless communications, fading is variation of the attenuation of a signal with various variables. These variables include time, geographical position, and radio frequency. Fading is often modeled as a random process. A fading channel is a ...
and phase distortion
In signal processing, phase distortion or phase-frequency distortion is distortion, that is, change in the shape of the waveform, that occurs when (a) a filter's phase response is not linear over the frequency range of interest, that is, the ph ...
can be easily counteracted. The advantage is that frequency domain equalization using FFTs requires less computation than conventional time-domain equalization, which require multi-tap FIR or IIR-filters. Less computations result in less compounded round-off error, which can be viewed as numerical noise.
A related concept is the combination of a single carrier transmission with the single-carrier frequency-domain-equalization (SC-FDE) scheme. The single carrier transmission, unlike SC-FDMA and OFDM, employs no IDFT or DFT at the transmitter, but introduces the cyclic prefix to transform the linear channel convolution into a circular one. After removing the cyclic prefix at the receiver, a DFT is applied to arrive in the frequency domain, where a simple single-carrier frequency-domain-equalization (SC-FDE) scheme can be employed, followed by the IDFT operation.
* DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced Sampling (signal processing), samples of a function (mathematics), function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discre ...
* IDFT: Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced Sampling (signal processing), samples of a function (mathematics), function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discre ...
* CP: Cyclic Prefix
* PS: Pulse Shaping In electronics and telecommunications, pulse shaping is the process of changing the waveform of transmitted pulses to optimize the signal for its intended purpose or the communication channel. This is often done by limiting the bandwidth of the tra ...
* DAC: Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
There are several DAC archi ...
* RF: Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the uppe ...
signal
* ADC: Analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
* LP-OFDMA: Linearly precoded OFDMA
Useful properties
# Low PAPR (crest factor) # Low sensitivity to carrier frequency offset # Less sensitive to non-linear distortion and hence, it allows the use of low-cost power amplifiers # Greater robustness against spectral nullsSee also
* Carrier interferometry *3GPP Long Term Evolution
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/ EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by ...
* OFDMA
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarrier ...
* Time-division multiple access
Time-division multiple access (TDMA) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, ...
References