simulation in manufacturing systems on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Simulation in manufacturing systems is the use of software to make computer models of manufacturing systems, so to analyze them and thereby obtain important information. It has been syndicated as the second most popular management science among manufacturing managers. However, its use has been limited due to the complexity of some software packages, and to the lack of preparation some users have in the fields of probability and statistics.
This technique represents a valuable tool used by engineers when evaluating the effect of capital investment in equipment and physical facilities like factory plants, warehouses, and distribution centers.
 Some other benefits include Just-in-time manufacturing, calculation of optimal resources required, validation of the proposed operation logic for controlling the system, and data collected during modelling that may be used elsewhere.
The following is an example: In a manufacturing plant one machine processes 100 parts in 10 hours but the parts coming to the machine in 10 hours is 150. So there is a buildup of inventory. This inventory can be reduced by employing another machine occasionally. Thus we understand the reduction in local inventory buildup. But now this machine produces 150 parts in 10 hours which might not be processed by the next machine and thus we have just shifted the in-process inventory from one machine to another without having any impact on overall production
Simulation is used to address some issues in manufacturing as follows: In workshop to see the ability of system to meet the requirement, To have optimal inventory to cover for machine failures.
Some other benefits include Just-in-time manufacturing, calculation of optimal resources required, validation of the proposed operation logic for controlling the system, and data collected during modelling that may be used elsewhere.
The following is an example: In a manufacturing plant one machine processes 100 parts in 10 hours but the parts coming to the machine in 10 hours is 150. So there is a buildup of inventory. This inventory can be reduced by employing another machine occasionally. Thus we understand the reduction in local inventory buildup. But now this machine produces 150 parts in 10 hours which might not be processed by the next machine and thus we have just shifted the in-process inventory from one machine to another without having any impact on overall production
Simulation is used to address some issues in manufacturing as follows: In workshop to see the ability of system to meet the requirement, To have optimal inventory to cover for machine failures.
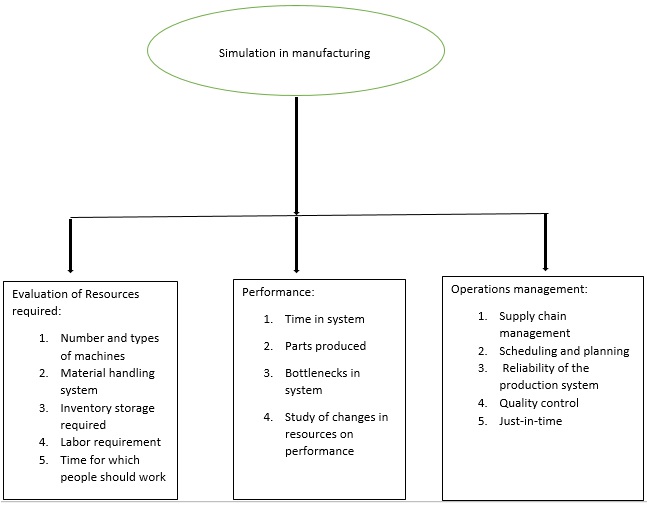
 The following is a list of common applications of simulation in manufacturing:
The following is a list of common applications of simulation in manufacturing:
Simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
can be used to predict the performance of an existing or planned system and to compare alternative solutions for a particular design problem.
Objectives
The most important objective of simulation in manufacturing is the understanding of the change to the whole system because of some local changes. It is easy to understand the difference made by changes in the local system but it is very difficult or impossible to assess the impact of this change in the overall system. Simulation gives us some measure of this impact. Measures which can be obtained by a simulation analysis are: * Parts produced per unit time * Time spent in system by parts * Time spent by parts in queue * Time spent during transportation from one place to another * In time deliveries made * Build up of the inventory * Inventory in process * Percent utilization of machines and workers. Some other benefits include Just-in-time manufacturing, calculation of optimal resources required, validation of the proposed operation logic for controlling the system, and data collected during modelling that may be used elsewhere.
The following is an example: In a manufacturing plant one machine processes 100 parts in 10 hours but the parts coming to the machine in 10 hours is 150. So there is a buildup of inventory. This inventory can be reduced by employing another machine occasionally. Thus we understand the reduction in local inventory buildup. But now this machine produces 150 parts in 10 hours which might not be processed by the next machine and thus we have just shifted the in-process inventory from one machine to another without having any impact on overall production
Simulation is used to address some issues in manufacturing as follows: In workshop to see the ability of system to meet the requirement, To have optimal inventory to cover for machine failures.
Some other benefits include Just-in-time manufacturing, calculation of optimal resources required, validation of the proposed operation logic for controlling the system, and data collected during modelling that may be used elsewhere.
The following is an example: In a manufacturing plant one machine processes 100 parts in 10 hours but the parts coming to the machine in 10 hours is 150. So there is a buildup of inventory. This inventory can be reduced by employing another machine occasionally. Thus we understand the reduction in local inventory buildup. But now this machine produces 150 parts in 10 hours which might not be processed by the next machine and thus we have just shifted the in-process inventory from one machine to another without having any impact on overall production
Simulation is used to address some issues in manufacturing as follows: In workshop to see the ability of system to meet the requirement, To have optimal inventory to cover for machine failures.
Methods
In the past, manufacturing simulation tools were classified as languages or simulators. Languages were very flexible tools, but rather complicated to use by managers and too time consuming. Simulators were more user friendly but they came with rather rigid templates that didn’t adapt well enough to the rapidly changing manufacturing techniques. Nowadays, there is software available that combines the flexibility and user friendliness of both, but still some authors have reported that the use of this simulation to design and optimize manufacturing processes is relatively low. One of the most used techniques by manufacturing system designers is the discrete event simulation. This type of simulation allows to assess the system’s performance by statistically and probabilistically reproducing the interactions of all its components during a determined period of time. In some cases, manufacturing systems modelling needs a continuous simulation approach. These are the cases where the states of the system change continuously, like, for example, in the movement of liquids in oil refineries or chemical plants. As continuous simulation cannot be modeled by digital computers, it is done by taking small discrete steps. This is a useful feature, since there are many cases where both, continuous and discrete simulation, have to be combined. This is called hybrid simulation, which is needed in many industries, for example, the food industry. A framework to evaluate different manufacturing simulation tools was developed by Benedettini & Tjahjono (2009) using the ISO 9241 definition of usability: “the extent to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a specified context of use.” This framework considered effectiveness, efficiency and user satisfaction as the three main performance criterion as follow: The following is a list of popular simulation techniques: # Discrete event simulation (DES) # System dynamics (SD) # Agent-based modelling (ABM) # Intelligent simulation: based on an integration of simulation and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques # Petri net # Monte Carlo simulation (MCS) # Virtual simulation: allows the user to model the system in a 3D immersive environment # Hybrid techniques: combination of different simulation techniques.Applications
 The following is a list of common applications of simulation in manufacturing:
The following is a list of common applications of simulation in manufacturing:
References
{{Reflist Manufacturing Simulation