silicon oxynitride on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Silicon oxynitride is a
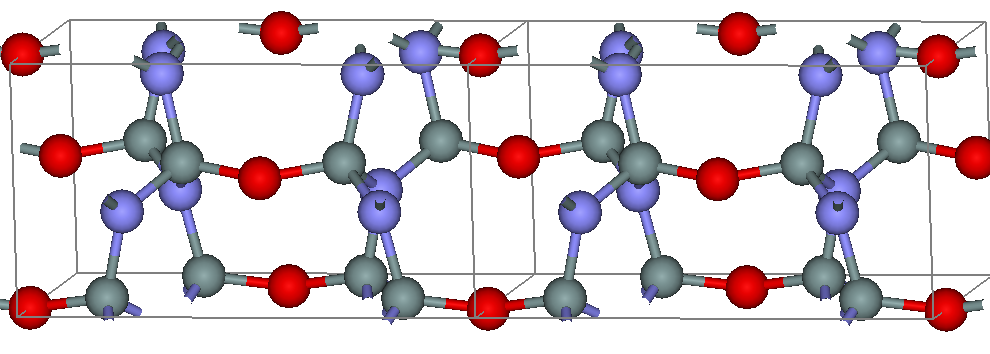 The crystalline structure of silicon oxynitride is built by SiN3O tetrahedra connected through oxygen atoms along the ''c'' axis and through nitrogen atoms perpendicular to it. The strong covalent bonding of this structure results in high
The crystalline structure of silicon oxynitride is built by SiN3O tetrahedra connected through oxygen atoms along the ''c'' axis and through nitrogen atoms perpendicular to it. The strong covalent bonding of this structure results in high
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
material with the chemical formula SiOxNy. While in amorphous forms its composition can continuously vary between SiO2 (silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
) and Si3N4 (silicon nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. (''Trisilicon tetranitride'') is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term ″''Silicon nitride''″ commonly re ...
), the only known intermediate crystalline phase is Si2N2O. It is found in nature as the rare mineral sinoite in some meteorites and can be synthesized in the laboratory.
Properties
 The crystalline structure of silicon oxynitride is built by SiN3O tetrahedra connected through oxygen atoms along the ''c'' axis and through nitrogen atoms perpendicular to it. The strong covalent bonding of this structure results in high
The crystalline structure of silicon oxynitride is built by SiN3O tetrahedra connected through oxygen atoms along the ''c'' axis and through nitrogen atoms perpendicular to it. The strong covalent bonding of this structure results in high flexural strength
Flexural strength, also known as modulus of rupture, or bend strength, or transverse rupture strength is a material property, defined as the Stress (mechanics), stress in a material just before it Yield (engineering), yields in a flexure test. T ...
and resistance to heating and oxidation up to temperatures of about 1600 °C.
Synthesis
Polycrystalline silicon oxynitride ceramics are primarily produced by nitridation of a mixture of Si and silicon dioxide at a temperature above melting point of silicon (1414 °C), in the range 1420–1500 °C: :3 Si + SiO2 + 2 N2 → 2 Si2N2O Silicon oxynitride materials with various stoichiometries may also arise as the products of pyrolysis of preceramic polymers, namely polysilanes and polyethoxysilsesquiazane. SiON materials thus obtained are referred to as polymer derived ceramics or PDCs. By using preceramic polymers, dense or porous Si oxynitride ceramics in complex forms can be obtained using shaping techniques more typically applied for polymers.Applications
Thin films of silicon oxynitride can be grown on silicon using a variety of plasma deposition techniques and used in microelectronics as a dielectric layer alternative tosilicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundan ...
and silicon nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. (''Trisilicon tetranitride'') is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term ″''Silicon nitride''″ commonly re ...
with the advantages of low leakage currents and high thermal stability. These films have an amorphous structure and therefore their chemical composition can widely deviate from Si2N2O. By changing the nitrogen/oxygen ratio in these films, their refractive index can be continuously tuned between the value of ~1.45 for silicon dioxide and ~2.0 for silicon nitride. This property is useful for gradient-index optics
Gradient-index (GRIN) optics is the branch of optics covering optical effects produced by a gradient of the refractive index of a material. Such gradual variation can be used to produce lenses with flat surfaces, or lenses that do not have the a ...
components such as graded-index fiber
A graded-index fiber, or gradient-index fiber, is an optical fiber whose core has a refractive index that decreases ''continuously'' with increasing radial distance from the optical axis of the fiber, as opposed to a step-index fiber, which ha ...
s.
Silicon oxynitrides can be doped with metal atoms. The most common example is sialon, a family of quaternary SiAlON compound. Quaternary silicon oxynitrides containing a lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (el ...
element, such as La, Eu or/and Ce are used as phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
s.
References
{{reflist, refs= {{cite book, author=Ralf Riedel, title=Ceramics science and technology: Structures, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=I-WFvgkBiEMC&pg=PA97, access-date=8 October 2011, date=18 April 2008, publisher=Wiley-VCH, isbn=978-3-527-31155-2, pages=97– {{cite book, author1=Albert R. Landgrebe, author2=Electrochemical Society. Dielectric Science and Technology Division, author3=Electrochemical Society. High Temperature Materials Division, title=Silicon nitride and silicon dioxide thin insulating films: proceedings of the sixth international symposium, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=aZ4brOPBhXoC&pg=PA191, access-date=8 October 2011, year=2001, publisher=The Electrochemical Society, isbn=978-1-56677-313-3, pages=191– {{cite book, author=E. S. Machlin, title=Materials Science in Microelectronics: The effects of structure on properties in thin films, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uZNZEgzJltoC&pg=PA36, access-date=8 October 2011, date=9 December 2005, publisher=Elsevier, isbn=978-0-08-044639-4, pages=36– {{cite journal, url=http://www.minsocam.org/msa/ammin/toc/Articles_Free/1997/Rubin_p1001-1006_97.pdf, journal=American Mineralogist, author=A. E. Rubin, title=Sinoite (Si2N2O): Crystallization from EL chondrite impact melts, volume=82, page=1001, year=1997, issue=9–10, doi=10.2138/am-1997-9-1016, bibcode=1997AmMin..82.1001R, s2cid=128629202 Ceramic materials Nitrides Oxides Silicon compounds