Silanone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
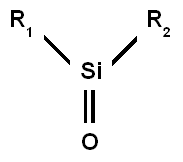 A silanone in chemistry is the
A silanone in chemistry is the
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
analogue of a ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bon ...
. The general description for this class of organic compounds
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
is R1R2Si=O, with silicon connected to a terminal oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
atom via a double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
and also with two organic residues (R). Silanones are extremely reactive and until 2013 were only detected by argon matrix isolation
Matrix isolation is an experimental technique used in chemistry and physics. It generally involves a material being trapped within an unreactive matrix. A ''host'' matrix is a continuous solid phase in which ''guest'' particles (atoms, molecules, ...
''On the proposed thermal interconversion of matrix-isolated dimethylsilylene and 1-methylsilene: their reactions with oxygen atom donors'' Charles A. Arrington, Robert West, Josef Michl J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105 (19), pp 6176–6177 ''Infrared spectroscopic evidence for silicon-oxygen double bonds: silanone and the silanoic and silicic acid molecules'' Robert Withnall, Lester Andrews J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1985, 107 (8), pp 2567–2568 or in the gas phase but not isolated. A synthesis of a stable silanone was reported in 2014. Silanones are of some interest to academic research, with their reactivity being of some relevance to the double bond rule
In chemistry, the double bond rule states that elements with a principal quantum number greater than 2 for their valence electrons ( period 3 elements and higher) tend not to form multiple bonds (e.g. double bonds and triple bonds). The double b ...
.
Silanones are unstable and favor oligomerisation
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relati ...
to siloxane
A siloxane is a functional group in organosilicon chemistry with the Si−O−Si linkage. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H(OSiH2)''n''OH and (OSiH2)n. Siloxanes also include branched compound ...
s. The reason for this instability is the weak pi bond
In chemistry, pi bonds (Ï€ bonds) are covalent chemical bonds, in each of which two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom, and in which this overlap occurs laterally. Each of these atomic orbita ...
with a small HOMO–LUMO energy gap
In chemistry, HOMO and LUMO are types of molecular orbitals. The acronyms stand for ''highest occupied molecular orbital'' and ''lowest unoccupied molecular orbital'', respectively. HOMO and LUMO are sometimes collectively called the ''fronti ...
caused by an unfavorable overlap between the p-orbitals of silicon and oxygen. A second reason for the observed instability is the strongly polarized silicon–oxygen bond
A silicon–oxygen bond ( bond) is a chemical bond between silicon and oxygen atoms that can be found in many inorganic and organic compounds. In a silicon–oxygen bond, electrons are shared unequally between the two atoms, with oxygen taking th ...
, Siδ+–Oδ−.
History
The first to postulate a silanone were Kipping & Lloyd in 1901,''XLVII.—Organic derivatives of silicon. Triphenylsilicol and alkyloxysilicon chlorides'' F. Stanley Kipping, Ph.D., D.Sc., F.R.S. and Lorenzo L. Lloyd J. Chem. Soc., Trans., 1901,79, 449-459 but their products were in fact siloxanes. It was not until 2014 that a stable silanone was reported.Filippou, A. C., Baars, B., Chernov, O., Lebedev, Y. N. and Schnakenburg, G. (2014), ''Silicon–Oxygen Double Bonds: A Stable Silanone with a Trigonal-Planar Coordinated Silicon Center.'' Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 53: 565–570. In this compound, silicon is bonded to a SIDipp (1,3-bis(2,6-iPr2-C6H3)imidazolidin-2-ylidene) group and a (Cp*)Cr(CO)3 group. Its stability is owed to the direct coordination of silicon tochromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and h ...
and to steric shielding
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
. The reported Si=O bond length
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest ...
is 1.526 Ã…, in line with expectations. It has been described as a cationic
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
metallosilanone.
Other strategies have recently been used to stabilise silanones, for example coordination to Lewis acids or bases and steric shielding
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
.
References
{{reflist Organosilicon compounds