
The Khalistan movement is a
Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
separatist movement seeking to create a homeland for Sikhs by establishing a
sovereign state, called Khālistān ('
Land of the
Khalsa'), in the
Punjab region. The proposed state would consist of land that currently forms
Punjab, India and
Punjab, Pakistan.
[: ]
Ever since the separatist movement gathered force in the 1980s, the territorial ambitions of Khalistan have at times included
Chandigarh, sections of the Indian Punjab, including the whole of
North India, and some parts of the western states of India.
[Crenshaw, Martha, 1995, ''Terrorism in Context'', ]Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsylvan ...
, p. 364 Prime Minister of Pakistan Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, according to
Jagjit Singh Chohan
Jagjit Singh Chohan was the founder of the Khalistan movement that sought to create an independent Sikh state in the Punjab region of India and Pakistan.
Politics
Jagjit Singh grew up in Tanda in Punjab's Hoshiarpur district, about 180 km ...
, had proposed all out help to create Khalistan during his talks with Chohan, following the conclusion of the
Indo-Pakistani War of 1971.
The call for a separate Sikh state began in the wake of the fall of the
British Empire.
In 1940, the first explicit call for Khalistan was made in a pamphlet titled "Khalistan". With financial and political support of the
Sikh diaspora, the movement flourished in the Indian state of Punjab – which has a
Sikh-majority population – continuing through the 1970s and 1980s, and reaching its zenith in the late 1980s. In the 1990s, the insurgency petered out,
and the movement failed to reach its objective for multiple reasons including a heavy police crackdown on separatists, factional infighting, and disillusionment from the Sikh population.
There is some support within India and the Sikh diaspora, with yearly demonstrations in protest of those killed during
Operation Blue Star. In early 2018, some militant groups were arrested by police in Punjab, India.
Former
Chief Minister of Punjab Amarinder Singh claimed that the recent extremism is backed by Pakistan's
Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) and "Khalistani sympathisers" in
Canada,
Italy, and the
UK.
Simranjit Singh Mann, elected in 2022 from Sangrur, is currently the only openly Khalistani MP in the Indian Parliament and his party,
Shiromani Akali Dal (Amritsar), is currently the only pro-Khalistan party in the Indian parliament.
Pre-1950s

Sikhs have been concentrated in the
Punjab region of
South Asia. Before its conquest by the British, the region around Punjab had been ruled by the confederacy of Sikh
Misl
The Misls (derived from an Arabic word wikt:مثل#Etymology_3, مِثْل meaning 'equal') were the twelve sovereign states of the Sikh Confederacy, which rose during the 18th century in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian ...
s founded by
Banda Bahadur. The Misls ruled over the entire Punjab from 1767 to 1799, until their confederacy was unified into the
Sikh Empire by
Maharajah Ranjit Singh from 1799 to 1849.
At the end of the
Second Anglo-Sikh War in 1849, the Sikh Empire dissolved into separate
princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
s and the
British province of Punjab. In newly conquered regions, "religio-nationalist movements emerged in response to British “
divide and rule” administrative policies, the perceived success of Christian missionaries converting Hindu, Sikhs and Muslims, and a general belief that the solution to the downfall among India's religious communities was a grassroots religious revival."
As the British Empire began to dissolve in the 1930s, Sikhs made their first call for a Sikh homeland.
When the
Lahore Resolution of the
Muslim League demanded Punjab be made into a Muslim state, the
Akalis viewed it as an attempt to usurp a historically Sikh territory. In response, the Sikh party
Shiromani Akali Dal argued for a community that was separate from Hindus and Muslims. The Akali Dal imagined Khalistan as a
theocratic state led by the
Maharaja of Patiala with the aid of a cabinet consisting of the representatives of other units. The country would include parts of present-day
Punjab, India, present-day
Punjab, Pakistan (including
Lahore), and the
Simla Hill States
The Hill States of India were princely states lying in the northern border regions of the British Indian Empire.
History
During the colonial Raj period, two groups of princely states in direct relations with the Province of British Punjab ...
.
Partition of India, 1947
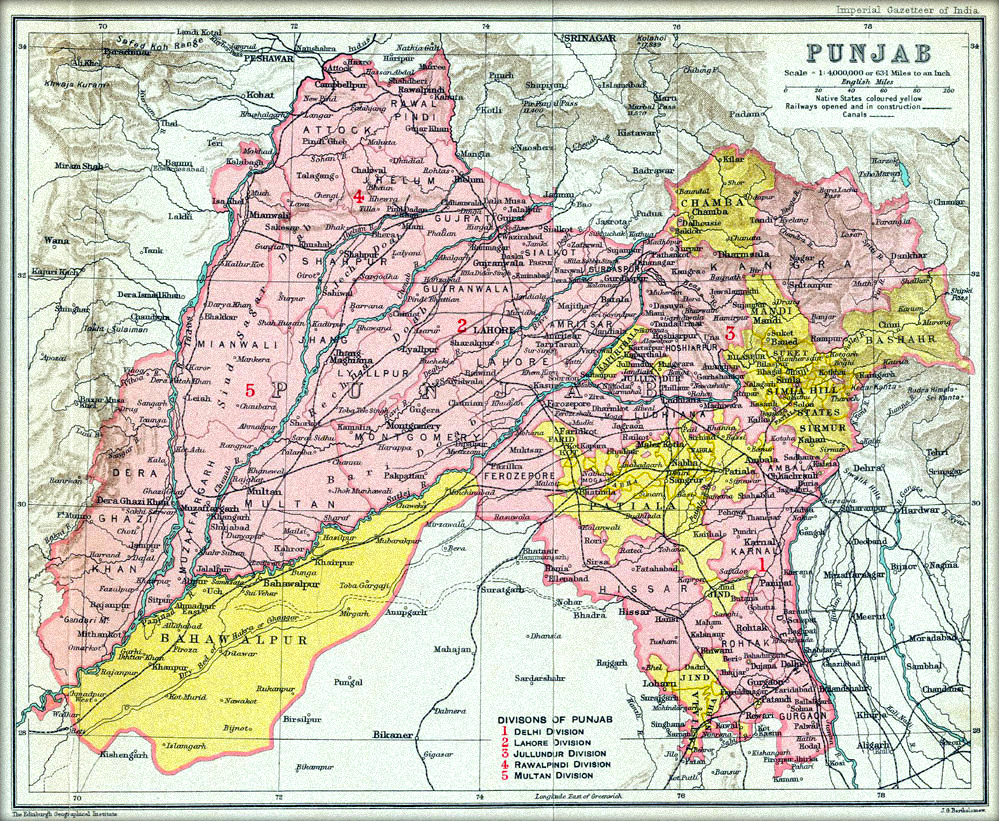
Before the 1947
partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
, Sikhs were not in majority in any of the districts of pre-partition
British Punjab Province other than
Ludhiana (where Sikhs formed 41.6% of the population). Rather, districts in the region had a majority of either the Hindus or Muslims depending on its location in the province.
British India was partitioned on a religious basis in 1947, where the Punjab province was divided between India and the newly-created Pakistan. As result, a majority of Sikhs, along with the Hindus, migrated from the Pakistani region to India's Punjab, which included present-day
Haryana and
Himachal Pradesh. The Sikh population, which had gone as high as 19.8% in some Pakistani districts in 1941, dropped to 0.1% in Pakistan, and rose sharply in the districts assigned to India. However, they would still be a minority in the Punjab province of India, which remained a Hindu-majority province.
Sikh relationship with Punjab (via Oberoi)

Sikh historian
Harjot Singh Oberoi argues that, despite the historical linkages between Sikhs and Punjab, territory has never been a major element of Sikh self-definition. He makes the case that the attachment of Punjab with Sikhism is a recent phenomenon, stemming from the 1940s. Historically,
Sikhism has been pan-Indian, with the
Guru Granth Sahib (the main scripture of Sikhism) drawing from works of saints in both North and South India, while several major seats in Sikhism (e.g.
Nankana Sahib in Pakistan,
Takht Sri Patna Sahib in
Bihar, and
Hazur Sahib in
Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
) are located outside of Punjab.
Oberoi makes the case that Sikh leaders in the late 1930s and 1940s realized that the dominance of
Muslims in Pakistan
Islam is the largest and the state religion of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. As much as 90% of the population follows Sunni Islam. Most Pakistani Sunni Muslims belong to the Hanafi school of jurisprudence, which is represented by the Ba ...
and of
Hindus in India was imminent. To justify a separate Sikh state within the Punjab, Sikh leaders started to mobilize meta-commentaries and signs to argue that Punjab belonged to Sikhs and Sikhs belong to Punjab. This began the territorialization of the Sikh community.
This territorialization of the Sikh community would be formalized in March 1946, when the Sikh political party of
Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Akali Party'') is a centre-right sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are man ...
passed a resolution proclaiming the natural association of Punjab and the Sikh religious community. Oberoi argues that despite having its beginnings in the early 20th century, Khalistan as a separatist movement was never a major issue until the late 1970s and 1980s when it began to militarize.
1950s to 1970s
There are two distinct narratives about the origins of the calls for a sovereign Khalistan. One refers to the events within India itself, while the other privileges the role of the
Sikh diaspora. Both of these narratives vary in the form of governance proposed for this state (e.g.
theocracy vs
democracy) as well as the proposed name (i.e. Sikhistan vs Khalistan). Even the precise geographical borders of the proposed state differs among them although it was generally imagined to be carved out from one of various historical constructions of the Punjab.
Emergence in India
Established on 14 December 1920,
Shiromani Akali Dal was a Sikh political party that sought to form a government in Punjab.
[Jetly, Rajshree. 2006. "The Khalistan Movement in India: The Interplay of Politics and State Power." ''International Review of Modern Sociology'' 34(1):61–62. .]
Following the 1947 independence of India, the
Punjabi Suba movement, led by the Akali Dal, sought the creation of a province (''
suba
Suba may refer to:
Groups of people
*Suba people (Kenya), a people of Kenya
**Suba language
*Suba people (Tanzania), a people of Tanzania
* Subha (writers), alternatively spelt Suba, Indian writer duo
Individual people
*Suba (musician), Serbian- ...
'') for
Punjabi people
The Punjabis ( Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Panjābīs), are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. The ...
. The Akali Dal's maximal position of demands was a
sovereign state (i.e. Khalistan), while its minimal position was to have an
autonomous state within India. The issues raised during the Punjabi Suba movement were later used as a premise for the creation of a separate Sikh country by proponents of Khalistan.
As the religious-based partition of India led to much bloodshed, the Indian government initially rejected the demand, concerned that creating a Punjabi-majority state would effectively mean yet again creating a state based on religious grounds.
However, in September 1966, the
Union Government
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, c ...
led by
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 ...
accepted the demand. On 7 September 1966, the
''Punjab Reorganisation Act'' was passed in Parliament, implemented with effect beginning 1 November 1966. Accordingly, Punjab was divided into the state of Punjab and
Haryana, with certain areas to
Himachal Pradesh.
Chandigarh was made a centrally administered
Union territory.
Anandpur Resolution
As Punjab and Haryana now shared the capital of Chandigarh, resentment was felt among Sikhs in Punjab.
Adding further grievance, a canal system was put in place over the rivers of
Ravi Ravi may refer to:
People
* Ravi (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
* Ravi (composer) (1926–2012), Indian music director
* Ravi (Ivar Johansen) (born 1976), Norwegian musical artist
* Ravi (music director) (1926–201 ...
,
Beas, and
Sutlej
The Sutlej or Satluj River () is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as ''Satadru''. It is the easternmost tributary of the Ind ...
, which flowed through Punjab, in order for water to also reach Haryana and
Rajasthan. As result, Punjab would only receive 23% of the water while the rest would go to the two other states. The fact that the issue would not be revisited brought on additional turmoil to Sikh resentment against Congress.
The
Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Akali Party'') is a centre-right sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are man ...
was defeated in the
1972 Punjab elections.
To regain public appeal, the party put forward the
Anandpur Sahib Resolution
The Anandpur Sahib Resolution was a statement with a list of demands made by the Punjabi Sikh political party, the Shiromani Akali Dal, in 1973.
Presentation in 1973
After the tenure of chief minister Gurnam Singh in the Punjab, newly demarcated ...
in 1973 to demand radical devolution of power and further autonomy to Punjab. The resolution document included both religious and political issues, asking for the recognition of Sikhism as a religion separate from Hinduism, as well as the transfer of
Chandigarh and certain other areas to Punjab. It also demanded that power be radically devolved from the central to state governments.
The document was largely forgotten for some time after its adoption until gaining attention in the following decade. In 1982, the Akali Dal and
Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale joined hands to launch the Dharam Yudh Morcha in order to implement the resolution. Thousands of people joined the movement, feeling that it represented a real solution to such demands as larger shares of water for irrigation and the return of Chandigarh to Punjab.
Emergence in the diaspora
According to the 'events outside India' narrative, particularly after 1971, the notion of a sovereign and independent state of Khalistan began to popularize among Sikhs in
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and
Europe. One such account is provided by the Khalistan Council which had moorings in
West London, where the Khalistan movement is said to have launched in 1970.
Davinder Singh Parmar migrated to London in 1954. According to Parmar, his first pro-Khalistan meeting was attended by less than 20 people and he was labelled as a madman, receiving only one person's support. Parmar continued his efforts despite the lack of a following, eventually raising the Khalistani flag in
Birmingham in the 1970s. In 1969, two years after losing the Punjab Assembly elections, Indian politician
Jagjit Singh Chohan
Jagjit Singh Chohan was the founder of the Khalistan movement that sought to create an independent Sikh state in the Punjab region of India and Pakistan.
Politics
Jagjit Singh grew up in Tanda in Punjab's Hoshiarpur district, about 180 km ...
moved to the
United Kingdom to start his campaign for the creation of Khalistan.
Apart from Punjab, Himachal, and Haryana, Chohan's proposal of Khalistan also included parts of
Rajasthan state.
Parmar and Chohan would meet in 1970 and formally announce the Khalistan movement at a London press conference, though being largely dismissed by the community as fanatical fringe without any support.
Chohan in Pakistan and US

Following the
Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Chohan visited
Pakistan as a guest of such leaders as
Chaudhuri Zahoor Elahi. Visiting
Nankana Sahib and several historical gurdwaras in Pakistan, Chohan utilized the opportunity to spread the notion of an independent Sikh state. Widely publicized by Pakistani press, the extensive coverage of his remarks introduced the international community, including those in India, to the demand of Khalistan for the first time. Though lacking public support, the term ''Khalistan'' became more and more recognizable. According to Chohan, during a talk with Prime Minister
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto of Pakistan, Bhutto had proposed to make Nankana Sahib the capital of Khalistan.
On 13 October 1971, visiting the United States at the invitation of his supporters in the
Sikh diaspora, Chohan placed an advertisement in the ''
New York Times'' proclaiming an independent Sikh state. Such promotion enabled him to collect millions of dollars from the diaspora,
eventually leading to charges in India relating to
sedition
Sedition is overt conduct, such as speech and organization, that tends toward rebellion against the established order. Sedition often includes subversion of a constitution and incitement of discontent toward, or insurrection against, estab ...
and other crimes in connection with his separatist activities.
Khalistan National Council
After returning to India in 1977, Chohan travelled to Britain in 1979. There, he would establish the
Khalistan National Council
The Khalistan movement is a Sikh separatist movement seeking to create a homeland for Sikhs by establishing a sovereign state, called Khālistān (' Land of the Khalsa'), in the Punjab region. The proposed state would consist of land that cur ...
, declaring its formation at
Anandpur Sahib on 12 April 1980. Chohan designated himself as President of the Council and Balbir Singh Sandhu as its Secretary General.
In May 1980, Chohan travelled to
London to announce the formation of Khalistan. A similar announcement was made in
Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Majha r ...
by Sandhu, who released stamps and currency of Khalistan. Operating from a building termed "Khalistan House", Chohan named a Cabinet and declared himself president of the "Republic of Khalistan," issuing symbolic Khalistan 'passports,' 'postage stamps,' and 'Khalistan dollars.' Moreover, embassies in Britain and other European countries were opened by Chohan.
It is reported that, with the support of a wealthy Californian peach magnate, Chohan opened an Ecuadorian bank account to further support his operation.
As well as maintaining contacts among various groups in Canada, the US, and Germany, Chohan kept in contact with the Sikh leader
Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale who was campaigning for a
theocratic Sikh homeland.
The globalized Sikh diaspora invested efforts and resources for Khalistan, but the Khalistan movement remained nearly invisible on the global political scene until the Operation Blue Star of June 1984.
R&AW
In later disclosures from former
R&AW special secretary G.B.S. Sidhu, R&AW itself helped "build the Khalistan legend," actively participated in the planning of
Operation Blue Star. While posted in
Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
, Canada in 1976 to look into the "Khalistan problem" among the Sikh diaspora, Sidhu found "nothing amiss" during the three years he was there,
stating that "Delhi was unnecessarily making a mountain of a molehill where none existed," that the agency created seven posts in West Europe and North America in 1981 to counter non-existent Khalistan activities, and that the deployed officers were "not always familiar with the Sikhs or the Punjab issue."
[ He described the secessionist movement as a "chimera" until the army operation, after which the insurgency would start.][ According to a New York Times article written just a few weeks after the operation, "Before the raid on the Golden Temple, neither the Government nor anyone else appeared to put much credence in the Khalistan movement. Mr. Bhindranwale himself said many times that he was not seeking an independent country for Sikhs, merely greater autonomy for Punjab within the Indian Union....One possible explanation advanced for the Government's raising of the Khalistan question is that it needs to take every opportunity to justify the killing in Amritsar and the invasion of the Sikhs' holiest shrine."][
]
Late 1970s to 1983
Delhi Asian Games (1982)
The Akali leaders, having planned to announce a victory for Dharam Yudh Morcha, were outraged by the changes to the agreed-upon settlement. In November 1982, Akali leader Harchand Singh Longowal announced that the party would disrupt the 9th annual Asian Games by sending groups of Akali workers to Delhi to intentionally get arrested. Following negotiations between the Akali Dal and the government failed at the last moment due to disagreements regarding the transfer of areas between Punjab and Haryana.Bhajan Lal
Bhajanlal Bishnoi (6 October 1930 – 3 June 2011) was a politician and three-time chief minister of the Indian state of Haryana. He became the Chief Minister for the first time in 1979, was re-elected in 1982, and became the chief minister for ...
, Chief Minister of Haryana and member of the INC
Inc. or inc may refer to:
* Incorporation (business), as a suffix indicating a corporation
* ''Inc.'' (magazine), an American business magazine
* Inc. No World, a Los Angeles-based band
* Indian National Congress, a political party in India
* I ...
party, responded by sealing the Delhi-Punjab border,
1984
Increasing militant activity
Widespread murders by followers of Bhindranwale occurred in 1980s' Punjab. Armed Khalistani militants of this period described themselves as ''kharku'',[Ghosh, Srikanta. 1997. ''Indian Democracy Derailed – Politics and Politicians.'' APH Publishing. . p. 95.] One such murder was that of DIG
Digging, also referred to as excavation, is the process of using some implement such as claws, hands, manual tools or heavy equipment, to remove material from a solid surface, usually soil, sand or rock (geology), rock on the surface of Earth. Di ...
Avtar Singh Atwal
Avtar Singh Atwal was a Deputy Inspector General in Punjab Police. He was murdered by a follower of Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale at the steps of Golden temple while coming out after prayers on 25 April 1983 His murder set in motion a chain of ev ...
, killed on 25 April 1983 at the gate of the Darbar Sahib,[Sharma, Puneet, dir. 2013.]
Operation Blue Star and the assassination of Indira Gandhi
(TV episode). ''Pradhanmantri
''Pradhanmantri'' () is an Indian television political documentary series, hosted by actor-director Shekhar Kapur on Hindi news channel ABP News. It premiered on 13 July 2013. It aimed to bring to the audience never-seen-before facts of Indian ...
'' Ep. 14. India: ABP News
ABP News is an Indian Hindi-language free-to-air television news channel owned by ABP Group. The news channel was launched in 1998 originally as STAR News before being acquired by ABP Group. It won the Best Hindi News Channel award in the 21st ...
. – via ABP News Hindi on YouTube.[Verma, Arvind. 2003.]
Terrorist Victimization: Prevention, Control, and Recovery, Case Studies from India
" pp. 89–98 in ''Meeting the Challenges of Global Terrorism: Prevention, Control, and Recovery'', edited by D. K. Das and P. C. Kratcoski. Lanham, MD: Lexington Books.
p. 89
Though it was common knowledge that those responsible for such bombings and murders were taking shelter in gurdwaras, the INC
Inc. or inc may refer to:
* Incorporation (business), as a suffix indicating a corporation
* ''Inc.'' (magazine), an American business magazine
* Inc. No World, a Los Angeles-based band
* Indian National Congress, a political party in India
* I ...
Government of India declared that it could not enter these places of worship, for the fear of hurting Sikh sentiments.Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 ...
, the Government would choose not to take action.[Sisson, Mary. 2011. "Sikh Terrorism." pp. 544–545 in ''The Sage Encyclopedia of Terrorism'' (2nd ed.), edited by G. Martin. Thousand Oaks, CA: ]Sage Publications
SAGE Publishing, formerly SAGE Publications, is an American independent publishing company founded in 1965 in New York by Sara Miller McCune and now based in Newbury Park, California.
It publishes more than 1,000 journals, more than 800 books ...
. . .
Constitutional issues
The Akali Dal began more agitation in February 1984, protesting against Article 25, clause (2)(b), of the Indian Constitution, which ambiguously explains that "the reference to Hindus shall be construed as including a reference to persons professing the Sikh, Jaina, or Buddhist religion," while also implicitly recognizing Sikhism as a separate religion: "the wearing and carrying of kripans 'sic''">sic.html" ;"title="'sic">'sic''shall be deemed to be included in the profession of the Sikh religion."[Sharma, Mool Chand, and A.K. Sharma, eds. 2004.]
Discrimination Based on Religion
" pp. 108–110 in ''Discrimination Based on Sex, Caste, Religion, and Disability''. New Delhi: National Council for Teacher Education
Archived
from the original on 2 June 2010. Retrieved 17 May 2020. Even today, this clause is deemed offensive by many religious minorities in India due to its failure to recognise such religions separately under the constitution.
Operation Blue Star
Operation Blue Star was an Indian military operation ordered by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 ...
, between 1 and 8 June 1984, to remove militant religious leader Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale and his armed followers from the buildings of the Harmandir Sahib complex (aka the Golden Temple) in Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Majha r ...
, Punjabthe most sacred site in Sikhism.Akali Dal
The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) (translation: ''Supreme Akali Party'') is a centre-right sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are man ...
President Harchand Singh Longowal had invited Bhindranwale to take up residence at the sacred temple complex, which the government would allege that Bhindranwale would later make into an armoury
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are mostly ...
and headquarters for his armed uprising.Nirankari
Nirankari ( pa, ਨਿਰੰਕਾਰੀ, ''lit.'' "formless one") is a sect of Sikhism.Harbans Singh, Editor-in-Chief (201Nirankaris Encyclopedia of Sikhism Volume III, Punjabi University, Patiala, pages 234–235 It was a reform movement found ...
s, as well as 39 Sikhs opposed to Bhindranwale, while a total of 410 dead and 1,180 injured came as result of Khalistani violence and riots.[ Tully, Mark, and Satish Jacob. 1985. ]
Amritsar: Mrs. Gandhi's Last Battle
' (5th ed.). London: Jonathan Cape
Jonathan Cape is a London publishing firm founded in 1921 by Herbert Jonathan Cape, who was head of the firm until his death in 1960.
Cape and his business partner Wren Howard set up the publishing house in 1921. They established a reputation ...
p. 147
As negotiations held with Bhindranwale and his supporters proved unsuccessful, Indira Gandhi ordered the Indian Army to launch Operation Blue Star. Along with the Army, the operation would involve Central Reserve Police Force, Border Security Force, and Punjab Police. Army units led by Lt. Gen.
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star rank, three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in ...
Kuldip Singh Brar (a Sikh), surrounded the temple complex on 3 June 1984. Just before the commencement of the operation, Lt. Gen. Brar addressed the soldiers:[ Gates, Scott, and Kaushik Roy. 2016.]
Insurgency and Counterinsurgency in Punjab
" pp. 163–175 in ''Unconventional Warfare in South Asia: Shadow Warriors and Counterinsurgency''. Surrey: Ashgate. . p. 167.
However, none of the soldiers opted out, including many "Sikh officers, junior commissioned officers and other ranks."IST
Ist or IST may refer to:
Information Science and Technology
* Bachelor's or Master's degree in Information Science and Technology
* Graduate School / Faculty of Information Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Japan
* Graduate School ...
).anti-tank
Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Triple Entente deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first deve ...
and machine-gun fire from the heavily fortified Akal Takht, and who possessed Chinese-made, rocket-propelled grenade launchers with armour-piercing capabilities. After a 24-hour shootout, the army finally wrested control of the temple complex.
Bhindranwale was killed in the operation, while many of his followers managed to escape. Army casualty figures counted 83 dead and 249 injured. According to the official estimate presented by the Indian Government, the event resulted in a combined total of 493 militant and civilian casualties, as well as the apprehension of 1592 individuals.[India. 10 July 1984. "White Paper on the Punjab Agitation." New Delhi: Government of India Press. ]
p. 40
U.K. Foreign Secretary William Hague attributed high civilian casualties to the Indian Government's attempt at a full frontal assault on the militants, diverging from the recommendations provided by the U.K. Military.[Hague, William. 2014.]
Allegations of UK Involvement in the Indian Operation at Sri Harmandir Sahib, Amritsar 1984
" (Policy paper
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. A white paper ...
). Available as
PDF
Retrieved 17 May 2020.
"The FCO files (Annex E) record the Indian Intelligence Co-ordinator telling a UK interlocutor, in the same time-frame as this public Indian report, that some time after the UK military adviser’s visit the Indian Army took over lead responsibility for the operation, the main concept behind the operation changed, and a frontal assault was attempted, which contributed to the large number of casualties on both sides."[Golden Temple attack: UK advised India but impact 'limited']
" '' BBC News''. 7 June 2014. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
"The adviser suggested using an element of surprise, as well as helicopters, to try to keep casualty numbers low – features which were not part of the final operation, Mr Hague said." Opponents of Gandhi also criticised the operation for its excessive use of force. Lieutenant General Brar later stated that the Government had "no other recourse" due to a "complete breakdown" of the situation: state machinery was under the militants' control; declaration of Khalistan was imminent; and Pakistan would have come into the picture declaring its support for Khalistan.
Nonetheless, the operation did not crush Khalistani militancy, as it continued.
According to the Mitrokhin Archive, in 1982 the Soviets used a recruit in the New Delhi residency named “Agent S” who was close to Indira Gandhi as a major channel for providing her disinformation regarding Khalistan. Agent S provided Indira Gandhi with false documents purporting to show Pakistani involvement to create religious disturbances and allegedly initiate a Khalistan conspiracy. After Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Gandhi (; 20 August 1944 – 21 May 1991) was an Indian politician who served as the sixth prime minister of India from 1984 to 1989. He took office after the 1984 assassination of his mother, then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, to beco ...
's visit to Moscow in 1983, the Soviets persuaded him that the US was engaged in secret support for the Sikhs. By 1984, according to Mitrokhin, the disinformation the Soviets provided had influenced Indira Gandhi to pursue Operation Blue Star.
Assassination of Indira Gandhi and anti-Sikh riots
 On the morning of 31 October 1984,
On the morning of 31 October 1984, Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 ...
was assassinated in New Delhi by her two personal security guards Satwant Singh and Beant Singh, both Sikhs, in retaliation for Operation Blue Star. The assassination would trigger the 1984 anti-Sikh riots
The 1984 Anti-Sikh Riots, also known as the 1984 Sikh Massacre, was a series of organised pogroms against Sikhs in India following the assassination of Indira Gandhi by her Sikh bodyguards. Government estimates project that about 2,800 Sikhs ...
across North India. While the ruling party, Indian National Congress (INC), maintained that the violence was due to spontaneous riots, its critics have alleged that INC members themselves had planned a pogrom against the Sikhs.[Guidry, John A., Michael D. Kennedy, and Mayer N. Zald, eds. 2000. Globalizations and Social Movements: Culture, Power, and the Transnational Public Sphere. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. . p. 319.]
The Nanavati Commission
The Justice G.T. Nanavati commission was a one-man commission headed by Justice G.T. Nanavati, a retired Judge of the Supreme Court of India, appointed by the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) government in May 2000, to investigate the "k ...
, a special commission created to investigate the riots, concluded that INC leaders (including Jagdish Tytler
Jagdish Tytler (born Jagdish Kapoor; 17 August 1944) is an Indian politician and former Member of Parliament. He has held several government positions, the last being as Minister of State for Overseas Indian Affairs, a post from which he resigne ...
, H. K. L. Bhagat, and Sajjan Kumar
Sajjan Kumar (born 23 September 1945) is an Indian politician. He was elected to the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India from Outer Delhi as a member of the Indian National Congress but resigned from the primary membership o ...
) had directly or indirectly taken a role in the rioting incidents.
1985 to present day
1985
Rajiv-Longowal Accord
Many Sikh and Hindu groups, as well as organisations not affiliated to any religion, have attempted to establish peace between the Khalistan proponents and the Government of India. Akalis continued to witness radicalization of Sikh politics, fearing disastrous consequences.Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Gandhi (; 20 August 1944 – 21 May 1991) was an Indian politician who served as the sixth prime minister of India from 1984 to 1989. He took office after the 1984 assassination of his mother, then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, to beco ...
. The Accordrecognizing the religious, territorial, and economic demands of the Sikhs that were thought to be non-negotiable under Indira Gandhi's tenureagreed to establish commissions and independent tribunals in order to resolve the Chandigarh issue and the river dispute, laying the basis for Akali Dal's victory in the coming elections.
Air India Flight 182

 Air India Flight 182 was an Air India flight operating on the Montréal- London- Delhi- Bombay route. On 23 June 1985, a
Air India Flight 182 was an Air India flight operating on the Montréal- London- Delhi- Bombay route. On 23 June 1985, a Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, t ...
operating on the route was blown up by a bomb mid-air off the coast of Ireland. A total of 329 people aboard were killed, 268 Canadian citizens, 27 British citizens and 24 Indian citizens, including the flight crew. On the same day, an explosion due to a luggage bomb was linked to the terrorist operation and occurred at the Narita Airport in Tokyo, Japan, intended for Air India Flight 301, killing two baggage handlers. The entire event was inter-continental in scope, killing 331 people in total and affected five countries on different continents: Canada, the United Kingdom, India, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and Ireland.
The main suspects in the bombing were members of a Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
separatist group called the Babbar Khalsa, and other related groups who were at the time agitating for a separate Sikh state of Khalistan in Punjab, India. In September 2007, the Canadian Commission of Inquiry investigated reports, initially disclosed in the Indian investigative news magazine '' Tehelka'', that a hitherto unnamed person, Lakhbir Singh Rode, had masterminded the explosions. However, in conclusion two separate Canadian inquiries officially determined that the mastermind behind the terrorist operation was in fact the Canadian, Talwinder Singh Parmar
Talwinder Singh Parmar (26 February 1944 – 15 October 1992) born in Kapurthala, Punjab, India was a sikh kharku. He was also the founder, leader, and Jathedar of Babbar Khalsa International, better known as Babbar Khalsa, a militant Sikh gro ...
.
Several men were arrested and tried for the Air India bombing. Inderjit Singh Reyat, a Canadian national and member of the International Sikh Youth Federation
The International Sikh Youth Federation (ISYF) is a proscribed organisation that aims to establish an independent homeland for the Sikhs of India in Khalistan. It is banned as a terrorist organisation under Australian, European Union, Japane ...
who pleaded guilty in 2003 to manslaughter
Manslaughter is a common law legal term for homicide considered by law as less culpable than murder. The distinction between murder and manslaughter is sometimes said to have first been made by the ancient Athenian lawmaker Draco in the 7th cen ...
, would be the only person convicted in the case.
Late 1980s
In 1986, when the insurgency was at its peak, the Golden Temple was again occupied by militants belonging to the All India Sikh Students Federation
The All India Sikh Students Federation (AISSF), is a Sikh student organisation and political organisation in India. AISSF was formed in 1943. as the youth wing of the Akali Dal, which is a Sikh political party in the Indian Punjab.
Origin
Befor ...
and Damdami Taksal. The militants called an assembly (Sarbat Khalsa
Sarbat Khalsa (lit. meaning ''all the Khalsa''; Punjabi: (Gurumukhi)), was a biannual deliberative assembly (on the same lines as a Parliament in a Direct Democracy) of the Sikhs held at Amritsar in Panjab during the 18th century. It literally t ...
) and, on 26 January, they would pass a resolution (''gurmattā'') in favour of the creation of Khalistan. However, only the Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee (SGPC) had the authority to appoint the '' jathedar'', the supreme religio-temporal seat of the Sikhs. The militants thus dissolved the SGPC and appointed their own jathedar, who turned out to refuse their bidding as well. Militant leader Gurbachan Singh Manochahal
Gurbachan Singh Manochahal was a Sikh extremist militant, who founded the Bhindranwale Tiger Force of Khalistan in 1984.
Early life
Gurbachan Singh was born on 6 June 1954 in the village Manochahal, Tarn Taran district in the Indian state of ...
thereby appointed himself by force.
On 29 April 1986, an assembly of separatist Sikhs at the Akal Takht made a declaration of an independent state of Khalistan, and a number of rebel militant groups in favour of Khalistan subsequently waged a major insurgency against the Government of India. A decade of violence and conflict in Punjab would follow before a return to normality in the region. This period of insurgency saw clashes of Sikh militants with the police, as well as with the Nirankari
Nirankari ( pa, ਨਿਰੰਕਾਰੀ, ''lit.'' "formless one") is a sect of Sikhism.Harbans Singh, Editor-in-Chief (201Nirankaris Encyclopedia of Sikhism Volume III, Punjabi University, Patiala, pages 234–235 It was a reform movement found ...
s, a mystical Sikh sect who are less conservative in their aims to reform Sikhism.
The Khalistani militant activities manifested in the form of several attacks, such as the 1987 massacre of 32 Hindu bus passengers near Lalru
Lalru is a town and a Municipal Council In Mohali District about 30 km from Chandigarh, the capital of both Haryana and IndianPunjab, on the Chandigarh-Ambala National Highway, NH 22. Lalru is having one of the toll tax barriers on this C ...
, and the 1991 killing of 80 train passengers in Ludhiana. Such activities continued on into the 1990s as the perpetrators of the 1984 riots remained unpunished, while many Sikhs also felt that they were being discriminated against and that their religious rights were being suppressed.Khaki election
In Westminster systems of government, a khaki election is any national election which is heavily influenced by wartime or postwar sentiment. In the British general election of 1900, the Conservative Party government of Lord Salisbury was returne ...
. The separatists boycotted the poll. The voter turnout was 24%. The Congress won this election and used it to further its anti-separatist campaign. Most of the separatist leadership was wiped out and the moderates were suppressed by end of 1993.
1990s
Indian security forces suppressed the insurgency in the early 1990s, while Sikh political groups such as the Khalsa Raj Party
Jagjit Singh Chohan was the founder of the Khalistan movement that sought to create an independent Sikh state in the Punjab region of India and Pakistan.
Politics
Jagjit Singh grew up in Tanda in Punjab's Hoshiarpur district, about 180 km ...
and SAD (A) continued to pursue an independent Khalistan through non-violent means.Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
Sikhs.Liviu Radu
Liviu Radu (20 November 1948 – 17 October 2015) was a Romanian science-fiction writer and translator.
Work Novels
*''Trip-Tic'' (1999)
*''Opțiunea'' (2004)
*''Spaime'' (2004, republished in 2014)
* ''Waldemar'' series
**''Waldemar'' (2007)
...
, the Romanian chargé d'affaires
A ''chargé d'affaires'' (), plural ''chargés d'affaires'', often shortened to ''chargé'' (French) and sometimes in colloquial English to ''charge-D'', is a diplomat who serves as an embassy's chief of mission in the absence of the ambassador ...
in New Delhi. This appeared to be in retaliation for Romanian arrests of Khalistan Liberation Force
Khalistan Liberation Force (KLF) is a militant group, and is a part of the Khalistan Movement and its goal to create a Sikh homeland called Khalistan via armed struggle. The KLF appears to have been a loose association of Khalistani militant gr ...
members suspected of the attempted assassination of Ribeiro.["World Notes India"](_blank)
Time magazine, 21 October 1991. Radu was released unharmed after Sikh politicians criticised the action.
In October 1991, the '' New York Times'' reported that violence had increased sharply in the months leading up to the kidnapping, with Indian security forces or Sikh militants killing 20 or more people per day, and that the militants had been "gunning down" family members of police officers.Embassy of the United States in New Delhi
The Embassy of the United States of America in New Delhi is the diplomatic mission of the United States of America in the Republic of India. The Embassy is headed by the U.S. Ambassador to India. The embassy complex is situated on a 28-acre pl ...
indicated that the responsible organisation was the Khalistan Commando Force
The Khalistan Commando Force (KCF) is a militant Khalistani organisation operating in the state of Punjab with prominent members based in Canada, the United Kingdom and Pakistan. Its objective is the creation of a Sikh independent state of Khali ...
.
2000s
Retribution
There have been serious charges levelled by human rights activists against Indian Security forces (headed by Sikh police officer, K. P. S. Gill), claiming that thousands of suspects were killed in staged shootouts and thousands of bodies were cremated/disposed of without proper identification or post-mortems. Human Rights Watch reported that, since 1984, government forces had resorted to widespread human rights violations to fight the militants, including: arbitrary arrest, prolonged detention without trial, torture, and summary execution
A summary execution is an execution in which a person is accused of a crime and immediately killed without the benefit of a full and fair trial. Executions as the result of summary justice (such as a drumhead court-martial) are sometimes include ...
s of civilians and suspected militants. Family members were frequently detained and tortured to reveal the whereabouts of relatives sought by the police. Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and sup ...
has alleged several cases of disappearances, torture, rape, and unlawful detentions by the police during the Punjab insurgency, for which 75–100 police officers had been convicted by December 2002.
Present-day activities
Present-day activities by Khalistani militants include the Tarn Taran blast, in which a police crackdown arrested 4 terrorists, one of whom revealed they were ordered by Sikhs for Justice
Sikhs for Justice (SFJ) is a US-based secessionist group that supports the secession of Punjab from India as Khalistan. Founded and primarily headed by lawyer Gurpatwant Singh Pannun in 2009. The organization was created in response to the murd ...
to kill multiple Dera leaders in India. Pro-Khalistan organisations such as Dal Khalsa are also active outside India, supported by a section of the Sikh diaspora. As of 25 December, there also have been inputs by multiple agencies about a possible attack in Punjab by Babbar Khalsa and Khalistan Zindabad Force
The Khalistan Zindabad Force (KZF) is a militant group and is part of the Khalistan movement to create a separate country Sikh homeland called Khalistan by carving Punjab and some parts of neighbouring states of Haryana, Rajasthan and Himachal ...
, according to Indian Media sources, are allegedly in contact with their Pakistani handlers and are trying to smuggle arms across the border.
In November 2015, a congregation of the Sikh community (i.e. a Sarbat Khalsa
Sarbat Khalsa (lit. meaning ''all the Khalsa''; Punjabi: (Gurumukhi)), was a biannual deliberative assembly (on the same lines as a Parliament in a Direct Democracy) of the Sikhs held at Amritsar in Panjab during the 18th century. It literally t ...
) was called in response to recent unrest in the Punjab region. The Sarbat Khalsa adopted 13 resolutions to strengthen Sikh institutions and traditions. The 12th resolution reaffirmed the resolutions adopted by the Sarbat Khalsa in 1986, including the declaration of the sovereign state of Khalistan.
Moreover, signs in favour of Khalistan were raised when SAD (Amritsar) President Simranjeet Singh Mann met with Surat Singh Khalsa
Surat Singh Khalsa (born 7 March 1933), also known as "Bapu Surat Singh Khalsa" is a civil rights and political activist, from the Indian state of Punjab. Surat Singh Khalsa has been involved with various political struggles related to Sikhs ...
, who was admitted to Dayanand Medical College & Hospital (DMCH). While Mann was arguing with ACP Satish Malhotra, supporters standing at the main gate of DMCH raised Khalistan signs in the presence of heavy police force. After a confrontation with the police authorities that lasted about 15–20 minutes, Mann was allowed to meet Khalsa along with ADCP Paramjeet Singh Pannu.
Despite residing outside India, there is a strong sense of attachment among Sikhs to their culture and religion. As such, Sikh groups operating from other countries could potentially revive the Khalistan Movement.KPS Gill
Kanwar Pal Singh Gill (29 December 1934 – 26 May 2017) was an Indian Police Service (IPS) officer. He served twice as DGP for the state of Punjab, India, where he is credited with having brought the Punjab insurgency under control. While man ...
.[ quoted i]
Rediff On the Net
/ref>
* In the later stages of the movement, militants lacked an ideological motivation.
* The entry of criminals and government loyalists into its ranks further divided the groups.
* Loss of sympathy and support from the Sikh population of Punjab.
* The divisions among the Sikhs also undermined this movement. According to Pettigrew non-Jat
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subse ...
urban Sikhs did not want to live in a country of "Jatistan." Further division was caused as the people in the region traditionally preferred police and military service as career options. The Punjab Police had a majority of Jat Sikh
Jat Sikh (also known by the more conventional endonym Jatt Sikh) is a sub-group of the Jat people and the Sikh religious group from the Indian subcontinent. They are one of the dominant communities in the Punjab owing to their large land holdin ...
s and the conflict was referred as ''"Jat against Jat"'' by Police Chief Gill.
* Moderate factions of Akali Dal led by Prakash Singh Badal
Parkash Singh Badal ( pa, ਪ੍ਰਕਾਸ਼ ਸਿੰਘ ਬਾਦਲ; born 8 December 1927) is an Indian politician who was Chief Minister of Punjab state from 1970 to 1971, from 1977 to 1980, from 1997 to 2002, and from 2007 to 2017. He ...
reclaimed the political positions in the state through all three assembly (namely parliamentary) and SGPC elections. The dominance of traditional political parties was reasserted over the militant-associated factions.
* The increased vigilance by security forces in the region against rise of separatist elements.Institute of Peace and Conflict Studies
The Institute of Peace and Conflict Studies (IPCS), was founded in 1996 as an independent think-tank to develop an alternative framework for Peace and Security in South Asia through independent research and analysis. It continues to be one of t ...
, noted that while a few groups continued to fight, "the movement has lost its popular support both in India and within the Diaspora community."
Militancy
During the late 1980s and the early 1990s, there was a dramatic rise in radical State militancy in Punjab. The 1984 military Operation Blue Star in the Golden Temple in Amritsar offended many Sikhs. The separatists used this event, as well as the following 1984 anti-Sikh riots
The 1984 Anti-Sikh Riots, also known as the 1984 Sikh Massacre, was a series of organised pogroms against Sikhs in India following the assassination of Indira Gandhi by her Sikh bodyguards. Government estimates project that about 2,800 Sikhs ...
, to claim that the interest of Sikhs was not safe in India and to foster the spread of militancy among Sikhs in Punjab. Some sections of the Sikh diaspora also began join the separatists with financial and diplomatic support.
A section of Sikhs turned to militancy in Punjab and several Sikh militant outfits proliferated in the 1980s and 1990s. Some militant groups aimed to create an independent state through acts of violence directed at members of the Indian government, army, or forces. A large numbers of Sikhs condemned the actions of the militants.[Puri, Harish K., Paramjit Singh Judge, and Jagrup Singh Sekhon. 1999. ''Terrorism in Punjab: Understanding Grassroots Reality''. New Delhi: Har-Anand Publications. pp. 68–71.] They mention that the pursuit of Khalistan itself was the motivation for only 5% of "militants."
Militant groups
There are several militant Sikh groups, such as the Khalistan Council, that are currently functional and provides organization and guidance to the Sikh community. Multiple groups are organized across the world, coordinating their military efforts for Khalistan. Such groups were most active in 1980s and early 1990s, and have since receded in activity. These groups are largely defunct in India but they still have a political presence among the Sikh diaspora, especially in countries such as Pakistan where they are not prescribed by law.
Most of these outfits were crushed by 1993 during the counter-insurgency
Counterinsurgency (COIN) is "the totality of actions aimed at defeating irregular forces". The Oxford English Dictionary defines counterinsurgency as any "military or political action taken against the activities of guerrillas or revolutionar ...
operations. In recent years, active groups have included Babbar Khalsa, International Sikh Youth Federation, Dal Khalsa, and Bhindranwale Tiger Force. An unknown group before then, the Shaheed Khalsa Force claimed credit for the marketplace bombings in New Delhi in 1997. The group has never been heard of since.
Major pro-Khalistan militant outfits include:
* Babbar Khalsa International (BKI)
** Listed as a terrorist organisation in the European Union,Terrorist Exclusion List
Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) is a designation for non-United States-based organizations deemed by the United States Secretary of State, in accordance with section 219 of the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965 (INA), to be involved ...
of the U.S. Government in 2004.
** Designated by the US and the Canadian courts for the bombing of Air India Flight 182 on 27 June 2002.Gurbachan Singh Manochahal
Gurbachan Singh Manochahal was a Sikh extremist militant, who founded the Bhindranwale Tiger Force of Khalistan in 1984.
Early life
Gurbachan Singh was born on 6 June 1954 in the village Manochahal, Tarn Taran district in the Indian state of ...
.
** Seems to have disbanded or integrated into other organisations after the death of Manochahal.Khalistan Commando Force
The Khalistan Commando Force (KCF) is a militant Khalistani organisation operating in the state of Punjab with prominent members based in Canada, the United Kingdom and Pakistan. Its objective is the creation of a Sikh independent state of Khali ...
(KCF)
** Formed by the Sarbat Khalsa
Sarbat Khalsa (lit. meaning ''all the Khalsa''; Punjabi: (Gurumukhi)), was a biannual deliberative assembly (on the same lines as a Parliament in a Direct Democracy) of the Sikhs held at Amritsar in Panjab during the 18th century. It literally t ...
in 1986.U.S. Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
(DOS).
** According to the DOS Khalistan Liberation Army
Khalistan Liberation Force (KLF) is a militant group, and is a part of the Khalistan Movement and its goal to create a Sikh homeland called Khalistan via armed struggle. The KLF appears to have been a loose association of Khalistani militant ...
(KLA)
** Reputed to have been a wing of, associated with, or a breakaway group of the Khalistan Liberation Force.
* Khalistan Liberation Force
Khalistan Liberation Force (KLF) is a militant group, and is a part of the Khalistan Movement and its goal to create a Sikh homeland called Khalistan via armed struggle. The KLF appears to have been a loose association of Khalistani militant gr ...
** Formed in 1986
** Believed to be responsible for several bombings of civilian targets in India during the 1980s and 1990s,["Bus explosion in India kills at least 14"](_blank)
CNN, 22 May 1996 sometimes in conjunction with Islamist Kashmir separatists.["Fatal bomb meant to disrupt Kashmiri elections"](_blank)
CNN, 21 April 1996
* Khalistan Zindabad Force
The Khalistan Zindabad Force (KZF) is a militant group and is part of the Khalistan movement to create a separate country Sikh homeland called Khalistan by carving Punjab and some parts of neighbouring states of Haryana, Rajasthan and Himachal ...
(KZF)
** Listed as a terrorist organisation by the EU.International Sikh Youth Federation
The International Sikh Youth Federation (ISYF) is a proscribed organisation that aims to establish an independent homeland for the Sikhs of India in Khalistan. It is banned as a terrorist organisation under Australian, European Union, Japane ...
(ISYF), based in the United Kingdom.
* All India Sikh Students Federation
The All India Sikh Students Federation (AISSF), is a Sikh student organisation and political organisation in India. AISSF was formed in 1943. as the youth wing of the Akali Dal, which is a Sikh political party in the Indian Punjab.
Origin
Befor ...
(AISSF)
* Dashmesh Regiment
The Dashmesh Regiment was a militant group, and is part of the Khalistan movement to create a Sikh homeland called Khalistan via armed struggle.
The Dashmesh Regiment ''jathebandi'' group has claimed responsibility for two of the killings in t ...
* Shaheed Khalsa Force
Abatement
The U.S. Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
found that Sikh extremism had decreased significantly from 1992 to 1997, although a 1997 report noted that "Sikh militant cells are active internationally and extremists gather funds from overseas Sikh communities."Rediff.com
Rediff.com (stylized as ''rediff.com'') is an Indian news, information, entertainment and shopping web portal. It was founded in 1996. It is headquartered in Mumbai, with offices in Bangalore, New Delhi and New York City.
, it had more than 300 e ...
, stated in an article, titled "It is fundamentalism again", that the Sikh "masses" had rejected terrorists.[: "Not only has the once powerful Khalistan movement virtually disappeared, even the appeal of identity seems to have considerably declined during the last couple of years."]
Reported in his paper, titled "From Bhindranwale to Bin Laden: Understanding Religious Violence", Director Mark Juergensmeyer of the Orfalea Centre for Global & International Studies, UCSB, interviewed a militant who said that "the movement is over," as many of his colleagues had been killed, imprisoned, or driven into hiding, and because public support was gone.
Outside of India
Operation Blue Star and its violent aftermaths popularized the demand for Khalistan among many Sikhs dispersed globally. Involvement of sections of Sikh diaspora turned out to be important for the movement as it provided the diplomatic and financial support. It also enabled Pakistan to become involved in the fueling of the movement. Sikhs in UK, Canada and USA arranged for cadres to travel to Pakistan for military and financial assistance. Some Sikh groups abroad even declared themselves as the Khalistani government in exile.
The Sikh place of worship, gurdwaras provided the geographic and institutional coordination for the Sikh community. Sikh political factions have used the gurdwaras as a forum for political organization. The gurdwaras sometimes served as the site for mobilization of diaspora for Khalistan movement directly by raising funds. Indirect mobilization was sometimes provided by promoting a stylized version of conflict and Sikh history. The rooms in some gurdwara exhibit pictures of Khalistani leaders along with paintings of martyrs from Sikh history. Gurdwaras also host speakers and musical groups that promote and encourage the movement. Among the diasporas, Khalistan issue has been a divisive issue within gurdwaras. These factions have fought over the control of gurdwaras and their political and financial resources. The fights between pro and anti-Khalistan factions over gurdwaras often included violent acts and bloodshed as reported from UK and North America. The gurdwaras with Khalistani leadership allegedly funnel the collected funds into activities supporting the movement.
Different groups of Sikhs in the diaspora organize the convention of international meetings to facilitate communication and establish organizational order. In April 1981 the first "International Convention of Sikhs," was held in New York and was attended by some 200 delegates. In April 1987 the third convention was held in Slough, Berkshire where the Khalistan issue was addressed. This meeting's objective was to "build unity in the Khalistan movement."
All these factors further strengthened the emerging nationalism among Sikhs. Sikh organizations launched many fund-raising efforts that were used for several purposes. After 1984 one of the objectives was the promotion of the Sikh version of "ethnonational history" and the relationship with the Indian state. The Sikh diaspora also increased their efforts to build institutions to maintain and propagate their ethnonational heritage. A major objective of these educational efforts was to publicize a different face to the non Sikh international community who regarded the Sikhs as "terrorists."
In 1993, Khalistan was briefly admitted in the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization, but was suspended in a few months. The membership suspension was made permanent on 22 January 1995.
Pakistan
Pakistan has long aspired to dismember India through its '' Bleed India'' strategy. Even before the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, then a member of the military regime of General Yahya Khan, stated, "Once the back of Indian forces is broken in the east, Pakistan should occupy the whole of Eastern India and make it a permanent part of East Pakistan.... Kashmir should be taken at any price, even the Sikh Punjab and turned into Khalistan."
General Zia-ul Haq
General Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq HI, GCSJ, ร.ม.ภ, (Urdu: ; 12 August 1924 – 17 August 1988) was a Pakistani four-star general and politician who became the sixth President of Pakistan following a coup and declaration of martial law in ...
, who succeeded Bhutto as the Head of State, attempted to reverse the traditional antipathy between Sikhs and Muslims arising from the partition violence by restoring Sikh shrines in Pakistan and opening them for Sikh pilgrimage. The expatriate Sikhs from England and North America that visited these shrines were at the forefront of the calls for Khalistan. During the pilgrims' stay in Pakistan, the Sikhs were exposed to Khalistani propaganda, which would not be openly possible in India. The ISI chief, General Abdul Rahman, opened a cell within ISI with the objective of supporting the " ikhs'..freedom struggle against India". Rahman's colleagues in ISI took pride in the fact that "the Sikhs were able to set the whole province on fire. They knew who to kill, where to plant a bomb and which office to target." General Hamid Gul argued that keeping Punjab destabilized was equivalent to the Pakistan Army having an extra division at no cost. Zia-ul Haq, on the other hand, consistently practised the art of plausible denial. The Khalistan movement was brought to a decline only after India fenced off a part of the Punjab border with Pakistan and the Benazir Bhutto
Benazir Bhutto ( ur, بینظیر بُھٹو; sd, بينظير ڀُٽو; Urdu ; 21 June 1953 – 27 December 2007) was a Pakistani politician who served as the 11th and 13th prime minister of Pakistan from 1988 to 1990 and again from 1993 t ...
government agreed to joint patrols of the border by Indian and Pakistani troops.
In 2006, an American court convicted Khalid Awan, a Muslim and Canadian of Pakistani descent, of "''supporting terrorism''" by providing money and financial services to the Khalistan Commando Force chief Paramjit Singh Panjwar in Pakistan.Intelligence Bureau Intelligence Bureau may refer to:
* Intelligence Bureau (India)
* Intelligence Bureau (Pakistan)
* Intelligence agency
See also
*Intelligence Bureau for the East, a World War I German organisation
*Intelligence agency
*National Intelligence Servic ...
indicated that Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence organisation was trying to revive Sikh militancy.
United States
'' The New York Times'' reported in June 1984 that Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 ...
conveyed to Helmut Schmidt and Willy Brandt, both of them being former Chancellors of West Germany, that United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) was involved in causing unrest in Punjab. It also reported that '' The Indian Express'' quoted anonymous officials from India's Intelligence establishment as saying that the CIA "masterminded" a plan to support the acolytes of Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale, who died a few days ago during Operation Blue Star, by smuggling weapons for them through Pakistan.B. Raman
Bahukutumbi Raman (14 August 1936 – 16 June 2013), also referred to as B. Raman, was an Additional Secretary of the Cabinet Secretariat of the Government of India and head of the counter-terrorism division of the Research and Analysis Win ...
, former Additional Secretary in the Cabinet Secretariat of India and a senior official of the Research and Analysis Wing
The Research and Analysis Wing (abbreviated R&AW; hi, ) is the foreign intelligence agency of India. The agency's primary function is gathering foreign intelligence, counter-terrorism, counter-proliferation, advising Indian policymakers, an ...
, the United States initiated a plan in complicity with Pakistan's General Yahya Khan in 1971 to support an insurgency for Khalistan in Punjab.
Canada
Immediately after Operation Blue Star, authorities were unprepared for how quickly extremism spread and gained support in Canada, with extremists "...threatening to kill thousands of Hindus by a number of means, including blowing up Air India flights." Canadian Member of Parliament Ujjal Dosanjh, a moderate Sikh, stated that he and others who spoke out against Sikh extremism in the 1980s faced a "reign of terror".Terry Milewski
Terry Milewski (born 1949) is a Canadian journalist, who was the senior correspondent for CBC News until his retirement in 2016.
Milewski has reported in television, radio, and print media, from many places around the world. Assignments have in ...
reported in a 2007 documentary for the CBC that a minority within Canada's Sikh community was gaining political influence even while publicly supporting terrorist acts in the struggle for an independent Sikh state.World Sikh Organization of Canada
World Sikh Organization (WSO) is a Sikh religious and non-profit organization whose 1984 founding goal was "to provide an effective, credible voice to represent Sikh interests on the world stage", after Operation Blue Star. Its stated goal is "t ...
(WSO), a Canadian Sikh human rights group that opposes violence and extremism,Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. ...
, saying it was a glorification of terrorism.Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh (; born 26 September 1932) is an Indian politician, economist and statesman who served as the 13th prime minister of India from 2004 to 2014. He is also the third longest-serving prime minister after Jawaharlal Nehru and Indir ...
, Prime Minister of India, expressed his concern that there might be a resurgence of Sikh extremism.Terry Milewski
Terry Milewski (born 1949) is a Canadian journalist, who was the senior correspondent for CBC News until his retirement in 2016.
Milewski has reported in television, radio, and print media, from many places around the world. Assignments have in ...
criticized the Khalistan movement as driven by the Pakistani government, and as a threat to Canadian interests.
United Kingdom
In February 2008, BBC Radio 4 reported that the Chief of the Punjab Police, NPS Aulakh, alleged that militant groups were receiving money from the British Sikh community. The same report included statements that although the Sikh militant groups were poorly equipped and staffed, intelligence reports and interrogations indicated that Babbar Khalsa was sending its recruits to the same terrorist training camps in Pakistan used by Al Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military targets in various countr ...
.Lord Bassam of Brighton
John Steven Bassam, Baron Bassam of Brighton, (born 11 June 1953) is a British Labour and Co-operative politician and a member of the House of Lords.
Background
Bassam grew up on a council estate in Great Bentley, Essex and went to the local b ...
, then Home Office minister, stated that International Sikh Youth Federation
The International Sikh Youth Federation (ISYF) is a proscribed organisation that aims to establish an independent homeland for the Sikhs of India in Khalistan. It is banned as a terrorist organisation under Australian, European Union, Japane ...
(ISYF) members working from the UK had committed "assassinations, bombings, and kidnappings" and were a "threat to national security."The London Evening Standard
The ''Evening Standard'', formerly ''The Standard'' (1827–1904), also known as the ''London Evening Standard'', is a local free daily newspaper in London, England, published Monday to Friday in tabloid format.
In October 2009, after bei ...
, stated that the Sikh Federation (UK) The Sikh Federation (UK) describes itself as a non-governmental organisation that works with the main political parties to promote relevant Sikh issues. The organisation is a major pro-Khalistan organisation and supports Khalistani secessionist acti ...
is the "successor" of the ISYF, and that its executive committee, objectives, and senior members ... are largely the same.Dabinderjit Singh Dabinderjit Singh Sidhu ( Punjabi: ਦਬਿੰਦਰਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸਿੱਧੂ) was a Director at the National Audit Office (United Kingdom) who retired early in May 2022 after more than 33 years. He is an internationally known and wel ...
was campaigning to have both the Babbar Khalsa and International Sikh Youth Federation de-listed as terrorist organisations.Stockwell Day
Stockwell Burt Day Jr. (born August 16, 1950) is a Canadian former politician who led the Canadian Alliance from 2000 to 2001, and a member of the Conservative Party of Canada.
A provincial cabinet minister from Alberta, Day served as minister ...
that "he has not been approached by anyone lobbying to delist the banned groups". Day is also quoted as saying "The decision to list organizations such as Babbar Khalsa, Babbar Khalsa International, and the International Sikh Youth Federation as terrorist entities under the Criminal Code is intended to protect Canada and Canadians from terrorism."
See also
* Sikhism in India
* Khalsa
* Sikhs for Justice
Sikhs for Justice (SFJ) is a US-based secessionist group that supports the secession of Punjab from India as Khalistan. Founded and primarily headed by lawyer Gurpatwant Singh Pannun in 2009. The organization was created in response to the murd ...
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Primary sources
*
* Julio Ribeiro. ''Bullet for Bullet: My Life as a Police Officer.'' New Delhi: Penguin Books, 1999.
The Ghost of Khalistan
– Sikh Times
*
*
* Ram Narayan Kumar ''et al.''
'' South Asia Forum for Human Rights The South Asia Forum for Human Rights (SAFHR) is a South Asia-focused human rights organization based in Kathmandu whose mission is to "promote respect for universal standards of human rights with emphasis on universality and interdependence of huma ...
, 2003.
*
*
*
Secondary sources
*
* Harjinder Singh Dilgeer.'' "Sikh History"'' in 10 volumes (volumes 7, 8, 9). Waremme, Belgium: Sikh University Press, 2010–11.
* Harjinder Singh Dilgeer. ''"Akal Takht: Concept and Role".'' Waremme, Belgium: Sikh University Press, 2011.
* Satish Jacob and Mark Tully. ''Amritsar: Mrs Gandhi's Last Battle.'' .
* Cynthia Keppley Mahmood. ''A Sea of Orange: Writings on the Sikhs and India.'' Xlibris Corporation,
* Ranbir Singh Sandhu. ''Struggle for Justice: Speeches and Conversations of Sant Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale.'' Ohio: SERF, 1999.
* Anurag Singh. ''Giani Kirpal Singh's Eye-Witness Account of Operation Bluestar.'' 1999.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
{{India separatist movements
Nationalism in India
History of Punjab, India (1947–present)
Sikh politics
Religiously motivated violence in India
Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization
 Sikhs have been concentrated in the Punjab region of South Asia. Before its conquest by the British, the region around Punjab had been ruled by the confederacy of Sikh
Sikhs have been concentrated in the Punjab region of South Asia. Before its conquest by the British, the region around Punjab had been ruled by the confederacy of Sikh  Before the 1947
Before the 1947  Sikh historian Harjot Singh Oberoi argues that, despite the historical linkages between Sikhs and Punjab, territory has never been a major element of Sikh self-definition. He makes the case that the attachment of Punjab with Sikhism is a recent phenomenon, stemming from the 1940s. Historically, Sikhism has been pan-Indian, with the Guru Granth Sahib (the main scripture of Sikhism) drawing from works of saints in both North and South India, while several major seats in Sikhism (e.g. Nankana Sahib in Pakistan, Takht Sri Patna Sahib in Bihar, and Hazur Sahib in
Sikh historian Harjot Singh Oberoi argues that, despite the historical linkages between Sikhs and Punjab, territory has never been a major element of Sikh self-definition. He makes the case that the attachment of Punjab with Sikhism is a recent phenomenon, stemming from the 1940s. Historically, Sikhism has been pan-Indian, with the Guru Granth Sahib (the main scripture of Sikhism) drawing from works of saints in both North and South India, while several major seats in Sikhism (e.g. Nankana Sahib in Pakistan, Takht Sri Patna Sahib in Bihar, and Hazur Sahib in  On the morning of 31 October 1984,
On the morning of 31 October 1984, 
 Air India Flight 182 was an Air India flight operating on the Montréal- London- Delhi- Bombay route. On 23 June 1985, a
Air India Flight 182 was an Air India flight operating on the Montréal- London- Delhi- Bombay route. On 23 June 1985, a