Sicilian Parliament on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Sicilian Parliament was the
The Sicilian Parliament was the
 In 1097 came the first conference in
In 1097 came the first conference in 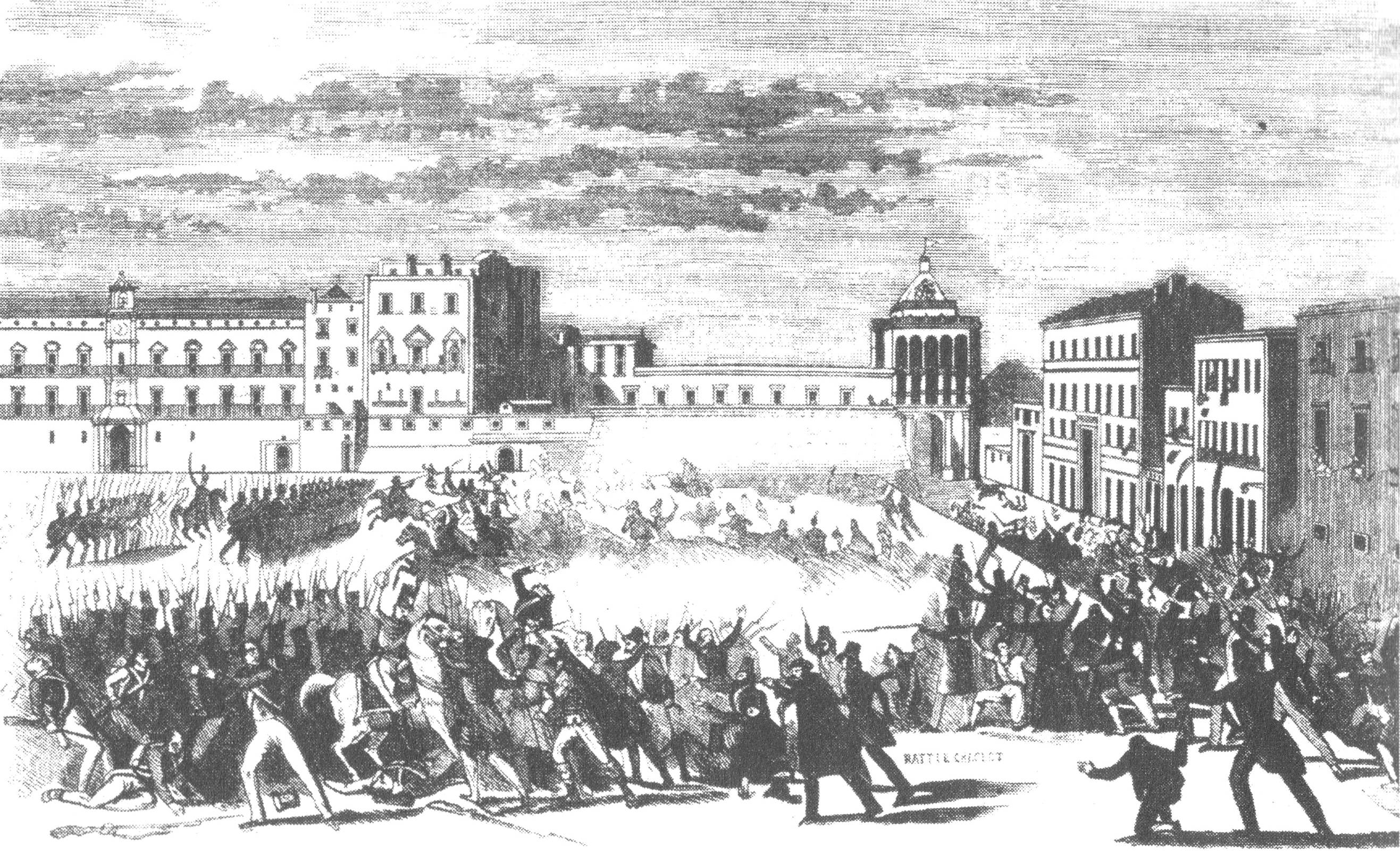 On 25 March 1848, the General Parliament of Sicily met in Palermo, with a revolutionary government composed of a president and ministers. Vincenzo Fardella of Torrearsa was elected president, to be followed by
On 25 March 1848, the General Parliament of Sicily met in Palermo, with a revolutionary government composed of a president and ministers. Vincenzo Fardella of Torrearsa was elected president, to be followed by Encyclopedia of 1848 Revolutions
/ref> The final reconstitution of the Parliament came at the end of
''Parlamenti Generali del Regno Di Sicilia: dall'anno 1446 sino al 1748''
Palermo, 1749 * Salvo Di Matteo
''Storia dell'antico Parlamento di Sicilia (1130-1849)
', Palermo, Mediterranea, 2012
Norman Palace, images and history
{{Sicily Kingdom of Sicily
 The Sicilian Parliament was the
The Sicilian Parliament was the legislature
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its p ...
of the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
.
History
The Sicilian Parliament is arguably one of the oldest parliaments in the world and the first legislature in the modern sense. In 1097 came the first conference in
In 1097 came the first conference in Mazara del Vallo
Mazara del Vallo (; ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Trapani, southwestern Sicily, Italy. It lies mainly on the left bank at the mouth of the Mazaro river.
It is an agricultural and fishing centre and its port gives shelter to the ...
convened by Roger I Roger I may refer to:
:''In chronological order''
* Roger I of Carcassonne (died 1012), Count of Carcassonne
* Roger I of Tosny (), Norman noble
* Roger I "de Berkeley" (died 1093), Norman noble, possibly the son of Roger I of Tosny - see Baron Ber ...
the Great Count. The parliament was initially travelling, as it had no official building to house it. The Sicilian Parliament was made up of three branches: one feudal, one Ecclesiastical, and one from the towns. The feudal branch was formed by noble representatives of counties and baronies; the ecclesiastical branch was formed by archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
s, bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
s, abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The fem ...
s and archimandrite
The title archimandrite ( gr, ἀρχιμανδρίτης, archimandritēs), used in Eastern Christianity, originally referred to a superior abbot (''hegumenos'', gr, ἡγούμενος, present participle of the verb meaning "to lead") who ...
s, while the state-owned branch was formed by representatives of 42 autonomous towns in Sicily. The first Norman parliament had only an advisory function- especially in taxation, economics and wars- and was responsible for confirmation of the sovereign. Members were chosen from the more powerful nobles.
Since 1130, meetings have been held in the Palazzo dei Normanni
The Palazzo dei Normanni (Norman Palace) is also called Royal Palace of Palermo. It was the seat of the Kings of Sicily with the Hauteville dynasty and served afterwards as the main seat of power for the subsequent rulers of Sicily. Since 1946 ...
, in Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
. Its first radical change came with Frederick II of Swabia
Frederick II (1090 – 6 April 1147), called the One-Eyed, was Duke of Swabia from 1105 until his death, the second from the Hohenstaufen dynasty. His younger brother Conrad was elected King of the Romans in 1138.
Life Early career
Frederi ...
, who allowed access to parts of civil society.
After a period in the background during the reign of Charles I of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the Capetian House of Anjou, second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and County of Fo ...
, the Parliament became the central focus of the organization of the Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers ( it, Vespri siciliani; scn, Vespiri siciliani) was a successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out at Easter 1282 against the rule of the French-born king Charles I of Anjou, who had ruled the Kingdom of S ...
. On 3 April 1282, during the uprising, the red and yellow flag with a central triskele was adopted by Parliament: today it is the flag of Sicily
The flag of Sicily ( scn, Bannera dâ Sicilia; it, Bandiera della Sicilia) shows a ''triskeles'' symbol (a figure of three legs arranged in rotational symmetry), and at its center a Gorgoneion (depiction of the head of Medusa) and a pair of ...
. With the Vespers and the subsequent settlement of Frederick III of Aragon in 1297, the Assembly strengthened its central role. At this time, the Parliament was permanently established at Castello Ursino
Castello Ursino ( scn, Casteddu Ursinu, lit=Bear Castle), also known as Castello Svevo di Catania, is a castle in Catania, Sicily, southern Italy. It was built in the 13th century as a royal castle of the Kingdom of Sicily, and is mostly known fo ...
, in Catania
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by ...
, at the ''Sala dei Parlamenti'' (Parliaments Hall). At this time, the Sicilian Parliament consisted primarily of landowners, mayors of cities, counts and barons, and was chaired and convened by the king. Parliament had the constitutional responsibility to elect the king and to guarantee the proper conduct of ordinary justice exercised by executioners, judges, notaries and other officials of the kingdom.
In 1410 the Sicilian Parliament was held at Palazzo Corvaja in Taormina
Taormina ( , , also , ; scn, Taurmina) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina, on the east coast of the island of Sicily, Italy. Taormina has been a tourist destination since the 19th century. Its beaches on ...
, in the presence of Queen Blanche I of Navarre
Blanche I (6 July 1387Anthony (1931) states that she was the fourth-born daughter of King Charles III of Navarre by Queen Eleanor, and she was preceded by Joan, Maria and Margaret and the two latter died early. Anthony defines Blanche's exact birt ...
- a historic meeting for the election of the King of Sicily
The monarchs of Sicily ruled from the establishment of the County of Sicily in 1071 until the "perfect fusion" in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816.
The origins of the Sicilian monarchy lie in the Norman conquest of southern Italy which occ ...
after the death of Martin II. Under the rule of the successive kings of Aragon, Sicily lost its political autonomy and a viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "k ...
ruled the island. Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
again summoned parliament in Palermo in 1532, which continued to meet under Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
, preserving its authority. Over time the importance of the Sicilian Parliament faded.
In Palermo, on 19 July 1812, the Sicilian Parliament, meeting in extraordinary session, declared the feudal regime abolished, promulgated the first Sicilian constitution, of English inspiration, and approved a radical reform of the state.
In 1816, the Parliament, along with the Kingdom of Sicily was abolished when the latter united with the Kingdom of Naples to form the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
.
The Parliament only met again during the Sicilian revolution of 1848
The Sicilian revolution of independence of 1848 ( scn, Rivuluzzioni nnipinnintista siciliana dû 1848) occurred in a year replete with revolutions and popular revolts. It commenced on 12 January 1848, and therefore was the first of the numerous ...
.
 On 25 March 1848, the General Parliament of Sicily met in Palermo, with a revolutionary government composed of a president and ministers. Vincenzo Fardella of Torrearsa was elected president, to be followed by
On 25 March 1848, the General Parliament of Sicily met in Palermo, with a revolutionary government composed of a president and ministers. Vincenzo Fardella of Torrearsa was elected president, to be followed by Ruggero Settimo
Ruggero Settimo (19 May 1778 – 2 May 1863) was an Italian politician, diplomat, and patriotic activist from Sicily. He was a counter-admiral of the Sicilian Fleet. He fought alongside the British fleet in the Mediterranean Sea against the ...
. After sixteen months of ''de facto'' autonomous rule, the Parliament was declared void by the Bourbon dynasty, who offered the vacant throne of Sicily to the Prince Ferdinando, Duke of Genoa, the second son of Carlo Alberto of Savoy. Though his claim was recognized by the British, Ferdinando declined the offer after the Sicilian defeat at the Battle of Novara. The life of the Parliament of 1848-49 was short, and already Ferdinand II of the Two Sicilies
Ferdinand II ( it, Ferdinando Carlo; scn, Ferdinannu Carlu; nap, Ferdinando Carlo; 12 January 1810 – 22 May 1859) was King of the Two Sicilies from 1830 until his death in 1859.
Family
Ferdinand was born in Palermo to King Francis I of the T ...
began to take possession of Sicily through the so-called "Gaeta decree" or Gaeta ultimatum of 28 February 1849, wherein he demanded greater powers of taxation and composed a government in which he held the bulk of the power. On 14 May that year, the Parliament was dissolved./ref> The final reconstitution of the Parliament came at the end of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, when, in order to defuse a budding separatist movement in Sicily, the island was granted special autonomy and its Parliament was reborn, on 25 May 1947, in Palermo, as the Sicilian Regional Assembly
The Sicilian Regional Assembly is the legislative body of Sicily. While it has a long history as an autonomous entity, the modern Region of Sicily was established by Royal Decree on 15 May 1946, before the Italian Republic. The Regional Assembly ...
.
References
Sources
*Antonino e Francesco Mongitore''Parlamenti Generali del Regno Di Sicilia: dall'anno 1446 sino al 1748''
Palermo, 1749 * Salvo Di Matteo
''Storia dell'antico Parlamento di Sicilia (1130-1849)
', Palermo, Mediterranea, 2012
External links
Norman Palace, images and history
{{Sicily Kingdom of Sicily
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
Historical legislatures
Palazzo dei Normanni
Defunct unicameral legislatures