Shuja-ud-Dowlah on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shuja-ud-Daula (b. – d. ) was the

 After the death of his father the Mughal
After the death of his father the Mughal
 After escaping from
After escaping from
/ref> To pay for the protection of British forces and assistance in war, Awadh gave up first the fort of
/ref>
 Shuja-ud-Daula died on 26 January 1775 in
Shuja-ud-Daula died on 26 January 1775 in
Subedar
Subedar is a rank of junior commissioned officer in the Indian Army; a senior non-commissioned officer in the Pakistan Army, and formerly a Viceroy's commissioned officer in the British Indian Army.
History
''Subedar'' or ''subadar'' was the ...
and Nawab of Oudh
The Nawab of Awadh or the Nawab of Oudh was the title of the rulers who governed the state of Awadh (anglicised as Oudh) in north India during the 18th and 19th centuries. The Nawabs of Awadh belonged to a dynasty of Persian origin from Nishap ...
and the Vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was a ...
of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
from 5 October 1754 to 26 January 1775.
Early life
Shuja-ud-Daula was the son of the MughalGrand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
Safdarjung
Abul Mansur Mirza Muhammad Muqim Ali Khan (c. 1708 – 5 October 1754), better known as Safdar Jang, was a major figure at the Mughal court during the declining years of the Mughal Empire. He became the second Nawab of Awadh when he succeeded S ...
chosen by Ahmad Shah Bahadur
Ahmad Shah Bahadur , also known as Mirza Ahmad Shah or Mujahid-ud-Din Ahmad Shah Ghazi (23 December 1725 – 1775 AD), was the fourteenth Mughal Emperor, born to Emperor Muhammad Shah. He succeeded his father to the throne in 1748, at the age ...
. Unlike his father Shuja-ud-Daula was known from an early age for his abilities to synthesize his subordinates, this skill would eventually cause him to emerge as the chosen Grand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
by Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
.
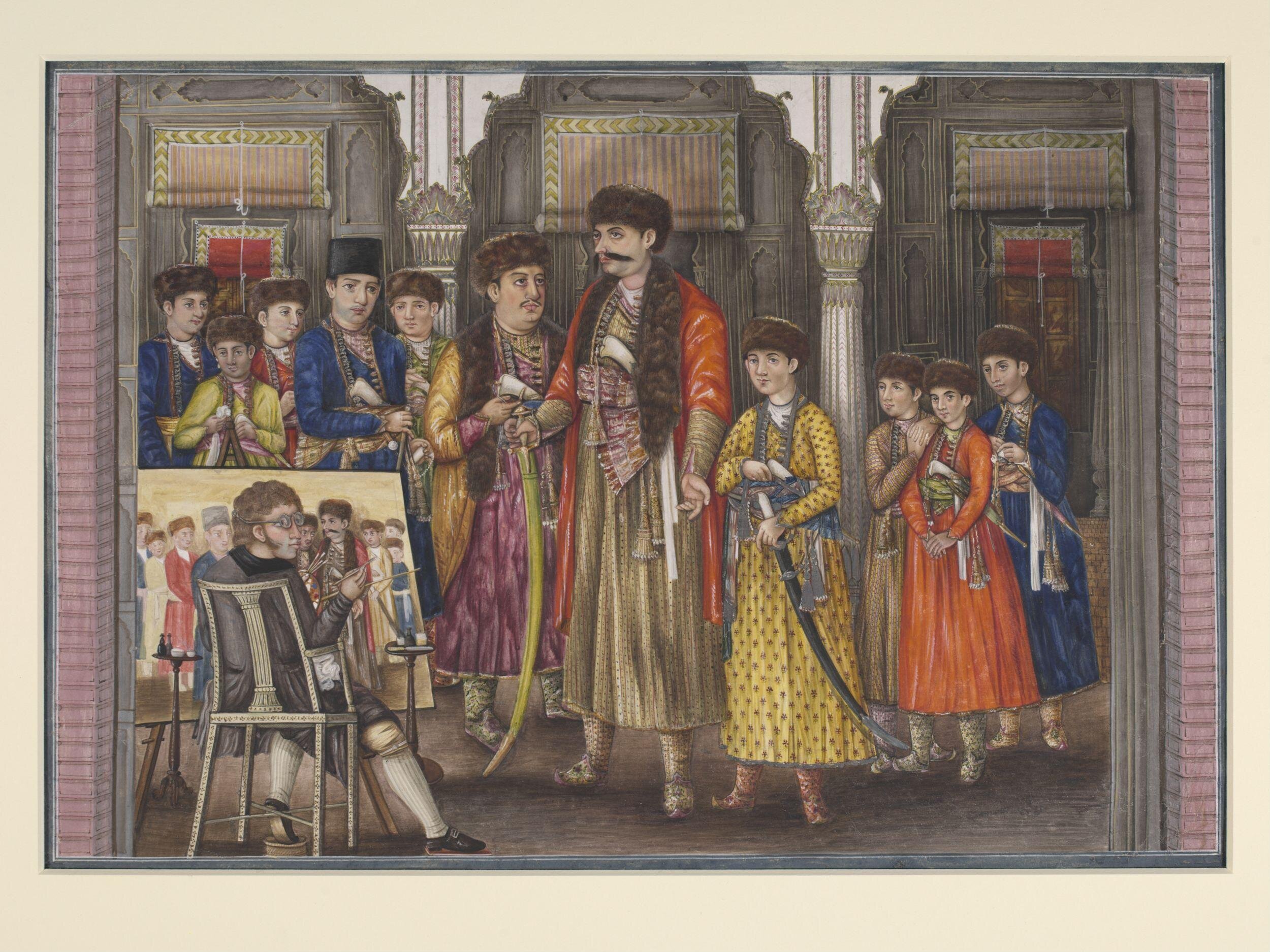
Shuja-ud-Daula was a giant man. Nearly seven feet tall, with oiled moustaches that projected from his face like a pair of outstretched eagle's wings, he was a man of immense physical strength. By 1763, he was past his prime, but still reputedly strong enough to cut off the head of a buffalo with a single swing of his sword, or lift up two of his officers, one in each hand.
Shuja-ud-Daula is also known to have assisted the Alivardi Khan
Alivardi Khan (1671 – 9 April 1756) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1740 to 1756. He toppled the Nasiri dynasty of Nawabs by defeating Sarfaraz Khan in 1740 and assumed power himself.
During much of his reign Alivardi encountered frequent Mar ...
on various occasions when the territories of the Nawab of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, ...
, were being ravaged by Raghoji I Bhonsle
Raghoji Bhonsle or Raghoji I Bhonsale or Raghuji the Great (1695 – February 1755) of the Bhonsale dynasty, was a Maratha general who took control of the Nagpur Kingdom in east-central India during the reign of Shahu I. His successors ruled ...
and his Marathas
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
. Thus Shuja-ud-Daula is known to have been a very respected figure among the servicemen of Alivardi Khan
Alivardi Khan (1671 – 9 April 1756) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1740 to 1756. He toppled the Nasiri dynasty of Nawabs by defeating Sarfaraz Khan in 1740 and assumed power himself.
During much of his reign Alivardi encountered frequent Mar ...
.

Nawab of Awadh

 After the death of his father the Mughal
After the death of his father the Mughal Grand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
Safdarjung
Abul Mansur Mirza Muhammad Muqim Ali Khan (c. 1708 – 5 October 1754), better known as Safdar Jang, was a major figure at the Mughal court during the declining years of the Mughal Empire. He became the second Nawab of Awadh when he succeeded S ...
in the year 1753, Shuja-ud-Daula was recognized as the next Nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian language, Persian,
Punjabi language, Punjabi ,
Sindhi language, Sindhi,
Urd ...
by the Mughal Emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
Ahmad Shah Bahadur
Ahmad Shah Bahadur , also known as Mirza Ahmad Shah or Mujahid-ud-Din Ahmad Shah Ghazi (23 December 1725 – 1775 AD), was the fourteenth Mughal Emperor, born to Emperor Muhammad Shah. He succeeded his father to the throne in 1748, at the age ...
.
Shuja-ud-Daula despised Imad-ul-Mulk
Feroze Jung III or Nizam Shahabuddin Muhammad Feroz Khan Siddiqi Bayafandi also known by his sobriquet Imad-ul-Mulk, was the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire allied with the Maratha Empire, who were often described as a de facto ruler of the ...
, an ally of the Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
s of the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
whose regime emerged after the Battle of Sikandarabad with the support of the Sadashivrao Bhau
Sadashivrao Bhau Peshwa (3 August 1730 – 14 January 1761) was son of Chimaji Appa (younger brother of Bajirao I) and Rakhmabai (Pethe family) and the nephew of Baji Rao I. He was a finance minister during the reign of Maratha emperor Chhatr ...
. Imad-ul-Mulk blinded Ahmad Shah Bahadur
Ahmad Shah Bahadur , also known as Mirza Ahmad Shah or Mujahid-ud-Din Ahmad Shah Ghazi (23 December 1725 – 1775 AD), was the fourteenth Mughal Emperor, born to Emperor Muhammad Shah. He succeeded his father to the throne in 1748, at the age ...
and placed Alamgir II on the Mughal imperial throne. Alamgir II and his son Prince Ali Gauhar, were often persecuted by Imad-ul-Mulk because they refused to abandon their peaceful terms with Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahm ...
, they also demanded the resignation of Imad-ul-Mulk mainly due to his relations with the Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
s.
Grand Vizier of the Mughal Empire
Prince Ali Gauhar fled fromDelhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
when he realized a conspiracy that would eventually lead to the murder of the Mughal Emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
Alamgir II. Shuja-ud-Daula welcomed and protected Prince Ali Gauhar, who then declared himself Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
and officially recognized Shuja-ud-Daula as the Grand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. Together they challenged the usurper Shah Jahan III, who was placed on the Mughal imperial throne by Sadashivrao Bhau
Sadashivrao Bhau Peshwa (3 August 1730 – 14 January 1761) was son of Chimaji Appa (younger brother of Bajirao I) and Rakhmabai (Pethe family) and the nephew of Baji Rao I. He was a finance minister during the reign of Maratha emperor Chhatr ...
and his forces, which plundered much of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
.
Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
was then advised to lead an expedition that would attempt to retake the eastern regions of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
from Mir Jafar who was supported by the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
. While Shuja-ud-Daula, Najib-ul-Daula
Najib ad-Dawlah ( ps, نجيب الدوله), also known as Najib Khan Yousafzai ( ps, نجيب خان), was a Rohilla Yousafzai Afghan who earlier served as a Mughal serviceman but later deserted the cause of the Mughals and joined Ahmed ...
and Mirza Jawan Bakht allied themselves with Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahm ...
and assisted his forces during the Second Battle of Sikandarabad
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of Time in physics, time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally t ...
in the year 1760 and later led a Mughal Army
The Army of the Mughal Empire was the force by which the Mughal emperors established their empire in the 15th century and expanded it to its greatest extent at the beginning of the 18th century. Although its origins, like the Mughals themselves, ...
of 43,000 during the Third Battle of Panipat.
Third Battle of Panipat
 After escaping from
After escaping from Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
due to the murder of his father the Mughal Emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
Alamgir II, the young Prince Ali Gauhar was well received by Shuja-ud-Daula. The Nawab of Awadh
The Nawab of Awadh or the Nawab of Oudh was the title of the rulers who governed the state of Awadh (anglicised as Oudh) in north India during the 18th and 19th centuries. The Nawabs of Awadh belonged to a dynasty of Persian origin from Nishapu ...
and the newly appointed Mughal Grand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
Shuja-ud-Daula assured Prince Ali Gauhar that he and Najib-ud-Daula
Najib ad-Dawlah ( ps, نجيب الدوله), also known as Najib Khan Yousafzai ( ps, نجيب خان), was a Rohilla Yousafzai Afghan who earlier served as a Mughal serviceman but later deserted the cause of the Mughals and joined Ahmed S ...
would initiate a struggle that would overthrow the Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
if Prince Ali Gauhar would lead what remained of the Mughal Army
The Army of the Mughal Empire was the force by which the Mughal emperors established their empire in the 15th century and expanded it to its greatest extent at the beginning of the 18th century. Although its origins, like the Mughals themselves, ...
against the expanding British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
.
Shuja's decision about whom to join as an ally in the Third Battle of Panipat was one of the decisive factors that determined the outcome of the war as lack of food due to the Afghans
Afghans ( ps, افغانان, translit=afghanan; Persian/ prs, افغان ها, translit=afghānhā; Persian: افغانستانی, romanized: ''Afghanistani'') or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry f ...
cutting the supply lines of Marathas was one of the reasons that Marathas could not sustain the day-long battle. Their forces were weak due to starvation and also fighting facing the sun.
Shuja was earlier not very sure about whose side should he take before the Third Battle of Panipat. Marathas were still further south then and it would have taken them considerable time to reach Shuja's province. In spite of His mother was of the opinion that he should join the Marathas as they had helped his father previously on numerous occasions he joined Abdali.
As the chosen Grand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first ...
of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, Shuja-ud-Daula commanded a sizeable army of Mughal troopers, who cut off the supplies of the Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
s and even defeated them in pitched confrontations during the Third Battle of Panipat and dispatched the Maratha leader Sadashivrao Bhau
Sadashivrao Bhau Peshwa (3 August 1730 – 14 January 1761) was son of Chimaji Appa (younger brother of Bajirao I) and Rakhmabai (Pethe family) and the nephew of Baji Rao I. He was a finance minister during the reign of Maratha emperor Chhatr ...
.
Battle of Buxar
Shuja is also known for his role in the Battle of Buxar, a battle that was no less definite in Indian history. He along with the forces of Mughal emperorShah Alam II
Shah Alam II (; 25 June 1728 – 19 November 1806), also known by his birth name Ali Gohar (or Ali Gauhar), was the seventeenth Mughal Emperor and the son of Alamgir II. Shah Alam II became the emperor of a crumbling Mughal empire. His powe ...
& Mir Qasim
Mir Qasim ( bn, মীর কাশিম; died 8 May 1777) was the Nawab of Bengal from 1760 to 1763. He was installed as Nawab with the support of the British East India Company, replacing Mir Jafar, his father-in-law, who had himself been su ...
ruler of Bengal were defeated by the British forces in one of the key battles in the history of British East India company.
Allahabad Treaty
He again fought British with the help of Marathas at Kara Jahanabad and was defeated. On 16 August 1765 AD he signed the Treaty of Allahabad, which said that Kora and Allahabad district will go to Company and the Company will get 5 million rupees from Awadh. British will be allowed free trade in Awadh and will help each other in case of war with other powers, which was a very shrewd politics of the Company.HISTORY OF AWADH (Oudh) a princely State of India by Hameed Akhtar Siddiqui/ref> To pay for the protection of British forces and assistance in war, Awadh gave up first the fort of
Chunar
Chunar is a city located in Mirzapur district of Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is nearby Mirzapur city. The railway tracks passing through Chunar Junction railway station leads to major destinations of India, including Howrah, Delhi, T ...
, then districts of Benaras
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tra ...
, Ghazipur
Ghazipur is a city in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. Ghazipur city is the administrative headquarters of the Ghazipur district, one of the four districts that form the Varanasi division of Uttar Pradesh.
The city of Ghazipur also constitute ...
and finally Allahabad
Allahabad (), officially known as Prayagraj, also known as Ilahabad, is a metropolis in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.The other five cities were: Agra, Kanpur (Cawnpore), Lucknow, Meerut, and Varanasi (Benares). It is the administrat ...
.Shuja-ud-daula (1754–1775)/ref>
Death and burial
 Shuja-ud-Daula died on 26 January 1775 in
Shuja-ud-Daula died on 26 January 1775 in Faizabad
Faizabad (Hindustani pronunciation: ɛːzaːbaːd is a city situated near the southern banks of Saryu river in Ayodhya district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The area of this Faizabad region is administered by Ayodhya Municipal Corpor ...
, the then capital of Awadh
Awadh (), known in British historical texts as Avadh or Oudh, is a region in the modern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, which was before independence known as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh. It is synonymous with the Kośāla region of ...
, and was buried in the same city. His burial place is a tomb and known as Gulab Bari
Gulab Bari () is the Tomb of Nawab Shuja-ud-Daula, located in Faizabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. This place has a good collection of roses of various varieties set by the sides of water fountains. Gulab Bari is the maqbara (Mausoleum) of Nawab ...
(Rose Garden).
Personal life
Shuja-ud-Daula's Turkic andIranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Twelver Shia
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
royal family ruling the Oudh
The Oudh State (, also Kingdom of Awadh, Kingdom of Oudh, or Awadh State) was a princely state in the Awadh region of North India until its annexation by the British in 1856. The name Oudh, now obsolete, was once the anglicized name of ...
(Awadh) state in India obtained their eunuchs (khwajasarais) through subduing Hindu kings rebellions. Jawahir Ali was a eunuch of Oudh state who was born a Hindu. The Rajas of Khairabad rebelled since they refused to pay taxes to the Twelver Shia district administrator Nawab Muhammad Ali Khan so Nawab Muhammad Ali defeated the Hindus in battle The castrated Hindu boys were converted to Twelver Shia Islam and given Muslim names after being enslaved and then educated. The Twelver Shia Turkic Nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian language, Persian,
Punjabi language, Punjabi ,
Sindhi language, Sindhi,
Urd ...
of Oudh Shuja-ud-Daula (a descendant of the Turkic Twelver Shia Qara Qoyunlu
The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu ( az, Qaraqoyunlular , fa, قره قویونلو), also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman "Kara Koyunlu, also spelled Qara Qoyunlu, Turkish Karakoyunlular, Eng ...
dynasty through his father Safdar Jang
Abul Mansur Mirza Muhammad Muqim Ali Khan (c. 1708 – 5 October 1754), better known as Safdar Jang, was a major figure at the Mughal court during the declining years of the Mughal Empire. He became the second Nawab of Awadh when he succeeded ...
) made Nawab Muhammad Ali Khan give his eunuchs including Jawahir Ali to him. Jawahir Ali (Joahir Ali) served as nazir eunuch to Bahu Begum (Bahu Begam, Bahoo Begum or Buhoo Begum) (Begum Amanat-uz Zahra Bano), the Iranian Persian wife of the Turkic Twelver Shia ruler of Oudh, Shuja-ud-Daula. Bahu Begum owned multiple eunuchs, all of them of Indian Hindu background. One of them was born a eunuch with defective genital and sold to the Nawab by his family, Darab Ali Khan and he was a general agent of Bahu Begam after Jawahir Ali. Jawahir Ali was the first general agent of Bahu Begam.
Bahu Begam's estates were managed by Javahir 'Ali Khan. The Twelver Shia cleric Mawlavi Muhammad Munir who came to Faizabad and was there during a riot in 1779 between Sufi pirs and physicians against Twelver Shia clerics. Muhammad Munir was paid a stipend and backed up by Javahir Ali. Javahir Ali sent soldiers to support the Twelver scholars against the physicians. The Twelver Shia Usuli ulama were also supported by Javahir Ali when they implemented Friday prayers 7 years after the riots. Javahir paid 20 people to make people attend the 5 mandatory prayers and Friday prayer during the winter and rainy season. Bahu Begum was of Persian Iranian descent. The British East India Company under Warren Hastings
Warren Hastings (6 December 1732 – 22 August 1818) was a British colonial administrator, who served as the first Governor of the Presidency of Fort William (Bengal), the head of the Supreme Council of Bengal, and so the first Governor-Genera ...
tortured the eunuchs Bahar Ali and Jawahir Ali after they arrested Bahu Begum in 1781 in order to force them to give their treasure over.
Jawahir Ali Khan ordered 2 fellow eunuchs belonging to Bahu Begum, Sa'adat and Basharat to assist the Qadi (Qazi) at Ali Beg Khan mosque. Due to cold weather, the eunuch minister Darab Ali Khan tried to stop Bahu Begam from reciting Fatiha at Imam Husain's tazia during Muharram but she went regardless and got a fever and cold.
Bahu Begum only allowed Jawahir to enter when she was on her Sedan Chair speaking before British East India Company representative Mr. Lumsden in Lucknow. Darab Ali Khan came from the Salone district, Rusulabad. Jawahir was interred in an imambarah made out of wood after he died in 1799 in Faizabad. Bahu Begum had another favourite eunuch, Tehsin Ali Khan who died on 27 August 1818. He constructed a mosque and owned a Serai. Bahu Begum's name was Amanat-uz Zahra and her eunuch Jawahar Ali Khan built an Imambara in Faizabad. Bahu Begam was the younger sister of Mirza Muhammad
''As there is a full account given of Jawahir 'Ali Ķbán in connection with Faizábád, there is no need to speak of him here. Having filled the office of the Nazárat on earth for thirty-four years after the death of Nusrat 'Ali ķhán, he was summoned in 1214 A.H. [1799 A.D.), to superintend the huris of Firdaus, and hastened. to Paradise. Then the lucrative appointments which he had vacated were conferred on Muhammad Dáráb. Ali Ķbán. Although Jawahir . 'Ali Khán had thrice the dignity and opulence of his father,* for his authority extended from the mountain of Butwal on the north to the banks of the Ganges on the south, and he had more than 10,000 horse and foot, and had personal property greater than all the other eunuchs of Faizábád had been able to collect in their whole lives, yet he was never known to utter an arrogant or haughty word, and never assumed any manner or a form of speech which savoured of pride or arrogance. As he had evinced from his early boyhood a taste for literature, he was constantly engaged in reading, and when any literary discussion took place, he used to leave the most urgent business to go and share its advantages. In his early years he was fond of Arabic, and becoming proficient in etymology, syntax, and logic, he entered on the study of Şadra; but owing to his tours and journeys, which he had to make to Lucknow each year and sometimes to the mountain of Butwal, he was unable to make further progress.''
''He was an able expositor of the ambiguities of Persian poetry. Enigmas and riddles were solved in gatherings around him. Above all, he was especially fond of historical works. He read from beginning to end the Sháhnáma, Hamla-i-Haidarí, the Masnavís of Jalálu'ddín Rúmi, Ma'ariju'nnabuwat, Rauzatu'ssafa, Habibu'ssiyar, Shahjabánnáma, Akbarnáma, Taimúrnáma, Táriķh Farishta, and every other book on which he could lay his hands. The duty of reading these aloud to him was imposed on me. He used to listen to them from sunset until midnight. I heard many narratives and tales while thus privileged with the enjoyment of his society. He always sought the company of scholars, poets, and men of science. He is dead and gone.''
''* The relation of an old eunuch to a younger one as guru and chelá (priest and novice) is often referred to in this work. When a eunuch adopted another they were spoken of as father and son. This is the relation here alluded to, Jawábir 'Ali being looked on as the adopted son of Nusrat 'Ali, whom he succeeded.'' Muhammad Faiz Bakhsh, "Memoirs of Delhi and Faizábád: Being a Translation of the Táríḳh Farahbaḳhsh of Muhammad Faiz Baḳhsh from the Original Persian, Volume 1", pages iv-v.
Yusuf Ali Khan and Ambar Ali Khan were 2 other eunuch boys who were raised with Jawahir Ali Khan. Ambar Ali Khan was taken prisoner in the same battle as Jawahir Ali Khan when the Twelver Shia Commissioner Muhammad Ali Khan defeated the Hindu Rajputs of Khairabad (Sitapur) and castrated the Hindu boys. Jawahir Ali Khan used white clothing for Mewatis, black clothing for irregulars and livery in mango green for household troops (Sahib Khanis) when he ordered his servants and soldiers to parade in Lucknow while he was administrator. Jawahir Ali patronized intellectuals and culture as well as engaging in horsemanship and archery practice every day. He did not wear ornate, expensive or elaborate clothing and did not do extravagant grooming, since as a high ranking eunuch (khwajasarai) his mistress did not need to flaunt her wealth through him. Jawahir Ali Khan cone had 1,000 servants shout "Din, Din" while raising banners and wearing white robes after taking off their black robes. One of his officials was Akhund Ahmad. Jawahir Ali had a dispute with his mistress Bahu Begum when he was blocking a road once and she sent a eunuch to tell him to stop it.
In popular culture
* In the 1994Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been de ...
TV series ''The Great Maratha
''The Great Maratha'' is an Indian historical drama television series directed by Sanjay Khan and produced by Numero Uno International Limited. The drama aired on DD National. The series is based on the life of Mahadaji Shinde. The show compr ...
'', Shuja's character was portrayed by Benjamin Gilani
Benjamin Gilani is an Indian film, television and stage actor who works in Hindi cinema.
Early life and career
Gilani was schooled at Bishop Cotton School, Shimla. He is a postgraduate from Delhi University having studied and taught English lit ...
.
* In the 2019 Bollywood film ''Panipat
Panipat () is a historic city in Haryana, India. It is 95 km north of Delhi and 169 km south of Chandigarh on List of National Highways in India, NH-1. The three major battles fought in First Battle of Panipat, 1526, Second Battle of ...
'', Shuja-ud-Daula is portrayed by Kunal Kapoor Kunal Kapoor may refer to:
* Kunal Kapoor (actor, born 1959), Indian film actor
* Kunal Kapoor (actor, born 1977), Indian actor, writer and entrepreneur
* Kunal Kapoor (cricketer) (born 1987), Indian cricketer
* Kunal Karan Kapoor (born 1982), In ...
.
References
Further reading
*Shuja-ud-Daulah – Vol. I, II (1754–1765) by Ashirbadi Lal SrivastavaExternal links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shuja-Ud-Daula 1732 births People from Lucknow Nawabs of Awadh 1775 deaths Indian Shia Muslims Indian people of Iranian descent 18th-century Iranian people