Shridhara-varman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sridharavarman (




 , ''
, ''
p58-59
/ref> was a
 Although Sridharavarman took the title of , the traditional title of the
Although Sridharavarman took the title of , the traditional title of the

 Another inscription of the same Sridhavarman, made by his
Another inscription of the same Sridhavarman, made by his
File:Rudrasimha II coin.jpg, 
 ) mentioned by
) mentioned by
Gupta script
The Gupta script (sometimes referred to as Gupta Brahmi script or Late Brahmi script)Sharma, Ram. '' 'Brahmi Script' ''. Delhi: BR Publishing Corp, 2002 was used for writing Sanskrit and is associated with the Gupta Empire of the Indian subcon ...
: 

Shri
Shri (; , ) is a Sanskrit term denoting resplendence, wealth and prosperity, primarily used as an honorific.
The word is widely used in South and Southeast Asian languages such as Marathi, Malay (including Indonesian and Malaysian), Javanese, ...
-dha-ra-va-rmma-na'', ruled CE)Buddhist Landscapes in Central India: Sanchi Hill and Archaeologies of Religious and Social Change, c. Third Century BC to Fifth Century AD, Julia Shaw, Routledge, 201p58-59
/ref> was a
Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
(Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
) ruler of Central India
Central India is a loosely defined geographical region of India. There is no clear official definition and various ones may be used. One common definition consists of the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh, which are included in alm ...
, around the areas of Vidisa, Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen, Raisen town, dist ...
and Eran
Eran is an ancient town and archaeological site in the Sagar district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It was one of the ancient mints for Indian dynasties as evidenced by the diverse coins excavated here. The site has 5th and 6th-century Gupta era ...
in the , just before the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
expansion in these areas. He calls himself a general and "righteous conqueror" () in an inscription, and ('King') and ('Great Satrap') in a probably later inscription at Eran, suggesting that he may have been a high-ranked officer who later rose to the rank of a King.
Rule
 Although Sridharavarman took the title of , the traditional title of the
Although Sridharavarman took the title of , the traditional title of the Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh ...
, he probably did not belong to the line of Chastana
Chashtana (Greek: (epigraphic), ; Brahmi: ; Kharosthi: , ) was a ruler of the Saka Western Satraps in northwestern India during 78-130 CE, when he was the satrap of Ujjain.
Name
Chashtana's name is attested in the Greek forms () and () ...
, the founder of the dynasty, and belonged to a different Saka family. He probably suffered a defeat by the Gupta Emperor Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
around , who then occupied the area around Eran
Eran is an ancient town and archaeological site in the Sagar district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It was one of the ancient mints for Indian dynasties as evidenced by the diverse coins excavated here. The site has 5th and 6th-century Gupta era ...
and made his own victorious inscription there.
Sridharavarman is probably the "Saka" ruler mentioned in the Allahabad pillar inscription of Samudragupta, as having "paid homage" to the Gupta Emperor, forced to "self-surrender, offering (their own) daughters in marriage and a request for the administration of their own districts and provinces".
After submitting to Samudragupta, he and his successor may have ruled a bit longer in Eastern Malwa, until they were vanquished by Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II (r.c. 376-415), also known by his title Vikramaditya, as well as Chandragupta Vikramaditya, was the third ruler of the Gupta Empire in India, and was one of the most powerful emperors of the Gupta dynasty.
Chandragupta continue ...
in his "conquest of the whole world".
Inscriptions

Kanakerha inscription
Sridharavarman is known from two inscriptions: the first one is theKanakerha inscription
The Kanakerha inscription, also spelled Kanakherha inscription, is an inscription found on the side of the hill of Sanchi, dating to the 3rd or 4th century CE.
The region of Sanchi-Vidisha was captured from the Satavahanas by the Western Satraps ...
at Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen, Raisen town, dist ...
.
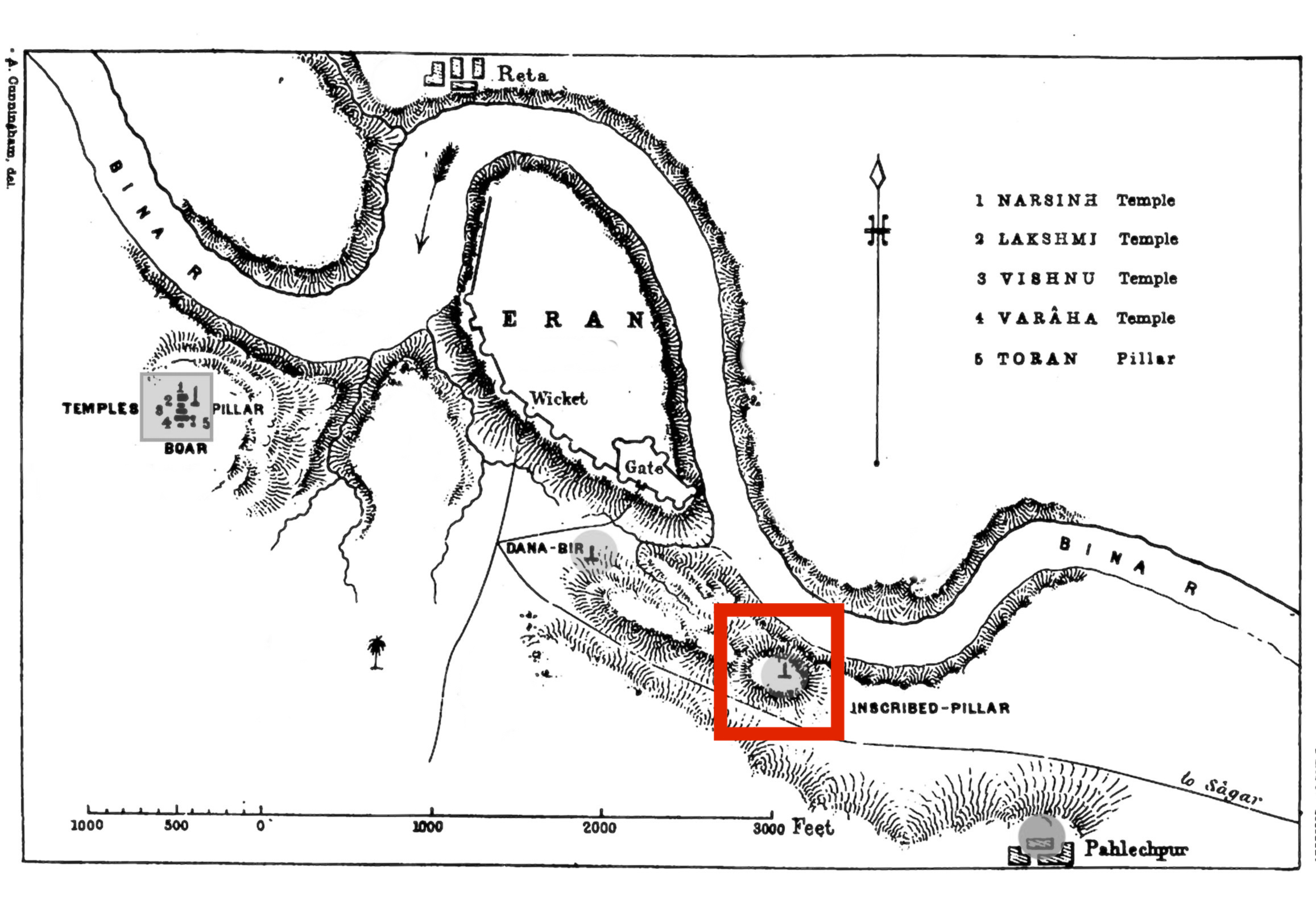
Eran inscription
 Another inscription of the same Sridhavarman, made by his
Another inscription of the same Sridhavarman, made by his Naga
Naga or NAGA may refer to:
Mythology
* Nāga, a serpentine deity or race in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain traditions
* Naga Kingdom, in the epic ''Mahabharata''
* Phaya Naga, mythical creatures believed to live in the Laotian stretch of the Mekong Riv ...
General Satyanaga, was made on a pillar at Eran
Eran is an ancient town and archaeological site in the Sagar district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It was one of the ancient mints for Indian dynasties as evidenced by the diverse coins excavated here. The site has 5th and 6th-century Gupta era ...
, only the top portion of which is remaining. The pillar is about 1 foot 6 inches in diameter. The inscription is dated to the 27th year of Sridharavarman's reign. Another famous inscription was later added on the same pillar, the inscription of Goparaja, who died in Eran during the rule of Gupta ruler Bhanugupta
Bhanugupta was one of the lesser known kings of the Gupta dynasty. He is only known from an inscription in Eran, and a mention in the Manjushri-mula-kalpa.
Only mentioned in the Eran inscription as a "Raja" and not a "Maharaja" or a "Maharajad ...
, who is also only known from this very inscription.
The Eran inscription of Sridharavarman reads:
At Eran, it seems that this inscription is succeeded chronologically by a monument and an inscription by Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
's Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
(), established "for the sake of augmenting his fame", who may therefore have ousted Sridharavarman in his campaigns to the West."During the course of this expedition he is believed to have attacked and defeated the Saka Chief Shridhar Varman, ruling over Eran-Vidisha region. He then annexed the area and erected a monument at Eran (modern Sagar District) "for the sake cf augmenting his fame"." in
Connected rulers
While theWestern Satrap
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India (Saurashtra (region), Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajastha ...
Rudrasimha II
Rudrasimha II (304–348) was a ruler of the Western Satraps He declared on his coins to be the son of a Lord (Svami) named Jivadaman.
His coinage is coeval with that of other rulers, who may have been sub-kings and were his sons: Yasodaman II ...
ruled in the western India, the Gupta Emperor Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
may have ousted Sridharavarman during his campaigns in Central India.
Seals with the names of other Saka rulers from Malwa in the 3rd century CE are known.
Rudrasimha II
Rudrasimha II (304–348) was a ruler of the Western Satraps He declared on his coins to be the son of a Lord (Svami) named Jivadaman.
His coinage is coeval with that of other rulers, who may have been sub-kings and were his sons: Yasodaman II ...
ruled the Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh ...
at the time of Sridharavarman.
File:Samudragupta_circa_335-380_CE.jpg, Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
ruled in the East at the time of Sridharavarman.
File:Allahabad pillar Samudragupta inscription Shaka word in Line 23.jpg, The vanquished "Śaka" (Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
in the Allahabad pillar (Line 23) was probably Sridharavarman.
References
{{reflist Western Satraps 4th-century Indian monarchs