Shin-Shinano Frequency Converter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 is the designation of a
is the designation of a
CIGRÉ B4 Compendium of HVDC Schemes, 2009.
(archived copy)
www.transmission.bpa.gov/cigresc14/Compendium/Shinshin%20Pictures.pdf
(archived copy) Converter stations Electric power infrastructure in Japan Tokyo Electric Power Company Asahi, Nagano Energy infrastructure completed in 1977 Energy infrastructure completed in 1992 {{Japan-struct-stub
 is the designation of a
is the designation of a back-to-back
Back to Back or back-to-back may refer to:
Music Songs
* "Back to Back" (Drake song), 2015
* "Back to Back" (Jeanne Pruett song), 1979
*"Back to Back", a song by Pretty Maids from the 1984 album ''Red Hot and Heavy''
*"Back to Back", a song by ...
high-voltage direct current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system (also called a power superhighway or an electrical superhighway) uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating curre ...
(HVDC) facility in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
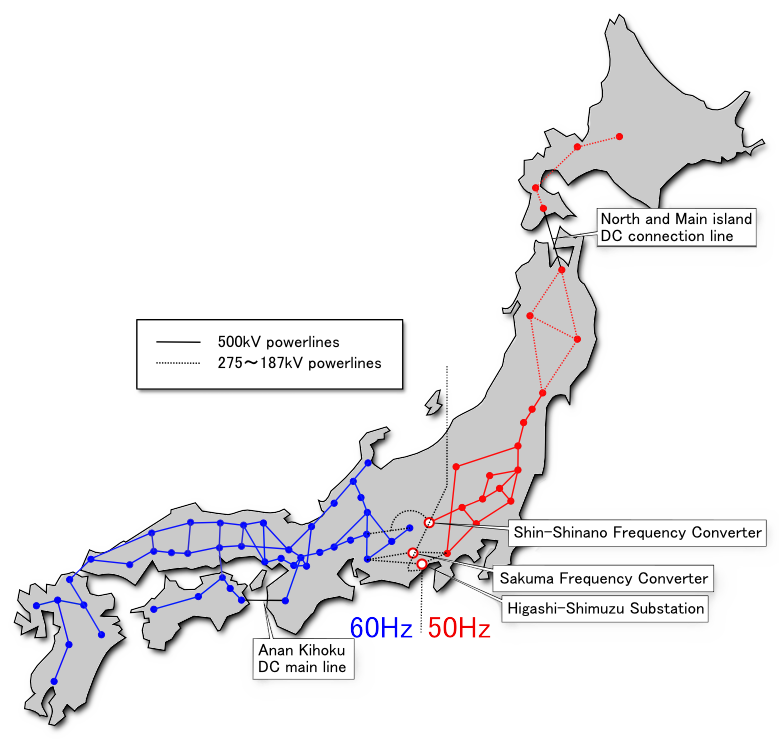
which forms one of four frequency converter stations that link Japan's western and eastern power grids. The other three stations are at Higashi-Shimizu, Minami-Fukumitsu
is the name given to an HVDC back-to-back station for the interconnection of the power grids of western and eastern Japan. This facility went in service in March 1999. It operates with a voltage of 125 kV and can transfer a power up to 300 mega ...
, and Sakuma Dam
The is a dam on the Tenryū River, located on the border of Toyone, Kitashitara District, Aichi Prefecture on the island of Honshū, Japan. It is one of the tallest dams in Japan and supports a 350 MW hydroelectric power station. Nearby a freq ...
.
Converter equipment
The HVDC back-to-back facility Shin Shinano uses line-commutatedthyristor
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current ...
converters. The station houses two converters, one of which opened in December 1977,Compendium of HVDC schemes, CIGRÉ Technical Brochure No. 003, 1987, pp100–103. the other in 1992. The original 1977 converter was one of the first thyristor-based HVDC schemes to be put into operation in the world and used oil-insulated, oil-cooled outdoor thyristor valve
In an electric power transmission system, a thyristor-controlled reactor (TCR) is a reactance connected in series with a bidirectional thyristor valve. The thyristor valve is phase-controlled, which allows the value of delivered reactive power t ...
s supplied by Hitachi
() is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It is the parent company of the Hitachi Group (''Hitachi Gurūpu'') and had formed part of the Ni ...
(60 Hz end) and Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure system ...
(50 Hz end). A special workshop was provided on the site, in which valve maintenance (for example replacing failed thyristors) could be carried out under clean conditions in order to avoid contamination of the oil.
The 1992 converter uses more conventional air-insulated, water-cooled thyristor valves. In 2008 the original 1977 converter was decommissioned and replaced by a third converter, similar in design to the 1992 converter but using light-triggered thyristors.
The Shin-Shinano link operates with a DC link voltage of 125 kV for each converter. The station was initially rated at 300 MW. In 1992, with the addition of the second 300 MW converter, the maximum transferable power was uprated to 600 MW.
See also
*Energy in Japan
Energy in Japan refers to energy and electricity production, consumption, import and export in Japan. The country's primary energy consumption was 477.6 Mtoe in 2011, a decrease of 5% over the previous year.
The country lacks significant do ...
*Kii Channel HVDC system
The Kii Channel HVDC system in Japan is, as of 2012, the highest-capacity high-voltage direct current (HVDC) submarine power cable system in the world to use a single bipole, with a rated power of 1400MW. The cross channel system between England ...
*HVDC Hokkaido–Honshu
, for short, is a high voltage direct current transmission line for the interconnection of the power grids of Hokkaidō (Hakodate static inverter station in Nanae) and Honshū ( Kamikita static inverter station in Tohoku, Aomori Prefecture), ...
References
External links
CIGRÉ B4 Compendium of HVDC Schemes, 2009.
(archived copy)
www.transmission.bpa.gov/cigresc14/Compendium/Shinshin%20Pictures.pdf
(archived copy) Converter stations Electric power infrastructure in Japan Tokyo Electric Power Company Asahi, Nagano Energy infrastructure completed in 1977 Energy infrastructure completed in 1992 {{Japan-struct-stub