Shepseskare on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shepseskare or Shepseskara (
 Finally, there is a single scarab seal reading "Shepeskare" ic/small> that the Egyptologist Flinders Petrie attributed to Shepseskare at the end of the 19th century. Modern scholars doubt this attribution and rather believe the scarab to be a work of the much later Saite period (685–525 BC) executed in archaic style. Equally, the scarab could belong to Gemenefkhonsbak Shepeskare, an obscure kinglet of
Finally, there is a single scarab seal reading "Shepeskare" ic/small> that the Egyptologist Flinders Petrie attributed to Shepseskare at the end of the 19th century. Modern scholars doubt this attribution and rather believe the scarab to be a work of the much later Saite period (685–525 BC) executed in archaic style. Equally, the scarab could belong to Gemenefkhonsbak Shepeskare, an obscure kinglet of
 Both the relative chronological position and absolute dates of Shepseskare's reign are uncertain.
The Saqqara Tablet records Shepseskare as the successor of Neferirkare Kakai and the predecessor of Neferefre, which became the traditional opinion among Egyptologists. Following discoveries in the early 1980s, the Czech Egyptologist Miroslav Verner advocates the hypothesis that Shepseskare succeeded, rather than preceded, Neferefre.
In support of this hypothesis, Verner first emphasizes the presence of several clay seal impressions bearing Shepseskare's Horus name "Sekhemkaw" (meaning "He whose apparitions are powerful") in the oldest part of Neferere's mortuary temple, which was not built "until Neferefre's death". This appears to suggest that Shepseskare ruled after—rather than before—Neferefre.
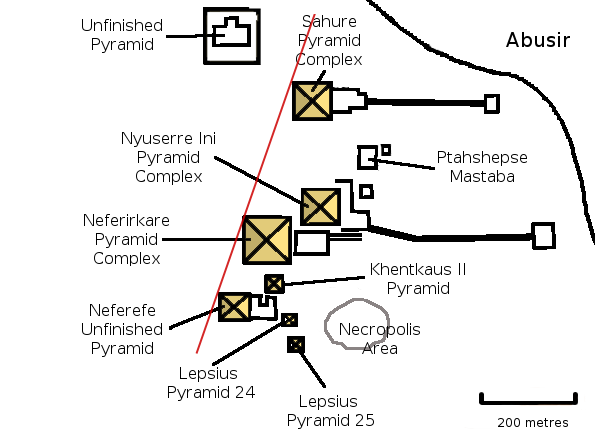
Verner's second argument concerns the alignment of pyramids of Sahure, Neferirkare Kakai and Neferefre: they form a line pointing to Heliopolis, just as the three pyramids of Giza do. In contrast, Shepseskare's unfinished pyramid does not fall on the line to Heliopolis, which strongly suggests that Neferefre's pyramid had already been in place when Shepseskare started his. Finally, Verner observes that Neferefre is known to have been Neferirkare's eldest son and around 20 years old when his father died so that he was in optimal position to inherit the throne. Shepseskare thus most likely took the throne after Neferefre. As Verner notes, while Shepseskare is noted as the immediate predecessor of Neferefre in the Saqqara tablet, "this slight discrepancy can ... be attributed to the oliticaldisorders of the time and its dynastic disputes."
Both the relative chronological position and absolute dates of Shepseskare's reign are uncertain.
The Saqqara Tablet records Shepseskare as the successor of Neferirkare Kakai and the predecessor of Neferefre, which became the traditional opinion among Egyptologists. Following discoveries in the early 1980s, the Czech Egyptologist Miroslav Verner advocates the hypothesis that Shepseskare succeeded, rather than preceded, Neferefre.
In support of this hypothesis, Verner first emphasizes the presence of several clay seal impressions bearing Shepseskare's Horus name "Sekhemkaw" (meaning "He whose apparitions are powerful") in the oldest part of Neferere's mortuary temple, which was not built "until Neferefre's death". This appears to suggest that Shepseskare ruled after—rather than before—Neferefre.
Verner's second argument concerns the alignment of pyramids of Sahure, Neferirkare Kakai and Neferefre: they form a line pointing to Heliopolis, just as the three pyramids of Giza do. In contrast, Shepseskare's unfinished pyramid does not fall on the line to Heliopolis, which strongly suggests that Neferefre's pyramid had already been in place when Shepseskare started his. Finally, Verner observes that Neferefre is known to have been Neferirkare's eldest son and around 20 years old when his father died so that he was in optimal position to inherit the throne. Shepseskare thus most likely took the throne after Neferefre. As Verner notes, while Shepseskare is noted as the immediate predecessor of Neferefre in the Saqqara tablet, "this slight discrepancy can ... be attributed to the oliticaldisorders of the time and its dynastic disputes."
Egyptian
''Egyptian'' describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of year ...
for "Noble is the Soul of Ra"; died 2458 BC) was an Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
ian king
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
, the fourth or fifth ruler of the Fifth Dynasty (2494–2345 BC) during the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynast ...
period. Shepseskare lived in the mid- 25th century BC and was probably the owner of an unfinished pyramid in Abusir
Abusir ( ; Egyptian ''pr wsjr'' ' "the resting place of Osiris"; ) is the name given to an ancient Egyptian archaeological pyramid complex comprising the ruins of 4 kings' pyramids dating to the Old Kingdom period, and is part of the ...
, which was abandoned after a few weeks of work in the earliest stages of its construction.
Following historical sources, Shepseskare was traditionally believed to have reigned for seven years, succeeding Neferirkare Kakai and preceding Neferefre on the throne, making him the fourth ruler of the dynasty. He is the most obscure ruler of this dynasty and the Egyptologist
Egyptology (from ''Egypt'' and Greek , ''-logia''; ) is the scientific study of ancient Egypt. The topics studied include ancient Egyptian history, language, literature, religion, architecture and art from the 5th millennium BC until the end ...
Miroslav Verner has strongly argued that Shepseskare's reign lasted only a few months at the most, after that of Neferefre. This conclusion is based upon the state and location of Shepseskare's unfinished pyramid in Abusir as well as the very small number of artefacts attributable to this king. Verner's arguments have now convinced several Egyptologists such as Darrell Baker and Erik Hornung.
Shepseskare's relations to his predecessor and successor are not known for certain. Verner has proposed that he was a son of Sahure
Sahure (also Sahura, meaning "He who is close to Ra, Re"; died 2477 BC) was a pharaoh, king of ancient Egypt and the second ruler of the Fifth dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty ( – BC). He reigned for around 13 years in the early 25th&nbs ...
and a brother to Neferirkare Kakai, who briefly seized the throne following the premature death of his predecessor and probable nephew, Neferefre. Shepseskare may himself have died unexpectedly or he may have lost the throne to another of his nephews, the future pharaoh Nyuserre Ini
Nyuserre Ini (also Niuserre Ini or Neuserre Ini; in Greek language, Greek known as Rathurês, ''Ῥαθούρης''; died 2422 BC) was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, king, the sixth ruler of the Fifth dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty during the Ol ...
. The possibility that Shepseskare was a short-lived usurper from outside the royal family cannot be totally excluded.
Attestations
Contemporaneous sources
Shepseskare was a king ofAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
, the fourth or fifth ruler of the Fifth Dynasty. Egypt was unified at the time, with its capital located at Memphis. Shepseskare is the least-known king of the Fifth Dynasty as very few artefacts dating to his reign have survived to this day. Only two cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in width, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
s of Shepseskare are known: one, made of bronze, bears Shepseskare's Horus name
The Horus name is the oldest known and used crest of ancient Egyptian rulers. It belongs to the " great five names" of an Egyptian pharaoh. However, modern Egyptologists and linguists are starting to prefer the more neutral term "serekh name". T ...
and was uncovered in the ruins of Memphis in the early 20th century. The second seal, of unknown provenance, is made of black serpentine and reads "Shepseskare beloved of the gods, Shepseskare beloved of Hathor
Hathor (, , , Meroitic language, Meroitic: ') was a major ancient Egyptian deities, goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god R ...
". Beyond these two seals the only surviving artefacts attributable to Shepseskare are five fragments of seal impressions on clay from Abusir
Abusir ( ; Egyptian ''pr wsjr'' ' "the resting place of Osiris"; ) is the name given to an ancient Egyptian archaeological pyramid complex comprising the ruins of 4 kings' pyramids dating to the Old Kingdom period, and is part of the ...
and six further fragments discovered in the mortuary temple and Sanctuary of the Knife of the Pyramid of Neferefre, also in Abusir. These fragments probably come from three different seals and were most likely placed on the doors of magazine rooms in the temple.
In 2022, a further clay seal impression of Shepseskare was uncovered in the immediate vicinity of Nyuserre's Abusir sun temple.Massimiliano Nuzzolo: ''A New Seal-impression of King Shepseskara and the Fifth Dynasty Chronology'', in ''Ägypten und Levante/Egypt and the Levant'' 34, (2024), pp. 393–418.
 Finally, there is a single scarab seal reading "Shepeskare" ic/small> that the Egyptologist Flinders Petrie attributed to Shepseskare at the end of the 19th century. Modern scholars doubt this attribution and rather believe the scarab to be a work of the much later Saite period (685–525 BC) executed in archaic style. Equally, the scarab could belong to Gemenefkhonsbak Shepeskare, an obscure kinglet of
Finally, there is a single scarab seal reading "Shepeskare" ic/small> that the Egyptologist Flinders Petrie attributed to Shepseskare at the end of the 19th century. Modern scholars doubt this attribution and rather believe the scarab to be a work of the much later Saite period (685–525 BC) executed in archaic style. Equally, the scarab could belong to Gemenefkhonsbak Shepeskare, an obscure kinglet of Tanis
Tanis ( ; ; ) or San al-Hagar (; ; ; or or ; ) is the Greek name for ancient Egyptian ''ḏꜥn.t'', an important archaeological site in the northeastern Nile Delta of ancient Egypt, Egypt, and the location of a city of the same name. Tanis ...
during the 25th Dynasty
The Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXV, alternatively 25th Dynasty or Dynasty 25), also known as the Nubian Dynasty, the Kushite Empire, the Black Pharaohs, or the Napatans, after their capital Napata, was the last dynasty of t ...
(760–656 BC).
Historical sources
The only ancient Egyptian king list mentioning Shepseskare is the Saqqara Tablet (on the 28th entry). The tablet was inscribed during the reign ofRamesses II
Ramesses II (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses) (; , , ; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of th ...
(1279–1213 BC), around 1,200 years after Shepseskare's lifetime, and records the dynastic succession Neferikare → Shepseskare → Neferkhare (a variant name of Neferefre).
Shepseskare is completely absent from another king list dating to the same period: the Abydos king list
The Abydos King List, also known as the Abydos Table or the Abydos Tablet, is a list of the names of 76 kings of ancient Egypt, found on a wall of the Temple of Seti I at Abydos, Egypt. It consists of three rows of 38 cartouches (borders enclos ...
, written during the reign of Seti I
Menmaatre Seti I (or Sethos I in Greek language, Greek) was the second pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom period, ruling or 1290 BC to 1279 BC. He was the son of Ramesses I and Sitre, and th ...
(1294–1279 BC). He is also absent from the Turin canon (reign of Ramses II), although in this case a lacuna affects the papyrus on which the list is written at the place where Shepseskare and Neferefre's names should have been. Of the two entries concerning Shepseskare and Neferefre on the king list, only one reign length is still legible and it has been variously read as one year, eleven years or one to four months. The damaged state of the papyrus also makes it impossible to decide safely whose reign length this is.
Shepseskare was also likely mentioned in the '' Aegyptiaca'', a history of Egypt written in the third century BC during the reign of Ptolemy II
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G ...
(283–246 BC) by the Egyptian priest Manetho
Manetho (; ''Manéthōn'', ''gen''.: Μανέθωνος, ''fl''. 290–260 BCE) was an Egyptian priest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom who lived in the early third century BCE, at the very beginning of the Hellenistic period. Little is certain about his ...
. No copies of the Aegyptiaca have survived to this day and it is now known only through later writings by Sextus Julius Africanus and Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
. Africanus relates that the ''Aegyptiaca'' mentioned the succession "Nefercheres → Sisires → Cheres" for the mid Fifth Dynasty. Nefercheres and Cheres are believed to be the hellenized forms for Neferirkare and Neferkhare (that is Neferefre), respectively. Thus, "Sisires" is traditionally believed to be the Greek name of Shepseskare, making Manetho's reconstruction of the Fifth Dynasty in good agreement with the Saqqara tablet. Furthermore, according to Africanus, Manetho credits Sisires with seven years of reign while other sources report Manetho's figure as nine years.
Reign
Chronological position
 Both the relative chronological position and absolute dates of Shepseskare's reign are uncertain.
The Saqqara Tablet records Shepseskare as the successor of Neferirkare Kakai and the predecessor of Neferefre, which became the traditional opinion among Egyptologists. Following discoveries in the early 1980s, the Czech Egyptologist Miroslav Verner advocates the hypothesis that Shepseskare succeeded, rather than preceded, Neferefre.
In support of this hypothesis, Verner first emphasizes the presence of several clay seal impressions bearing Shepseskare's Horus name "Sekhemkaw" (meaning "He whose apparitions are powerful") in the oldest part of Neferere's mortuary temple, which was not built "until Neferefre's death". This appears to suggest that Shepseskare ruled after—rather than before—Neferefre.
Verner's second argument concerns the alignment of pyramids of Sahure, Neferirkare Kakai and Neferefre: they form a line pointing to Heliopolis, just as the three pyramids of Giza do. In contrast, Shepseskare's unfinished pyramid does not fall on the line to Heliopolis, which strongly suggests that Neferefre's pyramid had already been in place when Shepseskare started his. Finally, Verner observes that Neferefre is known to have been Neferirkare's eldest son and around 20 years old when his father died so that he was in optimal position to inherit the throne. Shepseskare thus most likely took the throne after Neferefre. As Verner notes, while Shepseskare is noted as the immediate predecessor of Neferefre in the Saqqara tablet, "this slight discrepancy can ... be attributed to the oliticaldisorders of the time and its dynastic disputes."
Both the relative chronological position and absolute dates of Shepseskare's reign are uncertain.
The Saqqara Tablet records Shepseskare as the successor of Neferirkare Kakai and the predecessor of Neferefre, which became the traditional opinion among Egyptologists. Following discoveries in the early 1980s, the Czech Egyptologist Miroslav Verner advocates the hypothesis that Shepseskare succeeded, rather than preceded, Neferefre.
In support of this hypothesis, Verner first emphasizes the presence of several clay seal impressions bearing Shepseskare's Horus name "Sekhemkaw" (meaning "He whose apparitions are powerful") in the oldest part of Neferere's mortuary temple, which was not built "until Neferefre's death". This appears to suggest that Shepseskare ruled after—rather than before—Neferefre.
Verner's second argument concerns the alignment of pyramids of Sahure, Neferirkare Kakai and Neferefre: they form a line pointing to Heliopolis, just as the three pyramids of Giza do. In contrast, Shepseskare's unfinished pyramid does not fall on the line to Heliopolis, which strongly suggests that Neferefre's pyramid had already been in place when Shepseskare started his. Finally, Verner observes that Neferefre is known to have been Neferirkare's eldest son and around 20 years old when his father died so that he was in optimal position to inherit the throne. Shepseskare thus most likely took the throne after Neferefre. As Verner notes, while Shepseskare is noted as the immediate predecessor of Neferefre in the Saqqara tablet, "this slight discrepancy can ... be attributed to the oliticaldisorders of the time and its dynastic disputes."
Duration
In two articles published in 2000 and 2001, Verner argues that, contrary to what Manetho indicates, Shepseskare must have reigned for a couple of months at the most, a hypothesis already proposed by the French Egyptologist Nicolas Grimal in 1988. Verner's conclusion is based on the archeological record, in particular Shepseskare's intended pyramid at Abusir. Verner emphasizes that the progress of the pyramid, which is unfinished,was interrupted ndcorresponds to the work of several weeks, perhaps no more than one or two months. In fact, the place was merely leveled and the excavation of the pit for the construction of the underground funerary apartment had only commenced. Moreover, the owner of the building obviously wanted to demonstrate by his choice of place (half-way between Sahure's pyramid and the sun temple of Userkaf) his relationship to either Sahure or Userkaf. Theoretically, only two kings of the Fifth Dynasty whose pyramids had not yet been identified can be taken into consideration – Shepseskara or Menkauhor. However, according to a number of contemporaneous documents, Menkauhor ... probably completed ispyramid elsewhere, in North Saqqara or Dahshur. Shepseskara, therefore, seems to be the likelier owner of the unfinished platform for a pyramid in North Abusir. Anyway, the builder of the platform iz., Shepseskaremust have reigned for a very short time.The rediscovery in 2008 of the Headless Pyramid in
Saqqara
Saqqara ( : saqqāra ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in the markaz (county) of Badrashin in the Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for ...
and its subsequent attribution to Menkauhor Kaiu by the excavators under the direction of Zahi Hawass
Zahi Abass Hawass (; born May 28, 1947) is an Egyptians, Egyptian archaeology, archaeologist, Egyptology, Egyptologist, and former Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities (Egypt), Minister of Tourism and Antiquities, a position he held twice. He has ...
confirms Verner's attribution of the unfinished pyramid of Abusir to Shepseskare.
Unlike the other kings of the Fifth Dynasty, Shepseskare's name appears neither in the personal names of people of the time nor in the names of funerary estates. He is also absent from the titles and biographies of state officials. For example, the stela of the Fifth Dynasty official Khau-Ptah lists an uninterrupted sequence of kings whom he served under, namely Sahure, Neferirkare, Neferefre and Nyuserre. The omission of Shepseskare, be it between Neferirkare and Neferefre or between Neferefre and Nyuserre, indicates that his reign must have been very short. Since Manetho's ''Aegyptiaca'' dates to the third century BC, Khau-Ptah's contemporary account can be regarded as a more accurate indication of the political situation during the Fifth Dynasty.
Verner's arguments together with the scarcity of artefacts attributable to Shepseskare have now convinced many Egyptologists, such as Darrell Baker and Erik Hornung, that Shepseskare's reign was indeed ephemeral.
Family
In view of the scarcity of sources concerning Shepseskare, nothing is known for certain about his relation to his predecessors. He was most likely a member of the royal family, although the possibility that he was a usurper unrelated to his predecessors cannot be totally excluded. Silke Roth has proposed that Shepseskare was a son of Neferirkare Kakai and a brother of both Neferefre and Nyuserre Ini. Instead, Verner has proposed that Shepseskare was a son ofSahure
Sahure (also Sahura, meaning "He who is close to Ra, Re"; died 2477 BC) was a pharaoh, king of ancient Egypt and the second ruler of the Fifth dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty ( – BC). He reigned for around 13 years in the early 25th&nbs ...
who managed to briefly seize power after the premature death of Neferefre. This would explain the proximity of Shepseskare's unfinished pyramid to that of Sahure. Lending credence to this theory is the discovery by Verner and Tarek El Awady in 2005 of reliefs from the causeway of Sahure's pyramid complex showing him, his wife Meretnebty and their two sons Ranefer and Netjerirenre. The relief gives both sons the title of "king's eldest son", indicating that they were possibly twins. The relief further indicates that Ranefer took the throne as "Neferirkare king of Upper and Lower Egypt". Verner and Awady thus speculate that while Ranefer and his son Neferefre became kings, Netjerirenre could have attempted to seize the throne at the death of the latter. In this hypothesis Shepseskare would be the throne name of Netjerirenre. Verner had however himself written in 1997 that Shepseskare could equally be a son of Shepseskaf, last pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, or of Userkaf or Neferirkare Kakai as Roth suggested: so few are the actual evidences pertaining to the problem that all possibilities are just speculations. In yet another hypothesis, Jaromír Krejčí believes that Shepseskare was Neferefre's son.
Shepseskare's reign may have been cut short by his unexpected death or his claim to the throne could have been thwarted by Nyuserre Ini
Nyuserre Ini (also Niuserre Ini or Neuserre Ini; in Greek language, Greek known as Rathurês, ''Ῥαθούρης''; died 2422 BC) was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, king, the sixth ruler of the Fifth dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty during the Ol ...
, Neferefre's younger brother and the younger son of King Neferirkare and Queen Khentkaus II. Khentkaus II's pivotal role in Nyuserre's eventual accession to the throne might explain her high esteem in Egyptian folklore and "the additional enlargement and upgrading of her mortuary temple" by Nyuserre. Nyuserre also seemed to have been favored by powerful courtiers and officials, foremost among whom was Ptahshepses, who would become Nyuserre's son-in-law and vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a help ...
.
Building activities
Pyramid
An unfinished pyramid located in north Abusir, between the sun temple of Userkaf and the Pyramid of Sahure, is believed to belong to Shepseskare. The structure was discovered in 1980 by aCzechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
n archaeological team led by Miroslav Verner and seems to have been abandoned after no more than a few weeks or months of work. A square area of roughly was leveled and the digging of a T-shaped ditch was just started in its center. This ditch was to be left open during the pyramid construction to allow for simultaneous works on the pyramid filling and its substructures. This construction technique is common to all pyramids of the Fifth Dynasty and can directly be seen in the case of the Pyramid of Neferefre, which was also left unfinished. This technique as well as the location of the unfinished pyramid in the royal necropolis of the Fifth Dynasty indicates that it belonged in all likeliness to Shepseskare, the pyramids of the other kings of the dynasty being already known. If finished according to the established pattern, the pyramid would have reached high, similar to the Pyramid of Neferirkare.
Analyzing the fragments of clay seals bearing Shepeseskare's name, the Swiss Egyptologist Peter Kaplony has proposed that the ancient name of Shepseskare's pyramid could be reconstructed as ''Rsj-Špss-k3-Rˁ'', reading "Resj-Shespeskare" and meaning "The awakening of Shepseskare". Verner rejects this hypothesis, and he contests the reading of certain signs and their interpretation as the name of a pyramid.
Sun temple
Kaplony has proposed that Shepseskare started to build a sun temple named ''Ḥtp-jb-Rˁ'', reading "Hotepibre" and meaning "Satisfied is the heart of Ra". Although all the kings of the early to mid-Fifth Dynasty, from Userkaf to Menkauhor Kaiu, did build sun temples, Verner regards Kaplony's hypothesis as "sheer speculation" since it is based on the tentative reconstruction of a single clay seal. Verner first argues that this seal is not inscribed with Shepseskare's name but rather bears traces of a Horus name which could equally well be that ofDjedkare Isesi
Djedkare Isesi (known in Greek as Tancheres; died 2375 BC) was a king, the eighth and penultimate ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt in the late 25th century to mid-24th century BC, during the Old Kingdom. Djedkare succeeded Menkauhor Kaiu ...
. Second, Verner notes that the name of a sun temple is rarely found with that of the king who built it: more often it is found with the name of another king during whose reign the seal was made. Finally, he doubts that the sign reading ''Ḥtp'', "Hotep", is really part of the name of a sun temple. Instead, he believes it is more probable that the seal either refers to the sun temple of Neferirkare, named ''St-jb-Rˁ.w'', that is "Setibraw"; or to that of Nyuserre, which was called ''Šsp-jb-Rˁ'', "Shesepibre".
Mortuary temple of Neferefre
It is possible that Shepseskare continued the construction of the funerary complex of his predecessor. As Neferefre had died after a short reign, his pyramid complex was far from finished and neither the burial chamber nor the mortuary temple had been built. The planned pyramid was thus hastily changed into a square mastaba representing a stylized primeval hill and the accompanying mortuary temple was completed during the reign of Nyuserre. The presence of seals of Shepseskare in the oldest part of Neferefre's mortuary temple could indicate that the former also undertook construction works there. The evidence for such works is uncertain: these seals could have been placed on boxes which were later moved into the magazine rooms of the temple. For example, seals of Userkaf, Sahure and Neferirkare Kakai were also found in the temple, while these three pharaohs died before Neferefre's reign.Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Shepseskare 25th-century BC pharaohs Pharaohs of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt 3rd-millennium BC births 25th-century BC deaths