Sheep Farming In Namibia (2017) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are
 Another trait unique to domestic sheep as compared to wild ovines is their wide variation in color. Wild sheep are largely variations of brown hues, and variation within species is extremely limited. Colors of domestic sheep range from pure white to dark chocolate brown, and even spotted or
Another trait unique to domestic sheep as compared to wild ovines is their wide variation in color. Wild sheep are largely variations of brown hues, and variation within species is extremely limited. Colors of domestic sheep range from pure white to dark chocolate brown, and even spotted or  Depending on breed, sheep show a range of heights and weights. Their rate of growth and mature weight is a
Depending on breed, sheep show a range of heights and weights. Their rate of growth and mature weight is a  Sheep have good hearing, and are sensitive to noise when being handled.Smith et al., p. 5. Sheep have horizontal slit-shaped pupils, with excellent
Sheep have good hearing, and are sensitive to noise when being handled.Smith et al., p. 5. Sheep have horizontal slit-shaped pupils, with excellent
 The domestic sheep is a multi-purpose animal, and the more than 200
The domestic sheep is a multi-purpose animal, and the more than 200  Breeds are often categorized by the type of their wool. Fine wool breeds are those that have wool of great crimp and density, which are preferred for textiles. Most of these were derived from
Breeds are often categorized by the type of their wool. Fine wool breeds are those that have wool of great crimp and density, which are preferred for textiles. Most of these were derived from
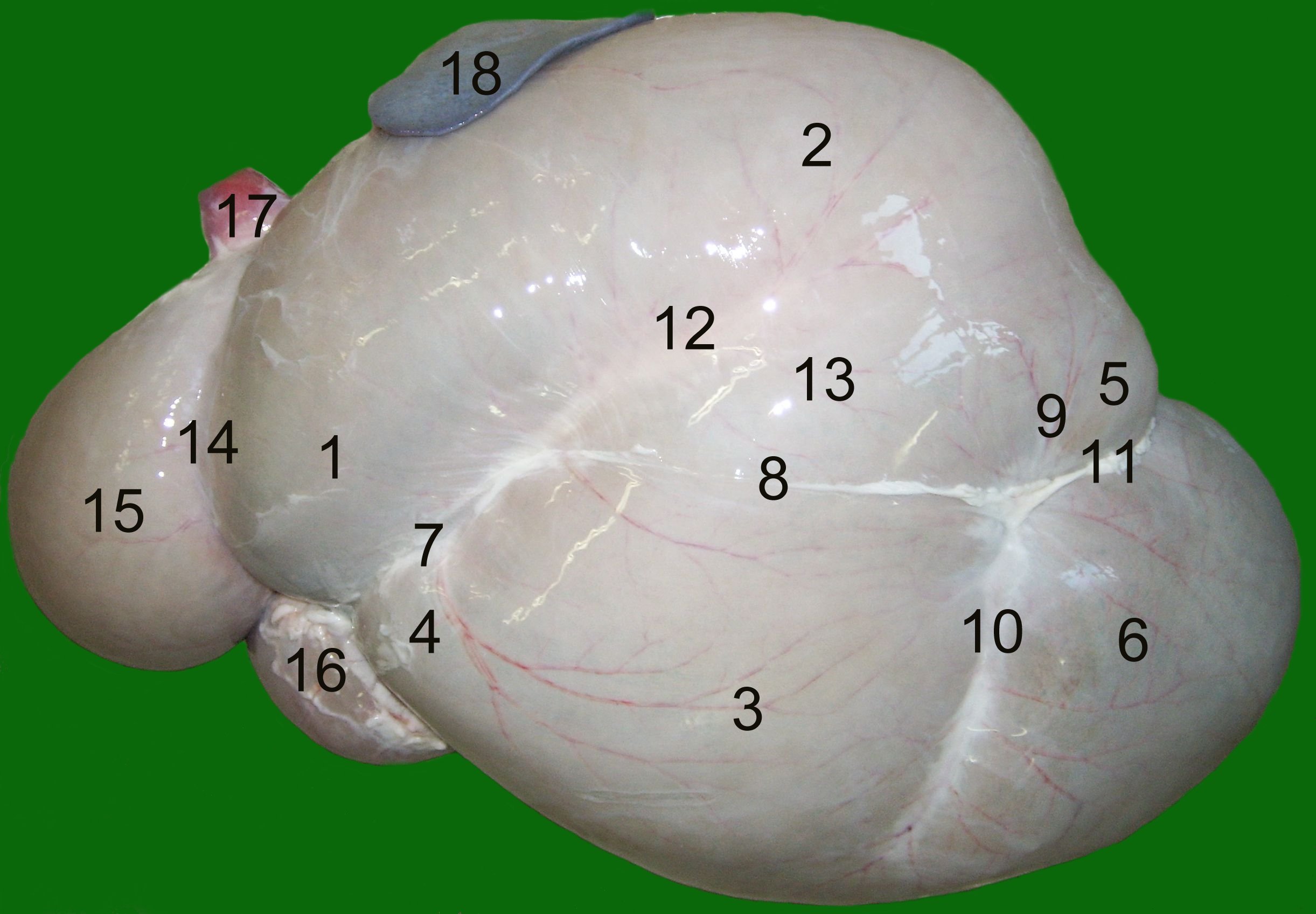 Like all ruminants, sheep have a complex digestive system composed of four chambers, allowing them to break down
Like all ruminants, sheep have a complex digestive system composed of four chambers, allowing them to break down 
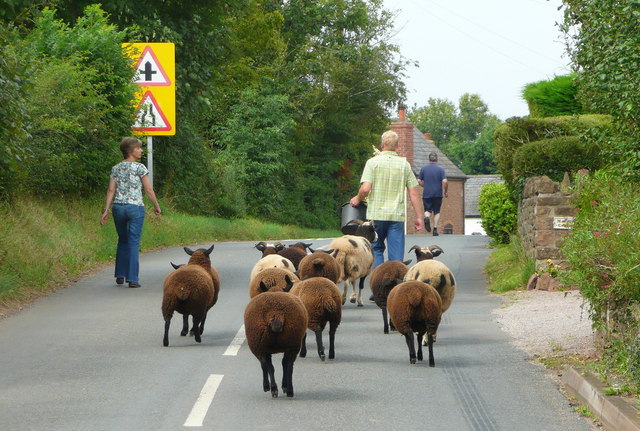
 Farmers exploit flocking behavior to keep sheep together on unfenced pastures such as hill farming, and to move them more easily. For this purpose shepherds may use
Farmers exploit flocking behavior to keep sheep together on unfenced pastures such as hill farming, and to move them more easily. For this purpose shepherds may use

 In sheep breeds lacking facial wool, the visual field is wide. In 10 sheep (Cambridge, Lleyn and Welsh Mountain breeds, which lack facial wool), the visual field ranged from 298° to 325°, averaging 313.1°, with binocular overlap ranging from 44.5° to 74°, averaging 61.7°.Piggins, D. and C. J. C. Phillips. 1996. The eye of the domesticated sheep and its implications for vision. Animal Science. 62: 301–308. In some breeds, unshorn facial wool can limit the visual field; in some individuals, this may be enough to cause "wool blindness". In 60 Merinos, visual fields ranged from 219.1° to 303.0°, averaging 269.9°, and the binocular field ranged from 8.9° to 77.7°, averaging 47.5°; 36% of the measurements were limited by wool,Hutson, G. D. 1980. Visual field, restricted vision and sheep movement in laneways. Appl. Anim. Ethol. 6: 175–187. although photographs of the experiments indicate that only limited facial wool regrowth had occurred since shearing. In addition to facial wool (in some breeds), visual field limitations can include ears and (in some breeds) horns, so the visual field can be extended by tilting the head. Sheep eyes exhibit very low
In sheep breeds lacking facial wool, the visual field is wide. In 10 sheep (Cambridge, Lleyn and Welsh Mountain breeds, which lack facial wool), the visual field ranged from 298° to 325°, averaging 313.1°, with binocular overlap ranging from 44.5° to 74°, averaging 61.7°.Piggins, D. and C. J. C. Phillips. 1996. The eye of the domesticated sheep and its implications for vision. Animal Science. 62: 301–308. In some breeds, unshorn facial wool can limit the visual field; in some individuals, this may be enough to cause "wool blindness". In 60 Merinos, visual fields ranged from 219.1° to 303.0°, averaging 269.9°, and the binocular field ranged from 8.9° to 77.7°, averaging 47.5°; 36% of the measurements were limited by wool,Hutson, G. D. 1980. Visual field, restricted vision and sheep movement in laneways. Appl. Anim. Ethol. 6: 175–187. although photographs of the experiments indicate that only limited facial wool regrowth had occurred since shearing. In addition to facial wool (in some breeds), visual field limitations can include ears and (in some breeds) horns, so the visual field can be extended by tilting the head. Sheep eyes exhibit very low
 Sheep follow a similar
Sheep follow a similar  Ovine
Ovine
 Sheep may fall victim to poisons,
Sheep may fall victim to poisons,  Common forms of preventive medication for sheep are
Common forms of preventive medication for sheep are
 Other than parasites and disease,
Other than parasites and disease,
 Sheep are an important part of the global agricultural economy. However, their once vital status has been largely replaced by other livestock species, especially the pig, chicken, and cow. China, Australia,
Sheep are an important part of the global agricultural economy. However, their once vital status has been largely replaced by other livestock species, especially the pig, chicken, and cow. China, Australia,  Domestic sheep provide a wide array of raw materials. Wool was one of the first textiles, although in the late 20th century wool prices began to fall dramatically as the result of the popularity and cheap prices for
Domestic sheep provide a wide array of raw materials. Wool was one of the first textiles, although in the late 20th century wool prices began to fall dramatically as the result of the popularity and cheap prices for
 Sheep meat and milk were one of the earliest staple proteins consumed by human civilization after the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture. Sheep meat prepared for food is known as either mutton or lamb, and approximately 540 million sheep are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. "Mutton" is derived from the
Sheep meat and milk were one of the earliest staple proteins consumed by human civilization after the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture. Sheep meat prepared for food is known as either mutton or lamb, and approximately 540 million sheep are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. "Mutton" is derived from the
 Sheep are generally too large and reproduce too slowly to make ideal research subjects, and thus are not a common model organism. They have, however, played an influential role in some fields of science. In particular, the
Sheep are generally too large and reproduce too slowly to make ideal research subjects, and thus are not a common model organism. They have, however, played an influential role in some fields of science. In particular, the
 Sheep have had a strong presence in many cultures, especially in areas where they form the most common type of livestock. In the English language, to call someone a sheep or ovine may allude that they are timid and easily led. In contradiction to this image, male sheep are often used as symbols of virility and power; the logos of the
Sheep have had a strong presence in many cultures, especially in areas where they form the most common type of livestock. In the English language, to call someone a sheep or ovine may allude that they are timid and easily led. In contradiction to this image, male sheep are often used as symbols of virility and power; the logos of the
 In British heraldry, sheep appear in the form of rams, sheep proper and lambs. These are distinguished by the ram being depicted with horns and a tail, the sheep with neither and the lamb with its tail only. A further variant of the lamb, termed the Pascal Lamb (heraldry), Paschal lamb, is depicted as carrying a Christian cross and with a Halo (religious iconography), halo over its head. Rams' heads, portrayed without a neck and facing the viewer, are also found in British armories. The fleece, depicted as an entire sheepskin carried by a ring around its midsection, originally became known through its use in the arms of the Order of the Golden Fleece and was later adopted by towns and individuals with connections to the wool industry.Arthur Fox-Davies, ''A Complete Guide to Heraldry'', T.C. and E.C. Jack, London, 1909, 211-213, https://archive.org/details/completeguidetoh00foxduoft. A sheep on a blue field is depicted on the Coat of arms of Denmark, greater/royal arms of the king of Denmark to represent the Faroe Islands. In 2004 a modernized arms has been adopted by the Faroe Islands, which based on a 15th century coat of arms.
In British heraldry, sheep appear in the form of rams, sheep proper and lambs. These are distinguished by the ram being depicted with horns and a tail, the sheep with neither and the lamb with its tail only. A further variant of the lamb, termed the Pascal Lamb (heraldry), Paschal lamb, is depicted as carrying a Christian cross and with a Halo (religious iconography), halo over its head. Rams' heads, portrayed without a neck and facing the viewer, are also found in British armories. The fleece, depicted as an entire sheepskin carried by a ring around its midsection, originally became known through its use in the arms of the Order of the Golden Fleece and was later adopted by towns and individuals with connections to the wool industry.Arthur Fox-Davies, ''A Complete Guide to Heraldry'', T.C. and E.C. Jack, London, 1909, 211-213, https://archive.org/details/completeguidetoh00foxduoft. A sheep on a blue field is depicted on the Coat of arms of Denmark, greater/royal arms of the king of Denmark to represent the Faroe Islands. In 2004 a modernized arms has been adopted by the Faroe Islands, which based on a 15th century coat of arms.
 In antiquity, symbolism involving sheep cropped up in religions in the ancient Near East, the Mideast, and the Mediterranean area: Çatalhöyük, ancient Egyptian religion, the Cana'anite and Phoenician tradition, Judaism, Greek mythology, Greek religion, and others. Religious symbolism and ritual involving sheep began with some of the first known faiths: Skulls of rams (along with bulls) occupied central placement in shrines at the Çatalhöyük settlement in 8,000 BCE. In Ancient Egyptian religion, the ram was the symbol of several gods: Khnum, Heryshaf and Amun (in his incarnation as a god of fertility). Other deities occasionally shown with ram features include the goddess Ishtar, the Phoenician god Baal-Hamon, and the Babylonian god Ea-Oannes. In Madagascar, sheep were not eaten as they were believed to be incarnations of the souls of ancestors.
There are many ancient Greek references to sheep: that of Chrysomallos, the golden-fleeced ram, continuing to be told through into the modern era. Astrology, Astrologically, Aries (astrology), Aries, the ram, is the first sign of the classical Greek zodiac, and the sheep is the eighth of the twelve animals associated with the 12-year cycle of in the Chinese zodiac, related to the Chinese calendar. In Mongolia, shagai are an ancient form of dice made from the cuboid bones of sheep that are often used for fortunetelling purposes.
In antiquity, symbolism involving sheep cropped up in religions in the ancient Near East, the Mideast, and the Mediterranean area: Çatalhöyük, ancient Egyptian religion, the Cana'anite and Phoenician tradition, Judaism, Greek mythology, Greek religion, and others. Religious symbolism and ritual involving sheep began with some of the first known faiths: Skulls of rams (along with bulls) occupied central placement in shrines at the Çatalhöyük settlement in 8,000 BCE. In Ancient Egyptian religion, the ram was the symbol of several gods: Khnum, Heryshaf and Amun (in his incarnation as a god of fertility). Other deities occasionally shown with ram features include the goddess Ishtar, the Phoenician god Baal-Hamon, and the Babylonian god Ea-Oannes. In Madagascar, sheep were not eaten as they were believed to be incarnations of the souls of ancestors.
There are many ancient Greek references to sheep: that of Chrysomallos, the golden-fleeced ram, continuing to be told through into the modern era. Astrology, Astrologically, Aries (astrology), Aries, the ram, is the first sign of the classical Greek zodiac, and the sheep is the eighth of the twelve animals associated with the 12-year cycle of in the Chinese zodiac, related to the Chinese calendar. In Mongolia, shagai are an ancient form of dice made from the cuboid bones of sheep that are often used for fortunetelling purposes.
 Sheep play an important role in all the Abrahamic faiths; Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Moses, King David and the Islamic prophet Muhammad were all shepherds. According to the Biblical story of the Binding of Isaac, a ram is sacrificed as a substitute for Isaac after an angel stays Abraham's hand (in the Islamic tradition, Abraham was about to sacrifice Ishmael). Eid al-Adha is a major annual festival in Islam in which sheep (or other animals) are sacrificed in remembrance of this act. Sheep are occasionally sacrificed to commemorate important secular events in Islamic cultures. Greeks and Romans sacrificed sheep regularly in religious practice, and Judaism once sacrificed sheep as a Korban (sacrifice), such as the Korban Pesach, Passover lamb. Ovine symbols—such as the ceremonial blowing of a shofar—still find a presence in modern Judaic traditions.
Collectively, followers of Christianity are often referred to as a flock, with Christ as the The Good Shepherd (Christianity), Good Shepherd, and sheep are an element in the Christian iconography of the Nativity of Jesus in art, birth of Jesus. Some Christian saints are considered Patron saints of occupations and activities, patrons of shepherds, and even of sheep themselves. Christ is also portrayed as the Sacrificial lamb of God (''Agnus Dei'') and Easter celebrations in
Sheep play an important role in all the Abrahamic faiths; Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Moses, King David and the Islamic prophet Muhammad were all shepherds. According to the Biblical story of the Binding of Isaac, a ram is sacrificed as a substitute for Isaac after an angel stays Abraham's hand (in the Islamic tradition, Abraham was about to sacrifice Ishmael). Eid al-Adha is a major annual festival in Islam in which sheep (or other animals) are sacrificed in remembrance of this act. Sheep are occasionally sacrificed to commemorate important secular events in Islamic cultures. Greeks and Romans sacrificed sheep regularly in religious practice, and Judaism once sacrificed sheep as a Korban (sacrifice), such as the Korban Pesach, Passover lamb. Ovine symbols—such as the ceremonial blowing of a shofar—still find a presence in modern Judaic traditions.
Collectively, followers of Christianity are often referred to as a flock, with Christ as the The Good Shepherd (Christianity), Good Shepherd, and sheep are an element in the Christian iconography of the Nativity of Jesus in art, birth of Jesus. Some Christian saints are considered Patron saints of occupations and activities, patrons of shepherds, and even of sheep themselves. Christ is also portrayed as the Sacrificial lamb of God (''Agnus Dei'') and Easter celebrations in 
American Sheep Industry
(Queensland)
National Sheep Association
(UK)
New Zealand Sheepbreeders Association
all articles available free online * View th
sheep genome
in Ensembl * {{Featured article Articles containing video clips Cosmopolitan mammals Herbivorous mammals Livestock Mammals described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Sheep,
domesticated
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. A ...
, ruminant
Ruminants ( suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. Th ...
mammals typically kept as livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to anima ...
. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis
''Ovis'' is a genus of mammals, part of the Caprinae subfamily of the ruminant family Bovidae. Its seven highly sociable species are known as sheep or ovines. Domestic sheep are members of the genus, and are thought to be descended from the w ...
'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poste ...
, the even-toed ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing post ...
s. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses phar ...
male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''.
Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon
The mouflon (''Ovis gmelini'') is a wild sheep native to Cyprus, the Caspian region from eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran.
It is thought to be the ancestor of all modern domestic sheep breeds.
Taxonomy
''Ovis gmelini'' was the sc ...
of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulati ...
. A sheep's wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
...
is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing
Sheep shearing is the process by which the woollen fleece of a sheep is cut off. The person who removes the sheep's wool is called a '' shearer''. Typically each adult sheep is shorn once each year (a sheep may be said to have been "shorn" or ...
. In Commonwealth countries, ovine
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated ...
meat is called lamb
Lamb or The Lamb may refer to:
* A young sheep
* Lamb and mutton, the meat of sheep
Arts and media Film, television, and theatre
* ''The Lamb'' (1915 film), a silent film starring Douglas Fairbanks Sr. in his screen debut
* ''The Lamb'' (1918 ...
when from younger animals and mutton
Lamb, hogget, and mutton, generically sheep meat, are the meat of domestic sheep, ''Ovis aries''. A sheep in its first year is a lamb and its meat is also lamb. The meat from sheep in their second year is hogget. Older sheep meat is mutton. Ge ...
when from older ones; in the United States, meat from both older and younger animals is usually called lamb. Sheep continue to be important for wool and meat today, and are also occasionally raised for pelts
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanke ...
, as dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting or processing (or both) of animal milk – mostly from cows or buffaloes, but also from goats, sheep, horses, or camels – for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on ...
animals, or as model organisms for science.
Sheep husbandry
Sheep farming or sheep husbandry is the raising and breeding of domestic sheep. It is a branch of animal husbandry. Sheep are raised principally for their meat (lamb and mutton), milk (sheep's milk), and fiber (wool). They also yield sheepskin ...
is practised throughout the majority of the inhabited world, and has been fundamental to many civilizations. In the modern era, Australia, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
, the southern and central South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
n nations, and the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles (O ...
are most closely associated with sheep production.
There is a large lexicon of unique terms for sheep husbandry which vary considerably by region and dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that ...
. Use of the word ''sheep'' began in Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
as a derivation of the Old English word '; it is both the singular and plural name for the animal. A group of sheep is called a flock. Many other specific terms for the various life stages of sheep exist, generally related to lambing, shearing, and age.
Being a key animal in the history of farming, sheep have a deeply entrenched place in human culture, and find representation in much modern language and symbology
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
. As livestock, sheep are most often associated with pastoral
A pastoral lifestyle is that of shepherds herding livestock around open areas of land according to seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. It lends its name to a genre of literature, art, and music ( pastorale) that de ...
, Arcadian
Arcadian may refer to:
* Arcadian, someone or something from, or related to:
** Arcadia (region), the ancient Greek region
** Arcadia (regional unit), the region in modern Greece
** Accademia degli Arcadi, the Italian literary academy founded in ...
imagery. Sheep figure in many mythologies
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), ...
—such as the Golden Fleece
In Greek mythology, the Golden Fleece ( el, Χρυσόμαλλον δέρας, ''Chrysómallon déras'') is the fleece of the golden-woolled,, ''Khrusómallos''. winged ram, Chrysomallos, that rescued Phrixus and brought him to Colchis, wh ...
—and major religions, especially the Abrahamic
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
traditions. In both ancient and modern religious ritual, sheep are used as sacrificial animals.
History
The exact line of descent from wild ancestors to domestic sheep is unclear. The most common hypothesis states that ''Ovis aries'' is descended from the Asiatic (''O. gmelini'') species ofmouflon
The mouflon (''Ovis gmelini'') is a wild sheep native to Cyprus, the Caspian region from eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran.
It is thought to be the ancestor of all modern domestic sheep breeds.
Taxonomy
''Ovis gmelini'' was the sc ...
; the European mouflon
The European mouflon (''Ovis aries musimon'') is a feral subspecies of the primitive domestic sheep. It was originally found only on the Mediterranean islands of Corsica and Sardinia, but has since been introduced into many other regions ...
(''Ovis aries musimon'') is a direct descendant of this population. Sheep were among the first animals to be domesticated by humankind (although the domestication of dogs probably took place 10 to 20 thousand years earlier); the domestication date is estimated to fall between 11,000 and 9,000 B.C in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
Ensminger, p. 4Weaver, pp. 11–14Simmons & Ekarius, p. 2 and possibly around 7,000 B.C. in Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh (; ur, ) is a Neolithic archaeological site (dated ) situated on the Kacchi Plain of Balochistan in Pakistan. It is located near the Bolan Pass, to the west of the Indus River and between the modern-day Pakistani cities of Quetta ...
in the Indus Valley. The rearing of sheep for secondary products, and the resulting breed development, began in either southwest Asia or western Europe. Initially, sheep were kept solely for meat, milk and skins. Archaeological evidence from statuary
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size; a sculpture t ...
found at sites in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
suggests that selection for woolly sheep may have begun around 6000 BC,Ensminger, p. 5Weaver, p. 11 and the earliest woven wool garments have been dated to two to three thousand years later.Smith et al., p. 8
Sheep husbandry spread quickly in Europe. Excavations show that in about 6000 BC, during the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
period of prehistory, the Castelnovien people, living around Châteauneuf-les-Martigues
Châteauneuf-les-Martigues (; oc, Castèunòu dau Martegue) is a commune in the Bouches-du-Rhône department in southern France. The La Mède refinery is nearby and has been in operation since 1935.
Population
See also
* Étang de Berre
* ...
near present-day Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Fran ...
in the south of France, were among the first in Europe to keep domestic sheep. Practically from its inception, ancient Greek civilization
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cultu ...
relied on sheep as primary livestock, and were even said to name individual animals.Weaver, p. 13 Ancient Romans
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
kept sheep on a wide scale, and were an important agent in the spread of sheep raising. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
, in his Natural History (''Naturalis Historia''), speaks at length about sheep and wool. European colonists spread the practice to the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
from 1493 onwards.EnsmingerWeaver, p. 12
Characteristics
Domestic sheep are relatively small ruminants, usually with a crimped hair called wool and often with horns forming alateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Helices
Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are:neotenic
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compare ...
as a result of selective breeding by humans. A few primitive breeds of sheep retain some of the characteristics of their wild cousins, such as short tails. Depending on breed, domestic sheep may have no horns at all (i.e. polled), or horns in both sexes, or in males only. Most horned breeds have a single pair, but a few breeds may have several. Another trait unique to domestic sheep as compared to wild ovines is their wide variation in color. Wild sheep are largely variations of brown hues, and variation within species is extremely limited. Colors of domestic sheep range from pure white to dark chocolate brown, and even spotted or
Another trait unique to domestic sheep as compared to wild ovines is their wide variation in color. Wild sheep are largely variations of brown hues, and variation within species is extremely limited. Colors of domestic sheep range from pure white to dark chocolate brown, and even spotted or piebald
A piebald or pied animal is one that has a pattern of unpigmented spots (white) on a pigmented background of hair, feathers or scales. Thus a piebald black and white dog is a black dog with white spots. The animal's skin under the white backgro ...
. Selection for easily dyeable white fleeces began early in sheep domestication, and as white wool is a dominant trait it spread quickly. However, colored sheep do appear in many modern breeds, and may even appear as a recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and ...
trait in white flocks. While white wool is desirable for large commercial markets, there is a niche market for colored fleeces, mostly for handspinning.Weaver The nature of the fleece varies widely among the breeds, from dense and highly crimped, to long and hairlike. There is variation of wool type and quality even among members of the same flock, so wool classing
Wool classing is the production of uniform, predictable, low-risk lines of wool, carried out by examining the characteristics of the wool in its raw state and classing (grading) it accordingly. Wool classing is done by a wool classer.
Basis for ...
is a step in the commercial processing of the fibre.
 Depending on breed, sheep show a range of heights and weights. Their rate of growth and mature weight is a
Depending on breed, sheep show a range of heights and weights. Their rate of growth and mature weight is a heritable
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inf ...
trait that is often selected for in breeding. Ewes typically weigh between , and rams between . When all deciduous teeth have erupted, the sheep has 20 teeth. Mature sheep have 32 teeth. As with other ruminants, the front teeth in the lower jaw bite against a hard, toothless pad in the upper jaw. These are used to pick off vegetation, then the rear teeth grind it before it is swallowed. There are eight lower front teeth in ruminants, but there is some disagreement as to whether these are eight incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, w ...
s, or six incisors and two incisor-shaped canines. This means that the dental formula
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolog ...
for sheep is either or There is a large diastema
A diastema (plural diastemata, from Greek διάστημα, space) is a space or gap between two teeth. Many species of mammals have diastemata as a normal feature, most commonly between the incisors and molars. More colloquially, the condition ...
between the incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, w ...
s and the molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
.
In the first few years of life one can calculate the age of sheep from their front teeth, as a pair of milk teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 255 are the first set of teeth in th ...
is replaced by larger adult teeth each year, the full set of eight adult front teeth being complete at about four years of age. The front teeth are then gradually lost as sheep age, making it harder for them to feed and hindering the health and productivity of the animal. For this reason, domestic sheep on normal pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or s ...
begin to slowly decline from four years on, and the life expectancy of a sheep is 10 to 12 years, though some sheep may live as long as 20 years.Smith et al.  Sheep have good hearing, and are sensitive to noise when being handled.Smith et al., p. 5. Sheep have horizontal slit-shaped pupils, with excellent
Sheep have good hearing, and are sensitive to noise when being handled.Smith et al., p. 5. Sheep have horizontal slit-shaped pupils, with excellent peripheral vision
Peripheral vision, or ''indirect vision'', is vision as it occurs outside the point of fixation, i.e. away from the center of gaze or, when viewed at large angles, in (or out of) the "corner of one's eye". The vast majority of the area in the ...
; with visual fields of about 270° to 320°, sheep can see behind themselves without turning their heads. Many breeds have only short hair on the face, and some have facial wool (if any) confined to the poll and or the area of the mandibular angle; the wide angles of peripheral vision apply to these breeds. A few breeds tend to have considerable wool on the face; for some individuals of these breeds, peripheral vision may be greatly reduced by "wool blindness", unless recently shorn about the face. Sheep have poor depth perception
Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions. Depth perception happens primarily due to stereopsi ...
; shadows and dips in the ground may cause sheep to baulk. In general, sheep have a tendency to move out of the dark and into well-lit areas, and prefer to move uphill when disturbed. Sheep also have an excellent sense of smell, and, like all species of their genus, have scent gland
Scent gland are exocrine glands found in most mammals. They produce semi-viscous secretions which contain pheromones and other semiochemical compounds. These odor-messengers indicate information such as status, territorial marking, mood, and s ...
s just in front of the eyes, and interdigitally on the feet. The purpose of these glands is uncertain, but those on the face may be used in breeding behaviors. The foot glands might also be related to reproduction, but alternative functions, such as secretion of a waste product or a scent marker to help lost sheep find their flock, have also been proposed.Smith et al., p. 4.
Comparison with goats
Sheep andgoat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of ...
s are closely related: both are in the subfamily Caprinae
The subfamily Caprinae, also sometimes referred to as the tribe Caprini, is part of the ruminant family Bovidae, and consists of mostly medium-sized bovids. A member of this subfamily is called a caprine, or, more informally, a goat-antelope ( ...
. However, they are separate species, so hybrids rarely occur and are always infertile. A hybrid of a ewe and a buck (a male goat) is called a sheep-goat hybrid, known as ''geep''. Visual differences between sheep and goats include the beard of goats and divided upper lip of sheep. Sheep tails also hang down, even when short or docked, while the short tails of goats are held upwards. Also, sheep breeds are often naturally polled (either in both sexes or just in the female), while naturally polled goats are rare (though many are polled artificially). Males of the two species differ in that buck goats acquire a unique and strong odor during the rut, whereas rams do not.
Breeds
 The domestic sheep is a multi-purpose animal, and the more than 200
The domestic sheep is a multi-purpose animal, and the more than 200 breeds
A breed is a specific group of domestic animals having homogeneous appearance (phenotype), homogeneous behavior, and/or other characteristics that distinguish it from other organisms of the same species. In literature, there exist several slig ...
now in existence were created to serve these diverse purposes. Some sources give a count of a thousand or more breeds, but these numbers cannot be verified, according to some sources. However, several hundred breeds of sheep have been identified by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
(FAO), with the estimated number varying somewhat from time to time: e.g. 863 breeds as of 1993, 1314 breeds as of 1995 and 1229 breeds as of 2006.FAO. 2007. State of the world's animal genetic resources for food and agriculture (These numbers exclude extinct breeds, which are also tallied by the FAO.) For the purpose of such tallies, the FAO definition of a breed is "either a subspecific group of domestic livestock with definable and identifiable external characteristics that enable it to be separated by visual appraisal from other similarly defined groups within the same species or a group for which geographical and/or cultural separation from phenotypically similar groups has led to acceptance of its separate identity." Almost all sheep are classified as being best suited to furnishing a certain product: wool, meat, milk, hides, or a combination in a dual-purpose breed. Other features used when classifying sheep include face color (generally white or black), tail length, presence or lack of horns, and the topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary s ...
for which the breed has been developed. This last point is especially stressed in the UK, where breeds are described as either upland (hill or mountain) or lowland breeds. A sheep may also be of a fat-tailed type, which is a dual-purpose sheep common in Africa and Asia with larger deposits of fat within and around its tail.
Merino
The Merino is a breed or group of breeds of domestic sheep, characterised by very fine soft wool. It was established in Spain near the end of the Middle Ages, and was for several centuries kept as a strict Spanish monopoly; exports of the bree ...
sheep, and the breed continues to dominate the world sheep industry. Downs breeds have wool between the extremes, and are typically fast-growing meat and ram breeds with dark faces.D’Arcy, J.B., Sheep Management & Wool Technology, NSW University Press, 1986, Some major medium wool breeds, such as the Corriedale
The Corriedale is a New Zealand breed of sheep. It was bred from about 1882 in the South Island by James Little, who cross-bred Merino and Lincoln Longwool sheep. The breed was officially recognised in 1911. It has been exported to Australia a ...
, are dual-purpose crosses of long and fine-wooled breeds and were created for high-production commercial flocks. Long wool breeds are the largest of sheep, with long wool and a slow rate of growth. Long wool sheep are most valued for crossbreeding to improve the attributes of other sheep types. For example: the American Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region in ...
breed was developed by crossing Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Linco ...
rams (a long wool breed) with fine-wooled Rambouillet
Rambouillet (, , ) is a subprefecture of the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region of France. It is located beyond the outskirts of Paris, southwest of its centre. In 2018, the commune had a population of 26,933.
Rambouillet l ...
ewes.
Coarse or carpet
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, nylon, or polyester hav ...
wool sheep are those with a medium to long length wool of characteristic coarseness. Breeds traditionally used for carpet wool show great variability, but the chief requirement is a wool that will not break down under heavy use (as would that of the finer breeds). As the demand for carpet-quality wool declines, some breeders of this type of sheep are attempting to use a few of these traditional breeds for alternative purposes. Others have always been primarily meat-class sheep.Wooster
A minor class of sheep are the dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting or processing (or both) of animal milk – mostly from cows or buffaloes, but also from goats, sheep, horses, or camels – for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on ...
breeds. Dual-purpose breeds that may primarily be meat or wool sheep are often used secondarily as milking animals, but there are a few breeds that are predominantly used for milking. These sheep produce a higher quantity of milk and have slightly longer lactation curves. In the quality of their milk, the fat and protein content percentages of dairy sheep vary from non-dairy breeds, but lactose content does not.Pulina et al. p. 2.
A last group of sheep breeds is that of fur or hair sheep, which do not grow wool at all. Hair sheep are similar to the early domesticated sheep kept before woolly breeds were developed, and are raised for meat and pelts. Some modern breeds of hair sheep, such as the Dorper
The Dorper is a South African breed of domestic sheep developed by crossing Dorset Horn and the Blackhead Persian sheep. The breed was created through the efforts of the South African Department of Agriculture to breed a meat
Meat is ...
, result from crosses between wool and hair breeds. For meat and hide producers, hair sheep are cheaper to keep, as they do not need shearing. Hair sheep are also more resistant to parasites and hot weather.
With the modern rise of corporate agribusiness
Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy,
in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise.
The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit w ...
and the decline of localized family farm
A family farm is generally understood to be a farm owned and/or operated by a family; it is sometimes considered to be an Estate (land), estate passed down by inheritance.
Although a recurring conceptual model, conceptual and archetype, archet ...
s, many breeds of sheep are in danger of extinction. The Rare Breeds Survival Trust
The Rare Breeds Survival Trust is a conservation charity whose purpose is to secure the continued existence and viability of the native farm animal genetic resources (FAnGR) of the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1973 by Joe Henson to pres ...
of the UK lists 22 native breeds as having only 3,000 registered animals (each), and The Livestock Conservancy
The Livestock Conservancy, formerly known as the American Livestock Breeds Conservancy (ALBC) and prior to that, the American Minor Breeds Conservancy, is a nonprofit organization focused on preserving and promoting rare breeds, also known as "h ...
lists 14 as either "critical" or "threatened". Preferences for breeds with uniform characteristics and fast growth have pushed heritage (or heirloom) breeds to the margins of the sheep industry. Those that remain are maintained through the efforts of conservation organizations, breed registries, and individual farmers dedicated to their preservation.
Diet
Sheep areherbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
mammals. Most breeds prefer to graze on grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in law ...
and other short roughage
Dietary fiber (in British English fibre) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by the ...
, avoiding the taller woody parts of plants that goats readily consume.Pugh, pp. 19. Both sheep and goats use their lip
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be ...
s and tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste bu ...
s to select parts of the plant that are easier to digest or higher in nutrition. Sheep, however, graze well in monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monoculture is widely used in intensive farming and in organic farming: both a 1,000-hectare/acre cornfield and a 10-ha/acre field of organic kale a ...
pastures where most goats fare poorly.
 Like all ruminants, sheep have a complex digestive system composed of four chambers, allowing them to break down
Like all ruminants, sheep have a complex digestive system composed of four chambers, allowing them to break down cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
from stems, leaves, and seed hulls into simpler carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s. When sheep graze, vegetation is chewed into a mass called a bolus, which is then passed into the rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allow ...
, via the reticulum
Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle—a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions. The constellation is best viewed b ...
. The rumen is a 19- to 38-liter (5 to 10 gallon) organ in which feed is fermented
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food p ...
.Simmons & Ekarius, p. 146. The fermenting organisms include bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. (Other important rumen organisms include some archaea, which produce methane from carbon dioxide.) The bolus is periodically regurgitated back to the mouth as cud
Cud is a portion of food that returns from a ruminant's stomach to the mouth to be chewed for the second time. More precisely, it is a bolus of semi-degraded food regurgitated from the reticulorumen of a ruminant. Cud is produced during the phy ...
for additional chewing and salivation
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can b ...
. After fermentation in the rumen, feed passes into the reticulum
Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle—a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions. The constellation is best viewed b ...
and the omasum
The omasum, also known as the bible, the fardel, the manyplies and the psalterium, is the third compartment of the stomach in ruminants. The omasum comes after the rumen and reticulum and before the abomasum. Different ruminants have different oma ...
; special feeds such as grains may bypass the rumen altogether. After the first three chambers, food moves into the abomasum
The abomasum, also known as the maw,The Cham ...
for final digestion before processing by the intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
s. The abomasum is the only one of the four chambers analogous to the human stomach, and is sometimes called the "true stomach".
Other than forage, the other staple feed for sheep is hay
Hay is grass, legumes, or other herbaceous plants that have been cut and dried to be stored for use as animal fodder, either for large grazing animals raised as livestock, such as cattle, horses, goats, and sheep, or for smaller domesticate ...
, often during the winter months. The ability to thrive solely on pasture (even without hay) varies with breed, but all sheep can survive on this diet. Also included in some sheep's diets are mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ...
s, either in a trace mix or in licks. Feed provided to sheep must be specially formulated, as most cattle, poultry, pig, and even some goat feeds contain levels of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
that are lethal to sheep. The same danger applies to mineral supplements such as salt lick
A mineral lick (also known as a salt lick) is a place where animals can go to lick essential mineral nutrients from a deposit of salts and other minerals. Mineral licks can be naturally occurring or artificial (such as blocks of salt that farm ...
s.
Grazing behavior
Sheep follow a diurnal pattern of activity, feeding from dawn to dusk, stopping sporadically to rest and chew theircud
Cud is a portion of food that returns from a ruminant's stomach to the mouth to be chewed for the second time. More precisely, it is a bolus of semi-degraded food regurgitated from the reticulorumen of a ruminant. Cud is produced during the phy ...
. Ideal pasture for sheep is not lawnlike grass, but an array of grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in law ...
es, legume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ...
s and forb
A forb or phorb is an herbaceous flowering plant that is not a graminoid (grass, sedge, or rush). The term is used in biology and in vegetation ecology, especially in relation to grasslands and understory. Typically these are dicots without woo ...
s. Types of land where sheep are raised vary widely, from pastures that are seeded and improved intentionally to rough, native lands. Common plants toxic to sheep are present in most of the world, and include (but are not limited to) cherry, some oaks and acorns, tomato, yew
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees.
It is most prominently given to any of various coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Taxus'':
* European yew or common yew (''Taxus baccata'')
* Pacific yew or western yew (''Taxus b ...
, rhubarb, potato, and rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; from Ancient Greek ''rhódon'' "rose" and ''déndron'' "tree") is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are nativ ...
.
Effects on pasture
Sheep are largelygrazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and other ...
herbivores, unlike browsing
Browsing is a kind of orienting strategy. It is supposed to identify something of relevance for the browsing organism. When used about human beings it is a metaphor taken from the animal kingdom. It is used, for example, about people browsing o ...
animals such as goats and deer that prefer taller foliage. With a much narrower face, sheep crop plants very close to the ground and can overgraze
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature rese ...
a pasture much faster than cattle. For this reason, many shepherds use managed intensive rotational grazing
In agriculture, rotational grazing, as opposed to continuous grazing, describes many systems of pasturing, whereby livestock are moved to portions of the pasture, called paddocks, while the other portions rest. Each paddock must provide all the n ...
, where a flock is rotated through multiple pastures, giving plants time to recover. Paradoxically, sheep can both cause and solve the spread of invasive plant species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species adv ...
. By disturbing the natural state of pasture, sheep and other livestock can pave the way for invasive plants. However, sheep also prefer to eat invasives such as cheatgrass
''Bromus tectorum'', known as downy brome, drooping brome or cheatgrass, is a winter annual Poaceae, grass native to Europe, southwestern Asia, and northern Africa, but has become Invasive species, invasive in many other areas. It now is present ...
, leafy spurge, kudzu
Kudzu (; also called Japanese arrowroot or Chinese arrowroot) is a group of climbing, coiling, and trailing deciduous perennial vines native to much of East Asia, Southeast Asia, and some Pacific islands, but invasive in many parts of the wor ...
and spotted knapweed
''Centaurea stoebe'', the spotted knapweed or panicled knapweed, is a species of '' Centaurea'' native to eastern Europe, although it has spread to North America, where it is considered an invasive species. It forms a tumbleweed, helping to incre ...
over native species such as sagebrush
Sagebrush is the common name of several woody and herbaceous species of plants in the genus '' Artemisia''. The best known sagebrush is the shrub '' Artemisia tridentata''. Sagebrushes are native to the North American west.
Following is an al ...
, making grazing sheep effective for conservation grazing
Conservation grazing or targeted grazing is the use of semi- feral or domesticated grazing livestock to maintain and increase the biodiversity of natural or semi-natural grasslands, heathlands, wood pasture, wetlands and many other habitats.
. Research conducted in Imperial County, California
Imperial County is a county on the southeast border of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 179,702, making it the least populous county in Southern California. The county seat is El Centro. Imperial is the ...
compared lamb grazing with herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
for weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place", or a plant growing where it is not wanted.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. ...
control in seedling alfalfa fields. Three trials demonstrated that grazing lambs were just as effective as herbicides in controlling winter weeds. Entomologist
Entomology () is the scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such as arach ...
s also compared grazing lambs to insecticides
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed t ...
for insect control in winter alfalfa. In this trial, lambs provided insect control as effectively as insecticides.
Behavior

Flock behavior
Sheep are flock animals and strongly gregarious; much sheep behavior can be understood on the basis of these tendencies. Thedominance hierarchy
In biology, a dominance hierarchy (formerly and colloquially called a pecking order) is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social groups interact, creating a ranking system. A dominant higher-ranking individual is so ...
of sheep and their natural inclination to follow a leader to new pastures were the pivotal factors in sheep being one of the first domesticated livestock species.Budiansky Furthermore, in contrast to the red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
and gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . This article also deals with the seven species included in two further genera, ''Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third ...
(two other ungulates of primary importance to meat production in prehistoric times), sheep do not defend territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
although they do form home ranges
A home range is the area in which an animal lives and moves on a periodic basis. It is related to the concept of an animal's territory which is the area that is actively defended. The concept of a home range was introduced by W. H. Burt in 1943. He ...
.Clutton-Brock, J., (1987). A Natural History of Domesticated Mammals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge pp.55 All sheep have a tendency to congregate close to other members of a flock, although this behavior varies with breed, and sheep can become stressed when separated from their flock members. During flocking, sheep have a strong tendency to follow, and a leader may simply be the first individual to move. Relationships in flocks tend to be closest among related sheep: in mixed-breed flocks, subgroups of the same breed tend to form, and a ewe and her direct descendants often move as a unit within large flocks. Sheep can become hefted
The raising of domestic sheep has occurred in nearly every inhabited part of the globe, and the variations in cultures and languages which have kept sheep has produced a vast lexicon of unique terminology used to describe sheep husbandry.
Terms ...
to one particular local pasture (heft) so they do not roam freely in unfenced landscapes. Lambs learn the heft from ewes and if whole flocks are culled it must be retaught to the replacement animals.
Flock behaviour in sheep is generally only exhibited in groups of four or more sheep; fewer sheep may not react as expected when alone or with few other sheep. Being a prey species, the primary defense mechanism of sheep is to flee from danger when their flight zone
The flight zone of an animal is the area surrounding an animal that if encroached upon by a potential predator or threat, including humans, will cause alarm and escape behavior. The flight zone is determined by the animal's flight distance, sometim ...
is entered. Cornered sheep may charge and butt, or threaten by hoof stamping and adopting an aggressive posture. This is particularly true for ewes with newborn lambs.
In regions where sheep have no natural predators, none of the native breeds of sheep exhibit a strong flocking behavior.
Herding
 Farmers exploit flocking behavior to keep sheep together on unfenced pastures such as hill farming, and to move them more easily. For this purpose shepherds may use
Farmers exploit flocking behavior to keep sheep together on unfenced pastures such as hill farming, and to move them more easily. For this purpose shepherds may use herding dog
A herding dog, also known as a stock dog, shepherd dog, sheep dog or working dog, is a type of dog that either has been trained in herding or belongs to breeds that are developed for herding.
Herding behavior
All herding behavior is m ...
s in this effort, with a highly bred herding
Herding is the act of bringing individual animals together into a group ( herd), maintaining the group, and moving the group from place to place—or any combination of those. Herding can refer either to the process of animals forming herds i ...
ability. Sheep are food-oriented, and association of humans with regular feeding often results in sheep soliciting people for food. Those who are moving sheep may exploit this behavior by leading sheep with buckets of feed.
Dominance hierarchy
Sheep establish a dominance hierarchy through fighting, threats and competitiveness. Dominant animals are inclined to be more aggressive with other sheep, and usually feed first at troughs. Primarily among rams, horn size is a factor in the flock hierarchy.Budiansky p. 78. Rams with different size horns may be less inclined to fight to establish the dominance order, while rams with similarly sized horns are more so.Merino
The Merino is a breed or group of breeds of domestic sheep, characterised by very fine soft wool. It was established in Spain near the end of the Middle Ages, and was for several centuries kept as a strict Spanish monopoly; exports of the bree ...
s have an almost linear hierarchy whereas there is a less rigid structure in Border Leicesters when a competitive feeding situation arises.
In sheep, position in a moving flock is highly correlated with social dominance, but there is no definitive study to show consistent voluntary leadership by an individual sheep.
Intelligence and learning ability
Sheep are frequently thought of as unintelligent animals. Their flocking behavior and quickness to flee and panic can make shepherding a difficult endeavor for the uninitiated. Despite these perceptions, aUniversity of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Unive ...
monograph on sheep reported their intelligence to be just below that of pigs and on par with that of cattle.
Sheep can recognize individual human and ovine faces and remember them for years; they can remember 50 other different sheep faces for over two years; they can recognize and are attracted to individual sheep and humans by their faces, as they possess similar specialized neural systems in the temporal and frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove b ...
s of their brains to humans and have a greater involvement of the right brain hemisphere. In addition to long-term facial recognition of individuals, sheep can also differentiate emotional states through facial characteristics. If worked with patiently, sheep may learn their names, and many sheep are trained to be led by halter
A halter or headcollar is headgear that is used to lead or tie up livestock and, occasionally, other animals; it fits behind the ears (behind the poll), and around the muzzle. To handle the animal, usually a lead rope is attached. On smalle ...
for showing and other purposes. Sheep have also responded well to clicker training
Clicker training is a positive reinforcement animal training method based on a bridging stimulus ( the clicker) in operant conditioning. The system uses conditioned reinforcers, which a trainer can deliver more quickly and more precisely than prima ...
. Sheep have been used as pack animals; Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken diale ...
nomads distribute baggage equally throughout a flock as it is herded between living sites.
It has been reported that some sheep have apparently shown problem-solving abilities; a flock in West Yorkshire
West Yorkshire is a metropolitan and ceremonial county in the Yorkshire and Humber Region of England. It is an inland and upland county having eastward-draining valleys while taking in the moors of the Pennines. West Yorkshire came into exis ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
allegedly found a way to get over cattle grid
A cattle grid – also known as a stock grid in Australia; cattle guard, or cattle grate in American English; vehicle pass, or stock gap in the Southeastern United States; Texas gate in western Canada and the northwestern United States; and a ...
s by rolling on their backs, although documentation of this has relied on anecdotal accounts.
Vocalisations
Sounds made by domestic sheep include bleats, grunts, rumbles and snorts. Bleating ("baaing") is used mostly for contact communication, especially between dam and lambs, but also at times between other flock members.Lynch, J.J., G. N Hinch and D. B. Adams. (1992). ''The Behaviour Of Sheep: Biological Principles And Implications For Production.'' CABI, Wallingford. 237 pp. The bleats of individual sheep are distinctive, enabling the ewe and her lambs to recognize each other's vocalizations. Vocal communication between lambs and their dam declines to a very low level within several weeks after parturition. A variety of bleats may be heard, depending on sheep age and circumstances. Apart from contact communication, bleating may signal distress, frustration or impatience; however, sheep are usually silent when in pain. Isolation commonly prompts bleating by sheep.Dwyer, C.M. (ed.) (2008). ''The Welfare Of Sheep.'' CABI, Wallingford, UK. 366 pp. Pregnant ewes may grunt when in labor. Rumbling sounds are made by the ram during courting; somewhat similar rumbling sounds may be made by the ewe, especially when with her neonate lambs. A snort (explosive exhalation through the nostrils) may signal aggression or a warning, and is often elicited from startled sheep.Senses

 In sheep breeds lacking facial wool, the visual field is wide. In 10 sheep (Cambridge, Lleyn and Welsh Mountain breeds, which lack facial wool), the visual field ranged from 298° to 325°, averaging 313.1°, with binocular overlap ranging from 44.5° to 74°, averaging 61.7°.Piggins, D. and C. J. C. Phillips. 1996. The eye of the domesticated sheep and its implications for vision. Animal Science. 62: 301–308. In some breeds, unshorn facial wool can limit the visual field; in some individuals, this may be enough to cause "wool blindness". In 60 Merinos, visual fields ranged from 219.1° to 303.0°, averaging 269.9°, and the binocular field ranged from 8.9° to 77.7°, averaging 47.5°; 36% of the measurements were limited by wool,Hutson, G. D. 1980. Visual field, restricted vision and sheep movement in laneways. Appl. Anim. Ethol. 6: 175–187. although photographs of the experiments indicate that only limited facial wool regrowth had occurred since shearing. In addition to facial wool (in some breeds), visual field limitations can include ears and (in some breeds) horns, so the visual field can be extended by tilting the head. Sheep eyes exhibit very low
In sheep breeds lacking facial wool, the visual field is wide. In 10 sheep (Cambridge, Lleyn and Welsh Mountain breeds, which lack facial wool), the visual field ranged from 298° to 325°, averaging 313.1°, with binocular overlap ranging from 44.5° to 74°, averaging 61.7°.Piggins, D. and C. J. C. Phillips. 1996. The eye of the domesticated sheep and its implications for vision. Animal Science. 62: 301–308. In some breeds, unshorn facial wool can limit the visual field; in some individuals, this may be enough to cause "wool blindness". In 60 Merinos, visual fields ranged from 219.1° to 303.0°, averaging 269.9°, and the binocular field ranged from 8.9° to 77.7°, averaging 47.5°; 36% of the measurements were limited by wool,Hutson, G. D. 1980. Visual field, restricted vision and sheep movement in laneways. Appl. Anim. Ethol. 6: 175–187. although photographs of the experiments indicate that only limited facial wool regrowth had occurred since shearing. In addition to facial wool (in some breeds), visual field limitations can include ears and (in some breeds) horns, so the visual field can be extended by tilting the head. Sheep eyes exhibit very low hyperopia
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, or hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blurred effect is due to incoming light being focused behind, in ...
and little astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at ni ...
. Such visual characteristics are likely to produce a well-focused retinal image of objects in both the middle and long distance. Because sheep eyes have no accommodation, one might expect the image of very near objects to be blurred, but a rather clear near image could be provided by the tapetum and large retinal image of the sheep's eye, and adequate close vision may occur at muzzle length. Good depth perception, inferred from the sheep's sure-footedness, was confirmed in "visual cliff" experiments; behavioral responses indicating depth perception are seen in lambs at one day old. Sheep are thought to have colour vision, and can distinguish between a variety of colours: black, red, brown, green, yellow and white.Alexander, G. and Shillito, E.E. (1978). Maternal responses in Merino ewes to artificially coloured lambs. Applied Animal Ethology, 4: 141–152 Sight is a vital part of sheep communication, and when grazing, they maintain visual contact with each other.Kilgour, R., (1977). Design sheep yards to suit the whims of sheep. N.Z. Farmer, 98(6): 29–31 Each sheep lifts its head upwards to check the position of other sheep in the flock. This constant monitoring is probably what keeps the sheep in a flock as they move along grazing. Sheep become stressed when isolated; this stress is reduced if they are provided with a mirror, indicating that the sight of other sheep reduces stress.Parrott, R.F., (1990). Physiological responses to isolation in sheep. Social Stress in Domestic Animals, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands: 1990. 212 -226
Taste is the most important sense in sheep, establishing forage preferences, with sweet and sour plants being preferred and bitter plants being more commonly rejected. Touch and sight are also important in relation to specific plant characteristics, such as succulence and growth form.Krueger, W.C., Laycock, W.A. and Price, D.A., (1974). Relationships of taste, smell, sight and touch on forage selection. Journal of Range Management, 27(4): 258–262
The ram uses his vomeronasal
The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum, in the nasal cavity just above the roof of the mouth (the hard palate) in various tetrapods. T ...
organ (sometimes called the Jacobson's organ) to sense the pheromones of ewes and detect when they are in estrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous p ...
. The ewe uses her vomeronasal organ for early recognition of her neonate lamb.
Reproduction
 Sheep follow a similar
Sheep follow a similar reproductive
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are al ...
strategy to other herd animals. A group of ewes is generally mated by a single ram, who has either been chosen by a breeder or (in feral
A feral () animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in some ...
populations) has established dominance through physical contest with other rams. Most sheep are seasonal breeder
Seasonal breeders are animal species that successfully mate only during certain times of the year. These times of year allow for the optimization of survival of young due to factors such as ambient temperature, food and water availability, and ch ...
s, although some are able to breed year-round. Ewes generally reach sexual maturity at six to eight months old, and rams generally at four to six months. However, there are exceptions. For example, Finnsheep ewe lambs may reach puberty as early as 3 to 4 months, and Merino ewes sometimes reach puberty at 18 to 20 months. Ewes have estrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous p ...
cycles about every 17 days, during which they emit a scent and indicate readiness through physical displays towards rams. A minority of rams (8% on average) display a preference for homosexuality
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to pe ...
and a small number of the females that were accompanied by a male fetus ''in utero'' are freemartin
A freemartin or free-martin (sometimes martin heifer) is an infertile female cattle with masculinized behavior and non-functioning ovaries. Phenotypically, the animal appears female, but various aspects of female reproductive development are a ...
s (female animals that are behaviorally masculine and lack functioning ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the bod ...
).
In feral sheep, rams may fight during the rut to determine which individuals may mate with ewes. Rams, especially unfamiliar ones, will also fight outside the breeding period to establish dominance; rams can kill one another if allowed to mix freely. During the rut, even usually friendly rams may become aggressive towards humans due to increases in their hormone levels.
After mating, sheep have a gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during preg ...
period of about five months, and normal labor takes one to three hours. Although some breeds regularly throw larger litters of lambs, most produce single or twin lambs. During or soon after labor, ewes and lambs may be confined to small lambing jugs, small pens designed to aid both careful observation of ewes and to cement the bond between them and their lambs.
 Ovine
Ovine obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surg ...
can be problematic. By selectively breeding ewes that produce multiple offspring with higher birth weights for generations, sheep producers have inadvertently caused some domestic sheep to have difficulty lambing; balancing ease of lambing with high productivity is one of the dilemmas of sheep breeding. In the case of any such problems, those present at lambing may assist the ewe by extracting or repositioning lambs. After the birth, ewes ideally break the amniotic sac
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo (and later fetus) until sh ...
(if it is not broken during labor), and begin licking clean the lamb. Most lambs will begin standing within an hour of birth. In normal situations, lambs nurse after standing, receiving vital colostrum
Colostrum, also known as beestings or first milk, is the first form of milk produced by the mammary glands of mammals (including humans) immediately following delivery of the newborn. Colostrum powder is rich in high protein and low in sugar and ...
milk. Lambs that either fail to nurse or are rejected by the ewe require help to survive, such as bottle-feeding or fostering by another ewe.
Most lambs begin life being born outdoors. After lambs are several weeks old, lamb marking
Lamb or The Lamb may refer to:
* A young sheep
* Lamb and mutton, the meat of sheep
Arts and media Film, television, and theatre
* ''The Lamb'' (1915 film), a silent film starring Douglas Fairbanks Sr. in his screen debut
* ''The Lamb'' (1918 ...
( ear tagging, docking, mulesing
Mulesing is the removal of strips of wool-bearing skin from around the breech (buttocks) of a sheep to prevent the parasitic infection flystrike (myiasis).
The wool around the buttocks can retain feces and urine, which attracts flies. The scar t ...
, and castrating
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses phar ...
) is carried out.Wooster Vaccinations are usually carried out at this point as well. Ear tags with numbers are attached, or ear marks are applied, for ease of later identification of sheep. Docking and castration are commonly done after 24 hours (to avoid interference with maternal bonding and consumption of colostrum) and are often done not later than one week after birth, to minimize pain, stress, recovery time and complications. The first course of vaccinations (commonly anti-clostridial) is commonly given at an age of about 10 to 12 weeks; i.e. when the concentration of maternal antibodies passively acquired via colostrum is expected to have fallen low enough to permit development of active immunity. Ewes are often revaccinated annually about 3 weeks before lambing, to provide high antibody concentrations in colostrum during the first several hours after lambing. Ram lambs that will either be slaughtered or separated from ewes before sexual maturity are not usually castrated. Objections to all these procedures have been raised by animal rights groups, but farmers defend them by saying they save money, and inflict only temporary pain.Simmons & Ekarius
Health
 Sheep may fall victim to poisons,
Sheep may fall victim to poisons, infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
, and physical injuries. As a prey species, a sheep's system is adapted to hide the obvious signs of illness, to prevent being targeted by predators. However, some signs of ill health are obvious, with sick sheep eating little, vocalizing excessively, and being generally listless. Throughout history, much of the money and labor of sheep husbandry has aimed to prevent sheep ailments. Historically, shepherds often created remedies by experimentation on the farm. In some developed countries, including the United States, sheep lack the economic importance for drug companies to perform expensive clinical trials required to approve more than a relatively limited number of drugs for ovine use. However, extra-label drug use in sheep production is permitted in many jurisdictions, subject to certain restrictions. In the US, for example, regulations governing extra-label drug use in animals are found in 21 CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) Part 530. In the 20th and 21st centuries, a minority of sheep owners have turned to alternative treatments such as homeopathy
Homeopathy or homoeopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine. It was conceived in 1796 by the German physician Samuel Hahnemann. Its practitioners, called homeopaths, believe that a substance that causes symptoms of a di ...
, herbalism
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remedie ...
and even traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medicine, alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logica ...
to treat sheep veterinary problems. Despite some favorable anecdotal evidence
Anecdotal evidence is evidence based only on personal observation, collected in a casual or non-systematic manner. The term is sometimes used in a legal context to describe certain kinds of testimony which are uncorroborated by objective, independ ...
, the effectiveness of alternative veterinary medicine has been met with skepticism in scientific journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research.
Content
Articles in scientific journals are mostly written by active scientists such ...
s. The need for traditional anti-parasite drugs and antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s is widespread, and is the main impediment to certified organic farming
Organic farming, also known as ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 on organic production and labelling of organic products and re ...
with sheep.
Many breeders take a variety of preventive measures to ward off problems. The first is to ensure all sheep are healthy when purchased. Many buyers avoid outlets known to be clearing houses for animals culled from healthy flocks as either sick or simply inferior. This can also mean maintaining a closed flock, and quarantining new sheep for a month. Two fundamental preventive programs are maintaining good nutrition and reducing stress in the sheep. Restraint, isolation, loud noises, novel situations, pain, heat, extreme cold, fatigue and other stressors can lead to secretion of cortisol, a stress hormone, in amounts that may indicate welfare problems.Gregory, N. G. 1998. Animal welfare and meat science. CABI, Wallingford, UK. 298 pp.Moberg, G. P. and J. A. Mench. 2000. The biology of animal stress: basic principles and implications for welfare. CABI, Wallingford, UK. pp. 1–21. Excessive stress can compromise the immune system. "Shipping fever" (pneumonic mannheimiosis, formerly called pasteurellosis) is a disease of particular concern, that can occur as a result of stress, notably during transport and (or) handling. Pain, fear and several other stressors can cause secretion of epinephrine (adrenaline). Considerable epinephrine secretion in the final days before slaughter can adversely affect meat quality (by causing glycogenolysis, removing the substrate for normal post-slaughter acidification of meat) and result in meat becoming more susceptible to colonization by spoilage bacteria. Because of such issues, low-stress handling is essential in sheep management. Avoiding poisoning is also important; common poisons are pesticide sprays, inorganic fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
, motor oil
Motor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances used for the lubrication of internal combustion engines. They typically consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, deterg ...
, as well as radiator coolant containing ethylene glycol.
 Common forms of preventive medication for sheep are
Common forms of preventive medication for sheep are vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
s and treatments for parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
. Both external and internal parasites are the most prevalent malady in sheep, and are either fatal, or reduce the productivity of flocks. Worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes (though not always).
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete worm ...
s are the most common internal parasites. They are ingested during grazing, incubate within the sheep, and are expelled through the digestive system (beginning the cycle again). Oral anti-parasitic medicines, known as drenches, are given to a flock to treat worms, sometimes after worm eggs in the feces has been counted to assess infestation levels. Afterwards, sheep may be moved to a new pasture to avoid ingesting the same parasites. External sheep parasites include: lice (for different parts of the body), sheep keds
Keds is an American brand of canvas shoes with rubber soles. Founded in 1916, the company is owned by Wolverine World Wide. The original shoe design, the Champion, was the first mass-marketed canvas-top "sneaker".
History
Early history
In 1 ...
, nose bots, sheep itch mites, and maggot
A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies.
E ...
s. Keds are blood-sucking parasites that cause general malnutrition and decreased productivity, but are not fatal. Maggots are those of the bot fly
Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are a family of flies known as the Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. '' Dermatobia homi ...
and the blow-fly
The Calliphoridae (commonly known as blow flies, blow-flies, carrion flies, bluebottles, greenbottles, or cluster flies) are a family of insects in the order Diptera, with almost 1,900 known species. The maggot larvae, often used as fishing b ...
, commonly ''Lucilia sericata
The common green bottle fly (''Lucilia sericata'') is a blowfly found in most areas of the world and is the most well-known of the numerous green bottle fly species. Its body is in length – slightly larger than a house fly – and has brilli ...
'' or its relative ''L. cuprina''. Fly maggots cause the extremely destructive condition of flystrike
Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) which grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some sp ...
. Flies lay their eggs in wounds or wet, manure-soiled wool; when the maggots hatch they burrow into a sheep's flesh, eventually causing death if untreated. In addition to other treatments, crutching
Crutching refers to the removal of wool from around the tail and between the rear legs of a sheep for hygiene purposes. It can also refer to removing wool from the heads of sheep (''wigging'' or ''eye-wooling''). It does not refer to the process ...
(shearing wool from a sheep's rump) is a common preventive method. Some countries allow mulesing
Mulesing is the removal of strips of wool-bearing skin from around the breech (buttocks) of a sheep to prevent the parasitic infection flystrike (myiasis).
The wool around the buttocks can retain feces and urine, which attracts flies. The scar t ...
, a practice that involves stripping away the skin on the rump to prevent fly-strike, normally performed when the sheep is a lamb. Nose bots are fly larvae that inhabit a sheep's sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the spheno ...
, causing breathing difficulties and discomfort. Common signs are a discharge from the nasal passage, sneezing, and frantic movement such as head shaking. External parasites may be controlled through the use of backliners, sprays or immersive sheep dip
Sheep dip is a liquid formulation of insecticide and fungicide which shepherds and farmers use to protect their sheep from infestation against external parasites such as itch mite (''Psoroptes ovis''), blow-fly, ticks and lice.
History
She ...
s.
A wide array of bacterial and viral diseases affect sheep. Diseases of the hoof, such as foot rot
Foot rot, or infectious pododermatitis, is a hoof infection commonly found in sheep, goats, and cattle. As the name suggests, it rots away the foot of the animal, more specifically the area between the two toes of the affected animal. It is extrem ...
and foot scald may occur, and are treated with footbaths and other remedies. Foot rot
Foot rot, or infectious pododermatitis, is a hoof infection commonly found in sheep, goats, and cattle. As the name suggests, it rots away the foot of the animal, more specifically the area between the two toes of the affected animal. It is extrem ...
is present in over 97% of flocks in the UK. These painful conditions cause lameness and hinder feeding. Ovine Johne's disease is a wasting disease that affects young sheep. Bluetongue disease
Bluetongue disease is a noncontagious, insect-borne, viral disease of ruminants, mainly sheep and less frequently cattle, yaks, goats, buffalo, deer, dromedaries, and antelope. It is caused by ''Bluetongue virus'' (''BTV''). The virus is t ...
is an insect-borne illness causing fever and inflammation of the mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
s. Ovine rinderpest
Ovine rinderpest, also commonly known as ''peste des petits ruminants'' (PPR), is a contagious disease primarily affecting goats and sheep; however, camels and wild small ruminants can also be affected. PPR is currently present in North, Cent ...
(or ''peste des petits ruminants'') is a highly contagious and often fatal viral disease affecting sheep and goats. Sheep may also be affected by primary or secondary photosensitization. Tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by '' Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usuall ...
can also afflict sheep through wounds from shearing
Sheep shearing is the process by which the woollen fleece of a sheep is cut off. The person who removes the sheep's wool is called a '' shearer''. Typically each adult sheep is shorn once each year (a sheep may be said to have been "shorn" or ...
, docking, castration, or vaccination. The organism also can be introduced into the reproductive tract by unsanitary humans who assist ewes during lambing.
A few sheep conditions are transmissible to humans. Orf
ORF or Orf may refer to:
* Norfolk International Airport, IATA airport code ORF
* Observer Research Foundation, an Indian research institute
* One Race Films, a film production company founded by Vin Diesel
* Open reading frame, a portion of t ...
(also known as scabby mouth, contagious ecthyma or soremouth) is a skin disease leaving lesions that is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. Cutaneous anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
is also called woolsorter's disease, as the spores can be transmitted in unwashed wool. More seriously, the organisms that can cause spontaneous enzootic abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregn ...
in sheep are easily transmitted to pregnant women. Also of concern are the prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It ...
disease scrapie
Scrapie () is a fatal, degenerative disease affecting the nervous systems of sheep and goats. It is one of several transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), and as such it is thought to be caused by a prion. Scrapie has been known since ...
and the virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and ...
that causes foot-and-mouth disease
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious disease, infectious and sometimes fatal virus (biology), viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including domestic and wild Bovidae, bovids. The virus causes ...
(FMD), as both can devastate flocks. The latter poses a slight risk to humans. During the 2001 FMD pandemic in the UK, hundreds of sheep were culled and some rare British breeds were at risk of extinction due to this.
Of the 600,300 sheep lost to the US economy in 2004, 37.3% were lost to predators, while 26.5% were lost to some form of disease. Poisoning accounted for 1.7% of non-productive deaths.
Predators
 Other than parasites and disease,
Other than parasites and disease, predation
Predation is a biological interaction
In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or o ...
is a threat to sheep and the profitability of sheep raising. Sheep have little ability to defend themselves, compared with other species kept as livestock. Even if sheep survive an attack, they may die from their injuries or simply from panic. However, the impact of predation varies dramatically with region. In Africa, Australia, the Americas, and parts of Europe and Asia predators are a serious problem. In the United States, for instance, over one third of sheep deaths in 2004 were caused by predation. In contrast, other nations are virtually devoid of sheep predators, particularly islands known for extensive sheep husbandry. Worldwide, canids
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a family (biology), biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamily, ...
—including the domestic dog—are responsible for most sheep deaths. Other animals that occasionally prey on sheep include: felines, bears, birds of prey, ravens and feral hogs.
Sheep producers have used a wide variety of measures to combat predation. Pre-modern shepherds used their own presence, livestock guardian dog
A livestock guardian dog (LGD) is a dog type bred for the purpose of protecting livestock from Predation, predators.
Livestock guardian dogs stay with the group of animals they protect as a full-time member of the flock or herd. Their ability ...
s, and protective structures such as barns and fencing. Fencing (both regular and electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described b ...
), penning sheep at night and lambing indoors all continue to be widely used. More modern shepherds used guns, traps
TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPSsubscription needed) is a periodic fever syndrome associated with mutations in a receptor (biochemistry), receptor for the molecule tumor necrosis factors, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) that is inheri ...
, and poisons to kill predators, causing significant decreases in predator populations. In the wake of the environmental and conservation movements, the use of these methods now usually falls under the purview of specially designated government agencies in most developed countries.
The 1970s saw a resurgence in the use of livestock guardian dogs and the development of new methods of predator control by sheep producers, many of them non-lethal. Donkeys and guard llama
A guard llama is a llama that is used in farming to protect sheep, goats, hens or other livestock from canidae such as coyotes, wolves, dingos, dogs, foxes and other predators. In the past, a single gelded (castrated) male was recommended. In m ...
s have been used since the 1980s in sheep operations, using the same basic principle as livestock guardian dogs. Interspecific pasturing, usually with larger livestock such as cattle or horses, may help to deter predators, even if such species do not actively guard sheep. In addition to animal guardians, contemporary sheep operations may use non-lethal predator deterrents such as motion-activated lights and noisy alarms.
Economic importance
 Sheep are an important part of the global agricultural economy. However, their once vital status has been largely replaced by other livestock species, especially the pig, chicken, and cow. China, Australia,
Sheep are an important part of the global agricultural economy. However, their once vital status has been largely replaced by other livestock species, especially the pig, chicken, and cow. China, Australia, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
have the largest modern flocks, and serve both local and exportation needs for wool and mutton. Other countries such as New Zealand have smaller flocks but retain a large international economic impact due to their export of sheep products. Sheep also play a major role in many local economies, which may be niche markets focused on organic or sustainable agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is farming in sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an understanding of ecosystem ser ...
and local food
Local food is food that is produced within a short distance of where it is consumed, often accompanied by a social structure and supply chain different from the large-scale supermarket system.
Local food (or "locavore") movements aim to co ...
customers. Especially in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed Industrial sector, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is al ...
, such flocks may be a part of subsistence agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no s ...
rather than a system of trade. Sheep themselves may be a medium of trade in barter economies.
synthetic fabric Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to:
Science
* Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis
* Synthetic o ...
s. For many sheep owners, the cost of shearing is greater than the possible profit from the fleece, making subsisting on wool production alone practically impossible without farm subsidies. Fleeces are used as material in making alternative products such as wool insulation
Wool insulation is made from sheep wool fibres that are either mechanically held together or bonded using between 5% and 20% recycled polyester adhesive to form insulating batts, rolls and ropes. Some companies do not use any adhesives or bondi ...
. In the 21st century, the sale of meat is the most profitable enterprise in the sheep industry, even though far less sheep meat is consumed than chicken, pork or beef.
Sheepskin
Sheepskin is the hide of a sheep, sometimes also called lambskin. Unlike common leather, sheepskin is tanned with the fleece intact, as in a pelt.Delbridge, Arthur, "The Macquarie Dictionary", 2nd ed., Macquarie Library, North Ryde, 1991 Uses
...
is likewise used for making clothes, footwear, rugs, and other products. Byproducts from the slaughter of sheep are also of value: sheep tallow
Tallow is a rendered form of beef or mutton fat, primarily made up of triglycerides.
In industry, tallow is not strictly defined as beef or mutton fat. In this context, tallow is animal fat that conforms to certain technical criteria, inclu ...
can be used in candle and soap making, sheep bone and cartilage has been used to furnish carved items such as dice and buttons as well as rendered glue and gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also ...
. Sheep intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
can be formed into sausage casings, and lamb intestine has been formed into surgical suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread ...
s, as well as strings for musical instruments and tennis rackets. Sheep droppings, which are high in cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
, have even been sterilized and mixed with traditional pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material ...
materials to make paper. Of all sheep byproducts, perhaps the most valuable is lanolin
Lanolin (from Latin 'wool', and 'oil'), also called wool yolk, wool wax, or wool grease, is a wax secreted by the sebaceous glands of wool-bearing animals. Lanolin used by humans comes from domestic sheep breeds that are raised specifically fo ...
: the waterproof, fatty substance found naturally in sheep's wool and used as a base for innumerable cosmetics
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protec ...
and other products.
Some farmers who keep sheep also make a profit from live sheep. Providing lambs for youth programs such as 4-H
4-H is a U.S.-based network of youth organizations whose mission is "engaging youth to reach their fullest potential while advancing the field of youth development". Its name is a reference to the occurrence of the initial letter H four times i ...
and competition at agricultural show
An agricultural show is a public event exhibiting the equipment, animals, sports and recreation associated with agriculture and animal husbandry. The largest comprise a livestock show (a judged event or display in which breeding stock is exhibi ...
s is often a dependable avenue for the sale of sheep. Farmers may also choose to focus on a particular breed of sheep in order to sell registered purebred
Purebreds are " cultivated varieties" of an animal species achieved through the process of selective breeding. When the lineage of a purebred animal is recorded, that animal is said to be " pedigreed". Purebreds breed true-to-type which means th ...
animals, as well as provide a ram rental service for breeding. A new option for deriving profit from live sheep is the rental of flocks for grazing; these "mowing
A mower is a person or machine that cuts (mows) grass or other plants that grow on the ground. Usually mowing is distinguished from reaping, which uses similar implements, but is the traditional term for harvesting grain crops, e.g. with reapers ...
services" are hired in order to keep unwanted vegetation down in public spaces and to lessen fire hazard
Fire safety is the set of practices intended to reduce the destruction caused by fire. Fire safety measures include those that are intended to prevent the ignition of an uncontrolled fire and those that are used to limit the development and eff ...
.
Despite the falling demand and price for sheep products in many markets, sheep have distinct economic advantages when compared with other livestock. They do not require expensive housing, such as that used in the intensive farming
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ...
of chickens or pigs. They are an efficient use of land; roughly six sheep can be kept on the amount that would suffice for a single cow or horse. Sheep can also consume plants, such as noxious weeds, that most other animals will not touch, and produce more young at a faster rate. Also, in contrast to most livestock species, the cost of raising sheep is not necessarily tied to the price of feed crops such as grain, soybeans and corn. Combined with the lower cost of quality sheep, all these factors combine to equal a lower overhead for sheep producers, thus entailing a higher profitability potential for the small farmer. Sheep are especially beneficial for independent producers, including family farms with limited resources, as the sheep industry is one of the few types of animal agriculture that has not been vertically integrated
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration is a term that describes the arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each member of the suppl ...
by agribusiness
Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy,
in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise.
The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit w ...
. However, small flocks, from 10 to 50 ewes, often are not profitable because they tend to be poorly managed. The primary reason is that mechanization is not feasible, so return per hour of labor is not maximized. Small farm flocks generally are used simply to control weeds on irrigation ditches or maintained as a hobby.
As food
 Sheep meat and milk were one of the earliest staple proteins consumed by human civilization after the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture. Sheep meat prepared for food is known as either mutton or lamb, and approximately 540 million sheep are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. "Mutton" is derived from the
Sheep meat and milk were one of the earliest staple proteins consumed by human civilization after the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture. Sheep meat prepared for food is known as either mutton or lamb, and approximately 540 million sheep are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. "Mutton" is derived from the Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligi ...
''moton'', which was the word for sheep used by the Anglo-Norman rulers of much of the British Isles in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. This became the name for sheep meat in English, while the Old English word ''sceap'' was kept for the live animal. Throughout modern history, "mutton" has been limited to the meat of mature sheep usually at least two years of age; "lamb" is used for that of immature sheep less than a year.
In the 21st century, the nations with the highest consumption of sheep meat are the Arab States of the Persian Gulf, New Zealand, Australia, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
, the United Kingdom and Ireland. These countries eat 14–40 lbs (3–18 kg) of sheep meat per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
, per annum. Sheep meat is also popular in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Africa (especially the Arab World
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
), the Caribbean, the rest of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, and parts of China. This often reflects a history of sheep production. In these countries in particular, dishes comprising alternative cuts and offal
Offal (), also called variety meats, pluck or organ meats, is the organs of a butchered animal. The word does not refer to a particular list of edible organs, which varies by culture and region, but usually excludes muscle. Offal may also ref ...
may be popular or traditional. Sheep testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testostero ...
s—called animelles
The testicles of calves, lambs, roosters, turkeys, and other animals are eaten in many parts of the world, often under euphemistic culinary names. Testicles are a by-product of the castration of young animals raised for meat, so they were pr ...
or lamb fries
Lamb fries are lamb testicles used as food. Historically they were parboiled, cut in half, and seasoned. Lamb testicles are served in a variety of cuisines, including Italian, Basque, breaded and fried in some barbecue restaurants, Chinese, Ca ...
—are considered a delicacy in many parts of the world. Perhaps the most unusual dish of sheep meat is the Scottish haggis
Haggis ( gd, taigeis) is a savoury pudding containing sheep's pluck (heart, liver, and lungs), minced with onion, oatmeal, suet, spices, and salt, mixed with stock, and cooked while traditionally encased in the animal's stomach though now a ...
, composed of various sheep innards cooked along with oatmeal and chopped onions inside its stomach. In comparison, countries such as the U.S. consume only a pound or less (under 0.5 kg), with Americans eating 50 pounds (22 kg) of pork and 65 pounds (29 kg) of beef. In addition, such countries rarely eat mutton, and may favor the more expensive cuts of lamb: mostly lamb chops and leg of lamb
Lamb, hogget, and mutton, generically sheep meat, are the meat of domestic sheep, ''Ovis aries''. A sheep in its first year is a lamb and its meat is also lamb. The meat from sheep in their second year is hogget. Older sheep meat is mutton. Gen ...
.
Though sheep's milk may be drunk rarely in fresh form, today it is used predominantly in cheese and yogurt making. Sheep have only two teat
A teat is the projection from the mammary glands of mammals from which milk flows or is ejected for the purpose of feeding young. In many mammals the teat projects from the udder. The number of teats varies by mammalian species and often corr ...
s, and produce a far smaller volume of milk than cows. However, as sheep's milk contains far more fat, solids
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structura ...
, and minerals than cow's milk, it is ideal for the cheese-making process. It also resists contamination during cooling better because of its much higher calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
content. Well-known cheeses made from sheep milk include the Feta
Feta ( el, φέτα, ) is a Greek brined white cheese made from sheep's milk or from a mixture of sheep and goat's milk. It is soft, with small or no holes, a compact touch, few cuts, and no skin. Crumbly with a slightly grainy texture, it is ...
of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, Roquefort
Roquefort is a sheep milk cheese from Southern France, and is one of the world's best known blue cheeses. Though similar cheeses are produced elsewhere, EU law dictates that only those cheeses aged in the natural Combalou caves of Roquefort- ...
of France, Manchego
Manchego (officially es, queso manchego, ) is a cheese made in the La Mancha region of Spain from the milk of sheep of the Manchega breed. It is aged between 60 days and 2 years.
Manchego has a firm and compact consistency and a buttery textu ...
from Spain, the Pecorino Romano
Pecorino Romano () is a hard, salty Italian cheese, often used for grating, made with sheep's milk. The name "pecorino" simply means "ovine" or "of sheep" in Italian; the name of the cheese, although protected, is a simple description rather t ...
(the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
word for sheep is ''pecore'') and Ricotta
Ricotta ( in Italian) is an Italian whey cheese made from sheep, cow, goat, or Italian water buffalo milk whey left over from the production of other cheeses. Like other whey cheeses, it is made by coagulating the proteins that remain after t ...
of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. Yogurts, especially some forms of strained yogurt
Strained yogurt, Greek yogurt, yogurt cheese, sack yogurt, or kerned yogurt is yogurt that has been strained to remove most of its whey, resulting in a thicker consistency than normal unstrained yogurt, while still preserving the distinctive ...
, may also be made from sheep milk. Many of these products are now often made with cow's milk, especially when produced outside their country of origin. Sheep milk contains 4.8% lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ...
, which may affect those who are intolerant.
As with other domestic animals, the meat of uncastrated males is inferior in quality, especially as they grow. A "bucky" lamb is a lamb which was not castrated early enough, or which was castrated improperly (resulting in one testicle being retained). These lambs are worth less at market.
In science
 Sheep are generally too large and reproduce too slowly to make ideal research subjects, and thus are not a common model organism. They have, however, played an influential role in some fields of science. In particular, the
Sheep are generally too large and reproduce too slowly to make ideal research subjects, and thus are not a common model organism. They have, however, played an influential role in some fields of science. In particular, the Roslin Institute
The Roslin Institute is an animal sciences research institute at Easter Bush, Midlothian, Scotland, part of the University of Edinburgh, and is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.
It is best known for creatin ...
of Edinburgh, Scotland
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
used sheep for genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar worki ...
research that produced groundbreaking results. In 1995, two ewes named Megan and Morag were the first mammals cloned
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical or virtually identical DNA, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction. In the field of biotechnology, ...
from differentiated cells, also referred to as gynomerogony. A year later, a Finnish Dorset sheep named Dolly, dubbed "the world's most famous sheep" in ''Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it i ...
'', was the first mammal to be cloned
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical or virtually identical DNA, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction. In the field of biotechnology, ...
from an adult somatic cell
A somatic cell (from Ancient Greek σῶμα ''sôma'', meaning "body"), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Such cells co ...
. Following this, Polly and Molly
Polly and Molly (born 1997), two ewes, were the first mammals to have been successfully cloned from an adult somatic cell and to be transgenic animals at the same time. This is not to be confused with Dolly the Sheep, the first animal to be su ...
were the first mammals to be simultaneously cloned and transgenic
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change the ...
.
As of 2008, the sheep genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
has not been fully sequenced, although a detailed genetic map
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be sepa ...
has been published, and a draft version of the complete genome produced by assembling sheep DNA sequences using information given by the genomes of other mammals. In 2012, a transgenic
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change the ...
sheep named "Peng Peng" was cloned by Chinese scientists, who spliced his genes with that of a roundworm (C. elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' ( ...
) in order to increase production of fats healthier for human consumption.
In the study of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
, the population of Soay sheep
The Soay sheep is a breed of domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') descended from a population of feral sheep on the island of Soay in the St Kilda Archipelago, about from the Western Isles of Scotland. It is one of the Northern European short-ta ...
that remain on the island of Hirta
Hirta ( gd, Hiort) is the largest island in the St Kilda archipelago, on the western edge of Scotland. The names (in Scottish Gaelic) and ''Hirta'' (historically in English) have also been applied to the entire archipelago. Now without a perman ...
have been used to explore the relation of body size and coloration to reproductive success. Soay sheep come in several colors, and researchers investigated why the larger, darker sheep were in decline; this occurrence contradicted the rule of thumb that larger members of a population tend to be more successful reproductively. The feral Soays on Hirta are especially useful subjects because they are isolated.
Sheep are one of the few animals where the molecular basis of the diversity of male sexual preferences has been examined. However, this research has been controversial, and much publicity has been produced by a study at the Oregon Health and Science University
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. ...
that investigated the mechanisms that produce homosexuality in rams. Organizations such as PETA campaigned against the study, accusing scientists of trying to cure homosexuality in the sheep. OHSU and the involved scientists vehemently denied such accusations.
Domestic sheep are sometimes used in medical research, particularly for researching cardiovascular physiology, in areas such as hypertension and heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
. Pregnant sheep are also a useful model for human pregnancy, and have been used to investigate the effects on fetal development of malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
and hypoxia. In behavioral sciences
Behavioral sciences explore the cognitive processes within organisms and the behavioral interactions between organisms in the natural world. It involves the systematic analysis and investigation of human and animal behavior through naturalist ...
, sheep have been used in isolated cases for the study of facial recognition Facial recognition or face recognition may refer to:
* Face detection, often a step done before facial recognition
* Face perception, the process by which the human brain understands and interprets the face
* Pareidolia, which involves, in part, se ...
, as their mental process of recognition is qualitatively similar to humans.
Cultural impact
 Sheep have had a strong presence in many cultures, especially in areas where they form the most common type of livestock. In the English language, to call someone a sheep or ovine may allude that they are timid and easily led. In contradiction to this image, male sheep are often used as symbols of virility and power; the logos of the
Sheep have had a strong presence in many cultures, especially in areas where they form the most common type of livestock. In the English language, to call someone a sheep or ovine may allude that they are timid and easily led. In contradiction to this image, male sheep are often used as symbols of virility and power; the logos of the Los Angeles Rams
The Los Angeles Rams are a professional American football team based in the Greater Los Angeles, Los Angeles metropolitan area. The Rams compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC Wes ...
football team and the Dodge Ram
The Ram pickup (marketed as the Dodge Ram until 2010) is a full-size pickup truck manufactured by Chrysler, Stellantis North America (formerly Chrysler Group LLC and FCA US LLC) and marketed from 2010 onwards under the Ram Trucks brand. The cur ...
pickup truck allude to males of the bighorn sheep
The bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis'') is a species of sheep native to North America. It is named for its large horns. A pair of horns might weigh up to ; the sheep typically weigh up to . Recent genetic testing indicates three distinct subspe ...
, ''Ovis canadensis''.
Counting sheep
Counting sheep is a mental exercise used in some Western cultures as a means of putting oneself to sleep.
In most depictions of the activity, the practitioner envisions an endless series of identical white sheep jumping over a fence, while ...
is popularly said to be an aid to sleep, and some ancient systems of counting sheep persist today. Sheep also enter in colloquial sayings and idiom
An idiom is a phrase or expression that typically presents a figurative, non-literal meaning attached to the phrase; but some phrases become figurative idioms while retaining the literal meaning of the phrase. Categorized as formulaic language, ...
frequently with such phrases as "black sheep
In the English language, black sheep is an idiom that describes a member of a group who is different from the rest, especially a family member who does not fit in. The term stems from sheep whose fleece is colored black rather than the more comm ...
". To call an individual a black sheep implies that they are an odd or disreputable member of a group. This usage derives from the recessive trait that causes an occasional black lamb to be born into an entirely white flock. These black sheep were considered undesirable by shepherds, as black wool is not as commercially viable as white wool. Citizens who accept overbearing governments have been referred to by the Portmanteau word, Portmanteau neologism of sheeple. Somewhat differently, the adjective "sheepish" is also used to describe embarrassment.
In heraldry
Religion and folklore
 Sheep play an important role in all the Abrahamic faiths; Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Moses, King David and the Islamic prophet Muhammad were all shepherds. According to the Biblical story of the Binding of Isaac, a ram is sacrificed as a substitute for Isaac after an angel stays Abraham's hand (in the Islamic tradition, Abraham was about to sacrifice Ishmael). Eid al-Adha is a major annual festival in Islam in which sheep (or other animals) are sacrificed in remembrance of this act. Sheep are occasionally sacrificed to commemorate important secular events in Islamic cultures. Greeks and Romans sacrificed sheep regularly in religious practice, and Judaism once sacrificed sheep as a Korban (sacrifice), such as the Korban Pesach, Passover lamb. Ovine symbols—such as the ceremonial blowing of a shofar—still find a presence in modern Judaic traditions.
Collectively, followers of Christianity are often referred to as a flock, with Christ as the The Good Shepherd (Christianity), Good Shepherd, and sheep are an element in the Christian iconography of the Nativity of Jesus in art, birth of Jesus. Some Christian saints are considered Patron saints of occupations and activities, patrons of shepherds, and even of sheep themselves. Christ is also portrayed as the Sacrificial lamb of God (''Agnus Dei'') and Easter celebrations in
Sheep play an important role in all the Abrahamic faiths; Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Moses, King David and the Islamic prophet Muhammad were all shepherds. According to the Biblical story of the Binding of Isaac, a ram is sacrificed as a substitute for Isaac after an angel stays Abraham's hand (in the Islamic tradition, Abraham was about to sacrifice Ishmael). Eid al-Adha is a major annual festival in Islam in which sheep (or other animals) are sacrificed in remembrance of this act. Sheep are occasionally sacrificed to commemorate important secular events in Islamic cultures. Greeks and Romans sacrificed sheep regularly in religious practice, and Judaism once sacrificed sheep as a Korban (sacrifice), such as the Korban Pesach, Passover lamb. Ovine symbols—such as the ceremonial blowing of a shofar—still find a presence in modern Judaic traditions.
Collectively, followers of Christianity are often referred to as a flock, with Christ as the The Good Shepherd (Christianity), Good Shepherd, and sheep are an element in the Christian iconography of the Nativity of Jesus in art, birth of Jesus. Some Christian saints are considered Patron saints of occupations and activities, patrons of shepherds, and even of sheep themselves. Christ is also portrayed as the Sacrificial lamb of God (''Agnus Dei'') and Easter celebrations in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
and Romania traditionally feature a meal of Paschal lamb. A church leader is often called the pastor, which is derived from the Latin word for shepherd. In many western Christian traditions bishops carry a staff, which also serves as a symbol of the episcopal office, known as a crosier, which is modeled on the shepherd's crook.
Sheep are key symbols in fables and nursery rhymes like ''The Wolf in Sheep's Clothing'', ''Little Bo Peep'', ''Baa, Baa, Black Sheep'', and ''Mary Had a Little Lamb''; novels such as George Orwell's ''Animal Farm'' and Haruki Murakami's ''A Wild Sheep Chase''; songs such as Johann Sebastian Bach, Bach's ''Sheep may safely graze'' (''Schafe können sicher weiden'') and Pink Floyd's "Sheep (Pink Floyd song), Sheep", and poems like William Blake's "The Lamb (poem), The Lamb".

See also
* Chris (sheep) * Dry Sheep Equivalent * Fictional sheep * Sheepfold * Shrek (sheep) * Sonny Wool * U.S. Sheep Experiment Station * Venray sheep companies * Sheep–goat hybridReferences
Sources
* * * * * * *External links
American Sheep Industry
(Queensland)
National Sheep Association
(UK)
New Zealand Sheepbreeders Association
all articles available free online * View th
sheep genome
in Ensembl * {{Featured article Articles containing video clips Cosmopolitan mammals Herbivorous mammals Livestock Mammals described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Sheep,