Shanyuan Treaty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
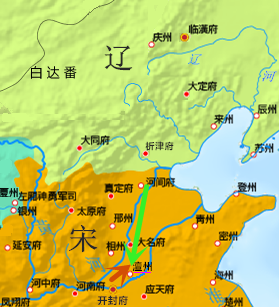 The Chanyuan Treaty () was signed between the
The Chanyuan Treaty () was signed between the
 The Chanyuan Treaty () was signed between the
The Chanyuan Treaty () was signed between the Northern Song dynasty
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ...
and the Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan language, Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that exi ...
in 1005, and marked a pivotal point in Chinese history and in the relations between the two dynasties. The treaty laid the foundation for approximately a century of relative peace between the two major powers, which lasted until the Alliance Conducted at Sea
The Alliance Conducted at Sea () was a political alliance in Chinese history between the Song and Jin dynasties in the early 12th century against the Liao dynasty. The alliance was negotiated from 1115 to 1123 by envoys who crossed the Bohai Sea.. ...
was formed between the Northern Song dynasty and the Jin dynasty in the early 12th century.
Liao–Song relations
Early on from the succession of the Song dynasty from theFive Dynasties
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century History of China#Imperial China, Imperial China. Five Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states quickly succeeded ...
in 960, relations between the Song and Liao were cordial. The Song had more important matters on their hand, namely conquering the remaining kingdoms in the south and north. After unifying the south in 979, the Song turned their eyes on the Liao. The Song destroyed the Northern Han state in 979. The Northern Han was a Shatuo Turk kingdom that considered itself the legitimate successor of the Later Han dynasty that fell in 950. As it was under the protection of the Liao, it engendered some friction between the two. However, what concerned the Song even more was the continued Liao possession of the strategic Sixteen Prefectures, which included present-day Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
.
After the Northern Han was destroyed by the Song, the emperor decided to march on Liao holdings in the Sixteen Prefectures. The Song forces were routed and the emperor had to retreat in ignominy.
The Song once again tried in 986, this time trying to take advantage of a boy emperor on the Liao throne. The Song advanced on the Sixteen Prefectures in three columns. However, the Liao won decisive victories on all three fronts, and diplomatic relations were soon resumed. Emperor Zhenzong
Emperor Zhenzong of Song (23 December 968 – 23 March 1022), personal name Zhao Heng, was the third emperor of the Song dynasty of China. He reigned from 997 to his death in 1022. His personal name was originally Zhao Dechang, but was change ...
succeeded to the Song throne in 997. Throughout the decade, relations between the Song and Liao worsened. In 999, the Liao Emperor Shengzong
Emperor Shengzong of Liao (16 January 972 – 25 June 1031), personal name Wenshunu, Sinicization, sinicised name Yelü Longxu, was the sixth Emperor of China, emperor of the Khitan people, Khitan-led Chinese Liao dynasty and its longest reigning ...
commenced annual attacks against the Song. While achieving victories in each, none were noteworthy. In 1004, this changed completely.
Liao invasion
Emperor Shengzong decided to launch an imperial expedition against the Song personally in the summer of 1004. He took Khitan cavalry and encamped about one hundred miles (160 kilometers) north of the Song capital ofKaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the No ...
. Reluctantly, Emperor Zhenzong marched northward to meet the Liao at Chanyuan. He decided upon Chanyuan because it was the first large city across from the Yellow River. The emperor believed that crossing the Yellow River in an imperial expedition would have great symbolic and psychological value. The Song begun to worry that the expedition was not safe for the emperor because the Kitans were making serious advances in Hebei Circuit. To make it safer, Kou Zhun, the lead planner of the expedition, implemented defensive measures such as digging trenches. Chanyuan's defenses was weakened after heavy fighting, resulting in many thousands of casualties, including many generals. However, the arrival of the emperor raised the Song troops' morale, making the battle ever-lastingly famous.
A Song giant crossbow killed the Liao Khitan leader Xiao Dalin in battle in January 1005. This led to major depression and despair among the Khitan and crippled the impetus of the Khitan offensive.WRIGHT, DAVID C. “THE SUNG-KITAN WAR OF A.D. 1004-1005 AND THE TREATY OF SHAN-YÜAN.” Journal of Asian History, vol. 32, no. 1, 1998, pp. 20-21. https://www.jstor.org/stable/41933065?seq=18.
Peace negotiations
From January 13 to January 18, 1005, the two sides worked out a peace treaty. Some sources say 1004 as it happened prior to the New Year on the Chineselunar calendar
A lunar calendar is a calendar based on the monthly cycles of the Moon's phases ( synodic months, lunations), in contrast to solar calendars, whose annual cycles are based only directly on the solar year. The most commonly used calendar, t ...
. While the Liao initially expected a territorial concession in Guannan, this demand was eventually abandoned. The specific terms of the treaty include:
# The Song will give the Liao an annual tribute of 200,000 bolts of raw silk and 100,000 taels of silver
# The State Finance Commission shall deliver these tributes to Hsiung-chou
# Civilians and the military will abide by the present territorial boundaries
# If there are robbers or bandits that flee arrest neither side shall give them refuge
# Neither the north nor the south shall grant licenses to sow or reap furrowed fields
# All moats and walls already in existence can be kept up but no new ones can be established
# Neither side shall make requests outside of this treaty.
Though not specifically stated in the treaty, the two imperial families used familiar terms with one another. The Khitan Emperor would address the Song Emperor as "elder brother", while the Song Emperor would address the Khitan Empress Dowager as "aunt". Despite the Song getting an arguably more prestigious position, opposition to this treaty among the Song was considerable, as it was believed that the Khitan were overexposed. Nevertheless, this treaty avoided any further major wars between the two.
Wang Jizhong
Wang a native Kaifeng, was captured by the Kitans in 1003 at the battle of Wang-Tu. The Kitan emperor awarded Wang with official rank in the Kitan bureaucracy. Wang made the best of his circumstances and spoke with the Kitans of the advantage of resolving their conflict with the Song peacefully. The dowager empress Ch'eng-t'ien, who was in actual control of the Kitan state at the time, had grown tired of war, and she listened to Wang's proposals. With the Liao empress dowager's approval, Wang submitted a memorial to the Song emperor through the Song prefect of Mochou, stating that the Liao court wished to restore friendly relations. So, Wang facilitated the first talks of peace between the two empires. He had inside information for both of the empires so he knew exactly what each of them wanted in return for peace so he proposed exactly that to both sides. In the end it was Wang who persuaded the empress to give up on her land claims which ultimately led to the Chanyuan Treaty.Significance of the treaty
The signing of the Chanyuan Treaty was the first time that the Liao forced the Song, who considered themselves the natural heirs to the Central Kingdom (Zhong Yuan), to recognize them as peers. This relationship lasted until 1125, when the Song broke the treaty by inviting theJurchens
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manch ...
(later known as Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
) to attack the Liao. The Jurchen attack in fact brought an end to both the Liao and the Northern Song relationship.
This treaty immediately reduced the strain on Liao finances. Politically speaking, these annual payments were used to facilitate the construction of Liao's central capital. Peace with the Song allowed the Liao to focus more on their internal affairs and its relations with other people. So, this capital ultimately allowed the Liao to establish an international trade network. Without these annual payments from the Song it would have been highly unlikely that the Liao would have been able to create such a trading network and become the international force that they did. Economically, these payments secured the Liao a steady source of income and even helped facilitate trade with its neighbors because it now had more resources to produce goods in which they specialized in. More importantly, this treaty led to the growth of international trade along the Liao-Song border.
This treaty allowed the Song to secure disputed territory in exchange for a very minimal yearly payment. In addition now that the war was over the Song were able to focus on other matters. For one, they were able to advance their foreign diplomacy. On a different note, the Song were able to stop their military spending which was putting a serious strain on their economy. In the grand scheme of things, the yearly payments were a far less burden than the Song's military spending against the Liao.
After the Treaty
This treaty became the basis for relations between the Song and other Chinese states including theWestern Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China tha ...
and the Jin dynasty. Xi Xia incursions in the northwest (at the urging of the Liao) forced the Song to raise their payments to 300,000 bolts of silk and 200,000 ounces of silver.
Along the way there were incidents that jeopardized the peace between the Liao and Song. Basically, in 1042 the Khitans threatened to launch a military expedition against the Northern Hedong circuit __NOTOC__
Hedong (, unless otherwise noted) may refer to these places in China:
Districts
* Hedong District, Sanya, in Sanya, Hainan
* Hedong District, Linyi, in Linyi, Shandong
*Hedong District, Tianjin, in Tianjin
Subdistricts
* Hedong Subdistri ...
in order to get the Song to increase their annual tributes to the Khitans. Then in 1076 the Song ceded the Liao a few parcels of land along the Hedong border. This inevitably created a predicament because the original guidelines of the treaty made sure that the Song did not cede any territory to the Liao.
The accounts of the treaty in the Liao records and the Song records does not tally with each faction. The altering of some details shows a great deal of political boundary maintenance and an attempt at keeping dignity bias, which is prevalent in the Song dynasty faction. After the treaty was signed, the nature of the relationship between these two states changed from one of purely political rivalry to a supposed fraternal relationship. For the first time in Chinese history there were two Sons of Heaven, recognized by each other.
See also
*List of treaties
This list of treaties contains known agreements, pacts, peaces, and major contracts between states, armies, governments, and tribal groups.
Before 1200 CE
1200–1299
1300–1399
1400–1499
1500–1599
1600–1699
1700–1799
...
References
* * *Wright, David (1998). ''The Sung-Kitan War of A.D. 1004-1005 and the treaty of Shan-Yuan''. Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 2–44 *Wright, David (2005). ''Sung's Foreign Relations with Kitan Liao''. Leiden ; Boston. PP-140-184 * Twitchett, Denis (1994). ''The Cambridge History of China: Alien Regimes and Border States''. Cambridge University Press. pp. 100–134 {{Song dynasty topics 1005 Khitan history Song dynasty politics Liao dynasty 11th-century treaties 11th century in China Peace treaties of China 1005 in Asia