Shaftment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
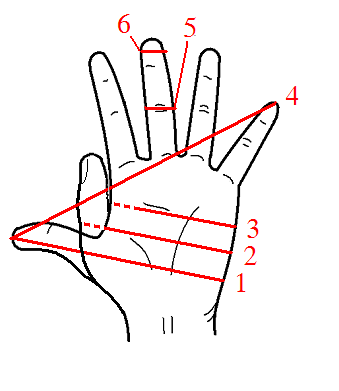 The shaftment is an obsolete unit of length defined since the 12th century as 6
The shaftment is an obsolete unit of length defined since the 12th century as 6
Units: S
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill - How Many? - A Dictionary of Units of Measurement
inch
Measuring tape with inches
The inch (symbol: in or ″) is a unit of length in the British imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to yard or of a foot. Derived from the Roman uncia ("twelfth") ...
es, which nowadays is exactly . A shaftment was traditionally the width of the fist and outstretched thumb. The lengths of poles, staves, etc. can be easily measured by grasping the bottom of the staff with thumb extended and repeating such hand over hand grips along the length of the staff.
History
It occurs in Anglo-Saxon written records as early as 910 and in English as late as 1474. After the modernfoot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made ...
came into use in the twelfth century, the shaftment was reinterpreted as exactly foot or .
Spelling and etymology
Other spellings include ''schaftmond'' and ''scaeftemunde'', and ''shathmont''. It is derived from Old English , in turn fromProto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branc ...
*''skaftaz'' (shaft) and OE , from the Proto-Germanic *''mund'', in turn from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
root *''man'' (hand.)
Two shaftments make a , literally .
This unit has mostly fallen out of use, as have others based on the human arm: digit ( shaftment), finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers ( Pentadactyly). Chambers ...
( shaftment), palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
**List of Arecaceae genera
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music
* Palm (ba ...
( shaftment) hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "h ...
({{2/3 shaftment), span
Span may refer to:
Science, technology and engineering
* Span (unit), the width of a human hand
* Span (engineering), a section between two intermediate supports
* Wingspan, the distance between the wingtips of a bird or aircraft
* Sorbitan ester ...
(1.5 shaftments), cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding No ...
(3 shaftments) and ell (7.5 shaftments).
References
Units: S
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill - How Many? - A Dictionary of Units of Measurement