Seyferth–Gilbert homologation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Seyferth–Gilbert homologation is a
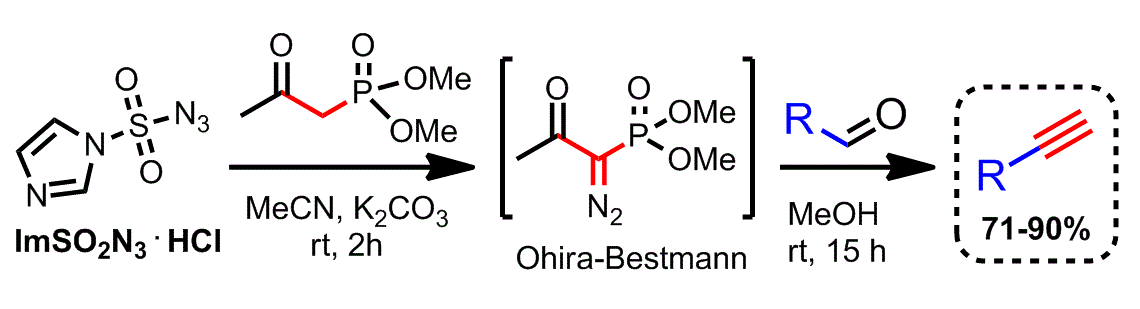 Recently a safer and more scalable approach has been developed for the synthesis of alkynes from aldehydes. This protocol takes advantage of a stable sulfonyl azide, rather than tosyl azide, for the ''in situ'' generation of the Ohira−Bestmann reagent.
Recently a safer and more scalable approach has been developed for the synthesis of alkynes from aldehydes. This protocol takes advantage of a stable sulfonyl azide, rather than tosyl azide, for the ''in situ'' generation of the Ohira−Bestmann reagent.
chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
of an aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromaticity, aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar ...
ketone 1 (or aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl grou ...
) with dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 and potassium tert-butoxide
Potassium ''tert''-butoxide is the chemical compound with the formula K+(CH3)3CO−. This colourless solid is a strong base (pKa of conjugate acid around 17), which is useful in organic synthesis. It exists as a tetrameric cubane-type cluster. ...
to give substituted alkynes 3. Dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 is often called the Seyferth–Gilbert reagent.
This reaction is called a '' homologation'' because the product has exactly one additional carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
more than the starting material.
Reaction mechanism
Deprotonation of the Seyferth–Gilbert reagent A gives an anion B, which reacts with the ketone to form the oxaphosphetane D. Elimination of dimethylphosphate E gives thevinyl
Vinyl may refer to:
Chemistry
* Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a particular vinyl polymer
* Vinyl cation, a type of carbocation
* Vinyl group, a broad class of organic molecules in chemistry
* Vinyl polymer, a group of polymers derived from vinyl m ...
diazo-intermediate Fa and Fb. The generation of nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
gas gives a vinyl
Vinyl may refer to:
Chemistry
* Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a particular vinyl polymer
* Vinyl cation, a type of carbocation
* Vinyl group, a broad class of organic molecules in chemistry
* Vinyl polymer, a group of polymers derived from vinyl m ...
carbene
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms.
The term "carbene" ma ...
G, which via a 1,2-migration forms the desired alkyne H.
Bestmann modification
The dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate carbanion can be generated ''in situ'' from dimethyl-1-diazo-2-oxopropylphosphonate (also called the Ohira-Bestmann reagent) by reaction withmethanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
and potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2 CO3. It is a white salt, which is soluble in water. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and gl ...
as the base by cleavage of the acetyl group as methyl acetate
Methyl acetate, also known as MeOAc, acetic acid methyl ester or methyl ethanoate, is a carboxylate ester with the formula CH3COOCH3. It is a flammable liquid with a characteristically pleasant smell reminiscent of some glues and nail polish remo ...
. Reaction of Bestmann's reagent with aldehydes gives terminal alkynes often in very high yield and fewer steps than the Corey–Fuchs reaction
The Corey–Fuchs reaction, also known as the Ramirez–Corey–Fuchs reaction, is a series of chemical reactions designed to transform an aldehyde into an alkyne. The formation of the 1,1-dibromoolefins via phosphine-dibromomethylenes was origina ...
.
The use of the milder potassium carbonate makes this procedure much more compatible with a wide variety of functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
s.
Improved ''in situ'' generation of the Ohira-Bestmann reagent
Other modifications
Another modification for less reactive aldehydes is made by replacement of potassium carbonate withcaesium carbonate
Caesium carbonate or cesium carbonate is a white crystalline solid compound. Caesium carbonate has a high solubility in polar solvents such as water, alcohol and DMF. Its solubility is higher in organic solvents compared to other carbonates l ...
in MeOH and results in a drastic yield increase.
See also
*Corey–Fuchs reaction
The Corey–Fuchs reaction, also known as the Ramirez–Corey–Fuchs reaction, is a series of chemical reactions designed to transform an aldehyde into an alkyne. The formation of the 1,1-dibromoolefins via phosphine-dibromomethylenes was origina ...
*Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction
The Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons (HWE) reaction is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry of stabilized phosphonate carbanions with aldehydes (or ketones) to produce predominantly E-alkenes.
In 1958, Leopold Horner published a modifi ...
*Wittig reaction
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Mos ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Seyferth-Gilbert homologation Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions Rearrangement reactions Name reactions