settle time on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
Second-Order System Example
Op Amp Settling Time
of Settling time and Risetime
for computing settling time, rise time, and other step response characteristics Transient response characteristics Systems_theory
 In
In control theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a ...
the settling time of a dynamical system
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a ...
such as an amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the v ...
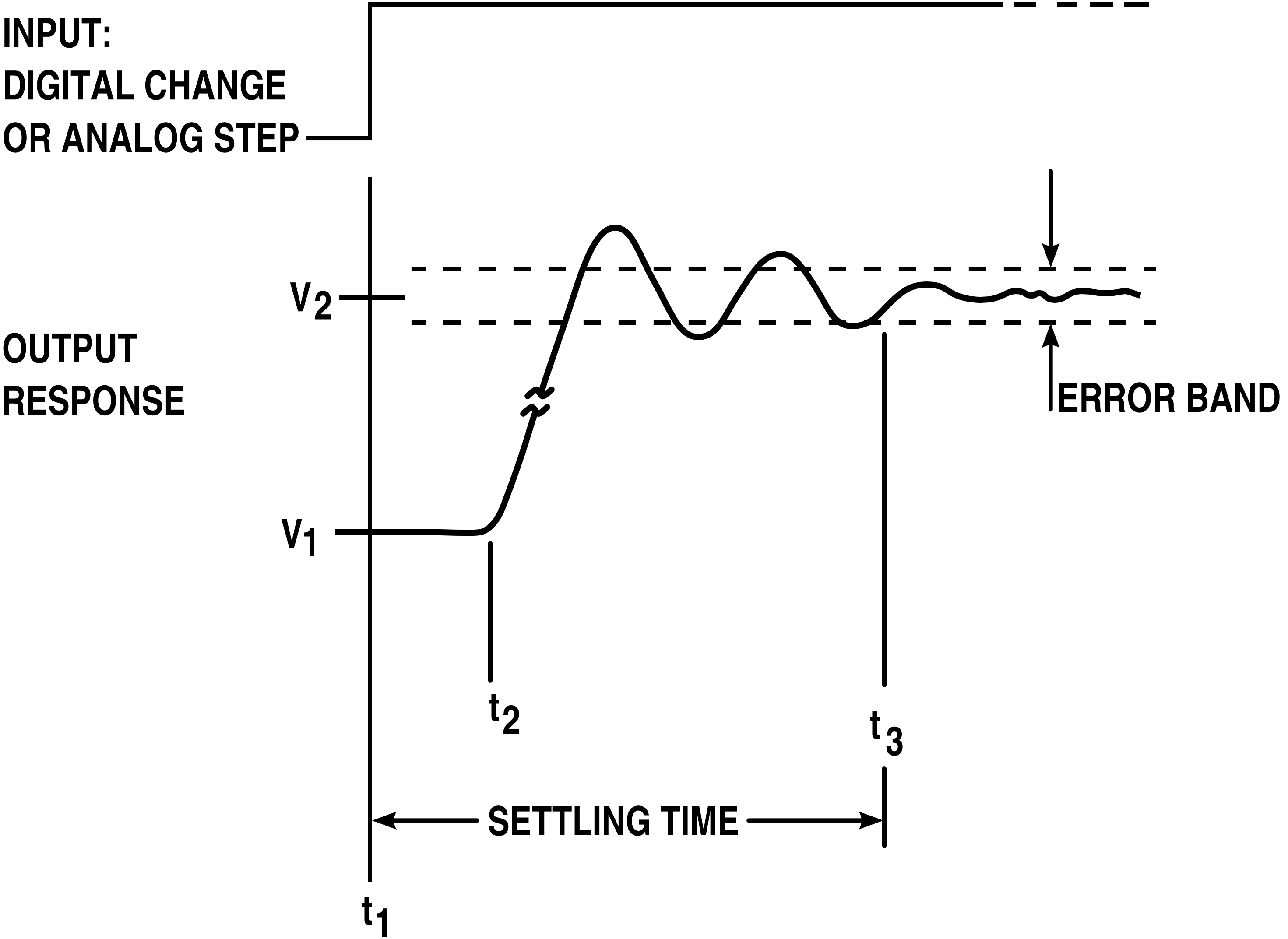
or other output device is the time elapsed from the application of an ideal instantaneous step input to the time at which the amplifier output has entered and remained within a specified error band.
Settling time includes a propagation delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics. ''Hold time'' is the minimum interval required for the logic level to remain on the input after triggering e ...
, plus the time required for the output to slew to the vicinity of the final value, recover from the overload condition associated with slew, and finally settle to within the specified error.
Systems with energy storage cannot respond instantaneously and will exhibit transient responses when they are subjected to inputs or disturbances.
Definition
Tay, Mareels and Moore (1998) defined settling time as "the time required for the response curve to reach and stay within a range of certain percentage (usually 5% or 2%) of the final value."Mathematical detail
Settling time depends on the system response andnatural frequency
Natural frequency, also known as eigenfrequency, is the frequency at which a system tends to oscillate in the absence of any driving force.
The motion pattern of a system oscillating at its natural frequency is called the normal mode (if all par ...
.
The settling time for a second order, underdamped
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. Examples incl ...
system responding to a step response
The step response of a system in a given initial state consists of the time evolution of its outputs when its control inputs are Heaviside step functions. In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the out ...
can be approximated if the damping ratio by
A general form is
Thus, if the damping ratio , settling time to within 2% = 0.02 is:
See also
*Rise time In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. These values may be expressed as ratiosSee for example , and . or, equivalen ...
* Time constant In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter (tau), is the parameter characterizing the response to a step input of a first-order, linear time-invariant (LTI) system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a sy ...
References
External links
{{wikisourcehas, a paper on settling time measurements., Wikisource:High accuracy settling time measurementsSecond-Order System Example
Op Amp Settling Time
of Settling time and Risetime
for computing settling time, rise time, and other step response characteristics Transient response characteristics Systems_theory