Setpoint (control System) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
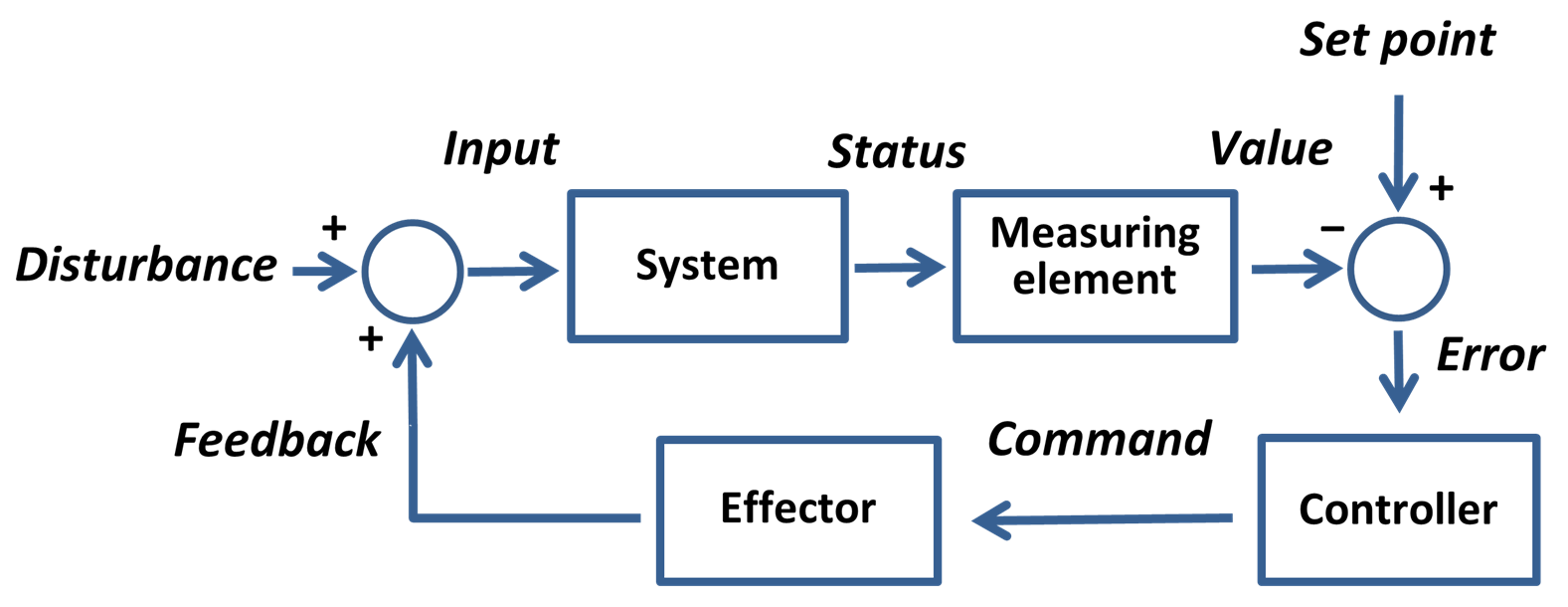 In
In
 In
In cybernetics
Cybernetics is a wide-ranging field concerned with circular causality, such as feedback, in regulatory and purposive systems. Cybernetics is named after an example of circular causal feedback, that of steering a ship, where the helmsperson m ...
and control theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a ...
, a setpoint (SP; also set point) is the desired or target value for an essential variable, or process value (PV) of a control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial c ...
. Departure of such a variable from its setpoint is one basis for error-controlled regulation using negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by ...
for automatic control.
Examples
Cruise control The SP-PV error can be used to return a system to its norm. An everyday example is thecruise control
Cruise control (also known as speed control, cruise command, autocruise, or tempomat) is a system that automatically controls the speed of a motor vehicle. The system is a servomechanism that takes over the throttle of the car to maintain a ste ...
on a road vehicle; where external influences such as gradients cause speed changes (PV), and the driver also alters the desired set speed (SP). The automatic control algorithm restores the actual speed to the desired speed in the optimum way, without delay or overshoot, by altering the power output of the vehicle's engine. In this way the SP-PV error is used to control the PV so that it equals the SP. A widespread use of SP-PV error control is the PID controller
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuou ...
.
Industrial applications
Special consideration must be given for engineering applications. In industrial systems, physical or process restraints may limit the determined set point. For example, a reactor which operates more efficiently at higher temperatures may be rated to withstand 500°C. However, for safety reasons, the set point for the reactor temperature control loop would be well below this limit, even if this means the reactor is running less efficiently.
See also
*Process control
An industrial process control in continuous production processes is a discipline that uses industrial control systems to achieve a production level of consistency, economy and safety which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. I ...
References
Classical control theory Control devices Control engineering Control loop theory Cybernetics Process engineering {{Tech-stub