Service Number (United States Army) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Service numbers were used by the United States Army from 1918 until 1969. Prior to this time, the Army relied on muster rolls as a means of indexing enlisted service members while officers were usually listed on yearly rolls maintained by the
 The highest Army officer service numbers were issued slightly above 05 850 999 although there are no clear records of who held these final numbers, again due to Social Security numbers being used for record keeping instead of service numbers. The last Regular Army service number was somewhere in the 130 000 to 140 000 range.
The highest Army officer service numbers were issued slightly above 05 850 999 although there are no clear records of who held these final numbers, again due to Social Security numbers being used for record keeping instead of service numbers. The last Regular Army service number was somewhere in the 130 000 to 140 000 range.
 After 1969, the Army completely converted to Social Security numbers for the identification of military personnel.
After 1969, the Army completely converted to Social Security numbers for the identification of military personnel.
"WWII US Army Enlistment Records Database"
{{US Army navbox Military life Identifiers History of the United States Army
United States War Department
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department (and occasionally War Office in the early years), was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army, a ...
. In the nineteenth century, the Army also used pay records as a primary means of identifying service members after discharge.
World War I
Service numbers (SNs) were first created in 1918 as a result of theUnited States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
becoming involved in World War I and the need for a record tracking system capable of indexing the millions of soldiers who were joining the ranks of the National Army. Prior to this time, the only way to index lists of soldiers was by use of rosters and muster rolls. As the strength of the National Army rose into the millions, this old method of musters and rosters became outdated and a new system had to be developed.
The decision to create Army service numbers was made in February 1918 with the first service numbers to be issued only to Army enlisted personnel; the Army officer corps was still relatively small, and the Navy was still maintaining ship rosters to keep track of its personnel. The Marine Corps and Coast Guard were also relatively small organizations without the need for a service number system to track personnel.
The first soldier to receive an Army service number during the First World War was Master Sergeant Arthur Crean
Arthur B. Crean was a master sergeant in the United States Army during World War I. He was the first United States armed forces member to be issued a service number and thus holds service #1 in the United States Army.
When U.S. Army service numb ...
who was designated to hold service number 1 in the National Army in February 1918. Throughout the remainder of World War I, service numbers were issued to most enlisted personnel with the numbers eventually ranging from 1 to 5 999 999.
In 1920, a year after the close of World War I, the Army introduced the first "service number prefix" which was intended to be a letter placed in front of the service number to provide additional information about the veteran. The first prefix to be created was R which was used to identify Regular Army personnel who had re-enlisted after the close of World War I and the disbandment of the National Army. Again, Arthur Crean was the first person to receive a service number prefix, and his new service number became R-1. The Army also created an F prefix for those who had served as World War I field clerks.
That same year, the Army opened up the service number rolls to officers and issued the first officer number to John J. Pershing
General of the Armies John Joseph Pershing (September 13, 1860 – July 15, 1948), nicknamed "Black Jack", was a senior United States Army officer. He served most famously as the commander of the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) on the Wes ...
. Pershing held officer service number 1 with the prefix O, making his service number O-1. In 1935, the Army created a second officer prefix, AO, intended for Regular Army officers who were aviators in the Army Air Corps Army Air Corps may refer to the following army aviation corps:
* Army Air Corps (United Kingdom), the army aviation element of the British Army
* Philippine Army Air Corps (1935–1941)
* United States Army Air Corps (1926–1942), or its p ...
.
The Army officer number system was determined simply by seniority and entry date into the Army officer corps; between 1921 and 1935, officer numbers ranged from 1 to 19 999. Enlisted service numbers continued in a similar fashion with enlisted numbers picking up where the World War I numbers had left off; between 1919 and 1940 the numbers ranged from 6 000 000 to 7 099 999. Enlisted personnel who were World War I veterans continued to hold their pre-6 million series service numbers.
World War II
By 1940, it was obvious to most in the U.S. military establishment that America would soon be involved in a major war. To that end,conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
had been introduced and the Army of the United States
The Army of the United States is one of the four major service components of the United States Army (the others being the Regular Army, the United States Army Reserve and the Army National Guard of the United States), but it has been inactive si ...
was activated as an augmentation force to serve in the coming war.
Due to the vast numbers of personnel entering the Army ranks, a major expansion to the service number system was required. The original concept was to simply continue with the old service number system and begin with new numbers starting at 8 000 000. The Army, however, chose a more complicated design with new numbers beginning at 10 000 000. The eight and nine million series were reserved for special uses; eight million series service numbers would later be used strictly by female Army personnel, while the nine million series service numbers were never issued.
Enlisted men
Wartime service numbers of the Regular Army and theArmy of the United States
The Army of the United States is one of the four major service components of the United States Army (the others being the Regular Army, the United States Army Reserve and the Army National Guard of the United States), but it has been inactive si ...
began at 10 000 000 and extended to 19 999 999. A subset of this series was reserved solely for those who had enlisted from recruiting stations outside of the 48 contiguous states of the United States. The first number after the "ten" would indicate the geographical region from which a person had enlisted with the remaining numbers an identification number for the soldier. The geographical codes were 10 1 (for Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
), 10 2 (for Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Cos ...
), 10 3 (for the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
) and 10 4 (for Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
). The remaining number codes (5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 0) were unassigned and used by various recruiting stations outside the United States.
The 11 000 000 through 19 999 999 series were issued to enlisted personnel who had enlisted within the boundaries of the 48 contiguous states and the territory of Alaska after 1 July 1940. The second number was determined by what group of states a person was recruited from, the next six were an identifying number for the service member; thus, for each geographical area there was an available range of 999,999 service numbers. The various geographical number codes were as follows:
11: Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
12: Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
13: Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
, Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
14: Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, Georgia, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
15: Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
16: Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
, Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
17: Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
, Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
, Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
, North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the Native Americans in the United States, indigenous Dakota people, Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north a ...
, South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the south ...
18: Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
19: Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
, Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
, Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on ...
During World War II, the US Army federalized a large number of National Guard personnel to augment the growing Army of the United States. Prior to 1940, there was no procedure to issue service numbers to National Guard personnel, since most personnel served completely under the authority of their state government
A state government is the government that controls a subdivision of a country in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, or ...
.
Beginning in 1940, National Guardsmen who were federalized were given Army service numbers in the 20 million range with numbers ranging from 20 000 000 to 20 999 999. Guardsmen federalized from Hawaii were issued service numbers beginning with 20 01 while 20 02 was used by men from Puerto Rico. With the exceptions of Hawaii and Puerto Rico, the first three numbers corresponded to a geographical area where a person had been federalized, and the last five were a personal identifier. The geographical codes matched those of voluntary enlistees, and were as follows:
20 1: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Vermont
20 2: Delaware, New Jersey, New York
20 3: Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Washington, D.C.
20 4: Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee
20 5: Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, West Virginia
20 6: Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin
20 7: Colorado, Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, Wyoming
20 8: Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas
20 9: Alaska, Arizona, California, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, Utah, Washington
The conscripted force of the Army of the United States were issued service numbers in the 30 million range. Service numbers ranged from 30 000 000 to 39 999 999. As with Regular Army or Army of the United States voluntary enlistee service numbers, the second number corresponded to a geographical area where a person had been drafted and the last six were a personal identifier. The geographical codes matched those of voluntary enlistees and National Guard personnel, and were as follows:
31: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Vermont
32: Delaware, New Jersey, New York
33: Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Washington, D.C.
34: Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee
35: Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, West Virginia
36: Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin
37: Colorado, Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, Wyoming
38: Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas
39: Alaska, Arizona, California, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, Utah, Washington
The 30 code was reserved for those who had been drafted from outside the United States with the third number following the "30" determining the extra-US draft location. The extra-US draft codes which were established were 30 1 (Hawaii), 30 2 (Panama), 30 3 (the Philippines), and 30 4 (Puerto Rico).
In 1942, the Army expanded the enlisted conscript service numbers and created the forty million service number series (40 000 000 to 49 999 999). These numbers were to be used for persons drafted from geographical areas that had exceeded their initially allotted 999,999 numbers. In all, the only forty million series numbers that were ever issued ranged from 42 000 000 to 46 999 999. The forty million series numbers were discontinued after World War II and never reused.
A final service number series of World War II was the ninety million series (90 000 000 to 99 999 999) which was reserved for members of the Philippine Army who had been called up to serve in the ranks of the U.S. Army. These numbers were rarely issued and the ninety million series was permanently discontinued after World War II.
During World War II, the Army also expanded the service number prefixes to include several new one letter designators in addition the original three prefixes (R, F, and O) which had been created after World War I. In all, the following prefixes were used during World War II.
A: Used by female members of the Women Army Corps
F: Used by field clerks during the First World War
K: Used by female reserve and specialist officers with service numbers 100 001 and higher
L: Used by enlisted members of the Women's Army Corps
N: Used by female nurse officers
O: Used by Regular Army officers
R: Used by Army enlisted personnel with service #s from 1 to 5 999 999 upon reenlistment
T: Used by flight officers appointed from an enlisted status
V: Used by officers of the Women Army Corps
W: Used by Regular Army Warrant Officers
Officers
Army officers continued to be assigned service numbers based on when they joined the officer corps with a service number range of 1 to 20 000. In 1935, the Army extended the service numbers to 499 999 and, in 1942, officer service numbers were extended again to 3 000 000. Officers of the Regular Army were assigned lower service numbers, with West Point graduates in the 1920s and 1930s receiving those in the 20 000 to 50 000 range. The service numbers 800 000 through 999 999 were reserved for officers with special duties, while higher service numbers were held by officers of the Officers' Reserve Corps, graduates of officer candidate schools, or those who had been directly commissioned from the enlisted ranks. By 1942, the Army had also discontinued the prefix O and established that all officer numbers would begin with a zero. For instance, an officer with the service number O-2 345 678 would have the number written in military records as 02 345 678.After the war
In October 1945, the Army discontinued the prefix "R" and issued the prefix "RA" to all members of the Regular Army. At the same time, the Army added several other R series prefixes to deal with special enlisted situations. In all, the R prefix series was: RA: Regular Army enlisted personnel RM: Regular Army enlisted personnel holding temporary appointments as Warrant Officers RO: Used by Regular Army enlisted personnel holding temporary reserve officer commissions RP: Retired enlisted personnel recalled to active duty RV: Female warrant officers granted reserve commissioned officer billets RW: Male warrant officers granted reserve commissioned officer billets After World War II, the Army of the United States was demobilized and the thirty and forty million series numbers were discontinued. Personnel of the Regular Army continued to be cycled through the 10 - 19 million series while Army officers continued to be issued numerical numbers determined by date of commission. By the end of the 1940s, the 3,000,000 service number cap for officers had yet to be reached.Korean War service numbers
At the end of the Second World War, the United States Army was reorganized into the following components: * Regular Army: The voluntary force of the United States Army * Army Reserve: The combined force formed from the older Enlisted and Officer Reserve Corps * Army of the United States: The peacetime draft force * Army National Guard: State military forces Between 1945 and 1947, the World War II draft force was slowly disbanded with the 30 and 40 million service number series formally discontinued. Personnel who chose to remain on active duty kept their original service numbers, regardless of their new component. TheUnited States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal ...
was also founded in September 1947, with enlisted personnel transferring into the new organization with their old Army service numbers while officers were either issued a new number or kept their Army number as well.
In 1948, the Army opened up the 50 million service number series. These numbers would range from 50 000 000 to 59 999 999 and would be assigned to personnel who were either drafted into the Army of the United States or who enlisted into the Army Reserve. As with the older 30 million numbers, the first two numbers were determined by the geographical region from which a soldier was drafted or had enlisted. Numbers beginning with "50" specified an entry location outside the United States with 0''50 0 reserved for Hawaii, 50 1 reserved for Panama and Puerto Rico, and 50 2 reserved for Alaska. Within the United States, the geographical codes were:
51: Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Vermont
52: Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Virginia, West Virginia
53: Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee
54: Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas
55: Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, Wisconsin, Wyoming
56: Arizona, California, Idaho, Georgia, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, Utah, Washington
Service numbers beginning with 57, 58, and 59 were not assigned a specific geographical region and were used for enlisted personnel in the Army Reserve or those assigned to special duties. When the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
began in 1950, this service number system was used throughout the conflict and through the remainder of the 1950s. The Regular Army service number system, ranging from 10 to 19 million, remained unchanged.
Officer service numbers during this period ranged from 50 000 to 500 000 (set aside for West Point graduates and Regular Army officers) and 500 001 to 3 000 000 used by reserve and direct appointment officers. All officer service numbers by this point were preceded by a zero.
Vietnam era service numbers
In 1954, one year after the close of the Korean War, the Army extended the range of officer service numbers by adding the three and four million series. The new officer service numbers ranged from 1 000 000 to 4 999 999; service numbers from 800 000 to 999 999 were still being used for special duty officers. In 1957, officer numbers were extended again this time to 5 999 999. It was also declared that the three million numbers (3 000 000 – 3 999 999) would only be issued towarrant officers
Warrant officer (WO) is a rank or category of ranks in the armed forces of many countries. Depending on the country, service, or historical context, warrant officers are sometimes classified as the most junior of the commissioned ranks, the most ...
. Service numbers below 500 000 were only issued to West Point graduates and other Regular Officers. By 1969, the highest service number issued to a West Point graduate was slightly above 120 000.
Enlisted service numbers during this post-Korea/pre-Vietnam era remained unchanged with the Regular Army continuing to cycle through the 10 - 19 million series while the draft force was assigned service numbers in the 50 to 59 million range. In 1966, with the increased US involvement of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, the Army realized that many more troops would be needed. The service number system had to be expanded, which resulted in the Army activating the 60 million enlisted service number series in 1967. Officer service numbers remained unchanged.
The new enlisted service numbers applied only to those drafted and ranged from 60 000 000 to 69 999 999 with the first two numbers a recruiting code and the last six a personal identifier. At the same time, there were still a wide variety of older enlisted numbers still active, ranging back to the thirty million series used during World War II.
By 1968, the Army had also declared the final version of service number prefixes. The most common prefixes were the following two letter codes:
ER: Used by enlisted members of the Army Reserve
FR: Used by some Army reservists from the late 1940s through 1962
KF: Used by female Regular Army officers
NG: Used by National Guard enlisted personnel
OF: Used by male Regular Army officers
UR: Used by draft personnel appointed as officers in the Regular Army
US: Used by conscripted enlisted personnel
The following special prefixes for medical personnel were also declared during the mid-1960s:
MJ: Used by Occupational Therapist Officers
MM: Used by Physical Therapist Officers
MN: Used by male members of the Army Nurse Corps
MR: Used by Army enlisted dieticians
The Army also used the following one letter prefixes for a brief period of time in the 1960s:
O: Used by some Army specialist officers
R: Used by Army officer dieticians
From the late 1950s to the mid-1960s, the Army also had established the following special prefix codes for female personnel:
WA: Used by enlisted members of the Women Army Corps
WL: Used by female Regular Army personnel granted officer commissions in the Army Reserve
WM: Used by female Regular Army personnel granted warrant officer commissions in the Army Reserve
WR: Used by female enlisted reservists attached to the Women Army Corps
The Regular Army prefix codes RA, RM, RO, RP, RV, and RW remained unchanged from their post World War II origins.
Discontinuation of Army service numbers
In 1968, the Army activated the seventy million series and in 1969 created eighty million numbers as well. The new numbers, which were to be issued only to the enlisted draft force, ranged from 70 000 000 to 89 999 999. By this time, however, service numbers had been informally discontinued and most military records used Social Security numbers to identify the service member. As a result, on July 1, 1969, service numbers were declared discontinued and no 70 or 80 million series numbers were ever issued. It was not recorded who exactly held the last service number of the United States Army. The highest service number for the draft force was in the 68 million range; however, since Social Security numbers were being commonly used instead of service numbers, the identity of the soldier who held this number is unknown. The Regular Army, which had issued service numbers by geographical codes since World War II, had several numbers which could be interpreted as the final service number of the 10–19 million series. The highest Army officer service numbers were issued slightly above 05 850 999 although there are no clear records of who held these final numbers, again due to Social Security numbers being used for record keeping instead of service numbers. The last Regular Army service number was somewhere in the 130 000 to 140 000 range.
The highest Army officer service numbers were issued slightly above 05 850 999 although there are no clear records of who held these final numbers, again due to Social Security numbers being used for record keeping instead of service numbers. The last Regular Army service number was somewhere in the 130 000 to 140 000 range.
 After 1969, the Army completely converted to Social Security numbers for the identification of military personnel.
After 1969, the Army completely converted to Social Security numbers for the identification of military personnel.
Social Security Numbers Discontinued
In December 2015, a U.S. Army press release announced that the Army was phasing out the use of soldiers' Social Security numbers on their dog tags. Instead it would use the soldiers' Department of Defense Identification Numbers, which are randomly-generated 10-digit numbers. The change would not happen all at once; it was being implemented "on an as-needed basis."Geographical Codes and Regular Army Distribution
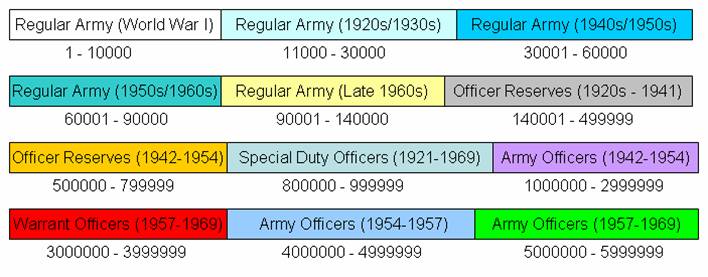
State Geographical Codes were used as the first two numbers of an Army or Air Force enlisted service number to indicate where a soldier had entered the U.S. military. For instance, the service number "12 345 678" would have a geographical code of 12 and a personal identification number of 345,678. A comparison of the state codes between the Regular Army, World War II draft force, and Korea/Vietnam draft force is as follows: In 1940, when the United States Army expanded its service numbers beyond ten million, the range of 10 000 000 to 10 999 999 was reserved for Regular Army enlisted personnel who joined from recruiting stations outside the United States. With 999,999 service numbers available in this range, the Regular Army was able to issue service numbers to extra-US enlistees, without repeating numbers, until the disestablishment of service numbers in 1969. The remaining range of 11 000 000 to 19 999 999 was reserved for Regular Army personnel who enlisted from within the United States with the first two numbers a geographical code and the last six a personal identifier. This gave geographical recruiting areas 999,999 service numbers a piece to allocate to new recruits. The Army directed that every effort should be made to avoid repeating service numbers and allocated only a certain block of numbers for certain time periods of enlistments. The matter was made even more complicated when the Regular Air Force came into being in 1947, also with instructions that the 11–19 million service numbers should not be repeated nor should an Air Force service member be given a service numbers already held by a Regular Army soldier. In general, both the Army and Air Force made every effort to avoid repeating service numbers although some mistakes did occur. The final breakdown of Regular Army service numbers by time period was as follows: Draft force service numbers in the 30 and 50 million range also used geographical codes but were free to use all 999,999 possible personal identification numbers for the entire period of the draft. The 30 million series was used for World War II draftees and the 50 million for the Korean War and early Vietnam. The 60 million series of the late Vietnam War was issued without restriction. Basic Training soldiers on July 1, 1969, were required to memorize both the Service Number and the Social Security number to accommodate the changeover to using only the Social Security number.Notable service numbers
The following service numbers have been held by some of the more famous veterans of the United States Army: * R-1:Arthur Crean
Arthur B. Crean was a master sergeant in the United States Army during World War I. He was the first United States armed forces member to be issued a service number and thus holds service #1 in the United States Army.
When U.S. Army service numb ...
* O-1: John J. Pershing
General of the Armies John Joseph Pershing (September 13, 1860 – July 15, 1948), nicknamed "Black Jack", was a senior United States Army officer. He served most famously as the commander of the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) on the Wes ...
* O-2: Leonard Wood
* O-57: Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was C ...
* O-668: Charles F. Humphrey
* O-2605: George S. Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
* O-3822: Dwight Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
* O-5284: Norman Cota
Norman Daniel "Dutch" Cota, Sr. (May 30, 1893 – October 4, 1971) was a senior United States Army officer who fought during World War II. Cota was heavily involved in the planning and execution of the Allied invasion of Normandy, in June 1944, co ...
* O-12043: Leslie Groves
* O-20362: William P. Yarborough
Lieutenant general (United States), Lieutenant General William Pelham Yarborough (May 12, 1912 – December 6, 2005) was a senior United States Army Officer (armed forces), officer. Yarborough designed the U.S. Army's Parachutist Badge#United Sta ...
* O-143128: Archibald Roosevelt
* O-565390: Clark Gable
William Clark Gable (February 1, 1901November 16, 1960) was an American film actor, often referred to as "The King of Hollywood". He had roles in more than 60 motion pictures in multiple genres during a career that lasted 37 years, three decades ...
* O-662062: Gene Roddenberry
Eugene Wesley Roddenberry Sr. (August 19, 1921 – October 24, 1991) was an American television screenwriter, producer, and creator of ''Star Trek: The Original Series'', its sequel spin-off series ''Star Trek: The Animated Series,'' and ''Sta ...
* 073 858: Norman Schwarzkopf, Jr.
Herbert Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. (; August 22, 1934 – December 27, 2012) was a United States Army general. While serving as the commander of United States Central Command, he led all coalition forces in the Gulf War.
Born in Trenton, Ne ...
* 0 357 403: Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
* 0 765 497: Russell Johnson
* 05 242 035: Homer Hickam
* 2371377: Ian Wolfe
* 32 325 070: Burl Ives
* 32 694 076: Burt Lancaster
* 32 698 169: Nehemiah Persoff
* 32 726 378: Charles Durning
* 32 738 306: Rod Serling
* 32 980 601: Karl Malden
* 33 455 116: William Windom (actor), William Windom
* 35 425 274: Basil Plumley
* 35 756 363: Don Knotts
* 36 896 415: Eddie Slovik
* 39 531 145: Elisha Cook, Jr.
* 39 563 856: DeForest Kelley
* 39 744 068: Robert Mitchum
* ER 11 229 770: Leonard Nimoy
* ER 11 530 137: Todd Akin
* NG 28 296 022: Brion James
* US 51 214 821: Richard Herd
* US 52 314 745: Frank Gorshin
* US 52 346 646: Robert Duvall
* US 53 310 761: Elvis Presley
* US 54 356 205: Dean Corll
According to U.S. Army records, despite efforts to avoid duplicate service numbers, there have been at least six occurrences of an Army soldier who was issued the service number "12 345 678".Freedom of Information Act response, United States Army Human Resources Command, April 2007
See also
*Service number (United States Armed Forces)References
Sources
* National Personnel Records Center, Instruction Memo 1865.20E, "Service Number Information", 14 April 1988 * Military Personnel Records Center, "Training Guide Concerning Military Service Numbers", 28 June 2009External links
"WWII US Army Enlistment Records Database"
{{US Army navbox Military life Identifiers History of the United States Army