Selgovae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Selgovae (
 The sole record of the Selgovae and their towns is their mention by Ptolemy in c. AD 150. Their name appears in the 8th century ''
The sole record of the Selgovae and their towns is their mention by Ptolemy in c. AD 150. Their name appears in the 8th century ''
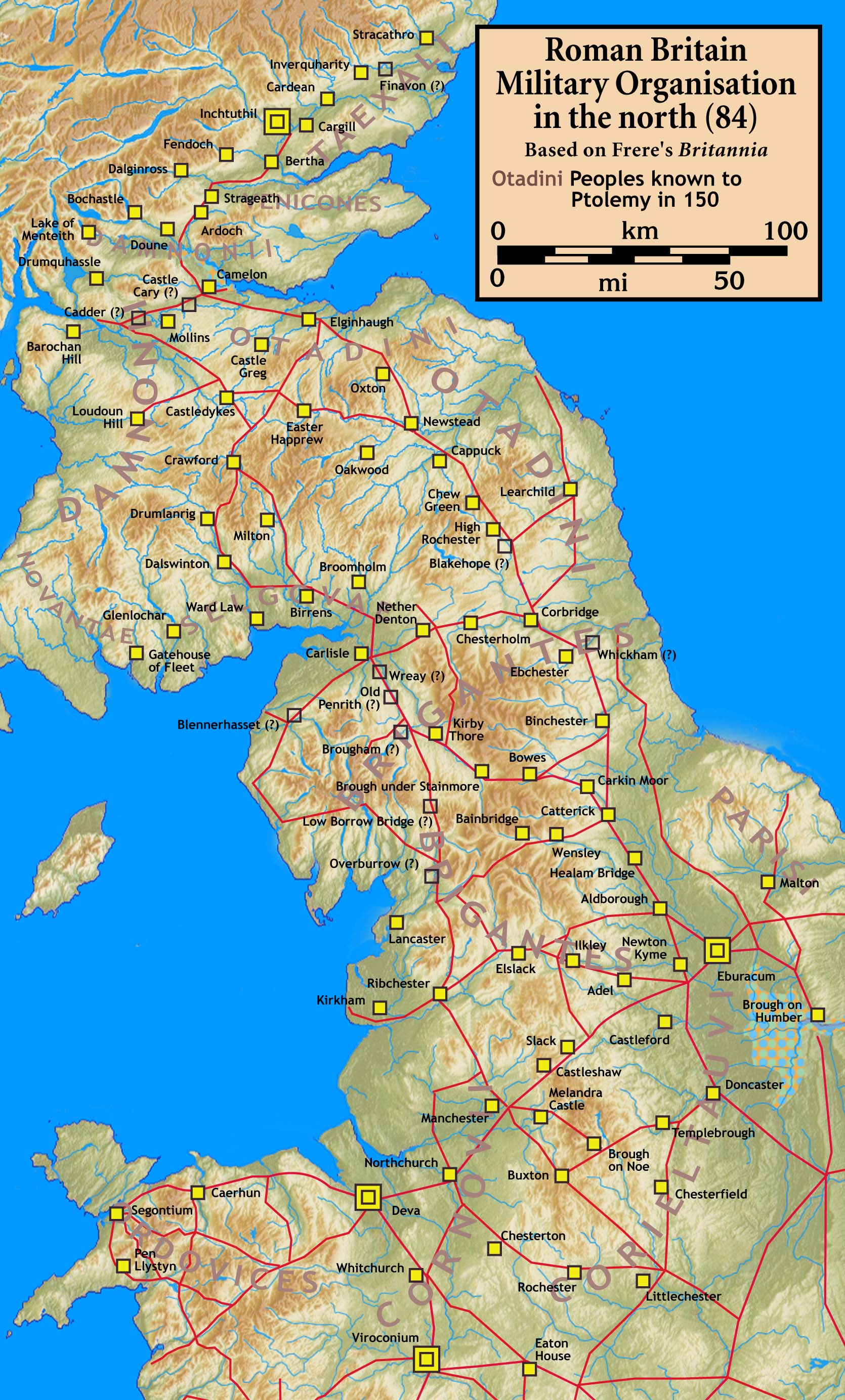 Archaeological evidence indicates that the Selgovae lived in two principal settlement types: stone-built huts and so-called "scooped enclosures", some of which were abandoned in the 1st century AD while others were established in the 2nd century and developed into multivallate structures. They had possibly lived in the area since the
Archaeological evidence indicates that the Selgovae lived in two principal settlement types: stone-built huts and so-called "scooped enclosures", some of which were abandoned in the 1st century AD while others were established in the 2nd century and developed into multivallate structures. They had possibly lived in the area since the
 When ''De Situ Britanniae'' was debunked as a fraud in 1845, Roy's misguided placement of Trimontium was retained by some historians, though he was no longer cited for his contribution. Furthermore, some historians not only accepted Roy's placement of Trimontium, but also returned the town to the Selgovae by moving their territory such that they would be near Eildon Hills. Ptolemy's placement of the Novantae in Galloway was retained, and since Ptolemy said that they were adjacent to the Selgovae, Novantae territory was greatly expanded beyond Galloway to be consistent with this thesis, which survives in a number of modern histories. – see, for example, the influential ''Iron Age Communities in Britain'', map of the tribes of Northern Britain, attributed to "various sources"
The result is that an 'error correction' to the sole legitimate historical reference (Ptolemy), made so that a fictional itinerary in ''De Situ Britanniae'' would seem more logical, is retained; and the sole legitimate historical reference is further 'corrected' by moving the Selgovae far from their only known location.
While Roy's historical work is largely ignored due to his unknowing reliance on a fraudulent source, his maps and drawings are untainted, and continue to be held in the highest regard. Roy's work is highly supported by the town Selkirk, which relates to the church of the Selgovae
When ''De Situ Britanniae'' was debunked as a fraud in 1845, Roy's misguided placement of Trimontium was retained by some historians, though he was no longer cited for his contribution. Furthermore, some historians not only accepted Roy's placement of Trimontium, but also returned the town to the Selgovae by moving their territory such that they would be near Eildon Hills. Ptolemy's placement of the Novantae in Galloway was retained, and since Ptolemy said that they were adjacent to the Selgovae, Novantae territory was greatly expanded beyond Galloway to be consistent with this thesis, which survives in a number of modern histories. – see, for example, the influential ''Iron Age Communities in Britain'', map of the tribes of Northern Britain, attributed to "various sources"
The result is that an 'error correction' to the sole legitimate historical reference (Ptolemy), made so that a fictional itinerary in ''De Situ Britanniae'' would seem more logical, is retained; and the sole legitimate historical reference is further 'corrected' by moving the Selgovae far from their only known location.
While Roy's historical work is largely ignored due to his unknowing reliance on a fraudulent source, his maps and drawings are untainted, and continue to be held in the highest regard. Roy's work is highly supported by the town Selkirk, which relates to the church of the Selgovae
Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
: *''Selgowī'') were a Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
tribe of the late 2nd century AD who lived in what is now the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county ...
and Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries (''Siorrachd Dhùn Phris'' in Gaelic) is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.
I ...
, on the southern coast of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
'', and there is no other historical record of them. Their cultural and ethnic affinity is commonly assumed to have been Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
.
Assertions that the Solway Firth
The Solway Firth ( gd, Tràchd Romhra) is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in ...
preserves the name of the Selgovae are without foundation. 'Solway' is Anglo-Saxon from the thirteenth century (''sol'' = 'mud', ''wæth'' = 'ford'), and this was the name of the main crossing at Eskmouth at that time. The firth has been known by various names in the past, and this one happened to be the survivor.
The historical record
Ptolemy
 The sole record of the Selgovae and their towns is their mention by Ptolemy in c. AD 150. Their name appears in the 8th century ''
The sole record of the Selgovae and their towns is their mention by Ptolemy in c. AD 150. Their name appears in the 8th century ''Ravenna Cosmography
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Text ...
'' as 'Segloes', but the document here is taken to be an imperfect copy of classical sources such as Ptolemy, and not an independent historical reference.
The Novantae
The Novantae were a people of the late 2nd century who lived in what is now Galloway and Carrick, in southwesternmost Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (written c. 150), and there is no other historical record of th ...
are unique among the peoples that Ptolemy names in that their location is reliably known to have been in Galloway due to the way he named several readily identifiable physical features. Since the Selgovae were adjacent to them, their homeland is similarly known.
Ptolemy said that the towns of the Selgovae were ''Carbantorigum'', ''Uxellum'', ''Corda'', and ''Trimontium''. However, there were no towns as such in the area at that time, so he was probably referring to Roman military
The military of ancient Rome, according to Titus Livius, one of the more illustrious historians of Rome over the centuries, was a key element in the rise of Rome over "above seven hundred years" from a small settlement in Latium to the capital o ...
camps and native strong points such as dun
A dun is an ancient or medieval fort. In Ireland and Britain it is mainly a kind of hillfort and also a kind of Atlantic roundhouse.
Etymology
The term comes from Irish language, Irish ''dún'' or Scottish Gaelic ''dùn'' (meaning "fort"), ...
s. In the ''Ravenna Cosmography'' the town names appear as ''Carbantium'', ''Uxela'', ''Corda'', and ''Trimuntium'', resp., and the towns are given in a list that does not associate any of the towns with any particular people.
Efforts have been made to determine the locations of the towns, but there is not enough information available to reach any degree of certainty, and the locations suggested are little more than guesswork.
In the 19th Century, ''Carbantorigum'' was thought to be the Motte of Urr
The Motte of Urr is the remains of a 12th-century motte-and-bailey castle located near the Haugh of Urr in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland.
History
Walter de Berkeley received Urr in 1165 from William I of Scotland. It was probably Walter who ...
by Skene
Skene may refer to:
* Skene, Aberdeenshire, a community in North East Scotland, United Kingdom
* Skene, Mississippi, an unincorporated community in Mississippi, United States
* Skene, Sweden, a village now part of Kinna, Sweden
* Skene (automobi ...
, and Rhys
Rhys or Rhŷs is a popular Welsh given name (usually male) that is famous in Welsh history and is also used as a surname. It originates from Deheubarth, an old region of South West Wales, with famous kings such as Rhys ap Tewdwr.
It is pronounced ...
thought the name derived from ''Carbantorion'' (''chariot town''). ''Uxellum'' was at Wardlaw Hill at Caerlaverock
Caerlaverock (; gd, Cille Bhlàthain) is a civil parish in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland.
The parish was historically in Dumfriesshire. The area includes:
* Caerlaverock Castle, a 13th-century castle, located south of Dumfries, Scotland
* Ca ...
according to Skene and Horsley; it was noted that the name sounds like Welsh ''uchel'' (''high'') or Gaelic ''uas'', ''uasal''. ''Corda'' was at Sanquhar
Sanquhar ( sco, Sanchar, gd, Seanchair) is a village on the River Nith in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, north of Thornhill and west of Moffat. It is a former Royal Burgh.
It is notable for its tiny post office, established in 1712 and con ...
, according to Skene. ''Trimontium'' was at Birrenswark Hill, according to Skene, who says its name probably represents Welsh ''Tref mynydd'' (''Town on a Mountain'').
Rhys
Rhys or Rhŷs is a popular Welsh given name (usually male) that is famous in Welsh history and is also used as a surname. It originates from Deheubarth, an old region of South West Wales, with famous kings such as Rhys ap Tewdwr.
It is pronounced ...
, agreeing with Wyntoun
Andrew Wyntoun, known as Andrew of Wyntoun (), was a Scottish poet, a Canon (priest), canon and prior of Loch Leven on St Serf's Inch and, later, a canon of St. Andrews.
Andrew Wyntoun is most famous for his completion of an eight-syllabled met ...
, thought that 'Selgovae' means 'the hunters' ( sga, selg, modern ga, sealg}; owl, selg, modern cy, hela} 'hunting').
Roman Era
 Archaeological evidence indicates that the Selgovae lived in two principal settlement types: stone-built huts and so-called "scooped enclosures", some of which were abandoned in the 1st century AD while others were established in the 2nd century and developed into multivallate structures. They had possibly lived in the area since the
Archaeological evidence indicates that the Selgovae lived in two principal settlement types: stone-built huts and so-called "scooped enclosures", some of which were abandoned in the 1st century AD while others were established in the 2nd century and developed into multivallate structures. They had possibly lived in the area since the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, and certainly during the pre-Roman Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
. The pattern of forts subsequently established in the area by the Romans suggests that the Selgovae lived in a number of distinct communities and probably had some degree of tribal and political organisation, perhaps influenced by individuals who had fled the Roman advance further south. They are thought to have had a tribal centre at Eildon Hill North near Melrose. They built a significant number of hillforts
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
, more so than their neighbours, which may explain why the Romans targeted them before the relatively less organised and therefore less threatening tribes to the west and north.
In his account of the campaigns of Gnaeus Julius Agricola
Gnaeus Julius Agricola (; 13 June 40 – 23 August 93) was a Roman general and politician responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. Born to a political family of senatorial rank, Agricola began his military career as a military tribun ...
(governor 78 – 84), Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
says that after a combination of force and diplomacy quieted discontent among the Britons who had been conquered previously, Agricola built forts in their territories in 79. In 80 he marched to the Firth of Tay
The Firth of Tay (; gd, Linne Tatha) is a firth on the east coast of Scotland, into which the River Tay (Scotland's largest river in terms of flow) empties. The firth is surrounded by four council areas: Fife, Perth and Kinross, City of Du ...
, campaigning against the peoples there. He did not return until 81, at which time he consolidated his gains in the lands that he had conquered.
The territory of the Selgovae was substantially planted with Roman forts at this time, at Broomholm, Blatobulgium
Blatobulgium was a Roman fort, located at the modern-day site known as Birrens, in Dumfriesshire, Scotland.
Name
Blatobulgium is recorded in the Antonine Itinerary. The name derives from the Brittonic roots ''*blāto-'' 'bloom, blossom' or ''*bl� ...
( Birrens), Ward Law, Milton, Drumlanrig, Dalswinton
Dalswinton is a small village in the historical county of Dumfriesshire in Dumfries and Galloway in the south of Scotland. It is located about northwest of Dumfries. To the east of the village a wind farm has been built with a capacity of 30&nb ...
, and at Glenlochar
Glenlochar ( Gd: ''Gleann Lochair'') is a hamlet on the western bank of the River Dee in the parish of Balmaghie in the historical county of Kirkcudbrightshire in Dumfries and Galloway. Glenlochar is located one and a half miles south of Balmag ...
on the eastern bank of the River Dee, which was perhaps the boundary between the Selgovae and the neighbouring Novantae
The Novantae were a people of the late 2nd century who lived in what is now Galloway and Carrick, in southwesternmost Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (written c. 150), and there is no other historical record of th ...
. This suggests (but does not confirm) that the Selgovae were among the British peoples who had strongly resisted Roman occupation. This is in contrast to the neighbouring Novantae, where there are no signs of Roman occupation save the fortlet at Gatehouse of Fleet
Gatehouse of Fleet ( sco, Gatehoose o Fleet gd, Taigh an Rathaid) is a town half in the civil parish of Girthon and half in the parish of Anwoth divided by the river Water of Fleet, Fleet, Kirkcudbrightshire, within the district council region o ...
, in the southeast of their territory.
Following the reorganisation of northern Roman Britain and the construction of Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
(c. 122), the only Roman forts in Selgovae territory were at Birrens and Netherby. However, with the construction of the Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as ''Vallum Antonini'', was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twe ...
and the re-occupation of territory north of Hadrian's Wall (c. 142), Selgovae territory was again heavily planted with Roman forts, at Netherby, Broomholm, Birrens, Burnswark, Raeburnfoot, Shieldhill, Milton, Drumlanrig, Dalswinton, Carzield, Lantonside, and Glenlochar. There were no Roman forts planted in the territory of the neighbouring Novantae.
When Rome largely abandoned its occupation of territory north of Hadrian's Wall under the reorganisation of Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
(c. 175), they nevertheless retained forts at Birrens and Netherby, though there would never again be a large-scale military occupation of Selgovae territory. Rome permanently abandoned Selgovae territory by 370.
Cultural affinity
The ethnic and cultural affinity of the Selgovae is assumed to have been Brittonic and there have been suggestions that they were an integral part of the tribe of theBrigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geogr ...
.
Archaeological evidence is scant, but it includes a Roman-era figure and inscription found at Birrens (the Roman Blatobulgium
Blatobulgium was a Roman fort, located at the modern-day site known as Birrens, in Dumfriesshire, Scotland.
Name
Blatobulgium is recorded in the Antonine Itinerary. The name derives from the Brittonic roots ''*blāto-'' 'bloom, blossom' or ''*bl� ...
) that was dedicated to 'Brigantia', similar to dedications found in known Brigantian territory in Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumb ...
and Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
. Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
says that the Brigantes were a large tribe,, ''Life of Agricola'', Chapter 17 and artefacts associated with the Brigantes have been found across the region just north of Hadrian's Wall, both in England and in Scottish Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries (''Siorrachd Dhùn Phris'' in Gaelic) is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.
I ...
and the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county ...
.
The Brigantes were troublesome to Roman rule, strongly resisting initial Roman occupation and frequently rising in efforts to throw off Roman rule. The Roman response was overwhelming force and the subsequent heavy plantation of forts of occupation. The heavy plantation of forts in Selgovae territory is similar to the Roman occupation of the Brigantes and unlike Roman treatment of other neighbouring peoples such as the Novantae
The Novantae were a people of the late 2nd century who lived in what is now Galloway and Carrick, in southwesternmost Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (written c. 150), and there is no other historical record of th ...
and Votadini
The Votadini, also known as the ''Uotadini'', ''Wotādīni'', ''Votādīni'', or ''Otadini'' were a Brittonic people of the Iron Age in Great Britain. Their territory was in what is now south-east Scotland and north-east England, extending fro ...
, who were never known to be at war with the Romans, and who were not heavily occupied.
Much later history, better recorded, shows that the territory of the Selgovae was continually associated with Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumb ...
(homeland of the Brigantes) and Alt Clud
Strathclyde (lit. "Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as Yr ...
(homeland of the Damnonii
The Damnonii (also referred to as Damnii) were a Brittonic people of the late 2nd century who lived in what became the Kingdom of Strathclyde by the Early Middle Ages, and is now southern Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geo ...
), both of which are known to have been Britonnic in culture and language.
Contradicting Ptolemy
Ptolemy's placement of the Selgovaean town of Trimontium was accepted to be somewhere along the southern coast of Scotland untilWilliam Roy
Major-General William Roy (4 May 17261 July 1790) was a Scottish military engineer, surveyor, and antiquarian. He was an innovator who applied new scientific discoveries and newly emerging technologies to the accurate geodetic mapping of Gr ...
(1726–1790) placed it far to the east at Eildon Hills
Eildon Hill lies just south of Melrose, Scotland in the Scottish Borders, overlooking the town. The name is usually pluralised into "the Eildons" or "Eildon Hills", because of its triple peak. The high eminence overlooks Teviotdale to the Sout ...
, near Newstead. Roy was trying to follow an itinerary given in the 1757 ''De Situ Britanniae
''The Description of Britain'', also known by its Latin name ' ("On the Situation of Britain"), was a literary forgery perpetrated by Charles Bertram on the historians of England. It purported to be a 15th-century manuscript by the English monk R ...
'', and moving Ptolemy's Trimontium made the itinerary seem more logical according to his historical work, ''Military Antiquities of the Romans in North Britain'' (1790, published posthumously in 1793). Roy did not alter Ptolemy's placement of the Selgovae in southern Scotland, but chose to assign Trimontium to a different people who were described in ''De Situ Britanniae''.
 When ''De Situ Britanniae'' was debunked as a fraud in 1845, Roy's misguided placement of Trimontium was retained by some historians, though he was no longer cited for his contribution. Furthermore, some historians not only accepted Roy's placement of Trimontium, but also returned the town to the Selgovae by moving their territory such that they would be near Eildon Hills. Ptolemy's placement of the Novantae in Galloway was retained, and since Ptolemy said that they were adjacent to the Selgovae, Novantae territory was greatly expanded beyond Galloway to be consistent with this thesis, which survives in a number of modern histories. – see, for example, the influential ''Iron Age Communities in Britain'', map of the tribes of Northern Britain, attributed to "various sources"
The result is that an 'error correction' to the sole legitimate historical reference (Ptolemy), made so that a fictional itinerary in ''De Situ Britanniae'' would seem more logical, is retained; and the sole legitimate historical reference is further 'corrected' by moving the Selgovae far from their only known location.
While Roy's historical work is largely ignored due to his unknowing reliance on a fraudulent source, his maps and drawings are untainted, and continue to be held in the highest regard. Roy's work is highly supported by the town Selkirk, which relates to the church of the Selgovae
When ''De Situ Britanniae'' was debunked as a fraud in 1845, Roy's misguided placement of Trimontium was retained by some historians, though he was no longer cited for his contribution. Furthermore, some historians not only accepted Roy's placement of Trimontium, but also returned the town to the Selgovae by moving their territory such that they would be near Eildon Hills. Ptolemy's placement of the Novantae in Galloway was retained, and since Ptolemy said that they were adjacent to the Selgovae, Novantae territory was greatly expanded beyond Galloway to be consistent with this thesis, which survives in a number of modern histories. – see, for example, the influential ''Iron Age Communities in Britain'', map of the tribes of Northern Britain, attributed to "various sources"
The result is that an 'error correction' to the sole legitimate historical reference (Ptolemy), made so that a fictional itinerary in ''De Situ Britanniae'' would seem more logical, is retained; and the sole legitimate historical reference is further 'corrected' by moving the Selgovae far from their only known location.
While Roy's historical work is largely ignored due to his unknowing reliance on a fraudulent source, his maps and drawings are untainted, and continue to be held in the highest regard. Roy's work is highly supported by the town Selkirk, which relates to the church of the Selgovae
See also
* Ptolemy's ''Geography'' *Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was ...
* Scotland during the Roman Empire
Scotland during the Roman Empire refers to the protohistory, protohistorical period during which the Roman Empire interacted with the area that is now Scotland. Despite sporadic attempts at conquest and government between the 1st and 4th centu ...
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * {{Iron Age tribes in Britain Tribes of ancient Scotland Celtic Britons Scotland in the Roman era 2nd century in Scotland Historical Celtic peoples Tribes mentioned by Ptolemy