Self-stimulatory Behavior on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Self-stimulatory behavior, also known as "stimming" and self-stimulation, is the repetition of physical movements, sounds, words, moving objects, or other repetitive behaviors. Such behaviors (also scientifically known as '
Self-stimulatory behavior, also known as "stimming" and self-stimulation, is the repetition of physical movements, sounds, words, moving objects, or other repetitive behaviors. Such behaviors (also scientifically known as '
 Stimming can sometimes be
Stimming can sometimes be
 Self-stimulatory behavior, also known as "stimming" and self-stimulation, is the repetition of physical movements, sounds, words, moving objects, or other repetitive behaviors. Such behaviors (also scientifically known as '
Self-stimulatory behavior, also known as "stimming" and self-stimulation, is the repetition of physical movements, sounds, words, moving objects, or other repetitive behaviors. Such behaviors (also scientifically known as 'stereotypies
A stereotypy (, or ) is a repetitive or ritualistic movement, posture, or utterance. Stereotypies may be simple movements such as body rocking, or complex, such as self-caressing, crossing and uncrossing of legs, and marching in place. They are ...
') are found to some degree in all people, especially those with developmental disabilities, and are especially frequent in people on the autism spectrum. People diagnosed with sensory processing disorder are also known to potentially exhibit stimming behaviors. Stimming has been interpreted as a protective response to overstimulation, in which people calm themselves by blocking less predictable environmental stimuli, to which they have a heightened sensitivity. A further explanation views stimming as a way to relieve anxiety and other negative or heightened emotions. Although some stimming behaviors are very beneficial at times, stimming has been highly stigmatized and dramatized. People who are neurodivergent often feel that they need to hide or decrease their self-stimulatory behavior, as it often elicits an undesirable response from those who do not understand the compulsion behind them. There are also potential mental health and well-being risks in suppressing stimming.
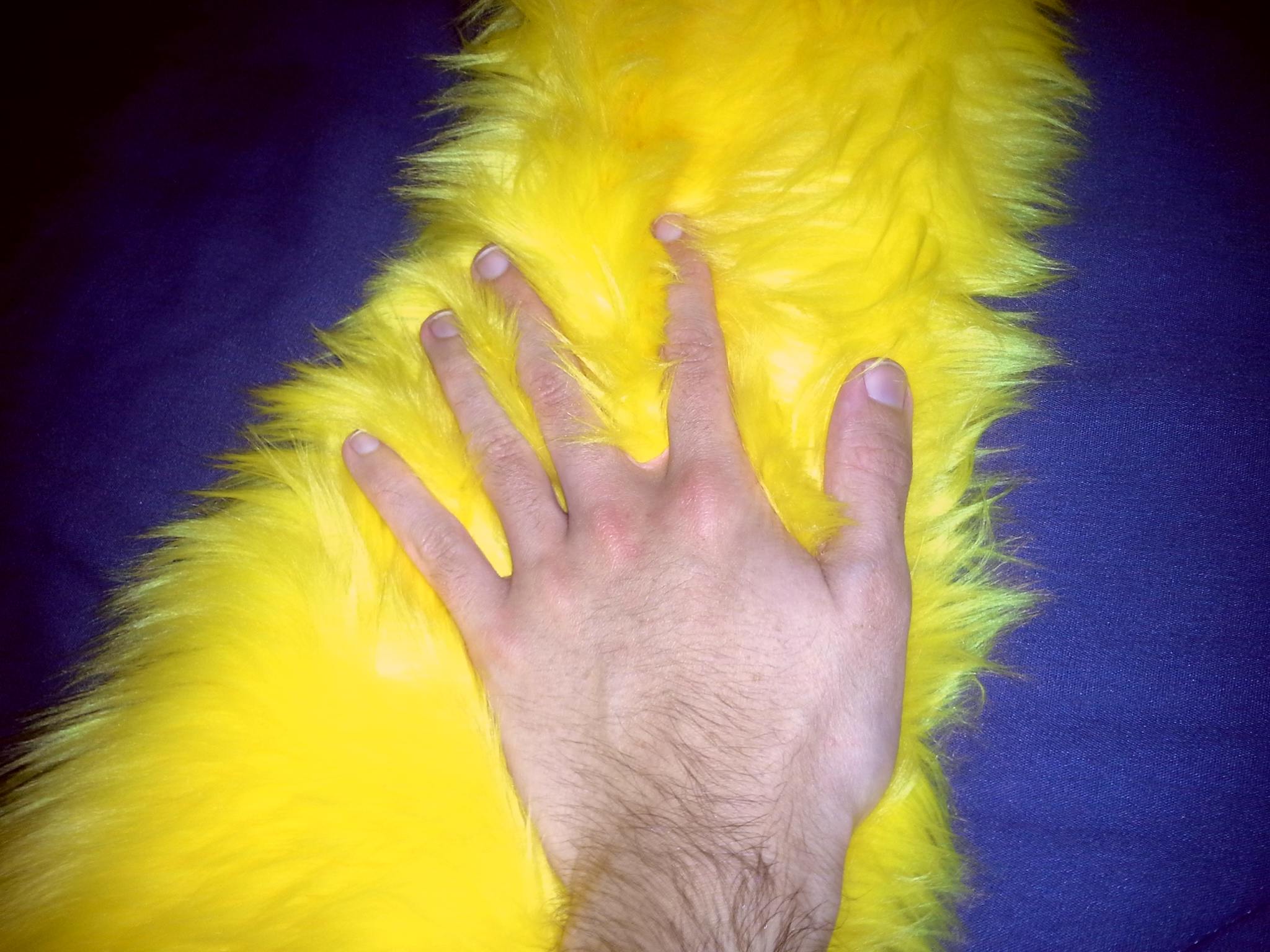
Stimming behaviors can consist of tactile, visual, auditory, vocal, proprioceptive (which pertains to limb sensing), olfactory, and vestibular stimming (which pertains to balance). Some common examples of stimming (sometimes called stims) include hand flapping, clapping, rocking, excessive or hard blinking, pacing, head banging, repeating noises or words, snapping fingers, and spinning objects. In some cases, stimming may be dangerous and physically harmful to the person doing it; for example, individuals may risk injuring themselves by forcefully banging their body parts against walls.
Stimming and autism
Stimming is almost always present in people on the autism spectrum but does not necessarily indicate its presence. The biggest difference between autistic and non-autistic stimming is the type of stim and the quantity of stimming. In the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', published by the American Psychiatric Association, stimming behavior is described as "stereotyped or repetitive motor mannerisms" and listed as one of the five key diagnostic criteria of autism spectrum disorder. Different perspectives suggest that stimming involves both sensory and motor functions. Underdevelopment of these sensorimotor functions can result in stimming behaviors produced by the person as a controllable response. One study which interviewed thirty-two autistic adults found that unpredictable and overwhelming environments caused stimming. Stimming can sometimes be
Stimming can sometimes be self-injurious
Self-harm is intentional behavior that is considered harmful to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues usually without a suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-injury and self-mutilati ...
, such as when it involves head-banging, hand-biting, excessive self-rubbing, and scratching the skin. While it is difficult to stop stimming entirely, there are ways to reduce time spent stimming and create safer stimming habits for an individual. Managing the sensory and emotional environment while increasing the amount of daily exercise can increase comfort levels for the person, which may reduce the amount of time spent stimming.
See also
*ASMR
Autonomous sensory meridian response (ASMR) is a tingling sensation that usually begins on the scalp and moves down the back of the neck and upper spine. A pleasant form of paresthesia, it has been compared with auditory-tactile synesthesia a ...
* Snoezelen
Snoezelen or controlled multisensory environment (MSE) is a therapy for people with autism and other developmental disabilities, dementia or brain injury. It consists of placing the person in a soothing and stimulating environment, called the "S ...
* Fidget spinner
* Hug machine
A hug machine, also known as a hug box, a squeeze machine, or a squeeze box, is a deep-pressure device designed to calm hypersensitive persons, usually individuals with autism spectrum disorders. The therapeutic, stress-relieving device was invent ...
References
{{Autism resources Autism Symptoms and signs of mental disorders Disability Anxiety