Seil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Seil (; gd, Saoil, ) is one of the Slate Islands, located on the east side of the Firth of Lorn, southwest of
 The '' Ravenna Cosmography'', which was compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around AD 700, mentions various Scottish island names. This document frequently used maps as a source of information and it has been possible to speculate about their modern equivalents based on assumptions about voyages made by early travellers 300–400 years prior to its creation. The island of ''Saponis'' mentioned in this list may refer to Seil.
Seil is probably a pre-Gaelic name, although a case has been made for a Norse derivation. It has also been argued that Seil could be the location of Hinba, an island associated with
The '' Ravenna Cosmography'', which was compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around AD 700, mentions various Scottish island names. This document frequently used maps as a source of information and it has been possible to speculate about their modern equivalents based on assumptions about voyages made by early travellers 300–400 years prior to its creation. The island of ''Saponis'' mentioned in this list may refer to Seil.
Seil is probably a pre-Gaelic name, although a case has been made for a Norse derivation. It has also been argued that Seil could be the location of Hinba, an island associated with 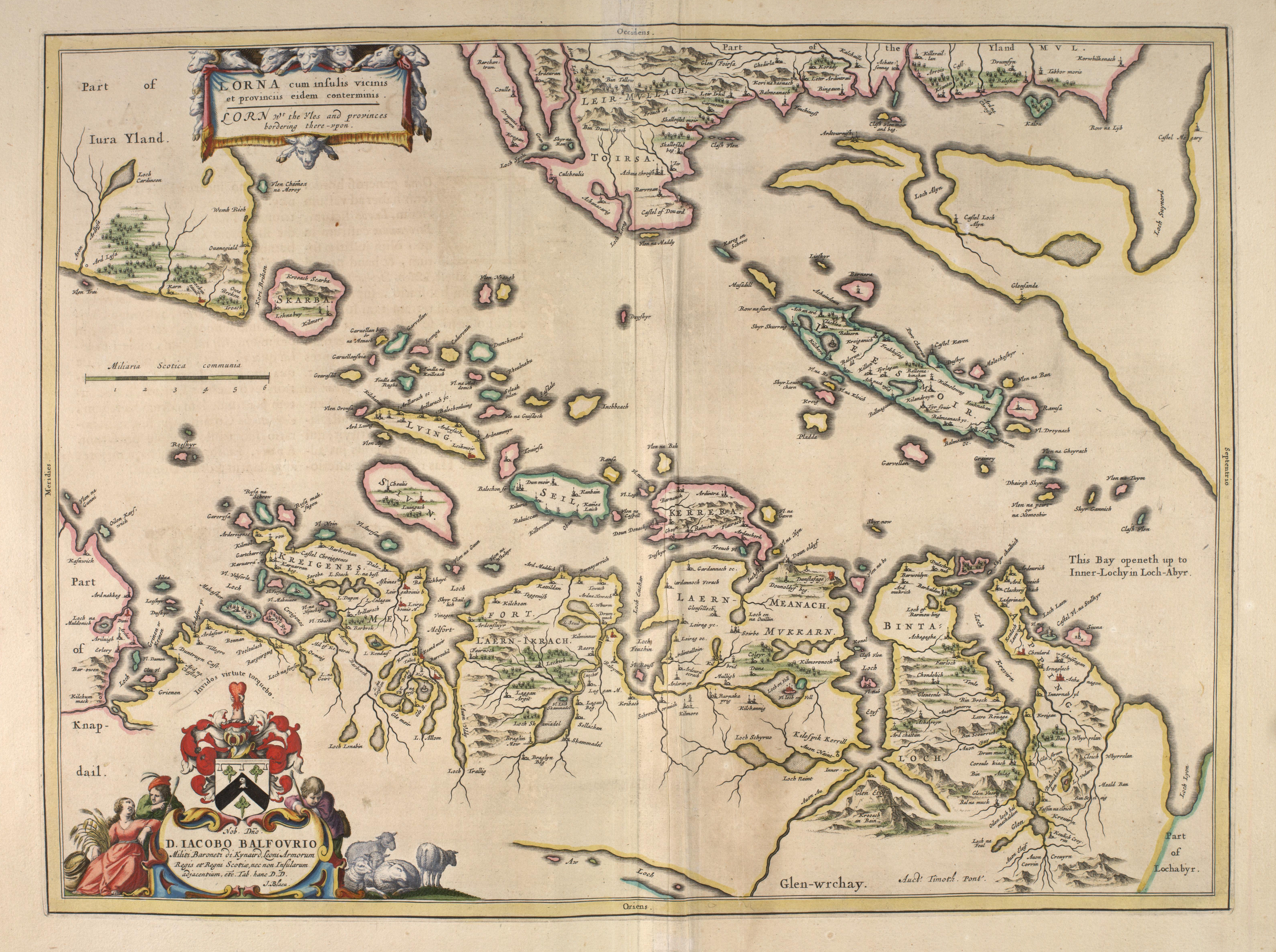 It has also been suggested that Seil may be the ''Innisibsolian'' referred to in the '' Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'', which records a victory of the Scots over a Viking force during the time of
It has also been suggested that Seil may be the ''Innisibsolian'' referred to in the '' Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'', which records a victory of the Scots over a Viking force during the time of
 Seil is separated from mainland Scotland by the Clachan Sound, which is only about at its narrowest point. To the west lies the sea-lane of the Firth of Lorn. The island of Luing lies across the Cuan Sound to the south and beyond are Lunga and Scarba. Smaller islands surrounding Seil are its companion Slate Islands of
Seil is separated from mainland Scotland by the Clachan Sound, which is only about at its narrowest point. To the west lies the sea-lane of the Firth of Lorn. The island of Luing lies across the Cuan Sound to the south and beyond are Lunga and Scarba. Smaller islands surrounding Seil are its companion Slate Islands of
 The Cenél Loairn kindred controlled what is today known as Lorn in the kingdom of Dalriada. The 7th-century ''Míniugud senchasa fher nAlban'' separates the Cenél Loairn into three subsidiary groups, of which the Cenél Salaich may have controlled Nether Lorn.
In the mid-16th century Monro wrote of Seil: ""
Ardfad Castle is a ruin in the northwest of Seil. It was the home of the Macdougalls of Ardencaple, but following the failure of King James VII to regain the thrones of England, Ireland and Scotland in the late 17th century the Macdougalls lost much of their lands to the Duke of Argyll. The castle was "a well-built structure of stone and lime, occupying a prominent situation on a crag and tail, not unlike Edinburgh Castle rock. In 1915, it was still fairly well preserved, with the walls standing to some height and two round corner towers"."Seil, Ardfad Castle"
The Cenél Loairn kindred controlled what is today known as Lorn in the kingdom of Dalriada. The 7th-century ''Míniugud senchasa fher nAlban'' separates the Cenél Loairn into three subsidiary groups, of which the Cenél Salaich may have controlled Nether Lorn.
In the mid-16th century Monro wrote of Seil: ""
Ardfad Castle is a ruin in the northwest of Seil. It was the home of the Macdougalls of Ardencaple, but following the failure of King James VII to regain the thrones of England, Ireland and Scotland in the late 17th century the Macdougalls lost much of their lands to the Duke of Argyll. The castle was "a well-built structure of stone and lime, occupying a prominent situation on a crag and tail, not unlike Edinburgh Castle rock. In 1915, it was still fairly well preserved, with the walls standing to some height and two round corner towers"."Seil, Ardfad Castle"
Canmore. Retrieved 31 May 2020. However, by 1971 only the remains of the southwest round tower survived. Seil then became part of the Netherlorn estates of the Breadalbane family (a branch of Clan Campbell) until the 20th century when their land was sold off as smaller farms and individual houses. In the early 16th century Muriel, daughter of the Thane of Calder, married Sir John Campbell, son of the Earl of Argyll at Inverary and so Clan Campbell of Cawdor was founded. "Many renowned and some infamous" clan members are buried at Kilbrandon churchyard on Seil. From the late 17th century the Dukes of Argyll began to lease land on a competitive basis rather than as a means of strengthening the welfare of their senior clansmen. This resulted in mass evictions from Seil and the surrounding area in 1669, long before the clearances as such.
Electric Scotland Retrieved 18 March 2012.
Southernhebrides.com. Retrieved 14 November 2009. Eilean-a-beithich was never re-opened although production did continue at Easdale, Luing and Balvicar. Changes in demand - clay tiles were rapidly replacing slate as the roofing material of choice - led to commercial production ceasing by 1911. Balvicar quarry re-opened from the late 1940s until the early 1960s but slate is no longer mined anywhere in the Slate Islands.
 Today, the island's commerce is largely dependent on agriculture, tourism and lobster fishing. The Ellenabeich Heritage Centre which opened in 2000, is run by the
Today, the island's commerce is largely dependent on agriculture, tourism and lobster fishing. The Ellenabeich Heritage Centre which opened in 2000, is run by the
 Seil is associated with the sixth century saint
Seil is associated with the sixth century saint
 The well-known pub Tigh na Truish (Gaelic for 'house of the trousers') at Clachan Seil is said to have obtained its name in the wake of the 1745
The well-known pub Tigh na Truish (Gaelic for 'house of the trousers') at Clachan Seil is said to have obtained its name in the wake of the 1745
 Alexander Beith Free Church Moderator spent about 4 years in this parish.
Alexander Beith Free Church Moderator spent about 4 years in this parish.
 In early summer the Clachan Bridge is covered in fairy foxgloves ('' Erinus alpinus''). The narrows that the bridge spans trapped a whale with a long lower jaw in 1835 and no fewer than 192 pilot whales in 1837, the largest of which was long.
According to wildlife experts the entire badger population of the island may have been deliberately exterminated in 2007. Forty of the animals, whose setts were believed to be long established, may have been gassed to death, according to the police. The police also expressed concerns that two golden eagles and one white-tailed sea eagle have been found poisoned near Seil in recent years, involving use of the banned substance carbofuran.
In early summer the Clachan Bridge is covered in fairy foxgloves ('' Erinus alpinus''). The narrows that the bridge spans trapped a whale with a long lower jaw in 1835 and no fewer than 192 pilot whales in 1837, the largest of which was long.
According to wildlife experts the entire badger population of the island may have been deliberately exterminated in 2007. Forty of the animals, whose setts were believed to be long established, may have been gassed to death, according to the police. The police also expressed concerns that two golden eagles and one white-tailed sea eagle have been found poisoned near Seil in recent years, involving use of the banned substance carbofuran.
File:Clachan Sound 05.JPG, Clachan Sound from
Slate Islands Heritage Trust
{{coord, 56, 18, 0, N, 5, 37, 12, W, display=title, region:GB_type:isle Slate Islands Islands of Argyll and Bute
Oban
Oban ( ; ' in Scottish Gaelic meaning ''The Little Bay'') is a resort town within the Argyll and Bute council area of Scotland. Despite its small size, it is the largest town between Helensburgh and Fort William. During the tourist season, th ...
, in Scotland. Seil has been linked to the mainland by bridge since the late 18th century.
The origins of the island's name are unclear and probably pre-Gaelic. Part of the kingdom of Dalriada in the 7th century, by the sixteenth century Seil seems to have been primarily agricultural in nature. It became part of the estates of the Breadalbane family and in the early 18th century they began to exploit the rich potential of the Neoproterozoic slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
beds. The excavations from the island's quarries were exported all over the world during the course of the next two centuries. Today, the economy is largely dependent on agriculture and tourism.
The "dangerous seas" of the Firth of Lorn have claimed many lives and there are several shipwrecks in the vicinity of Seil. Kilbrandon Church has fine examples of stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
windows and an association with St Brendan
Brendan of Clonfert (c. AD 484 - c.577), is one of the early Irish monastic saints and one of the Twelve Apostles of Ireland. He is also referred to as Brendan the Navigator, Brendan the Voyager, Brendan the Anchorite, Brendan the Bold. The ...
.
Etymology
There is some linguistic continuity between the earliest and modern names for many of the larger islands surrounding Scotland. However, the derivations of many of these names are obscure "suggesting that they were coined very early on, some perhaps by the earliest settlers after the Ice Age." Even when names used both in the historic past and the present have some apparent meaning this may indicate a phonetic resemblance to an older name, but one that may be "so old and so linguistically and lexically opaque that we do not have any plausible referents for them." The '' Ravenna Cosmography'', which was compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around AD 700, mentions various Scottish island names. This document frequently used maps as a source of information and it has been possible to speculate about their modern equivalents based on assumptions about voyages made by early travellers 300–400 years prior to its creation. The island of ''Saponis'' mentioned in this list may refer to Seil.
Seil is probably a pre-Gaelic name, although a case has been made for a Norse derivation. It has also been argued that Seil could be the location of Hinba, an island associated with
The '' Ravenna Cosmography'', which was compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around AD 700, mentions various Scottish island names. This document frequently used maps as a source of information and it has been possible to speculate about their modern equivalents based on assumptions about voyages made by early travellers 300–400 years prior to its creation. The island of ''Saponis'' mentioned in this list may refer to Seil.
Seil is probably a pre-Gaelic name, although a case has been made for a Norse derivation. It has also been argued that Seil could be the location of Hinba, an island associated with St Columba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is toda ...
. Reasons include the island's association with St Brendan
Brendan of Clonfert (c. AD 484 - c.577), is one of the early Irish monastic saints and one of the Twelve Apostles of Ireland. He is also referred to as Brendan the Navigator, Brendan the Voyager, Brendan the Anchorite, Brendan the Bold. The ...
, its location on an inshore trade route from Antrim to the north and its suitability for a substantial settlement. The ''Muirbolcmar'' (great sea bag) referred to in texts about Hinba could refer to the Seil Sound and narrows at Clachan Bridge
The Clachan Bridge is a simple, single-arched, hump-backed, masonry bridge spanning the Clachan Sound, southwest of Oban in Argyll, Scotland. It links the west coast of the Scottish mainland to the island of Seil.
The bridge was originally d ...
where the "bag" captures the rapidly flowing water that floods under the bridge. Rae, equating "Hinba" with the Gaelic ''Inbhir'', notes that the adjacent mainland parish of Kilninver means "church of Inbhir" and suggests that the derivation of "Seil" maybe of Scandinavian origin with similarities to the East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
n place name ''Zijl'' or ''Syl'' meaning a "seep or passage of water". This, he proposes, could have been a Norse interpretation of Hinba/Inbhir. However, Mac an Tàilleir notes that Kilninver or ''Cill an Inbhir'' "appears to mean 'church by the river mouth', and an older form of ''Cill Fhionnbhair'', 'Finbar's church' appears".
 It has also been suggested that Seil may be the ''Innisibsolian'' referred to in the '' Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'', which records a victory of the Scots over a Viking force during the time of
It has also been suggested that Seil may be the ''Innisibsolian'' referred to in the '' Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'', which records a victory of the Scots over a Viking force during the time of Donald II
Domnall mac Causantín ( Modern Gaelic: , IPA: �t̪oːvnəɫ̪ˈmaʰkˈxoːʃɪm, anglicised as Donald II (died 900), was King of the Picts or King of Alba in the late 9th century. He was the son of Constantine I (Causantín mac Cináeda). Donald ...
in the 9th century. The name used in the 12th century '' Book of Leinster'' is ''Sóil''.
The earliest comprehensive written list of Hebridean island names was undertaken by Donald Monro in his '' Description of the Western Isles of Scotland'' of 1549 in which Seil is listed. The modern spelling of "Seil" also appears in the 1654 ''Blaeu Atlas of Scotland
The book commonly known as Blaeu Atlas of Scotland, the fifth volume of '' Theatrum Orbis Terrarum Sive Atlas Novus'', is the first known atlas of Scotland and Ireland. It was compiled by Joan Blaeu, and contains 49 engraved maps and 154 pages of ...
''.
Geography
 Seil is separated from mainland Scotland by the Clachan Sound, which is only about at its narrowest point. To the west lies the sea-lane of the Firth of Lorn. The island of Luing lies across the Cuan Sound to the south and beyond are Lunga and Scarba. Smaller islands surrounding Seil are its companion Slate Islands of
Seil is separated from mainland Scotland by the Clachan Sound, which is only about at its narrowest point. To the west lies the sea-lane of the Firth of Lorn. The island of Luing lies across the Cuan Sound to the south and beyond are Lunga and Scarba. Smaller islands surrounding Seil are its companion Slate Islands of Easdale
Easdale ( gd, Eilean Èisdeal) is one of the Slate Islands, in the Firth of Lorn, Scotland. Once the centre of the Scottish slate industry, there has been some recent island regeneration by the owners. This is the smallest of the Inner Hebrides ...
, Torsa, Belnahua and Shuna. Eilean Dubh Mòr
Eilean Dubh Mòr ( gd, big black island) is an uninhabited island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. It lies at the mouth of the Firth of Lorn, between the islands of Lunga and Garbh Eileach
Garbh Eileach is an uninhabited island in the Inn ...
is to the south-west with the Garvellachs
The Garvellachs (Scottish Gaelic: Garbh Eileaich) or Isles of the Sea form a small archipelago in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Part of the Argyll and Bute council area, they lie west of Lunga and northwest of Scarba and have been uninhabited ...
beyond, with Insh to the north west.
Seil forms part of Nether Lorn, a region of Argyll between Loch Awe and Loch Melfort
''Loch'' () is the Scottish Gaelic, Scots and Irish word for a lake or sea inlet. It is cognate with the Manx lough, Cornish logh, and one of the Welsh words for lake, llwch.
In English English and Hiberno-English, the anglicised spelling ...
that includes the offshore islands located in the modern council area of Argyll and Bute. The highest point on the island is the summit of Meall Chaise at above sea level.
Seil is some miles from Oban, travelling north by road along the B844 and A 816.
Balvicar
Balvicar ( gd, Baile a' Bhiocair) is a village on the island of Seil, a small island southwest of Oban, Scotland. It is one of three villages on the island along with Ellenabeich and Clachan-Seil. It was a former slate-mining village beginning ...
, in the centre of the island, is the main settlement and has a harbour with commercial fishing boats, the island shop, and a golf club. On the west side of the island lies the former slate-mining village of Ellenabeich
Ellenabeich (Scottish Gaelic: ''Eilean nam Beitheach'', meaning "island of the birchwoods.") is a small village on the isle of Seil (Scottish Gaelic: ''Saoil'') – an island on the east side of the Firth of Lorn, 7 miles (11 km) southwest o ...
. This village, known for its white slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
worker's cottages, has attracted an "artist's colony" and has a number of holiday cottages.
There are three other small settlements; Cuan at the southern tip, Oban Seil north of Balvicar and Clachan Seil, which is closest to the Clachan Bridge.
Geology
The larger part of the bedrock of Seil is provided by the Neoproterozoic age Easdale Slate Formation, a pyritic,graphitic
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large ...
pelite belonging to the Easdale Subgroup of the Dalradian Argyll Group
The Argyll Group is a thick sequence of metamorphosed Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks that outcrop across the Central Highlands of Scotland, east of the Great Glen, as well as appearing in the north of Ireland. It is a subdivision of the Dalrad ...
. Zones of metamorphosed intrusive igneous rocks occur within the southeast of the island. Andesitic lavas of the Lorn Plateau Lava Formation dominate the west of the island. Seil is cut by numerous NW-SE aligned basalt and micro gabbro dykes which form a part of the ‘Mull Swarm’ which is of early Palaeogene age.
Raised marine deposits of sand and gravel occur widely around the margins of the island, a legacy of late Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
changes in relative sea-level.
History
 The Cenél Loairn kindred controlled what is today known as Lorn in the kingdom of Dalriada. The 7th-century ''Míniugud senchasa fher nAlban'' separates the Cenél Loairn into three subsidiary groups, of which the Cenél Salaich may have controlled Nether Lorn.
In the mid-16th century Monro wrote of Seil: ""
Ardfad Castle is a ruin in the northwest of Seil. It was the home of the Macdougalls of Ardencaple, but following the failure of King James VII to regain the thrones of England, Ireland and Scotland in the late 17th century the Macdougalls lost much of their lands to the Duke of Argyll. The castle was "a well-built structure of stone and lime, occupying a prominent situation on a crag and tail, not unlike Edinburgh Castle rock. In 1915, it was still fairly well preserved, with the walls standing to some height and two round corner towers"."Seil, Ardfad Castle"
The Cenél Loairn kindred controlled what is today known as Lorn in the kingdom of Dalriada. The 7th-century ''Míniugud senchasa fher nAlban'' separates the Cenél Loairn into three subsidiary groups, of which the Cenél Salaich may have controlled Nether Lorn.
In the mid-16th century Monro wrote of Seil: ""
Ardfad Castle is a ruin in the northwest of Seil. It was the home of the Macdougalls of Ardencaple, but following the failure of King James VII to regain the thrones of England, Ireland and Scotland in the late 17th century the Macdougalls lost much of their lands to the Duke of Argyll. The castle was "a well-built structure of stone and lime, occupying a prominent situation on a crag and tail, not unlike Edinburgh Castle rock. In 1915, it was still fairly well preserved, with the walls standing to some height and two round corner towers"."Seil, Ardfad Castle"Canmore. Retrieved 31 May 2020. However, by 1971 only the remains of the southwest round tower survived. Seil then became part of the Netherlorn estates of the Breadalbane family (a branch of Clan Campbell) until the 20th century when their land was sold off as smaller farms and individual houses. In the early 16th century Muriel, daughter of the Thane of Calder, married Sir John Campbell, son of the Earl of Argyll at Inverary and so Clan Campbell of Cawdor was founded. "Many renowned and some infamous" clan members are buried at Kilbrandon churchyard on Seil. From the late 17th century the Dukes of Argyll began to lease land on a competitive basis rather than as a means of strengthening the welfare of their senior clansmen. This resulted in mass evictions from Seil and the surrounding area in 1669, long before the clearances as such.
Slate quarrying
In 1730 Colin Campbell of Carwhin was appointed as the Captain of Ardmaddy and tasked with exploiting the area's natural resources. At this time Easdale slate had been used from as early as the 12th century using seasonal labour from the Ardmaddy estate. In 1745 Campbell created the Easdale Marble and Slate Company in order to place extractions from the area on a more commercial basis. At that point Easdale was producing 1 million slates per annum; when Thomas Pennant visited two years later production had increased by 250% and as further quarries were opened this further increased the company's production to 5 million per annum by 1800. The little island ofEilean-a-beithich
Eilean-a-beithich or Eilean nam Beitheach ("island of the birches") was once one of the Slate Islands, located in Easdale Sound between Easdale and Seil, in the Inner Hebrides.
In 1549, Dean Monro wrote: "''Narrest Seunay layes ther a litle iyl ...
between Seil and Easdale was quarried down to a depth of and other slate quarries were opened on Luing and at Balvicar. Railway lines were laid to take the rock from the quarries to nearby harbours. Peak production was reached in the 1860s at 9 million slates per annum, with export destinations including England, Nova Scotia, the West Indies, the US, Norway and New Zealand. The 6th Earl of Breadalbane had less interest in the industry than his predecessors although during the time of the 7th Earl a new quarry was opened at Ardencaple. However, disaster struck in 1881. In the early morning of 22 November a severe gale from the south-west wind and an exceptionally high tide flooded the quarries on Easdale and at Eilean-a-beithich "a large rocky buttress which supported a sea wall gave way under the excessive pressure of water"."Netherlorn and its Neighbourhood:Chapter II - Easdale"Electric Scotland Retrieved 18 March 2012.
Southernhebrides.com. Retrieved 14 November 2009. Eilean-a-beithich was never re-opened although production did continue at Easdale, Luing and Balvicar. Changes in demand - clay tiles were rapidly replacing slate as the roofing material of choice - led to commercial production ceasing by 1911. Balvicar quarry re-opened from the late 1940s until the early 1960s but slate is no longer mined anywhere in the Slate Islands.
Economy and transport
 Today, the island's commerce is largely dependent on agriculture, tourism and lobster fishing. The Ellenabeich Heritage Centre which opened in 2000, is run by the
Today, the island's commerce is largely dependent on agriculture, tourism and lobster fishing. The Ellenabeich Heritage Centre which opened in 2000, is run by the Slate Islands Heritage Trust
The Slate Islands Heritage Trust is a charity formed in 1999 with the objective of advancing the education of the public on matters relating to the life and times of the people of the Scottish Slate Islands. It states its objectives are " ....to ...
. Located in a former slate quarry-worker's cottage, the centre has displays about life in the 19th century, slate quarrying and the local flora, fauna and geology.
Seil has been linked to the Scottish mainland since 1792/3 when the Clachan Bridge
The Clachan Bridge is a simple, single-arched, hump-backed, masonry bridge spanning the Clachan Sound, southwest of Oban in Argyll, Scotland. It links the west coast of the Scottish mainland to the island of Seil.
The bridge was originally d ...
was built by engineer Robert Mylne. Also known as the "Bridge Over the Atlantic", the bridge was constructed with a span and has an arch above the sea bed in order to allow small craft of up to to pass under it.
Ferries sail from Ellenabeich to Easdale
Easdale ( gd, Eilean Èisdeal) is one of the Slate Islands, in the Firth of Lorn, Scotland. Once the centre of the Scottish slate industry, there has been some recent island regeneration by the owners. This is the smallest of the Inner Hebrides ...
, and from Cuan to Luing across the Cuan Sound. This stretch of water is only wide but the spring tides race through it at up to . The Easdale ferry uses a chain and cog wheels designed by John Whyte in the mid 19th century.
Religion
 Seil is associated with the sixth century saint
Seil is associated with the sixth century saint Brendan of Clonfert
Brendan of Clonfert (c. AD 484 - c.577), is one of the early Celtic Christianity, Irish monastic saints and one of the Twelve Apostles of Ireland. He is also referred to as Brendan the Navigator, Brendan the Voyager, Brendan the Anchorite, Br ...
who established a monastery on the Garvellachs and at a later date a cell on the site of Kilbrandon Church to which he gave his name. The modern church, located between Balvicar and Cuan, has five stained glass windows by Douglas Strachan illustrating scenes from the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee ( he, יָם כִּנֶּרֶת, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ar, بحيرة طبريا), also called Lake Tiberias, Kinneret or Kinnereth, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest ...
. The central window depicts a ship in distress and "the portrayal in glowing colour of the storm's sweep, the crew's terror, and Christ's self-possession, has a lively drama unique in Highland stained glass".
Folklore and media
 The well-known pub Tigh na Truish (Gaelic for 'house of the trousers') at Clachan Seil is said to have obtained its name in the wake of the 1745
The well-known pub Tigh na Truish (Gaelic for 'house of the trousers') at Clachan Seil is said to have obtained its name in the wake of the 1745 Jacobite Rebellion
, war =
, image = Prince James Francis Edward Stuart by Louis Gabriel Blanchet.jpg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = James Francis Edward Stuart, Jacobite claimant between 1701 and 1766
, active ...
. Supposedly, shore-going islanders swapped their kilts for trousers here after Highland dress was banned.
Parts of '' Ring of Bright Water'' were filmed on Seil.
Notable people
 Alexander Beith Free Church Moderator spent about 4 years in this parish.
Alexander Beith Free Church Moderator spent about 4 years in this parish.
Arthur Murray, 3rd Viscount Elibank
Lieutenant-Colonel Arthur Cecil Murray, 3rd Viscount Elibank, CMG, DSO (27 March 1879 – 5 December 1962) was a British army officer and politician.
Early life and education
Murray was the fourth son of (1st) Viscount Elibank of Selkirkshir ...
and his wife, the actress Faith Celli
Faith Celli (27 November 1888 – 16 December 1942), born Dorothy Faith Standing, was an English actress, particularly associated with the plays of J. M. Barrie and A. A. Milne. She had a 20-year career from 1907, after which she retired from the ...
, purchased property on Seil in the 1930s. They converted a row of derelict cottages into a substantial dwelling and created the garden at An Cala, near Ellanabeich.
The artist C. John Taylor lived at Ellanabeich for many years until his death in 1998. His painting of the Clachan Bridge "Bridge Over The Atlantic" sold nearly a million copies.
Frances Shand Kydd, the mother of Diana, Princess of Wales
Diana, Princess of Wales (born Diana Frances Spencer; 1 July 1961 – 31 August 1997) was a member of the British royal family. She was the first wife of King Charles III (then Prince of Wales) and mother of Princes William and Harry. Her ac ...
lived on the island for many years until her death in 2004.
Shipwrecks
The Firth of Lorn is the seaway used by vessels going to and from Oban and Fort William from points south and the seas around Seil contain the sites of various shipwrecks. The wooden sailing ship ''Norval'' ran aground in fog near the southern tip of Insh on 20 September 1870. The wreckage was still visible in 1995. On 15 August 1900 the ironsteamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
''Apollo'' ran aground on Bono Reef south west of Seil. She was carrying a cargo of granite cobble stones from Aberdeen to Newport
Newport most commonly refers to:
*Newport, Wales
*Newport, Rhode Island, US
Newport or New Port may also refer to:
Places Asia
*Newport City, Metro Manila, a Philippine district in Pasay
Europe
Ireland
*Newport, County Mayo, a town on the ...
. The wreck lies in a gully some down amidst thick kelp. In February 1933 the Clyde puffer ''Hafton'' en route from Toboronochy on Luing to Mull sprung a leak and foundered about into the journey. The crew of five took to a small boat and reached Ellanabeich safely. A wreck of unknown provenance has been recorded east of Rubha Garbh Airde at the northern end of Seil.
Wildlife
 In early summer the Clachan Bridge is covered in fairy foxgloves ('' Erinus alpinus''). The narrows that the bridge spans trapped a whale with a long lower jaw in 1835 and no fewer than 192 pilot whales in 1837, the largest of which was long.
According to wildlife experts the entire badger population of the island may have been deliberately exterminated in 2007. Forty of the animals, whose setts were believed to be long established, may have been gassed to death, according to the police. The police also expressed concerns that two golden eagles and one white-tailed sea eagle have been found poisoned near Seil in recent years, involving use of the banned substance carbofuran.
In early summer the Clachan Bridge is covered in fairy foxgloves ('' Erinus alpinus''). The narrows that the bridge spans trapped a whale with a long lower jaw in 1835 and no fewer than 192 pilot whales in 1837, the largest of which was long.
According to wildlife experts the entire badger population of the island may have been deliberately exterminated in 2007. Forty of the animals, whose setts were believed to be long established, may have been gassed to death, according to the police. The police also expressed concerns that two golden eagles and one white-tailed sea eagle have been found poisoned near Seil in recent years, involving use of the banned substance carbofuran.
Gallery
Clachan Bridge
The Clachan Bridge is a simple, single-arched, hump-backed, masonry bridge spanning the Clachan Sound, southwest of Oban in Argyll, Scotland. It links the west coast of the Scottish mainland to the island of Seil.
The bridge was originally d ...
, looking north
File:Easdale Village - panoramio.jpg, The flooded quarry and village of Ellenabeich
Ellenabeich (Scottish Gaelic: ''Eilean nam Beitheach'', meaning "island of the birchwoods.") is a small village on the isle of Seil (Scottish Gaelic: ''Saoil'') – an island on the east side of the Firth of Lorn, 7 miles (11 km) southwest o ...
with the outline of the former island of Eilean-a-beithich
Eilean-a-beithich or Eilean nam Beitheach ("island of the birches") was once one of the Slate Islands, located in Easdale Sound between Easdale and Seil, in the Inner Hebrides.
In 1549, Dean Monro wrote: "''Narrest Seunay layes ther a litle iyl ...
at centre left and Easdale
Easdale ( gd, Eilean Èisdeal) is one of the Slate Islands, in the Firth of Lorn, Scotland. Once the centre of the Scottish slate industry, there has been some recent island regeneration by the owners. This is the smallest of the Inner Hebrides ...
beyond
File:Isle of Seil 05.JPG, Slate on the shoreline of Seil
File:Quarry at Balvicar, Seil Island - geograph.org.uk - 65348.jpg, Flooded slate quarry near Balvicar
Balvicar ( gd, Baile a' Bhiocair) is a village on the island of Seil, a small island southwest of Oban, Scotland. It is one of three villages on the island along with Ellenabeich and Clachan-Seil. It was a former slate-mining village beginning ...
File:Oban Seil - geograph.org.uk - 385656.jpg, The scattered settlement of Oban Seil
File:Balvicar Bay From Ardshellach Farm - geograph.org.uk - 1719527.jpg, Balvicar Bay in winter, seen from mainland Scotland, looking towards the heights of Bàrr Mòr
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Slate Islands Heritage Trust
{{coord, 56, 18, 0, N, 5, 37, 12, W, display=title, region:GB_type:isle Slate Islands Islands of Argyll and Bute