segmented mirror on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A segmented mirror is an array of smaller mirrors designed to act as segments of a single large curved mirror. The segments can be either spherical or asymmetric (if they are part of a larger parabolic reflector). They are used as objectives for large
A segmented mirror is an array of smaller mirrors designed to act as segments of a single large curved mirror. The segments can be either spherical or asymmetric (if they are part of a larger parabolic reflector). They are used as objectives for large
/ref> It was later independently rediscovered and further developed under the leadership of Dr. Jerry Nelson at the
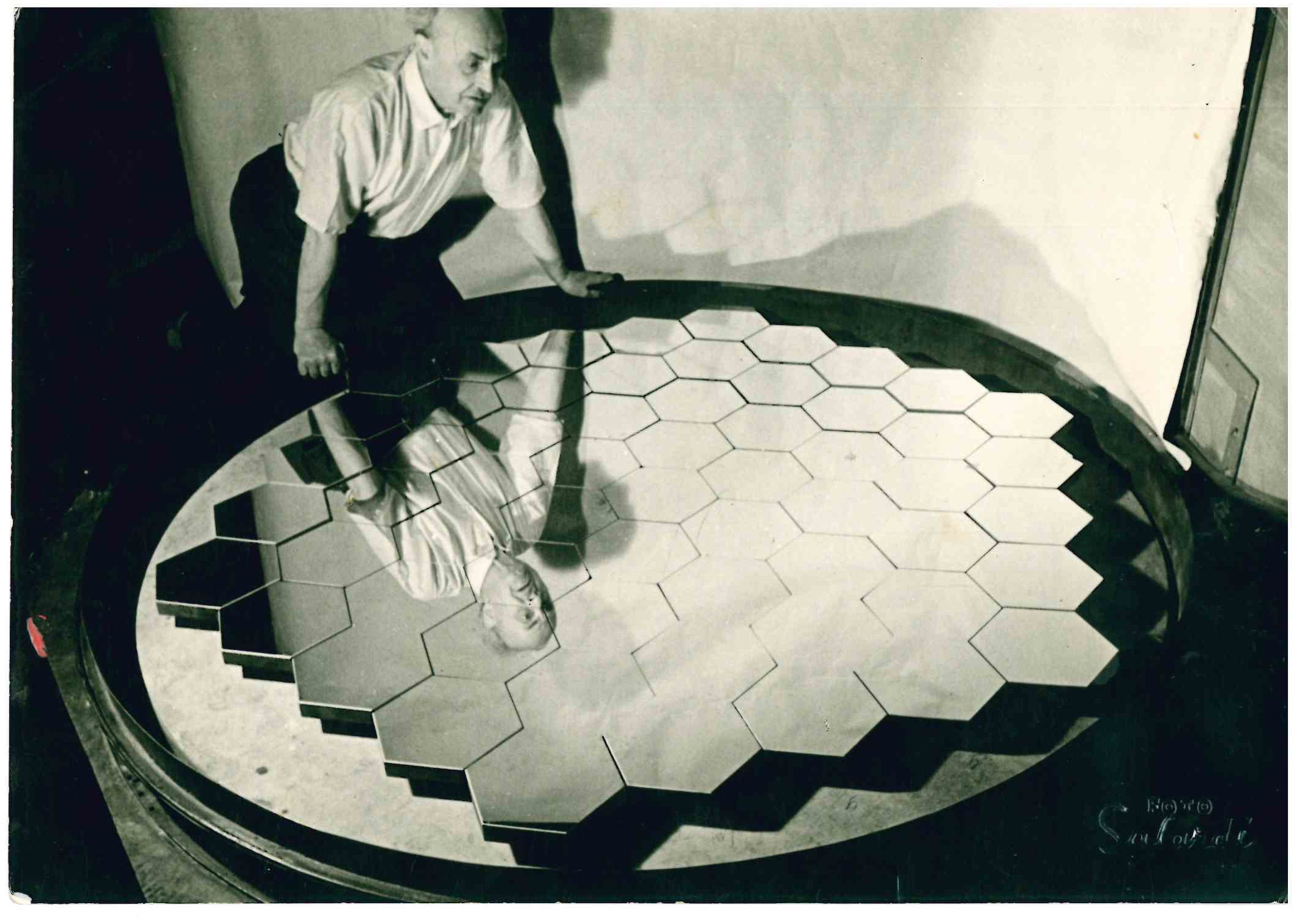 There is a technological limit for primary mirrors made of a single rigid piece of glass. Such non-segmented, or ''monolithic mirrors'' can not be constructed larger than about eight meters in diameter. The largest monolithic mirrors in use are currently the two primary mirrors of the Large Binocular Telescope, each with a diameter of 8.4 meters. The use of segmented mirrors is therefore a key component for large-aperture
There is a technological limit for primary mirrors made of a single rigid piece of glass. Such non-segmented, or ''monolithic mirrors'' can not be constructed larger than about eight meters in diameter. The largest monolithic mirrors in use are currently the two primary mirrors of the Large Binocular Telescope, each with a diameter of 8.4 meters. The use of segmented mirrors is therefore a key component for large-aperture
tooz
to out-couple the light from their light guides, which is used as an optical smartglass element.
reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternati ...
s. To function, all the mirror segments have to be polished to a precise shape and actively aligned by a computer-controlled active optics system using actuators built into the mirror support cell.
The concept was pioneered by Guido Horn D'Arturo, who built the first working segmented mirror in 1952, after twenty years of research;Bonoli, F. "Guido Horn d'Arturo and the first multi-mirror telescopes: 1932-1952." Memorie della Societa Astronomica Italiana 89 (2018): 448./ref> It was later independently rediscovered and further developed under the leadership of Dr. Jerry Nelson at the
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL, Berkeley Lab) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in the Berkeley Hills, hills of Berkeley, California, United States. Established i ...
and University of California
The University of California (UC) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university, research university system in the U.S. state of California. Headquartered in Oakland, California, Oakland, the system is co ...
during the 1980s, and since then all the necessary technologies have spread worldwide to the point that essentially all future large optical telescopes plan to use segmented mirrors.
Application
 There is a technological limit for primary mirrors made of a single rigid piece of glass. Such non-segmented, or ''monolithic mirrors'' can not be constructed larger than about eight meters in diameter. The largest monolithic mirrors in use are currently the two primary mirrors of the Large Binocular Telescope, each with a diameter of 8.4 meters. The use of segmented mirrors is therefore a key component for large-aperture
There is a technological limit for primary mirrors made of a single rigid piece of glass. Such non-segmented, or ''monolithic mirrors'' can not be constructed larger than about eight meters in diameter. The largest monolithic mirrors in use are currently the two primary mirrors of the Large Binocular Telescope, each with a diameter of 8.4 meters. The use of segmented mirrors is therefore a key component for large-aperture telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
s. Using a monolithic mirror much larger than 5 meters is prohibitively expensive due to the cost of both the mirror, and the massive structure needed to support it. A mirror beyond that size would also sag slightly under its own weight as the telescope was rotated to different positions, changing the precision shape of the surface. Segments are also easier to fabricate, transport, install, and maintain over very large monolithic mirrors.
Segmented mirrors do have the drawback that each segment may require some precise asymmetrical shape, and rely on a complicated computer-controlled mounting system. All of the segments also cause diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
effects in the final image.
Another application for segmented mirrors can be found in the augmented reality
Augmented reality (AR), also known as mixed reality (MR), is a technology that overlays real-time 3D computer graphics, 3D-rendered computer graphics onto a portion of the real world through a display, such as a handheld device or head-mounted ...
sector to minimize the size of the optical components. A partial reflective segmented mirror array is used btooz
to out-couple the light from their light guides, which is used as an optical smartglass element.
Telescopes using segmented mirrors
Some of the largest optical telescopes in the world use segmented primary mirrors. These include, but are not limited to the following telescopes:Keck Telescopes
The twin Keck Telescopes are the most prominent of theMauna Kea Observatories
The Mauna Kea Observatories (MKO) are a group of independent astronomical research facilities and large telescope observatories that are located at the summit of Mauna Kea on Hawaii (island), Hawaiʻi, United States. The facilities are located i ...
at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea (, ; abbreviation for ''Mauna a Wākea''); is a dormant Shield volcano, shield volcano on the Hawaii (island), island of Hawaii. Its peak is above sea level, making it the List of U.S. states by elevation, highest point in Hawaii a ...
in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, United States. Both telescopes feature primary mirrors.
Hobby-Eberly Telescope
The Hobby-Eberly Telescope (HET) is a 9.2-meter (30-foot) telescope located at the McDonald Observatory,West Texas
West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the desert climate, arid and semiarid climate, semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Texas, Wichita Falls, Abilene, Texa ...
at an altitude of 2,026 m (6,647 ft). Its primary mirror is constructed from 91 hexagonal segments. The telescope's main mirror is fixed at a 55 degree angle and can rotate around its base. A target is tracked by moving the instruments at the focus of the telescope; this allows access to about 70–81% of the sky at its location and a single target can be tracked for up to two hours.
Southern African Large Telescope
The Southern African Large Telescope (SALT) is a 10-meter telescope dedicated on spectroscopy for most of its observing time. It shares similarities with the Hobby-Eberly Telescope and also consists of 91 hexagonal mirror segments, each 1 meter across, resulting in a total hexagonal mirror of 11.1 m by 9.8 m. It is located close to the town ofSutherland
Sutherland () is a Counties of Scotland, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area in the Scottish Highlands, Highlands of Scotland. The name dates from the Scandinavian Scotland, Viking era when t ...
in the semi-desert region of the Karoo, South Africa. It is a facility of the South African Astronomical Observatory, the national optical observatory of South Africa.
Gran Telescopio Canarias
Also known as the GranTeCan, the Canaries Great Telescope uses a total of 36 segmented mirrors. With a primary mirror of , it is currently the world's largest optical telescope, located at theRoque de los Muchachos Observatory
Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (, ORM) is an astronomical observatory located in the municipality of Garafía on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The observatory site is operated by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Can ...
on the island of La Palma, in the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
in Spain.
LAMOST
The Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fibre Spectroscopic Telescope is a survey telescope located in the Hebei Province of China. It consists of two rectangular mirrors, made up of 24 and 37 segments, respectively. Each hexagonal segment is 1.1 metre in size.James Webb Space Telescope
The 18 mirror segments of theJames Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, Lis ...
were mostly fabricated in 2011. The space telescope
A space telescope (also known as space observatory) is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO ...
was launched by an Ariane 5 from Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas region of France in South America. Kourou is located approxim ...
on December 25, 2021.
Next-generation telescopes
Three extremely large telescopes will be the next generation of segmented-mirror telescopes and are planned to be commissioned in the 2020s. The Giant Magellan Telescope uses seven large segments and is either grouped with segmented mirrors telescopes or its own category. The Thirty Meter Telescope is to be built at the Mauna Kea Observatories in Hawaii, though construction is on hold. This will use 492 hexagonal segments. The Extremely Large Telescope will be the largest of all three, using a total of 798 segments for its primary mirror. Its first light is expected for 2028.Diffraction spikes
See also
* List of largest optical reflecting telescopes * Cherenkov Telescope ArrayReferences
External links
* {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Optical telescope components Mirrors