Segimer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Segimer or Sigimer ( la, Segimerus or ; fl.
Segimer or Sigimer ( la, Segimerus or ; fl.
 Segimer or Sigimer ( la, Segimerus or ; fl.
Segimer or Sigimer ( la, Segimerus or ; fl. 1st century BC
The 1st century BC, also known as the last century BC and the last century BCE, started on the first day of 100 BC and ended on the last day of 1 BC. The AD/BC notation does not use a year zero; however, astronomical year numberi ...
) was a chieftain
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribe, tribal society or chiefdom.
Tribe
The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia.
Tribal societies are sometimes categori ...
of the Germanic Cherusci
The Cherusci were a Germanic tribe that inhabited parts of the plains and forests of northwestern Germany in the area of the Weser River and present-day Hanover during the first centuries BC and AD. Roman sources reported they considered themsel ...
tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English language, English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in p ...
. He is chiefly remembered as the father of Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of ge ...
, who led the Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
to victory over the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
at Teutoburg Forest
The Teutoburg Forest ( ; german: Teutoburger Wald ) is a range of low, forested hills in the German states of Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia. Until the 17th century, the official name of the hill ridge was Osning. It was first renamed th ...
in AD9.
Life
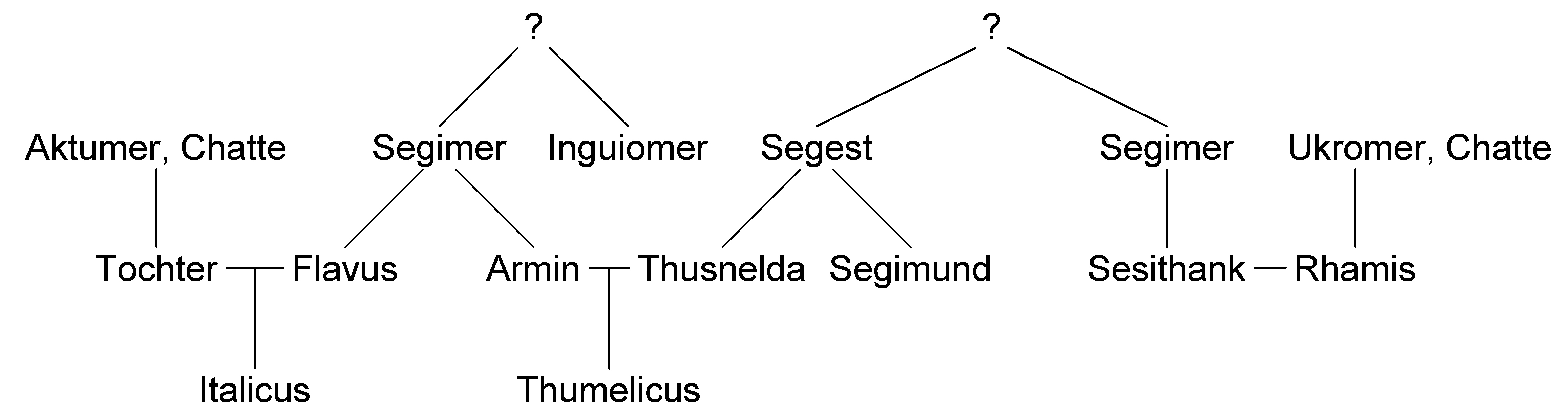
Segimer was a chief of the Cherusci during the late 1st centuryBC and early 1st centuryAD. He may have led the Cherusci in their successful ambush ofDrusus
Drusus may refer to:
* Claudius (Tiberius Claudius Drusus) (10 BC–AD 54), Roman emperor from 41 to 54
* Drusus Caesar (AD 8–33), adoptive grandson of Roman emperor Tiberius
* Drusus Julius Caesar (14 BC–AD 23), son of Roman emperor Tiberiu ...
's army at Arbalo in the summer or autumn of 11BC. By winter, Drusus was maintaining a Roman garrison in Cherusci territory and, following Drusus's campaigns, the Cherusci became an ally
An ally is a member of an alliance.
Ally may also refer to:
Place names
* Ally, Cantal, a commune in the Cantal department in south-central France
* Ally, County Tyrone, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Ally, Haute-Loire, a commun ...
of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
. Segimer had two sons, known only by their Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
names
A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A persona ...
Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of ge ...
and Flavus
Flavus is the Latin word for yellow or blond and has given the name to many, more or less yellow, objects:
* Subrius Flavus, a failed Roman conspirator against the Emperor Nero
* Flavus, brother of Arminius
See also
* Flavius
* Flava (disambi ...
. They were closely involved with the Romans and both joined the Roman military
The military of ancient Rome, according to Titus Livius, one of the more illustrious historians of Rome over the centuries, was a key element in the rise of Rome over "above seven hundred years" from a small settlement in Latium to the capital o ...
. His son Arminius led the Germans to victory over three Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of ...
s in the Battle of Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius Quinctilius V ...
in AD9. Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
's account of the battle includes that Segimer was Arminius's second in command during the battle. Segimer is not mentioned by Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his t ...
in his accounts of Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ...
's subsequent reprisal campaigns in Germany, although his brother Inguiomer
Inguiomer or Ingomar ( la, Inguiomerus; fl. 1st century AD) was a leader of the Cherusci. He is chiefly remembered as the uncle of Arminius.
Name
Alexander Haggerty Krappe proposed the name derives from Old Germanic , related to Yngvi, the olde ...
appears. Arminius appears to have succeeded Segimer as chieftain at some point in the early 1st century AD and was subsequently attacked by the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Origin
...
chieftain Maroboduus
Maroboduus (d. AD 37) was a king of the Marcomanni, who were a Germanic Suebian people. He spent part of his youth in Rome, and returning, found his people under pressure from invasions by the Roman empire between the Rhine and Elbe. He led th ...
together with his uncle Inguiomer in AD17 or 18.
Segimer's son Flavus appears to have remained loyal to Rome throughout the period and his son Italicus
Italicus Rosolio di Bergamotto is a bergamot rosolio (a type of aperitivo) manufactured in Italy. The liqueur uses bergamot from Calabria and citrons from Sicily, along with Italian flower varieties. The spirit was created by an Italian bartend ...
succeeded Arminius as chieftain with Roman assistance.Velleius Paterculus
Marcus Velleius Paterculus (; c. 19 BC – c. AD 31) was a Roman historian, soldier and senator. His Roman history, written in a highly rhetorical style, covered the period from the end of the Trojan War to AD 30, but is most useful for the per ...
br>2, 118, 2See also
* ''Barbarians
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be less c ...
'', a 2020 TV show in which Segimer appears
References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * . 1st-century BC monarchs in Europe 1st-century monarchs in Europe 1st-century BC Germanic people 1st-century Germanic people Cherusci rulers {{Europe-royal-stub